Unit - 2
Lathe
Lathe: Introduction
Lathe Machine is the most widely used lathe machine and still, it is, in every workshop, this machine is present. The operation like Turning, facing, grooving, Knurling, threading and more, such operations are performed on this type of machine.
Centre lathe machine has all the parts such as bed, Saddle, headstock, and tailstock, etc. The headstock of an engine lathe is rigid and tailstock is moveable which is further used to support an operation like knurling. It can easily feed the cutting tool in both directions i.e. longitudinal and lateral directions with the help of feed mechanisms. Center Lathe machines are driven by the gear mechanism or pulley mechanism. It has three types of driven mechanisms, and those are Belt-driven, Motor-driven, gear head type.
The Centre Lathe is used to manufacture cylindrical shapes from a range of materials including; steels and plastics. Many of the components that go together to make an engine work have been manufactured using lathes. These may be lathes operated directly by people (manual lathes) or computer controlled lathes (CNC machines) that have been programmed to carry out a particular task. A basic manual center lathe is shown below. This type of lathe is controlled by a person turning the various handles on the top slide and cross slide in order to make a product / part.
The headstock of a center lathe can be opened, revealing an arrangement of gears. These gears are sometimes replaced to alter the speed of rotation of the chuck. The lathe must be switched off before opening, although the motor should automatically cut off if the door is opened while the machine is running (a safety feature).
The speed of rotation of the chuck is usually set by using the gear levers. These are usually on top of the headstock or along the front and allow for a wide range of speeds.
However, sometimes the only way to set the lathe to a particular speed is to change the gear arrangement inside the headstock. Most machines will have a number of alterative gear wheels for this purpose.
Construction of simple lathe:
i) Basic element:
A lathe machine tool consists of several parts like:
- Headstock
- Bed
- Tailstock
- Carriage
- Saddle
- Cross-slide
- Compound rest
- Tool post
- Apron
- Lead Screw
- Feed rod
- Chuck
- Main spindle
- Leg
1) Head Stock:
Head Stock is situated at the left side of the lathe bed and it is the house of the driving mechanism and electrical mechanism of a Lathe machine tool.
- It holds the job on its spindle nose having external screw threads and internally Morse taper for holding lathe center. And it is rotating at a different speed by cone pulley or all geared drive. There is a hole throughout spindle for handling long bar work.
- Head Stock transmits power from the spindle to the feed rod, lead screw and thread cutting mechanism.
Accessories mounted on headstock spindle:
- Three jaw chuck
- Four jaw chuck
- Lathe center and lathe dog
- Collect chuck
- Faceplate
- Magnetic chuck
A separate speed change gearbox is placed below headstock to reduce the speed in order to have different feed rates for threading and automatic lateral movement of the carriage. The feed rod is used for most turning operation and the lead screw is used for thread cutting operation.
2) Bed:
It is the base of the lathe machine. It is made of single piece casting of Semi-steel (Chilled Cast Iron). The bed consists of two heavy metal slides running lengthwise, with ways or ‘V’ formed upon them and rigidly supported with cross girths.
- It is sufficiently rigid and good damping capacity to absorb vibration.
- It prevents the deflection produced by the cutting forces.
- It supports the headstock, tailstock, carriage and other components of the lathe machine.
3) Tail Stock:
Tail Stock is situated on the right side above the lathe bed. It is used for:
- Support the long end of the job for holding and minimizes its sagging.
- It holds the tool for performing different operations like drilling, reaming, tapping, etc.
And it is also used for a small amount of taper for a long job by offsetting the tailstock
4) Carriage:
The carriage is used for support, guide and feed the tool against the job when the machining is done.
- It holds moves and controls the cutting tool.
- It gives rigid supports to the tool during operations.
- It transfers power from feed rod to cutting tool through apron mechanism for longitudinal cross-feeding.
- It simplifies the thread cutting operation with the help of lead screw and half nut mechanism.
It consists of:
- Saddle
- Cross-slide
- Compound rest
- Tool post
- Apron
It provides three movements to the tool:
- Longitudinal feed-through carriage movement
- Cross feed-through cross slide movement
- Angular feed-through top slide movement
5) Saddle:
Generally, it is made up of ‘H’ shaped casting and it has a ‘V’ guide and a flat guide for mounting it on the lathe bed guide ways.
6) Cross-slide:
It is assembled on the top of the saddle. The top surface of the cross-slide is provided with T-slot.
7) Compound rest:
It supports the tool post and cutting tool in its various positions. It can be swiveled at any desired position in the horizontal plane. It is necessary for turning angles and boring short tapers.
8) Tool post:
It is the topmost portion of the carriage and it is used to hold various cutting tools or tool holders. There are three types of tool post commonly used and those are:
- Ring and rocker tool post
- Square head tool post
- Quick change tool post
9) Apron:
An apron is a house of the feed mechanism. It is fastened to the saddle and hangover in front of the bed.
10) Lead screw:
A lead screw is also known as a power screw or a translation screw. It converts rotational motion to linear motion. Lead Screw is used for Thread Cutting operation in a lathe machine tool.
11) Feed Rod:
Feed rod is used to move the carriage from the left side to the right side and also from the right side to the left side.
12) Chuck:
Chuck is used to holding the work piece securely.
There are generally 2 types of chucks:
- 3 jaw self-cantering chuck
- 4 jaw independent chuck
13) Main Spindle:
The spindle is a hollow cylindrical shaft in which long jobs can pass through it.
It is designed so well that the thrust of the cutting tool does not deflect the spindle.
14) Leg:
Legs are carrying an entire load of a lathe machine tool and transfer to the ground. The legs are firmly secured to the floor by the foundation bolt.
Types:
There are varieties of alternative lathe varieties, temporary descriptions of that are given here.
Bench Lathes:
Because the name suggests, these lathes are placed on a bench or a table. They need low power, are sometimes operated by hand feed, and are accustomed machine little work pieces. Tool room lathes have high exactitude, enables the machining of components to shut dimensional tolerances.
Special-purpose Lathes:
These lathes are used for applications (such as railroad wheels, gun barrels, and rolling-mill rolls) with piece of work sizes as giant as 1.7 m in diameter by eight m long and capacities of 450 kilowatt
Tracer Lathes:
These lathes have special attachments that are capable of turning components with varied contours. Conjointly known as a duplicating lathe or contouring lathe, the cutting implement follows a path that duplicates the contour of a template, like a pencil following the form of a plastic stencil. However, operations generally performed on a tracer lathe are replaced mostly by numerical-control lathes and turning centers.
Automatic Lathes:
Lathes became more and more machine-controlled over the years; manual machine controls are replaced by varied mechanisms that modify machining operations to follow a definite prescribed sequence. In an exceedingly absolutely automatic lathe, components are fed and removed mechanically, whereas in semi-automatic machines, these functions are performed by the operator. (The cutting remains automatic.) Automatic lathes could have a horizontal or vertical spindle and are appropriate for medium- to high-volume production. Lathes that don't have tailstocks are known as chucking machines or checkers. They used for machining individual items of normal or irregular shapes and are either single- or multiple-spindle varieties. In another kind of automatic lathe, the bar stock is fed sporadically into the lathe and an area is machined and discontinue from the top of the bar stock.
