Unit - 3
Adjustment of Dumpy Level & Trignometrical Levelling
Adjustment of auto level:
At every installation of a stage tool, transient adjustment is needed to be done previous to any workforce observation.
It entails a few nicely described operations which can be required to be done in right sequence. The transient adjustment of a dumpy stage is composed of
(1) Setting, (2) Leveling and (3) Focusing.
During Setting, the tripod stand is installation at a handy peak having its head horizontal (via eye estimation).
The tool is then constant on the pinnacle with the aid of using rotating the decrease a part of the tool with proper hand and retaining firmly the top component with left hand.
Before fixing, the leveling screws are required to be delivered in among the tribes and trivet. The bull's eye bubble (round bubble), if present, is then delivered to the center with the aid of using adjusting the tripod legs.
Next, Leveling of the tool is carried out to make the vertical axis of the tool surely vertical. It is finished with the aid of using sporting out the subsequent steps:
Step 1: The stage tube is delivered parallel to any of the foot screws, with the aid of using rotating the top a part of the tool.
Step 2: The bubble is delivered to the center of the extent tube with the aid of using rotating each the foot screws both inward and outward.
Step 3: The stage tube is then delivered over the 0.33 foot screw once more with the aid of using rotating the top a part of the tool.
Step 4: The bubble is alternatively delivered to the center of the extent tube with the aid of using rotating the 0.33 foot screw both inward and outward.
Step 5: Repeat Step 1 with the aid of using rotating the top a part of the tool with inside the identical quadrant of the circle after which Step 2.
Step 6: Repeat Step three with the aid of using rotating the top a part of the tool with inside the identical quadrant of the circle after which Step 4.
Step 7: Repeat Steps five and 6, until the bubble stays relevant in each the positions.
Step 8: By rotating the top a part of the tool via one hundred eighty o, the extent tube is delivered parallel to first foot screws in opposite order.
The bubble will stay with inside the center if the tool is in everlasting adjustment.
Auto Level Setup
1. Setup your tripod as stage as viable, step on tripod legs to power into the floor.
2. Attach car stage to the tripod.
3. Adjust stage so bubble is focused in vial.
4. Adjust recital till crosshairs are clear.
5. Adjust the goal lens till item you're sighting on is clear.
Care of Auto Levels If the tool turns into moist go away it unpacked. Wipe down tool, easy and dry delivery case.
Pack up tool best whilst it's far flawlessly dry. Never contact the glass with fingers, use tender easy lint-unfastened material to easy lens.
Checking Auto Level Accuracy
1. Set up tool in a place this is as stage as viable and which is set 220 ft. Long. Place matching stage rods or portions of strapping with inside the floor approximately two hundred ft. Aside with the faces towards every other. Position and stage the tool in order that the gap from the tool to every rod is the identical measure.
2. Take a studying on every rod with the tool (or mark every piece of strapping wherein the crosshair is sighted).
3. Move transit to every other spot on the road and take readings and mark each rods once more.
4. The distinction among the marks at the rod might be the mistake of the tool. The blunders desires to be corrected with the aid of using a able restore technician.
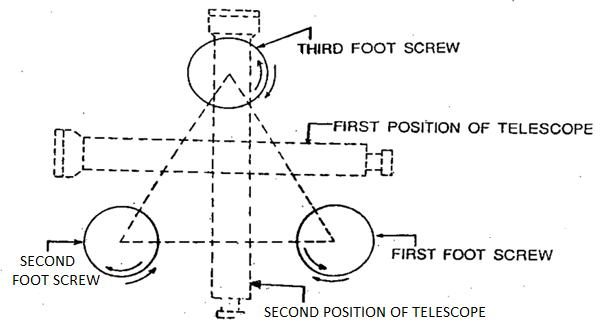
Fig: Temporary adjustment of dumpy level
Principle axes of dumpy level:
In a nicely adjusted dumpy level, favored members of the family amongst essential traces are
1. Axis of the extent tube is perpendicular to the Vertical axis
2. Horizontal pass hair have to lie in an aircraft perpendicular to the Vertical axis, in order that it will lie in a Horizontal aircraft while the tool is nicely leveled.
