Unit - 1
Introduction
In today's world, technology is growing very fast, and we are getting in touch with different new technologies day by day.
Here, one of the booming technologies of computer science is Artificial Intelligence which is ready to create a new revolution in the world by making intelligent machines. The Artificial Intelligence is now all around us. It is currently working with a variety of subfields, ranging from general to specific, such as self-driving cars, playing chess, proving theorems, playing music, Painting, etc.
AI is one of the fascinating and universal fields of Computer science which has a great scope in future. AI holds a tendency to cause a machine to work as a human.

Fig 1: Example
Artificial Intelligence is composed of two words Artificial and Intelligence, where Artificial defines "man-made," and intelligence defines "thinking power", hence AI means "a man-made thinking power."
So, we can define AI as:
"It is a branch of computer science by which we can create intelligent machines which can behave like a human, think like humans, and able to make decisions."
Artificial Intelligence exists when a machine can have human based skills such as learning, reasoning, and solving problems With Artificial Intelligence you do not need to preprogram a machine to do some work, despite that you can create a machine with programmed algorithms which can work with own intelligence, and that is the awesomeness of AI.
It is believed that AI is not a new technology, and some people says that as per Greek myth, there were Mechanical men in early days which can work and behave like humans.
Why Artificial Intelligence?
Before Learning about Artificial Intelligence, we should know that what is the importance of AI and why should we learn it. Following are some main reasons to learn about AI:
● With the help of AI, you can create such software or devices which can solve real-world problems very easily and with accuracy such as health issues, marketing, traffic issues, etc.
● With the help of AI, you can create your personal virtual Assistant, such as Cortana, Google Assistant, Siri, etc.
● With the help of AI, you can build such Robots which can work in an environment where survival of humans can be at risk.
● AI opens a path for other new technologies, new devices, and new Opportunities.
Goals of Artificial Intelligence
Following are the main goals of Artificial Intelligence:
- Replicate human intelligence
- Solve Knowledge-intensive tasks
- An intelligent connection of perception and action
- Building a machine which can perform tasks that requires human intelligence such as:
● Proving a theorem
● Playing chess
● Plan some surgical operation
● Driving a car in traffic
- Creating some system which can exhibit intelligent behavior, learn new things by itself, demonstrate, explain, and can advise to its user.
What Comprises Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence is not just a part of computer science even it's so vast and requires lots of other factors which can contribute to it. To create the AI first we should know that how intelligence is composed, so the Intelligence is an intangible part of our brain which is a combination of Reasoning, learning, problem-solving perception, language understanding, etc.
To achieve the above factors for a machine or software Artificial Intelligence requires the following discipline:
● Mathematics
● Biology
● Psychology
● Sociology
● Computer Science
● Neurons Study
● Statistics
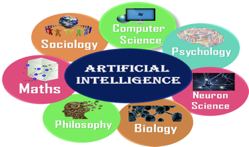
Fig 2: Factors of Artificial intelligence
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Following are some main advantages of Artificial Intelligence:
● High Accuracy with less errors: AI machines or systems are prone to less errors and high accuracy as it takes decisions as per pre-experience or information.
● High-Speed: AI systems can be of very high-speed and fast-decision making, because of that AI systems can beat a chess champion in the Chess game.
● High reliability: AI machines are highly reliable and can perform the same action multiple times with high accuracy.
● Useful for risky areas: AI machines can be helpful in situations such as defusing a bomb, exploring the ocean floor, where to employ a human can be risky.
● Digital Assistant: AI can be very useful to provide digital assistant to the users such as AI technology is currently used by various E-commerce websites to show the products as per customer requirement.
● Useful as a public utility: AI can be very useful for public utilities such as a self-driving car which can make our journey safer and hassle-free, facial recognition for security purpose, Natural language processing to communicate with the human in human-language, etc.
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Every technology has some disadvantages, and the same goes for Artificial intelligence. Being so advantageous technology still, it has some disadvantages which we need to keep in our mind while creating an AI system. Following are the disadvantages of AI:
● High Cost: The hardware and software requirement of AI is very costly as it requires lots of maintenance to meet current world requirements.
● Can't think out of the box: Even we are making smarter machines with AI, but still they cannot work out of the box, as the robot will only do that work for which they are trained, or programmed.
● No feelings and emotions: AI machines can be an outstanding performer, but still it does not have the feeling so it cannot make any kind of emotional attachment with human, and may sometime be harmful for users if the proper care is not taken.
● Increase dependency on machines: With the increment of technology, people are getting more dependent on devices and hence they are losing their mental capabilities.
● No Original Creativity: As humans are so creative and can imagine some new ideas but still AI machines cannot beat this power of human intelligence and cannot be creative and imaginative.
Key takeaway
AI is one of the fascinating and universal fields of Computer science which has a great scope in future.
AI holds a tendency to cause a machine to work as a human.
Artificial Intelligence is not a new word and not a new technology for researchers. This technology is much older than you would imagine. Even there are the myths of Mechanical men in Ancient Greek and Egyptian Myths. Following are some milestones in the history of AI which defines the journey from the AI generation to till date development.

Fig 3: Image of AI history
Maturation of Artificial Intelligence (1943-1952)
● Year 1943: The first work which is now recognized as AI was done by Warren McCulloch and Walter pits in 1943. They proposed a model of artificial neurons.
● Year 1949: Donald Hebb demonstrated an updating rule for modifying the connection strength between neurons. His rule is now called Hebbian learning.
● Year 1950: The Alan Turing who was an English mathematician and pioneered Machine learning in 1950. Alan Turing publishes "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" in which he proposed a test. The test can check the machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to human intelligence, called a Turing test.
The birth of Artificial Intelligence (1952-1956)
● Year 1955: An Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon created the "first artificial intelligence program "Which was named as "Logic Theorist". This program had proved 38 of 52 Mathematics theorems, and find new and more elegant proofs for some theorems.
● Year 1956: The word "Artificial Intelligence" first adopted by American Computer scientist John McCarthy at the Dartmouth Conference. For the first time, AI coined as an academic field.
