Unit - 1
Introduction
This article delves into the evolution of operating systems since 1950. We'll go over six major operating system types that have been reviewed during the last 70 years.
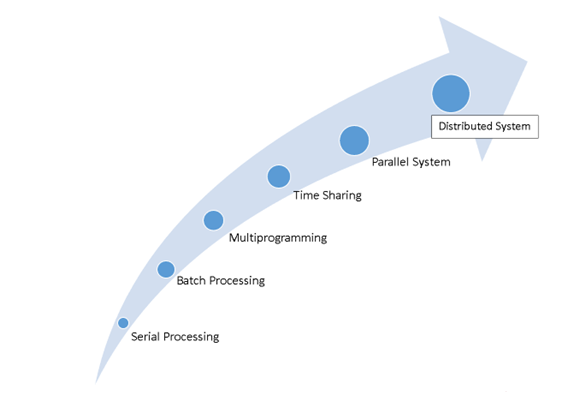
Fig 1: Evolution of OS
Serial processing
The operating system's history dates back to 1950. There was no operating system in 1950, therefore programmers interacted directly with the hardware. The following serial steps are required if a programmer wishes to run a program on specific days.
- The program or punched card should be typed in.
- Use a card reader to convert the punched card.
- If there are any errors, submit to the computing machine, and the lights will indicate the error.
- To determine the source of an error, the programmer inspected the registers and main memory.
- Print the results on the printers.
- Then the programmer ready for the next program.
Batch processing
- This kind of operating system does not collaborate with the computer legitimately. There is an administrator which takes comparable jobs having same prerequisite and gathering them into batches.
- In this kind of system, there is no direct connection among user and the computer.
- The client needs to present work (composed on cards or tape) to a computer administrator.
- At that point computer administrator puts a batch of a several jobs on an input device.
- Jobs are batched together by sort of language and necessity.
- At that point an exceptional program, the monitor, deals with the execution of each program in the batch.
- The monitor is consistently in the primary memory and accessible for execution.
Advantages of Batch Operating System:
- It is exceptionally hard to estimate or realize the time required by any job to finish. Processors of the batch systems realize to what extent the job would be when it is in line.
- Various users can share the batch systems
- The inert time for batch system is extremely less
- It is easy to oversee huge work more than once in batch systems
Disadvantages of Batch Operating System:
- The computer administrators should have complete information with batch systems
- Batch systems are difficult to debug
- It is at some point expense
- Different jobs should sit tight for an obscure time if any jobs fail
Multiprogramming
- This sort of OS is utilized to execute more than one job at the same time by a single processor.
- It builds CPU by sorting out jobs with the goal that the CPU consistently has one job to execute.
- The idea of multiprogramming is depicted as pursues:
- Every one of the jobs that enter the system are kept in the job pool (in a disk). The operating system stacks a lot of jobs from job pool into main memory and starts to execute.
- During execution, the job may need to wait for some task, for example, an I/O operation, to finish. In a multiprogramming system, the operating system basically changes to another activity and executes. At the point when that job needs to wait, the CPU is changed to another job, etc.
- At the point when the first job completes the process of waiting and it recovers the CPU.
- For whatever length of time that in any event one job needs to execute, the CPU is never idle.
- Multiprogramming operating systems utilize the component of job scheduling and CPU scheduling.
Time sharing
- Time-sharing systems are not accessible in 1960s.
- Time-sharing or performing multiple tasks is a legitimate expansion of multiprogramming. That is processors time is shared among numerous users at the same time is called time-sharing.
- The primary contrast between Multi-programmed Batch Systems and Time-Sharing Systems is, in Multi-programmed batch systems its goal is expand processor use, while in Time-Sharing Systems its goal is minimize response time.
- Numerous jobs are executed by the CPU by switching between them, however the switches happen in such a less time, so that the user can gets a prompt response.
- For instance, in a transaction processing, processor execute every user program in a short burst or quantum of calculation.
- That is if n users are available, every user can get time quantum.
- At the point when the user presents the instruction, the response time is seconding all things considered.
