Unit II
Planning
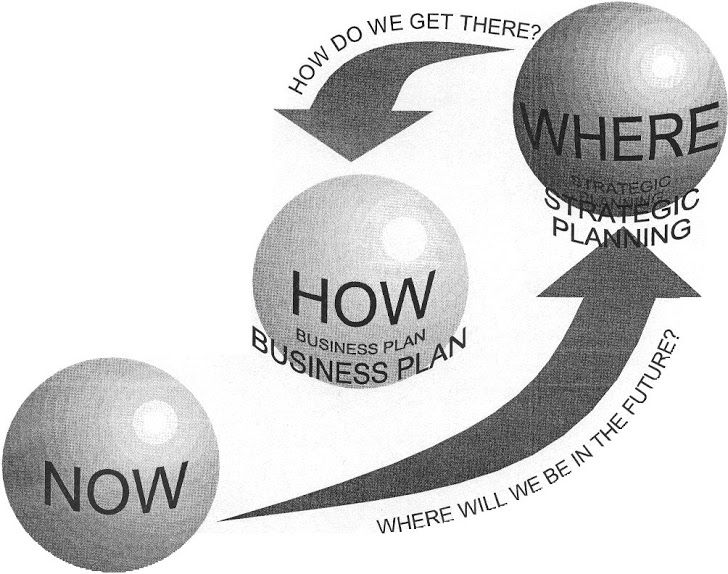
Meaning
Just as management is a never-ending activity, so is planning. In fact, business planning is one of the main functions of management. It sets the stage for all subsequent management functions like organizing, leading, etc. Let's understand the concept of planning.
We already know what planning is, it is deciding in advance what to do. It is the basis for all future plans of the organization. Planning bridges the gap between where the organization currently is and where it wants to be.
So, in essence, business planning comprises setting goals for the organization and developing an idea of action to realize these goals. Once goals are set, managers and workers can have a clear vision of what to work towards.
Managers are a very important part of the business planning function. Planning requires innovation, creativity, and multitasking on the part of managers. And planning is a function that managers at all levels must perform, that is, upper, middle and lower management.
Planning is one among the foremost important and essential functions of management. It is an activity that managers at all levels must carry out. So, depending on the level of management, the type of plan will be different. Let's look at the different types of management plans.
Plan types
Planning is a ubiquitous management function; it has an extensive scope. So, all managers at all levels participate in planning. However, the plans made by the higher-level manager will be different from those made by the lower managers.
Plans also differ in what they seek to achieve and the methods that will be used to achieve them. So, let's look at the types of plans managers are faced with.
Goals
This is the first step in planning the organization's action plan. Goals are the foundation of any business and the desired goal / outcome that the business plans to achieve, thus they are the end point of all planning activity.
For example, one of the goals of an organization might be to increase sales by 20%. The manager will then plan all the activities of the organization with this ultimate goal in mind. When framing your organization's goals, a few points should be kept in mind.
- Goals should be framed for a single activity in mind.
- They must be results oriented. The objective must not frame any action
- The objectives must not be vague, they must be quantitative and measurable.
- They should not be unrealistic. The objectives must be achievable.
Objective
Strategy
Obviously, this is the next type of plan, the next step that follows the objectives. A strategy is a complete and comprehensive plan to achieve these objectives. A strategy may be a plan that has three specific dimensions
Set long-term goals
Select a specific course of action
Allocate the necessary resources for the plan.
The training strategy is generally reserved for the top level of management. In fact, it defines all future decisions and the long-term scope and general direction of the company.
Politics
Policies are generic statements, which are basically a guide to channel energies towards a specific strategy. It is the general way for an organization to understand, interpret and implement strategies. Like for example, most companies have a return policy or a hiring policy or a pricing policy, etc.
Policies are set at all levels of management, from primary policies at the highest level to secondary policies. Managers must formulate policies to assist employees navigate a situation with predetermined decisions. They also help employees make decisions in unexpected situations.