At that time high-level computer languages such as FORTRAN, LISP, or COBOL were invented. And the enthusiasm for AI was very high at that time.
The golden years-Early enthusiasm (1956-1974)
● Year 1966: The researchers emphasized developing algorithms which can solve mathematical problems. Joseph Weizenbaum created the first chatbot in 1966, which was named as ELIZA.
● Year 1972: The first intelligent humanoid robot was built in Japan which was named as WABOT-1.
The first AI winter (1974-1980)
● The duration between years 1974 to 1980 was the first AI winter duration. AI winter refers to the time period where computer scientist dealt with a severe shortage of funding from government for AI researches.
● During AI winters, an interest of publicity on artificial intelligence was decreased.
A boom of AI (1980-1987)
● Year 1980: After AI winter duration, AI came back with "Expert System". Expert systems were programmed that emulate the decision-making ability of a human expert.
● In the Year 1980, the first national conference of the American Association of Artificial Intelligence was held at Stanford University.
The second AI winter (1987-1993)
● The duration between the years 1987 to 1993 was the second AI Winter duration.
● Again, Investors and government stopped in funding for AI research as due to high cost but not efficient result. The expert system such as XCON was very cost effective.
The emergence of intelligent agents (1993-2011)
● Year 1997: In the year 1997, IBM Deep Blue beats world chess champion, Gary Kasparov, and became the first computer to beat a world chess champion.
● Year 2002: for the first time, AI entered the home in the form of Roomba, a vacuum cleaner.
● Year 2006: AI came in the Business world till the year 2006. Companies like Facebook, Twitter, and Netflix also started using AI.
Deep learning, big data and artificial general intelligence (2011-present)
● Year 2011: In the year 2011, IBM's Watson won jeopardy, a quiz show, where it had to solve the complex questions as well as riddles. Watson had proved that it could understand natural language and can solve tricky questions quickly.
● Year 2012: Google has launched an Android app feature "Google now", which was able to provide information to the user as a prediction.
● Year 2014: In the year 2014, Chatbot "Eugene Goostman" won a competition in the infamous "Turing test."
● Year 2018: The "Project Debater" from IBM debated on complex topics with two master debaters and also performed extremely well.
● Google has demonstrated an AI program "Duplex" which was a virtual assistant and which had taken hairdresser appointment on call, and lady on other side didn't notice that she was talking with the machine.
Now AI has developed to a remarkable level. The concept of Deep learning, big data, and data science are now trending like a boom. Nowadays companies like Google, Facebook, IBM, and Amazon are working with AI and creating amazing devices. The future of Artificial Intelligence is inspiring and will come with high intelligence.
Application
Artificial intelligence is used in a variety of ways in today's society. It is becoming increasingly important in today's world because it can efficiently handle complicated problems in a variety of areas, including healthcare, entertainment, banking, and education. Our daily lives are becoming more comfortable and efficient as a result of artificial intelligence.
The following are some of the areas where Artificial Intelligence is used:
● AI in Astronomy - Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be extremely helpful in resolving complicated challenges in the universe. AI technology can assist in gaining a better understanding of the cosmos, including how it operates, its origin, and so on.
● AI in Healthcare - In the previous five to ten years, AI has become more beneficial to the healthcare business and is expected to have a big impact.
AI is being used in the healthcare industry to make better and faster diagnoses than humans. AI can assist doctors with diagnosis and can alert doctors when a patient's condition is deteriorating so that medical assistance can be provided before the patient is admitted to the hospital.
● AI in Gaming - AI can be employed in video games. AI machines can play strategic games like chess, in which the system must consider a vast number of different options.
● AI in Robotics - In Robotics, Artificial Intelligence plays a significant role. Typically, conventional robots are programmed to execute a repetitive task; but, using AI, we may construct intelligent robots that can perform tasks based on their own experiences rather than being pre-programmed.
Humanoid Robots are the best instances of AI in robotics; recently, the intelligent Humanoid Robots Erica and Sophia were built, and they can converse and behave like people.
● AI in Finance - The banking and AI businesses are the ideal complements to each other. Automation, chatbots, adaptive intelligence, algorithm trading, and machine learning are all being used in financial activities.
● AI in Data Security - Data security is critical for every business, and cyber-attacks are on the rise in the digital age. AI can help you keep your data safe and secure. Some examples are the AEG bot and the AI2 Platform, which are used to better determine software bugs and cyber-attacks.
● AI in Social Media - Facebook, Twitter, and Snapchat, for example, have billions of user accounts that must be kept and handled in a very efficient manner. AI has the ability to organize and manage large volumes of data. AI can go through a large amount of data to find the most recent trends, hashtags, and user requirements.
● AI in Travel & Transport - For the travel industry, AI is becoming increasingly important. AI is capable of doing a variety of travel-related tasks, including making travel arrangements and recommending hotels, flights, and the best routes to customers. The travel industry is utilizing AI-powered chatbots that can engage with clients in a human-like manner to provide better and faster service.
● AI in Automotive Industry - Some automotive companies are utilizing artificial intelligence to provide a virtual assistant to their users in order to improve performance. Tesla, for example, has released TeslaBot, an intelligent virtual assistant.
Various industries are presently working on self-driving automobiles that will make your ride safer and more secure.
● AI in education - Grading can be automated with AI, giving the instructor more time to educate. As a teaching assistant, an AI chatbot can communicate with students.
In the future, AI could serve as a personal virtual tutor for pupils, available at any time and from any location.
Key takeaway
Artificial Intelligence is not a new word and not a new technology for researchers. This technology is much older than you would imagine. Even there are the myths of Mechanical men in Ancient Greek and Egyptian Myths. Following are some milestones in the history of AI which defines the journey from the AI generation to till date development.
The representation function captures the important aspects of a problem and makes them available to a problem-solving technique. Expressiveness (the outcome of abstracting a feature) and efficiency (computational complexity) are two important variables to consider when considering knowledge representation.
These trade-offs can be seen in the computer representation of floating-point numbers. To be exact, to completely explain a real number, an infinite string of digits is required. This is impossible to achieve with a finite instrument like a computer.

Fig 4: Representation
Another common representation in computer science is the array.