Automatic Bar Machines:
Conjointly known as automatic screw machines, these machine tools are designed for high-production-rate machining of screws and similar rib components. All operations on these machines are performed mechanically with tools connected to a special turret. When every half or screw is machined to finished dimensions, the bar stock is fed forward mechanically through the outlet within the spindle then discontinue. Automatic bar machines are also equipped with single or multiple spindles. Capacities vary from 3- to 150-mm diameter bar stock. Long stock is supported by special fixtures because it enters the spindle hole.
Single-spindle automatic bar machines are like turret lathes and are equipped with varied cam-operated mechanisms. There are 2 forms of single spindle machines. In Swiss-type-automatic the cylindrical surface of the solid-bar stock is machined with a series of tools that move radially and within the same plane toward the piece of work. The bar stock is clamped near to the support spindle, that minimizes deflections thanks to cutting forces. These machine tools are capable of high-precision machining of small-diameter components. The opposite single-spindle machine (called the American type) is comparable to a tiny low automatic turret lathe. The turret is on a vertical plane, and every one motions of the machine parts are controlled by cams. Automatic bar machines are currently equipped with laptop numerical management, eliminating the employment of cams, and also the operation is programmed for a selected product.
Multiple-spindle automatic bar machines generally have from four to eight spindles organized in an exceedingly circle on an outsized drum, with every carrying a personal piece of work. The cutting tools are organized in varied positions within the machine and move in each axial and radial direction. Every half is machined little by little because it moves from one station to successive. As a result of all operations is meted out at the same time, the cycle time per half is reduced.
Turret Lathes:
These machine tools are capable of activity multiple cutting operations, comparable to turning, boring, drilling, thread cutting, and facing. Many cutting tools (usually as several as six) are mounted on the polygonal shape main turret, that is turned when every specific cutting operation is completed. The lathe sometimes includes a sq. Turret on the cross-slide, mounting as several as four cutting tools. The piece of work (generally an extended, spherical bar stock) is advanced a planned distance through the chuck. When the half is machined, it does discontinue by a tool mounted on the sq. Turret that moves radially into the piece of work. The rod then is advanced identical planned distance, and also the next half is machined. Turret lathes (either the bar kind or the chucking type) are versatile, and also the operations is also meted out either by hand, victimization the gate (capstan wheel), or mechanically. Once found out properly, these machines don't need extremely experienced operators.
Vertical turret lathes are available; they're additional appropriate for brief, significant work pieces with diameters as giant as 1.2 m. The turret lathe shown in figure is understood as a ram-type turret lathe-one during which the ram slides in an exceedingly separate base on the saddle. The short stroke of the turret slide limits this machine to comparatively short work pieces and lightweight cuts in each small- and medium-quantity production. In another vogue (called the saddle type), the most turret is put in directly on the saddle, that slides on the bed. The length of the stroke is proscribed solely by the length of the bed. This kind of lathe is made additional heavily and is employed to machine giant work pieces. As a result of the significant weight of the parts, saddle-type lathe operations are slower than ram type operations.
Computer-controlled Lathes:
Within the most advanced lathes, movement and management of the machine and its parts are achieved by laptop numerical control (CNC). These lathes typically are equipped with one or additional turrets and every turret are supplied with a spread of tools and perform many operations on totally different surfaces of the piece of work. Work piece diameters is also the maximum amount as one m. To require advantage of latest cutting-tool materials, computer-controlled lathes are designed to work quicker and have higher power obtainable compared with alternative lathes. They’re equipped with automatic tool changers (ATCs). Their operations are faithfully repetitive, maintain the required dimensional accuracy, and need less experienced labor (once the machine is about up). They’re appropriate for low- to medium volume production.
Mechanism and attachments for various operations:
To carry out distinctive lathe system operations on a lathe, the work piece can be supported and pushed via way of means of any individual of the subsequent strategies:
- Work piece held among centers and device pushed via way of means of companies and capture plates.
- Work piece hung on a mandrel that's supported among centers and pushed via way of means of companies and capture plates. Held and pushed via way of means of chuck with the alternative quit supported at the tailstock center.
- Held and pushed via way of means of a chuck or a faceplate or a perspective plate.
- The above strategies of conserving the paintings can be categorized beneath heading: Work piece held among centers.
- Work piece held via way of means of a chuck or some other fixtures. A lathe system is usually utilized in metalworking, steel spinning, woodturning, and glass working.
- The diverse operations that it could carry out encompass the subsequent: sanding, slicing, knurling, drilling, and deforming of gear which might be hired in growing items that have symmetry approximately the axis of rotation.
- Some of the maximum not unusual place merchandise of the lathe system are crankshafts, camshafts, desk legs, bowls, and candlestick holders.
- The first lathe system that changed into ever advanced changed into the -man or woman lathe system which changed into designed via way of means of the Egyptians in approximately 1300 BC.
- Primarily, there are matters which might be completed on this lathe system set-up.
- The first is the turning of the timber running piece manually via way of means of a rope; and the second one is the slicing of shapes with inside the timber via way of means of using a pointy device.
- As civilizations progressed, there were steady changes and upgrades over the authentic -man or woman lathe system, most significantly at the manufacturing of the rotary movement.
The manufacturing of the rotary movement consequently developed in keeping with the subsequent procedures: the Egyptians guide turning via way of means of hand; the Romans addition of a turning bow; the creation of the pedal with inside the Middle Ages; using the steam engines at some point of the Industrial Revolution; the employment of person electric powered vehicles with inside the nineteenth and mid twentieth centuries; and the contemporary of that's the adaption of numerically managed mechanisms in controlling the lathe
For the lathe system to characteristic and carry out its operations, diverse critical elements are included together.
These necessities elements make up the lathe system.
Machine specifications:
Machine tools are defined as machines used for carrying out the metal cutting processes and surface finish processes by removing the material from the work piece in the form of chips.
A lathe is one of the oldest & most important machine tools ever developed. The job to be machined is rotated & the cutting tool is moved relative to the job. That is why, it’s also called as “Turning Machine”. A Lathe was basically developed to machine cylindrical surfaces. But many other operations can also be performed on lathes. E.g.-facing, parting, necking, knurling, taper turning & forming. We also can perform operations of other machine tools on a lathe, e.g. Drilling, reaming, milling & drilling operation etc. lathe is called the mother of the entire machine tool family. The lathe can be defined as a machine tool which holds the work between two rigid & strong centers, or in a chuck or face plate while the latter revolves. The cutting tool is rigidly held & supported in a tool post & feed against the revolving work.
Planer and shaper:
Planning and shaping are similar operations, which differ only in the kinematics of the process. Planning is a machining operation in which the primary cutting motion is performed by the work piece and feed motion is imparted to the cutting tool. In shaping, the primary motion is performed by the tool, and feed by the work piece.
Milling
Milling is a process of producing flat and complex shapes with the use of multi-point (or multi-tooth) cutting tool. The axis of rotation of the cutting tool is perpendicular to the direction of feed, either parallel or perpendicular to the machined surface. Milling is usually an interrupted cutting operation
Since the teeth of the milling cutter enter and exit the work piece during each revolution.