Procedure
Procedures are the following types of plans. They are a step-by-step guide to the routine to perform the activities. All employees must follow these staggered sequences so that activities can be carried out in an organized manner.
The procedures are described in chronological order. So, when employees follow the instructions in order and completely, the success of the activity is practically guaranteed.
Take, for example, the procedure for admitting a student to a university. The procedure begins with the completion of an application form. It will be followed by a collection of documents and the classification of applications accordingly.
Rules
Rules are very specific statements that define an action or a non-action. Also, the rules do not allow any flexibility, they are final. All employees of the organization must follow and enforce the rules. Not following the rules can have serious consequences.
The rules create an environment of discipline in the organization. They guide the actions and behaviour of all employees in the organization. The "no smoking" rule is an example.
Program
Programs are a detailed statement that describes policies, rules, objectives, procedures, etc. of a company. These programs are important in the implementation of all kinds of plans. They create a link between the objectives, procedures and rules of the company.
Primary programs are conducted at the top level of management. To support the primary program, all managers will undertake other programs at the middle and lower levels of management.
Methods
The methods prescribe the ways in which the specific tasks of a procedure must be performed. Additionally, the methods are very specific and detailed instructions on how employees should perform each task in the planned procedure. So, managers form methods to formalize routine jobs.
Methods are very important types of plans for an organization. They help in the following ways
- Give clear instructions to employees, eliminate any confusion
- Ensures uniformity in employee actions
- Standardize routine jobs
- It acts as a general guide for employees and managers.
Budget
A budget is a statement of the expected results that managers expect from the company. Budgets are also a significant statement, so they are expressed in mathematical terms. A budget quantifies the prognosis or future of the organization.
There are several means to prepare budgets that managers make. There is the obvious financial budget, which forecasts the profit of the company. Then there are the operating budgets generally prepared by lower-level managers. Cash budgets control the cash inflows and outflows of the business.
Significance of business planning
Planning is an important function of management; it tells the manager where the organization should go. It also helps the organization reduce uncertainty. Let's take a look at some important planning functions.
1] Planning provides a sense of direction
Planning means drawing up a predetermined plan of action for the organization. Actually, it establishes in advance what and how the work should be done. This helps provide workers and managers with a sense of direction, a guide in some way. Without planning, your actions would be uncoordinated and disorganized.
2] Planning reduces uncertainty
Planning not only sets goals, but also anticipates any future changes in the industry or organization. So, it allows managers to prepare for these changes and allows them to deal with uncertainties. Planning takes into account past events and trends and prepares managers for any uncertain events.
3] Planning reduces waste
The detailed plans made take into account the needs of all departments. This ensures that all departments are in tune with the plan and that all their activities are coordinated. There is clarity in thought that leads to clarity in action. All work is done without interruptions or loss of time or resources,
4] Planning invokes innovation
Planning actually involves a lot of innovation on the part of managers. Being the first management function is a very difficult activity. It encourages the manager to broaden his horizons and forces him to think differently. That is why managers must be creative, insightful and innovative.
5] Make decisions = Facilitate
In business planning, the objectives of the organization have been set, an action plan has been developed and predictions have even been made for future events. This makes it easy for all managers at all levels to make decisions with some ease. The decision-making process also becomes faster.
6] Sets standards
Once business planning is done, managers have now established goals and standards. This provides the manager's standards against which he can measure actual performance. This will help the organization to measure whether the objectives have been met or not. Therefore, planning is a prerequisite for control.
An overview to highlight the Differences
While business planning is mandatory and a need for every organization, it has some restrictions. Let's take a look at some of it:
1] Stiffness
Once the planning function is completed and the action plan is established, the manager tends to just follow the plan. The manager may not be in a position to change the plan depending on the circumstances. Or the manager may not be willing to change the plan. This type of rigidity is not ideal for an organization.
