Unit 2
Boiler Corrosion, Caustic Embrittlement)
Boiler Corrossion:
Corrison :-
- Corrison in boiler tube ( heat exchange tube is ) mainly due to presence of dissolved gaseous like CO2 , O2 in water and due to presence of acids in water presence of Mgcl2 directly attacks the boiler metal and corrodes it.
- Corrison is the destruction of metal by chemical or electro chemical attack of the envoriment . In boilers if feed water contains dissolved oxyegen when wter is boiled O2 is set free . This metal of boiled 2fe+2H2O+O2 - - - - - - - - - 2FE(OH)2 - - - - - - - - Fe ( OH ) 2 -------- Fe2O3.H20 Formation of rust by adding calculated quantity of hydracine to water oxygen from water can be removed
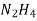 +O2 -------------------
+O2 -------------------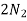 +
+ 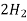 O
O
3. In low pressure boilers sodium sulphaite is used for removing oxygen.
4. If water contains dissolved co2 it form carbonic acid with water this acid produces local corrison called as pitting .
5. Carbon dioxide and oxygen are to be removed from feed water by deaeration . Co2 can be removed by lime treatment . As an internal treatment . Co2 is converted to ammonium carbonate by addition of ammonia.
6. Excess ammonia evaporates in boiler along with steam and gas in condenser.
7. Acidity of water can be decreased by adding calculated quantity of NaOH to it so that Ph of water will be in between 8 and 9 ph units.
Priming and foaming :-
Processes :-
- When a boiler is steaming (i.e producing steam ) rapidly some particles of liquid water are carried along with the steam . This processes of wet stram formation is called priming.
- Priming is caused by :-
- The presence of large amount of dissolved solids
- High steam velocites
- Sudden boiling
- Improper boiler design
- Sudden increase in steam production rate
3. Foaming :-
- It is the production of persistent foam or bubbles in boilers which do not break easily.
- Foaming is due to presence of substance like oils ( which greatly reduce the surface tension of water )
4. Priming and foaming usually occur togther. They are objectionable because:-
- Dissolved salts in boiler water are carried by the wet steam to super – heater and turbine blades where they get deposit as water evaporates . This deposite reduce their efficiency.
- Dissolved salts may entire in the parts of other machinery where steam is being used there by decreasing the life of the machinery.
- Actual height of water column Cnnot be judge property there by making the maintance of boiler pressure becomes difficult.
Priming can be avoided by :-
- Fitting mechinical steam puritires
- Avoiding rapid change in steaming rate
- Maintaning low water levels in boilers
- Efficent softening and filteration of boiler – feed water
Foaming can be avoided by ;-
- Adding anti – foaming chemical like castor , oil or
- Removing oil from boilerr water by adding compounds like sodium aluminate.
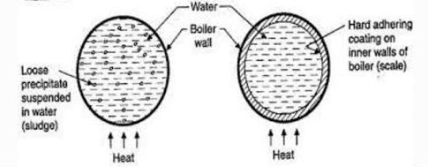
Sludge formation-
Sludge formation , scale formation
- In boiler water evaporates continously and the concentration of salts left behind goes on increasing . After the saturation point they get precipitated.
- If the precipitate remains in boiler tube as loose and slimy matter is called sludge.
- If some of the precipitated matter adhers strongly and forms strong bad conducting layer on their inner side of boiler tube , then it is known as scale.
Sludge :-
( formation of sludge )
- The loose slimy mass of salts precipitated in boiler water is the sludge.
- They are generally formed at cooler portion of boiler and they loosely deposit in the parts of boiler tube where flow rate is slow e.g vlves bends
- Sludges are easy to remove by using brushes detergent solutions blow down opreation e.t.c .
Disadvanatages of sludges :-
- They tend to waste some portion of heat.
- Edcessive sludge formation distrub working of boiler and sometimes may choke up the pipe .
Prevention of sludges :-
- Use of water contaning very low quantity of total disolved solids.
- Frequently making blow down opreation i.e replacing salts concentrated water with fresh water.
Scales :-
A] formation of scales :-
Scale is the hard and strongly adhered coating to the inner surface of boiler and it is a bad conductor of heat. It is the main source of boiler trouble.
It is caused due to :-
- Decomposition of bicarbonates :-
At high temprature bicarbonates decompose into sticky water insolube material.
Ca ( HcO3)2 ----------------- CaCO3 + H2O + CO2
Mg ( HCo3)2 - - -------------- Mg (Oh)2 + 2CO2
2. Hydrolsis of magnesium salts :-
At higher temprature magnesium salts undergo hydrolysis.
MgCl2 + 2H2O ---------------------- mg ( OH)2 + 2HCl
3. Presence of silica :-
The source of ssilica is ( form) from sand and filter .silica may be in the form of colloidal particles. And it can be deposite as calcium silicate or magnesium silicate as firmly adhering materials.
4. Decreased solublity of CaSO4 :-
CaSo4 has lesser solublity at higher temprature hence at high temprature CaSo4 present in boiler feed water will precipitate as hard scale forming materials.
B] Disadvantages of scale :-
1. Waste of fuel :-
Scales are bad conductors of heat and resultes in the reduction of heat transfer to the boiler . Higher the thickness of scale greater than the wastage of fuel there by . It has been reported that 0.25 cm . Scale would increase fuel consuption by aboyut 2 to 3 percent.
Thickness of scale | 0.325 mm | 0.625mm | 1.25mm | 2.5 mm |
Wastage of fuel | 10 percent | 15 percent | 50 percent | 80 ercent |
3. over heating of boiler :-
Scale being pooe conducter of heat it reduces transfer of heat from boiler to boiler water . To keep the required steam pressure we need to overheat the boiler .
4. boiler saftey :-
Due to the scale formation the overheating of boiler is done in order to maintain constant stream supply with required pressure . This overheating makes boiler metal to become soft and weak . This cause distortation of boiler tube and becomes dangerous in morden high pressure boiler .
5. Danger of Explosion :-
When thick scale cracks due to uneven expansions the water come suddenly suddenly in contact with the overhead boiler metal. This cause large amount of steam formation suddenly and sudden high pressure is developed . Due to sudden high pressure is devloped . Due to sudden high pressure the softer boiler metal may burst with explosion.
C] Removal of scales :-
Scales are removeed from time by different ways.
- By use of suitable chemicals the scale can be dissolved and removed.
- Use of scraper or wire brush for thin scales to remove.
- Thick s ales may br removed by hammer and chisle.
- The thermal shocks technique is used to remove hard brittle scale . In this method empty boiler is heated and cooled by cold water suddenly . While sudden cooling the contracting boiler metal excerts pressure on scale to crack them.
- Blow down opreation used if scales are loosely adhering.
D] prevention of scales :-
It is better to minimize scales formation and reduce the problems in steam generation.
- Use of softened water.
- Adding sodium phosphate to the water
- Frequent blow down operations to remove the scales when they are thin.
- Adding sodium aluminate which can trap the scale forming particles.
- Adding organic chemicals like tannin which forms coating on the scale forming particles . This matter becomes easily removable by blow down operation.
Caustic Embrittlement :-
- It is a type of corrison caused by high concentration of sodium hydroxide in boiler water sodium carbonate hydroxide in the boiler and extent of hydrolysis increases with temprature.
Na2CO3 + H2O ----------------- 2Na.OH + CO2
2. Sodium hydroxide reacts with metal ion to form ion to form iron oxide and hydrogen.
3. When metral oxide coating cracks, chemical attack continues into metal along grain boundaries . Through the cracks , water flows , wwhen it evaporates sodium hydroxide is left there.
4. This attack iron of boiler.
5. This type of corrision of boiler parts particularly at stress parts caused due to chemical of caustic soda ( NaOH) Is called as embrittlement.
6. During water softening by soda – limes , processes Na2CO3 is added to water as precipitant . Caustic embrittlement can be prevented by addition lignins or tannos which help in blocking of hair cracks.
Softening methods :-
Water used for industrial purpose ( such as for steam generation) should be sufficiently pure it should be therfore be freed from hardness producing salts before put to use the processes of removing hardness producing salts from water is known as softening water is known as softening of water . In industry main three methods employed for softening of water are
- Ion exchange or de ionisation
- Zeolite
- Lime soda processes
- Ion exchange or de ionization or de mineralization ion exchange resins are insoluble cross linked long chain organic polymers with a microporous structure and the functional group attached to the chains are responsible for the ion exchange properties resins contaning acidic function groups are capable of exchaning their anions with other anions which comes in their contact the ion exchange resins may be classified as :-
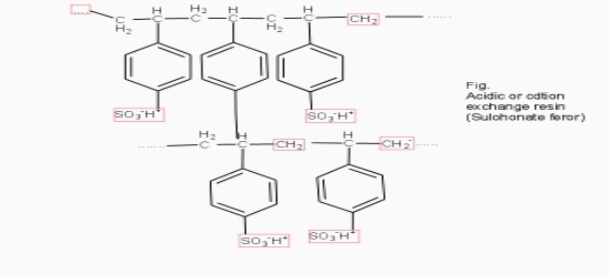
Cation exchange resins ( RH+) :-
They are mainly styrene divinly benzene co-polymers which on sulphonation or carbonoxylation become capable to exchange their hydrogen ions with the cations in the water.
