UNIT 5
Inflation Accounting
Meaning of Inflation accounting
Definition- Inflation Accounting refers to Identify and incorporating the changes in prices of assets and liability of a company over a period of time.
Inflation accounting shows the real financial position of the company during inflationary period by adjusting the financial statement of the company. It is a special accounting technique used during the high inflation period. It involves adjustments in the financial statements of a company according to the current price index exist in the economy.
Inflation accounting refers to recording of business transaction at current value. In order to analyze the impact of changes in price, cost revenue, asset and liabilities of the company.
Objectives of inflation accounting
- To remove the various distortions with which financial statement based on historical cost suffer.
- To provide inter-period comparison more meaningful.
- To improve the meaning and measurement of income and expenses in the face of changing the purchasing power of money.
- To improve decision making in the organization.
Importance of inflation accounting
- Exhibits true position: Inflation accounting shows the true financial status of company by reflecting all books of accounts at current price. In accordance with current price index it adjusts all record for determining real profitability.
2. Avoids profit overstatement: For avoiding any overstatements of profits this branch of accounting keeps a check on financial statements of companies. All expenses and income are recorded at current values which remove overstatement of business income.
3. Calculate right depreciation: Inflation accounting calculates right depreciation by charging correct amount of depreciation through calculating it on present value instead of historical value. Charging right depreciation facilitates business in easy replacement of assets.
4. Easy profit comparison: For determining the company profitability it enables firms in easy comparison of their inter-periods performance. Inflation accounting adjusts effects of prices changes on all expenses and incomes listed in financial statements that avoids distortion of historical data.
5. Provides correct information: Based on present price level inflation accounting provides correct information to shareholders and workers. In absence of such information there may be a chance of higher dividend and higher wages being demanded by these people.
Key takeaways –
- Inflation accounting shows the real financial position of the company during inflationary period by adjusting the financial statement of the company.
Breakeven analysis
Breakeven is a financial tool which helps the company to determine after which stage they will be profitable. Breakeven point is where the company neither make money nor losses money, but covers all the cost incurred.
Breakeven is useful in studying the relationship between cost and revenue. It is a point at which total cost and total revenue are equal. It is no gain no loss situation, though opportunity costs have been paid and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return.
Components of breakeven analysis
Fixed costs
Fixed costs are also called overhead costs. These fixed costs occurs after taking the decision to start an economic activity and these costs are directly related to the level of production, but not the quantity of production. Fixed costs include interest, taxes, salaries, rent, depreciation costs, labour costs, energy costs etc. Irrespective of the production these costs are fixed in nature. In case of no production also the costs must be incurred.
Variable costs
Variable costs are directly proportional to the quantity of production. The costs will increase or decrease in direct relation to the production volume. These costs include cost of raw material, packaging cost, fuel and other costs that are directly related to the production.
Formula
Break even quantity = Fixed costs / (Sales price per unit – Variable cost per unit)
Where:
- Fixed costs are costs that do not change with varying output (e.g., salary, rent, building machinery).
- Sales price per unit is the selling price (unit selling price) per unit.
- Variable cost per unit is the variable costs incurred to create a unit.
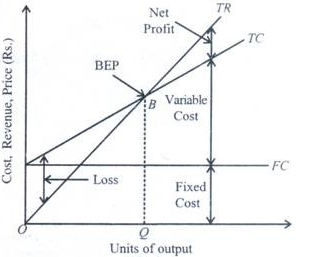
It is also known as “cost –volume-profit analysis”. In the above figure, TR is total revenue curve is straight line from the origin, as every unit of output contributes to revenue. TC is total cost curve is fixed and variable cost which starts from vertical axis and rises linearly. B is the breakeven point at OQ level of output where all the cost has incurred.
Benefits of Break-even analysis
- Catch missing expenses: In a new business, it happens that few expenses are missed. With the help of break-even analysis, to reach breakeven point all the financial commitments are reviewed.
- Set revenue targets: Once the break-even analysis is complete, the company knows how much to be sold to be profitable. This will help to set more concrete sales goals.
- Make smarter decisions: break even analysis helps in making good decision based on the facts to become successful
- Better Pricing: Finding the break-even point will help in pricing the products better. This tool is highly used for providing the best price of a product that can lead to maximum profit without increasing the existing price.
- Cover fixed costs: Doing a break-even analysis helps in covering all fixed cost incurred.
For an example:
Variable costs per unit: Rs. 400
Sale price per unit: Rs. 600
Desired profits: Rs. 4,00,000
Total fixed costs: Rs. 10,00,000
Solution
Break even quantity = Fixed costs / (Sales price per unit – Variable cost per unit)
= 10,00,000/ (600 – 400)
Break Even Point = Rs. 10,00,000/ Rs. 200 = 5000 units
Next, this number of units can be shown in rupees by multiplying the 5,000 units with the selling price of Rs. 600 per unit.
We get Break Even Sales at 5000 units x Rs. 600 = Rs. 30,00,000.
Example

Calculate
Break-even point in terms of sales value and in units.
Number of units that must be sold to earn a profit of Rs. 90,000.
Solution
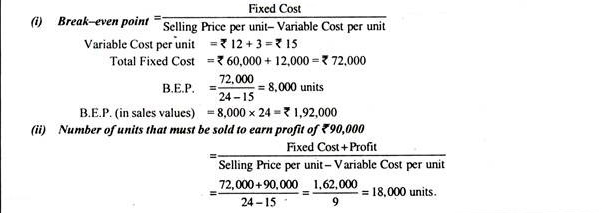
Example
Suppose XYZ Ltd is expecting to sell 10,000 units at a price of Rs10 each. The variable cost associated with the product is Rs5 per unit, and the fixed cost is coming Rs15,000 per year. Do the break-even analysis for the given case.
Solution
Break even quantity = Fixed costs / (Sales price per unit – Variable cost per unit)
= 15000/ (10 – 5)
Break Even Point = Rs. 15,000/ 5 = 3000 units
Examples
From the following information, calculate the break-even point in units and in sales value:
Output = 3,000 units
Selling price per unit = Rs. 30
Variable cost per unit =Rs. 20
Total fixed cost = Rs. 20,000
Solution
Break even quantity = Fixed costs / (Sales price per unit – Variable cost per unit)
= 20000/ (30 – 20)
Break Even Point = Rs. 20,000/ 10 = 2000 units
We get Break Even Sales at 2000 units x Rs. 30 = Rs. 60000
Key takeaways –
- Breakeven is a financial tool which helps the company to determine after which stage they will be profitable.
Sources
- S. P. Gupta : Management Accounting
- B. K. Mehta & K. L. Gupta : Management Accounting
- Manmohan and Goyal : Management Accounting
- Hingorani and Others : Management Accounting
- R. N. Anthony : Management Accounting
- Agarwal and Mehta : Management Accounting