3. The Line of sight is parallel to the axis of the extent tube.
4. The optical axis, the axis of the goal lens and the road of sight have to coincide
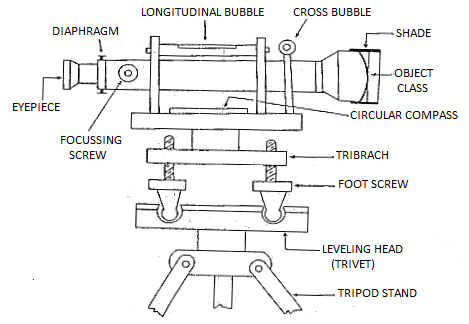
Fig: Dumpy level axes
Relationship:
Also, an assistant could be required for a dumpy degree survey. Once the whole lot is ready, the subsequent steps have to be accompanied for a success dumpy degree survey.
At first, the tripod is configured nicely to maintain the dumpy degree. The tripod top have to be adjusted till its miles on the attention degree.
Then, legs of the tripod have to be moved to a balanced role to maintain the tool nicely. Finally, tripod legs have to be constant through urgent them to the ground.
The dumpy degree tool is installation at the pinnacle of the tripod. Foot screw is used to screw the tool tightly at the tripod.
As the extent head may be very sensitive, unique care is needed on this step.
To paintings nicely, it's miles very critical to make the dumpy degree absolutely horizontal.
Using foot-screws (leveling screws) the dumpy degree is ready to a leveled condition.
Leveling screws have to be adjusted till the alignment bubble is with inside the middle of the marker.
The operator appears via the eyepiece of the telescope.
An assistant holds an E meter or team of workers vertical on the factor below measurement.
Usually, this team of workers has each imperial and metric measurements.
The 'E' at the team of workers is equal to 5 centimeters.
The elevations (levels) of various factors is collected with the assist of the tool and team of workers.
Measurement normally begins off evolved from a benchmark with the recognized top decided through a preceding survey, or an arbitrary factor with an assumed top.
Fundamental axes of dumpy degree:
i) The vertical axis
Ii) The axis of bubble tube
Iii) The line of collimation
Iv) The axis of the telescope
Relations of Fundamental axes:
i) The axis of the extent tube have to be perpendicular to the vertical axis.
Ii) The line of collimation have to be parallel to the axis of the bubble tube.
Iii) Axis of telescope and line of collimation have to coincide.
Testing and adjustment of bubble axis and line of collimation:
The everlasting changes of various degree are made to set up the constant relationships among its essential lines:
1. Permanent Adjustments of a Dumpy Level
2. Permanent Adjustments of a Cooke’s Reversible Level
3. Permanent Adjustments of a Cushing’s Level
4. Permanent Adjustments of the Y-Level
5. Permanent Adjustments of a Tilting Level.
1. Permanent Adjustments of a Dumpy Level:
In a duress degree, there are handiest changes as he telescope is rigidly constant to the spindle.
1. The axis of the bubble tube ought to be perpendicular to the vertical axis.
2. The line of collimation ought to be parallel to the axis of the bubble tube.
First Adjustment: To make the axis of the bubble tube perpendicular to the vertical axis.
Object:
The item of this adjustment is to make sure that if the tool is as soon as levelled up, the bubble stays with inside the center of its run for all positions of the telescope.
Necessity:
The adjustment is made handiest for the ease of taking readings quickly. Since its miles essential that the bubble ought to be critical whilst taking any studying, a whole lot time is wasted if this adjustment isn't always made as if so the bubble must be added in center each time for every pointing of the telescope.