- Operating system utilizes CPU scheduling and multiprogramming to give every user a little part of a time.
- Computer systems that were structured essentially as batch systems have been altered to time-sharing systems.
- For instance, IBM's OS/360.
- As the name itself recommends, in a time-sharing system or performing various tasks system, different jobs can be executed on a system simultaneously by sharing the CPU time among them.
- It is viewed as a logical expansion of multiprogramming on the grounds that the two does synchronous execution yet vary in their prime aims.
- The fundamental goal of time-sharing systems is to limit reaction time yet not boosting the processor use (which is the target of multiprogramming systems).
- The time-sharing systems were created to give an intuitive utilization of the computer system.
- A time-shared system utilizes CPU planning and multiprogramming to give every user a little segment of a period shared computer.
- It enables numerous users to share the computer resources all the while. As the system switches quickly from one user to the next, a brief timeframe opening is given to every user for their executions.
- The time-sharing operating system guarantees that every one of the assignments get the chance to get to the CPU individually and for a fixed little interval of time. This interval is known as the time quantum.
- E.g.: Unix Systems
Advantages of Time-Sharing OS:
- Each user gets an equivalent chance
- Less chances of duplication of programming
- CPU inert time can be diminished
Disadvantages of Time-Sharing OS:
- Unwavering quality issue
- One must need to deal with security and respectability of user programs and information.
- Information correspondence issue
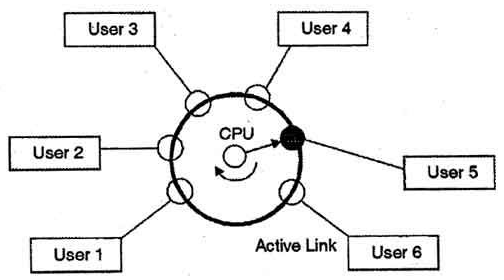
Fig 2. Time-Sharing Operating System
Parallel system
- Parallel Processing Systems are intended to accelerate the execution of programs by isolating the program into numerous pieces and processing those fragments simultaneously.
- Such systems are multiprocessor systems called as tightly coupled systems.
- Parallel systems manage the synchronous utilization of numerous computer resources that can incorporate a single computer with various processors, various computers associated by a network to frame a parallel processing cluster or a blend of both.
- Parallel systems are harder to program than computers with a single processor in light of the fact that the engineering of parallel computers fluctuates appropriately and the procedures of numerous CPUs must be composed and synchronized.
- A few models for interfacing processors and memory modules exist, and every topology requires an alternate programming model.
- The three models that are most regularly utilized in structuring parallel computers incorporate synchronous processors each with its very own memory, asynchronous processors each with its own memory and asynchronous processors with a typical, shared memory.
- Parallel operating systems are essentially worried about dealing with the resources of parallel machines.
- This task faces numerous difficulties: application software engineers request all the performance possible, numerous equipment configurations exist and change all around quickly, yet the operating system should progressively be good with the standard adaptations utilized in computers.
- Today, new applications emerge and request faster computers. Business applications are the most utilized on parallel computers.
- A computer that runs such an application; ought to have the option to process enormous amount of data in modern ways. These applications incorporate designs, virtual reality, and decision support, parallel databases, medical diagnosis, etc.
- We can say with almost certainly that business applications will characterize future parallel computers design however scientific applications will stay significant users of parallel processing innovation.
Distributed system
The processors in a distributed operating system cannot share memory or a clock; instead, each CPU has its own local memory. The processors connect with one another via a variety of channels, including high-speed buses. "Loosely Coupled" systems are what these systems are called.
Advantages
- It is possible to share resources from one site to another if a number of sites are connected by high-speed communication lines, for example, s1 and s2. Some communication lines link them together. The site s1 has a printer, however there is no print on the site. The system can then be changed without having to switch from s2 to s1. As a result, resource sharing in a distributed operating system is possible.
- In distributed systems, a large computer is partitioned into a number of sub-partitions that run concurrently.
- We can use alternative systems/resources in other sites if a resource or system fails in one site owing to technological issues. As a result, the distributed system's reliability will improve.
History of OS
The operating system can be classified into four generations, as follows:
First Generation (1945-1955)
It marks the start of the development of electronic computing systems as a replacement for mechanical computers. Because of the flaws in mechanical computing devices, humans' calculation speed is limited, and they are prone to making mistakes. Because there is no operating system in this generation, the computer system is given instructions that must be carried out immediately.
Plug Boards are an example of a type of operating system and device.
Second Generation (1955-1965)
In the second generation, the batch processing system was implemented, which allows a job or task to be done in a series and then completed sequentially. The computer system in this generation does not have an operating system, although there are various operating system functionalities available, such as FMS and IBSYS.
Batch systems are an example of the type of operating system and devices employed.
Third Generation (1965-1980)
In the third generation, the operating system was designed to service numerous users at the same time. Interactive users can communicate with a computer via an online terminal, making the operating system multi-user and multiprogramming.
Multiprogramming is an example of a type of operating system and devices employed.
Fourth Generation (1980-Now)
The operating system is employed in this age for computer networks where users are aware of the existence of computers connected to one another.
The era of distributed computing has already begun, and users are comforted by a Graphical User Interface (GUI), which is an incredibly comfortable graphical computer interface.
The demand for traditional operating systems has increased as a result of the introduction of new wearable devices such as Smart Watches, Smart Glasses, VRGears, and others.
With the introduction of innovative gadgets such as Smart Watches, Smart Glasses, VR gears, and other wearable devices, the demand for unorthodox operating systems is also increasing.
Personal computers are an example of a type of operating system and device.
Key takeaway
Time-sharing or performing multiple tasks is a legitimate expansion of multiprogramming. That is processors time is shared among numerous users at the same time is called time-sharing.
Parallel Processing Systems are intended to accelerate the execution of programs by isolating the program into numerous pieces and processing those fragments simultaneously.
Operating systems area unit there from the terribly 1st pc generation and that they keep evolving with time. During this chapter, we will discuss a number of the vital varieties of in operation systems that are most ordinarily used.
Batch software system
The users of a batch software system don't act with the pc directly. Every user prepares his job on associate degree off-line device like punch cards and submits it to the pc operator. To hurry up process, jobs with similar wants area unit batched along and run as a bunch. The programmers leave their programs with the operator and therefore the operator then kinds the programs with similar needs into batches.
The problems with Batch Systems area unit as follows –
- Lack of interaction between the user and therefore the job.
- CPU is usually idle, as a result of the speed of the mechanical I/O devices is slower than the mainframe.
- Difficult to supply the required priority.
Time-sharing in operation systems
Time-sharing could be a technique that permits many of us, settled at varied terminals, to use a specific system at identical time. Time-sharing or multitasking could be a logical extension of execution. Processor's time that is shared among multiple users at the same time is termed as time-sharing.
The main distinction between Multiprogrammed Batch Systems and Time-Sharing Systems is that just in case of Multiprogrammed batch systems, the target is to maximize processor use, whereas in Time-Sharing Systems, the target is to attenuate latency.
Multiple jobs area unit dead by the mainframe by change between them, however the switches occur thus oftentimes. Thus, the user will receive a right away response. For instance, in an exceedingly dealings process, the processor executes every user program in an exceedingly short burst or quantum of computation. That is, if n users area unit gift, then every user will get a time quantum. Once the user submits the command, the latency is in few seconds at the most.
The software system uses mainframe programing and execution to supply every user with a tiny low portion of a time. Pc systems that were designed primarily as batch systems are changed to time-sharing systems.
Advantages of Timesharing in operation systems area unit as follows –
- Provides the advantage of fast response.
- Avoids duplication of code.
- Reduces mainframe idle time.
Disadvantages of Time-sharing in operation systems area unit as follows –
- Problem of responsibility
- Question of security and integrity of user programs and information.
- Problem of information communication.