It is more intuitive and efficient than the memory architecture used in computer hardware for many problems.
Search
● The second part of intelligent issue solving is search, which is based on a representation.
● On their journey to solving a problem, humans usually evaluate a variety of alternate options
○ Such as chess
○ Player reviews alternative moves, select the “best” move
○ A player can also consider a short term gain
Consider “tic-tac-toe”
● Begin with a blank board.
● The first player can put an X wherever on the board.
● Each move generates a new board, giving the opponent eight possible reactions, and so on…
● Each board can be thought of as a state in a graph to describe this collection of alternative movements.
● The graph's link represents a valid motion.
● A state space graph is the resulting structure.
“tic-tac-toe” state space graph
Tic Tac Toe is also known as Noughts and Crosses or Xs and Os, and it is a game in which players take turns marking spaces in a 3x3 grid with their own marks. If three consecutive marks (Horizontal, Vertical, and Diagonal) are made, the player who owns these movements wins.
Tic-Tac-Toe is a basic two-player game that we used to enjoy as youngsters (especially in boring classrooms). In this game, two players compete to place their respective emblems in a 3x3 grid. The game is won by the person who can line up three of their symbols in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row. If neither player succeeds, the game finishes in a tie. If both players always use their best strategy, the game will always finish in a tie.
Fig 5: Tic tac toe board
Because the grid is small and there are only two players, the number of possible moves for each board state is minimal, allowing Tree-based search techniques such as Alpha-Beta pruning to provide a computationally practical and accurate solution for creating a Computer-based Tic-Tac-Toe player.
We look at an approximation (Learning-based) method to the same game in this post. Even if a superior approach (Alpha-beta pruning) exists, the approximate method presents an alternative that could be useful if the board's complexity grows. In addition, the code changes required to implement it would be minor.
Tic-tac-toe is a popular game in which two players, X and O, alternate marking places in a 33-square grid. The game is won by the player who can line up three of their markings in a vertical, horizontal, or diagonal row.
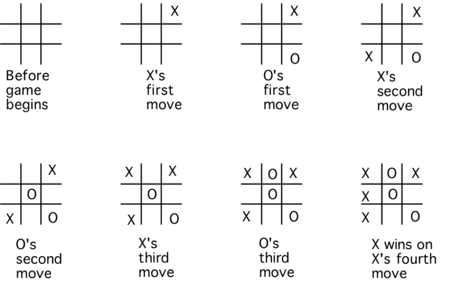
Fig 6: Tic tac toe game
Properties
From a mathematical standpoint, the game has two key characteristics:
Property 1: The game acknowledges that the person who employs this optimal approach will win or tie, but not lose.
Property 2: The number of different possible matches is limited.
Algorithm
The Alpha Beta search is a practical and general algorithm for winning/drawing the game, based on qualities 1 and 2.
At each turn, the algorithm considers all of the possible outcomes of each move (which are feasible owing to property 2) and selects the one that will result in a win or a tie (possible due to property 1).
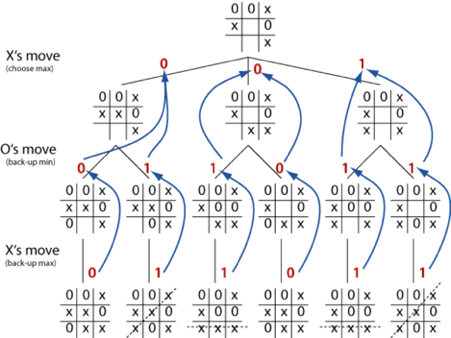
An AI player who uses the alpha beta search method to choose each move will never lose. To make the game more realistic, add a stochastic feature so that the AI player moves randomly rather than following the alpha beta algorithm each time with a predetermined probability. This will add realism to the game by making the AI player more human, and it will occasionally lose.
Key takeaway
Tic Tac Toe is also known as Noughts and Crosses or Xs and Os, and it is a game in which players take turns marking spaces in a 3x3 grid with their own marks.
The game is won by the person who can line up three of their symbols in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row.
A production system, also known as a production rule system, is a computer programme that is typically used to provide artificial intelligence. It consists primarily of a set of behavior rules, but it also includes the mechanism that allows the system to follow those rules as it responds to changes in the environment.
Components of Production System
The following are the primary components of Artificial Intelligence's Production System:
Global Database: In Artificial Intelligence, the global database is the fundamental data structure used by the production system.
Set of Production Rules: The global database is used by the production rules. Each rule usually has a precondition that the global database either meets or doesn't. When the prerequisite is met, the rule is normally followed. The database is changed when the rule is applied.
A Control System: When a termination condition on the database is satisfied, the control system determines which appropriate rule should be used and stops the computation. The control system resolves conflicts when numerous rules are set to fire at the same time.
Features of Production System in Artificial Intelligence
The following are the primary characteristics of the production system:
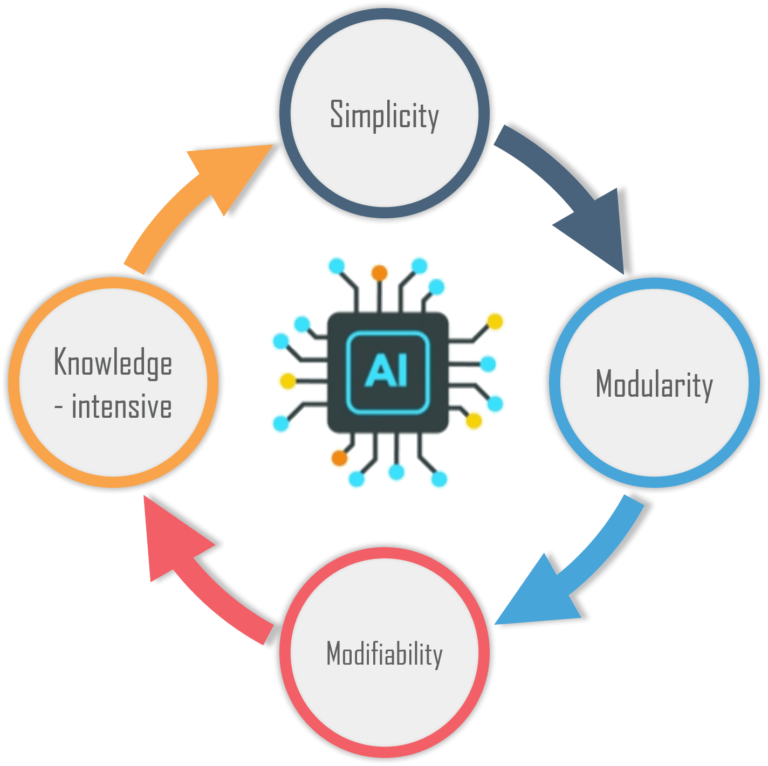
Simplicity: Because they use the "IF-THEN" pattern, each statement in a production system is unique and uniform. This form simplifies the depiction of knowledge. The readability of production regulations is improved by this aspect of the production system.
