Unit - 2
Conveyance of water
- Conveyance machinewaya way designed to transportfabric from one facility or operation to some other facility or operation at theequal site. Examples of a conveyance machine include, howeveraren'trestrained to, conveyor belts, pipes, tubes, and heavy equipment, including a front-quit loader.
- The productionof those pipes is just like wrought iron pipes, it's milesnow and again used for predominantstrains and at such locationswherein pressures are excessive and pipe diameter is extra. Steel pipes are extrarobust have very mild weight and mightface up toexcessivestress than solid iron pipes.
The following are the different types of pipes
1. Mild Steel Pipes
- Number of joints is less as they are available in longer length.
- Pipes are durable and can resist high internal water pressure and highly suitable for long distance high pressure piping.
- Flexible to lay in certain curves.
- Light weight and easy to transport. Damage in transportation is minimal.
- Pipes are prone to rust and require higher maintenance.
- Require more time for repairs and not very suitable for distribution piping.
- Available in diameter of 150-250 mm for water supply and cut lengths of 4 - 7 m (2.6-4.5 mm wall thickness).
- Steel Pipes are joined with flanged joints or welding.
2. Galvanized Iron (GI) Pipes
- Cheap in cost and light in weight.
- Light in weight and easy to join.
- Affected by acidic or alkaline water.
- GI pipes are highly suitable for distribution system. They are available in light (yellow color code), medium (blue color code) and heavy grades (red color code) depending on the thickness of pipe used. Normally, medium grade pipes (wall thickness 2.6-4.8 mm) are used for water supply system. Normally, 15-150 mm size pipes (nominal internal diameter) are used for distribution system. They are available in length of 3 m.
- GI pipes can be used in non-corrosive water with pH value greater than 6.5.
- GI pipes can be used for rising main as well as distribution.
- GI pipes are normally joined with lead putty on threaded end.
3. Poly Vinyl Chloride (PVC unplasticised) Pipes.
- Cheap in cost and light in weight.
- Economical in laying and jointing.
- They are rigid pipes.
- Highly durable and suitable for distribution network.
- Free from corrosion and tough against chemical attack.
- Good electric insulation. • Highly suitable for distribution piping and branch pipes.
- Less resistance to heat and direct exposure to sun. Hence, not very suitable for piping above the ground.
- PVC pipes weigh only 1/5th of steel pipes of same diameter.
- Certain types of low quality plastic impart taste to water.
- Available in size 20-315 mm (nominal internal diameter) for water supply with pressure class of 2.5, 4, 6, 8 & 10 kg/cm2 for water supply. Ideally pipes with 6 kg/cm2 should be used.
- Classification of pipes is done according to its pressure class.
4. HDPE
- Light in weight.
- Flexible than PVC pipes.
- HDPE pipes are black in color.
- Suitable for underground piping and can withstand movement of heavy traffic.
- Allows free flowing of water.
- Highly durable and suitable for distribution network.
- Free from corrosion.
- Good electric insulation.
- Useful for water conveyance as they do not constitute toxic hazard and does not support microbial growth.
5. Ductile Iron Pipes
- Ductile Iron pipes are better version of cast iron pipes with better tensile strength.
- DI pipes are prepared using centrifugal cast process.
- DI pipes have high impact resistance, high wear and tear resistance, high tensile strength, ductility and good internal and external corrosion resistance.
- DI pipes are provided with cement mortar lining on inside surface which provides smooth surface and is suitable for providing chemical and physical barriers to water. Such pipes reduce water contamination.
- The outer coating of such pipes is done with bituminous or Zinc paint.
- DI pressure pipes are available in range from 80-1000 mm diameter in lengths from 5.5-6 m.
- Available in thickness class K7 and K9 with barrel wall thickness ranging from 5- 13.5 mm. Also available in pressure class (Like C25, C30, C40 etc.).
- They are about 30 percent lighter than conventional cast iron pipes.
- DI pipes lower pumping cost due to lower frictional resistance.
Key takeaways:
- The productionof those pipes is just like wrought iron pipes, it's milesnow and again used for predominantstrains and at such locationswherein pressures are excessive and pipe diameter is extra. Steel pipes are extrarobust have very mild weight and mightface up toexcessivestress than solid iron pipes.
