Unit - 2
Leveling and Contouring
Leveling:
Leveling is a department of surveying in civil engineering to degree stages of various factors with admire to a hard and fast factor together with elevation of a building, peak of 1 factor from floor etc.
Levelling or leveling (American English; see spelling variations) is a department of surveying, the item of that's to set up or confirm or degree the peak of distinctive factors relative to a datum.
It is extensively utilized in geodesy and cartography to degree geodetic peak, and in production to degree peak variations of production artifacts. It is likewise called spirit levelling and differential levelling.
Optical levelling employs an optical stage, which includes a precision telescope with crosshairs and stadia marks. The go hairs are used to set up the extent factor at the target, and the stadia permit range-finding; stadia are typically at ratios of one hundred:
1, wherein case one meter among the stadia marks at the levelling body of workers represents one hundred meters from the target.
The whole unit is commonly installed on a tripod, and the telescope can freely rotate 360° in a horizontal aircraft. The surveyor adjusts the device's stage through coarse adjustment of the tripod legs and best adjustment the usage of 3 precision levelling screws at the device to make the rotational aircraft horizontal.
The surveyor does this with the usage of a bull's eye stage constructed into the device mount. The surveyor seems through the eyepiece of telescope whilst an assistant holds a vertical stage body of workers that's a graduated in inches or centimeters. The stage body of workers is positioned vertically the usage of a stage, with its foot at the factor for which the extent dimension is required.
The telescope is turned around and centered till the extent body of workers is it seems that seen with inside the crosshairs. In the case of an excessive accuracy guide stage, the best stage adjustment is made through an altitude screw, the usage of an excessive accuracy bubble stage constant to the telescope.
This may be considered through a replicate at the same time as adjusting or the ends of the bubble may be displayed with inside the telescope, which additionally permits warranty of the correct stage of the telescope at the same time as the sight is being taken.
However, with inside the case of an automated stage, altitude adjustment is carried out robotically through a suspended prism because of gravity, so long as the coarse levelling is correct inside positive limits.
When stage, the body of workers commencement analyzing on the crosshairs is recorded, and a figuring out mark or marker positioned in which the extent body of workers rested at the item or role being surveyed.
Different types of levels:
Levels are the exclusive units used for leveling in surveying. There are diverse styles of degrees together with dumpy degree, Y degree, Cushing’s degree, tilting degree, coke’s reversible degree and automated degree units for leveling in surveying.
The system of measuring vertical distances in surveying is known as leveling. To carry out leveling, we want a few degree units to cognizance or to examine the item. Nowadays, the era additionally brought in surveying and so many straightforward measuring units are designed.
Here we talk approximately the exclusive degrees utilized in leveling.
1. Dumpy Level
Dumpy degree is the maximum usually used tool in leveling. In this degree the telescope is restrained towards motion in its horizontal aircraft and telescope is constant to its support. A bubble tube is furnished at the pinnacle of the telescope. But however, the leveling head may be turned around in horizontal aircraft with the telescope.
2. Y Level
Y degree or Wye-degree is composed y-fashioned frames which helps the telescope. Telescope cane be eliminated from the y-fashioned helps via way of means of freeing clamp screws furnished.
These y-fashioned frames are organized to vertical spindle which allows to purpose the rotation of telescope. Compared to dumpy degree, modifications may be unexpectedly examined in y- degree. But, there can be a risk of frictional put on of open components of degree.
3. Cushing’s Level
In case of Cushing’s degree, the telescope is restrained towards rotation in its longitudinal axis and it's far non-removable. But, the item stop and eye piece stop may be interchangeable and reversible.
4. Tilting Level
Tilting degree consist a telescope which enabled for the horizontal rotation in addition to rotation approximately four diploma in its vertical aircraft. Centering of bubble may be without difficulty executed on this sort of degree.
But, for each setup bubble is to be targeted with the assist of tilting screw. The fundamental benefit of tilting degree is it's far beneficial whilst the few observations are to be desirous about one setup of degree.
5. Cooke’s Reversible Level
Cooke’s reversible degree is the aggregate of dumpy degree and y-degree. In this tool, the telescope may be reversed without rotation the tool. Collimation mistakes may be removed in this example due to bubble left and bubble proper studying of telescope.
6. Automatic Level
Automatic degree is just like the dumpy degree. In this example the telescope is constant to its helps. Circular spirit may be connected to the aspect of the telescope for approximate leveling. For extra correct leveling, compensator is hooked up within the telescope.
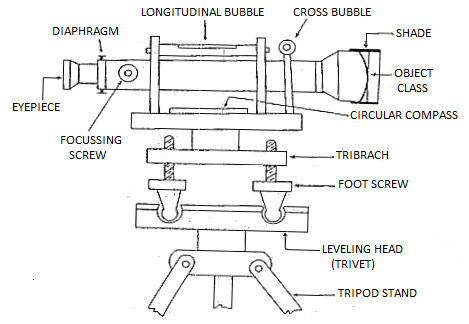
Study of Dumpy Level:
Dumpy degree is the maximum usually used tool in leveling. In this degree the telescope is restrained towards motion in its horizontal aircraft and telescope is constant to its support. A bubble tube is furnished at the pinnacle of the telescope. But however, the leveling head may be turned around in horizontal aircraft with the telescope.
The telescope is inner focusing telescope is a steel tube carries 4 fundamental components as given beneath.
- Objective lens
- Negative lens
- Diaphragm
- Eye-piece
- Objective Lens
Objective lens must be made because the aggregate of crown glass and flint glass. Because of this a few defects like round aberration and chromatic aberration may be eliminated.
A skinny layer coating which has smaller refractive index than glass is furnished at the goal lens to lessen the loss because of reflection.
Negative Lens Negative lens positioned co axial to the goal lens. So, the optical axis for each lenses is same.
Diaphragm is outfitted within the fundamental tube which includes move hairs (vertical and horizontal) and those are adjusted through capstan headed screws. The move hairs are product of darkish steel as filament wires which might be inserted in diaphragm ring in precise position. For stadia leveling purposes, greater horizontal move hairs are furnished above and beneath the horizontal wire.
Eyepiece lens permit the cap potential to sight the item collectively with move hairs. The photograph visible through eye piece is magnified and inverted.
Some eyepieces erect the photograph into ordinary view and people are known as erecting eyepieces.
About Dump Level Instrument: -
The dumpy degree is an optical device used for surveying and levelling operations. It accommodates of a telescope tube, firmly held among collars and adjusting screws.
The whole device is staged via way of means of the vertical spindle. The telescope positioned at the dumpy degree may be circled among the horizontal plane.
Relative elevation of survey factors at the land may be decided via the dumpy degree. The dumpy degree become invented via way of means of William Gravatt, in 1832.
Being a civil engineer, he invented the dumpy degree even as the usage of Y (Wye) degree device
Principle of Dumpy Level Instrument:
The dumpy degree operates at the precept via way of means of organizing a visible courting among or extra factors, via a built in telescope and a bubble degree. The acceptable degree of accuracy may be completed via steps.
It is likewise referred to as via numerous names together with Surveyors stages, Builders degree, Dumpy degree or maybe its pre-incidental version “Y (Wye) Level”.
Accuracy of Dumpy degree over different levelling units: The high cause for the usage of Dumpy degree over different levelling units is its accuracy.
A dumpy degree is thought for excessive accuracy values for maximum of the Tachometric methods.
The accuracy of a dumpy degree may be inside 1:4000 for each one hundred m.
Use of Dumpy degree in Surveying:
- Dumpy degree holds extensive significance with inside the surveying of a production web website online.
- The degree of accuracy and handiness of dumpy degree has made it a distinguished desire among surveyors.
- The high cause for acting levelling on a production web website online is to make the sector degree and even.
- To decide the variations in peak among factors. To degree the peak and distance of various places of surveying land via the precept of relativity.
- To degree following distance among numerous factor at the surveying land. Setting out stages and willing surfaces for production.
- To draw contours on land.
Temporary adjustments of dumpy level:
At every installation of a degree tool, transient adjustment is needed to be done previous to any group of workers observation.
It includes a few nicely described operations which might be required to be done in right sequence.
The transient adjustment of a dumpy degree is composed of (1) Setting, (2) Leveling and (3) Focusing.
During Setting, the tripod stand is installation at a handy peak having its head horizontal (via eye estimation).
The tool is then constant on the top with the aid of using rotating the decrease a part of the tool with proper hand and keeping firmly the higher element with left hand. Before fixing, the leveling screws are required to be delivered in among the tri Brach and trivet.
The bull's eye bubble (round bubble), if present, is then delivered to the center with the aid of using adjusting the tripod legs. Next, Leveling of the tool is carried out to make the vertical axis of the tool actually vertical. It is finished with the aid of using wearing out the subsequent steps:
Step 1: The degree tube is delivered parallel to any of the foot screws, with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool.
Step 2: The bubble is delivered to the center of the extent tube with the aid of using rotating each the foot screws both inward and outward.
Step 3: The degree tube is then delivered over the 0.33 foot screw once more with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool.
Step 4: The bubble is however delivered to the center of the extent tube with the aid of using rotating the 0.33 foot screw both inward and outward.
Step 5: Repeat Step 1 with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool with inside the identical quadrant of the circle after which Step 2.
Step 6: Repeat Step three with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool with inside the identical quadrant of the circle after which Step 4.
Step 7: Repeat Steps five and 6, until the bubble stays imperative in each the positions.
Step 8: By rotating the higher a part of the tool via a hundred and eighty o, the extent tube is delivered parallel to first foot screws in opposite order.
The bubble will stay with inside the center if the tool is in everlasting adjustment. Focusing is needed to be carried out so that you can shape picture via goal lens on the aircraft of the diaphragm and to view the clean picture of the item via eye-piece.
This is being done with the aid of using putting off parallax with the aid of using right focusing of goal and eye-piece.
For focusing the eye-piece, the telescope is first pointed toward the sky. Then the hoop of eye-piece is became both in and out till the cross-hairs are visible sharp and distinct.
Focusing of eye-piece relies upon at the imaginative and prescient of observer and for this reason required every time there may be extrude in observer.
For focusing the goal, the telescope is first pointed toward the item.
Then, the focusing screw is became till the picture of the item seems clean and sharp and there may be no relative motion among the picture and the cross-hairs.
This is needed to be carried out earlier than taking any observation.
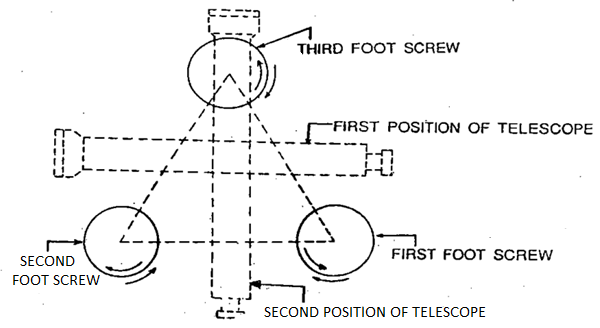
Fig: Temporary adjustment of dumpy level
Principle of leveling:
Simple leveling
When the leveling tool is well leveled, the bubble tube axis and the road of sight can be horizontal and the vertical axis of the tool can be vertical. The bubble ought to be significant and traverse. The line of sight will stay in a horizontal aircraft while the telescope is rotated.
Thus if the telescope is sighted toward a personnel saved on a factor of recognized elevation, the peak or elevation of the road of sight may be decided. If the telescope is now directed to personnel saved on factors of unknown elevation, the personnel readings may be read.
