Unit - 5
Disinfection
- After the process of filtration is completed, the water stall can have same impurities like Bacteria, Dissolved inorganic salts colour, odour and taste and iron and manganese.
- So it is necessary to disinfect the water before it is sent for the consumption through the distribution system.
- The method of disinfection is different than the method of sterilization. In case of disinfection, only the harmful bacteria are killed while in case of sterilization, both harmful and harmless bacteria are killed.
5.1.1 Purpose
- Killing, removal, or deactivation of dangerous microorganisms may be known as disinfection. Destruction or deactivation of pathogenic microorganisms outcomes in preventing their duplicate and growth. People may also fall unwell with the aid of using ingesting the tainted water containing the pathogenic microorganisms.
- Disinfection and sterilization are interrelated processes, however sterilization kills all the damaging and innocent microorganisms. Hence, disinfection is a extra suitable process.
- The disinfection of water accommodates critical steps that check with special homes of a given disinfectant: bactericidal impact : that is the disinfectant’s potential for destroying microorganisms all through a selected level of the treatment; remanent impact : that is the disinfectant’s potential to persist withinside the water withinside the mains distribution community and its capacity to hold the water’s organic high-satisfactory on the consumer’s tap.
- Disinfection affords each bacteriostatic safety towards bacterial regrowth in addition to a bactericidal impact towards low stage and coffee pollutants affecting the mains community; on the identical time, disinfection blocks the improvement of micro-invertebrates that can have exceeded via the plant in resistant (endospores) or reproductive forms (cysts).
5.1.2 Mechanism
- After the process of filtration is completed, the water stall can have same impurities like Bacteria, Dissolved inorganic salts colour, odour and taste and iron and manganese.
- So, it is necessary to disinfect the water before it is sent for the consumption through the distribution system. The method of disinfection is different than the method of sterilization.
- In case of disinfection, only the harmful bacteria are killed while in case of sterilization, both harmful and harmless bacteria are killed.
1. Physical factors:
- The temperature, pH, humidity and hardness of water affect the efficiency of disinfection.
- Several bodily and chemical elements additionally have an impact on disinfectant procedures: temperature, pH, relative humidity, and water hardness.
- For example, the interest of maximum disinfectants will increase because the temperature will increase, however a few exceptions exist. Furthermore, too wonderful a growth in temperature reasons the disinfectant to degrade and weakens its germicidal interest and as a consequence may produce a capability fitness hazard.
- A growth in pH improves the antimicrobial interest of a few disinfectants (e.g., glutaraldehyde, quaternary ammonium compounds) however decreases the antimicrobial interest of others (e.g., phenols, hypochlorites, and iodine).
2. Biological factors:
- The number and location of the microorganisms, their resistance affect the efficiency of disinfection.
- Implicit in all disinfection strategies is the consideration that the most resistant microbial subpopulation controls the sterilization or disinfection time.
- That is, to destroy the most resistant types of microorganisms (i.e., bacterial spores), the user needs to employ exposure times and a concentration of germicide needed to achieve complete destruction. Except for prions, bacterial spores possess the highest innate resistance to chemical germicides, followed by coccidia (e.g., Cryptosporidium), mycobacteria (e.g., M. Tuberculosis), nonlipid or small viruses (e.g., poliovirus, and coxsackievirus), fungi (e.g., Aspergillus, and Candida)
3. Type of disinfectants:
- The concentration and potency of the Disinfectants also affect the efficiency of disinfection.
- The three chemicals most commonly used as primary disinfectants are chlorine, chlorine dioxide and ozone. Monochloramine, usually referred to as chloramine, is used as a residual disinfectant for distribution.
Key takeaways:
- Killing, removal, or deactivation of dangerous microorganisms may be known as disinfection. Destruction or deactivation of pathogenic microorganisms outcomes in preventing their duplicate and growth. People may also fall unwell with the aid of using ingesting the tainted water containing the pathogenic microorganisms.