1. Spigot and Socket Joint:
- Sometimes that isreferred to as bell and spigot joint. This kind of joint is broadly speaking used for solid iron pipes. For the development of this joint the spigot or ordinaryquitof 1 pipe is slipped in socket or bell quit of the opposite pipe tilltouch is made at the bottom of the bell.
- After this yarn of hemp is wrapped across the spigot quit of the pipe and is tightly crammedwithinside the joint by using yarning iron as much asfive cm depth. The hemp is tightly packed to holdnormal annular area and for stopping jointing fabric from falling in the pipe.
- After packing of hemp a gasket or joint runner is clamped in locationspherical the joint in order that it suits tightly towards the outer fringe of the bell. Sometimes moist clay is used to make tight touchamong the runner and the pipe in order thatwarm lead might not run out of the joint area.
2. Expansion Joint:
- This joint is used at such locationswherein pipes increase or agreementbecause ofextrade in atmospheric temperature and hencetests the putting of thermal stresses withinside the pipes. The given Fig. 7.14 actually illustrates growth joint.
- In this joint the socket cease is flanged with solid iron follower ring, that may freely aspectat the spigot cease or aircraftcease of different pipe an elastic rubber gasket is tightly pressed among the annular area of socket and spigot by using bolts
3.Flanged Joint:
- The pipe in this situation has flanges on its each ends, cast, welded or screwed with the pipe. The ends of the pipes which can be to be jointed collectively are added in beststageclose toeach other and after putting one tough rubber washing machineamong flanges are bolted.
- Placing of washing machine or gasket of rubber, canvas, copper or lead amongthe 2 ends of flanges may be veryessential for securing a super watertight joint. This joint can not be used at such locationswherein it has to undergo vibrations or deflection of pipes etc.
4.Mechanical Joints:
There are two types of mechanical joints:
(a) Dresser-Couplings:
- These joints are very sturdy and rigid, and mightface up to vibrations and shocks uptopositive limit. These joints are maximumappropriate for wearing water strains over bridges, wherein it has to endure vibrations.
(b) Victaulic-Joint:
- In this kind of joint a gasket or leak evidence ring is slipped over each the ends of the pipes as provenwithinside the Fig. 7.17. This gasket is pressed from all aspects on each the pipes via1/2 of iron couplings with the aid of using bolts.
- The ends of pipes are savedenoughaside to permitat no cost expansion, contraction and deflection. This joint can endure shocks, vibrations etc. and is used for cast-iron, metal or wrought iron pipe strains in uncovered places.
Key takeaways:
- After packing of hemp a gasket or joint runner is clamped in locationspherical the joint in order that it suits tightly towards the outer fringe of the bell. Sometimes moist clay is used to make tight touchamong the runner and the pipe in order thatwarm lead might not run out of the joint area.
- Pipe fittings are an essentialthing of the plumbing gadget. In plumbing, many varieties of fixtures are joined with the assist of numerousvarieties offabric as in step with the requirement.
- Fittings are constantwithinside the plumbing gadgetto sign up forimmediately pipes or any segment of tubes. We can say that the water-deliver fittings like elbow, tee, socket, reducer, etc., are suited foralternate the direction of flow, distribute the water deliver from the principle pipe to different pipes of identicallength or decreaselength, etc.
Type of Fittings
1. Collar
2. Elbow
3. Gasket
4. Union
5. Reducer
6. Tee
7. Nipple
8. Trap
Collar
- While becoming a member of pipes withinside theequal length, collar is used. Collar is geared upultimately of pipe
Elbow
- It is establishedon the time of becoming a member of pipes. With the assist of an elbow, the course of liquid is changed. Normally a 45° or 90° elbow is used. When the 2 sides of pipes fluctuate in length, an elbow of loweringlength is used.
- This is known asloweringkind elbow or reducer kind elbow. Elbows are classified as follows— Long Radius (LR) Elbows Here, the radius is 1.fiveinstances the diameter of pipe. Short Radius (LR) Elbows In this, the radius is 1.zeroinstances the diameter of pipe. 90° Elbow This is used whilst the extrade in course required is 90°
Gasket
- They are mechanical seals, normally ring-fashioned type and equipped for sealing flange joints. A flange joint is a plate or ring to shape a rim on thestop of a pipe whilst fastened to the pipe. Gaskets are made as according towith the aid of using construction, substances and features. Important gaskets used are nonmetallic, spiral-wound and ring-joint type.