2] Not ideal in dynamic conditions micas
In an economic environment, something is rarely stagnant or static. Economic, political, environmental and legal conditions continue to change. In such a dynamic environment, it becomes difficult to predict future changes. And if a manager cannot forecast accurately, the plan can fail.
3] Planning can also reduce creativity.
While making a plan requires creativity, managers blindly follow the plan. They don't change the plan according to the dynamic nature of the business. Sometimes they don't even make the right suggestions to top management. Work becomes routine.
4] Planning is expensive
Planning is an expensive process. Because it is an intellectual and creative process, it is necessary to hire specialized professionals for the job. Also, it involves a lot of research and data collection and number processing. At times, the cost of the planning process can outweigh its benefits.
5] Not completely accurate
When planning, we have to predict the upcoming and forecast certain future events in the organization and the industry. So, of course, there cannot be one hundred percent certainty in such cases. So, it can be said that business planning lacks precision.
Key takeaways:
- A business plan is a written document that describes the core business activities and objectives of a company and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Start-ups use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- Companies can submit a longer traditional business plan or a shorter lean-start business plan.
- Planning is an important function of management; it tells the manager where the organization should go.
- While business planning is mandatory and a need for every organization, it has some restrictions
Everything you would like to understand about strategic planning. Strategic planning means planning strategies and implementing them to realize the objectives of the organization.
Start by asking yourself simple questions like: What are we doing? Should we keep doing it or change our line or the way we work? what's the impact of social, political, technological and other factors on our operations? Are we prepared to simply accept these changes, etc.?
Strategic planning helps to understand what we are and where we would like to travel in order that environmental threats and opportunities are often taken advantage of, given the strengths and weaknesses of the organization.
Strategic planning may be a systematic and formally documented process for deciding what few key decisions a corporation, viewed as a company whole, must make correctly so as to prosper within the years to return.
Strategic planning - Meaning
Strategic planning means planning strategies and implementing them to realize the objectives of the organization. Start by asking yourself simple questions like: What are we doing? Should we keep doing it or change our line or the way we work? what's the impact of social, political, technological and other factors on our operations? Are we able to accept these changes, etc.?
Strategic planning helps to understand what we are and where we would like to travel in order that environmental threats and opportunities are often taken advantage of, given the strengths and weaknesses of the organization.
Strategic planning is that the formalization of designing during which plans are remodelled long periods of your time for the effective and efficient achievement of the organization's objectives. Strategic planning is predicated on an in depth environmental scan. It's a projection of environmental threats and opportunities and an attempt to mix them with the strengths and weaknesses of the organization.
While long-term planning might not be fully equipped to soak up environmental impacts, strategic planning is completed to know, anticipate, and absorb environmental vagaries. Strategic planning is an ongoing process. Whenever business organizations want to realize a better rate of growth or change their operations, they need a far better management data system, they coordinate the activities of various departments, they eliminate complacency of organizations; they create strategic plans.
Planning are some things we do before taking action; that’s, it's an anticipated decision-making. It's a process of deciding what to try to and the way to try to it before action is required.
The strategic plan of the corporate is that the start line for planning. It is a guide for the event of solid sub-plans to realize organizational objectives. The goal of strategic planning is to assist a corporation select and organize its businesses during a way that keeps it healthy despite unexpected changes within the environment. It's intended to shape or reshape the company's businesses and products to supply targeted growth and profit.
An interesting question which will come to mind is how conventional long-term planning gave thanks to strategic planning. Before the primary 1970s, managers who made long-term plans generally assumed that plans for the long run were simply extensions of what the organization had exhausted the past.
However, environmental shocks during the 1970s and 1980s, like energy crises, deregulation of the many industries, accelerating technological change, and increasing global competition undermined this approach to long-term planning.
These changes within the "rules of the game" forced managers to develop a scientific approach to analysing the environment, assessing the strengths and weaknesses of their organization, and identifying opportunities where the organization could have a competitive advantage. As a result, the worth d was recognized
Strategic planning concept:
Planning is related to the future. A planning process implies different degrees of future.