Test:
(i) Set-up the extent on corporation floor and degree it cautiously via way of tripod-legs and foot-screws. The bubble will now be critical in positions at proper angles to every other, one being parallel to a couple of foot-screw and the alternative over the 1/3 foot-screw.
(ii) Bring the telescope over a couple of foot-screws or over the 1/3 foot-screw and flip it via a hundred and eighty with inside the horizontal plane. If the bubble nevertheless stays critical, the adjustment is correct.
Adjustment:
(i) If the bubble does now no longer stay with inside the center, be aware down the deviations of the bubble from the center, say it's miles ‘2n’ department over the bubble 1/2 of manner returned i.e., ‘n’ divisions via way of elevating or decreasing cease of the bubble tube by capstan headed should and the ultimate 1/2 of with the pair of foot-screws below the telescope at its gift position.
(ii) Turn the telescope via 90° in order that it lies over the unmarried foot- screw under the telescope or parallel to a couple of this screw or pair of foot -screws and produce the bubble with inside the center of its run by this screw pair of foot-screws.
(iii) Rotate the telescope and notice if the bubble stays critical for all positions of the telescope. If now no longer repeat the entire procedure till the adjustment is correct.
Second Adjustment:
To make the Line of collimation parallel to the axis of the bubble tube. Object: The item of this adjustment is to set the road of collimation parallel to the bubble axis so that after the bubble is centered, the road of collimation ought to turn out to be precisely horizontal and now no longer stay willing as in any other case it'd be.
Necessity:
The entire feature of a degree is to supply a horizontal line of collimation, that is feasible handiest if the above situation is satisfied. Test and Adjustments: The collimation blunders can be examined via way of any of the subsequent 3 strategies after which the essential changes are made: First Method (Two-Peg Method.):
Test:
(i) Drive pegs A and B at a distance of (D) meters say 60 to a hundred meters on a reasonably degree floor.
Drive some other peg at O precisely halfway among A and B (Fig. 7.36) Incorrect and Correct Line of Collimation
(ii) Set up and degree the tool at O and take the body of workers readings on A and B. The bubble should be with inside the center whilst the readings are being taken. Let the body of workers readings on A and B, be a and b respectively.
(Iii) Shift the extent and set it up a factor O1, d metersfar from A (or B) and alongside the equal line BA (Fig. 7.37).
Stages the tool appropriately and take body of workers readings on A and B with the bubble critical. Let the readings be a1 and b1 respectively. (The degree can also be installation at a factor among A and B, d meters far from A or B.
Incorrect and Correct Line of Collimation
(iv) Find the distinction among the body of workers readings a and b, and that among the body of workers readings a1 and b1.
The distinction of body of workers readings a and b offers the genuine distinction in elevation among A and B because the tool become installation precisely halfway among A and B and that the returned and for sight distances had been precisely distinction, while the distinction among a1 and b1 offers the plain If the 2 variations are equal, the road of collimation is in adjustment, in any other case it's miles willing and wishes adjustment.
Adjustment:
(i) Find out whether or not the distinction is an upward thrust or a fall from the peg A to B. If a is extra than b, the peg A is decrease than peg B and the floor is growing from A to B. If b is extra than a, the floor is falling from A to B.
(ii) Find out the studying at the some distance peg B on the equal degree are of a1 via way of including the genuine distinction to a1 if it's miles a fall, or via way of subtracting the genuine distinction from a1 if it's miles a upward thrust. Let the studying be b2.
(iii) If b1 is extra than b2, the road of collimation is Inclined upwards and if b1 is smaller than b2, the road of collimation is willing downwards. b1 – b2 (distinction of b1 and b2) is the collimation blunders with inside the distance “D”.
Key Takeaways:
- Care of Auto Levels If the tool turns into moist go away it unpacked. Wipe down tool, easy and dry delivery case.
- Leveling screws have to be adjusted till the alignment bubble is with inside the middle of the marker.