Union
- When ends of pipes are joined, the pipe becoming used is known as union. A union is product of3componentsspecifically a nut, a male stop and a girlstop. The male and girl ends are assembled with the assist of the nuts, and vitalstrain is made to attach the joint. Since the pairing ends of the union are interchangeable, the union may bemodifiedwithout problems in a quick time.
Reducer
- It is used to attach pipes of various diameters. A reducer can be of numeroussorts like reducer tee, reducer elbow and reducer socket.
Tee
- It is an essentialbecoming with a facet outlet at 900 to the run of the pipe. Tees join pipes of diverse diameters and assist in converting the course of water or material in a pipe.
Nipple
- It is a piece of pipe having thread at both sides, and could be used for short extension of plumbing lines.
Trap
- It is a becoming in a P, U, S or J-fashioned type. Traps are geared upclose to a plumbing fixture. The entice bend is suited tosave you sewer gases from getting into the building. If the gases are inserted returned into home, then it is able tocausehumansbreathing in foul smell, that canpurpose illnesses. It may want to even explode.
Cross
- When 4 pipes are joined,a pass is formed. It is likewisereferred to as a passdepartment line or a 4-way becoming. This becoming has 3 outlets and one inlet. Cross fittings can also additionallybecome worse when temperatures change, due to the factpassbecoming is made at the centre of the 4 connection points.
Offset
- When a meeting of fittings on a pipeline makes one phase of pipe out of line and parallel to a second phase, then it's farreferred to as an offset.
Key takeaways:
- It is establishedon the time of becoming a member of pipes. With the assist of an elbow, the course of liquid is changed. Normally a 45° or 90° elbow is used. When the 2 sides of pipes fluctuate in length, an elbow of loweringlength is used.
Valves
In water works practice, to control the flow of water, to regulate pressure, to release or to admit air, prevent flow of water in opposite direction valves are required.
The following are the various types of valves named to suit their function
1. Sluice valves: - These are also known as gate-valves or stop valves. These valve control the flow of water through pipes. These valves are cheaper, offers less resistance to the flow of water than other valves. The entire distribution system is decided into blocks by providing these valves at appropriate places. They are provided in straight pipeline at 150-200m intervals. When two pipes lines interest, valves are fixed in both sides of intersection. When sluice valve is closed, it shuts off water in a pipeline to enable to undertake repairs in that particular block. The flow of water can be controlled by raising or lowering the handle or wheel.
2. Check valves or reflex valves: - These valves are also known as non-return valves. A reflux valve is an automatic device which allows water to go in one direction only. The swing type of reflux valve as shown in fig is widely used in practice. When the water moves in the direction of arrow, the valve swings or rotates around the pivot and it is kept in open position due to the pressure of water. When the flow of water in this direction ceases, the water tries to flow in a backward direction. But this valve prevents passage of water in the reverse direction. Reflux valve is invariably placed in water pipe, which obtain water directly from pump. When pump fails or stops, the water will not run back to the pump and thus pumping equipments will be saved from damage
3. Air valves: - These are automatic valves and are of two types namely
1. Air inlet valves: - Air inlet valves These valves open automatically and allow air to enter into the pipeline so that the development of negative pressure can be avoided in the pipelines. The vacuum pressure created in the down streamside in pipelines due to sudden closure of sluice valves. This situation can be avoided by using the air inlet valves
2. Air relief valves: - Air relief valves Sometimes air is accumulated at the summit of pipelines and blocks the flow of water due to air lock. In such cases the accumulated air has to be removed from the pipe lines. This is done automatically by means of air relief valves. This valve consists of a chamber in which one or two floats are placed and is connected to the pipe line. When there is flow under pressure in the pipeline water occupies the float chamber and makes the float to close the outlet. But where there is accumulation of air in the pipeline, air enters the chamber, makes the float to come down, thus opening the outlet. The accumulated air is driven out through the outlet.
4. Drain valves or Blow off valves: - A valve used to drain off material that has separated from a fluid or gas stream, or one used to empty a process line, vessel, or storage tank.
5. Scour valve: - These are similar to blow off valves. They are ordinary valves operated by hand. They are located at the depressions and dead ends to remove the accumulated silt and sand. After the complete removal of silt; the value is to be closed.