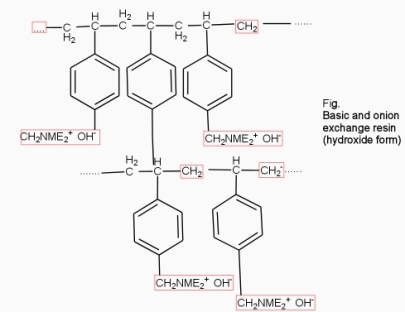
2. Anion exchange resins :-
They are styrene – divinly benzene or amine fermaldehyde which contain amino or quaternary ammonium or4 quaternary phosphonium or tertiary sulphonium group as an integral part of the resin matrix.these after treatment with dilute NaOH solution become capable to exchange their OH- anions with anions in water .
Processes :-
The hard water is passed first through cation exchange column which removes all the cations like Ca²+ , Mg² + e.t.c . From it and equivalent amount of H+ ions are released from this column Water
2RH+ + Ca².+ ---------------------- R2Ca2+ + 2H
2RH+ Mg2+ --------------------------- R2Mg2+ 2H+
After cation exchange column the hard water passed through anion like cl- . Present in the water and equivalent amount of OH- ions are released from this column to water,
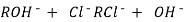
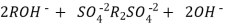
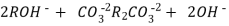
H+ And OH – ions ( released from cation exchange and anion exchange columns respectively ) get combined to produce water molecule.
H+ + OH - -- ----------------- H2O
Thus,
The water coming out form the exchanger is free from cations as well as an ions . Ion free water is known as de mineralizes water.
Zeolite processes: -
Chemical structure of sodium zeolite may be represented as Na2O. AL2O3. XSIO2.Y.H2O where x=2-10 and Y=2-6 zeolite is hydrated sodium aluminum silicate capable of exchanging reversibility its sodium ions for hardness producing ions in water zeolites are known as zeolite. Zeolite are also known as permutits.
Zeolite are of two types
- Natural zeolites :- are non – porous for example natrolite Na2O3.
- Synthetic zeolites: - they are prepared by heating together china clay and soda ash. Such zeolite possesses higher exchange capacity per unit weight than natural zeolites.
Processes :-
For softening of water by zeolite processes hard water is percolated at a specified rate through a bed of zeolite kept in a cylinder (shown in fig.)
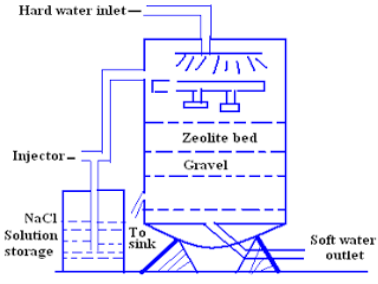
The hardness causing ion are retained by the zeolite as caze and MgZe while the out-going water contain sodium salts reaction take place during the softening processes are
Ca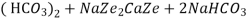
Mg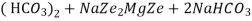
Ca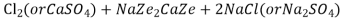
M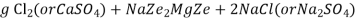
Regeneration-
After some time, the zeolite is completely converted into calcium and magnesium zeolite and it ceases to soften water,i.e. it gets exhausted.
At this stage the supply of hard water is stopped and the exhausted zeolite is reclaimed by treating the bed with a concentrated ( 10 percent ) brine ( NaCl ) solution.
The washings (containing CaCl2 and MgCl2 ) are led to drain and the regenerated zeolite bed thus obtained is used again for softening purpose.
Limitations of zeolite processes :-
- If the supply of water is turbid the suspended matter must be removed (by coagulation, factorization, etc.) before the water is admitted to the zeolite bed , otherwise the turbidity will clog the processes of zeolite bed there by anking it inactive.
- If water contains large quantities of colored ions such as Mn2+ they must be removed first because these ions produce manganese and iron zeolite which cannot be easily regenerated.
- Mineral acids if present in water destroy the zeolite bed and therefore they must be neutralized with soda before admitting the water to the zeolite softening plant.
Advantages of zeolite processes:-
- It removes the hardness almost completely and water of about 10 ppm hardness is produced
- The equipment used is compact occupying a small space
- No impurities are precipitated so there is no danger of sludge formation in the treated water at later stage
- The processes automatically adjust itself for variation in hardness of incoming water
- It is quite clean
- It requires less time for softening
- It requires less skill for maintenance as well as operation