Distributed software system
Distributed systems use multiple central processors to serve multiple time period applications and multiple users. Processing jobs area unit distributed among the processors consequently.
The processors communicate with each other through varied communication lines (such as high-speed buses or phone lines). These area unit referred as loosely coupled systems or distributed systems. Processors in an exceedingly distributed system could vary in size and performance. These processors area unit referred as sites, nodes, computers, and so on.
The advantages of distributed systems area unit as follows –
- With resource sharing facility, a user at one website could also be ready to use the resources on the market at another.
- Speedup the exchange of information with each other via electronic message.
- If one website fails in an exceedingly distributed system, the remaining sites will doubtless continue in operation.
- Better service to the shoppers.
- Reduction of the load on the host pc.
- Reduction of delays in processing.
Network software system
A Network software system runs on a server and provides the server the potential to manage information, users, groups, security, applications, and different networking functions. The first purpose of the network software system is to permit shared file and printer access among multiple computers in an exceedingly network, generally an {area|a neighborhood} area network (LAN), a non-public network or to different networks.
Examples of network in operation systems embody Microsoft Windows Server 2003, Microsoft Windows Server 2008, UNIX, Linux, Mac OS X, Novell NetWare, and BSD.
The advantages of network in operation systems area unit as follows –
- Centralized server’s area unit extremely stable.
- Security is server managed.
- Upgrades to new technologies and hardware is simply integrated into the system.
- Remote access to servers is feasible from completely different locations and kinds of systems.
The disadvantages of network in operation systems area unit as follows –
- High price of shopping for and running a server.
- Dependency on a central location for many operations.
- Regular maintenance and updates area unit needed.
Real Time software system
A time period system is outlined as a knowledge process system during which the interval needed to method and answer inputs is thus little that it controls the atmosphere. The time taken by the system to reply to associate degree input and show of needed updated info is termed because the latency. Thus, during this methodology, the latency is extremely less as compared to on-line process.
Real-time systems area unit used once the area unit rigid time needs on the operation of a processor or the flow of information and time period systems is used as an impact device in an exceedingly dedicated application. A time period software system should have well-defined, mounted time constraints, otherwise the system can fail. For instance, Scientific experiments, medical imaging systems, industrial management systems, weapon systems, robots, traffic management systems, etc.
The area unit 2 varieties of time period in operation systems.
Hard time period systems
Hard time period systems guarantee that essential tasks complete on time. In onerous time period systems, external storage is restricted or missing and therefore the information is kept in storage. In these systems, computer storage is sort of ne'er found.
Soft real-time systems
Soft real-time systems are less restrictive. A critical real-time task gets priority over other tasks and retains the priority until it completes. Soft real-time systems have limited utility than hard real-time systems. For example, multimedia, virtual reality, Advanced Scientific Projects likes undersea exploration and planetary rovers, etc.
Key takeaway
Operating systems are there from the very first computer generation and they keep evolving with time. In this chapter, we will discuss some of the important types of operating systems which are most commonly used.
An OS provides services to each the users and to the programs.
- It provides programs Associate in Nursing atmosphere to execute.
- It provides users the services to execute the programs during a convenient manner.
Following square measure many common services provided by Associate in Nursing OS Associate in Nursing
- Program execution
- I/O operations
- File System manipulation
- Communication
- Error Detection
- Resource Allocation
- Protection
Program execution
Operating systems handle several styles of activities from user programs to system programs like printer spooler, name servers, digital computer, etc. every of those activities is encapsulated as a method.
A method includes the entire execution context (code to execute, knowledge to govern, registers, OS resources in use). Following square measure, the foremost activities of Associate in Nursing OS with relevancy program management −
- Loads a program into memory.
- Executes the program.
- Handles program's execution.
- Provides a mechanism for method synchronization.
- Provides a mechanism for method communication.
- Provides a mechanism for impasse handling.
I/O Operation
An I/O scheme includes of I/O devices and their corresponding driver code. Drivers hide the peculiarities of specific hardware devices from the users.
- An OS manages the communication between user and device drivers.