Some parts of the organization require planning for many years into the future, while others require planning only for a short period.
For example, capital spending is related to a long-term period, while a year's budget is short-term in nature. The first is called strategic planning or long-term planning.
"Strategic planning" can be defined as the process of determining the organization's objectives and the resources that will be used to achieve these objectives, as well as the policies that guide the investment use, and arrangement of these resources.
Examples of strategic planning in an organization are: business diversification into new lines, planned growth rate in sales, type of products to be offered, etc. Strategic planning encompasses all functional areas of the business and is affected within the existing and long-term. Framework of economic, technological, social and political factors.
It also involves the analysis of various environmental factors, particularly with regard to how an organization relates to its environment. Generally, for most organizations, the strategic planning period varies between three and five years.
Strategic planning process:
The strategic planning process consists of the subsequent steps:
1. Determination of mission and objectives:
Strategic planning begins with determining the mission of the organization. The main objectives for which the organization has been created must be clearly defined. Strategic planning deals with the long-term relationship of an organization with its external environment. Then, the business mission must be set in terms of the social impact of the organization.
2. Environmental analysis:
To identify opportunities and threats, the external environment of the organization is analyzed. A list of important factors that can affect the activities of the organization is prepared.
3. Self-assessment:
In the next step, the strengths and weaknesses of the organization are analyzed. This analysis will allow the company to capitalize on its strengths and minimize its weaknesses. The company can use external opportunities by focusing on its internal capacity. By combining its strengths with environmental opportunities, a company can face competition and achieve growth.
4. Strategic decision making:
Then strategic alternatives are generated and evaluated. After that, a strategic decision is made to reduce the performance gap. The organization must select the alternative that best suits its capabilities. For example, to grow, a company may enter new markets or develop new products or sell more in current markets.
The choice of strategy depends on the external environment, the perception of management, the attitude of management towards risk, past strategies and the power and efficiency of management.
5. Implementation and control of the strategy:
Once the strategy is decided, it must be translated into tactical operational plans. Programs and budgets are developed for each function. Control must be developed to evaluate performance as the strategy is implemented.
Whenever actual results are below expectations, the strategy should be reviewed or re-evaluated. It must be modified and adapted to changes within the external environment.
Importance of strategic planning:
Strategic planning offers the subsequent benefits:
1. Economic benefits:
Companies that make strategic plans have good sales, low costs, high EPS (earnings per share) and high profits. Companies have economic benefits if they create strategic plans. Companies like Reliance, Infosys, Tata, Wipro, Deloitte, etc. they're the giants that report good financial results as a results of sound strategic planning.
2. Guide to organizational activities:
Strategic planning guides members toward organizational goals. Unify organizational activities and efforts toward long-term goals. Guide members to become who they need to become and to try to what they need to try to. It focuses on specific goals that make it clear to members during which direction to maneuver. Making a profit is a smaller amount significant than getting a rate of growth of 10% per annum.
Paying high dividends is a smaller amount significant than paying dividends at a 40% rate. Meeting the requirements of society is a smaller amount meaningful than providing free education to schoolchildren during a specific community. Resource allocation and attempts to realize objectives are facilitated by clear specifications in strategic planning. It makes the objectives operational and provides the proper direction to the activities of the organization.
3. Competitive advantage:
In the world of globalization, companies that have a competitive advantage (ability to deal with competitive forces) have better financial and sales results. This is often possible if you foresee the longer term. The longer term is often predicted through strategic planning. It enables managers to anticipate problems before they arise and resolve them before they worsen.
4. Minimize risk:
Strategic planning provides knowledge to evaluate risk and frame strategies to attenuate risk and invest in safe business opportunities. The probabilities of creating mistakes and selecting the incorrect goals and methods are therefore reduced.
Risk is inherent altogether businesses and it's almost certain that not anticipating risk through strategic planning will cause business failure, unless proven otherwise accidentally. Business companies operating during a dynamic, changing, and risky environment cannot deal with a scarcity of strategy, the incorrect strategy development, or ineffective strategy implementation.