- The item of this adjustment is to make sure that if the tool is as soon as levelled up, the bubble stays with inside the center of its run for all positions of the telescope.
Trignometrical Leveling:
Trigonometric leveling is the system of figuring out the unique elevation of station from located vertical attitude and recognized distance.
• The vertical attitude are measured via way of means of manner of theodolite.
• The horizontal distance might also additionally both measured or computed.
• Relative heights are calculated using trigonometric formula. If the space among the device station and item is small, correction of earth curvature and mirrored image isn't required.
• If the space among the device station and item is massive the mixed correction = 0.0673 D2, for earth’s curvature and mirrored image is required, had been D = distance in Km.
• If the vertical attitude is +ve, the correction is taken as +ve.
• If the vertical attitude is –ve, the correction is taken as –ve.
Trigonometric Leveling is the department of Surveying wherein we discover the vertical distance among factors with the assist of a few measurements of the vertical angles and the recognized distances.
The recognized distances are both assumed to be horizontal or the geodetic lengths on the imply sea level (MSL).
The distances are measured immediately (as with inside the aircraft surveying) or they may be computed as with inside the geodetic surveying. Trigonometric Leveling may be completed in following ways.
Observations taken for the peak and distances Geodetic Observations. In the 1st, we will degree the horizontal distance among the given factors, if accessible. We take the commentary of the vertical angles after which compute the distances the use of them.
If the distances are massive sufficient then we must offer the correction for the curvature and refraction and that we offer to the linearly to the distances that we've computed. In the 2nd, i. e geodetic observations, the distances among the 2 factors are geodetic distances and the ideas of the aircraft surveying aren't relevant here.
- The corrections for the curvature and refraction are implemented immediately to the angles. Now let’s speak diverse instances to discover the distinction in elevation among the 2 factors.
- It is an oblique approach of levelling wherein the relative elevation of diverse factors are decided from vertical attitude and horizontal distance measured with a theodolite and tape / chain / Tachometer respectively.
- It isn't always as correct as direct leveling however may be used for topographic paintings or wherein direct levelling isn't always possible.
- This method if levelling paintings is typical to discover a RL of any factor which has elevation could be very high / low.
- In those strategies after putting the device at any area first again sight analyzing is taken then attitude of elevation is measured to the target.
Indirect Leveling:
- When there isn't always a smooth direct approach of measuring a liquid, fuel line or stable inside the gadget operators ought to use an oblique approach.
- The oblique approach of stage dimension includes changing readouts and facts of an acknowledged quantity, together with stress ratio to the volume.
- Because all acknowledged materials have a few weight and consequently exert a measurable pressure over a particular place inside the gadget, this pressure may be measured in kilos in line with rectangular inch.
- When technicians have decided how an awful lot stress is exerted at a particular place in line with rectangular inch, the peak of the substance on the subject of that measuring factor can then additionally be decided.
- However, it’s critical for operators to be aware that oblique stage dimension is touchy to the precise gravity of the substance, in addition to the substance’s temperature.
- It is important to don't forget those elements at some stage in all oblique stage dimension paintings due to the fact they are able to have an effect on the accuracy of the calculations and measurements.
- For example, kerosene has an extraordinary precise gravity from water.
- Therefore any oblique dimension of the extent of kerosene inside a software ought to component in kerosene’s precise gravity of 0.82.
- Both direct and oblique strategies of stage dimension are relevant to a number of business stage evaluation applications.
- By making use of an isolation valve in every of those strategies, corporations can offer ease of subject calibration, enhance protection conditions, and reap greater correct measurements in their inventory.
This is an oblique approach of leveling wherein the distinction in elevation of the factors is decided from the found distances measured and vertical angles.
The vertical angles are measured with transit, and the distances are measured at once or computed trigonometrically.
Trigonometrically leveling is generally applied in topographical paintings to discover the elevation of the pinnacle of buildings, chimneys, church spires, etc. Also, it can be used to its benefit in hard terrains like mountainous areas.
