Unit 1
Hardness can be defined as a soap consuming capacity of water sample .soaps are sodium salts of fatty acids like oleic acid , palmetic acid and stearic acid . They dissolve ereadily .in water to form lather due to which it has cleansing property.


- But compounds of fatty acids with other metals done dissolve in water.
- If water contains other metal ions like calcium and magnesium ions they react with sodium salts of long chain fatty acids to form in soluble soap which we observe as curd.
 2
2
( calcium stearate )
- If water contains other metal ions like calcium and magnesium ions they react with sodium salts of long chain fatty acids to form in soluble soap which we observe as curd
 2
2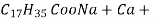
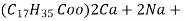
( calcium stearate )
- These other metal ions are responsible for the hardness of water most important metal of ions which cause hardness to water are calcium and magnesium ions.
- The hardness of water along can be calculated from the amount of calcium and magnesium ions present in water along with bicarbonates ,sulphates chlorides and nitrates.
TYPES OF WATER | HARDNESS |
Soft | 0 - 75 |
Moderately hard | 75 - 150 |
Hard | 150 - 300 |
Very hard | Above 300 |
Types of hardness : -
Temporary hardness ( carbonate) :- v
- When water containing calcium and magnesium bicarbonates is heated , bicarbonate decompose and from insoluble carbonate and form hydroxide.
- On filtering such water , soft water is obtained.
- The hardness which can be removed by more boiling is refferd as ‘temporaryhardness ’ or bicorbonate hardness.

 Ca
Ca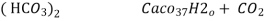

Mg 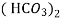
 Mg
Mg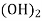 + 2 CO
+ 2 CO 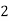
( Bicarbonates)
Permanent hardness :-
- The term permanent hardness ornon carbonate is the term applied to the hardness caused by dissolved chlorides , nitrates and sulphate of calcium and magnesium.
- This cannot be removed by boiling the water sample.
- Sum of temporary and permanent hardness is referred to as total hardness.
Alkaline or carbonate and non – alkaline or non – carbonate hardness :-
- Like all carbonate and bicarbonate , calcium and magnesium carbonate and bicarbonate are alkaline.
- Then hardness due to the carbonate and bicarbonate is called alkaline hardness or carbonate hardness.
- The alkalinity can be measures by titration with standard mineral acid using methyl orange and or phenol pthalelin as an indicator.
4. As the sulphate and chloride are neutral salts , the hardness caused by presence of calcium and magnesium sulphate , chlorides and nitrates is termed as non alkaline hardness or non carbonate hardness.
Unit of Hardness:
- Parts of per million (ppm) is the parts of the calcium carbonate equivalent hardness per 10 raise to 6 parts of water i.e 1 ppm = 1 part of
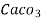 eq hardness in
eq hardness in 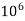 parts of water .
parts of water . - Milligram per liter is the number of milligram of
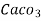 equivalent hardness present per liter of water.
equivalent hardness present per liter of water.
Thus,
1 mg/l = 1 mg of 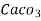 eq. Hardness of 1L of water .
eq. Hardness of 1L of water .
But 1 L OF Water weighs.
= 1 kg = 1000 g = 1000*1000 mg = 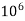 mg
mg
Therefore,
1mg/l = 1 mg of 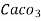 eq. Per
eq. Per 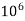 mg of water.
mg of water.
= 1 part of 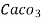 eq. Per
eq. Per 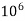 mg of water
mg of water
= 1 part of 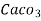 eq. Per
eq. Per 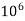 parts of water
parts of water
=1 ppm
3. Clarke’s degree is number of grains (1/7000lb) of 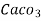 equivalent hardness per gallon (10lb) of water. Or it is parts of
equivalent hardness per gallon (10lb) of water. Or it is parts of 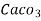 equivalent hardness per 70000 parts of water.
equivalent hardness per 70000 parts of water.
Thus,
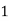 ° clark = 1 grain of
° clark = 1 grain of 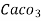 eq. Hardness per gallon of water.
eq. Hardness per gallon of water.
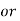 1° c l = 1 part of
1° c l = 1 part of 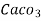 eq. Hardness per 70000 parts of water .
eq. Hardness per 70000 parts of water .
4. Degree French (°fr) is the part of 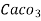 equivalent hardness per
equivalent hardness per 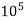 part of water .
part of water .
Thus,
1°fr = 1 part of 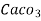 hardness eq. Per
hardness eq. Per 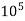 parts of water.
parts of water.
5. Milli equivalent per liter (meq / L )is the number of milli equivalents of hardness present per liter.
Thus,
1meq/L = 1 meq of 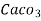 per L of water
per L of water
= 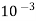 * 50 g of
* 50 g of 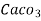 eq. Per liter.
eq. Per liter.
= 50 mg of 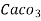 eq per litre.
eq per litre.
= 50 mg / l of 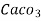 eq = 50 ppm.
eq = 50 ppm.
Relation between various units of hardness
- 1 ppm = 1 mg / L 0.1° fr = 0.07° Cl = 0.02 meq/L
- 1 mg/L = 1 ppm = 0.1° fr = 0.07° cl = 0.02 meq / L
- 1°cl = 1.433° fr = 14.3 ppm = 14.3 mg / L = 0.286 meq / L
- 1° fr = 10 ppm = 10 mg/ L = 0.7° cl = 0.2 meq / L
- 1 meq/ l = 50 mg/ l = 50ppm = 5° fr = 0.35° cl
The hardness due to all hardness causing salts , known as total hardness.
Total hardness = temporary + permanent
Estimation of hardness :-
Hardness of weather can be determined by two methods.
1) Soap solution method :-
- Total hardness of water can be determined by titrating a fixed volume of water sample (100ml) against standard alcoholic soap solution.
- Appearance of stable lather which persists for two minutes is the end point of titration.
- In the beginning sodium soap will precipitate all the hardness causing metal ions in the form of their soap (card) and then it will form free lather.
- If same water sample is boiled for 30minutes and then titrated against same soap solution the titration reading corresponds to permanent hardness.
- The difference between two measurements corresponds to the temporary hardness of water.
2) EDTA method :-
- Hardness of water can be determined more accurately by EDTA method.
- In this method 100ml of water sample is taken in titration flask to this 3ml of buffer an 08 ph 10 is added.
- Then it is titrated against 0.01m EDTA using electron black T as an indicator.
- At the end point wine red color changes to blue color.
- From barettereading , total hardness of water sample can be calculated using the formula.
1000ml of 1MEDTA = Caco3 = 100 get Caco3
6. Suppose barette reading is xml for 100 ml of water sample. Then for one liter of sample 10x ml EDTA is required.
As ,
100 ml 1MEDTA = Caco3 = 100 get Caco3
1 ml 0.01 EDTA = 1 mg Caco3
10 x ml 0.01m EDTA = 10 x mg Caco3
7. Hardness can be expressed as mg of Caco3 present in 10 mg ( 1 liter ) of water i.e ppm .
Hardness of such water sample will be 10 x ppm
8. If titration is carried out after boiling the water sample for 30 min the reading will correspond to permanent hardness corresponds to temporary hardness of water sample.
9. Ethylene- diamineteracetic acid (EDTA) IS PRACTICALLY Insoluble in water it is represented as H4Y.
DIAGRAM
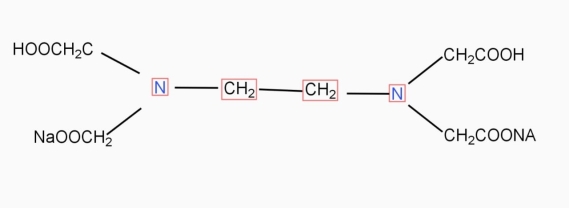
INaqueous solution ionises as
Na2H2Y  2Na+ + H2Y2-
2Na+ + H2Y2-
It forms 1:1 complex with Ca++ and Mg++ metal ions present in water sample when indicators is added to water sample colored ( red ) metal indicator complex is formed
When this is titrated with EDTA solution
H2Y²- ions react with Ca++ or Mg++ ions from metal indicators complex because these two have more affinity towards EDTA. So more stable metal EDTA complex is formed .at the same time HIn² -ve ions are set free ( blue ).
So at the end point colour changes from red to blue.
A natural water may be alkaline due to presence of hydroxide bicarbonates and carbonates compound dissolve in water.
Hydroxides 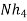 OH ,NaOH
OH ,NaOH
Bicarbonates Ca (Hco3)2
Carbonates Mgco3 , Feco3
Hydroxides and carbonates and stronger bases than bicarbonates.
- When an alkaline water is titrated with a strong acid first all OH get neutralized then all the caco3 – ions are half neutralized + OHCo3- .
- Till this stage ,ph of mixture decreases to about 8.2 and completion of this stage is indicated by change in color of phenolphthalein.
- On continued addition of acid during titration all the HCO3 in the titration mixture ( produce by half neutralization of CO3 and present from beginning ) get neutralized and completion of this stage is indicated by methyl orange color change at about3.7 ph.