5. Beneficial for companies with an extended gestation gap:
The time span between investment decisions and therefore the generation of income from those investments is named the gestation. During this era, changes in technological or political forces can affect the implementation of selections and plans can therefore fail. Strategic planning discounts the longer term and allows managers to face threats and opportunities. Big amount of money is required in projects followed by expected financial returns.
6. Promotes motivation and innovation:
Strategic planning involves managers at the very best levels. Not only are they committed to goals and methods, but they also come up with new ideas for strategy implementation. This promotes motivation and innovation. It also provides motivation to lower-level people once they know that their efforts are contributing to the organization's goals.
The satisfied workforce is that the strength of the organization. Save huge costs in reducing absenteeism, job turnover, role conflicts, etc. It promotes discipline within the organization and improves the effectiveness of human resources and also organizational effectiveness.
7. Optimal use of resources:
Strategic planning makes better use of resources to realize maximum performance. Resources are scarce and strategic planning helps to use them where they're needed most.
If your grand strategy is correct, any number of tactical mistakes are often made, and yet the corporate succeeds.
Limitations of strategic planning:
- Lack of knowledge:
Strategic planning requires tons of data, training and knowledge. Managers must have high conceptual skills and skills to form strategic plans. If they are doing not have the knowledge and skill to organize strategic plans, the specified results won't be achieved. It'll also end in huge financial losses for the organization. This limitation is often overcome by training managers to form strategic plans.
2. Interdependence of units:
If business units at different levels (corporate level, business level, and functional level) aren't coordinated, it can create problems for the effective implementation of strategic plans.
3. Managerial perception:
To avoid developing risky goals and methods that they will not be ready to achieve, managers can land on sub-optimal goals and plans. Sometimes short-term commitments also defer long-term strategy development.
4. Financial considerations:
Strategic planning requires an excellent deal of your time, money, and energy. Managers are often constrained by these considerations when making effective strategic plans. These limitations are generally conceptual and may be overcome through rational, systematic and scientific planning. Researchers have shown that companies that make strategic plans outperform people who don't.
5. Exchange problems:
The factor acts more as a limiting think about light of changes in future conditions. During a complex and rapidly changing environment, the succession of latest problems is usually magnified by implications that make planning difficult. The matter of change is more complex in long-term planning.
Current conditions tend to weigh heavily on planning and, by overshadowing future needs, can sometimes cause errors in judgment. Factors like changing technology, consumer tastes and needs, business conditions, and lots of others change rapidly and sometimes in unpredictable ways. Under such conditions, the design activities administered in one period might not be relevant for an additional period because the conditions in two periods are quite different.
6. Failure of people:
There are many reasons why people fail to plan, both at the formulation and implementation levels. a number of the foremost important failures are the shortage of commitment to planning, the shortage of development, solid strategies, the shortage of clear and meaningful objectives, the tendency to overlook the premises of designing , the lack to ascertain the scope of the plan, inability to ascertain planning as a rational approach, over-reliance on past experience, failure to use limiting factor principles, lack of support from top management, lack of delegation of authority, lack of control techniques adequate and resistance to vary .
These factors are liable for improper planning or incorrect planning within the organizations in question.
7. Time and cost:
When browsing the strategic planning process, managers must also consider both time and price factors. The varied steps of designing can go as far as possible because there's no limit to precision in planning tools. But planning is suffering from time and price factors.
Time may be a limiting factor for all managers within the organization and if they're busy preparing elaborate reports and directions beyond a particular level, they're risking their effectiveness. Excessive time spent securing information and trying to suit it into a compact plan is dysfunctional within the organization.
8. Stiffness:
Often people feel that planning provides rigidity in management action. Many sorts of internal inflexibilities are often the results of planning itself. Planning stifles initiative from employees and forces managers to adopt a rigid or straitjacket mode of performing their work. In fact, rigidity can make management work harder than necessary. This will end in lag in job performance, lack of initiative, and failure to adapt to the changing environment.