Modularity: This means that the production rules codify the knowledge in separate chunks. Information can be thought of as a collection of unrelated facts that can be added or removed from the system with little or no negative consequences.
Modifiability: This refers to the ability to change rules. It enables the creation of production rules in a skeletal form first, before fine-tuning them to suit a given application.
Knowledge-intensive: The production system's knowledge base contains only pure knowledge. There is no control or programming information in this section. Each production rule is usually represented as an English sentence, and the semantics problem is overcome by the representation's structure.
The AI reflex agent converts states into actions. When these agents fail to work in an environment where the state of mapping is too vast for the agent to handle, the stated problem dissolves and is delivered to a problem-solving domain, which divides the large stored problem into smaller storage areas and resolves them one at a time. The desired objectives will be the final integrated action.
Different sorts of issue-solving agents are defined and used at an atomic level without any internal state observable with a problem-solving algorithm based on the problem and their working domain. By describing problems and many solutions, the problem-solving agent executes precisely. So we may say that issue solving is a subset of artificial intelligence that includes a variety of problem-solving approaches such as tree, B-tree, and heuristic algorithms.
Because they immediately transfer states to actions, reflex agents are characterised as the simplest agents. Unfortunately, these agents are unable to function in situations where the mapping is too huge to store and learn. On the other hand, a goal-based agent considers future behaviors as well as the desired outcomes.
The problem-solving agent is a sort of goal-based agent that uses atomic representation and has no internal states observable to the problem-solving algorithms.
AI issue-solving steps: The nature of humans and their actions is closely related to the challenge of AI. As a result, we require a set of defined steps to solve an issue, which makes human labor simple.
These are the steps that must be completed in order to solve a problem:
Goal Formulation: This is the first and most basic stage in fixing an issue. It organises discrete steps to establish a target/goals that necessitate some action in order to be achieved. AI agents are currently used to formulate the goal.
Formulation of the Problem: It is one of the most important elements in the
Problem-solving: process since it determines what action should be performed to attain the stated goal. This essential aspect of AI is reliant on a software agent, which consists of the components listed below to formulate the linked problem.
Components needed to formulate the problem:
Initial state: This state necessitates a beginning state for the task, which directs the AI agent toward a predetermined goal. In this condition, new methods also initialise a specific class to solve the problem domain.
Action: In this stage of issue formulation, all feasible actions are performed using a function with a specific class taken from the initial state.
Transition: In this step of issue formulation, the actual action taken by the previous action stage is combined with the final stage to be passed on to the next stage.
Goal test: This stage determines if the integrated transition model achieved the specified goal or not; if it did, stop the activity and move on to the next stage to calculate the cost of achieving the goal.
Path costing: is a component of problem-solving that assigns a numerical value to the expense of achieving the goal. It necessitates the purchase of all necessary hardware, software, and human labor.
Key takeaway
The problem-solving agent is a sort of goal-based agent that uses atomic representation and has no internal states observable to the problem-solving algorithms.
The state space search representation is the foundation of the majority of AI methods. In two fundamental respects, its structure corresponds to the structure problem solving.
It allows for a formal statement of an issue as the requirement to change one circumstance into another using a set of allowed operations.
It allows us to define the process of solving a specific problem as a mix of recognised procedures and search. The broad method of traversing space in order to identify a path from one state to another that is good.
Search is a critical step in solving a difficult problem for which no other direct methods exist.
The following steps must be taken in order to offer a formal description of a problem:
● Define a state space that encompasses all of the relevant objects' potential configurations.
● Within that space, specify one or more states that depict a conceivable condition in which the problem-solving process could begin. These are known as the first states.
● Specify one or more states that would be acceptable as a problem solution. These are referred to as goal states.
● Create a collection of rules that describe the possible actions (operators).
Water Jug Problem
Problem:
You are handed two jugs as a problem. One with a capacity of 4 gallons and another with a capacity of 3 gallons. Neither is equipped with a measuring device. The jugs can be filled with water with the help of a pump. How do you get 2 gallons of water into a 4 gallon jug exactly?
Solution:
For this problem, the state space is a collection of ordered pairs of integers (x, y) with x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and y = 0, 1, 2, 3. The figures x and y reflect the number of gallon of water in a 4 gallon jug and a 3 gallon jug, respectively. The initial condition is (0, 0). Because the issue does not specify how many gallon must be in the 3 gallon jug, the objective state is (2, n) for any value of n.
Production Rule of water jug problem

Assumptions
We've assumed that we can fill a jug with water from the pump and then spill the water onto the ground. There is no such thing as a measuring device:
Example of a Solution:

Production Systems
The structure for tackling the AI problem is provided by the production system. It consists of the following:
● A set of rules with a left side that establishes application and a right side that details the operation to be carried out.
● One or more knowledge/databases that convert whatever information is needed for the task at hand.
● A control strategy that specifies the sequence in which the rules are compared to the database, as well as a method for resolving conflicts that happen when multiple rules match at the same time.
● A rule applier.
Different aspects of representation and explanation may be present in a problem. It is vital to assess the problem along numerous critical dimensions in order to select the most effective approach for a given challenge.
It is required to examine the problem using various key aspects in order to determine the most effective method for a given problem:
● Is it possible to break the problem down into smaller, easier subproblems?
