Unit - 2
Levelling
Key Takeaways:
It is the art of measuring the relative heights or elevations of the points or objects on the surface of the earth is called as levelling.
When the dumpy level is to be set on a new point on ground, then the temporary adjustments are to be made.
Temporary adjustments are carried out in the following steps:
a) Setting up of the dumpy level
b) Levelling:
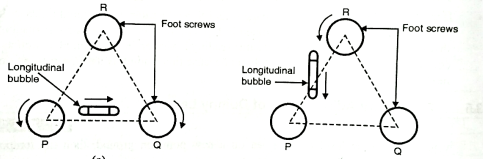
Fig.2.1: Levelling up with three-foot screws ‘PQR’
c) Focusing the eyepiece:
d) Focusing the object glass
Key Takeaways:
Temporary adjustments are carried out in the following steps:
In this method, the reduced level of collimation plane or height of instrument is determined for each set up of dumpy level and then reduced levels (R.L.) of the other points are found out with respect to the plane of collimation or height of instrument.
Procedure:
Step 1: To prepare the format of level page before levelling work start:
Staff Station | B.S | I.S | F.S | H.I | R.L | Remark |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 2: To find the height of instrument (H.I.) or R.L. of plane of collimation:
Height of instrument (H.I.) = R.L. of bench mark + B.S. reading.
Step 3: To find R.L. of intermediate points or change points:
R.L. of intermediate points= Height of instrument – Intermediate sight reading
=H.I.-I.S. reading
R.L.. of change point =Height of instrument - Fore sight reading =H.I.-F.S. reading
Step 4: To find new height of instrument or new plane of collimation:
R.L. of new height of instrument = R.L. of change point + B.S.
Step 5: To find reduced levels of the remaining points:
Step 6: To finish the levelling work:
Step 7: To find arithmetical check:
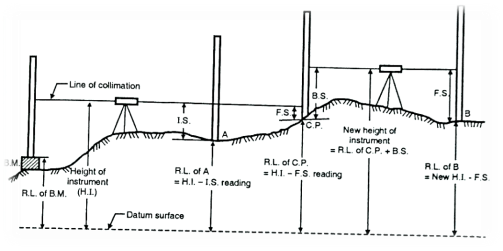
Fig.2.2: H.I Reading Method
Arithmetical check:
Key Takeaways:
In this method, the reduced level of collimation plane or height of instrument is determined for each set up of dumpy level and then reduced levels (R.L.) of the other points are found out with respect to the plane of collimation or height of instrument
Staff Station | B.S | I.S | F.S | Rise | Fall | R.I | Remark |
B.M |
|
|
|
|
|
| B.M |
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If the staff reading of second point in level page is higher than the first, then it indicates fall which is then to be subtracted from R.L. of previous point.
If the staff reading of second point in level page is lower than the first one, then it indicates rise which is further to be added to the R.L. of previous point. Refer to Fig.
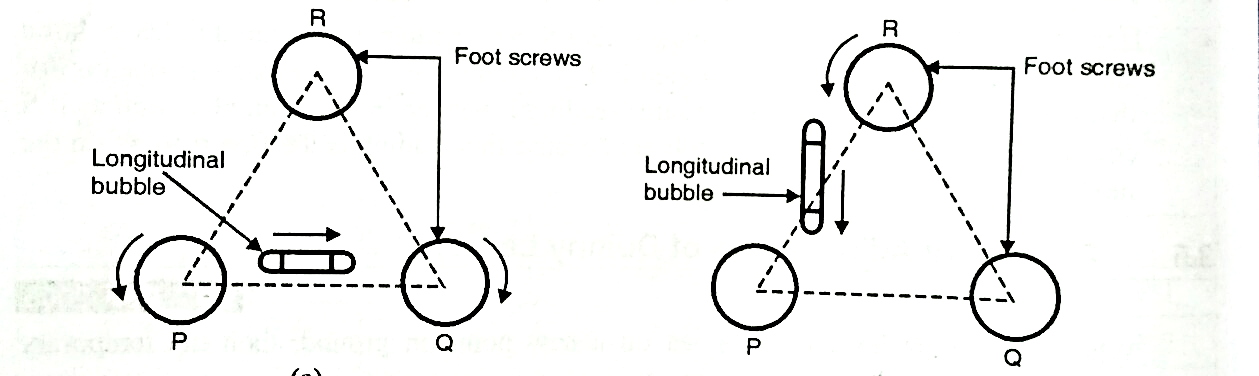
Fig.2.3: Rise and Fall method
Note that, the check can be taken at each level page and on R.L. of every intermediate points.