Drilling
Drilling is a process of producing round holes in a solid material or enlarging existing holes with the use of multi-point cutting tools called drills or drill bits. Various cutting tools are available for drilling, but the most common is the twist drill.
Basis for selection of cutting speed:
1. Cutting velocity is described because the velocity (commonly in ft in keeping with minute) of a device while its miles slicing the paintings.
2. Feed price is described as device’s distance travelled in the course of one spindle revolution.
3. Feed price and slicing velocity decide the price of fabric elimination, strength requirements, and floor finish.
4. Feed price and slicing velocity are broadly speaking decided with the aid of using the fabric that’s being cut. In addition, the deepness of the cut, length and circumstance of the lathe, and stress of the lathe must nonetheless be considered.
5. Roughing cuts (0.01 in. To 0.03 in. Intensity of cut) for maximum aluminum alloys run at a feedrate of .1/2 inches in keeping with minute (IPM) to 0.02 IPM even as completing cuts (0.002 in. To 0.012 in. Intensity of cut) run at 0.002 IPM to 0.004 IPM.
6. As the softness of the fabric decreases, the slicing velocity increases.
Additionally, because the slicing device fabric will become stronger, the slicing velocity increases.
7. Remember, for every thousandth intensity of cut, the diameter of the inventory is decreased with the aid of using thousandths.
A lathe paintings slicing velocity can be described because the price at which a factor at the paintings circumference travels beyond the slicing device.
Cutting velocity is constantly expressed in meters in keeping with minute (m/min) or in ft in keeping with minute (ft/min.) enterprise needs that machining operations be finished as fast as possible; consequently modern slicing speeds ought to be used for the sort of fabric being cut.
If a slicing velocity is just too excessive, the slicing device side breaks down rapidly, ensuing in time misplaced recondition the device.
With too gradual a slicing velocity, time may be misplaced for the machining operation, ensuing in low manufacturing rates. Based on studies and trying out with the aid of using metal and slicing device manufacturers, see lathe slicing velocity desk beneath.
The slicing speeds for excessive velocity metal indexed beneath are encouraged for green steel elimination rates.
These speeds can be numerous barely to shift elements including the circumstance of the machine, the sort of paintings fabric and sand or difficult spots with inside the steel.
Feed and depth of cut:
1. Cutting velocity is described because the velocity (commonly in ft in keeping with minute) of a device while its miles slicing the paintings.
2. Feed price is described as device’s distance travelled in the course of one spindle revolution.
3. Feed price and slicing velocity decide the price of fabric elimination, strength requirements, and floor finish.
4. Feed price and slicing velocity are broadly speaking decided with the aid of using the fabric that’s being cut. In addition, the deepness of the cut, length and circumstance of the lathe, and stress of the lathe must nonetheless be considered.
5. Roughing cuts (0.01 in. To 0.03 in. Intensity of cut) for maximum aluminum alloys run at a feedrate of .1/2 inches in keeping with minute (IPM) to 0.02 IPM even as completing cuts (0.002 in. To 0.012 in. Intensity of cut) run at 0.002 IPM to 0.004 IPM.
6. As the softness of the fabric decreases, the slicing velocity increases. Additionally, because the slicing device fabric will become stronger, the slicing velocity increases.
7. Remember, for every thousandth intensity of cut, the diameter of the inventory is decreased with the aid of using thousandths. A lathe paintings slicing velocity can be described because the price at which a factor at the paintings circumference travels beyond the slicing device.
Cutting velocity is constantly expressed in meters in keeping with minute (m/min) or in ft in keeping with minute (ft/min.) enterprise needs that machining operations be finished as fast as possible; consequently modern slicing speeds ought to be used for the sort of fabric being cut.
If a slicing velocity is just too excessive, the slicing device side breaks down rapidly, ensuing in time misplaced recondition the device.
With too gradual a slicing velocity, time may be misplaced for the machining operation, ensuing in low manufacturing rates.
Based on studies and trying out with the aid of using metal and slicing device manufacturers, see lathe slicing velocity desk beneath.
The slicing speeds for excessive velocity metal indexed beneath are encouraged for green steel elimination rates.
These speeds can be numerous barely to shift elements including the circumstance of the machine, the sort of paintings fabric and sand or difficult spots with inside the steel.
The RPM at which the lathe must be set for slicing metals is as follows: To decide the RPM of the lathe even as appearing techniques on it:
The following are the lathe machine formula commonly used to calculate in turning operations:
Depth of Cut
Depth of cut = (d1 – d2)/2
The depth of cut (t) is the perpendicular distance measured from the machined surface to the uncut surface of the work piece. In a lathe machine, the depth of cut is shown as follows:
Where,
- d1 – diameter of the work piece surface before machining.
- d2 – diameter of the machined surface.
Another factor remaining fixed, the depth of cut changes inversely as the cutting speed. For general purpose, the ratio of the depth of cut to the feed varies from 10:1
The cutting speed (v) of a tool is the speed at which the metal is removed by the tool from the workpiece. In a lathe, it is the peripherical speed of the work past the cutting too
Time estimation for turning operations such as facing:
Facing is a turning operation wherein the work piece is machined to its middle.
It entails transferring the slicing device perpendicular to the work piece’s axis of rotation.
This operation may be finished at a steady floor pace (sfm, m/min.), that is recommended, or at a steady rotational pace (rpm), which isn't recommended.
Facing at a steady rpm decreases the slicing pace, due to the fact the diameter of the going through floor steadily decreases through the quantity of a feed in keeping with revolution.
The nearer a slicing device is to the middle of a work piece, the decrease the slicing pace. It processes 0 on the middle of a work piece.
A low slicing pace can purpose built-up edge.
Time required = Length of cut / Feed X RPM
Step turning, taper turning, threading, knurling:
Step turning:
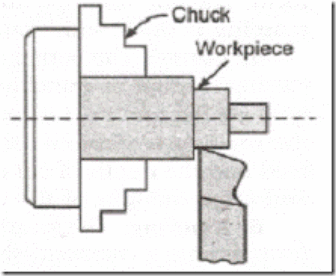
Step turning is a turning procedure wherein collection of steps having exclusive diameters is produced with the lathe gadget.
Procedure
- Fix the cylindrical work piece into the chuck and stable it nicely. Select the device and stable the device with inside the device submit.
- Bring the tailstock in advance and take a look at if the tooltip middle aligns with the middle of the lifeless middle.
- Adjust the device submit in order that most effective the reducing factor of the device comes in touch with the work piece.
- Set the rate of the spindle and route of rotation.
- Start the motor and take a look at if the work piece is rotating nicely and now no longer wobbling because it rotates.
- First, perform the going through operation via way of means of adjusting the device submit (rotate approximately 30-60 stages approx.) touching the tooltip to the face of the work piece, and use the pass feed spindle to provide intensity of reduce radial to the work piece.
- If the task is lengthy and slim then drill a hollow and makes use of the tailstock lifeless middle to help the work piece.
- Once going through operation is done, perform the turning operation in order that the work piece is flawlessly cylindrical.
- Then degree the diameter of the work piece, determine the step lengths and dia of the steps.
- Start the gadget, contact the tooltip to the flat round face of the task then mark the primary dia of the step. Bring the device radially out.
