UNIT 4
Inventory Valuation
Inventory valuation is an accounting practice which is followed by companies at the time they are preparing their financial statements to find out the value of unsold inventory stock. Inventory stock is an asset for an organization, and it needs to have a financial value to record it in the balance sheet. This value helps in determining the inventory turnover ratio, which in turn will help to plan your purchasing decisions.
Inventory valuation method is the total cost associated with the current inventory. In other words, it is the total amounts of money have been spent on acquiring the inventory and storing it.
Techniques of inventory control
- First in – First Out Method:
It is a method of pricing the issue of materials in the order in which they are purchased. In other words the materials are issued in the order in which they arrive in the store. This method is considered suitable in times of falling price because the material cost charged to production will be high while the replacement cost of materials will be low. In case of rising prices this method is not suitable.
Advantages of FIFO:
- It is simple and easy to operate.
- In case of falling prices, this method gives better results.
- Closing stocks represents the market prices.
Disadvantages:
- If the prices fluctuate frequently, this method may lead to clerical errors.
- In case of rising prices this method is not advisable.
- The material costs charged to same job are likely to show different rates.
2. Weighted Average Price Method:
This method removes the limitation of Simple Average Method in that it also takes into account the quantities which are used as weights in order to find the issue price. This method uses total cost of material available for issue divided by the quantity available for issue.
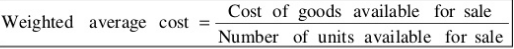
Advantages
- It is more scientific and smoothens the fluctuations in purchase price
- Inventory is valued at one rate
Disadvantages
- It is tedious – requires the issue price to be computed each time a consignment is received
3. LIFO (Last in first out method):
Under this method most recent purchase will be the first to be issued. It means the most recently items produced are sold first. The issues are priced out at the most recent batch received and continue to be charged until a new batch received is arrived into stock. It is a method of pricing the issue of material using the purchase price of the latest unit in the stock.
Advantages:
- Based on the replacement cost Stocks issued at more recent price represent the current market value
- It is simple to understand and easy to apply.
- Since material cost is charged at more recent price, product cost will tend to be more realistic
- It minimizes unrealized inventory gains and tends to show the conservative profit.
Disadvantages:
- Valuation of inventory under this method is not acceptable in preparation of financial accounts.
- It renders cost comparison between jobs difficult.
- It involves more clerical work and sometimes valuation may go wrong.
Key takeaways – inventory valuation methods includes LIFO, FIFO, weighted average cost
Meaning of Inflation accounting
Definition- Inflation Accounting refers to Identify and incorporating the changes in prices of assets and liability of a company over a period of time.
Inflation accounting shows the real financial position of the company during inflationary period by adjusting the financial statement of the company. It is a special accounting technique used during the high inflation period. It involves adjustments in the financial statements of a company according to the current price index exist in the economy.
Inflation accounting refers to recording of business transaction at current value. In order to analyze the impact of changes in price , cost, revenue, asset and liabilities of the company.
Objectives of inflation accounting
- To remove the various distortions with which financial statement based on historical cost suffer.
- To provide inter-period comparison more meaningful.
- To improve the meaning and measurement of income and expenses in the face of changing the purchasing power of money.
- To improve decision making in the organization.
Importance of inflation accounting
- Exhibits true position: Inflation accounting shows the true financial status of company by reflecting all books of accounts at current price. In accordance with current price index it adjusts all record for determining real profitability.
2. Avoids profit overstatement: For avoiding any overstatements of profits this branch of accounting keeps a check on financial statements of companies. All expenses and income are recorded at current values which remove overstatement of business income.
3. Calculate right depreciation: Inflation accounting calculates right depreciation by charging correct amount of depreciation through calculating it on present value instead of historical value. Charging right depreciation facilitates business in easy replacement of assets.
4. Easy profit comparison: For determining the company profitability it enables firms in easy comparison of their inter-periods performance. Inflation accounting adjusts effects of prices changes on all expenses and incomes listed in financial statements that avoids distortion of historical data.
5. Provides correct information: Based on present price level inflation accounting provides correct information to shareholders and workers. In absence of such information there may be a chance of higher dividend and higher wages being demanded by these people.
Key takeaways - Inflation accounting shows the real financial position of the company during inflationary period by adjusting the financial statement of the company.
Sources
- S. P. Gupta : Management Accounting
- B. K. Mehta & K. L. Gupta : Management Accounting
- Manmohan and Goyal : Management Accounting
- Hingorani and Others : Management Accounting
- R. N. Anthony : Management Accounting
- Agarwal and Mehta : Management Accounting