Sum of backsights- sum of foresights=Sum of all rise-sum of all fall
In short, EB.S.-EF.S. = Rise-Fall= Last R.L. -First R.L.
Key Takeaways:
In this method, instead of H.I. column in the format of level page, two columns of rise and fall are introduced for calculation of R.L's. Difference of levels between consecutive points is found by comparing the staff readings on the two points for the same setting of the instrument.
Curvature:
where,
d is the distance in km from the level to the staff station.
True staff reading = observed staff reading -0.0785 d²
Refraction:
where d is taken in km.
Key Takeaways:
In precise levelling work or when the sights are long, the effects of curvature and refraction have to be taken into account. It is evident that a horizontal line departs from a level surface because of the curvature of earth.
Key Takeaways:
Sensitiveness or the sensitivity of a stage tube is its functionality of displaying small deviations of the tube from the horizontal.
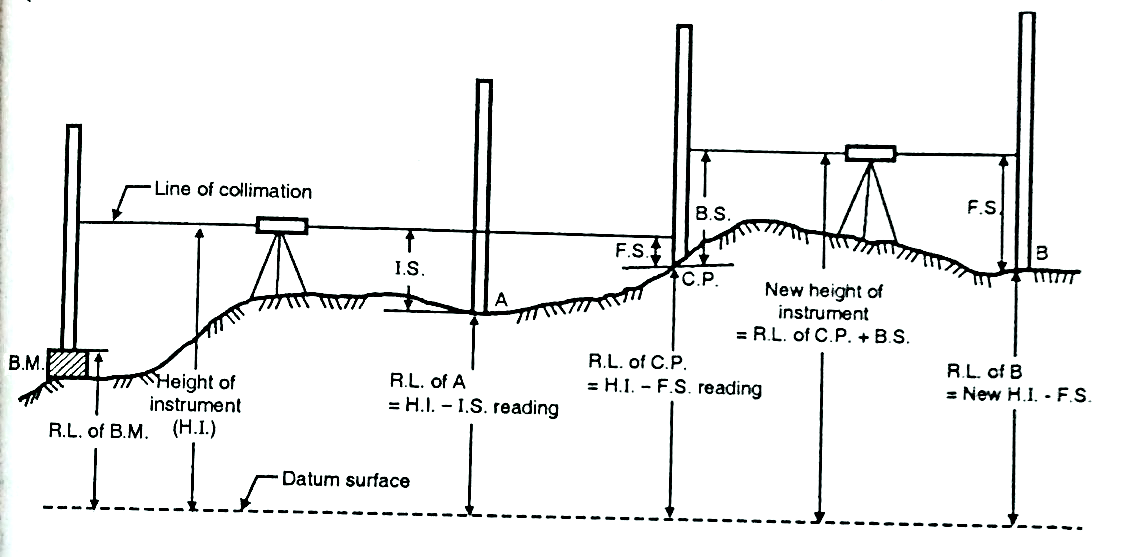
Fig.2.4: Reciprocal Levelling
Instrumental errors:
1. Error due to imperfect adjustment:
2. Error due to sluggish Bubble:
3. Faulty Focusing tube:
4. The levelling staff:
Natural errors:
Personal errors:
Mistakes in manipulation:
Mistakes in manipulation includes mistakes in
Mistake in reading the staff:
The common mistakes in reading the staff are
Mistakes in recording and computing:
Key Takeaways:
There are three types of errors:
Procedure:
The range of bar code is 1.8 m to 100 m and the bar code can read within this range of 1.8 m to 100 m away from the instrument.
The messages line 'instrument not level", low battery and memory full are displayed on the screen.
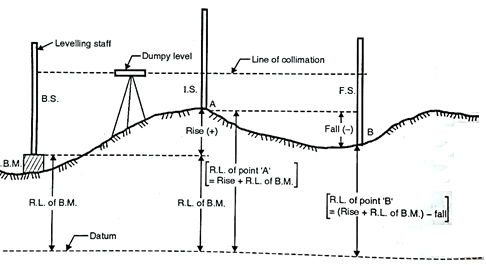
Fig.2.5: Digital level
Key Takeaways:
It is an automatic level consisting of pendulum compensator. It is capable for normal optical levelling with a rod graduated in meter or feet. Digital level have a provision to take readings automatically by using a bar code.
References: