UNIT- III
MARKET
Market: A place where parties (seller and buyer) are engaged in exchange of goods and services is called a market.
Types of market:
1)Physical market
2) Non physical / virtual market
3)Auction market
4) Intermediate goods market
5) Black market
6) Knowledge market
7) Financial market:
a) Stock market
b) Bond market
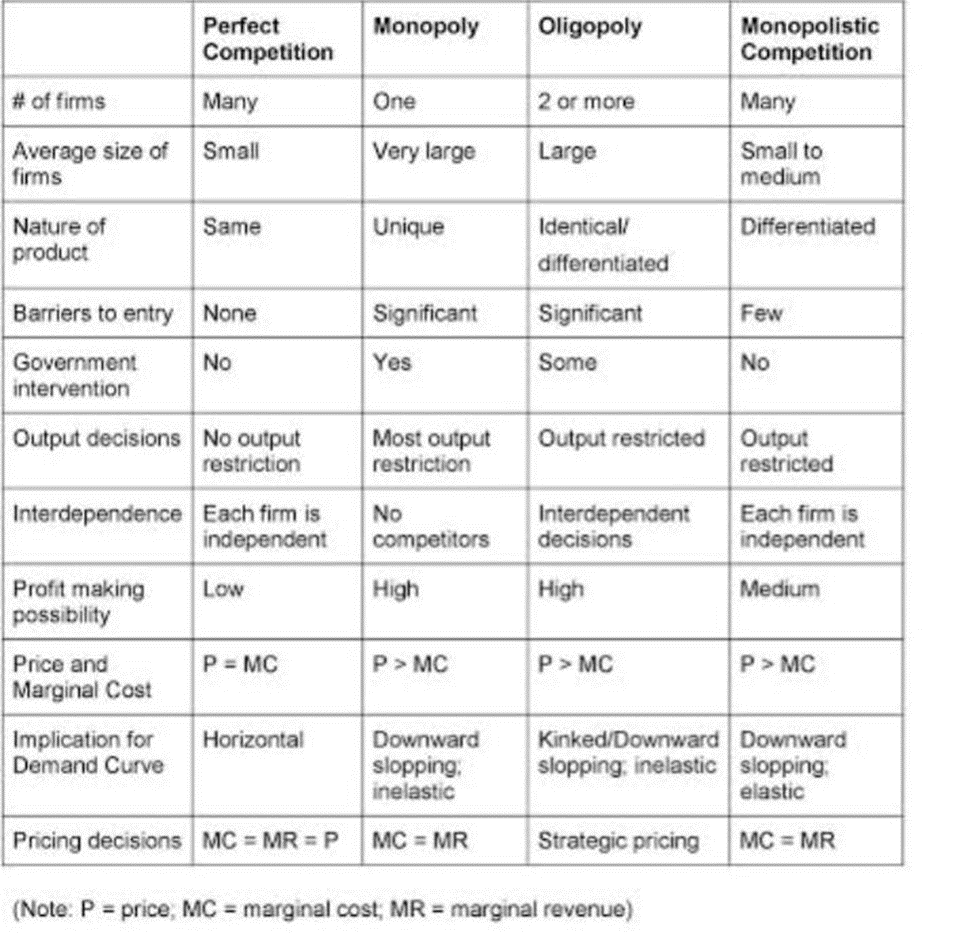
Market structure refers to a degree of competition in a market. Some other determinants of market are nature of products, number of sellers and consumer, economies of scale etc. There are basic four types of market structure in any economy, not all of these market structure really exists as they are theoretical concept
1)Perfect competition: In this type of market there are large number of buyers and sellers. Products in this market are completely identical to each other (homogeneous). Only motive of firms is profit maximization. There is free entry and exit and no concept like consumer preference.
2)Monopolistic competition: There are large number of sellers and buyers in this market. Sellers do not sell homogeneous products. Concept of consumer preference exists in this type of market. Sellers are almost price setter as they charge marginally higher price than original cost or maximum retail price.