Depending on the sector situations and the measurements which can be made with the devices available, there can be innumerable cases.
A try has been made to remedy some cases, and plenty of extra may be solved via way of means of the reader himself.
Elevation of point with base of an object accessible inaccessible in the same vertical plane:
When the bottom of the item is inaccessible we use an oblique approach of surveying.
A tachometer is used to degree the gap among the 2 factors with the usage of an analytical lens.
There are methods Stadia approach: In this approach diaphragm of the tachometer are supplied with stadia hair the distinction among group of workers intercept offers stadia analyzing.
Tangential Method: on this approach, the tachometer isn't always supplied with stadia hairs, the analyzing is taken via way of means of unmarried horizontal hair.
D=(f/L)S + (f + d)
D=horizontal distance between tachometer and stadia rod.
f/L = multiplying constant
S= Staff Intercept
Elevation formula:
v = KS sin (2)/2 + cos(2)
= Theta= Angle of elevation or depression.
K & C = Tachometric Constant
Substance method and tangential method is also used to find the elevation between two points.
There may be two cases to find height of an object using a theodolite:
1. When the base of the object is accessible.
2. When the base of the object is inaccessible.
1. Base of the Object being Accessible
To find the height of the object above a Bench Mark (or above the instrument-station):
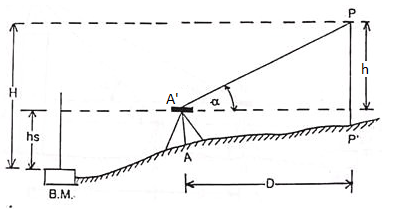
Let H = the height of the object above the B.M.
h = the height of the object above the instrument axis.
hs = height of the instrument axis above the B.M.
α = the vertical angle observed at the instrument-station.
D = the horizontal distance in meters measured from the instrument-station to the base of the object.
Then, h = D tan α
H = h + hs = D tan α + hs
When the distance D is large, the correction for curvature and refraction, viz. { 0.0673 (D/1000)2} Shall have to be applied.
If the height of the object above the instrument-station is to be found out, then add the height of the instrument axis to the height of the object above the instrument axis. The height of the instrument axis may be obtained in two ways.
(i) By measuring the height of centre of the eye-piece above the station point by a steel tape.
(ii) By readings the staff through the object-glass when held just near the eye-piece end.
2. Base of the Object being Inaccessible [Fig. (a & b)]:
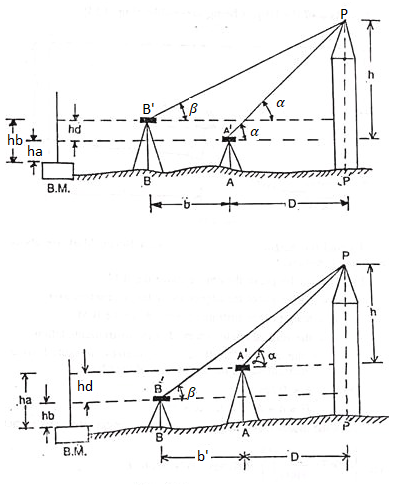
To find the height of the object above a bench mark (B.M.):
(i) Choose two stations A and B suitable on a fairly level ground so that they lie in a vertical plane passing through the object in line with the object, and measure the distance between them accurately.
(ii) Set up the instrument over the station. A and level it accurately.
(iii) With the altitude bubble central and with the vertical vernier reading zero, take a reading on the staff held on the B.M. Or reference point.
(iv) Bisect the object P and read both veneers. Change the face, again sight P and read both veneers, Take mean of the four readings, which is the correct value of the vertical angle.
(v) Shift the instrument to B and take similar observations as at A.
Let α = the angle of elevation observed at A.
β = the angle of elevation observed at B.
b = the horizontal distance between the instrument-stations A and B.