From which the decreased stages of the unknown factors may be decided.
Terms utilized in levelling
Some of the typically used phrases in levelling are described as follows:
Station
Station is a factor whose elevation is to be decided or it’s far the point that's to be marked at a given elevation. It is the factor wherein the personnel is held for taking observations from a levelling tool.
Height of the tool (HI)
It is the elevation or decreased degree of the road of sight with appreciate to the datum.
Height of the tool isn't always the peak of the road of sight above the floor wherein the levelling tool is installation.
Height of the tool= elevation of BM+ backsight
Balancing of sight
To lessen the impact of instrumental and different errors, this approach is followed. The distance of the factor wherein the backsight is taken and the gap of the factor wherein a foresight is taken, as measured from the tool station, needs to be about same.
This is referred to as balancing of points of interest. The intermediate points of interest do now no longer observe the situation of same duration of points of interest.
Differential levelling
Differential levelling is likewise known as compound levelling or non-stop levelling. It is followed while the factors whose elevation is to be decided are too a long way aside or the distinction in elevation is just too large.
In this levelling, the tool needs to be setup at numerous positions and at every installation the precept of easy levelling is used.
Some of the phrases related to differential levelling are defined as follows:
Backsight (BS) or Backsight studying
It is a personnel studying taken on a factor of recognized elevation, as on a benchmark or an alternate factor. This is likewise known as a plus sight. The backsight is the primary personnel studying taken after the extent is installation and leveled on the factor.
Foresight (FS) or Foresight studying
It is a personnel studying taken on a factor whose elevation needs to be decided through levelling process. It is likewise referred to as minus sight. The foresight is likewise taken toward an alternate factor. It is the closing studying taken earlier than the tool is shifted.
Elevation of station= top of tool (HI) – foresight (FS) or intermediate sight (IS)
Intermediate sight (IS)
It is the personnel readings taken on personnel held at different factors whose elevations are to be decided earlier than the foresight is taken. Intermediate points of interest are all personnel readings among the B.S and F.S Change factor or Turning factor (TP)
It is a factor denoting the moving of the extent. It is a station at which each BS and FS readings are taken. Stable and nicely described gadgets ought to be selected as alternate factors for correct results.
Reduction of levels:
1. Collimation Method:
It is composed in locating the elevation of the aircraft of collimation i.e. (H.I.) for each putting of the tool after which acquiring the decreased ranges of the factors as regards to the respective plan of collimation To begin with, the H.L is calculated with the aid of using including the returned sight of the R.L. Of the beginning factor.
The decreased ranges of the intermediate factor and the primary extrude factor are then acquired with the aid of using subtracting the respective readings from the H.I. When the tool is shifted, a brand new aircraft of collimation is installation and the peak of that's calculated with the aid of using including returned sight studying to the R.L. Of the primary extrude factor.
The decreased ranges of the successive factors and the second one extrude factor arc located out with the aid of using subtracting their group of workers readings from this new H.I.
The procedure is repeated till all of the R.Ls are labored out, after which the arithmetical test is applied.
Arithmetical Check: The distinction among the sum of the returned points of interest and the sum of the fore points of interest need to be identical to the distinction of the primary and the final R.Ls i.e. Σ B.S. – Σ F.S. = Last R.L. -First R.L. This test verifies the calculation of R.Ls. Of the planes of collimation and of the extrude factors only.
This technique might also additionally greater in reality be understood with the aid of using the subsequent instance of longitudinal levelling from flag – group of workers decrease base to downstream parapet of culvert no
2. Rise and Fall Method:
In this technique, the distinction among consecutive factors is calculated with the aid of using evaluating every factor after the primary with that right now previous it.
The distinction in their group of workers studying suggests upward thrust or fall in accordance as any group of workers studying is smaller or extra than that on the previous factor. The R.L. Of every factor is then located with the aid of using including upward thrust or subtracting fall to or from the R.L. Of the previous factor.
Collimation Method:
1. In the case of greater intermediate readings, there may be tremendous saving of labor and time because it entails only some calculations.
2. There isn't any any test at the R.Ls of intermediate stations.
3. There are assessments for arithmetical accuracy i.e. the distinction among the sum of returned points of interest of fore points of interest need to be identical to the distinction of the Kits and final R.Ls.
4. It is typically used for longitudinal and pass levelling operations and for giving ranges of roads and canals and comparable constructional works.
Rise and Fall Method:
1. It is an exhausting technique as group of workers studying of every factor at the ground, after the primary is as compared with that previous it, and the distinction of degree entered as an upward thrust or fall.
2. There is an entire test at the discount of R.Ls. Of intermediate stations.
3. There are 3 assessments for arithmetical accuracy.
The distinction among the sum of the returned points of interest and the sum of the fore points of interest need to be identical to that among the sum of the sum of rises and the sum of the falls in addition to that among the
Its. And the final it is typically used for earth paintings calculations and different unique levelling operations.
Booking the Staff Readings:
The following factors need to be stored in view even as coming into the group of workers readings in a degree eye-e book:
1. The readings need to be entered with inside the respective columns as quickly as they may be taken and with inside the order in their observation.
2. The first access on the extent eye-e book web page is continually a B.S and the final one a F.S.
3. The fore and returned points of interest of the extrude factors need to be written with inside the identical horizontal line.
4. The H.I need to be written with inside the identical horizontal line contrary the returned sight.
5. While sporting ahead the studying from one web page of the extent – eye-e book to the , if the final studying is an intermediate sight, it's far entered in each I.S and F. S. Column in this web page and I.S. And B.S. Columns as first access at the web page.
The entries with inside the ultimate columns towards it need to additionally be repeated at the web page.
6. Brief description with neat sketches in admire of bench marks, extrude factors and different vital factors need to receive with inside the statement column.
Classification of levelling:
Types of Leveling in Surveying
- Direct leveling
- Trigonometric leveling
- Barometric leveling
- Stadia leveling
Direct Leveling
It is the most normally used method of leveling. In this method, measurements are decided straight away from leveling device. Based on the statement elements and device positions direct leveling is break up into different types as follows:
- Simple leveling
- Differential leveling
- Fly leveling
- Profile leveling
- Precise leveling
- Reciprocal leveling
Simple Leveling
It is a smooth and essential form of leveling in which the leveling device is placed some of the elements which elevation is to be find out. Leveling rods are placed at that elements and sighted them through leveling device. It is finished best at the same time as the elements are toward each specific without any obstacles.
Differential Leveling
Differential leveling is finished at the same time as the space amongst elements is more. In this approach, variety of inter stations are located and device is shifted to each station and decided the elevation of inter station elements. Finally difference amongst proper elements is decided.
Fly Leveling
Fly leveling is completed at the same time as the benchmark will be very far from the art work station. In such case, a short bench mark is located at the art work station this is located based totally definitely on the proper benchmark. Even it isn't pretty specific it's far used for identifying approximate diploma.
Profile Leveling
Profile leveling is typically accompanied to find out elevation of things along a line which encompass for road, rails or rivers etc. In this situation, readings of intermediate stations are taken and reduced diploma of each station is found. From this circulate segment of the alignment is drawn.
Precise Leveling
Precise leveling is much like differential leveling but in this situation higher specific is wanted. To reap immoderate specific, excessive statement method is finished. The accuracy of 1 mm in line with 1 km is finished.
Reciprocal Leveling
When it isn't feasible to find out the leveling device in some of the inter visible elements, reciprocal leveling is finished. This case appears in case of ponds or rivers etc. in case of reciprocal leveling, device is set toward 1st station and sighted with inside the route of 2d station.
Trigonometric Leveling
The approach of leveling in which the elevation of aspect or the difference amongst elements is measured from the decided horizontal distances and vertical angles with inside the location is called trigonometric leveling.
Trigonometric Leveling
In this method, trigonometric own circle of relatives contributors are used to find out the elevation of an aspect from mindset and horizontal distance so, it's far called as trigonometric leveling.
Barometric Leveling
Barometer is a device used to diploma surroundings at any altitude. So, in this method of leveling, atmospheric pressure at precise elements is decided, based totally mostly on which the vertical difference amongst elements is decided. It is a difficult estimation and used
Stadia Leveling
It is a modified form of trigonometric leveling in which Tachometer principle is used to determine the elevation of aspect. In this situation the street of sight is inclined from the horizontal. It is more accurate and suitable for surveying in hilly terrains.
Profile Leveling:
Profile leveling is one of the maximum not unusual place packages of going for walks stages and vertical distance dimension for the surveyor.
The outcomes are plotted with inside the shape of a profile, that's a drawing that suggests a vertical go segment.
Profiles are required for the layout and production of roads, curbs, sidewalks, pipelines, etc. In quick, profile leveling refers back to the procedure of figuring out the elevation of factors at the floor at usually uniform intervals alongside a non-stop line.
Equipment used for profile leveling Dumpy level Leveling staff Tripod Staff bubble Chain or Tape Procedure for profile levelling
1. Longitudinal levelling
Profile leveling is basically similar to benchmark leveling, with one fundamental distinction.
At every tool position, in which an HI is decided through a again sight rod studying on a benchmark or turning point, numerous extra foresight readings can be taken on as many factors as desired.
These extra readings are known as rod photographs, and the elevation of all the ones factors is decided through subtracting the rod shot from the HI at that tool location. (See determine 1) Plotting the Profile The profile drawing is largely a graph of elevations, plotted at the vertical axis, as a characteristic of stations, plotted on horizontal axis.
A gridded sheet known as profile paper is used to devise the profile information from the sector book. All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
The elevation or elevation scale is usually exaggerated; that is, it is ‘stretched’ in contrast to the horizontal scale.
For instance the vertical scale is probably 10 instances larger. The horizontal line at the lowest of the profile does now no longer vital ought to begin at 0 elevation
2. Cross sectioning levelling
Cross sectioning levelling is every other technique in profile levelling. The time period go-segment normally refers to an enormously quick profile view of the floor, that's drawn perpendicular to the path centerline of a motorway or different styles of linear projects.
Cross-sectional drawings are mainly vital for estimating the earthwork volumes had to assemble a roadway; they display the prevailing floor elevations, the proposed reduce or fill facet slopes, and the grade elevation for the street base.
There is truly no distinction in manner among profile and go-segment leveling besides for the shape of the sector notes.
Cross-segment rod photographs are generally taken all through the path profile survey from the equal tool positions used to take rod photographs alongside the centerline.
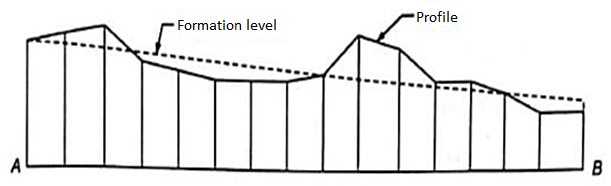
Fig: Profile levelling
Key Takeaways:
- If the telescope is now directed to personnel saved on factors of unknown elevation, the personnel readings may be read.
- In this levelling, the tool needs to be setup at numerous positions and at every installation the precept of easy levelling is used.
- The entries with inside the ultimate columns towards it need to additionally be repeated at the web page.
Longitudinal and Cross section:
Longitudinal Section
A Long Section is a profile view of a floor alongside a selected course, which plots elevation towards the gap alongside the course e.g. Floor profile alongside the middle line of a road, railway or river. In a protracted phase, elevations are decided alongside a set course.