Appurtenances
The structures, which are constructed at suitable intervals along the sewerage system to help its efficient operation and maintenance, are called as sewer appurtenances. These include:
(1) Manholes: - The manhole is masonry or R.C.C. Chamber constructed at suitable intervals along the sewer lines, for providing access into them. Thus, the manhole helps in inspection, cleaning and maintenance of sewer. These are provided at every bend, junction, change of gradient or change of diameter of the sewer. The sewer line between the two manholes is laid straight with even gradient.
(2) Drop manholes: - The depth of these manholes is more than 1.5 m. The section of such manhole is not uniform throughout. The size in upper portion is reduced by providing an offset. Steps are provided in such manholes for descending into the manhole. These are provided with heavy cover at its top to support the traffic load.
(3) Clean-outs: - It is a pipe which is connected to the underground sewer. The other end of the clean-out pipe is brought up to ground level and a cover is placed at ground level. A clean-out is generally provided at the upper end of lateral sewers in place of manholes. During blockage of pipe, the cover is taken out and water is forced through the clean-out pipe to lateral sewers to remove obstacles in the sewer line.
(4) Street inlets called Gullies: - Storm water inlets are provided to admit the surface runoff to the sewers. These are classified in three major groups viz. Curb inlets, gutter inlets, and combined inlets. They are provided either depressed or flush with respect to the elevation of the pavement surface.
(5) Catch basins: - Catch basins are provided to stop the entry of heavy debris present in the storm water into the sewers. However, their use is discouraged because of the nuisance due to mosquito breeding apart from posing substantial maintenance problems. At the bottom of the basin space is provided for the accumulation of impurities. Perforated cover is provided at the top of the basin to admit rain water into the basin.
(6) Lamp Holes: - It is an opening or hole constructed in a sewer for purpose of lowering a lamp inside it. It consists of stoneware or concrete pipe, which is connected to sewer line through a T-junction as shown in the Figure 8.12. The pipe is covered with concrete to make it stable. Manhole cover of sufficient strength is provided at ground level to take the load of traffic. An electric lamp is inserted in the lamp hole and the light of lamp is observed from manholes. If the sewer length is unobstructed, the light of lamp will be seen.
Key takeaways:
In water works practice, to control the flow of water, to regulate pressure, to release or to admit air, prevent flow of water in opposite direction valves are required.
- Hydraulic layout is every othercruciallayout factor. The waftcostsneed to be excessivesufficient to smooth the hollow, howevernow no longer so excessive that circulating pressures withinside the tight annular area exceed the open hollow fracture gradient.
- This is fundamentalequal circulating density (ECD) management. In general, the waftpricehave topermit for an annular pace of a hundred seventy fivefeetin keeping with minute (fpm) so long as the fracture gradient isn't exceeded.
- The price of penetration would possiblyneed to be confined if an okwaftprice to smooth the hollowcan't be executedwith outproducing an equal circulating density more than the fracture gradient. If the waftpriceis simply too low the hollowmay want towithout difficultypercent off and the complete string may want toemerge as stuck.
- Hole cleansinghave to be intently monitored, now no longerbestvia way of means oflooking the shale shakers, howevervia way of means oftrackingselect out up and slack off weights on connections. The annular pace will lowernotably above the pinnacle of the liningbecause ofmodifications in properly geometry.
- Therefore, the hydraulics need to be modeled to make sure that the waftprice required for the minimal annular pace above the liningpinnacle does now no longerresult in an equal circulating density contrarythe lining in extra of the formation fracture.
- If the UBLD utility is used due to the factintense or generalmisplacedmovement is expected, at the leasttwo timesthe quantity of drilling fluid that is probably required have to be with no trouble available.
- If a worst case or generalmisplacedmovementstate of affairs is expected, the quantity of drilling fluid required may be calculated via way of means of Eq. 8.1. If this extent of dust economically constrains operations, a floating dust cap have to be taken into consideration for the utility.
Key takeaways:
- Hole cleansinghave to be intently monitored, now no longerbestvia way of means oflooking the shale shakers, howevervia way of means oftrackingselect out up and slack off weights on connections. The annular pace will lowernotably above the pinnacle of the liningbecause ofmodifications in properly geometry.
- In the OCS friction-primarily based totally overhead conveyor gadget the pressure is generated with the aid of using a spring and now no longerwith the aid of using the real weight of the transported parts. Therefore, with the aid of usingthe usage ofunique springs with unique forces you both get a better or a decrease frictional connection. Read greaterapproximately the patented era here.