- Stop the gadget, take a Venire caliper and mark the step duration onto the task practice a few chalk in order that the mark is without problems seen whilst it begins off evolved rotating with inside the chuck.
- Then begin the gadget simply contact the tooltip on that mark, to have step one duration seen.
- Carry at the turning procedure as much as that marked duration from the quilt of the work piece to create step one, hold a watch at the device because the dia of the work piece reduces and is ready to attain the marked diameter at the flat round face of the work piece.
- Use hard reduce to take away most fabric then completing cuts may be given because the device processes marked diameter. Once step one is created.
- You may also word that on the nook of the step i.e. on the junction in which the small dia of the step meets the bigger dia has a few radius or wedge form which may be corrected via way of means of feeding the device to the wedge and getting rid of the fabric grade by grade till a great step is formed.
- Mark the second one dia and duration of the step and keep on the procedure till the preferred range of steps are formed.
Key Takeaways:
- This kind of lathe is made additional heavily and is employed to machine giant work pieces.
- As civilizations progressed, there were steady changes and upgrades over the authentic -man or woman lathe system, most significantly at the manufacturing of the rotary movement.
- Feed price is described as device’s distance travelled in the course of one spindle revolution.
Introduction to Capstan:
Capstan and Turret Lathe:
A capstan and turret lathe are used to manufacture any number of identical work pieces in less time. These lathes are the next step in the evolution of engine lathes. Pratt and Whitney invented the capstan lathe for the first time in 1860.
The capstan and turret lathe consists of:
1. Bed
2. Headstock with all gears
3. A saddle with a four-station tool post that can hold four different tools.
4. A tool-post attached to the carriage's back. It inverts the position of a parting tool. The tool post on the cross slide is manually indexed.
5. Instead of a tailstock, this machine has a hexagonal turret positioned on a slide that rests on the bed.
Working of Capstan and Turret Lathe
The turret's six faces can each contain six or more different tools. Each tool can be brought in line with the lathe axis in a regular succession by automatically indexing the turret. Collets or chucks are used to hold the work pieces.
The Capstan or Ram Type Lathe
The figure depicts a capstan or ram type lathe. The hexagonal turret is carried on ram or a short slide by this mechanism.
The ram is mounted longitudinally on a saddle that is attached to the lathe bed ways. This machine is made of lightweight materials and is ideal for processing smaller diameter bars.
The tools are installed on the hexagonal turret's six faces and the square turret's six faces.
When the ram moves from left to right, the feeding movement is obtained. The turret indexes automatically when the ram is shifted backwards. The tool mounted on the next face then goes to work.
Adjustable stops govern the longitudinal and cross feed movement of the turret saddle and cross slide.
Different tools set at different stations are enabled by these stops. To move by a preset amount in order to perform different operations on repeating work pieces without having to measure the length or diameter of the machined surface in each case.
A capstan and turret lathe's unique properties allow it to execute a variety of tasks, including:
1. Turning.
2. Drilling.
3. Boring.
4. Cutting the thread
5. Reaming.
6. Necking.
7. Chamfering.
8. Cutting-off.
9. And a slew of other procedures performed in a predictable order to generate a huge number of similar components in a short period of time.
The Turret or Saddle Type Lathe
Another sort of lathe machine is the turret lathe. It is used for repetitive production of same duplicate parts, which by the nature of their cutting process are usually replaceable. The hexagonal turret as depicted in the illustration.
It is directly installed on a saddle, and the entire unit slides back and forth on the bed ways to apply feed.
The construction of this sort of turret lathe machine is more substantial. It's especially well-suited to chucking and larger-diameter bar work. Longer work pieces can be fed into the machine than a capstan lathe can.
Principle Parts of Capstan and Turret Lathes
Except for the turret, the turret lathe has essentially the same components as the engine lathe. It also has a complicated mechanism that makes it appropriate for large production tasks.
Following are the main parts of a capstan and turret lathe,
- Bed.
- Headstock.
- Cross slide and saddle.
- The turret saddle and auxiliary slide.
1. Bed
The carriage and turret saddle are installed on the bed, which is a large box-like casting with precise guide ways. Under heavy-duty conditions, the bed is designed to ensure strength, rigidity, and alignment stability.
2. Headstock
The headstock is constructed from massive castings. It's at the far end of the bed, on the left. The following are the various types of headstocks used in capstan and turret lathes:
- Step cone pulley driven headstock.
- Direct electric motor driven headstock.
- All geared headstock.
- Preemptive or preselected headstock.
1. Step Cone Pulley Driven Headstock
Small capstan lathes are fitted to this style of headstock, which is the most basic. When the lathe is used to process work pieces with a tiny and nearly constant diameter. Only three or four steps of the pulley can meet the machine's requirements.
Unlike an engine lathe, where the machine spindle may be started, stopped, and reversed by pushing a foot pedal, the machine requires a unique countershaft.
2. Electric Motor Driven Headstock
Both the machine's spindles and the motor's armature shaft are one and the same in an electric motor-driven headstock.
Direct control of the motor allows for any speed differential or reversal. Three or four are available, and the machine is designed for work pieces with smaller diameters that revolve at high speeds.
3. All Geared Headstock
The headstocks on larger lathes are geared, and a separate mechanism is used to change the speed by actuating levers. The machine was not stopped while the speed was changed.
4. Preemptive or Preselected Headstock
It's an all-geared headstock with features like speedy stopping, starting, and speed charging for various tasks, as well as the ability to push a button or pull a lever.
The spindle speed must alter for different activities and for turning different diameters. The next operation's needed speed is chosen ahead of time. And the speed-changing lever has been set to the desired setting.
A button or a lever is simply actuated when the initial operation is completed. And, without stopping the machine, the spindle begins rotating at the set speed for the second operation. Friction clutches have an impact on this innovative mechanism.
5. Cross-Slide and Saddle
Hand-operated cross slides are secured on the lathe bed at the desired position in small capstan lathes. Larger lathes and heavy-duty turret lathes are frequently supplied with two carriage configurations.
- Conventional type carriage
- Side hung type carriage
1. The Conventional Type Carriage
The traditional carriage spans the distance between the front and back bed-ways. It also has four station tool posts in the front and one rear tool post at the back of the cross slide.
2. The Side-hung Type Carriage
The saddle rides on the top and bottom guide ways on the front of the lathe bed on the side-hung type carriage, which is usually equipped with heavy-duty turret lathes. The design allows for the swinging of a bigger diameter work piece without the cross-slide interfering. Hand or power feeding can be used to feed the saddle and cross slide longitudinally or across.
Stop-bars or shafts can be used to control the longitudinal movement of each tool. It's positioned against the bed's and carriage's halt. These stops are placed such that each tool feeds into the work to the desired length, allowing the job to be duplicated without having to check the machining length for each operation.
These act as a dead-stop for small head-operated tool movement to complete the cut after stopping the first trip out the feed. To synchronize with the tool's indexing, the stop bars are indexed by hand.
The tools are fixed on the tool post, and the correct heights are achieved with the help of a rocking or parking piece.