● Is it possible to disregard or employ solution steps?
● Is the universe of problems predictable?
● Is the best answer to the problem evident when compared to all other possibilities?
● Is the desired outcome a state word or a state path?
● Is a huge quantity of knowledge required to solve the problem, or is it only necessary to limit the search?
References:
- E.Rich and K. Knight, Artificial Intelligence, Tata McGraw Hill, 2008.
- Artificial intelligence and soft computing for beginners by Anandita Das Bhattachargee, Shroff Publishers
- Artificial Intelligence – A Practical Approach: Patterson, Tata McGraw Hill, 3rd Edition
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence – Charniak (Pearson Education)
Unit - 1
Introduction
In today's world, technology is growing very fast, and we are getting in touch with different new technologies day by day.
Here, one of the booming technologies of computer science is Artificial Intelligence which is ready to create a new revolution in the world by making intelligent machines. The Artificial Intelligence is now all around us. It is currently working with a variety of subfields, ranging from general to specific, such as self-driving cars, playing chess, proving theorems, playing music, Painting, etc.
AI is one of the fascinating and universal fields of Computer science which has a great scope in future. AI holds a tendency to cause a machine to work as a human.

Fig 1: Example
Artificial Intelligence is composed of two words Artificial and Intelligence, where Artificial defines "man-made," and intelligence defines "thinking power", hence AI means "a man-made thinking power."
So, we can define AI as:
"It is a branch of computer science by which we can create intelligent machines which can behave like a human, think like humans, and able to make decisions."
Artificial Intelligence exists when a machine can have human based skills such as learning, reasoning, and solving problems With Artificial Intelligence you do not need to preprogram a machine to do some work, despite that you can create a machine with programmed algorithms which can work with own intelligence, and that is the awesomeness of AI.
It is believed that AI is not a new technology, and some people says that as per Greek myth, there were Mechanical men in early days which can work and behave like humans.
Why Artificial Intelligence?
Before Learning about Artificial Intelligence, we should know that what is the importance of AI and why should we learn it. Following are some main reasons to learn about AI:
● With the help of AI, you can create such software or devices which can solve real-world problems very easily and with accuracy such as health issues, marketing, traffic issues, etc.
● With the help of AI, you can create your personal virtual Assistant, such as Cortana, Google Assistant, Siri, etc.
● With the help of AI, you can build such Robots which can work in an environment where survival of humans can be at risk.
● AI opens a path for other new technologies, new devices, and new Opportunities.
Goals of Artificial Intelligence
Following are the main goals of Artificial Intelligence:
- Replicate human intelligence
- Solve Knowledge-intensive tasks
- An intelligent connection of perception and action
- Building a machine which can perform tasks that requires human intelligence such as:
● Proving a theorem
● Playing chess
● Plan some surgical operation
● Driving a car in traffic
- Creating some system which can exhibit intelligent behavior, learn new things by itself, demonstrate, explain, and can advise to its user.
What Comprises Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence is not just a part of computer science even it's so vast and requires lots of other factors which can contribute to it. To create the AI first we should know that how intelligence is composed, so the Intelligence is an intangible part of our brain which is a combination of Reasoning, learning, problem-solving perception, language understanding, etc.
To achieve the above factors for a machine or software Artificial Intelligence requires the following discipline:
● Mathematics
● Biology
● Psychology
● Sociology
● Computer Science
● Neurons Study
● Statistics
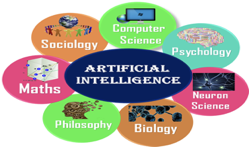
Fig 2: Factors of Artificial intelligence
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence
Following are some main advantages of Artificial Intelligence:
● High Accuracy with less errors: AI machines or systems are prone to less errors and high accuracy as it takes decisions as per pre-experience or information.
● High-Speed: AI systems can be of very high-speed and fast-decision making, because of that AI systems can beat a chess champion in the Chess game.
● High reliability: AI machines are highly reliable and can perform the same action multiple times with high accuracy.
● Useful for risky areas: AI machines can be helpful in situations such as defusing a bomb, exploring the ocean floor, where to employ a human can be risky.
● Digital Assistant: AI can be very useful to provide digital assistant to the users such as AI technology is currently used by various E-commerce websites to show the products as per customer requirement.
● Useful as a public utility: AI can be very useful for public utilities such as a self-driving car which can make our journey safer and hassle-free, facial recognition for security purpose, Natural language processing to communicate with the human in human-language, etc.
Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
Every technology has some disadvantages, and the same goes for Artificial intelligence. Being so advantageous technology still, it has some disadvantages which we need to keep in our mind while creating an AI system. Following are the disadvantages of AI:
● High Cost: The hardware and software requirement of AI is very costly as it requires lots of maintenance to meet current world requirements.
● Can't think out of the box: Even we are making smarter machines with AI, but still they cannot work out of the box, as the robot will only do that work for which they are trained, or programmed.
● No feelings and emotions: AI machines can be an outstanding performer, but still it does not have the feeling so it cannot make any kind of emotional attachment with human, and may sometime be harmful for users if the proper care is not taken.
● Increase dependency on machines: With the increment of technology, people are getting more dependent on devices and hence they are losing their mental capabilities.
● No Original Creativity: As humans are so creative and can imagine some new ideas but still AI machines cannot beat this power of human intelligence and cannot be creative and imaginative.
Key takeaway
AI is one of the fascinating and universal fields of Computer science which has a great scope in future.
AI holds a tendency to cause a machine to work as a human.
Artificial Intelligence is not a new word and not a new technology for researchers. This technology is much older than you would imagine. Even there are the myths of Mechanical men in Ancient Greek and Egyptian Myths. Following are some milestones in the history of AI which defines the journey from the AI generation to till date development.