At every tool position, in which an HI is decided through a again sight rod studying on a benchmark or turning point, numerous extra foresight readings can be taken on as many factors as desired.
These extra readings are known as rod photographs, and the elevation of all the ones factors is decided through subtracting the rod shot from the HI at that tool location. (See determine 1) Plotting the Profile The profile drawing is largely a graph of elevations, plotted at the vertical axis, as a characteristic of stations, plotted on horizontal axis.
A gridded sheet known as profile paper is used to devise the profile information from the sector book. All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
Cross Section:
A pass phase is a profile view of a floor at proper angles to a selected course. E.g. At proper angles to a road, river of railway. It plots elevation towards the gap alongside the pass phase line. Cross phase measurements are typically taken at an everyday durations alongside the course.
Cross sectioning levelling is every other technique in profile levelling. The time period go-segment normally refers to an enormously quick profile view of the floor, that's drawn perpendicular to the path centerline of a motorway or different styles of linear projects.
Cross-sectional drawings are mainly vital for estimating the earthwork volumes had to assemble a roadway; they display the prevailing floor elevations, the proposed reduce or fill facet slopes, and the grade elevation for the street base.
There is truly no distinction in manner among profile and go-segment leveling besides for the shape of the sector notes.
Reciprocal Levelling:
Reciprocal leveling is a surveying method wherein readings are taken from each instructions among factors to be able to lessen errors. In surveying, to degree is to discover the relative elevation of various factors with inside the land.
Reciprocal leveling is beneficial while you are leveling among factors which might be very some distance from every other.
At some distance distances, the earth’s curvature and atmospheric refraction can motive sizable leveling calculation errors, extra than at brief distances. For example, you've got factor an on one aspect of a canyon and factor B on the opposite aspect. You role your surveying tool near factor
A and degree its distance from the ground. From the identical role, you degree factor B’s distance from the ground. Next, you're taking your device throughout the canyon near factor B.
Now, you're taking the identical measurements you probably did earlier than however from the alternative direction.
By calculating the distinction among those pairs of measurements, you could decide what the leveling mistakes is to reach at what a definitely degree line might be.
Finding Difference in Levels
Let us say A and B are two points.
- The instrument is set up near A and readings on the staff are noted (x1 and y1)
- The instrument is shifted near B and readings on staff are again noted (x2 and y2)
Assuming the curvature and refraction error combined bee.
The error occurred when the instrument is close to 'A' is considered equal to the error occurred when the instrument is close to 'B' because the instrument is shifted quickly and there is not much change in refraction error.
The difference in levels, h = (y1 - x1) = (y2 - x2)
Considering a combined errors e,
The difference in level h = ((y1 - e) - x1)
It can also be written as, h = (y2 - (x2 - e))
On adding these two equations, 2h = (y1 - x1) + (y2 - x2)
So, h = 0.5((y1 - x1) + (y2 - x2))
Corrections for curvature and refraction:
Curvature correction (Cc)
- When levelling is done in a large area, the curvature of Earth is considered.
- The horizontal line is not a level line, because of which the staff reading is more than expected, this is called curvature correction.
- The effect of curvature is to increase the staff reading that is the error is positive and so the correction is negative.
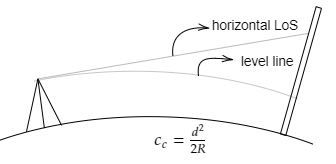
Fig: Curvature Correction
The curvature correction (Cc) is mathematically expressed as,
Cc = d^2/2R
Where, d: the length of the sight or the distance from the instruments to the staff station in kilometers
R= the radius of the earth = 6371 kilometres
So, Cc = 0.0785d^2
True staff reading = observed staff reading - 0.0785d^2
Refraction correction (Cr)
- The rays of light passing through the atmosphere of different density bend down. It results in this type of correction.
- The effect of refraction is 1/7th time the curvature correction but is of opposite nature. Hence the correction for refraction is additive to the staff reading.
Cr = 1/7 x Cc
So, Cr = 1/7 x 0.0785d^2 = 0.0112 x d^2
True staff reading = observed staff reading + 0.0112 x d^2
Combined correction(C)
The effect of curvature is to increase the staff reading and the effect of refraction is to decrease the staff reading. One more thing is the curvature error is more than the refraction error. So the combined effect is to increase staff reading. Hence, the combined correction is subtractive in nature.
C = 0.0785d^2 - 0.0112 x d^2 = 0.0673 x d^2
Therefore the true staff reading after both the corrections,
True staff reading = observed staff reading - 0.0673 x d^2
Distance to the visible horizon:
The horizon is the obvious line that separates the floor of a celestial frame from its sky while regarded from the attitude of an observer on or close to the floor of the applicable frame.
This line divides all viewing instructions primarily based totally on whether or not it intersects the applicable frame's floor or now no longer.
The proper horizon is sincerely a theoretical line, that may simplest be located to any diploma of accuracy while it lies alongside a distinctly clean floor together with that of Earth's oceans.
At many locations, this line is obscured via way of means of terrain, and on Earth it could additionally be obscured via way of means of lifestyles paperwork together with timber and/or human constructs together with buildings.
The ensuing intersection of such obstructions with the sky is referred to as the seen horizon. On Earth, while searching at a sea from a shore, the part of the ocean closest to the horizon is referred to as the offing.
The proper horizon surrounds the observer and it's far commonly assumed to be a circle, drawn at the floor of a superbly round version of the Earth. Its middle is beneath the observer and beneath sea stage.
Its distance from the observer varies from each day because of atmospheric refraction that is significantly laid low with climate conditions.
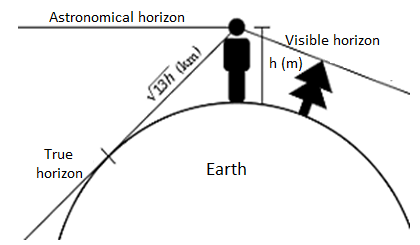
Fig: Visible horizon
Also, the better the observer's eyes are from sea stage, the farther away the horizon is from the observer.
For instance, in preferred atmospheric conditions, for an observer with eye stage above sea stage via way of means of 1.70 meters (five toes 7 in), the horizon is at a distance of approximately five kilometers (3.1 mi). When located from very excessive standpoints, together with an area station, the horizon is a great deal farther away and it encompasses a miles large place of Earth's floor.
In this case, the horizon might now no longer be an excellent circle, now no longer even an aircraft curve together with an ellipse, in particular while the observer is above the equator, because the Earth's floor may be higher modeled as an ellipsoid than as a sphere.
Anyway, I digress. If you're at the tuna tower of a game fishing boat you will be 15, 20, 25 toes above the floor of the water.
Once you understand your top of eye you truly plug that into the subsequent formulation:
1.17 instances the rectangular root of your top of eye = Distance to the horizon in nautical miles
For example, in case your top of eye is nine toes above the floor of the water, the formulation could be:
1.17 instances the rectangular root of nine = Distance to the horizon in nautical miles. 1.17 * 3 = 3.fifty one nautical miles
Key Takeaways:
- All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
- Now, you're taking the identical measurements you probably did earlier than however from the alternative direction.
- Its distance from the observer varies from each day because of atmospheric refraction that is significantly laid low with climate conditions.
References:
1. Surveying and Levelling by Kanetkar and Kulkarni (Vol. I) Pune Vidhatigrihan Prakashan
2. Surveying and Levelling by Dr. B.C. Punmia (Vol. I & II) Laxmi Pub.
3. Advance Surveying - Total Station, GIS and Remote Sensing by Pearson Education Satheesh Gopi & R. Sathikumar & N. Madhu
Unit - 2
Leveling and Contouring
Unit - 2
Leveling and Contouring
Leveling:
Leveling is a department of surveying in civil engineering to degree stages of various factors with admire to a hard and fast factor together with elevation of a building, peak of 1 factor from floor etc.
Levelling or leveling (American English; see spelling variations) is a department of surveying, the item of that's to set up or confirm or degree the peak of distinctive factors relative to a datum.
It is extensively utilized in geodesy and cartography to degree geodetic peak, and in production to degree peak variations of production artifacts. It is likewise called spirit levelling and differential levelling.
Optical levelling employs an optical stage, which includes a precision telescope with crosshairs and stadia marks. The go hairs are used to set up the extent factor at the target, and the stadia permit range-finding; stadia are typically at ratios of one hundred:
1, wherein case one meter among the stadia marks at the levelling body of workers represents one hundred meters from the target.
The whole unit is commonly installed on a tripod, and the telescope can freely rotate 360° in a horizontal aircraft. The surveyor adjusts the device's stage through coarse adjustment of the tripod legs and best adjustment the usage of 3 precision levelling screws at the device to make the rotational aircraft horizontal.
The surveyor does this with the usage of a bull's eye stage constructed into the device mount. The surveyor seems through the eyepiece of telescope whilst an assistant holds a vertical stage body of workers that's a graduated in inches or centimeters. The stage body of workers is positioned vertically the usage of a stage, with its foot at the factor for which the extent dimension is required.
The telescope is turned around and centered till the extent body of workers is it seems that seen with inside the crosshairs. In the case of an excessive accuracy guide stage, the best stage adjustment is made through an altitude screw, the usage of an excessive accuracy bubble stage constant to the telescope.
This may be considered through a replicate at the same time as adjusting or the ends of the bubble may be displayed with inside the telescope, which additionally permits warranty of the correct stage of the telescope at the same time as the sight is being taken.
However, with inside the case of an automated stage, altitude adjustment is carried out robotically through a suspended prism because of gravity, so long as the coarse levelling is correct inside positive limits.
When stage, the body of workers commencement analyzing on the crosshairs is recorded, and a figuring out mark or marker positioned in which the extent body of workers rested at the item or role being surveyed.
Different types of levels:
Levels are the exclusive units used for leveling in surveying. There are diverse styles of degrees together with dumpy degree, Y degree, Cushing’s degree, tilting degree, coke’s reversible degree and automated degree units for leveling in surveying.
The system of measuring vertical distances in surveying is known as leveling. To carry out leveling, we want a few degree units to cognizance or to examine the item. Nowadays, the era additionally brought in surveying and so many straightforward measuring units are designed.
Here we talk approximately the exclusive degrees utilized in leveling.
1. Dumpy Level
Dumpy degree is the maximum usually used tool in leveling. In this degree the telescope is restrained towards motion in its horizontal aircraft and telescope is constant to its support. A bubble tube is furnished at the pinnacle of the telescope. But however, the leveling head may be turned around in horizontal aircraft with the telescope.
2. Y Level
Y degree or Wye-degree is composed y-fashioned frames which helps the telescope. Telescope cane be eliminated from the y-fashioned helps via way of means of freeing clamp screws furnished.
These y-fashioned frames are organized to vertical spindle which allows to purpose the rotation of telescope. Compared to dumpy degree, modifications may be unexpectedly examined in y- degree. But, there can be a risk of frictional put on of open components of degree.
3. Cushing’s Level
In case of Cushing’s degree, the telescope is restrained towards rotation in its longitudinal axis and it's far non-removable. But, the item stop and eye piece stop may be interchangeable and reversible.
4. Tilting Level
Tilting degree consist a telescope which enabled for the horizontal rotation in addition to rotation approximately four diploma in its vertical aircraft. Centering of bubble may be without difficulty executed on this sort of degree.
But, for each setup bubble is to be targeted with the assist of tilting screw. The fundamental benefit of tilting degree is it's far beneficial whilst the few observations are to be desirous about one setup of degree.