The Turret Saddle and Auxiliary Slide
The turret saddle spans the gap between two bed-ways in a capstan lathe. Furthermore, the top face is precisely cut to serve as a bearing surface for the auxiliary slide. On the lathe bed-ways, the saddle is adjusted and clamped in the desired position. The auxiliary slide holds the hexagonal turret.
In a turret, the top of the saddle is directly attached on the turret, and any movement of the saddle affects the turret. The turret's mobility can be controlled by hand or by power. The turret is a tool storage with a hexagonal design that can accommodate six or more tools.
Each turret face is meticulously machined. Each face has precisely bored holes through the center OD to accommodate shanks of various tool holders.
When aligned with the headstock spindle, the center line of each hole aligns with the lathe's axis. In addition to these holes, each face of the turret has four tapped holes for fastening various tool holding attachments.
There is a clamping mechanism in the center of the turret on the top of it that locks the turret to the saddle.
The saddle is equipped with six stop bars.
For duplicating work pieces, this restricts the movement of each tool installed on each face of the turret to a set amount.
The turret is moved away from the spindle nose when one operation is accomplished. A device on the bed and in the turret saddle automatically indexes the turret. So that the tool on the following face is parallel to the work.
Difference between Capstan and Turret Lathe Machine:
The following 17 Point is the Difference between Capstan and Turret Lathe Machine:
Sr. No. | Capstan Lathe Machine | Turret Lathe Machine |
1. | The capstan lathe is a light-duty equipment that can be used for a variety of tasks. | This is a powerful machine. |
2. | In The tool head is mounted in the ram, and the ram is positioned on the saddle of the capstan lathe. | The saddle is where the tool head is affixed. |
3. | To This ram movement necessitates the provision of nourishment. | It is necessary to supply feed saddle movement here. |
4. | Because ram movement is limited for small type work pieces, this is employed. | And because the ram movement is not limited or set, this one is employed for larger work pieces. |
5. | Because of the light construction, this is a quick form of work. | This is a machine that works slowly. |
6. | A Because of the non-rigid design, a hefty cut is not possible. | In Turret lathe, turret lathe, turret lathe Because to the robust design, heavy cutting is not possible. |
7. | It is a horizontal lathe of some sort. | However, this one can be used for both horizontal and vertical tasks. |
8. | Crosswise movement of the turret head is not possible. | The turret head can be moved crosswise here. |
9. | In The turret head on the capstan lathe is easy to move because it glides over the ram. | It It's tough to move the turret head and saddle at the same time. |
10. | To The collect is used to retain the workpiece. | A jaw chuck is utilized to hold the workpiece here. |
11. | This machine can only machine work pieces up to 60mm in diameter. | This machine can only machine work pieces with a diameter of 60mm. |
12. | This lathe machine has a smaller lengthwise movement. | There's more. |
13. | The head of the turret can be moved manually. | The head of the turret cannot be moved manually. |
14. | Because there is a certain amount of feed and cut depth, machining is constrained compared to a turret lathe. | Machining can be improved by increasing the feed rate and cutting depth. |
15. | Construction is lighter. | The construction is substantial. |
16. | There is no such facility as a turret lathe here. | In The ability to move the turret at a right angle to the lathe axis is provided by a turret lathe. |
17. | Both can be mass-produced in large quantities. | Both can be mass-produced in large quantities. |
Shaper: Introduction, types, specification, description of machines, cutting parameters
Introduction:
- A shaper is a sort of gadget device that makes use of linear relative movement among the work piece and a single-factor slicing device to gadget a linear tool path.
- Its reduce has similarities to that of a lathe, besides that it is (archetypally) linear in preference to helical.
- A single-factor slicing device is rigidly held with inside the device holder, that's established at the ram. The paintings piece is rigidly held in a vice or clamped at once at the desk.
- The desk can be supported on the outer quit. The ram reciprocates and the slicing device, held with inside the device holder, actions backwards and forwards over the paintings piece.
- In a fashionable shaper, slicing of fabric takes location at some point of the ahead stroke of the ram and the go back stroke stays idle. The go back is ruled via way of means of a short go back mechanism.
- The intensity of the reduce increments via way of means of transferring the work piece, and the work piece is fed via way of means of a pawl and ratchet mechanism.
- The work piece mounts on a rigid, field-fashioned desk in the front of the gadget. The top of the desk may be adjusted to healthy this workpiece, and the desk can traverse sideways under the reciprocating device, that's established at the ram.
- Table movement can be managed manually, however is commonly superior via way of means of an automated feed mechanism performing at the feeds crew. The ram slides backward and forward above the paintings.
- At the front quit of the ram is a vertical device slide that can be adjusted to both facet of the vertical aircraft alongside the stroke axis.
- This device-slide holds the clapper field and device post, from which the device may be located to reduce a straight, flat floor at the pinnacle of the workpiece.
- The device-slide allows feeding the device downwards to deepen a reduce.
- This flexibility, coupled with the usage of specialized cutters and device holders, allow the operator to reduce inner and outside tools teeth.
Types:
1. Bases on the Type of Driving Mechanism
Following are the distinct varieties of shaper machines primarily based totally at the sort of using mechanism
1. Crank Type Shaper Machine
These are very not unusual place varieties of shaper machines, that's the usage of to keep the workpiece at the desk.
The device is reciprocating in movement same to the duration of the stroke favored even as the paintings is clamped in role on an adjustable desk. In construction, the crank shaper employs a crank mechanism to alternate the round movement of a massive equipment called “bull equipment” integrated with inside the device to the reciprocation movement of the ram.
It makes use of a crank mechanism to transform the round movement of the bull equipment into the reciprocating movement of the ram. The ram includes a device head at its cease & offers the reducing movement.
2. Gear Type Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the ram is reciprocating. The ram is affecting because of reciprocating movement with the rack and pinion.
The rack enamel are reduce without delay under the ram mesh with the spur equipment. The pace and the route wherein the device will traverse rely on the quantity of gears with inside the equipment train. This sort of shaper device isn't broadly the usage of in any industry.
3. Hydraulic Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the reciprocating movement of the ram is supplied with the aid of using the hydraulic mechanism. The Hydraulic shaper makes use of the oil beneath excessive strain.
The cease of the piston rod is hooked up to the ram. The excessive-strain oil first acts on one aspect of the piston after which on the opposite inflicting the piston to reciprocating and the movement is transmitted to the ram.
The major benefits of this sort of shaper device are that the reducing pace and pressure of the ram pressure are constant.
From begin to cease of the reduce without making noise and operates quietly.
2. Based on Ram Travel
Following are the distinct varieties of shaper machines primarily based totally on ram travel
1. Horizontal Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the ram is reciprocating. The ram conserving the device on a horizontal axis and reciprocate.
This sort of shaper is the usage of for the manufacturing of flat surfaces, outside grooves, keyways, etc.
2. Vertical Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the ram reciprocating with inside the vertical plane
. In this, the desk holds the workpiece. Vertical shapers perhaps crank driven, rack-driven, screw-driven, or hydraulic power-driven.
The vertical shaper could be very handy for machining inner surfaces, keyways, slots, or grooves. The workpiece can flow in any given route including the cross, longitudinal or rotary movements. This sort of shaper is appropriate for machining inner surfaces, slots & keyways.