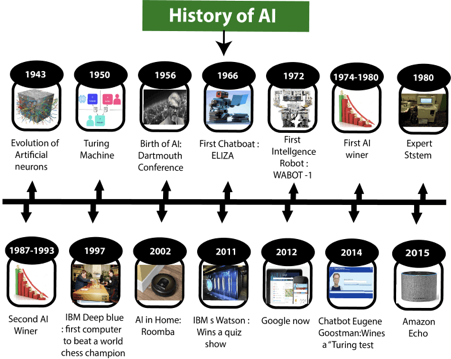
Fig 3: Image of AI history
Maturation of Artificial Intelligence (1943-1952)
● Year 1943: The first work which is now recognized as AI was done by Warren McCulloch and Walter pits in 1943. They proposed a model of artificial neurons.
● Year 1949: Donald Hebb demonstrated an updating rule for modifying the connection strength between neurons. His rule is now called Hebbian learning.
● Year 1950: The Alan Turing who was an English mathematician and pioneered Machine learning in 1950. Alan Turing publishes "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" in which he proposed a test. The test can check the machine's ability to exhibit intelligent behavior equivalent to human intelligence, called a Turing test.
The birth of Artificial Intelligence (1952-1956)
● Year 1955: An Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon created the "first artificial intelligence program "Which was named as "Logic Theorist". This program had proved 38 of 52 Mathematics theorems, and find new and more elegant proofs for some theorems.
● Year 1956: The word "Artificial Intelligence" first adopted by American Computer scientist John McCarthy at the Dartmouth Conference. For the first time, AI coined as an academic field.
At that time high-level computer languages such as FORTRAN, LISP, or COBOL were invented. And the enthusiasm for AI was very high at that time.
The golden years-Early enthusiasm (1956-1974)
● Year 1966: The researchers emphasized developing algorithms which can solve mathematical problems. Joseph Weizenbaum created the first chatbot in 1966, which was named as ELIZA.
● Year 1972: The first intelligent humanoid robot was built in Japan which was named as WABOT-1.
The first AI winter (1974-1980)
● The duration between years 1974 to 1980 was the first AI winter duration. AI winter refers to the time period where computer scientist dealt with a severe shortage of funding from government for AI researches.
● During AI winters, an interest of publicity on artificial intelligence was decreased.
A boom of AI (1980-1987)
● Year 1980: After AI winter duration, AI came back with "Expert System". Expert systems were programmed that emulate the decision-making ability of a human expert.
● In the Year 1980, the first national conference of the American Association of Artificial Intelligence was held at Stanford University.
The second AI winter (1987-1993)
● The duration between the years 1987 to 1993 was the second AI Winter duration.
● Again, Investors and government stopped in funding for AI research as due to high cost but not efficient result. The expert system such as XCON was very cost effective.
The emergence of intelligent agents (1993-2011)
● Year 1997: In the year 1997, IBM Deep Blue beats world chess champion, Gary Kasparov, and became the first computer to beat a world chess champion.
● Year 2002: for the first time, AI entered the home in the form of Roomba, a vacuum cleaner.
● Year 2006: AI came in the Business world till the year 2006. Companies like Facebook, Twitter, and Netflix also started using AI.
Deep learning, big data and artificial general intelligence (2011-present)
● Year 2011: In the year 2011, IBM's Watson won jeopardy, a quiz show, where it had to solve the complex questions as well as riddles. Watson had proved that it could understand natural language and can solve tricky questions quickly.
● Year 2012: Google has launched an Android app feature "Google now", which was able to provide information to the user as a prediction.
● Year 2014: In the year 2014, Chatbot "Eugene Goostman" won a competition in the infamous "Turing test."
● Year 2018: The "Project Debater" from IBM debated on complex topics with two master debaters and also performed extremely well.
● Google has demonstrated an AI program "Duplex" which was a virtual assistant and which had taken hairdresser appointment on call, and lady on other side didn't notice that she was talking with the machine.
Now AI has developed to a remarkable level. The concept of Deep learning, big data, and data science are now trending like a boom. Nowadays companies like Google, Facebook, IBM, and Amazon are working with AI and creating amazing devices. The future of Artificial Intelligence is inspiring and will come with high intelligence.
Application
Artificial intelligence is used in a variety of ways in today's society. It is becoming increasingly important in today's world because it can efficiently handle complicated problems in a variety of areas, including healthcare, entertainment, banking, and education. Our daily lives are becoming more comfortable and efficient as a result of artificial intelligence.
The following are some of the areas where Artificial Intelligence is used:
● AI in Astronomy - Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be extremely helpful in resolving complicated challenges in the universe. AI technology can assist in gaining a better understanding of the cosmos, including how it operates, its origin, and so on.
● AI in Healthcare - In the previous five to ten years, AI has become more beneficial to the healthcare business and is expected to have a big impact.
AI is being used in the healthcare industry to make better and faster diagnoses than humans. AI can assist doctors with diagnosis and can alert doctors when a patient's condition is deteriorating so that medical assistance can be provided before the patient is admitted to the hospital.
● AI in Gaming - AI can be employed in video games. AI machines can play strategic games like chess, in which the system must consider a vast number of different options.
● AI in Robotics - In Robotics, Artificial Intelligence plays a significant role. Typically, conventional robots are programmed to execute a repetitive task; but, using AI, we may construct intelligent robots that can perform tasks based on their own experiences rather than being pre-programmed.
Humanoid Robots are the best instances of AI in robotics; recently, the intelligent Humanoid Robots Erica and Sophia were built, and they can converse and behave like people.
● AI in Finance - The banking and AI businesses are the ideal complements to each other. Automation, chatbots, adaptive intelligence, algorithm trading, and machine learning are all being used in financial activities.
● AI in Data Security - Data security is critical for every business, and cyber-attacks are on the rise in the digital age. AI can help you keep your data safe and secure. Some examples are the AEG bot and the AI2 Platform, which are used to better determine software bugs and cyber-attacks.
● AI in Social Media - Facebook, Twitter, and Snapchat, for example, have billions of user accounts that must be kept and handled in a very efficient manner. AI has the ability to organize and manage large volumes of data. AI can go through a large amount of data to find the most recent trends, hashtags, and user requirements.
● AI in Travel & Transport - For the travel industry, AI is becoming increasingly important. AI is capable of doing a variety of travel-related tasks, including making travel arrangements and recommending hotels, flights, and the best routes to customers. The travel industry is utilizing AI-powered chatbots that can engage with clients in a human-like manner to provide better and faster service.