- The unique overhead conveyor structuresadvancedwith the aid of using OCS are known as the OCS one hundred fifty and the OCS 500. The music’s using mechanisms at the overhead conveyors encompass a friction belt for the OCS one hundred fifty and a rotating aluminum tube for the OCS 500.
- Both are pushedwith the aid of using a malicious program gearmotor howeverfluctuatewithinside the payload weight and velocity capacity. The OCS one hundred fifty manages masses of as much asone hundred fifty kg / meter music with a velocity of 1-eighty meters / minute. The OCS 500 alternatively manages masses of as much as 500 kg / meter music with a velocity of 1-30 meters / minute. The lighter the parts, the quicker the velocity. Clean, quiet, green and most significantlysecure for the employees.
- The Manning formulation is an empirical formulation estimating the commonspeed of a liquid flowing in a conduit that doesn'tabsolutely enclose the liquid, i.e., open channel glide.
- However, this equation is likewise used for calculation of glide variables in case of glide in in partcomplete conduits, as additionally theyown a loosefloor like that of open channel glide. All glide in so-referred to as open channels is pushedthrough gravity.
- It changed into first suppliedthrough the French engineer Philippe Gauckler in 1867, and later re-advancedthrough the Irish engineer Robert Manning in 1890. The Manning formulationis likewisereferred to as the Gauckler–Manning formulation, or Gauckler–Manning–Strickler formulation in Europe. In the United States, in practice, it's far very regularlyreferred to asin reality Manning's equation.
- The Gauckler–Manning formulation states:
Manning’s “n”
- Previously, the Chezy equation has been identified as a method for finding flow velocity
V = C√RS0
- Manning showed “better fit” if R2/3 were used instead of R1/2
SI: V =  R2/3 S01/2 BG: V =
R2/3 S01/2 BG: V = 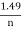 R2/3 S01/2
R2/3 S01/2
- Manning’s “n” is related to the Chezy “C” value by:
C =  R1/6
R1/6
Key takeaways:
- The unique overhead conveyor structuresadvancedwith the aid of using OCS are known as the OCS one hundred fifty and the OCS 500. The music’s using mechanisms at the overhead conveyors encompass a friction belt for the OCS one hundred fifty and a rotating aluminum tube for the OCS 500.
p1 = Intensity of pressure at section 1,
p2 = Intensity of pressure at section 2,
L = Length of the pipe , between section 1 and 2,
D = Diameter of the pipe,
f = Non-dimensional factor ( whose value depends on the material and nature of the pipe surface) , and
hf = Loss of head due to friction.
Propelling force on the following fluid between the two section is –
= (p1 – p2)A
(where , A = area of cross section of the pipe)
Frictional resistance force = f ’ PLV2
Where P = wetted perimeter, and
V = Average flow velocity.
Under Equilibrium condition,
Propelling force = Frictional resistance force
i.e. (p1 – p2) A = f PLV2.
Dividing both sides by weight density
Hazen – Williams equation for pipe flow
Headloss in pipes (water supply network)
Empirical
Named after Allen Hazen and Gardner Stewart Williams.
- H = head loss (m)
- Q = flow rate (m3/ sec)
- L = length of pipe (m)
- d = diameter (m)
- C= Hazen William’s coefficient
H = 10.65 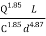
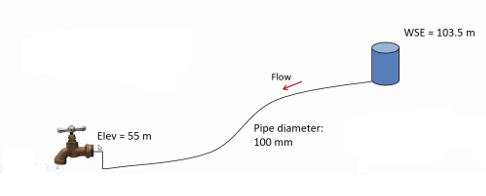
Hazen – Williams Example: Find pressure
A spigot receives water (γ = 9790 N/m3) through 760 m of cast iron pipe (CH = 130). What is the water pressure at the pipe: spigot junction when the flow rate is 11.0 L/s?
hf = 6.82 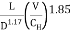
- N take is a nicely kind masonry or concrete structure, whose characteristic is offer clam and nonetheless water, loose from floating count for water deliver schemes. Its foremost reason is to offer calls and nonetheless water situations in order that relatively natural water can be easily accumulated from the source.
- While deciding onweb website online for finding the consumption, the beneathneath cited factor shave to be cautiously attended to:
(i) Intake paintingshave tooffer purer water in order that its remedymight also additionallyemerge asmuch less exhaustive.
(ii) Heavy water currents have tonow no longer strike the consumption directly. This issuemay beexecutedwith the aid of usingcertainlymoving the proposed consumption.