Many people feel that planning has limited value because the simplest results are often obtained by confusing the kinds of operations during which each situation is addressed when and if it seems relevant to the immediate problem. Although this planning rigidity factor may be a limiting factor, but without planning, it's really difficult to work particularly in large organizations.
Planning also involves costs on a part of the organization. The varied factors discussed above contribute to the restrictions of strategic planning, either by making planning ineffective or by making planned work less.
Key takeaways:
- Strategic planning means planning strategies and implementing them to realize the objectives of the organization.
- Strategic planning means planning strategies and implementing them to realize the objectives of the organization.
- Planning is related to the future. A planning process implies different degrees of future.
- Business diversification into new lines, planned growth rate in sales, type of products to be offered, etc.
- Strategic planning is crucial for a company, as it creates a roadmap that a company must follow and correct when necessary.
- The first part of a strategic plan is the business plan, which describes the business purpose, budgets, goals, and mission statement.
- Taking time to evaluate your business on an ongoing basis will allow you to determine how well your results adhere to your plan. This will allow you to make adjustments or duplicate the way the business is run.
- Communicating your strategic decide to your employees is critical in order that most are on an equivalent page and dealing toward an equivalent goal.
- Reviewing and monitoring your business will highlight the strengths and weaknesses of your business so that you can continue with what is working well and eliminate what is hindering your business growth.
- Flexible companies can find it easier to make changes to their structure and plans, while inflexible companies can get irritated by a changing environment.
- A strategic manager can oversee strategic management plans and design ways for organizations to achieve their benchmark goals.
An overview
Decision making is that the act of selecting between the available alternatives. There are countless decisions that humans make on a day-to-day basis. In business enterprises, decisions are made at every step. It's also considered one among the important functions of management.
Decision making concept
Decision making is that the act of selecting between the available alternatives. There are countless decisions that humans make on a day-to-day basis. In business enterprises, decisions are made at every step. It's also considered one among the important functions of management. Management functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating and controlling are administered through decisions. Deciding is feasible when there are two or more alternatives to unravel one problem or difficulty. If there's just one alternative, it's not about making decisions. Management without decision is believed to be a person without a backbone. Therefore, deciding may be a problem-solving approach by choosing a selected course of action among several alternatives.
Decision making is that the selection, supported some criteria, of two or more possible alternatives. "- George R. Terry
In conclusion, we will say that call making is that the process of selecting a selected course of action among several alternatives to unravel organizational problems or difficulties.
Goal / Objectives/ Importance Achievement:
Decision-making is vital to realize organizational goals / objectives within the given time and budget. Find the simplest alternative, use resources appropriately, and satisfy employees within the workplace. As a result, the goals or objectives of the organization are often achieved supported the specified result.
Employee motivation:
Decision making is vital to motivate employees within a corporation. Provides a general operating framework and guidelines for the operational level of staff. It also provides different sorts of facilities and benefits on time. As a result, employees are motivated for his or her job or work consistent with the wants of the organization.
Appropriate use of resources:
An organization has various resources like man, money, method, material, machine, market and knowledge. Of these resources are used correctly without leakage or waste with the assistance of the proper decision at the proper time. As a result, a corporation can operate at minimal cost.
Selection of the simplest alternative:
As we know, the matter has multiple solutions. Deciding is vital to pick the simplest alternative among several alternatives analysing them one by one using various financial, statistical and accounting tools / techniques.
Management performance evaluation:
Decision-making isn't only important in selecting the simplest alternative, but also essential in evaluating a manager's performance. The standard / success of the manager depends largely on the number of correct decisions that he can bring the success of the organization. Therefore, deciding is vital in judging the performance of the highest level of management.
Essential element / component:
Decision making is an important element / component for organizational success because without making the proper decision at the proper time, nothing is often accomplished consistent with plan.