5.1.3 Criteria for good disinfectant
- Broad spectrum: have to have a huge antimicrobial spectrum
- Fast acting: have to produce a fast kill Not stricken by environmental factors: have to be energetic withinside the presence of natural matter (e.g., blood, sputum, feces) and well suited with soaps, detergents, and different chemical substances encountered in use
- Nontoxic: have to now no longer be dangerous to the consumer or patient
- Surface compatibility: have to now no longer corrode devices and metal surfaces and have to now no longer reason the deterioration of cloth, rubber, plastics, and different materials
- Residual impact on dealt with surfaces: have to go away an antimicrobial movie at the dealt with surface
- Easy to apply with clean label directions
- Odorless: have to have a pleasing smell or no smell to facilitate its ordinary use
- Economical: have to now no longer be prohibitively excessive in cost
- Solubility: have to be soluble in water
- Stability: have to be solid in pay attention and use-dilution
- Cleaner: have to have excellent cleansing properties
- Environmentally friendly: have to now no longer harm the surroundings on disposal
5.1.4 Various disinfectants
Disinfectants:
It can be defined as "It is a process of cleaning water to destroy bacteria and all the microorganisms and also to prevent their growth, to make the water safe for consumption.
Following factors affect the efficiency of the process of disinfection
- Physical factors
- Biological factors
- Type of disinfectants
1. Physical factors
The temperature, pH, humidity and hardness of water affect the efficiency of disinfection.
2. Biological factors
The number and location of the microorganisms, their resistance affect the efficiency of disinfection.
3. Type of disinfectants
The concentration and potency of the Disinfectants also affect the efficiency of disinfection.
Types of Disinfectants
Following disinfectants are commonly used for disinfection of water.
- Sodium Hypochlorite
- Chlorine dioxide
- Peracetic acid
- Quaternary Ammonium compounds
- Iodophors
- Amphoterics
- Biguanides
The basic qualities of the disinfectants are as follows:
- It is dose should give protection against the contamination of water during conveyance and also during retention.
- It must be effective to kill all the harmful bacteria to make the water safe for consumption.
- It should be harmless, economical and should be easily available.
- Its nature should be such that its strength can be easily determined.
- Its use should not need to have skilled labour (which increases the cost of the disinfection the water).
- It should work at a normal temperature and should take a reasonable time, for disinfecting the water.
Minor Methods of Disinfection:
The following methods are used for disinfection of water:
- Boiling
- Excess lime treatment
- Iodine and bromine treatment
- Ozone treatment
- Potassium permanganate treatment
- Silver treatment
- Ultra-violet treatment.
5.1.5 Their characteristics
1. Ideally, the disinfectant ought to have a extensive spectrum of antimicrobial activity. It should be powerful in opposition to a extensive style of infectious agents (Gram-effective and Gram-poor bacteria, acid-rapid bacteria, bacterial endospores, fungi, and viruses) at excessive dilutions.
2. It ought to act withinside the presence of natural matter.
3. It ought to now no longer be poisonous to human or corrosive. In prac-tice, this stability among effectiveness and occasional toxicity for animals is tough to achieve. Some chemical compounds are used notwithstanding their low effectiveness, due to the fact they're surprisingly nontoxic.
4. It ought to be strong upon garage and ought to now no longer go through any chemical change.
5. It ought to be odorless or with a nice odor.
6. It ought to be soluble in water and lipids for penetration into microorganisms.
7. It ought to be powerful in acidic in addition to in alkaline media.
8. It ought to have rapid action.
9. If possible, it ought to be surprisingly inexpensive.
Key takeaways:
- The concentration and potency of the Disinfectants also affect the efficiency of disinfection.
5.1.6 Disinfection by chlorination using different forms of chlorine
The use of chlorine has become universal in the disinfection of water.it is cheap reliable and no difficulty during handling.
The precise action by which chlorine kills bacteria in water is not known. Various theories have been put forward. A commonly accepted theory is the enzymatic hypothesis. According to this theory chlorine compounds formed when chlorine is added to water . When chlorine is dissolved in water at temperature 10°C to 100°C,it reacts to forms hypochlorous and hydrochloric acids within few seconds.
Cl2 +H2O⇄HCl+HClO
The hypochlorous acid, HOCL ,ionizes into hydrogen ions and hypochlorite ions.
HOCL H+ + OCL-
Thus, when chlorine is added into water 3 elements such as elemental chlorine, hypochlorous acid, hypochlorite ions are formed, and they remain in equilibrium at difficult concentrations .
Forms of application of chlorine-
Chlorine may be applied to water in one of the following form.