5. Cooke’s Reversible Level
Cooke’s reversible degree is the aggregate of dumpy degree and y-degree. In this tool, the telescope may be reversed without rotation the tool. Collimation mistakes may be removed in this example due to bubble left and bubble proper studying of telescope.
6. Automatic Level
Automatic degree is just like the dumpy degree. In this example the telescope is constant to its helps. Circular spirit may be connected to the aspect of the telescope for approximate leveling. For extra correct leveling, compensator is hooked up within the telescope.
Study of Dumpy Level:
Dumpy degree is the maximum usually used tool in leveling. In this degree the telescope is restrained towards motion in its horizontal aircraft and telescope is constant to its support. A bubble tube is furnished at the pinnacle of the telescope. But however, the leveling head may be turned around in horizontal aircraft with the telescope.
The telescope is inner focusing telescope is a steel tube carries 4 fundamental components as given beneath.
- Objective lens
- Negative lens
- Diaphragm
- Eye-piece
- Objective Lens
Objective lens must be made because the aggregate of crown glass and flint glass. Because of this a few defects like round aberration and chromatic aberration may be eliminated.
A skinny layer coating which has smaller refractive index than glass is furnished at the goal lens to lessen the loss because of reflection.
Negative Lens Negative lens positioned co axial to the goal lens. So, the optical axis for each lenses is same.
Diaphragm is outfitted within the fundamental tube which includes move hairs (vertical and horizontal) and those are adjusted through capstan headed screws. The move hairs are product of darkish steel as filament wires which might be inserted in diaphragm ring in precise position. For stadia leveling purposes, greater horizontal move hairs are furnished above and beneath the horizontal wire.
Eyepiece lens permit the cap potential to sight the item collectively with move hairs. The photograph visible through eye piece is magnified and inverted.
Some eyepieces erect the photograph into ordinary view and people are known as erecting eyepieces.
About Dump Level Instrument: -
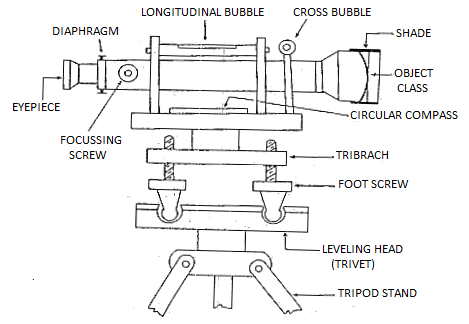
The dumpy degree is an optical device used for surveying and levelling operations. It accommodates of a telescope tube, firmly held among collars and adjusting screws.
The whole device is staged via way of means of the vertical spindle. The telescope positioned at the dumpy degree may be circled among the horizontal plane.
Relative elevation of survey factors at the land may be decided via the dumpy degree. The dumpy degree become invented via way of means of William Gravatt, in 1832.
Being a civil engineer, he invented the dumpy degree even as the usage of Y (Wye) degree device
Principle of Dumpy Level Instrument:
The dumpy degree operates at the precept via way of means of organizing a visible courting among or extra factors, via a built in telescope and a bubble degree. The acceptable degree of accuracy may be completed via steps.
It is likewise referred to as via numerous names together with Surveyors stages, Builders degree, Dumpy degree or maybe its pre-incidental version “Y (Wye) Level”.
Accuracy of Dumpy degree over different levelling units: The high cause for the usage of Dumpy degree over different levelling units is its accuracy.
A dumpy degree is thought for excessive accuracy values for maximum of the Tachometric methods.
The accuracy of a dumpy degree may be inside 1:4000 for each one hundred m.
Use of Dumpy degree in Surveying:
- Dumpy degree holds extensive significance with inside the surveying of a production web website online.
- The degree of accuracy and handiness of dumpy degree has made it a distinguished desire among surveyors.
- The high cause for acting levelling on a production web website online is to make the sector degree and even.
- To decide the variations in peak among factors. To degree the peak and distance of various places of surveying land via the precept of relativity.
- To degree following distance among numerous factor at the surveying land. Setting out stages and willing surfaces for production.
- To draw contours on land.
Temporary adjustments of dumpy level:
At every installation of a degree tool, transient adjustment is needed to be done previous to any group of workers observation.
It includes a few nicely described operations which might be required to be done in right sequence.
The transient adjustment of a dumpy degree is composed of (1) Setting, (2) Leveling and (3) Focusing.
During Setting, the tripod stand is installation at a handy peak having its head horizontal (via eye estimation).
The tool is then constant on the top with the aid of using rotating the decrease a part of the tool with proper hand and keeping firmly the higher element with left hand. Before fixing, the leveling screws are required to be delivered in among the tri Brach and trivet.
The bull's eye bubble (round bubble), if present, is then delivered to the center with the aid of using adjusting the tripod legs. Next, Leveling of the tool is carried out to make the vertical axis of the tool actually vertical. It is finished with the aid of using wearing out the subsequent steps:
Step 1: The degree tube is delivered parallel to any of the foot screws, with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool.
Step 2: The bubble is delivered to the center of the extent tube with the aid of using rotating each the foot screws both inward and outward.
Step 3: The degree tube is then delivered over the 0.33 foot screw once more with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool.
Step 4: The bubble is however delivered to the center of the extent tube with the aid of using rotating the 0.33 foot screw both inward and outward.
Step 5: Repeat Step 1 with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool with inside the identical quadrant of the circle after which Step 2.
Step 6: Repeat Step three with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool with inside the identical quadrant of the circle after which Step 4.
Step 7: Repeat Steps five and 6, until the bubble stays imperative in each the positions.
Step 8: By rotating the higher a part of the tool via a hundred and eighty o, the extent tube is delivered parallel to first foot screws in opposite order.
The bubble will stay with inside the center if the tool is in everlasting adjustment. Focusing is needed to be carried out so that you can shape picture via goal lens on the aircraft of the diaphragm and to view the clean picture of the item via eye-piece.
This is being done with the aid of using putting off parallax with the aid of using right focusing of goal and eye-piece.
For focusing the eye-piece, the telescope is first pointed toward the sky. Then the hoop of eye-piece is became both in and out till the cross-hairs are visible sharp and distinct.
Focusing of eye-piece relies upon at the imaginative and prescient of observer and for this reason required every time there may be extrude in observer.
For focusing the goal, the telescope is first pointed toward the item.
Then, the focusing screw is became till the picture of the item seems clean and sharp and there may be no relative motion among the picture and the cross-hairs.
This is needed to be carried out earlier than taking any observation.
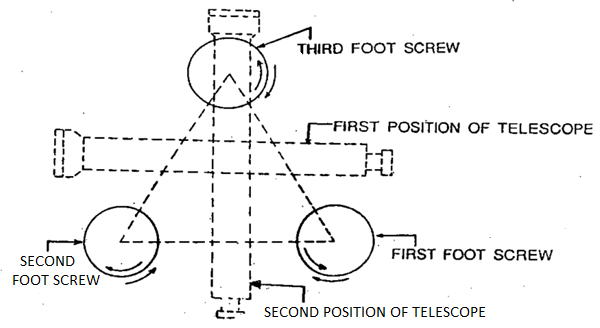
Fig: Temporary adjustment of dumpy level
Principle of leveling:
Simple leveling
When the leveling tool is well leveled, the bubble tube axis and the road of sight can be horizontal and the vertical axis of the tool can be vertical. The bubble ought to be significant and traverse. The line of sight will stay in a horizontal aircraft while the telescope is rotated.
Thus if the telescope is sighted toward a personnel saved on a factor of recognized elevation, the peak or elevation of the road of sight may be decided. If the telescope is now directed to personnel saved on factors of unknown elevation, the personnel readings may be read.
From which the decreased stages of the unknown factors may be decided.
Terms utilized in levelling
Some of the typically used phrases in levelling are described as follows:
Station
Station is a factor whose elevation is to be decided or it’s far the point that's to be marked at a given elevation. It is the factor wherein the personnel is held for taking observations from a levelling tool.
Height of the tool (HI)
It is the elevation or decreased degree of the road of sight with appreciate to the datum.
Height of the tool isn't always the peak of the road of sight above the floor wherein the levelling tool is installation.
Height of the tool= elevation of BM+ backsight
Balancing of sight
To lessen the impact of instrumental and different errors, this approach is followed. The distance of the factor wherein the backsight is taken and the gap of the factor wherein a foresight is taken, as measured from the tool station, needs to be about same.
This is referred to as balancing of points of interest. The intermediate points of interest do now no longer observe the situation of same duration of points of interest.
Differential levelling
Differential levelling is likewise known as compound levelling or non-stop levelling. It is followed while the factors whose elevation is to be decided are too a long way aside or the distinction in elevation is just too large.
In this levelling, the tool needs to be setup at numerous positions and at every installation the precept of easy levelling is used.
Some of the phrases related to differential levelling are defined as follows:
Backsight (BS) or Backsight studying
It is a personnel studying taken on a factor of recognized elevation, as on a benchmark or an alternate factor. This is likewise known as a plus sight. The backsight is the primary personnel studying taken after the extent is installation and leveled on the factor.
Foresight (FS) or Foresight studying
It is a personnel studying taken on a factor whose elevation needs to be decided through levelling process. It is likewise referred to as minus sight. The foresight is likewise taken toward an alternate factor. It is the closing studying taken earlier than the tool is shifted.
Elevation of station= top of tool (HI) – foresight (FS) or intermediate sight (IS)
Intermediate sight (IS)
It is the personnel readings taken on personnel held at different factors whose elevations are to be decided earlier than the foresight is taken. Intermediate points of interest are all personnel readings among the B.S and F.S Change factor or Turning factor (TP)
It is a factor denoting the moving of the extent. It is a station at which each BS and FS readings are taken. Stable and nicely described gadgets ought to be selected as alternate factors for correct results.
Reduction of levels:
1. Collimation Method:
It is composed in locating the elevation of the aircraft of collimation i.e. (H.I.) for each putting of the tool after which acquiring the decreased ranges of the factors as regards to the respective plan of collimation To begin with, the H.L is calculated with the aid of using including the returned sight of the R.L. Of the beginning factor.
The decreased ranges of the intermediate factor and the primary extrude factor are then acquired with the aid of using subtracting the respective readings from the H.I. When the tool is shifted, a brand new aircraft of collimation is installation and the peak of that's calculated with the aid of using including returned sight studying to the R.L. Of the primary extrude factor.
The decreased ranges of the successive factors and the second one extrude factor arc located out with the aid of using subtracting their group of workers readings from this new H.I.
The procedure is repeated till all of the R.Ls are labored out, after which the arithmetical test is applied.
Arithmetical Check: The distinction among the sum of the returned points of interest and the sum of the fore points of interest need to be identical to the distinction of the primary and the final R.Ls i.e. Σ B.S. – Σ F.S. = Last R.L. -First R.L. This test verifies the calculation of R.Ls. Of the planes of collimation and of the extrude factors only.
This technique might also additionally greater in reality be understood with the aid of using the subsequent instance of longitudinal levelling from flag – group of workers decrease base to downstream parapet of culvert no
2. Rise and Fall Method:
In this technique, the distinction among consecutive factors is calculated with the aid of using evaluating every factor after the primary with that right now previous it.
The distinction in their group of workers studying suggests upward thrust or fall in accordance as any group of workers studying is smaller or extra than that on the previous factor. The R.L. Of every factor is then located with the aid of using including upward thrust or subtracting fall to or from the R.L. Of the previous factor.