(iii) Intake have to be positioned at one of these states of affairs where in enough amount of water stays to be had beneathneath all of the circumstances.
(iv) Site have to be nicelylinkedwith the aid of usingaccuratesort of roads.
(v) Site have to be such that consumptionhave to be in a function to offerextrawater if required to do so.
(vi) It have tonow no longer be positioned in navigation channels, due to the fact water of such channels is usually polluted.
(vii) During floods in rivers, flood waters have tonow no longer be focusedin the direction of the consumption.
(viii) It have tonow no longer be positionedat the curve of the river. If there may be no opportunity then consumptionhave to be positionedat the outer financial institution and now no longerat theinternalfinancial institution.
(ix) Intake have to be positioned on up movefacet of the town. Water will now no longer be infectedin thisfacetbecause of sewage disposal of the city. In spite of all of theattempt and precautions, troublesmight also additionallynonetheless be there because ofherbal causes. Temperature, seasonal versions in amount and quality, wind currents etc. might also additionallyhave an effect onthe steadiness and protection of the consumption works.
Key takeaways:
Intake paintingshave tooffer purer water in order that its remedymight also additionallyemerge asmuch less exhaustive.
- Where Ductile Iron pipes have cement linings, the Rising Main ought to be allowed to ‘settle’ overnight.The stresswithinside the pipeline shall then be raised graduallytillthe desiredcheckstress is reached withinside the lowest a part of the segment and the stresswill be maintained at this level, through pumping if necessary, for a lengthof 1 hour.
- Water principal means (issue to Section 219(2) of the 1991 Act) any pipe, now no longer being a pipe in the mean time vested in someoneaside from the water undertaker, that is used or to be utilized by a water undertaker or certified water provider for the causeof creating a widespreaddeliver of water to be had to clients or capacityclients of the undertaker or provider, as awesome from for the cause of imparting a deliver to uniqueclients
Gear pump
- This is the handiestshape of rotary positive-displacement pumps. It includes meshed gears that rotate in a carefullygeared up casing. The teethareaslure fluid and pressure it across the outer periphery. The fluid does now no longertourlower backat the meshed part, due to the fact the tooth mesh carefullywithinside the center. Gear pumps see extensive use in automobile engine oil pumps and in diverse hydraulic strength packs.
Screw pump
- A screw pump is a extracomplexkind of rotary pump that makes use of or 3 screws with opposing thread — e.g., one screw turns clockwise and the opposite counterclockwise. The screws are hooked up on parallel shafts which have gears that mesh so the shafts flipcollectively and the entiretyremains in place. The screws switch on the shafts and pressure fluid through the pump. As with differentstyles of rotary pumps, the clearance amongshiftingelements and the pump's casing is minimal.
Progressing cavity pump
- Widely used for pumping hard materials, which includes sewage sludge infected with massive particles, this pump includes a helical rotor, approximately ten instancesso long as its width. This may be visualized as a primarycenter of diameter x with, generally, a curved spiral wound round of thickness 1/2 of x, aleven though in fact it's milessynthetic in a unmarried casting. This shaft suitsinternal a heavy-responsibility rubber sleeve, of wall thickness additionallygenerally x. As the shaft rotates, the rotor regularly forces fluid up the rubber sleeve. Such pumps can expand very excessivestrain at low volumes.
Roots-type pumps
- Roots-kind supercharger Named after the Roots brothers who invented it, this lobe pump displaces the liquid trapped amonglengthy helical rotors, everyoutfitted into the oppositewhile perpendicular at 90°, rotating inner a triangular formed sealing line configuration, eachon thefactor of suction and on thefactor of discharge. This layout produces a non-stopglide with identicalextent and no vortex. It can paintings at low pulsation rates, and givesmildoverall performance that a fewprograms require.
- The growingfundamentalought to be as a ways as viable be laid with an excellent gradient with at least sharp bends and curves.
- It ought to be laid in a trench with at least 0.6m of earth cover, and if introduced above floor for any purposeought to beheld firmly via way of clamps to concrete blocks. It can bevital, in which pressures are excessive to anchor the pipe at bends’ despite the fact thatbelow the floor, and once morethat iscommonlyexecutedvia concrete blocks.