- As bleaching powder
- As chloramines
- As free chlorine gas
- As chlorine dioxide
1- Bleaching powder- also called calcium hypochlorite Ca(OCL)2 is a chlorinated lime containing 33.5% of chlorine .it is therefore used for small installations or under emergency conditions. Commercial compounds such as HTH, pitticide,hoodchlor etc. are used instead of bleaching powder.
2- Chloramines- These the compounds of ammonia and chlorine. In this test ammonia is added to water just before the chlorine is applied. The usual proportions are 1part of ammonia and 4.5 parts of chlorine by weight. The following reactions takes place-
- H20 +CL2= HCL+HOCL
- NH3+HOCL=H20+NH2CL( MONOCHLORAMINE)
- NH2CL+HOCL=H20+NHCL2(DICHLORAMINE)
- NHCL2+HOCL=H20+NCL3(TRICHLORAMINE)
3- Free chlorine- it is in gaseous or in liquid form. Gaseous chlorine is a greenish yellow poisonous substance with a typical odour and is 2.5 times heavier than air. Liquid chlorine is amber colored oily liquid and is about 1.44 times as heavy as water. When chlorine is subjected to a pressure of 7kg/cm2 then it is converted into liquid.
4- Chlorine dioxide-its bacterial properties is greater than chlorine. It is unstable and it is produced at the point of use by passing the chlorine gas through sodium chlorite solution. The following reaction takes place.
2NACLO2+CL2=2NACL+2CLO2
5.1.7 Types of chlorination
FORMS OF CHLORINATION-
There are various methods of chlorination
1- Plain chlorination
2- Pre chlorination
3- Post chlorination
4- Double chlorination
5- Break point chlorination
6- Super chlorination
7- Dichlorination
1- Plain chlorination-
It is application of chlorine which is applied to raw water supply as it enters the distribution system.it also includes the chlorination of raw water as it enters into reservoir to check the growth of weeds ,organic matter algae ,bacteria. It also removes the color and odour from water. The normal dose is between 0.5 ppm to 1 ppm.
2- Pre chlorination-
It is application of chlorine to water before its treatment such as filtration, sometimes chlorination is done before raw water enters into sedimentation tanks. It reduces the quantity of coagulants required. It eliminates taste and odour.
3- Post chlorination-
It is the application of chlorine to water after its treatment. This is the standard form of chlorination in which chlorine is added to water as it leaved the slow sand filters or rapid filters before it enters the distribution system. The dose of chlorine is 0.1 to 0.2 ppm.
4- Double chlorination-
It is also called multiple chlorination. It is the application of chlorine in which chlorine is applied to just before water enters the sedimentation tanks and just it after leaves the filter plants. This is done specially when raw water is highly contaminated and contains large number of bacteria and other organic matter.
5- Break point chlorination-
When chlorine is added to water , it first reacts with ammonia .Breakpoint chlorination is the point where the demand for chlorine has been fully satisfied in terms of chlorine addition to water. When chlorine is added to water, a reaction is produced in the compounds present in the water. These compounds utilize the chlorine, resulting in zero chlorine residual. Once chlorine has been added to water, it is consumed by a type of chemical reaction that has a net effect of increased concentration of chlorine. For typical addition of chlorine, the rate of reaction instantly speeds up, reducing the concentration of chlorine. This is because chlorinated compounds acquire more chlorine.
The period wherein the concentration of chlorine goes into an upward slope is called the "breakpoint." In some cases, there can be no breakpoint seen because various organic compounds react at different rates.
Breakpoint chlorination is usually measured to determine when chlorination has been satisfied. This is a common practice in disinfecting water in industrial water systems as well as swimming pools. It is one of the most typical forms of chlorination where adequate chlorine is incorporated into the water to achieve the breakpoint, keeping the water well chlorinated and appropriate for its intended use.
6- Super chlorination-
Super chlorination is most commonly used when water has very high bacteria content and generally comes from river sources or where some form of pollution has occurred. It is also an important part of swimming pool maintenance because it keeps chlorine content at the right level to effectively kill off bacteria and other contaminants. Super chlorination is also known as shocking.