E.g. Cereal market and tooth paste market are Monopolistic market.
3)Oligopoly: There are only few dominant firms in the market and buyers are far more than sellers. Firm uses their market influence to set prices and to maximize profit. So, the consumer becomes Price taker. New entry for firms and their further settlement in market is difficult.
4)Monopoly: There is only one seller in monopoly market, who controls whole of the market and fixes price according to their own will. Consumer do not have any alternative so they buy product no matter what price is.
Market agency: Agency which helps customer in implementation and management of market strategies to achieve their business goals.
E.g: propaganda, Ruckus, Response marketing.
They are also known as Marketing firms
Functions of marketing agency:
Types of marketing agency:
1)Full service digital marketing agency:
a) PPC
b) SEO
c)website maintenance
d)web design and development
e) social media and advertisement management
f) review management.
2) Specialized marketing agency:
. One or more of specialized services like web design and CEO.
3) Traditional marketing strategy:
a) Public relation
b) Broadcast marketing
c) Brand management
d) Print marketing
Benefits of marketing agency:
Marketable surplus: That quantity of produce, which can be available to non-farming population of country after farmer meets his own genuine requirements (payment of wages, family consumption, payment of electricity bills, purchase of seed and fertilizers etc)
Marketing surplus can be expressed as: MS = P – C.
Here, MS is marketable surplus, P is Total production and C is Total requirement.
E.g.: Farmer produce = 100 quintals
Total requirement = 20 quintals
MS= P - C
= 100 Q – 20 Q
= 80 Q
Marketable surplus is a theoretical concept of surplus and is Subjective. Rise in MS helps in expansion of industrial sector. As we better know MS is that portion of produce left after exclusion of farmers requirement, available to sell. So, this concept directly relates to Production of agriculture. Hence, reason for low productivity becomes obvious reasons of low marketable surplus. If productivity of agriculture increases constantly than MS will also increase constantly.
Reasons for low productivity/Marketable surplus:
1) Insufficiency of permanent means of irrigation: Indian farmers are heavily dependent on rainfall as they don’t have proper and permanent means of Irrigation. Stability in Agricultural output needs permanent means of irrigation across all over India.
2) Lack of Financial resources: Farmers requires short term credit facility to purchase
Farming equipment, seeds, fertilizers etc. Bulk of farmers are dependent on non-Institutional financial resources (landlords, relatives, moneylenders) who charges exorbitant heavy rates. This breaks down farmer’s capability of high productivity.
3) Lack of Awareness: Due to illiteracy and unawareness farmer’s remains unaware of government's schemes and programmes (PM fasal bima yojna, PM kisan mandhaan yojna etc) initiated by govt. for welfare of farmers.
4) Traditional outlook: Farmers continue to rely on Traditional wisdom, means they consider farming as means of subsistence than business venture. Farmers should grow as an entrepreneur.
5) Exploitative relation between landlords and tenants: landlords rent out their holding to farmers and relying on rental income they exploit their tenants (actual tiller of soil) by charging higher rents.
Following are the reason of low productivity of agriculture, which directly results in low marketable surplus. Measures like use of permanent means of irrigation, proper availability of Financial resources, modern Outlook etc can be help in increase of marketable surplus.
Regulated market: It is an idealized market where government or other organization controls forces of supply and demand and regulates market actions.
It includes decision relating to allowance of entrance in market and deciding what prices can be charged. Basic philosophy behind establishment of regulated market is elimination of malpractices.
Role of Regulated market:
Importance of regulation of agricultural markets:
Government of India with an objective to protect the interest of farmers and to regulate market, has enacted some legislations as follows:
Agricultural Produce Market Act:
Under the provision of Agricultural Produce market act, the state government brings particular area under regulations by market yard, main assembling market, sub market yard and notifying market.
In 2003, Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India set up committee to formulate model law on agriculture marketing. Committees gave report in 2003 and National Conference of state Agriculture minister gave out unanimous opinion to enact law on Agricultural marketing.
Provision of APMA are: