UNIT – 1
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is the science of energy transfer and its effects on the physical properties of substance.
It deals with the transfer of energy of all kind from one form to another. It is based on first and second law of thermodynamics.
The name thermodynamics derives from Greek words thermo and dynamics meaning heat and mechanical power respectively.
Thermodynamics has wide range of applications. It is useful in the design of energy conversion devices such as internal combustion engine, steam and gas turbine, design of refrigeration and air conditioning equipment like refrigerators, air conditioners, water coolers and ice plants.
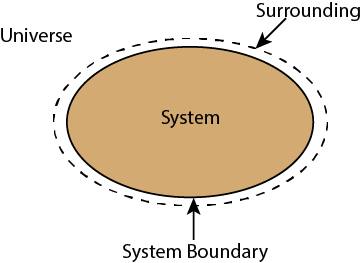
Whenever a change is to be analysed it is essential to specify the region in which the change take place. This is done by drawing a boundary around the region. Boundary may be real or imaginary.
Everything within the boundary is called the system. The region outside the boundary is called surroundings.
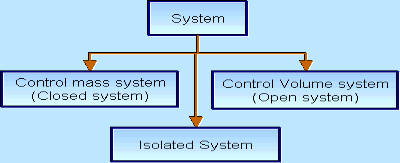
There are three types of Thermodynamics systems.
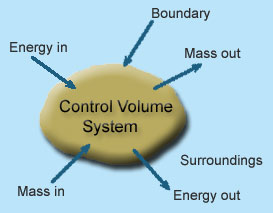
1 - Open system : If mass and energy both cross the boundary of a system it is called open system .in open system both mass and energy can transfer across the boundaries and the mass within the system may not be constant .most of the engineering devices are open systems involving flow of fluids through them.
Example of open system
- Boiler – In boiler water convert from liquid to vapour phase. So mass and energy both transfer the boundary.
- Hydraulic turbine wheel – In this device potential energy of water convert into mechanical works. Water enters the wheel from head race side and leaves it to the tail race from the other end, and as such mass cross the system boundary.
- Motor-car engine – The engine sucks charge which is mixture of air and petrol and finally exhausts the gases to the surrounding atmosphere.
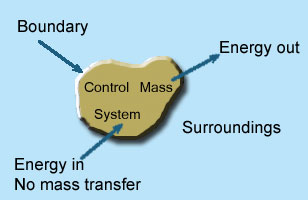
2 – Closed system: If the mass within the boundary of the system does not change, it is called closed system. A closed system does not allow any mass transfer across the boundary but allow transfer of energy across the boundary.
Example of closed system
- Piston cylinder assembly –the gas can reject or receive heat, expand or contract but no mass cross the boundary of system.
- Ignition system – electric energy cross the boundary to cause a spark between electrodes an initiate combustion .there is heat transfer but not mass across the system.
Pressure cooker, refrigerator, ice cream freezer etc. are the example of closed system.
3 - Isolated system : Neither mass nor energy cross the boundary of a system .it is called an isolated system . In this no mass and energy cross the system
Example of isolated system
- Universe can be considered as an isolated system
- Fluid enclosed in a perfectly insulated closed vessel (thermos flask)
States is the conditions of system identified by thermodynamics properties .the state of the system in thermodynamics equilibrium can be represented by a point with properties as coordinate’s .the system exist at a definite state when all the properties have a definite value.
Intensive property: If the property is independent of mass of the system is called an intensive property.
Example - Pressure, temperature, density, velocity, height, viscosity are the example of intensive property.
Extensive property: If the property is proportional to the mass of the system it is called an extensive property.
Example- volume, surface area, potential energy, kinetic energy, internal energy, electric charge.
A system is said to be in the states of thermodynamics equilibrium if the value of the property is the same at all the points in the system. Or the system is said to exist in thermodynamics equilibrium when no change in any macroscopic property is registered, if the system is isolated from its surrounding.
The system is said to be in thermodynamic equilibrium if the conditions for following three equilibrium is satisfied:
- Mechanical equilibrium
- Chemical equilibrium
- Thermal equilibrium
1-Mechanical equilibrium: When there are no unbalanced forces within the system and between the system and the surrounding, the system is said to be under mechanical equilibrium.
The system is also said to be in mechanical equilibrium when the pressure throughout the system and between the system and surrounding is same. Whenever some unbalance forces exist within the system, they will get neutralized to attain the condition of equilibrium. Two systems are said to be in mechanical equilibrium with each other when their pressures are same.
2-Chemical equilibrium: The system is said to be in chemical equilibrium when there are no chemical reactions going on within the system or there is no transfer of matter from one part of the system to other due to diffusion. Two systems are said to be in chemical equilibrium with each other when their chemical potentials are same.
3-Thermal equilibrium: When the system is in mechanical and chemical equilibrium and there is no spontaneous change in any of its properties, the system is said to be in thermal equilibrium. When the temperature of the system is uniform and not changing throughout the system and also in the surroundings, the system is said to be thermal equilibrium. Two systems are said to be thermal equilibrium with each other if their temperatures are same.
Thermodynamics process represents a transition in which a system changes from one state to another. When the path is completely specified then the change of state is called a process. A Process is defined as the transformation of the system from one fixed state to another fixed state. When any one of the properties changes, the working substance or system is said to have undergone a process.
Some of the processes are identified by special names as given below :
- Isobaric process (constant pressure process.
- Isochoric process (constant volume process)
- Isothermal process (constant temperature process)
- Isentropic process (constant entropy process)
- Adiabatic process(perfectly insulated process)
Cycle : Any process or series of processes whose end state are identical is called a cycle. Or Series of thermodynamic processes, the end states of which are identical, is called a thermodynamic cycle. In a thermodynamic cycle, chemical composition of the working fluid during the process does not change. Thus all the properties in the initial and final states remain unchanged.
Example - water that circulates through the steam power plant. There is a change of phase during the process, but the end states are same.
If two system are each in thermal equilibrium with the third system then the two system are in thermal equilibrium which each other.
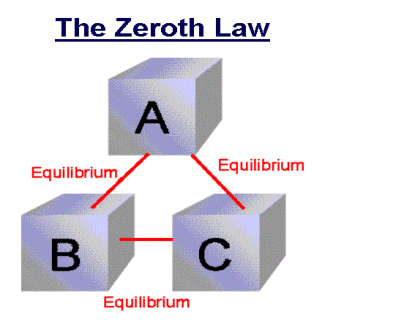
When a body A is in thermal equilibrium with a body B , and also separately with a body C ,then B and C will thermal equilibrium with each other .this is known as the Zeroth law of thermodynamics.