Unit IV
Business language and presentation
Importance of Business Language
Foreword
In this unit, we will consider how to use language effectively, especially the persuasive methods that are the purpose of most business communication, and the basic principles that underpin all forms of communication.
We investigate many nonverbal factors that affect communication. This usually arises from the unconscious aspect of our own perceptions, attitudes and behaviours. You need to be aware of these in order to communicate effectively.
The next section discusses important aspects of the basic skills of reading, speaking, and listening.
Finally, consider your note-taking skills, the situations in which you may need them (more than you can imagine in the context of your business), and the different approaches that may be adopted.
The importance of language
Whatever communication channel you use, written or verbal, face-to-face, or through some intermediary
– The effectiveness of the message depends heavily on the individual words chosen to reflect your meaning. Recipient responses are coded in the language, even when using signatures and images.
We have a language-based culture used to convey all our emotions, thoughts, attitudes and prejudices. Or you can deliberately manipulate it to generate puns, double meanings, poems or prose. There are also perceptions used to describe events, people, and landscapes. Orassy (or verbal communication) is as language-dependent as literacy (written communication).
We use an educational and experience-based internal selection process to select words or phrases that are suitable for all contexts in which we find ourselves. Often, our vocabulary depends on the vocabulary of the person with whom we communicate. In certain situations, you may unknowingly adopt Mannerism or Accents. What is certain is that we take words for granted, the meaning we attribute to them is true, our pronunciation is correct, and we use them properly. It means believing that it is a context. You may not be aware of the taglines and tags that you use many times in oral or written communication. Example:
"Hmm" "Yeah"
"You know" "It's great"
"Swings and Roundabout"
Language has a purpose of communication. This does not mean that it is always simple. Careful wording and information can change the overall perceived meaning of a phrase or sentence. Example:
"Do you think you need to use Susan in a production briefing?" "Well, she's very talented ---"
You can feel "but" in the reaction, and nonetheless nothing is said to be harmful to Susan.
Improper use of foreign languages is intentional and aims to establish a sense of superiority or unity, such as:
"Exaggeration? Moi!"
To complicate matters, the recipient of your communication may have a different set of meanings attached to the words or phrases you use, and thus in a completely different way than you intended. You may see your message.
"The relationship between academic theory and marketing practices reflects a relative position on important aspects of differentiation and cost-effectiveness."
What does this mean? It shows a lack of complete understanding of its own statement. We also combine different ideas to form incomprehensible jargon.
Effective use of language
"Sticks and stones can break my bones, but words don't hurt me."
Is this true! It is not only the words of others that can hurt us, but our own words that can hurt our reputation and professional status.
So how can we use a language that accurately reflects our goals and is clearly understood by the people with whom we communicate? There are some basic rules and techniques that support effective communication, such as verbal, visual, and written.
- Keep in mind the purpose of communication.
- Plan communication – channels, places, times, people.
- Aim for brevity.
- Make sure the idea is clearly expressed.
- Observe the relevant points.
- Avoid unnecessary jargon and jargon.
- Prioritize simple things over complex ones.
- Make sure the communication is logically structured.
- Know what you are talking about: Be well explained.
- Use the appropriate tone and style.
- Use the appropriate language (French, English, etc.) that all stakeholders can understand.
- Be positive.
- Check and evaluate the error.
- Don't let your language become boring, clichéd, dishonest, or hypocritical.
- Do not patronize.
- Do not waffle.
- Respect the views and opinions of the recipient.
- Respond to feedback.
- Plan and evaluate communication
Factors Affecting Language Use
The following factors affect not only the use of language, but also the use of the recipient of the communication.
- Year
- Culture
- Sex
- Race
- Religion
- Status
- Environment
- Education
- Technical knowledge / expertise
- Organizational culture
- Previous meetings / experiences
“Global Village” means that more and more organizations are collaborating with other organizations around the world. The development of the EU will mean an increasingly European environment for British organizations. Proper use of the language becomes more and more apparent.
There are many mistakes in product names and slogans as a result of not taking culture and language into account. For example:
- “Hoover sack” banned in the United States.
- Australian condom brand "Scotch tape".
- “Bums” – potato chips sold in Spain. Not available in the UK under this name.
In France, it is advisable to avoid the delicate political issue of "Franglais". (Parking, stop-)
Common Errors in English
Factors Affecting Language Use
The following factors affect not only the use of language, but also the use of the recipient of the communication.