Collimation Method:
1. In the case of greater intermediate readings, there may be tremendous saving of labor and time because it entails only some calculations.
2. There isn't any any test at the R.Ls of intermediate stations.
3. There are assessments for arithmetical accuracy i.e. the distinction among the sum of returned points of interest of fore points of interest need to be identical to the distinction of the Kits and final R.Ls.
4. It is typically used for longitudinal and pass levelling operations and for giving ranges of roads and canals and comparable constructional works.
Rise and Fall Method:
1. It is an exhausting technique as group of workers studying of every factor at the ground, after the primary is as compared with that previous it, and the distinction of degree entered as an upward thrust or fall.
2. There is an entire test at the discount of R.Ls. Of intermediate stations.
3. There are 3 assessments for arithmetical accuracy.
The distinction among the sum of the returned points of interest and the sum of the fore points of interest need to be identical to that among the sum of the sum of rises and the sum of the falls in addition to that among the
Its. And the final it is typically used for earth paintings calculations and different unique levelling operations.
Booking the Staff Readings:
The following factors need to be stored in view even as coming into the group of workers readings in a degree eye-e book:
1. The readings need to be entered with inside the respective columns as quickly as they may be taken and with inside the order in their observation.
2. The first access on the extent eye-e book web page is continually a B.S and the final one a F.S.
3. The fore and returned points of interest of the extrude factors need to be written with inside the identical horizontal line.
4. The H.I need to be written with inside the identical horizontal line contrary the returned sight.
5. While sporting ahead the studying from one web page of the extent – eye-e book to the , if the final studying is an intermediate sight, it's far entered in each I.S and F. S. Column in this web page and I.S. And B.S. Columns as first access at the web page.
The entries with inside the ultimate columns towards it need to additionally be repeated at the web page.
6. Brief description with neat sketches in admire of bench marks, extrude factors and different vital factors need to receive with inside the statement column.
Classification of levelling:
Types of Leveling in Surveying
- Direct leveling
- Trigonometric leveling
- Barometric leveling
- Stadia leveling
Direct Leveling
It is the most normally used method of leveling. In this method, measurements are decided straight away from leveling device. Based on the statement elements and device positions direct leveling is break up into different types as follows:
- Simple leveling
- Differential leveling
- Fly leveling
- Profile leveling
- Precise leveling
- Reciprocal leveling
Simple Leveling
It is a smooth and essential form of leveling in which the leveling device is placed some of the elements which elevation is to be find out. Leveling rods are placed at that elements and sighted them through leveling device. It is finished best at the same time as the elements are toward each specific without any obstacles.
Differential Leveling
Differential leveling is finished at the same time as the space amongst elements is more. In this approach, variety of inter stations are located and device is shifted to each station and decided the elevation of inter station elements. Finally difference amongst proper elements is decided.
Fly Leveling
Fly leveling is completed at the same time as the benchmark will be very far from the art work station. In such case, a short bench mark is located at the art work station this is located based totally definitely on the proper benchmark. Even it isn't pretty specific it's far used for identifying approximate diploma.
Profile Leveling
Profile leveling is typically accompanied to find out elevation of things along a line which encompass for road, rails or rivers etc. In this situation, readings of intermediate stations are taken and reduced diploma of each station is found. From this circulate segment of the alignment is drawn.
Precise Leveling
Precise leveling is much like differential leveling but in this situation higher specific is wanted. To reap immoderate specific, excessive statement method is finished. The accuracy of 1 mm in line with 1 km is finished.
Reciprocal Leveling
When it isn't feasible to find out the leveling device in some of the inter visible elements, reciprocal leveling is finished. This case appears in case of ponds or rivers etc. in case of reciprocal leveling, device is set toward 1st station and sighted with inside the route of 2d station.
Trigonometric Leveling
The approach of leveling in which the elevation of aspect or the difference amongst elements is measured from the decided horizontal distances and vertical angles with inside the location is called trigonometric leveling.
Trigonometric Leveling
In this method, trigonometric own circle of relatives contributors are used to find out the elevation of an aspect from mindset and horizontal distance so, it's far called as trigonometric leveling.
Barometric Leveling
Barometer is a device used to diploma surroundings at any altitude. So, in this method of leveling, atmospheric pressure at precise elements is decided, based totally mostly on which the vertical difference amongst elements is decided. It is a difficult estimation and used
Stadia Leveling
It is a modified form of trigonometric leveling in which Tachometer principle is used to determine the elevation of aspect. In this situation the street of sight is inclined from the horizontal. It is more accurate and suitable for surveying in hilly terrains.
Profile Leveling:
Profile leveling is one of the maximum not unusual place packages of going for walks stages and vertical distance dimension for the surveyor.
The outcomes are plotted with inside the shape of a profile, that's a drawing that suggests a vertical go segment.
Profiles are required for the layout and production of roads, curbs, sidewalks, pipelines, etc. In quick, profile leveling refers back to the procedure of figuring out the elevation of factors at the floor at usually uniform intervals alongside a non-stop line.
Equipment used for profile leveling Dumpy level Leveling staff Tripod Staff bubble Chain or Tape Procedure for profile levelling
1. Longitudinal levelling
Profile leveling is basically similar to benchmark leveling, with one fundamental distinction.
At every tool position, in which an HI is decided through a again sight rod studying on a benchmark or turning point, numerous extra foresight readings can be taken on as many factors as desired.
These extra readings are known as rod photographs, and the elevation of all the ones factors is decided through subtracting the rod shot from the HI at that tool location. (See determine 1) Plotting the Profile The profile drawing is largely a graph of elevations, plotted at the vertical axis, as a characteristic of stations, plotted on horizontal axis.
A gridded sheet known as profile paper is used to devise the profile information from the sector book. All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
The elevation or elevation scale is usually exaggerated; that is, it is ‘stretched’ in contrast to the horizontal scale.
For instance the vertical scale is probably 10 instances larger. The horizontal line at the lowest of the profile does now no longer vital ought to begin at 0 elevation
2. Cross sectioning levelling
Cross sectioning levelling is every other technique in profile levelling. The time period go-segment normally refers to an enormously quick profile view of the floor, that's drawn perpendicular to the path centerline of a motorway or different styles of linear projects.
Cross-sectional drawings are mainly vital for estimating the earthwork volumes had to assemble a roadway; they display the prevailing floor elevations, the proposed reduce or fill facet slopes, and the grade elevation for the street base.
There is truly no distinction in manner among profile and go-segment leveling besides for the shape of the sector notes.
Cross-segment rod photographs are generally taken all through the path profile survey from the equal tool positions used to take rod photographs alongside the centerline.
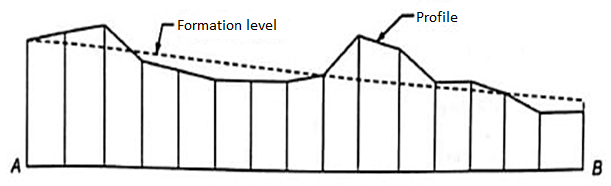
Fig: Profile levelling
Key Takeaways:
- If the telescope is now directed to personnel saved on factors of unknown elevation, the personnel readings may be read.
- In this levelling, the tool needs to be setup at numerous positions and at every installation the precept of easy levelling is used.
- The entries with inside the ultimate columns towards it need to additionally be repeated at the web page.
Longitudinal and Cross section:
Longitudinal Section
A Long Section is a profile view of a floor alongside a selected course, which plots elevation towards the gap alongside the course e.g. Floor profile alongside the middle line of a road, railway or river. In a protracted phase, elevations are decided alongside a set course.
At every tool position, in which an HI is decided through a again sight rod studying on a benchmark or turning point, numerous extra foresight readings can be taken on as many factors as desired.
These extra readings are known as rod photographs, and the elevation of all the ones factors is decided through subtracting the rod shot from the HI at that tool location. (See determine 1) Plotting the Profile The profile drawing is largely a graph of elevations, plotted at the vertical axis, as a characteristic of stations, plotted on horizontal axis.
A gridded sheet known as profile paper is used to devise the profile information from the sector book. All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
Cross Section:
A pass phase is a profile view of a floor at proper angles to a selected course. E.g. At proper angles to a road, river of railway. It plots elevation towards the gap alongside the pass phase line. Cross phase measurements are typically taken at an everyday durations alongside the course.
Cross sectioning levelling is every other technique in profile levelling. The time period go-segment normally refers to an enormously quick profile view of the floor, that's drawn perpendicular to the path centerline of a motorway or different styles of linear projects.
Cross-sectional drawings are mainly vital for estimating the earthwork volumes had to assemble a roadway; they display the prevailing floor elevations, the proposed reduce or fill facet slopes, and the grade elevation for the street base.
There is truly no distinction in manner among profile and go-segment leveling besides for the shape of the sector notes.
Reciprocal Levelling:
Reciprocal leveling is a surveying method wherein readings are taken from each instructions among factors to be able to lessen errors. In surveying, to degree is to discover the relative elevation of various factors with inside the land.
Reciprocal leveling is beneficial while you are leveling among factors which might be very some distance from every other.
At some distance distances, the earth’s curvature and atmospheric refraction can motive sizable leveling calculation errors, extra than at brief distances. For example, you've got factor an on one aspect of a canyon and factor B on the opposite aspect. You role your surveying tool near factor
A and degree its distance from the ground. From the identical role, you degree factor B’s distance from the ground. Next, you're taking your device throughout the canyon near factor B.
Now, you're taking the identical measurements you probably did earlier than however from the alternative direction.
By calculating the distinction among those pairs of measurements, you could decide what the leveling mistakes is to reach at what a definitely degree line might be.
Finding Difference in Levels
Let us say A and B are two points.
- The instrument is set up near A and readings on the staff are noted (x1 and y1)
- The instrument is shifted near B and readings on staff are again noted (x2 and y2)
Assuming the curvature and refraction error combined bee.
The error occurred when the instrument is close to 'A' is considered equal to the error occurred when the instrument is close to 'B' because the instrument is shifted quickly and there is not much change in refraction error.
The difference in levels, h = (y1 - x1) = (y2 - x2)
Considering a combined errors e,
The difference in level h = ((y1 - e) - x1)
It can also be written as, h = (y2 - (x2 - e))
On adding these two equations, 2h = (y1 - x1) + (y2 - x2)
So, h = 0.5((y1 - x1) + (y2 - x2))
Corrections for curvature and refraction:
Curvature correction (Cc)
- When levelling is done in a large area, the curvature of Earth is considered.
- The horizontal line is not a level line, because of which the staff reading is more than expected, this is called curvature correction.
- The effect of curvature is to increase the staff reading that is the error is positive and so the correction is negative.
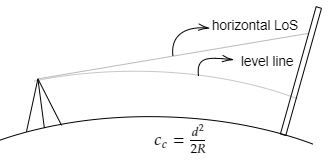
Fig: Curvature Correction
The curvature correction (Cc) is mathematically expressed as,
Cc = d^2/2R
Where, d: the length of the sight or the distance from the instruments to the staff station in kilometers
R= the radius of the earth = 6371 kilometres
So, Cc = 0.0785d^2
True staff reading = observed staff reading - 0.0785d^2
Refraction correction (Cr)
- The rays of light passing through the atmosphere of different density bend down. It results in this type of correction.
- The effect of refraction is 1/7th time the curvature correction but is of opposite nature. Hence the correction for refraction is additive to the staff reading.