 O ( PH = 8.2 )
O ( PH = 8.2 )
 + H+
+ H+  H2O + CO2 ( PH = 3.7 0)
H2O + CO2 ( PH = 3.7 0)
Procedure :-
The alkalineties due to the three type of ions can be easily determined by neutralisation titration.
- Take V ml ( generally 25 ml ) of the alkaline water in conical flask and add 2 drops of phenopthalein indicator in it .
- Titrate this sample against standard strong acid solution ( x n ) from burette till pin k colour changes to colourless . Klet the burette be V 1 ml .
- Add few drops of methyl orange indicator into the same titrarting mixture changes to orange .
Note the burette reading as V 2 ml ( from initial )
Calculations :-
P = phenolphthalein alkalinity = 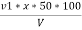
= PPM Caco3 equivalent
M = methyl orange alkalinity = total alkalinity
= 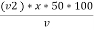 ppm Caco3 equivalent
ppm Caco3 equivalent
The possible combinatuions of alkalinites in water are:-
- Only OH-
- Only HCO3-
- ONLY CO3-
- OH- and CO3 – Togther
Formula :-
Hardness of water by EDTA
1) When standard hard water is used
Total hardness of water sample = 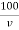 .
. 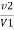 . Mg. CaCo3
. Mg. CaCo3
Where,
M = mgCaco3 in titrated standard hard water
V1 = EDTA volume for titrated standard hard water
V2 = EDTA volume for V ml water sample
2) When EDTA of known molarity used
Total hardness of water sample =  *z*
*z*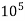 MgCo3
MgCo3
Where,
Y = EDTA volume for V ml of water sample
Z = molarity of EDTA solution
Chloride ions in water sample :-
Cl- quantity = 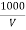 yz (35.5) mgel/L
yz (35.5) mgel/L
Where,
Y = volume of AgNo3
Z = molarity of AgNo3
Alkalinites in water sample
Phenolphthalien alkalinty
P = 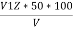 PPM Caco3 equivalent
PPM Caco3 equivalent
Methyl orange alkalinity
M = 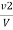 * z * 50 * 1000 ppm
* z * 50 * 1000 ppm
Where ,
V1 = volume of acid for V ml water sample in titraton with use of phenolphthalein indicator.
V2 = volume of acid for V ml water sample in the continued titration using methyl orange indicator.
Z = normally of acid in barette.
In steam geeneration and to increase the lige of the boiler .