- Year
- Culture
- Sex
- Race
- Religion
- Status
- Environment
- Education
- Technical knowledge / expertise
- Organizational culture
- Previous meetings / experiences
“Global Village” means that more and more organizations are collaborating with other organizations around the world. The development of the EU will mean an increasingly European environment for British organizations. Proper use of the language becomes more and more apparent.
There are many mistakes in product names and slogans as a result of not taking culture and language into account. For example:
- “Hoover sack” banned in the United States.
- Australian condom brand "Scotch tape".
- “Bums” – potato chips sold in Spain. Not available in the UK under this name.
In France, it is advisable to avoid the delicate political issue of "Franglais". (Parking, stop-)
Today, entrepreneurs, investors, medical professionals, technicians, everyone is doing business in some way. Everyone must skills to write down effectively. Anyone who wants a clear understanding needs to learn how to use grammatically correct sentences.
Purpose of business writing
Business writing aims to speak as effectively and concisely as possible. It has to be on target, as most people are busy and don't want to waste time reading unnecessarily long messages.
The business world today is highly competitive and you don't want to lose business due to write errors. The truth is that if your text contains errors, the reader may think you are not serious or you are a beginner. Imagine a contract bid with an error-filled bid. At first glance you can lose your contract.
Common business writing errors
Some are the result of ignorance, while others are the result of oversight. These can be fixed by reading at least twice before sending the message.
Before moving on, keep in mind that English is not particularly easy and everyone makes mistakes from time to time. It just happens. However, keeping these tips handy will help you focus on and eliminate the most common errors in writing. It's a step-by-step process.
You vs we
"Your" is a possessive pronoun used to convey that something or a person belongs to someone. Used when talking about possession. On the other hand, "you" is an abbreviation for "you". In voice communication, "you" sounds like "you." Therefore, if you are not careful, you can easily confuse the two.
Here is an example:
Wrong example: Where are your cats?
Correct answer: Where is your cat?
The hint here is that if you can replace it with "you" and it still makes sense, then "you" is correct. For example, "you are sweating" are often written as "you are sweating".
Me vs you
When I was young, I learned that I couldn't say "you and me" or "James and me." Most people may have fixed it, but using "you and me" is not necessarily wrong.
It is an error to mention "James and that i will work thereon tonight". However, it is correct to say "Please forward the email to James and me". The correct sentence in the first example is "James and I will work on it tonight."
The above example is confusing, isn't it? How does one know when to use "I" or "I"? The correct test tip is to remove others and say a sentence in your mind. If the sentence makes sense in the absence of others, you are right. For example, it doesn't make sense to say "I'll work on it tonight." This tells us that the "I" in the sentence is wrong.
There vs. Them
"There" can be quite confused with "they". "There" is used to refer to a place, and "they" are multiple possessive pronouns. Used to say something belongs to more than one person.
Wrong example: An executive meeting by 8am tomorrow.
Correct Answer: There will be an executive meeting by 8am tomorrow.
Correct Answer: They ran out of points allocation for the month.
Sometimes we know the difference between the two, but we mistakenly write one because we think we wrote the other. If you know this is a common error, you will have to double-check each time you use any of these words, so don't replace them.
That vs. It
This pair is famous for confusing even the most skilled writers. At first glance, they look very similar. But they are very different. "Its" is a possessive pronoun used to refer to ownership. On the other hand, "it" is an abbreviation for "it".
Wrong example: It's raining.
Correct answer: It's raining.
What I like most about new printers is their flexibility.
Note that not all possessive pronouns have apostrophes. Another tip to consider is that if you can replace it with "yes", then "yes" is correct. This mistake is so subtle that most people are unaware of it.
Use "they" for your brand
Brands and other entities are collective and should be called singular. It must be "they" because one might quickly conclude that a company is made up of many people. But the opposite is true. When pertaining to a brand, the right pronoun is "it".
Wrong example: Apple has upgraded the App Store.
Correct: Apple has upgraded the App Store.
Note that brands and entities are collective nouns and will be treated as singular nouns.
Irregular verb
These are stubborn verbs that do not follow the general pattern of the past tense and are lent out with an "ed" to indicate the past tense. Irregular verbs can present difficult times for non-native speakers. Here is an example:
Present tense: i will be able to sing a song for you tomorrow.