Generalized function:
Decision making may be a generalized function of managers whose objective is to realize organizational objectives. Decisions must be made altogether management functions, like planning, organization, motivation, direction, and control, and altogether functional areas like production, marketing, finance, personnel, and research and development. It indicates that call making extends to several areas of the organization.
Steps within the decision-making process
For the rationality, reliability, and applicability of selections, managers must follow a sequential set of steps. a choice is claimed to be rational if the acceptable means are chosen to realize the specified ends.
Develop an alternate course of action:
As we know, a drag has multiple solutions. Therefore, the choice maker must develop the varied possible alternatives for a far better decision. While developing the choice course of action, he / she will also use his / her own knowledge, skills, experiences and technical support from the professional planner and experts.
Identification of the problem:
The initial stage of the decision-making process is identifying the precise problem. The matter can occur thanks to the gap between thinking and doing the method. The rationale for the issues is often internal or external. Decision makers must identify the right issues before making any decisions. It's not employment or a simple task. Therefore, you'll use your own knowledge, skills, experience, and gather information from internal and external sources. Identifying the right problem is believed to be almost half the decision-making process.
Problem analysis:
After identifying the right problem, the choice maker must analyze the matter systematically and scientifically in terms of cost, time, legality, organizational resources, and therefore the short- and long-term impact of the matter. In analysing the matter, she will use various financial, accounting, and statistical tools or techniques.
Selection of the best alternative:
After analysing the various alternatives, the decision maker has to select the best alternative among the various alternatives considering both the short and long-term impact. For this purpose, he / she can use her knowledge, skills and experiences. She may also worry about other stakeholders to make a better decision.
Decision review:
The last step in the decision-making process is to get responses or feedback from other stakeholders in the organization. If the answer is positive, the decision-making process is completed successfully. If the answer is no, then you must go through the first step to make a new organizational decision.
Evaluation of the alternative course of action:
After developing several possible alternatives, the decision maker must evaluate all the alternatives one by one to make a better decision. In this step, she should try to find the answers to the following questions.
- Is the alternative feasible in terms of cost, time, legality and other organizational resources or not?
- Is the alternative satisfactory to solve the organizational problems or not?
- Do the characteristics of the alternatives correspond to the business objectives or not?
Committee and Group Decision-making Process
Essential elements of the group decision-making process
Results of the group decision-making process Having an effective group decision-making process can be an important source of productivity improvement for your organization. Some surveys show that almost 50% of participants consider unfocused projects and meetings to be the main source of lost time and productivity during the workday. Many of these meetings support the group's decision-making activities. Any improvement in the group's decision-making process increases the value generated from a decision and at the same time improves organizational productivity.
The first option: What level of participation is needed?
When starting to make a decision, an initial choice must be made regarding the level of collaborative decision-making that is needed. Additional factors that will influence this choice include the value of the decision, the complexity, the time available, the number of alternative solutions, and the level of understanding required for the needs / wants.
The Vroom-Yetton-Jago decision tree can also help you choose the level of participation with simple answers to eight questions.
Select process
With the level of participation determined, a group decision-making process should be used to manage the activities and discussions that will generate the outcome of the decision. The process must:
- Planning decision-making that includes defining the success factors or criteria for the decision;
- Identify and generate decision alternatives;
- Manage the implementation of the decision.
- Please see our decision-making process for more information and details.
- Facilitation of group activities and discussions for decision-making
When it comes to larger groups, an effective group decision-making process will address how group interactions will be managed and facilitated. This should be addressed in the initial planning to ensure that the benefits of the group's contribution and coordination can be realized at all appropriate steps in the decision-making process. Good facilitation can avoid the inappropriate exchange of relevant information and process losses that are characterized by the meeting surveys mentioned within the opening paragraph.
Group facilitation or coordination should aim to:
- Motivate people to work together
- Provide clarity of objectives
- Structure group discussions and provide explicit coordination where mechanisms are clearly and intentionally described to eliminate any misunderstandings in intent
- Provide information to establish common understanding (such as definition of key terms) and promote appropriate exchange
- Provide mechanisms for the storage, retrieval, exchange, summary and repetition of information.