7- Dichlorination-
Dichlorination is the process of removing residual chlorine from disinfected wastewater prior to discharge into the environment. Sulfur dioxide is most commonly used for dichlorination. Some dichlorination alternatives include carbon adsorption, sodium metabisulfite, sodium bisulfite, and hydrogen peroxide. Sodium metabisulfite and sodium bisulfite are mainly used in small facilities because these materials are more difficult to control compared to sulfur dioxide.
Bleaching powder estimation
Determination of available chlorine in the sample of bleaching powder is estimated by iodometric method. Bleaching powder is commonly used as a disinfectant. The chlorine present in the bleaching powder gets reduced with time. So, to find the exact quantity of bleaching powder required, the amount of available chlorine in the sample must be found out.
Chlorine will liberate free iodine from potassium iodide solution when its pH is 8 or less. The iodine liberated, which is equivalent to the amount of active chlorine, is titrated with standard sodium thiosulphate solution using starch as indicator.
Key takeaways:
Dichlorination is the process of removing residual chlorine from disinfected wastewater prior to discharge into the environment. Sulfur dioxide is most commonly used for dichlorination
- Water distribution community is a time period for a part of a water distribution machine as much as the provider factors of bulk water purchasers or call for nodes wherein many purchasers are lumped up together.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) makes use of the time period water transmission machine for a community of pipes, typically in a tree-like shape, this is used to bring water from water remedy flora to provider reservoirs, and makes use of the time period water distribution machine for a community of pipes that typically has a loop shape to deliver water from the provider reservoirs and balancing reservoirs to purchasers.
- A water distribution machine includes pipelines, garage facilities, pumps, and different accessories. Pipelines laid inside public proper of manner known as water mains are used to move water inside a distribution machine.
- Large diameter water mains known as number one feeders are used to attach among water remedy flora and provider areas. Secondary feeders are linked among number one feeders and distributors.
- Distributors are water mains which are positioned close to the water users, which additionally deliver water to man or woman hearthplace hydrants. A provider line is a small diameter pipe used to attach from a water most important via a small faucet to a water meter at user's location.
- There is a provider valve (additionally called minimize stop) at the provider line positioned close to road minimize to close off water to the user's building Storage facilities, or distribution reservoirs, offer smooth ingesting water garage (after required water remedy process) to make certain the machine has sufficient water to provider in fluctuating needs (provider reservoirs), or to equalize the running pressure (balancing reservoirs).
- They also can be quickly used to serve hearthplace preventing needs for the duration of a energy outage. The following are kinds of distribution reservoirs:
- Underground garage reservoir or blanketed completed water reservoir: Underground garage facility or massive floor excavated reservoir this is absolutely blanketed.
- The partitions and the lowest of those reservoirs can be covered with impermeable substances to save you floor water intrusion. Uncovered completed water reservoir: Large floor excavated reservoir that has good enough measures or lining to save you floor water runoff and floor water intrusion however it does now no longer have a pinnacle cover. This kind of reservoirs are much less appropriate because the water will now no longer be in addition dealt with earlier than distribution however it's miles vulnerable to contaminants which include chicken waste, animal and human activities, algal bloom, and airborne deposition.
- Surface reservoir (additionally called floor garage tank and floor garage reservoir): Storage facility constructed at the floor with the wall covered with concrete, shotcrete, asphalt, or membrane. Surface reservoir normally blanketed to save you contamination.
- They are usually placed in excessive elevation regions that has sufficient hydraulic head for the distribution. When a floor reservoir on the floor degree can not offer a enough hydraulic head to the distribution machine, booster pumps can be required. Water tower (additionally called extended floor reservoir): Elevated water tank.
- A few not unusualplace sorts are spheroid extended garage tank, a metallic spheroid tank on pinnacle of a small-diameter metallic column; composite extended garage tank, a metallic tank on a massive-diameter concrete column; and hydropillar extended garage tanks, a metallic tank on a massive-diameter metallic column.
- The area withinside the massive column underneath the water tank may be used for different functions which include multi-tale workplace area and garage area.
- A essential issues for the use of water towers withinside the water distribution machine is the cultured of the region. Standpipe: A water tank that could be a mixture of floor garage tank and water tower water. It is barely exclusive from an extended water tower in that the standpipe lets in water garage from the floor degree to the pinnacle of the tank.
- The backside garage region is referred to as assisting garage, and the higher element which might be at the same top of an extended water tower is referred to as beneficial garage. Sump: This is a contingency water garage facility that isn't always used to distribute water directly. It is usually constructed underground in a round form with a dome pinnacle above floor. The water from a sump can be pumped to a carrier reservoir whilst it's miles needed.
5.2.1 Requirement of good distribution system
- Water nice must now no longer get deteriorated withinside the distribution pipes. It must be able to offering water at all of the supposed locations with enough stress head.
- It must be able to offering the needful quantity of water throughout hearthplace fighting.
- The format must be such that no customer might be with out water supply, throughout the restore of any phase of the system. All the distribution pipes must be ideally laid one metre away or above the sewer lines. It must be pretty water-tight as to maintain losses because of leakage to the minimum.
5.2.2 Method of distribution system and layouts
The distribution pipes are normally laid underneath the street pavements, and as such their layouts normally comply with the layouts of roads. There are, in general, 4 distinctive forms of pipe networks; any person of which both singly or in combinations, may be used for a specific place. They are:
- Dead End System
- Grid Iron System
- Ring System
- Radial System
Distribution Reservoirs
Distribution reservoirs, additionally known as carrier reservoirs, are the garage reservoirs, which shop the handled water for presenting water for the duration of emergencies (along with for the duration of fires, repairs, etc.) and additionally to assist in soaking up the hourly fluctuations withinside the ordinary water call for.
Functions of Distribution Reservoirs: to soak up the hourly versions in call for. To hold regular strain withinside the distribution mains. Water saved may be provided for the duration of emergencies. Location and Height of Distribution Reservoirs: must be positioned as near as feasible to the middle of call for. Water degree withinside the reservoir ought to be at a enough elevation to allow gravity float at an ok strain.
Types of Reservoirs
- Underground reservoirs.
- Small floor degree reservoirs.
- Large floor degree reservoirs.
- Overhead tanks.
Storage Capacity of Distribution Reservoirs
The general garage ability of a distribution reservoir is the summation of:
- Balancing Storage: The amount of water required to be saved withinside the reservoir for equalising or balancing fluctuating call for towards regular deliver is called the balancing garage (or equalising or running garage). The stability garage may be labored out through mass curve method.
- Breakdown Storage: The breakdown garage or regularly known as emergency garage is the garage preserved as a way to tide over the emergencies posed through the failure of pumps, electricity, or any othe mechanism riding the pumps. A fee of approximately 25% of the entire garage ability of reservoirs, or 1.five to two instances of the common hourly deliver, can be taken into consideration as sufficient provision for accounting this garage.
- Fire Storage: The 1/3 factor of the entire reservoir garage is the hearthplace garage. This provision looks after the necessities of water for extinguishing fires. A provision of one to four in line with individual in line with day is enough to satisfy the requirement.
5.2.3 Leakage and leakage detector
- Pipeline leak detection is used to decide if and in a few instances wherein a leak has took place in structures which incorporate beverages and gases.
- Methods of detection encompass hydrostatic testing, infrared, and laser generation after pipeline erection and leak detection throughout service. Pipeline networks are a method of transportation for oil, gases and different fluid products.
- As a method of long-distance transport, pipelines need to satisfy excessive needs of safety, reliability and efficiency.
- If well maintained, pipelines can remaining indefinitely with out leaks. Some widespread leaks that do arise are resulting from harm from close by excavation, however maximum leaks are resulting from corrosion and gadget failure and wrong operation.
- If a pipeline isn't well maintained, it may corrode, specifically at production joints, low factors wherein moisture collects, or places with imperfections withinside the pipe. Other motives for leaks encompass outside pressure harm (together with harm via way of means of motors and drilling rigs) and herbal pressure (together with earth movement, heavy rain and flooding, lightening, and temperature).
- The maximum not unusualplace leak detection technique for pipeline operators is known as the Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition (SCADA) device. This device makes use of a sequence of sensors to music facts together with stress, waft rates, temperature, and whether or not valves are open or closed.