D = the distance of the object from the near station.
h = height of the object P above instrument axis at A’.
Ha =the staff reading at the B.M. When the instrument is at A.
hb = the staff reading at the B.M. When the instrument is at B.
hd = the level difference between the two positions of the instrument axis.
= ha – hb
(a) When the Instrument at farther station B is higher than that the near station A (Fig. a):
h = D ……………………(i)
h – hd = (D + b) tanβ ……………………(ii)
Putting the value of h from (i) in (ii),
D tan α – hd = (D+b) tan β = D tan β + b tan β.
Or D tan α – D tan β = b tan β + hd
Or D = b tan β hd/ tan α – tan β
Put this value of D in (i), then
h = b tan β + hd/ tan α – tan β tan α …………………….(Eqn.9.1.)
Height of the object above the BM,
H = h + ha ……………………………(Eqn. 9.2)
(b) When the instrument at father station B is lower than that at the near station A (Fig b):
Here, h = D tan α ……………………(i)
h + hd = (D + b) tan β ………………..(ii)
Then working as above,
h = b tan β + hd/ tan α – tan β . Tan α ……………….(Eqn. 9.3)
And H = h + hd ……………………(Eqn. 9.4)
Key Takeaways:
- When the bottom of the item is inaccessible we use an oblique approach of surveying.
- There are methods Stadia approach: In this approach diaphragm of the tachometer are supplied with stadia hair .the distinction among group of workers intercept offers stadia analyzing.
Contours:
A contour map is a map illustrated with contour strains, as an example a topographic map, which therefore indicates valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes.
The contour c programming language of a contour map is the distinction in elevation among successive contour strains.
The gradient of the feature is constantly perpendicular to the contour strains. When the strains are near collectively the significance of the gradient is large: the variant is steep.
A stage set is a generalization of a contour line for features of any range of variables.
Contour strains are curved, immediately or a combination of each strains on a map describing the intersection of an actual or hypothetical floor with one or greater horizontal planes.
The configuration of those contours lets in map readers to deduce the relative gradient of a parameter and estimate that parameter at particular places.
Contour strains can be both traced on a seen 3-dimensional version of the floor, as whilst a photogrammetric viewing a stereo-version plots elevation contours, or interpolated from the predicted floor elevations, as whilst a pc software threads contours through a community of commentary factors of location centroids.
In the latter case, the approach of interpolation impacts the reliability of man or woman isoclines and their portrayal of slope, pits and peaks.
Characteristics and uses:
Contouring in surveying is the dedication of elevation of diverse factors at the floor and solving those factors of equal horizontal positions with inside the contour map.
To exercising vertical manage leveling paintings is executed and concurrently to exercising horizontal manage chain survey or compass survey or aircraft desk survey is to be executed.
If the theodolite is used, each horizontal and vertical controls may be executed from the equal instrument. Based at the units used you'll classify the contouring in exceptional groups.
Contour Maps and Its Uses A contour maps includes contour traces which might be imaginary traces connecting factors of same elevation. Such traces are drawn at the plan of a place after setting up decreased tiers of numerous factors with inside the vicinity. The contour traces in a place are drawn retaining distinction in elevation of among consecutive traces constant. For example, the contour map in suggests contours in a place with contour c language of one m. On contour traces the extent of traces is likewise written.
Characteristics of Contour Maps
The contours maps have the subsequent characteristics:
Contour traces need to close, now no longer always with inside the limits of the plan.
Widely spaced contour suggests flat surface.
Closely spaced contour suggests steep floor.
Equally spaced contour suggests uniform slope. Irregular contours imply choppy surface.
Approximately concentric closed contours with reducing values in the direction of center simply a pond.
Approximately concentric closed contours with growing values in the direction of center imply hills.
Contour traces with U-form with convexity in the direction of decrease floor imply ridge 9. Contour traces with V-formed with convexity in the direction of better floor imply valley.