- Establish the communication channels necessary to satisfy the complexity needs of the tasks.
- Offer methods to reconcile conflicting information and the meaning of shared information.
- Address social needs for rules of interaction (such as equal treatment) and facilitate non-conflicting personal goals
- Promote objectivity, equitable participation and consensus while meeting objectives.
- Intervene in crisis, maintain order and resolve emotional conflicts
- Optimize the integration of knowledge, opinions and preferences in the collective decision of the group.
- Make the decision and meet the performance objectives of the decision-making process to achieve the required decision quality
- An important approach to avoiding groupthink captures minority positions, helping to avoid decision-making biases and potentially leading to a different path to follow. Additionally, many problem decompositions approaches and project management methods have been integrated with individual decision-making techniques to address team decision-making.
Choosing the group decision-making method
When executing the process, it will be necessary to determine the method to be used You may consider setting a minimum stake for validity.
Consensus: the majority agrees and no one objects.
Unanimous - Everyone must agree.
There is an astonishing amount of research devoted to understanding these various methods, and the group decision-making process will be most efficient when specific methods are selected during decision planning using the participation level option described above.
Tools to support the group decision-making process
Software tools can provide significant process support by addressing many of the needs identified above. Group decision-making techniques are provided in many tools and often incorporate methods for combining individual responses into proven decision-making techniques, such as Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA).
For large groups, the complexity in managing communications and tasks can be eased with the project management tools currently used in the organization. Once the group decision-making process for the specific decision has been defined, look for a tool or tools that address the specific needs of:
- Determine the level of participation;
- Facilitate group communication;
- Sharing information;
- Combining group entry;
- Task management;
- Apply the agreed decision-making technique or techniques;
- Record of information on decisions and;
- Provide the necessary reports.
- High-value, complex, and uncertain decisions can also benefit from expert facilitation or training, particularly if there is the expectation of heightened emotions and conflict in motivation.
Key takeaways:
- An organizational structure describes how certain activities are directed to achieve the objectives of an organization.
- Successful organizational structures define each employee's job and how it fits into the overall system.
- A centralized structure has a defined chain of command, while decentralized structures give almost all employees receiving a high level of personal agency.
- An organization chart graphically represents the structure of an organization, highlighting the different jobs, departments, and responsibilities that connect the company's employees to each other and to the management team.
- Organizational charts can be broad-based, representing the overall company, or they can be department or unit specific, focusing on a wheel radius.
- Most organizational charts are structured using the "hierarchical" model, which shows management or other senior officials at the top and lower-level employees below them.
- Authority is that the right to execute or order. It also allows its owner to allocate the organization's resources to realize organizational goals.
- Barnad offers some guidelines for what managers can do to extend the likelihood that their orders are going to be accepted and obeyed.
- Each type exists only to permit people to hold out the various sorts of responsibilities that are entrusted to them.
- In general, line authority refers to matters that directly involve production, sales, finance, etc. of the management system and, as a result, with the achievement of objectives.
References:
- Harold koontz and Heinz Weihrich, Essentials of Management, Pearson Education.
- Stephen Robbins and M. Coulter, Management, Pearson Education
- Stephen P Robbins, David A Decenzo, Sangh Mitra Bhattacharya and Madhu Shree Manda Agarwal,
- Fundamentals of Management, Essentials, Concepts and Applications, Pearson Education
- Drucker Peter F, Practice of Management, Mercury Book, Landon
- George Terry Principle of Management, Richard D Irwin
- Newman summer and Gilbert, Management, PHI
- James H Donnelly, Fundamental of Management, Pearson Education
- Chhabra, T.N. Essential of Management. Sun India
- Griffin Management Principles and Application, Cengage Learning
- Robert Kreitner, Management Theory and Application, Cengage Learning