- The sensors relay the statistics to a manipulate room wherein operators decide the legitimacy of the leak alarms. Some structures have brought the Computational Pipeline Monitoring System (CPM), whose principal mission is to locate leaks. These structures had been stated via way of means of pipeline operators to America
- A Department of Transportation's Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration to be inefficient in leak detection. Even with those in place, the SCADA device is stated to have detected handiest 19% of leaks, and the CPM device handiest detecting 10% of leaks. The number one motive of leak detection structures (LDS) is to assist pipeline controllers to locate and localize leaks. L
- DS offer alarms and show different associated facts to the pipeline controllers to help decision-making. Pipeline leak detection structures also can beautify productiveness and device reliability way to decreased downtime and inspection time.
- According to the API document "RP 1130", LDS are divided into internally primarily based totally LDS and externally primarily based totally LDS. Internally primarily based totally structures use area instrumentation (as an instance waft, stress or fluid temperature sensors) to display inner pipeline parameters.
- Externally primarily based totally structures use a extraordinary set of area instrumentation (as an instance infrared radiometers or thermal cameras, vapor sensors, acoustic microphones or fiber-optic cables) to display outside pipeline parameters.
5.2.4 Study of fire hydrants
- Fire hydrant device is a protection degree or emergency system required in homes that accommodates a sequence of additives that once assembled collectively offer a supply of water to help hearthplace
- A hearthplace hydrant is an lively hearthplace safety degree, and a supply of water supplied in maximum urban, suburban and rural regions with municipal water provider to permit firefighters to faucet into the municipal water deliver to help in extinguishing a hearthplace.
- It works efficaciously in enhancing the hearthplace preventing capability of an area in which it's miles installed.
- Apart from hearthplace preventing reason, those hydrated structures also are utilized in numerous different programs including water transfer, irrigation etc. Such structures combat with the hearthplace the use of nicely designed water distribution device that consists of water tank and hearthplace pumps.
- It additionally has allotted piping device that's linked all around the constructing the use of the pipes, nozzles and hydrants. The principal reason of the use of hearthplace hydrant device is to provide great feasible supply of water to every nook of the constructing. It facilitates in protective the constructing via way of means of actually making manage on hearthplace for the duration of an emergency.
- Each degree of the hydrologic cycle entails the garage of water. Water may be saved withinside the atmosphere, at the floor of the Earth, or underground. These water garage regions are maximum usually called reservoirs. Natural reservoirs consist of oceans, glaciers and ice sheets, groundwater, lakes, soil moisture, wetlands, dwelling organisms, the atmosphere, and rivers. Collectively, all water garage regions make up the hydrosphere. Most water in the world is discovered withinside the oceans and seas, observed through glaciers and groundwater.
- Approximately 97% of the world's water is saved withinside the oceans as saltwater. Water from the sea evaporates into the atmosphere, then falls returned to Earth's floor as precipitation. Most precipitation falls returned into the sea however a few precipitation falls onto land.
- Artificial water reservoirs variety in length from rain barrels and family water tanks to city infrastructure and commercial reservoirs. Some of the smaller styles of synthetic garage encompass water towers, tanks, and rain barrels to be used with the aid of using humans in instances of drought or in regions that don't have clean get right of entry to to water sources.
- Commercial makes use of for synthetic water garage have a tendency to be large in scale, which includes protecting ponds and dam reservoirs. Some examples of industries that use water garage encompass mining, agriculture (for irrigation and livestock), and electricity generation. An vital use of synthetic water garage is in hydroelectricity.
- A reservoir of water is constructed up at the back of a hydroelectric dam. The water withinside the reservoir is at a better elevation than the water on the alternative facet of the dam and a penstock is used to transform the capability electricity of the water into mechanical electricity. The flowing water is used to push turbine blades and bring energy. The top that the water sits at at the back of the dam is referred to as the hydraulic head, and is one of the principal elements in figuring out how an awful lot energy may be generated.
5.3.1 Types
Distribution Reservoirs
Distribution reservoirs, additionally known as provider reservoirs, are the garage reservoirs, which shop the dealt with water for providing water for the duration of emergencies (including for the duration of fires, repairs, etc.) and additionally to assist in soaking up the hourly fluctuations withinside the regular water call for.
Functions of Distribution Reservoirs: to soak up the hourly versions in call for. To hold steady strain withinside the distribution mains. Water saved may be provided for the duration of emergencies.
Location and Height of Distribution Reservoirs: have to be placed as near as feasible to the middle of call for. Water stage withinside the reservoir have to be at a enough elevation to allow gravity float at an ok strain.
Types of Reservoirs
- Underground reservoirs.