Cr = 1/7 x Cc
So, Cr = 1/7 x 0.0785d^2 = 0.0112 x d^2
True staff reading = observed staff reading + 0.0112 x d^2
Combined correction(C)
The effect of curvature is to increase the staff reading and the effect of refraction is to decrease the staff reading. One more thing is the curvature error is more than the refraction error. So the combined effect is to increase staff reading. Hence, the combined correction is subtractive in nature.
C = 0.0785d^2 - 0.0112 x d^2 = 0.0673 x d^2
Therefore the true staff reading after both the corrections,
True staff reading = observed staff reading - 0.0673 x d^2
Distance to the visible horizon:
The horizon is the obvious line that separates the floor of a celestial frame from its sky while regarded from the attitude of an observer on or close to the floor of the applicable frame.
This line divides all viewing instructions primarily based totally on whether or not it intersects the applicable frame's floor or now no longer.
The proper horizon is sincerely a theoretical line, that may simplest be located to any diploma of accuracy while it lies alongside a distinctly clean floor together with that of Earth's oceans.
At many locations, this line is obscured via way of means of terrain, and on Earth it could additionally be obscured via way of means of lifestyles paperwork together with timber and/or human constructs together with buildings.
The ensuing intersection of such obstructions with the sky is referred to as the seen horizon. On Earth, while searching at a sea from a shore, the part of the ocean closest to the horizon is referred to as the offing.
The proper horizon surrounds the observer and it's far commonly assumed to be a circle, drawn at the floor of a superbly round version of the Earth. Its middle is beneath the observer and beneath sea stage.
Its distance from the observer varies from each day because of atmospheric refraction that is significantly laid low with climate conditions.
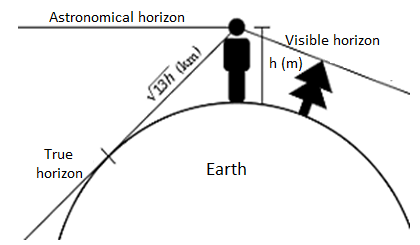
Fig: Visible horizon
Also, the better the observer's eyes are from sea stage, the farther away the horizon is from the observer.
For instance, in preferred atmospheric conditions, for an observer with eye stage above sea stage via way of means of 1.70 meters (five toes 7 in), the horizon is at a distance of approximately five kilometers (3.1 mi). When located from very excessive standpoints, together with an area station, the horizon is a great deal farther away and it encompasses a miles large place of Earth's floor.
In this case, the horizon might now no longer be an excellent circle, now no longer even an aircraft curve together with an ellipse, in particular while the observer is above the equator, because the Earth's floor may be higher modeled as an ellipsoid than as a sphere.
Anyway, I digress. If you're at the tuna tower of a game fishing boat you will be 15, 20, 25 toes above the floor of the water.
Once you understand your top of eye you truly plug that into the subsequent formulation:
1.17 instances the rectangular root of your top of eye = Distance to the horizon in nautical miles
For example, in case your top of eye is nine toes above the floor of the water, the formulation could be:
1.17 instances the rectangular root of nine = Distance to the horizon in nautical miles. 1.17 * 3 = 3.fifty one nautical miles
Key Takeaways:
- All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
- Now, you're taking the identical measurements you probably did earlier than however from the alternative direction.
- Its distance from the observer varies from each day because of atmospheric refraction that is significantly laid low with climate conditions.
References:
1. Surveying and Levelling by Kanetkar and Kulkarni (Vol. I) Pune Vidhatigrihan Prakashan
2. Surveying and Levelling by Dr. B.C. Punmia (Vol. I & II) Laxmi Pub.
3. Advance Surveying - Total Station, GIS and Remote Sensing by Pearson Education Satheesh Gopi & R. Sathikumar & N. Madhu
Unit - 2
Leveling and Contouring
Leveling:
Leveling is a department of surveying in civil engineering to degree stages of various factors with admire to a hard and fast factor together with elevation of a building, peak of 1 factor from floor etc.
Levelling or leveling (American English; see spelling variations) is a department of surveying, the item of that's to set up or confirm or degree the peak of distinctive factors relative to a datum.
It is extensively utilized in geodesy and cartography to degree geodetic peak, and in production to degree peak variations of production artifacts. It is likewise called spirit levelling and differential levelling.
Optical levelling employs an optical stage, which includes a precision telescope with crosshairs and stadia marks. The go hairs are used to set up the extent factor at the target, and the stadia permit range-finding; stadia are typically at ratios of one hundred:
1, wherein case one meter among the stadia marks at the levelling body of workers represents one hundred meters from the target.
The whole unit is commonly installed on a tripod, and the telescope can freely rotate 360° in a horizontal aircraft. The surveyor adjusts the device's stage through coarse adjustment of the tripod legs and best adjustment the usage of 3 precision levelling screws at the device to make the rotational aircraft horizontal.
The surveyor does this with the usage of a bull's eye stage constructed into the device mount. The surveyor seems through the eyepiece of telescope whilst an assistant holds a vertical stage body of workers that's a graduated in inches or centimeters. The stage body of workers is positioned vertically the usage of a stage, with its foot at the factor for which the extent dimension is required.
The telescope is turned around and centered till the extent body of workers is it seems that seen with inside the crosshairs. In the case of an excessive accuracy guide stage, the best stage adjustment is made through an altitude screw, the usage of an excessive accuracy bubble stage constant to the telescope.
This may be considered through a replicate at the same time as adjusting or the ends of the bubble may be displayed with inside the telescope, which additionally permits warranty of the correct stage of the telescope at the same time as the sight is being taken.
However, with inside the case of an automated stage, altitude adjustment is carried out robotically through a suspended prism because of gravity, so long as the coarse levelling is correct inside positive limits.
When stage, the body of workers commencement analyzing on the crosshairs is recorded, and a figuring out mark or marker positioned in which the extent body of workers rested at the item or role being surveyed.
Different types of levels:
Levels are the exclusive units used for leveling in surveying. There are diverse styles of degrees together with dumpy degree, Y degree, Cushing’s degree, tilting degree, coke’s reversible degree and automated degree units for leveling in surveying.
The system of measuring vertical distances in surveying is known as leveling. To carry out leveling, we want a few degree units to cognizance or to examine the item. Nowadays, the era additionally brought in surveying and so many straightforward measuring units are designed.
Here we talk approximately the exclusive degrees utilized in leveling.
1. Dumpy Level
Dumpy degree is the maximum usually used tool in leveling. In this degree the telescope is restrained towards motion in its horizontal aircraft and telescope is constant to its support. A bubble tube is furnished at the pinnacle of the telescope. But however, the leveling head may be turned around in horizontal aircraft with the telescope.
2. Y Level
Y degree or Wye-degree is composed y-fashioned frames which helps the telescope. Telescope cane be eliminated from the y-fashioned helps via way of means of freeing clamp screws furnished.
These y-fashioned frames are organized to vertical spindle which allows to purpose the rotation of telescope. Compared to dumpy degree, modifications may be unexpectedly examined in y- degree. But, there can be a risk of frictional put on of open components of degree.
3. Cushing’s Level
In case of Cushing’s degree, the telescope is restrained towards rotation in its longitudinal axis and it's far non-removable. But, the item stop and eye piece stop may be interchangeable and reversible.
4. Tilting Level
Tilting degree consist a telescope which enabled for the horizontal rotation in addition to rotation approximately four diploma in its vertical aircraft. Centering of bubble may be without difficulty executed on this sort of degree.
But, for each setup bubble is to be targeted with the assist of tilting screw. The fundamental benefit of tilting degree is it's far beneficial whilst the few observations are to be desirous about one setup of degree.
5. Cooke’s Reversible Level
Cooke’s reversible degree is the aggregate of dumpy degree and y-degree. In this tool, the telescope may be reversed without rotation the tool. Collimation mistakes may be removed in this example due to bubble left and bubble proper studying of telescope.
6. Automatic Level
Automatic degree is just like the dumpy degree. In this example the telescope is constant to its helps. Circular spirit may be connected to the aspect of the telescope for approximate leveling. For extra correct leveling, compensator is hooked up within the telescope.
Study of Dumpy Level:
Dumpy degree is the maximum usually used tool in leveling. In this degree the telescope is restrained towards motion in its horizontal aircraft and telescope is constant to its support. A bubble tube is furnished at the pinnacle of the telescope. But however, the leveling head may be turned around in horizontal aircraft with the telescope.
The telescope is inner focusing telescope is a steel tube carries 4 fundamental components as given beneath.
- Objective lens
- Negative lens
- Diaphragm
- Eye-piece
- Objective Lens
Objective lens must be made because the aggregate of crown glass and flint glass. Because of this a few defects like round aberration and chromatic aberration may be eliminated.
A skinny layer coating which has smaller refractive index than glass is furnished at the goal lens to lessen the loss because of reflection.
Negative Lens Negative lens positioned co axial to the goal lens. So, the optical axis for each lenses is same.
Diaphragm is outfitted within the fundamental tube which includes move hairs (vertical and horizontal) and those are adjusted through capstan headed screws. The move hairs are product of darkish steel as filament wires which might be inserted in diaphragm ring in precise position. For stadia leveling purposes, greater horizontal move hairs are furnished above and beneath the horizontal wire.
Eyepiece lens permit the cap potential to sight the item collectively with move hairs. The photograph visible through eye piece is magnified and inverted.
Some eyepieces erect the photograph into ordinary view and people are known as erecting eyepieces.
About Dump Level Instrument: -
The dumpy degree is an optical device used for surveying and levelling operations. It accommodates of a telescope tube, firmly held among collars and adjusting screws.
The whole device is staged via way of means of the vertical spindle. The telescope positioned at the dumpy degree may be circled among the horizontal plane.
Relative elevation of survey factors at the land may be decided via the dumpy degree. The dumpy degree become invented via way of means of William Gravatt, in 1832.
Being a civil engineer, he invented the dumpy degree even as the usage of Y (Wye) degree device
Principle of Dumpy Level Instrument:
The dumpy degree operates at the precept via way of means of organizing a visible courting among or extra factors, via a built in telescope and a bubble degree. The acceptable degree of accuracy may be completed via steps.
It is likewise referred to as via numerous names together with Surveyors stages, Builders degree, Dumpy degree or maybe its pre-incidental version “Y (Wye) Level”.
Accuracy of Dumpy degree over different levelling units: The high cause for the usage of Dumpy degree over different levelling units is its accuracy.
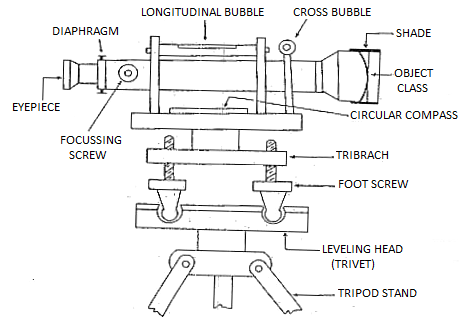
A dumpy degree is thought for excessive accuracy values for maximum of the Tachometric methods.
The accuracy of a dumpy degree may be inside 1:4000 for each one hundred m.
Use of Dumpy degree in Surveying:
- Dumpy degree holds extensive significance with inside the surveying of a production web website online.
- The degree of accuracy and handiness of dumpy degree has made it a distinguished desire among surveyors.
- The high cause for acting levelling on a production web website online is to make the sector degree and even.