3. Based on the Table Design
Following are the distinct varieties of shaper machines primarily based totally at the desk design
1. Standard Shaper Machine
In this sort of shaper device, the desk has handiest movements, vertical and horizontal, to provide the feed. That’s why it's far called a well-known shaper device. Here the desk isn't assisting on the outer cease.
2. Universal Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, further to the 2 moments i.e. vertical and horizontal, the desk may be transferring on a willing axis, and additionally it could swivel on its personal axis.
Since the workpiece hooked up at the may be adjusted in distinct planes, the shaper is appropriate for a distinct sort of operations and is given the name “Universal”. This sort of shaper is generally the usage of the device room works.
4. Based on Cutting Stroke
Following are the distinct varieties of shaper machines primarily based totally on reducing stroke
1. Push reduce Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the steel is eliminated with inside the ahead movement of the ram. These are generally used varieties of shaper machines.
2. Draw reduce Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the steel is eliminated with inside the backward movement of the ram. In this shaper, the device is constant with inside the device head with inside the opposite route in order that it offers the reducing movement with inside the opposite stroke of the ram.
Specifications of shaper machine:
Technical Specification of Shaping Machine
Model | JF-SH-24 and 26 | JF-SH-30 | JF-SH-32 | JF-SH-36 | JF-SH-42 |
Capacity |
|
|
|
|
|
Length of ram stroke | 610 mm / 660 mm | 762 mm | 815 mm | 915 mm | 1070 mm |
Length of ram | 1325 mm | 1400 mm | 1536 mm | 1640 mm | 2135 mm |
Length X width of ram bearing | 995 mm x 280 mm | 995 mm x 280 mm | 1145 mm x 300 mm | 1145 mm x 300 mm | 1600 mm x 405 mm |
Max / min Distance from table to ram | 485 mm / 109 mm | 485 mm / 109 mm | 521 mm / 140 mm | 521 mm / 140 mm | 521 mm / 140 mm |
Table |
|
|
|
|
|
Working surface of table | 610 mm x 330 mm | 762 mm x 370 mm | 810 mm x 387 mm | 915 mm x 387 mm | 1050 mm x 562 mm |
Max. Horizontal table travel | 665 mm | 670 mm | 762 mm | 865 mm | 1070 mm |
Max. Vertical table travel | 432 mm | 435 mm | 381 mm | 381 mm | 457 mm |
Angular movement of table | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. | Fix | Fix | Fix |
Tool Head |
|
|
|
|
|
Max. Tool shank size | 38 mm x 21 mm | 38 mm x 21 mm | 38 mm x 21 mm | 38 mm x 21 mm | 38 mm x 25 mm |
Max. Vertical travel of tool slide | 152 mm | 152 mm | 152 mm | 228 mm | 305 mm |
Max. Swivel of tool head | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. |
Speeds & feeds |
|
|
|
|
|
Diameter of clutch pulley | 311 mm | 311 mm | 405 mm | 405 mm | 405 mm |
Number of ram speeds / strokes | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
Range of ram strokes per minute | 12-72 | 12-72 | 12-67 | 12-67 | 10-60 |
Range of table feeds / stroke | 0.22 – 0.88 | 0.22 – 0.88 | 0.22 - 0.88 | 0.22 – 0.88 | 0.22 – 0.88 |
Tool head feed | Hand feed | Hand feed | Hand feed | Hand feed | Hand feed |
Electric equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
Main motor drive 960 rpm | 3 hp | 3 hp | 5 hp | 5 hp | 7.5 hp |
V belt section | B – 57 | B – 58 | b-72 | b-72 | b-85 |
Motor starter | 5 amp | 5 amp | 15 amp | 15 amp | 15 amp |
Description:
Shaper Machine Parts:
Shaper Machine includes following components:
- Base
- Column Table
- Cross rail
- Ram
- Clapper Box
- Elevating Screw
- Shaper Machine
Let’s recognize one with the aid of using one, Base: The base is the maximum essential a part of the shaper as it holds all of the hundreds of the machine. It is made of solid iron. It absorbs vibration and different forces that arise even as acting shaping operations.
Column: The column is established at the base. It is likewise made of solid iron. Column helps the ram this is transferring ahead and backward for operation. It additionally acts for masking the power mechanism.
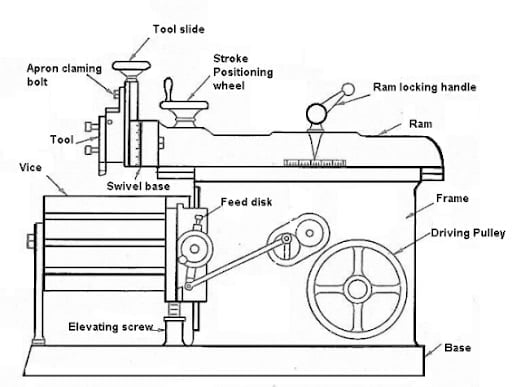
Table: It is established at the saddle. It is likewise one of the essential components of the machine. The desk may be moved crosswise with the aid of using rotating the cross feed rod and additionally for vertical with the aid of using rotating the raising screw. It is a box-like casting with an as it should be machined facet and pinnacle surfaces. These surfaces having T-Slots for clamping the work. In heavier kind shaper machines, the desk clamped with desk assist to make it extra rigid.
Cross rail: It is likewise established at the column on which the saddle is established. The vertical motion and Horizontal motion is given to the desk with the aid of using elevating or decreasing the go rail the use of the raising screw and with the aid of using transferring the saddle the use of the go feed screw.
Ram: The Ram reciprocates and it includes the device head wherein unmarried factor slicing device is attached. The device head is with inside the clapper box, which reasons slicing movement simplest in an ahead stroke of the ram. The feed or intensity of reduce of the device is given with the aid of using down feed screw.
Shaper Machine Working:
In short, the shaper works at the precept of the Quick go back movement mechanism. Let’s recognize in intensity, Shaper Machine As you could see the above diagram of Shaper machine, the device is preserve with the aid of using Ram and work piece is constant over desk.
When we turn on the electricity the ram reciprocates with recognize to the desk meaning the slicing device cuts work piece cloth with inside the ahead route and while transferring go back there may be no reduce.
The slicing system take region at low velocity of ram and go back stroke take region at excessive velocity. With using hand transverse wheel we are able to do up and down of the desk.
Cutting parameters:
The shaper is a reciprocating system device (see fig.1) supposed to provide flat surfaces (like horizontal, vertical, or willing surfaces).
Generally, the shaper can produce flat floor via way of means of the usage of brief go back mechanism. Modern shapers can generate contoured floor.
The steel operating shaper became advanced via way of means of James Nesmith an, Englishman in 1836.
Shaper Operation: Cutting Gears/Spines Machining irregularity curved floor Machining Horizontal/Vertical Surface Machining Angular Surface Machining V/ Keyway in block A shaper operates via way of means of shifting a hardened slicing device ahead and backwards throughout the work piece.
On the go back stroke, Tool is lifted clean of the work piece, decreasing the slicing motion to at least one course only.
By adjusting of ram and mechanism, stroke can be adjusted and stroke duration also can be adjusted.
It movements quicker at the go back (non-slicing) stroke than at the ahead (slicing stroke). This motion is through a slotted hyperlink or Whitworth hyperlink brief go back mechanism.
Photographic view of shaper system Material and method Aluminum alloy 6061 is one of the maximum drastically used of the 6000 collection aluminum alloys.
It is an in general warmth treatable extruded alloy with medium to excessive power capabilities.
Aluminium | 98.8 |
Magnesium | 0.8-1.2 |
Silicon | 0.4-0.8 |
Iron | Max 0.7 |
Copper | 0.15-0.4 |
Zinc | Max 0.25 |
Titanium | Max 0.15 |
Manganese | Max 0.15 |
Chromium | 0.04-0.35 |
Others | 0.05 |
Key Takeaways:
- Each turret face is meticulously machined. Each face has precisely bored holes through the center OD to accommodate shanks of various tool holders.
- Its reduce has similarities to that of a lathe, besides that it is (archetypally) linear in preference to helical.
- These are very not unusual place varieties of shaper machines, that's the usage of to keep the workpiece at the desk.
Quick Return Mechanism: Definition, Types, Working Principle, Applications, Advantages, Disadvantages:
A quick return motion mechanism is used in the shaper and slitter machine in which the circular motion is converted into reciprocating motion so that the slider moves forward and backwards. The cutting process occurs in the forward motion, but there is no corresponding cutting in the reverse direction.
- Quick Return Mechanism Types:
Quick return mechanisms come in three varieties:
- Whitworth Quick Return mechanism
- Crank and Slotted Link Mechanism and
- Hydraulic Drive
- Whitworth Quick Return Mechanism:
The oscillatory motion is created by converting the rotating motion. The bull gear is utilized in this device, which features a crank pinion.
The connecting rod connects the pin at one end to the ram at the other end of the connecting rod, which slides over the crankpin and into the slot of a crank plate.
The pinion is driven by the electric motor shaft, which rotates the gear. The bull gear now rotates in tandem with the crankpin, and the sliding block moves into the crank plate's groove.
As a result of this operation, the connecting rod causes the ram to travel up and down.
- Crank and Slotted Link Mechanism:
Whitworth devised this system in the 1800s. A slider, crank, fixed link, slotted lever, connecting rod, and ram make up the mechanism.
The slider and fixed link are connected to the crank. When the cranks begin to rotate, the connecting rod pushes the ram forward and backward.
From rotational motion, the motion is translated to linear motion here.
Please see the diagram for a better understanding.
Crank and slotted link mechanisms are commonly employed in shaping machines such as slitters and shapers to produce flat surfaces on work pieces.
In this mechanism, the return stroke is substantially faster than the forward stroke.
- Hydraulic Drive:
The hydraulic drive has a reciprocating piston inside the hydraulic cylinder. Between the ram and the piston lies the piston rod. As a result, the piston reciprocates with the ram.
There are two entries at the cylinder's end, as shown in the diagram. A control valve with four passages is installed below it.
The remaining two entries from the cylinder to the control valve are connected through a reservoir.
Quick Return Mechanism Working Principle:
There are four links in the diagram, and they are Slider, Crank, Frame, and Slotted Lever. It is also linked by a pair, which are as follows:
- Frame and Slotted lever: Changing the Pair
- Now Frame and Crank: Changing the Pair
- Crank and Slider: Changing the Pair
- Now Slider and Slotted lever: Sliding Couple
- There are three turning Pairs and one sliding pair. It is also known as the Inversion of the Single slider crank chain mechanism. The connecting rod is fixed here.
1. The slider is free to slide in the slotted lever, and the slotted lever's upper end is linked to the shaper machine's ram by a linkage.
2. At points A and B, the crank and slotted lever are attached to the frame.
3. The crank and slotted lever are connected to each other via a slider.
When the power is turned on, the crank begins to rotate, and the motion is transferred to the slider, which is fitted inside the slotted lever and therefore begins to oscillate.
Now, when the ram moves ahead, it creates an angle of beta, which is registered, and it creates an angle of alpha, which is also documented.
The beta angle is greater than the alpha angle, as shown in the diagram. As a result, cutting strokes take longer than returning strokes.
Applications of Quick Return Mechanism:
These are the following applications of Quick return mechanism:
1. It is used to flatten the workpiece in the shaper machine.
2. The same machine is utilized in the Slitter and Planer.
3. It’s also found in the Screw press, the Mechanical Actuator, and the Rotary Internal Combustion Engine.
Advantages of Quick Return Mechanism:
These are the advantages of Quick return mechanism:
1. The procedure is fully automated.
2. The mechanism's construction isn't overly sophisticated.
3. It can cut, flatten, and slot the workpiece, among other tasks.
4. Because of the quick return stroke, the idle time is reduced.
Disadvantages of Quick Return Mechanism:
Disadvantages of Quick return mechanism are:
1. Because there is no contact with the work during the returning stroke, no cutting occurs, and the process takes a long time to complete.
2. In comparison to the return stroke, the forward stroke takes a long time.
3. Performing procedures requires more electricity.
4. Friction exists between the slider and the piston.
5. Continuous Because of the heat generated inside the piston, it will not work, and wear and tear may occur.
6. Linkage balancing is a serious issue because this device is also related to links.
Table feed mechanism, attachments for shaper, work holding devices, shaper operations:
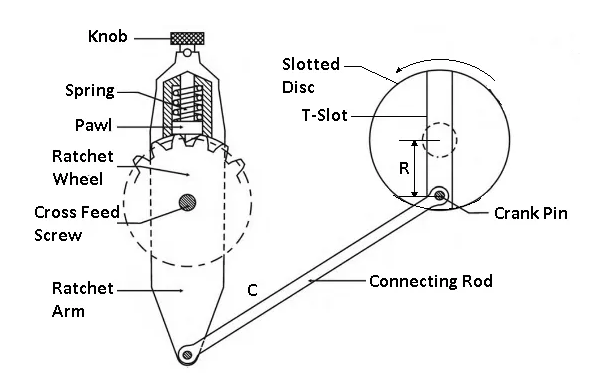
The computerized feed mechanism of the desk could be very simple.
This is finished via way of means of rotating a ratchet wheel, installed on the cross feed screw.
This permits a corresponding same rotation of the cross feed screw after every stroke.
Arrangement of parts It includes a slotted disc, which includes a T-slot, as proven with inside the figure.
In this slot is geared up an adjustable pin and to that is connected a connecting rod. The different cease of the connecting rod is hooked up to the decrease cease of the rocker arm of the pawl mechanism.
The rocker arm swings approximately the screw C, and at its higher cease includes a spring-loaded pawl, as proven. Working Note, that the decrease cease of the pawl is beveled on one side.
This association allows the electricity feed to perform in both direction, however the identical ought to be set to perform for the duration of the go back stroke only.
If otherwise, the mechanism can be subjected to intense stress. In a few ultra-modern kinds of shapers, can pushed feed mechanisms are supplied that are extra green and offer a much broader variety of feed.
Variation with inside the feed may be supplied via way of means of various the space R among the disc center and the center of the adjustable pin.
Larger the stated distance more can be the feed and vice versa.
The quantity of feed to take delivery of relies upon the kind of end required at the job.