Wrong past tense: I singed a song for you yesterday.
Correct answer: I sang a song for you yesterday.
Oral Presentation Skills
There is a myth that great speakers are born, not made. This is often based on the misconception that somehow certain individuals have the innate ability to stand ahead of an audience with no anxiety and provides a moving, dynamic speech. The reality is, however, that great speakers generally spend years developing and practicing their art of communication. All great speakers had to learn the fundamentals of organization, preparation, delivery and dealing with anxiety. So as to do anything well, it takes constant practice and a mastery of the fundamentals. Speaking is not any different.
One of the foremost important techniques you'll apply to become a more confident and effective speaker is to scale back anxiety. If implemented, the subsequent tips could help reduce your anxiety before your next presentation:
- Organize – focus on your presentation.
- Visualize – Mentally rehearse an ideal presentation with questions and answers.
- Practice – Standing up, out loud, using visual aids. Obtain feedback from others.
- Breathe – sit up or stand erect, not relaxed. Inhale deeply variety of times. Focus on Relaxing!
- Release Tension – Try isometric exercises. Tighten and release your muscles. Start with toes and end with fists.
- Move – Flex your muscles – don’t lock! Use a cordless microphone.
- Eye Contact with the Audience – Think one on one. Connect with the audience and make yourself personable. Use the feedback and energy you receive from your audience.
Planning your presentation is another component to becoming an efficient speaker and presenter. There are essentially two steps that should be followed before delivering a presentation: 1) develop your objectives and 2) analyze your audience. In preparation, one must identify the values, needs and constraints of the attendees and the level of data of the audience. For instance, do not use slang, jargon, acronyms, or technical terms without explanation. It should even be determined beforehand “what will work” and “what won’t work”. In other words, what will gain you the foremost favourable reaction. In order to establish these items in advance, you ought to put yourself within the shoes of the people that will be listening to your presentation.
The next phase towards improving your effective public speaking skills is organizing your thoughts. There is variety of steps to the present process:
Step #1 Brainstorm main ideas. Use index cards or post it notes and only use one idea per card.
Step #2 State the sub points. Ideally there should be between 2-5 sub points in your presentation. Be specific using explanations, data and evidence to back up your points.
Step #3 State the benefits. Specifically state the advantages before and at the end of the body of your presentation.
Step #4 Develop hand-outs. Hand-outs should reinforce details, summarize action items and include supporting data.
Step #5 Develop visual aids (PowerPoint slides, charts and graphs). Visual aids should be wont to focus the eye of your audience, reinforce the verbal message and to stimulate interest. Confine mind that effective presentations are people-centred, not media-cantered. Too many presentations believe the media to hold the message. While the media can certainly help, it’s your interaction and rapport with the audience that creates the difference between an efficient or ineffective presentation.
Step #6 Main idea preview/review sentence (i.e. tell them what you’re getting to tell them, tell them, then tell them what you told them).
Step #7 Develop the introduction. Get the audience to focus their attention on you, provide background information and introduce yourself – who you're and why you’re qualified.
Step #8 Develop the conclusion. Your conclusion should be persuasive sort of a “call to action”. Spell out what specifically they have to do, when and the way .
The delivery of your presentation is another key to a successful presentation. An efficient presentation should be delivered within the following sequence:
- Introduction
- Preview Sentence
- Main Ideas and Sub Ideas
- Benefits
- Review Sentence
- Conclusion
In order to return across to your audience as confident and persuasive, you should consider the way you physically deliver your points to your audience. The subsequent are some helpful tips to assist you achieve A level of confidence in delivering your presentation:
Level of confidence in delivering your presentation:
- Posture – get up straight, but avoid being stiff. Don’t shift your weight from side to side.
- Movement – Keep yourself a minimum of 4-8 feet from the front row – don’t pace!
- Gestures – Your presentation should be a sort of animated conversation. Avoid keeping your hands in your pockets or on your hips, crossing your arms or wringing your hands.
- Eye Contact – don't look at the back of the room or over their heads. Maintain good eye contact to create rapport, trust and confidence.
- Use your Voice – Avoid being monotone which is usually caused by anxiety. Also avoid talking too fast. When people are nervous, they often trip on their words. Be cognizant of your volume. Make sure that everybody can hear you.
Oral Presentation Importance
Oral presentations are one of the best platforms that combine nonverbal cues with effective language skills to add a wide range of aspects to communication. It allows individuals to confidently present their thoughts and views in front of a living audience.
This task requires a lot of effort, ideas, and enthusiasm, but proper planning, preparation, and practice are important if you really want to make an effective oral presentation.
Start with the plan. Of course, you need a strong plan to convey your thoughts and perspectives related to a particular topic. To do this, presenters need to gather the materials and information they need, come up with new ideas, and organize them in a proper way.
Please be well prepared before giving a presentation. Start with a topic slide. This prepares the viewer for attending the presentation. Remember to add rationale and include conclusions.
8 important tips to help you prepare for your oral presentation:
- Keep your viewers interested with relevant images and graphics. If you are using PowerPoint for your presentation, you can download free PowerPoint graphics and backgrounds from this website.
- Don't overload your slides with too much information or numbers.
- Be careful when choosing text and background colors. It is also advisable to avoid the use of distracting backgrounds that can distract the audience.
- You need to use the correct font size. The text is 32 points and the headline is 36 points.
- The trick of emphasizing important text with prominent colors has always proven to be very successful. This not only draws the user's attention quickly, but also helps improve text retention.
- Instead of using complex diagrams, add simple, easy-to-understand diagrams.
- Try to maintain the proper order of the slides so that the audience can easily grasp the issues being discussed.
- Practice is the key to success. It is imperative to rehearse the topic long before the presentation, as "practice perfects the person".
People are adopting this technology because of the many benefits that come with it. Some of them are discussed here.
- An immediate way to convey and receive information.
- It provides the audience with a better opportunity to understand the speaker's context.
- The presenter can get immediate feedback on his work and research by judging the reaction as well as the body language of the audience.
- High level of understanding and transparency
- It gives the audience the right flexibility and allows them to make the right decisions on a particular topic.
- Effective oral presentations can save effort, time, and money not only for the speaker but also for the listener.
- It can be used to convey sensitive information to selected groups of individuals, ultimately improving the level of information transmission and exchange.
- Oral communication raises the level of participation.
At times, excessive anxiety can ruin your entire presentation. Whether you're a first-time presenter, a tenth presentation, or whatever, include these points in your presentation to get quick results.
Characteristics
Features of Oral Presentation
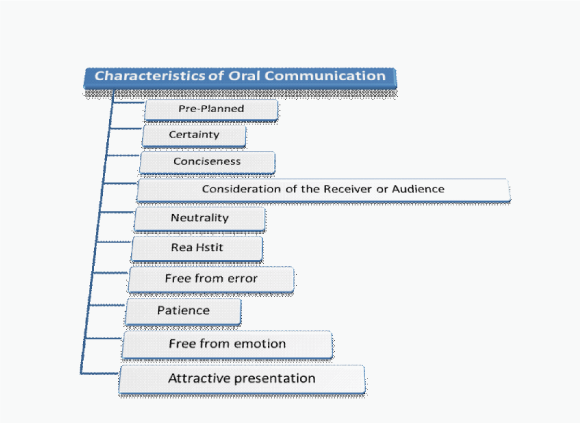
Flow chart
For oral presentations, four characteristics determine the quality of the presentation. Preparation, delivery, audience, and visuals need to be considered and completed before a solid presentation can be made. The speaker can control each of these four functions to ensure that the message is fully received.
Preparation
A strong oral presentation begins with a sound survey, regardless of topic. Gather the information you need and select only the information that is essential to convey the message you need. Don't overwhelm the shared ideas of the mountain of research. Know when to cut and trim distracting facts.
Delivery
After preparing the information, practice delivering the presentation. Speakers need to be familiar and knowledgeable, not mechanical. The information needs to sound fresh and conversational to attract the audience. Oral presentations come in many forms, but presentations should not sound like rehearsals. Natural language flows and the individuality of the speaker brings the topic to life. Practice in front of a mirror or with a video camera to check your voice tone, intonation, and pace.
Audience
Audience is the most unpredictable feature of oral presentations. Speakers need to know the type of audience when preparing and practicing their presentation. The audience determines the tone, language, and type of visuals. If the audience is young and informal, the presentation can include more casual tones and words, and perhaps more flashy visuals. On the other hand, if the audience is academic or professional, the tone and language can be formal and sophisticated, and the visual wonders can come from substance and information rather than flash. .. Talented speakers can read the audience during the broadcast and change the presentation accordingly.
Visual
Visual assistance is an important part of oral presentation. Visuals captivate the audience and add another dynamic to the speaker-audience relationship. Visual aids should be tailored to the type of audience and appropriate for your settings. Consider using computers, objects, experiments, handouts, projections, others, photographs, and demonstrations. Visual aids need to be relevant and cohesive to the topics discussed.
Speakers are also visual to the audience. Dress accordingly and practice oral presentations in the allotted space. To avoid awkwardness, use the space provided and practice your movements before your presentation.
Always come early to set up your visuals so that your presentation goes smoothly.
Presentation Plan
Formal presentations of statistics may be divided into principal categories: presentation abilities and private shows.
These factors are interwoven and may be defined as the instruction, presentation, and practice of linguistic and nonverbal verbal exchange.
This article describes what displays are and defines a few crucial terms related to presentation competencies.
Many human beings are anxious when requested to provide their first public talk. A number of these early fears can be mitigated by means of proper preparation to put the foundation for a powerful presentation.
The presentation is ...
Presentations are a method of conversation that may be adapted to a ramification of conversational conditions, such as conversations with organizations, speeches at meetings, and motives to teams.
Presentations can also be used as a wide term that consists of other "speech engagements," inclusive of wedding speeches and incomes factors at video meetings.
To be powerful, you want to carefully don't forget the methods and manner of imparting step-with the aid of-step practise and statistics.
Shows want to convey a message to listeners, often with "convincing" factors. As an instance, you might speak approximately the high-quality paintings of your organisation, what you could provide your company, and why you need to acquire additional investment on your mission.
An essential detail of the presentation
Creating a presentation is a manner to carry your mind and thoughts in your audience, and a lot of our articles on communique also are relevant right here. See what's verbal exchange? For plenty.
Remember the following key components of your presentation:
Surroundings
To completely understand the context of your presentation, ask your self the subsequent questions:
When and wherein do you give your presentation?
There may be a international of distinction among a small room with natural mild and a casual atmosphere and a large lecture room illuminated with the aid of degree lighting fixtures. The 2 require completely unique shows and distinctive techniques.
Is it in a setting you're acquainted with, or is it someplace new?
In case you're in a new vicinity, it's really worth visiting in advance, or at least arriving early to get used to the room.
Is the presentation in a proper or casual putting?
Work settings are greater or much less formal through definition, however there are also various ranges of formalness.
Is the presentation directed to a small organization or a large quantity of humans?
Are you already familiar with the audience?
With a brand new target audience, you need to construct consider quickly and efficiently to make them your side.
What equipment and technologies are to be had and what are you expected to apply?
Specifically, you need to ask about Mike and whether he's expected to face in one region or circulate around.
What are you and your target market watching for to research from your presentation?
Find out how you are "billed" to provide you clues approximately the statistics you need to consist of on your presentation.
Presenter
The role of the presenter is to speak with the target market and control the presentation.
But, understand that this may additionally encompass passing control for your target market, specifically in case you need some interplay.
Target market
The target market receives the presenter's message.
However, this reception is filtered and motivated through the listener's personal enjoy, information, non-public values and extra.
Message
One or extra messages are added to the target market through the presenter.
Messages may be more desirable not handiest by spoken language (verbal communication), however also by way of techniques including voice projection, body language, gestures, eye touch (nonverbal conversation), and visible aids.
The message is likewise motivated via the expectations of the target audience. As an instance, if you are asked to speak on one precise subject matter and pick out to talk on some other topic, your target audience may deliver your message on board, even in case you supply a excellent presentation. It's far low. They decide that your presentation has failed because you are not meeting their expectancies.
Response
The response of the target market, and accordingly the fulfilment of the presentation, relies upon in large part on whether or not you, as a presenter, delivered the message successfully, and whether or not it lived up to their expectancies.
As a presenter, you do not manage the expectations of your audience. All you could do is find out what they've said approximately you from the conference organizers and what they expect. Only if you realize it can you be confident in offering something that meets your expectations.
Method
How will the presentation be delivered?
Shows are normally introduced immediately to the audience. However, it is able to be introduced from a far-off place over the net the use of a video conferencing system consisting of Skype.