- To decide the variations in peak among factors. To degree the peak and distance of various places of surveying land via the precept of relativity.
- To degree following distance among numerous factor at the surveying land. Setting out stages and willing surfaces for production.
- To draw contours on land.
Temporary adjustments of dumpy level:
At every installation of a degree tool, transient adjustment is needed to be done previous to any group of workers observation.
It includes a few nicely described operations which might be required to be done in right sequence.
The transient adjustment of a dumpy degree is composed of (1) Setting, (2) Leveling and (3) Focusing.
During Setting, the tripod stand is installation at a handy peak having its head horizontal (via eye estimation).
The tool is then constant on the top with the aid of using rotating the decrease a part of the tool with proper hand and keeping firmly the higher element with left hand. Before fixing, the leveling screws are required to be delivered in among the tri Brach and trivet.
The bull's eye bubble (round bubble), if present, is then delivered to the center with the aid of using adjusting the tripod legs. Next, Leveling of the tool is carried out to make the vertical axis of the tool actually vertical. It is finished with the aid of using wearing out the subsequent steps:
Step 1: The degree tube is delivered parallel to any of the foot screws, with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool.
Step 2: The bubble is delivered to the center of the extent tube with the aid of using rotating each the foot screws both inward and outward.
Step 3: The degree tube is then delivered over the 0.33 foot screw once more with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool.
Step 4: The bubble is however delivered to the center of the extent tube with the aid of using rotating the 0.33 foot screw both inward and outward.
Step 5: Repeat Step 1 with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool with inside the identical quadrant of the circle after which Step 2.
Step 6: Repeat Step three with the aid of using rotating the higher a part of the tool with inside the identical quadrant of the circle after which Step 4.
Step 7: Repeat Steps five and 6, until the bubble stays imperative in each the positions.
Step 8: By rotating the higher a part of the tool via a hundred and eighty o, the extent tube is delivered parallel to first foot screws in opposite order.
The bubble will stay with inside the center if the tool is in everlasting adjustment. Focusing is needed to be carried out so that you can shape picture via goal lens on the aircraft of the diaphragm and to view the clean picture of the item via eye-piece.
This is being done with the aid of using putting off parallax with the aid of using right focusing of goal and eye-piece.
For focusing the eye-piece, the telescope is first pointed toward the sky. Then the hoop of eye-piece is became both in and out till the cross-hairs are visible sharp and distinct.
Focusing of eye-piece relies upon at the imaginative and prescient of observer and for this reason required every time there may be extrude in observer.
For focusing the goal, the telescope is first pointed toward the item.
Then, the focusing screw is became till the picture of the item seems clean and sharp and there may be no relative motion among the picture and the cross-hairs.
This is needed to be carried out earlier than taking any observation.
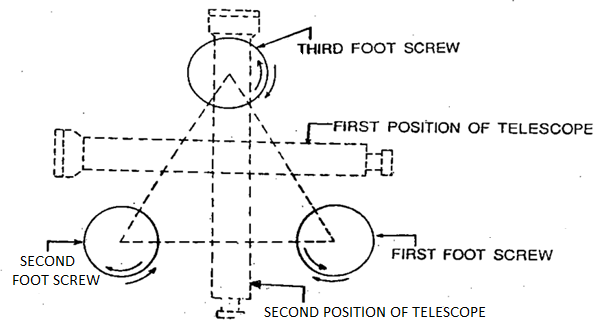
Fig: Temporary adjustment of dumpy level
Principle of leveling:
Simple leveling
When the leveling tool is well leveled, the bubble tube axis and the road of sight can be horizontal and the vertical axis of the tool can be vertical. The bubble ought to be significant and traverse. The line of sight will stay in a horizontal aircraft while the telescope is rotated.
Thus if the telescope is sighted toward a personnel saved on a factor of recognized elevation, the peak or elevation of the road of sight may be decided. If the telescope is now directed to personnel saved on factors of unknown elevation, the personnel readings may be read.
From which the decreased stages of the unknown factors may be decided.
Terms utilized in levelling
Some of the typically used phrases in levelling are described as follows:
Station
Station is a factor whose elevation is to be decided or it’s far the point that's to be marked at a given elevation. It is the factor wherein the personnel is held for taking observations from a levelling tool.
Height of the tool (HI)
It is the elevation or decreased degree of the road of sight with appreciate to the datum.
Height of the tool isn't always the peak of the road of sight above the floor wherein the levelling tool is installation.
Height of the tool= elevation of BM+ backsight
Balancing of sight
To lessen the impact of instrumental and different errors, this approach is followed. The distance of the factor wherein the backsight is taken and the gap of the factor wherein a foresight is taken, as measured from the tool station, needs to be about same.
This is referred to as balancing of points of interest. The intermediate points of interest do now no longer observe the situation of same duration of points of interest.
Differential levelling
Differential levelling is likewise known as compound levelling or non-stop levelling. It is followed while the factors whose elevation is to be decided are too a long way aside or the distinction in elevation is just too large.
In this levelling, the tool needs to be setup at numerous positions and at every installation the precept of easy levelling is used.
Some of the phrases related to differential levelling are defined as follows:
Backsight (BS) or Backsight studying
It is a personnel studying taken on a factor of recognized elevation, as on a benchmark or an alternate factor. This is likewise known as a plus sight. The backsight is the primary personnel studying taken after the extent is installation and leveled on the factor.
Foresight (FS) or Foresight studying
It is a personnel studying taken on a factor whose elevation needs to be decided through levelling process. It is likewise referred to as minus sight. The foresight is likewise taken toward an alternate factor. It is the closing studying taken earlier than the tool is shifted.
Elevation of station= top of tool (HI) – foresight (FS) or intermediate sight (IS)
Intermediate sight (IS)
It is the personnel readings taken on personnel held at different factors whose elevations are to be decided earlier than the foresight is taken. Intermediate points of interest are all personnel readings among the B.S and F.S Change factor or Turning factor (TP)
It is a factor denoting the moving of the extent. It is a station at which each BS and FS readings are taken. Stable and nicely described gadgets ought to be selected as alternate factors for correct results.
Reduction of levels:
1. Collimation Method:
It is composed in locating the elevation of the aircraft of collimation i.e. (H.I.) for each putting of the tool after which acquiring the decreased ranges of the factors as regards to the respective plan of collimation To begin with, the H.L is calculated with the aid of using including the returned sight of the R.L. Of the beginning factor.
The decreased ranges of the intermediate factor and the primary extrude factor are then acquired with the aid of using subtracting the respective readings from the H.I. When the tool is shifted, a brand new aircraft of collimation is installation and the peak of that's calculated with the aid of using including returned sight studying to the R.L. Of the primary extrude factor.
The decreased ranges of the successive factors and the second one extrude factor arc located out with the aid of using subtracting their group of workers readings from this new H.I.
The procedure is repeated till all of the R.Ls are labored out, after which the arithmetical test is applied.
Arithmetical Check: The distinction among the sum of the returned points of interest and the sum of the fore points of interest need to be identical to the distinction of the primary and the final R.Ls i.e. Σ B.S. – Σ F.S. = Last R.L. -First R.L. This test verifies the calculation of R.Ls. Of the planes of collimation and of the extrude factors only.
This technique might also additionally greater in reality be understood with the aid of using the subsequent instance of longitudinal levelling from flag – group of workers decrease base to downstream parapet of culvert no
2. Rise and Fall Method:
In this technique, the distinction among consecutive factors is calculated with the aid of using evaluating every factor after the primary with that right now previous it.
The distinction in their group of workers studying suggests upward thrust or fall in accordance as any group of workers studying is smaller or extra than that on the previous factor. The R.L. Of every factor is then located with the aid of using including upward thrust or subtracting fall to or from the R.L. Of the previous factor.
Collimation Method:
1. In the case of greater intermediate readings, there may be tremendous saving of labor and time because it entails only some calculations.
2. There isn't any any test at the R.Ls of intermediate stations.
3. There are assessments for arithmetical accuracy i.e. the distinction among the sum of returned points of interest of fore points of interest need to be identical to the distinction of the Kits and final R.Ls.
4. It is typically used for longitudinal and pass levelling operations and for giving ranges of roads and canals and comparable constructional works.
Rise and Fall Method:
1. It is an exhausting technique as group of workers studying of every factor at the ground, after the primary is as compared with that previous it, and the distinction of degree entered as an upward thrust or fall.
2. There is an entire test at the discount of R.Ls. Of intermediate stations.
3. There are 3 assessments for arithmetical accuracy.
The distinction among the sum of the returned points of interest and the sum of the fore points of interest need to be identical to that among the sum of the sum of rises and the sum of the falls in addition to that among the
Its. And the final it is typically used for earth paintings calculations and different unique levelling operations.
Booking the Staff Readings:
The following factors need to be stored in view even as coming into the group of workers readings in a degree eye-e book:
1. The readings need to be entered with inside the respective columns as quickly as they may be taken and with inside the order in their observation.
2. The first access on the extent eye-e book web page is continually a B.S and the final one a F.S.
3. The fore and returned points of interest of the extrude factors need to be written with inside the identical horizontal line.
4. The H.I need to be written with inside the identical horizontal line contrary the returned sight.
5. While sporting ahead the studying from one web page of the extent – eye-e book to the , if the final studying is an intermediate sight, it's far entered in each I.S and F. S. Column in this web page and I.S. And B.S. Columns as first access at the web page.
The entries with inside the ultimate columns towards it need to additionally be repeated at the web page.
6. Brief description with neat sketches in admire of bench marks, extrude factors and different vital factors need to receive with inside the statement column.
Classification of levelling:
Types of Leveling in Surveying
- Direct leveling
- Trigonometric leveling
- Barometric leveling
- Stadia leveling
Direct Leveling
It is the most normally used method of leveling. In this method, measurements are decided straight away from leveling device. Based on the statement elements and device positions direct leveling is break up into different types as follows:
- Simple leveling
- Differential leveling
- Fly leveling
- Profile leveling
- Precise leveling
- Reciprocal leveling
Simple Leveling
It is a smooth and essential form of leveling in which the leveling device is placed some of the elements which elevation is to be find out. Leveling rods are placed at that elements and sighted them through leveling device. It is finished best at the same time as the elements are toward each specific without any obstacles.
Differential Leveling
Differential leveling is finished at the same time as the space amongst elements is more. In this approach, variety of inter stations are located and device is shifted to each station and decided the elevation of inter station elements. Finally difference amongst proper elements is decided.
Fly Leveling
Fly leveling is completed at the same time as the benchmark will be very far from the art work station. In such case, a short bench mark is located at the art work station this is located based totally definitely on the proper benchmark. Even it isn't pretty specific it's far used for identifying approximate diploma.
Profile Leveling
Profile leveling is typically accompanied to find out elevation of things along a line which encompass for road, rails or rivers etc. In this situation, readings of intermediate stations are taken and reduced diploma of each station is found. From this circulate segment of the alignment is drawn.
Precise Leveling
Precise leveling is much like differential leveling but in this situation higher specific is wanted. To reap immoderate specific, excessive statement method is finished. The accuracy of 1 mm in line with 1 km is finished.
Reciprocal Leveling
When it isn't feasible to find out the leveling device in some of the inter visible elements, reciprocal leveling is finished. This case appears in case of ponds or rivers etc. in case of reciprocal leveling, device is set toward 1st station and sighted with inside the route of 2d station.