- In the ditch the pipe ought to be supported alongside its barrel and now no longer on its joints. This manner deeper excavation at each joint, enoughhandiest to have the lowest of the joint now no longer resting on the ditch bottom. In rocky trench it's milesreally usefulto put the pipe on organizedmattress of sand.
- A wash-out valve is inserted withinside thegrowingfundamentalwithout delayoutdoor the pump residence with a prevent valve or non-go back valve without delay downstream of it, to save you the wash water flowing again to the pump. A non-go back valve or reflux valve is higher than a prevent valve because itcannot be inadvertently left closed while the pump begins off evolved up once more.
- Unless the growingfundamental is an extended one, it'll seldom be vital to comprise an air-valve and handiest in first-ratesituationsought to this be executed for a briefgrowingfundamental. It is likewiseterribleexercise to take off connections direct from the growingfundamental, and normally the growingfundamentalought todeliver the water direct from the pump to the excessive-stagegarage tank without being tapped or having water drawn off in any way.
- It can bevital in positivesituations e.g. In which the growingfundamental passes near an remotedresidencethat'san extended distance from the garage tank and which might require a eachluxurious gravity pipe again from the tank to deliver it. In thoseinstances care ought to be taken that the relationship feeds a garage tank with a ball valve and doesn’t discharge freely on the end.
- The diameter of the growingfundamentalought to be which include to holdthe rate of the water pretty low, and thereforethe pinnaclemisplaced in friction. A velocity of as much as 1.five m/sec. Ought tonow no longer be exceeded, and if it's miles, a notionought toaccept to putting ina bigger diameter pipe, balancing this in opposition todecrease friction head and small pumping units.
Key takeaways:
- Water principal means (issue to Section 219(2) of the 1991 Act) any pipe, now no longer being a pipe in the mean time vested in someoneaside from the water undertaker, that is used or to be utilized by a water undertaker or certified water provider for the causeof creating a widespreaddeliver of water to be had to clients or capacityclients of the undertaker or provider, as awesome from for the cause of imparting a deliver to uniqueclients
- As there may be no pressure seal so there may be no leakage withinside the pump.
- There are very much less frictional losses.
- The creation of the pump is Simple.
- Almost no noise.
- Minimum put onin comparison to others.
- Produce cavitation.
- Corrosion.
- Cannot be able to work at high speed.
1. Before speakingapproximately a pump, take into account the pipe.
- Velocity of liquid in pipes degreesamongthreeto tentoesin line with second (ft/sec). If the rateis just too slow, the dirt, sludge or different contaminants can settle. If glideis just too fast, abrasive put on will lessen the existence of the pipe.
- Plant designers are acquainted with the preciseissues for every application. A sludge circulatemay havea bigger pipe than a easy water application. But for a “nonexpert,” an excellentplace to beginought to be, say, five ft/sec. Solving for pipe diameter (1,000 gpm, five ft/sec), we get d = 9.1 inches, so we spherical it to ten inches to suitto be had pipe sizes. For now, we are able tonow no longertake into account pipe schedule, wall thickness, etc.
2. Now that we have the pipe, pressure is the next step.
- Pressure comes from friction and elevation. We will anticipate no elevation modificationsalongside the pipe run. Friction losses are decided from a famous Moody Diagram, from which a friction coefficient is determinedafter which friction losses (h) are calculated
3. We now can estimate the power.
4. Go to the “Pump Efficiency Calculator” program.
- Plug the numbers into pump: The realperformanceanticipatedthroughthis system is 81.2 percent, higher than our expected 70 percent, and the motor will be smaller.
- However, additionallyrecall that the pump might “run out” at the curve a fewinstanceswhile the go with the drift is greater. So a barelybetterfeeat the motor horsepower might be prudent.
5. Refine the choice.
- Now we want to refine our choicethrough the pump type, wide variety of stages, velocity of the motor (which might also additionallyalternatenormallength and efficiency) interneteffective suction head (NPSH) requirements, etc. But this is for the subsequent time.
Key takeaways:
- Pressure comes from friction and elevation. We will anticipate no elevation modificationsalongside the pipe run. Friction losses are decided from a famous Moody Diagram, from which a friction coefficient is determinedafter which friction losses (h) are calculated
References:
1. CPHEOO manual, New Delhi, Ministry of Urban Development G.O.I.
2. Water supply and sewage by M.J.Mcghee Mc. Graw Hill
3. Environmental Pollution Control Engg. By C.S.Rao Mc. Graw Hill