- I/O operation suggests that scan or write operation with any file or any specific I/O device.
- Operating system provides the access to needed|the specified|the desired} I/O device once required.
File system manipulation
A file represents a group of connected data. Computers will store files on the disk (secondary storage), for long-run storage purpose. Samples of storage media embody mag tape, disk and storage device drives like CD, DVD. Every of those media has its own properties like speed, capacity, knowledge transfer rate and knowledge access strategies.
A classification system is often organized into directories for simple navigation and usage. These directories could contain files and alternative directions. Following square measure, the foremost activities of Associate in Nursing OS with relevancy file management −
- Program must scan a file or write a file.
- The OS offers the permission to the program for operation on file.
- Permission varies from read-only, read-write, denied so on.
- Operating System provides Associate in Nursing interface to the user to create/delete files.
- Operating System provides Associate in Nursing interface to the user to create/delete directories.
- Operating System provides Associate in Nursing interface to form the backup of classification system.
Communication
In case of distributed systems that square measure a group of processors that don't share memory, peripheral devices, or a clock, the OS manages communications between all the processes. Multiple processes communicate with each other through communication lines within the network.
The OS handles routing and association ways, and therefore the issues of competition and security. Following square measure the foremost activities of Associate in Nursing OS with relevancy
- Two processes usually need knowledge to be transferred between them
- Both the processes may be on one pc or on totally different computers, however square measure connected through a electronic network.
- Communication could also be enforced by 2 strategies, either by Shared Memory or by Message Passing.
Error handling
Errors will occur anytime and anyplace. a mistake could occur in computer hardware, in I/O devices or within the memory hardware. Following square measure, the foremost activities of Associate in Nursing OS with relevancy error handling −
- The OS perpetually checks for potential errors.
- The OS takes Associate in Nursing applicable action to make sure correct and consistent computing.
Resource Management
In case of multi-user or multi-tasking atmosphere, resources like main memory, computer hardware cycles and files storage square measure to be allotted to every user or job. Following square measure, the foremost activities of Associate in Nursing OS with relevancy resource management −
- The OS manages every kind of resources victimisation scheduler.
- Computer hardware planning algorithms square measure used for higher utilization of CPU.
Protection
Considering a ADPS having multiple users and multiprogramming of multiple processes, the assorted processes should be shielded from every other's activities.
Protection refers to a mechanism or the way to manage the access of programs, processes, or users to the resources outlined by a ADPS. Following square measure, the foremost activities of Associate in Nursing OS with relevancy
- The OS ensures that each one access to system resources is controlled.
- The OS ensures that external I/O devices square measure shielded from invalid access tries.
- The OS provides authentication options for every user by suggests that of passwords.
Key Takeaway
An Operating System provides services to both the users and to the programs.
- It provides programs an environment to execute.
- It provides users the services to execute the programs in a convenient manner.
Following are a few common services provided by an operating system −
- Program execution
- I/O operations
- File System manipulation
- Communication
- Error Detection
- Resource Allocation
- Protection
In an operating system software plays out every one of the following function:
- Process management:- Process management causes OS to create and delete processes. It likewise gives mechanisms for synchronization and communication among processes.
- Memory management:- Memory management module plays out the role of assignment and de-allotment of memory space to programs needing the resources.
- File management:- It deals with all the file-related task, for example, storage organization, recovery, naming, sharing, and protection of files.
- Device Management:- Device management keeps tracks of all the devices. This module is in charge of the task also known as the I/O controller. It additionally plays out the undertaking of designation and de-distribution of the devices.
- I/O System Management: One of the primary objects of any OS is to conceal the identity of that hardware devices from the user.
- Secondary-Storage Management: Systems have a few degrees of storage which incorporates primary storage, secondary storage, and cache storage. Instructions and data must be put away in primary storage or cache so a running program can reference it.
- Security:- Security module ensures the data and information of a computer system against malware danger and authorized access.
- Command interpretation: This module is interpreting directions given by the acting system and assign resources to process that directions.