Trigonometric Leveling
The approach of leveling in which the elevation of aspect or the difference amongst elements is measured from the decided horizontal distances and vertical angles with inside the location is called trigonometric leveling.
Trigonometric Leveling
In this method, trigonometric own circle of relatives contributors are used to find out the elevation of an aspect from mindset and horizontal distance so, it's far called as trigonometric leveling.
Barometric Leveling
Barometer is a device used to diploma surroundings at any altitude. So, in this method of leveling, atmospheric pressure at precise elements is decided, based totally mostly on which the vertical difference amongst elements is decided. It is a difficult estimation and used
Stadia Leveling
It is a modified form of trigonometric leveling in which Tachometer principle is used to determine the elevation of aspect. In this situation the street of sight is inclined from the horizontal. It is more accurate and suitable for surveying in hilly terrains.
Profile Leveling:
Profile leveling is one of the maximum not unusual place packages of going for walks stages and vertical distance dimension for the surveyor.
The outcomes are plotted with inside the shape of a profile, that's a drawing that suggests a vertical go segment.
Profiles are required for the layout and production of roads, curbs, sidewalks, pipelines, etc. In quick, profile leveling refers back to the procedure of figuring out the elevation of factors at the floor at usually uniform intervals alongside a non-stop line.
Equipment used for profile leveling Dumpy level Leveling staff Tripod Staff bubble Chain or Tape Procedure for profile levelling
1. Longitudinal levelling
Profile leveling is basically similar to benchmark leveling, with one fundamental distinction.
At every tool position, in which an HI is decided through a again sight rod studying on a benchmark or turning point, numerous extra foresight readings can be taken on as many factors as desired.
These extra readings are known as rod photographs, and the elevation of all the ones factors is decided through subtracting the rod shot from the HI at that tool location. (See determine 1) Plotting the Profile The profile drawing is largely a graph of elevations, plotted at the vertical axis, as a characteristic of stations, plotted on horizontal axis.
A gridded sheet known as profile paper is used to devise the profile information from the sector book. All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
The elevation or elevation scale is usually exaggerated; that is, it is ‘stretched’ in contrast to the horizontal scale.
For instance the vertical scale is probably 10 instances larger. The horizontal line at the lowest of the profile does now no longer vital ought to begin at 0 elevation
2. Cross sectioning levelling
Cross sectioning levelling is every other technique in profile levelling. The time period go-segment normally refers to an enormously quick profile view of the floor, that's drawn perpendicular to the path centerline of a motorway or different styles of linear projects.
Cross-sectional drawings are mainly vital for estimating the earthwork volumes had to assemble a roadway; they display the prevailing floor elevations, the proposed reduce or fill facet slopes, and the grade elevation for the street base.
There is truly no distinction in manner among profile and go-segment leveling besides for the shape of the sector notes.
Cross-segment rod photographs are generally taken all through the path profile survey from the equal tool positions used to take rod photographs alongside the centerline.
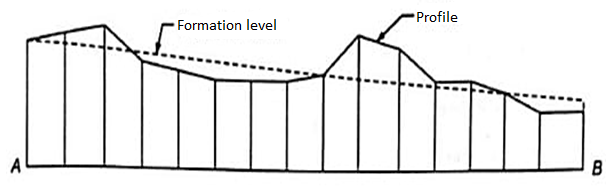
Fig: Profile levelling
Key Takeaways:
- If the telescope is now directed to personnel saved on factors of unknown elevation, the personnel readings may be read.
- In this levelling, the tool needs to be setup at numerous positions and at every installation the precept of easy levelling is used.
- The entries with inside the ultimate columns towards it need to additionally be repeated at the web page.
Longitudinal and Cross section:
Longitudinal Section
A Long Section is a profile view of a floor alongside a selected course, which plots elevation towards the gap alongside the course e.g. Floor profile alongside the middle line of a road, railway or river. In a protracted phase, elevations are decided alongside a set course.
At every tool position, in which an HI is decided through a again sight rod studying on a benchmark or turning point, numerous extra foresight readings can be taken on as many factors as desired.
These extra readings are known as rod photographs, and the elevation of all the ones factors is decided through subtracting the rod shot from the HI at that tool location. (See determine 1) Plotting the Profile The profile drawing is largely a graph of elevations, plotted at the vertical axis, as a characteristic of stations, plotted on horizontal axis.
A gridded sheet known as profile paper is used to devise the profile information from the sector book. All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
Cross Section:
A pass phase is a profile view of a floor at proper angles to a selected course. E.g. At proper angles to a road, river of railway. It plots elevation towards the gap alongside the pass phase line. Cross phase measurements are typically taken at an everyday durations alongside the course.
Cross sectioning levelling is every other technique in profile levelling. The time period go-segment normally refers to an enormously quick profile view of the floor, that's drawn perpendicular to the path centerline of a motorway or different styles of linear projects.
Cross-sectional drawings are mainly vital for estimating the earthwork volumes had to assemble a roadway; they display the prevailing floor elevations, the proposed reduce or fill facet slopes, and the grade elevation for the street base.
There is truly no distinction in manner among profile and go-segment leveling besides for the shape of the sector notes.
Reciprocal Levelling:
Reciprocal leveling is a surveying method wherein readings are taken from each instructions among factors to be able to lessen errors. In surveying, to degree is to discover the relative elevation of various factors with inside the land.
Reciprocal leveling is beneficial while you are leveling among factors which might be very some distance from every other.
At some distance distances, the earth’s curvature and atmospheric refraction can motive sizable leveling calculation errors, extra than at brief distances. For example, you've got factor an on one aspect of a canyon and factor B on the opposite aspect. You role your surveying tool near factor
A and degree its distance from the ground. From the identical role, you degree factor B’s distance from the ground. Next, you're taking your device throughout the canyon near factor B.
Now, you're taking the identical measurements you probably did earlier than however from the alternative direction.
By calculating the distinction among those pairs of measurements, you could decide what the leveling mistakes is to reach at what a definitely degree line might be.
Finding Difference in Levels
Let us say A and B are two points.
- The instrument is set up near A and readings on the staff are noted (x1 and y1)
- The instrument is shifted near B and readings on staff are again noted (x2 and y2)
Assuming the curvature and refraction error combined bee.
The error occurred when the instrument is close to 'A' is considered equal to the error occurred when the instrument is close to 'B' because the instrument is shifted quickly and there is not much change in refraction error.
The difference in levels, h = (y1 - x1) = (y2 - x2)
Considering a combined errors e,
The difference in level h = ((y1 - e) - x1)
It can also be written as, h = (y2 - (x2 - e))
On adding these two equations, 2h = (y1 - x1) + (y2 - x2)
So, h = 0.5((y1 - x1) + (y2 - x2))
Corrections for curvature and refraction:
Curvature correction (Cc)
- When levelling is done in a large area, the curvature of Earth is considered.
- The horizontal line is not a level line, because of which the staff reading is more than expected, this is called curvature correction.
- The effect of curvature is to increase the staff reading that is the error is positive and so the correction is negative.
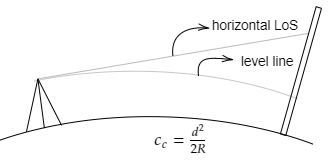
Fig: Curvature Correction
The curvature correction (Cc) is mathematically expressed as,
Cc = d^2/2R
Where, d: the length of the sight or the distance from the instruments to the staff station in kilometers
R= the radius of the earth = 6371 kilometres
So, Cc = 0.0785d^2
True staff reading = observed staff reading - 0.0785d^2
Refraction correction (Cr)
- The rays of light passing through the atmosphere of different density bend down. It results in this type of correction.
- The effect of refraction is 1/7th time the curvature correction but is of opposite nature. Hence the correction for refraction is additive to the staff reading.
Cr = 1/7 x Cc
So, Cr = 1/7 x 0.0785d^2 = 0.0112 x d^2
True staff reading = observed staff reading + 0.0112 x d^2
Combined correction(C)
The effect of curvature is to increase the staff reading and the effect of refraction is to decrease the staff reading. One more thing is the curvature error is more than the refraction error. So the combined effect is to increase staff reading. Hence, the combined correction is subtractive in nature.
C = 0.0785d^2 - 0.0112 x d^2 = 0.0673 x d^2
Therefore the true staff reading after both the corrections,
True staff reading = observed staff reading - 0.0673 x d^2
Distance to the visible horizon:
The horizon is the obvious line that separates the floor of a celestial frame from its sky while regarded from the attitude of an observer on or close to the floor of the applicable frame.
This line divides all viewing instructions primarily based totally on whether or not it intersects the applicable frame's floor or now no longer.
The proper horizon is sincerely a theoretical line, that may simplest be located to any diploma of accuracy while it lies alongside a distinctly clean floor together with that of Earth's oceans.
At many locations, this line is obscured via way of means of terrain, and on Earth it could additionally be obscured via way of means of lifestyles paperwork together with timber and/or human constructs together with buildings.
The ensuing intersection of such obstructions with the sky is referred to as the seen horizon. On Earth, while searching at a sea from a shore, the part of the ocean closest to the horizon is referred to as the offing.
The proper horizon surrounds the observer and it's far commonly assumed to be a circle, drawn at the floor of a superbly round version of the Earth. Its middle is beneath the observer and beneath sea stage.
Its distance from the observer varies from each day because of atmospheric refraction that is significantly laid low with climate conditions.
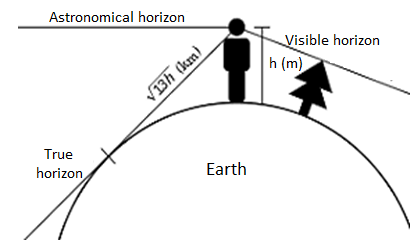
Fig: Visible horizon
Also, the better the observer's eyes are from sea stage, the farther away the horizon is from the observer.
For instance, in preferred atmospheric conditions, for an observer with eye stage above sea stage via way of means of 1.70 meters (five toes 7 in), the horizon is at a distance of approximately five kilometers (3.1 mi). When located from very excessive standpoints, together with an area station, the horizon is a great deal farther away and it encompasses a miles large place of Earth's floor.
In this case, the horizon might now no longer be an excellent circle, now no longer even an aircraft curve together with an ellipse, in particular while the observer is above the equator, because the Earth's floor may be higher modeled as an ellipsoid than as a sphere.
Anyway, I digress. If you're at the tuna tower of a game fishing boat you will be 15, 20, 25 toes above the floor of the water.
Once you understand your top of eye you truly plug that into the subsequent formulation:
1.17 instances the rectangular root of your top of eye = Distance to the horizon in nautical miles
For example, in case your top of eye is nine toes above the floor of the water, the formulation could be:
1.17 instances the rectangular root of nine = Distance to the horizon in nautical miles. 1.17 * 3 = 3.fifty one nautical miles
Key Takeaways:
- All profile drawings should have a right name block, and each axes should be absolutely categorized with stations and elevations.
- Now, you're taking the identical measurements you probably did earlier than however from the alternative direction.
- Its distance from the observer varies from each day because of atmospheric refraction that is significantly laid low with climate conditions.
References:
1. Surveying and Levelling by Kanetkar and Kulkarni (Vol. I) Pune Vidhatigrihan Prakashan
2. Surveying and Levelling by Dr. B.C. Punmia (Vol. I & II) Laxmi Pub.
3. Advance Surveying - Total Station, GIS and Remote Sensing by Pearson Education Satheesh Gopi & R. Sathikumar & N. Madhu