It's also essential to consider if your story is recorded and posted to net, people may additionally have get admission to to it for numerous years. Which means that simultaneous references need to be minimized.
Challenge
Many elements can affect the effectiveness of ways a message is communicated to a target audience.
For instance, background noise and different distractions, overly warm or cool rooms, time zones and the state of interest of the audience can all have an effect on the level of attention of the target market.
As a presenter, you need to be prepared to deal with such issues and strive to hold your target market centered for your message.
Steps to prepare a presentation
Presentation planning
Getting ready a maze presentation may be an overwhelming experience if you allow it to be one. The following strategies and processes are provided to help you wreck down what might be taken into consideration a big task into smaller, greater possible tasks.
Step 1: examine your target market
Step one in getting ready a presentation is to examine more approximately the target audience you intend to speak. It's an amazing concept to get statistics about your target market's heritage, values, and pursuits so that you can recognize what your target market expects from your presentation.
Step 2: choose a topic
Then, if viable, choose the audience and the topic you are inquisitive about. It is a whole lot easier to offer a presentation that your target audience reveals relevant, and it'll be more amusing to observe the topic you are interested in.
Step 3: define the reason of the presentation
After choosing a subject, describe the cause of your presentation in one concise declaration. The purpose is to specify exactly what you want your target market to analyze out of your presentation. Determine the cause and level of content primarily based on the time of the presentation and the history knowledge of the target market. Use this assertion to cognizance on researching and growing your presentation. Put together the content of the presentation
Step 4: put together the frame of the presentation
After defining the reason of the presentation, decide the amount of records that can be presented in the allowed time. Additionally, use your knowledge of the audience to put together the ideal degree of element presentation. I don't need to devise a presentation this is too basic or too advanced.
The body of the presentation is the place to offer your ideas. To provide your ideas in a compelling manner, you want to give an explanation for and aid them. Techniques that let you do that encompass:
- Present facts and facts
- Examine prices from professionals
- Accomplice personal stories
- Provide a vivid rationalization
Also, understand that it's miles crucial to provide variety when making plans the body of your presentation. Listeners may additionally speedy become bored with many facts or concentrate to memories one after another.
Step 5: prepare implementation and conclusions
After making ready the frame of the presentation, determine a way to begin and quit the speak. Make certain the introduction draws the attention of the target market and the conclusions summarize and repeat your key factors. In different words, "inform them what you are attempting to mention to them. Inform them. And tell them what you are trying to say to them."
At the outlet of your presentation, it is critical to get the attention and interest of your target audience. In any other case, the listener could have a difficult time turning to different locations and undoing. The available techniques are:
- Create referrals associated with your listeners' dreams, values, and needs
- Ask inquiries to stimulate thinking
- Proportion your private experience
- Begin with jokes and funny stories
- Undertaking cartoons and colourful visuals
- Make stimulating or stimulating feedback
- Supply a completely unique demonstration
At the hole, we need to articulate the topic and the cause of the presentation. By articulating the topic and cause, listeners can awareness for your primary ideas and without difficulty follow them.
At the cease of the presentation, spotlight the primary ideas you've got conveyed. Remember the fact that listeners do no longer remember the entire presentation, however handiest the principal thoughts. Reinforcing and confirming the primary thoughts will assist the audience don't forget them exercise and provide
Step 6: exercise delivering your presentation
The general public spend hours getting ready a presentation, but little time to practice it. When training your presentation, you could reduce the wide variety of instances you assert phrases and phrases along with "uh," "nicely," and "." these behavior can easily undermine the credibility of the speaker. You may also nice-tune your content to make sure which you create the most vital factors within the allotted time.
Further to planning the content of your presentation, you need to present superior mind on the way you need to deliver it. Do you need to devote your presentation to memory, guide it with a card, or examine it from a script? As a substitute, you may use a aggregate of strategies. Please read the pros and cons of the four delivery techniques defined beneath that will help you make a decision.’
References:
- Lesikar, R.V. & Flatley, M.E.; Basic Communication Skills for Empowering the Internet Generation, Tata
- McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd. New Delhi.
- Bovee, and Thrill, Business Communication Today, Pearson Education
- Shirley Taylor, Communication for Business, Pearson Education
- Locker and Kaczmarek, Business Communication: Building Critical Skills, TMH