● AI in Automotive Industry - Some automotive companies are utilizing artificial intelligence to provide a virtual assistant to their users in order to improve performance. Tesla, for example, has released TeslaBot, an intelligent virtual assistant.
Various industries are presently working on self-driving automobiles that will make your ride safer and more secure.
● AI in education - Grading can be automated with AI, giving the instructor more time to educate. As a teaching assistant, an AI chatbot can communicate with students.
In the future, AI could serve as a personal virtual tutor for pupils, available at any time and from any location.
Key takeaway
Artificial Intelligence is not a new word and not a new technology for researchers. This technology is much older than you would imagine. Even there are the myths of Mechanical men in Ancient Greek and Egyptian Myths. Following are some milestones in the history of AI which defines the journey from the AI generation to till date development.
The representation function captures the important aspects of a problem and makes them available to a problem-solving technique. Expressiveness (the outcome of abstracting a feature) and efficiency (computational complexity) are two important variables to consider when considering knowledge representation.
These trade-offs can be seen in the computer representation of floating-point numbers. To be exact, to completely explain a real number, an infinite string of digits is required. This is impossible to achieve with a finite instrument like a computer.

Fig 4: Representation
Another common representation in computer science is the array.
It is more intuitive and efficient than the memory architecture used in computer hardware for many problems.
Search
● The second part of intelligent issue solving is search, which is based on a representation.
● On their journey to solving a problem, humans usually evaluate a variety of alternate options
○ Such as chess
○ Player reviews alternative moves, select the “best” move
○ A player can also consider a short term gain
Consider “tic-tac-toe”
● Begin with a blank board.
● The first player can put an X wherever on the board.
● Each move generates a new board, giving the opponent eight possible reactions, and so on…
● Each board can be thought of as a state in a graph to describe this collection of alternative movements.
● The graph's link represents a valid motion.
● A state space graph is the resulting structure.
“tic-tac-toe” state space graph
Tic Tac Toe is also known as Noughts and Crosses or Xs and Os, and it is a game in which players take turns marking spaces in a 3x3 grid with their own marks. If three consecutive marks (Horizontal, Vertical, and Diagonal) are made, the player who owns these movements wins.
Tic-Tac-Toe is a basic two-player game that we used to enjoy as youngsters (especially in boring classrooms). In this game, two players compete to place their respective emblems in a 3x3 grid. The game is won by the person who can line up three of their symbols in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row. If neither player succeeds, the game finishes in a tie. If both players always use their best strategy, the game will always finish in a tie.
Fig 5: Tic tac toe board
Because the grid is small and there are only two players, the number of possible moves for each board state is minimal, allowing Tree-based search techniques such as Alpha-Beta pruning to provide a computationally practical and accurate solution for creating a Computer-based Tic-Tac-Toe player.
We look at an approximation (Learning-based) method to the same game in this post. Even if a superior approach (Alpha-beta pruning) exists, the approximate method presents an alternative that could be useful if the board's complexity grows. In addition, the code changes required to implement it would be minor.
Tic-tac-toe is a popular game in which two players, X and O, alternate marking places in a 33-square grid. The game is won by the player who can line up three of their markings in a vertical, horizontal, or diagonal row.
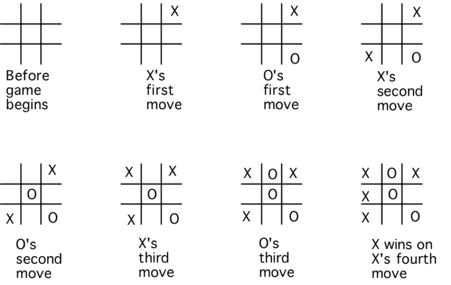
Fig 6: Tic tac toe game
Properties
From a mathematical standpoint, the game has two key characteristics:
Property 1: The game acknowledges that the person who employs this optimal approach will win or tie, but not lose.
Property 2: The number of different possible matches is limited.
Algorithm
The Alpha Beta search is a practical and general algorithm for winning/drawing the game, based on qualities 1 and 2.
At each turn, the algorithm considers all of the possible outcomes of each move (which are feasible owing to property 2) and selects the one that will result in a win or a tie (possible due to property 1).
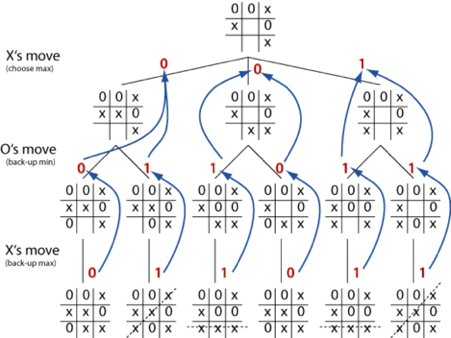
An AI player who uses the alpha beta search method to choose each move will never lose. To make the game more realistic, add a stochastic feature so that the AI player moves randomly rather than following the alpha beta algorithm each time with a predetermined probability. This will add realism to the game by making the AI player more human, and it will occasionally lose.
Key takeaway
Tic Tac Toe is also known as Noughts and Crosses or Xs and Os, and it is a game in which players take turns marking spaces in a 3x3 grid with their own marks.
The game is won by the person who can line up three of their symbols in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row.
A production system, also known as a production rule system, is a computer programme that is typically used to provide artificial intelligence. It consists primarily of a set of behavior rules, but it also includes the mechanism that allows the system to follow those rules as it responds to changes in the environment.
Components of Production System
The following are the primary components of Artificial Intelligence's Production System:
Global Database: In Artificial Intelligence, the global database is the fundamental data structure used by the production system.
Set of Production Rules: The global database is used by the production rules. Each rule usually has a precondition that the global database either meets or doesn't. When the prerequisite is met, the rule is normally followed. The database is changed when the rule is applied.
A Control System: When a termination condition on the database is satisfied, the control system determines which appropriate rule should be used and stops the computation. The control system resolves conflicts when numerous rules are set to fire at the same time.