Contour traces usually do now no longer meet or intersect every other.
If contour traces are assembly in a few portion, it suggests lifestyles of a vertical cliff
Uses of Contour Maps
- Contour maps are extraordinarily beneficial for diverse engineering works:
- A civil engineer research the contours and reveals out the character of the floor to identify.
- Suitable web website online for the venture works to be taken up.
- By drawing the segment with inside the plan, it's miles viable to discover profile of the floor alongside that line.
- It allows in locating out intensity of reducing and filling, if formation degree of road/railway is determined.
- Indivisibility of any factors may be located with the aid of using drawing profile of the floor alongside that line.
- The routes of the railway, road, canal or sewer traces may be determined so that you can decrease and stability earthworks.
- Catchment vicinity and subsequently amount of water glide at any factor of calla or river may be located.
- This look at could be very essential in finding bunds, dams and additionally to discover flood tiers.
- From the contours, it's miles viable to decide the capability of a reservoir.
Method of locating contouring:
Contours may be drawn, if the horizontal or vertical measurements of the well decided on factors are known. There are essentially 2 techniques of contouring – Direct Method and Indirect Method.
1. Direct Method of Contouring:
High diploma of precision is needed for large-scale maps with small contour interval. In the Direct Method of contouring, the decreased stage of diverse decided on factors on a contour line are acquired and their positions are placed.
The contours are then drawn with the aid of using becoming a member of those factors. It may be very correct approach however may be very tedious and time consuming.
By stage and Staff : In this a sequence of factors having the equal team of workers readings and therefore the equal elevations are plotted and joined with the aid of using a clean curve.
By hand stage/Abney stage : In this approach the tool may also stands over the bench mark and the team of workers guy is moved to a degree at the contour which needs to be plotted.
As quickly because the tool may also observes the specified team of workers studying for a selected contour, he instructs the team of workers guy to forestall and locates the placement of the factor.
2. Indirect Method of Contouring:
It is appropriate for undulated floor and hilly regions. In this the factors are decided on at random. The positions and elevations of which aren't always placed on a contour line.
Tracing contour is the technique wherein the placement and decreased stage of all such factors is then decided. The contours are then drawn with the aid of using interpolation approach.
A. Method of Squares:
This is likewise referred to as co-ordinate approach of finding contours. The complete vicinity is split into squares or rectangles forming a grid. The elevations of corners are decided and the specified contours are interpolated.
This approach may be very appropriate for a small open vicinity wherein contours are required at a loss vertical interval.
This is likewise appropriate for large-scale mapping.
B. Method of Cross-Sections:
In this approach a transit traverse is run. This approach is appropriate for road, railway and canal survey i.e. for direction surveys.
C. Tachometric Method:
This is almost appropriate for hilly regions and all locations wherein aircraft desk surveying is impractical. The elevations and distances are calculated from the discovered information and lines are interpolated.
D. Plane Table Method:
In this, the gap and elevation of the team of workers factor is decreased with the aid of using trigonometric relations.
The observer scales the computed distance alongside the plotted line to find the factor and writes the computed elevation in one of these manner that the plotted function of the factor coincides with the decimal factor of the elevation value.
Key Takeaways:
- The contour c programming language of a contour map is the distinction in elevation among successive contour strains.
- The configuration of those contours lets in map readers to deduce the relative gradient of a parameter and estimate that parameter at particular places.
- If the theodolite is used, each horizontal and vertical controls may be executed from the equal instrument. Based at the units used you'll classify the contouring in exceptional groups.
References:
1. Surveying and Levelling by Kanetkar and Kulkarni (Vol. I) Pune Vidhatigrihan Prakashan
2. Surveying and Levelling by Dr. B.C. Punmia (Vol. I & II) Laxmi Pub.
3. Advance Surveying - Total Station, GIS and Remote Sensing by Pearson Education Satheesh Gopi & R. Sathikumar & N. Madhu