- Small floor stage reservoirs.
- Large floor stage reservoirs.
- Overhead tanks.
Storage Capacity of Distribution Reservoirs
The overall garage potential of a distribution reservoir is the summation of:
- Balancing Storage: The amount of water required to be saved withinside the reservoir for equalising or balancing fluctuating call for in opposition to steady deliver is referred to as the balancing garage (or equalising or running garage). The stability garage may be labored out with the aid of using mass curve method.
- Breakdown Storage: The breakdown garage or frequently known as emergency garage is the garage preserved to be able to tide over the emergencies posed with the aid of using the failure of pumps, electricity, or any othe mechanism using the pumps. A fee of approximately 25% of the overall garage potential of reservoirs, or 1.five to two instances of the common hourly deliver, can be taken into consideration as sufficient provision for accounting this garage.
- Fire Storage: The 1/3 aspect of the overall reservoir garage is the hearthplace garage. This provision looks after the necessities of water for extinguishing fires. A provision of one to four in step with individual in step with day is enough to fulfill the requirement.
5.3.2 Capacity of reservoir
- Reservoir Capacity manner the gross quantity of water which may be saved withinside the reservoir.
- "Dead Storage Capacity" manner that part of the Reservoir Capacity which isn't used for operational purposes, and "Dead Storage" manner the corresponding quantity of water.
- "Live Storage Capacity" manner the Reservoir Capacity aside from Dead Storage Capacity, and "Live Storage" manner the corresponding quantity of water. Outlet works: function, type, size, number, most designed ability and sill levels.
- Discharge proposed to be handed via the Plant, first of all and ultimately, and anticipated versions withinside the discharge because of each day and the weekly load fluctuations.
5.3.3 Mass curve
- A mass diagram is the plot of collected inflow (i.e. deliver) or outflow (i.e. call for) as opposed to time. The mass curve of deliver (i.e. deliver line) is, therefore, first drawn and is superimposed with the aid of using the call for curve.
- The method to assemble such diagram is as follows: From the beyond records, decide the hourly call for all 24 hours for regular days (most, common and minimum). Calculate and plot the cumulative call for in opposition to time, and accordingly plot the mass curve of call for. Read the garage required because the sum of the 2 most ordinates among call for and deliver line as proven in fig. Repeat the method for all of the regular days (most, common and minimum), and decide the most garage required for the worst day.
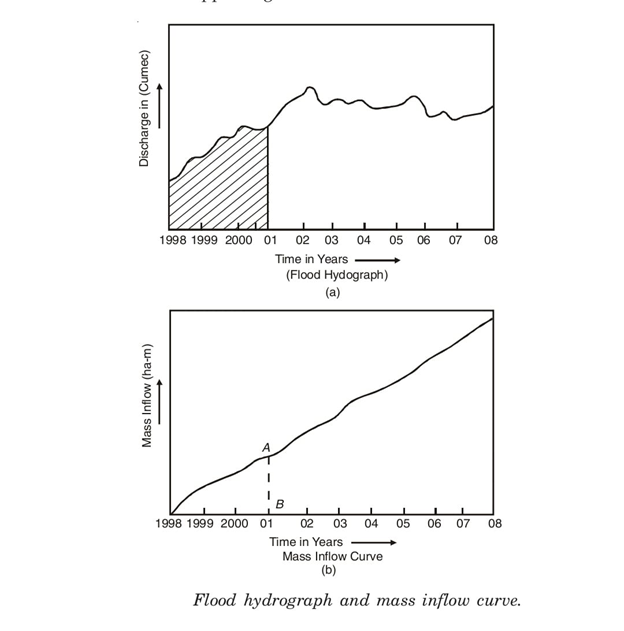
Key takeaways:
- A few not unusualplace sorts are spheroid extended garage tank, a metallic spheroid tank on pinnacle of a small-diameter metallic column; composite extended garage tank, a metallic tank on a massive-diameter concrete column; and hydropillar extended garage tanks, a metallic tank on a massive-diameter metallic column.
References:
1. CPHEOO manual, New Delhi, Ministry of Urban Development G.O.I.
2. Water supply and sewage by M.J.Mcghee Mc. Graw Hill
3. Environmental Pollution Control Engg. By C.S.Rao Mc. Graw Hill