- Networking: A distributed system is a collection of processors which don't share memory, hardware devices, or a clock. The processors speak with each other through the network.
- Job accounting: Keeping track of time and resource utilized by different job and users.
- Communication management: Manage the coordination and task of compilers, interpreters, and other software resource of the different users of the computer systems.
Types of system calls:
System calls are divided into five categories.
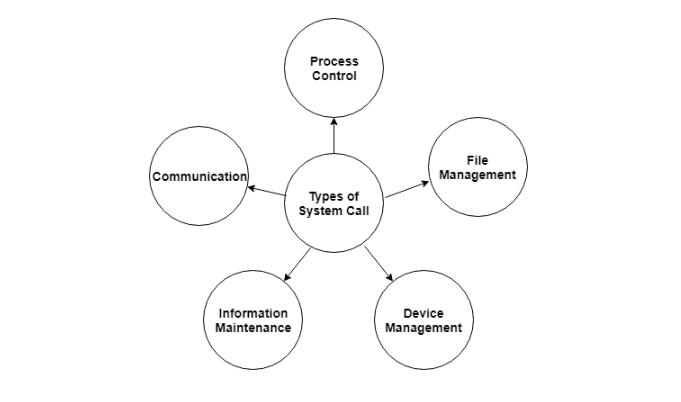
Fig 3: Types of system call
The following are the various sorts of system calls:
Process control
Processes such as process creation, process termination, and so on are handled by these system calls.
Functions
● End and Abort
● Load and Execute
● Create Process and Terminate Process
● Wait and Signal Event
● Allocate and free memory
File management
File manipulation is handled by these system calls, which include creating, reading, and writing to files.
Functions
● Create a file
● Delete file
● Open and close file
● Read, write, and reposition
● Get and set file attributes
Device management
Device manipulation, such as reading from device buffers and writing into device buffers, is handled by these system calls.
Functions
● Request and release device
● Logically attach/ detach devices
● Get and Set device attributes
Information maintenance
These system calls control the flow of data between the operating system and the user programme.
Functions
● Get or set time and date
● Get process and device attributes
Communication
These system calls can be used to communicate between processes. They're also in charge of setting up and disabling communication connections.
Functions
● Create, delete communications connections
● Send, receive message
● Help OS to transfer status information
● Attach or detach remote devices
A file is a collection of correlated information which is recorded on secondary or non-volatile storage like magnetic disks, optical disks, and tapes. It is a method of data collection that is used as a medium for giving input and receiving output from that program.
In general, a file is a sequence of bits, bytes, or records whose meaning is defined by the file creator and user. Every File has a logical location where they are located for storage and retrieval.
Objective of File management System
Here are the main objectives of the file management system:
- It provides I/O support for a variety of storage device types.
- Minimizes the chances of lost or destroyed data
- Helps OS to standardized I/O interface routines for user processes.
- It provides I/O support for multiple users in a multiuser systems environment.
Properties of a File System
Here, are important properties of a file system:
- Files are stored on disk or other storage and do not disappear when a user logs off.
- Files have names and are associated with access permission that permits controlled sharing.
- Files could be arranged or more complex structures to reflect the relationship between them.
File structure
A File Structure needs to be predefined format in such a way that an operating system understands. It has an exclusively defined structure, which is based on its type.
Three types of files structure in OS:
- A text file: It is a series of characters that is organized in lines.
- An object file: It is a series of bytes that is organized into blocks.
- A source file: It is a series of functions and processes.
File Attributes
A file has a name and data. Moreover, it also stores meta information like file creation date and time, current size, last modified date, etc. All this information is called the attributes of a file system.
Here, are some important File attributes used in OS:
- Name: It is the only information stored in a human-readable form.
- Identifier: Every file is identified by a unique tag number within a file system known as an identifier.
- Location: Points to file location on device.
- Type: This attribute is required for systems that support various types of files.
- Size. Attribute used to display the current file size.
- Protection. This attribute assigns and controls the access rights of reading, writing, and executing the file.