Features of Production System in Artificial Intelligence
The following are the primary characteristics of the production system:

Simplicity: Because they use the "IF-THEN" pattern, each statement in a production system is unique and uniform. This form simplifies the depiction of knowledge. The readability of production regulations is improved by this aspect of the production system.
Modularity: This means that the production rules codify the knowledge in separate chunks. Information can be thought of as a collection of unrelated facts that can be added or removed from the system with little or no negative consequences.
Modifiability: This refers to the ability to change rules. It enables the creation of production rules in a skeletal form first, before fine-tuning them to suit a given application.
Knowledge-intensive: The production system's knowledge base contains only pure knowledge. There is no control or programming information in this section. Each production rule is usually represented as an English sentence, and the semantics problem is overcome by the representation's structure.
The AI reflex agent converts states into actions. When these agents fail to work in an environment where the state of mapping is too vast for the agent to handle, the stated problem dissolves and is delivered to a problem-solving domain, which divides the large stored problem into smaller storage areas and resolves them one at a time. The desired objectives will be the final integrated action.
Different sorts of issue-solving agents are defined and used at an atomic level without any internal state observable with a problem-solving algorithm based on the problem and their working domain. By describing problems and many solutions, the problem-solving agent executes precisely. So we may say that issue solving is a subset of artificial intelligence that includes a variety of problem-solving approaches such as tree, B-tree, and heuristic algorithms.
Because they immediately transfer states to actions, reflex agents are characterised as the simplest agents. Unfortunately, these agents are unable to function in situations where the mapping is too huge to store and learn. On the other hand, a goal-based agent considers future behaviors as well as the desired outcomes.
The problem-solving agent is a sort of goal-based agent that uses atomic representation and has no internal states observable to the problem-solving algorithms.
AI issue-solving steps: The nature of humans and their actions is closely related to the challenge of AI. As a result, we require a set of defined steps to solve an issue, which makes human labor simple.
These are the steps that must be completed in order to solve a problem:
Goal Formulation: This is the first and most basic stage in fixing an issue. It organises discrete steps to establish a target/goals that necessitate some action in order to be achieved. AI agents are currently used to formulate the goal.
Formulation of the Problem: It is one of the most important elements in the
Problem-solving: process since it determines what action should be performed to attain the stated goal. This essential aspect of AI is reliant on a software agent, which consists of the components listed below to formulate the linked problem.
Components needed to formulate the problem:
Initial state: This state necessitates a beginning state for the task, which directs the AI agent toward a predetermined goal. In this condition, new methods also initialise a specific class to solve the problem domain.
Action: In this stage of issue formulation, all feasible actions are performed using a function with a specific class taken from the initial state.
Transition: In this step of issue formulation, the actual action taken by the previous action stage is combined with the final stage to be passed on to the next stage.
Goal test: This stage determines if the integrated transition model achieved the specified goal or not; if it did, stop the activity and move on to the next stage to calculate the cost of achieving the goal.
Path costing: is a component of problem-solving that assigns a numerical value to the expense of achieving the goal. It necessitates the purchase of all necessary hardware, software, and human labor.
Key takeaway
The problem-solving agent is a sort of goal-based agent that uses atomic representation and has no internal states observable to the problem-solving algorithms.
The state space search representation is the foundation of the majority of AI methods. In two fundamental respects, its structure corresponds to the structure problem solving.
It allows for a formal statement of an issue as the requirement to change one circumstance into another using a set of allowed operations.
It allows us to define the process of solving a specific problem as a mix of recognised procedures and search. The broad method of traversing space in order to identify a path from one state to another that is good.
Search is a critical step in solving a difficult problem for which no other direct methods exist.
The following steps must be taken in order to offer a formal description of a problem:
● Define a state space that encompasses all of the relevant objects' potential configurations.
● Within that space, specify one or more states that depict a conceivable condition in which the problem-solving process could begin. These are known as the first states.
● Specify one or more states that would be acceptable as a problem solution. These are referred to as goal states.
● Create a collection of rules that describe the possible actions (operators).
Water Jug Problem
Problem:
You are handed two jugs as a problem. One with a capacity of 4 gallons and another with a capacity of 3 gallons. Neither is equipped with a measuring device. The jugs can be filled with water with the help of a pump. How do you get 2 gallons of water into a 4 gallon jug exactly?
Solution:
For this problem, the state space is a collection of ordered pairs of integers (x, y) with x = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and y = 0, 1, 2, 3. The figures x and y reflect the number of gallon of water in a 4 gallon jug and a 3 gallon jug, respectively. The initial condition is (0, 0). Because the issue does not specify how many gallon must be in the 3 gallon jug, the objective state is (2, n) for any value of n.
Production Rule of water jug problem

Assumptions
We've assumed that we can fill a jug with water from the pump and then spill the water onto the ground. There is no such thing as a measuring device:
Example of a Solution:

Production Systems
The structure for tackling the AI problem is provided by the production system. It consists of the following:
● A set of rules with a left side that establishes application and a right side that details the operation to be carried out.
● One or more knowledge/databases that convert whatever information is needed for the task at hand.
● A control strategy that specifies the sequence in which the rules are compared to the database, as well as a method for resolving conflicts that happen when multiple rules match at the same time.
● A rule applier.
Different aspects of representation and explanation may be present in a problem. It is vital to assess the problem along numerous critical dimensions in order to select the most effective approach for a given challenge.
It is required to examine the problem using various key aspects in order to determine the most effective method for a given problem:
● Is it possible to break the problem down into smaller, easier subproblems?
● Is it possible to disregard or employ solution steps?
● Is the universe of problems predictable?
● Is the best answer to the problem evident when compared to all other possibilities?
● Is the desired outcome a state word or a state path?
● Is a huge quantity of knowledge required to solve the problem, or is it only necessary to limit the search?
References:
- E.Rich and K. Knight, Artificial Intelligence, Tata McGraw Hill, 2008.
- Artificial intelligence and soft computing for beginners by Anandita Das Bhattachargee, Shroff Publishers
- Artificial Intelligence – A Practical Approach: Patterson, Tata McGraw Hill, 3rd Edition
- Introduction to Artificial Intelligence – Charniak (Pearson Education)