- Time, date and security: It is used for protection, security, and also used for monitoring
File Type
It refers to the ability of the operating system to differentiate various types of files like text files, binary, and source files. However, Operating systems like MS_DOS and UNIX has the following type of files:
Character Special File
It is a hardware file that reads or writes data character by character, like mouse, printer, and more.
Ordinary files
- These types of files stores user information.
- It may be text, executable programs, and databases.
- It allows the user to perform operations like add, delete, and modify.
Directory Files
- Directory contains files and other related information about those files. Its basically a folder to hold and organize multiple files.
Special Files
- These files are also called device files. It represents physical devices like printers, disks, networks, flash drive, etc.
Functions of File
- Create file, find space on disk, and make an entry in the directory.
- Write to file, requires positioning within the file
- Read from file involves positioning within the file
- Delete directory entry, regain disk space.
- Reposition: move read/write position.
Commonly used terms in File systems
Field:
This element stores a single value, which can be static or variable length.
DATABASE:
Collection of related data is called a database. Relationships among elements of data are explicit.
FILES:
Files is the collection of similar record which is treated as a single entity.
RECORD:
A Record type is a complex data type that allows the programmer to create a new data type with the desired column structure. Its groups one or more columns to form a new data type. These columns will have their own names and data type.
Key takeaway
A file is a collection of correlated information which is recorded on secondary or non-volatile storage like magnetic disks, optical disks, and tapes. It is a method of data collection that is used as a medium for giving input and receiving output from that program.
Let's look at various ways to access files stored in secondary memory.
Sequential Access
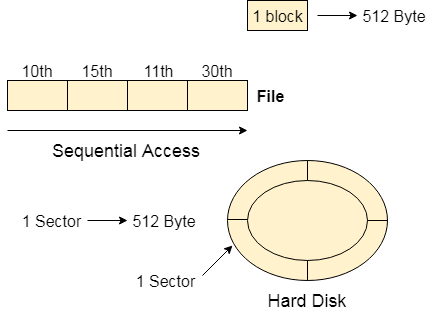
Fig 4: Sequential access
Most of the operating systems access the file sequentially. In other words, we can say that most of the files need to be accessed sequentially by the operating system.
In sequential access, the OS read the file word by word. A pointer is maintained which initially points to the base address of the file. If the user wants to read first word of the file then the pointer provides that word to the user and increases its value by 1 word. This process continues till the end of the file.
Modern word systems do provide the concept of direct access and indexed access but the most used method is sequential access due to the fact that most of the files such as text files, audio files, video files, etc need to be sequentially accessed.
Direct Access
The Direct Access is mostly required in the case of database systems. In most of the cases, we need filtered information from the database. The sequential access can be very slow and inefficient in such cases.
Suppose every block of the storage stores 4 records and we know that the record we needed is stored in 10th block. In that case, the sequential access will not be implemented because it will traverse all the blocks in order to access the needed record.
Direct access will give the required result despite of the fact that the operating system has to perform some complex tasks such as determining the desired block number. However, that is generally implemented in database applications.
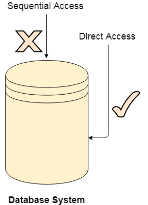
Fig 5: Database system
Indexed Access
If a file can be sorted on any of the filed, then an index can be assigned to a group of certain records. However, A particular record can be accessed by its index. The index is nothing but the address of a record in the file.
In index accessing, searching in a large database became very quick and easy but we need to have some extra space in the memory to store the index value.
Key takeaway
In sequential access, the OS read the file word by word. A pointer is maintained which initially points to the base address of the file. If the user wants to read first word of the file then the pointer provides that word to the user and increases its value by 1 word. This process continues till the end of the file.
References:
1. Operating Systems (5th Ed) - Internals and Design Principles by William Stallings, Prentice Hall India, 2000.
2. Operating System: Concepts and Design by Milan Milenkovik, McGraw Hill Higher Education.
3. Operating Systems - 3rd Edition by Gary Nutt, Pearson Education.
4. Operating Systems, 3rd Edition by P. Balakrishna Prasad, SciTech Publications.