For difficult machining, heavier cuts are hired, and thus, a rough feed is needed. Against this, a finer feed is hired in completing operations
. The slotted disc at its returned includes a spur tools that's pushed via way of means of the bull tools. As the disc rotates thru this tools the adjustable pin, being eccentric with the disc center.
This reasons the connecting rod to reciprocate. This, in turn, makes the rocker arm to swing approximately the screw C to transport the pall over one or extra teeth.
Thus transmit an intermittent movement to the cross feed screw which movements the desk.
Work holding devices:
Carriers and seize plates
These are in preferred used for riding the paintings piece whilst it's miles held in among facilities particularly head inventory and tail inventory. Carriers also are known as because the riding dogs. These are connected to the paintings piece with the aid of using the assist of setscrews. Where because the seize plates are pinned to the headstock.
Face plates
Faceplates are used for containing the ones paintings pieces, which can't be held each with the aid of using facilities and with the aid of using chucks.
The production of the faceplates could be very simple. It includes a middle bore and undeniable and radial slots thru the plate for facilitating the conserving of the paintings piece. The relevant bore has a radius same to that of the radius of the spindle of the lathe. And the apparent and radial slots offer a wholesome platform for containing the roles with the aid of using the usage of T-bolts and clamps.
Angle plates
These are used in conjunction with faceplates for preserving the given paintings piece horizontal i.e. perpendicular to the device used. Angle plates encompass faces, that are enormously machined, and those additionally have the supply of holes for the clean clamping of the paintings piece to it.
Mandrels
This sort of paintings conserving gadgets are hired for containing formerly drilled or bored hollow so that it will facilitate powerful outer floor machining.
The paintings is loaded over the mandrels among the facilities. The ends of the mandrels are made barely smaller than the authentic diameter. This is executed for powerful gripping of the mandrel with inside the chuck or every other conserving device. In preferred the fabric used for the producing of the mandrels is obvious carbon steel. Various styles of mandrels are in usage
Chucks
A chuck is a piece conserving device. It is used for containing paintings over a lathe machine, that's having massive duration and small diameter, and additionally for jobs, that are not able to mount on among the facilities i.e., head inventory and tail inventory facilities.
A chuck is likewise hired whilst a non-axis symmetrical item is to be installed over the lathe. The chucks are maximum typically used paintings conserving gadgets.
These are constant without delay to the spindle of the lathe with the aid of screws and an again plate. In preferred there are numerous styles of chuck, that have their personal significance and particular applications
Rests
Rest is a piece conserving device, that's used to keep the paintings piece whilst the paintings piece of very lengthy duration are to be held. In preferred whilst a protracted piece is to be held it could have without delay held then there arises deflection with inside the paintings piece due its personal weight. So to save you the deflection with inside the paintings piece rests of numerous sorts are used.
Shaper Operations:
1. Machining of horizontal floor
Crossfade to the desk is given to start with via way of means of hand till the reduce starts. After that electricity feed may be employed. After the reduce is finished, the gadget is stopped and the paintings inspected. If greater cloth is to be removed, the system is repeated till the preferred floor is obtained.
A unique precaution is needed in putting the device for horizontal slicing. The device must be held vertically in any such manner that it’s slicing side factors in a course barely far from the paintings, as moves, because of the slicing pressure, it'll pass far from the paintings in place of digging into it.
2. Machining Vertical Surfaces
A vertical reduce is made at the same time as machining the cease of a workpiece, squaring up a block or slicing a shoulder. The paintings is hooked up with inside the vice or without delay at the desk and the floor to be machined is cautiously aligned with the axis of the ram. A facet slicing device is ready at the device put up and the location and duration of stroke are adjusted.
The vertical slide is ready as it should be at 0 role. This is vital to allow the device to transport upwards and far from the paintings throughout the go back stroke. This prevents the facet of the device from dragging at the planed vertical floor throughout the go back stroke. The down–feed is given via way of means of rotating the down feed screw via way of means of hand.
The feed is set 0.25mm given on the cease of every go back stroke. Both roughing and completing cuts are completed to finish the job.
3. Machining Angular Surface
Shaper gadget operation - Machining of Angular Surface In this shaper gadget operation, an angular reduce is completed at any perspective apart from a proper perspective to the horizontal or to the vertical plane. The paintings is ready at the desk and the vertical slide of the teeth head is swiveled to the specified perspective both closer to the left or closer to proper from the vertical role.
The apron is then similarly swiveled far from the paintings in order that the device will clean the paintings throughout the go back stroke. The down feed is given via way of means of rotating the down feed screw. The angular floor also can be machined in a well-known shaper or via way of means of the usage of a well-known vice without swiveling the device head.
4. Machining Irregular Surfaces Machining of Irregular floor
A shaper also can produce a contoured floor, i.e. a convex or concave floor or a aggregate of any of the above surfaces. To manufacture a small contoured floor a forming device is used. If the curve is large, electricity go feed at the side of guide down feed is so adjusted that the wool will hint the specified contour. If the contour (workpiece shape) has too many ups and downs each the feeds are operated via way of means of hand.
For machining abnormal surfaces a spherical nostril device is used. For a shallow reduce the apron can be set vertical however if the curve is pretty sharp, the apron in swiveled closer to the proper or left far from the floor to be reduce.
The determine suggests the machining of a concave floor the usage of a spherical nostril device.
5. Cutting Slots and Keyways
Machining of External keyway with appropriate tools, a shaper can very effectively gadget slots or grooves on paintings or reduce outside keyways on shafts and inner keyways on pulleys or gears. For slicing slots or keyways on shafts and inner keyways on pulleys or gears.
For slicing keyways or slots a rectangular nostril device much like a parting device is used. External keyways are made on a shaft via way of means of first drilling a hollow on the blind cease of the keyway.
The diameter of the hollow must be 0.five to 0.8mm oversize than the width of the keyway and the intensity must be approximately 1.5mm large than the intensity of the keyway. This is critical to depart clearance at the device on the cease of the stroke.
The duration and role of stroke are cautiously adjusted in order that the stroke will terminate precisely on the clearance hollow.
The pace is decreased at the same time as slicing keyways. Internal keyways are reduce via way of means of protecting the device on a unique device holder in order that the device put up will now no longer hit in opposition to the paintings on the cease of the stroke.
The clapper block is locked with inside the clapper field to save you the device from lifting throughout the go back stroke. Lubrication is vital at the paintings to save you the slicing fringe of the device shape put on because of dragging.
6. Machining Splines or Cutting Gears
This varieties of shaper gadget operations completed via way of means of the usage of an index center, illustrated in a tools or similarly spaced splined can be reduce. The paintings is positioned among centers, and a spline is reduce much like the slicing of a keyway.
After the primary spline is reduce, the paintings is circled via a predetermined quantity via way of means of the usage of the index plate and index pin.
The outer edge of a tools clean is divided, and similarly spaced grooves are reduce the usage of an index plate having right hollow circles. While slicing tools a forming device is used.
Key Takeaways:
- The paintings is loaded over the mandrels among the facilities.
- The ends of the mandrels are made barely smaller than the authentic diameter.
- The paintings is ready at the desk and the vertical slide of the teeth head is swiveled to the specified perspective both closer to the left or closer to proper from the vertical role.
The principle of the planner machine is the concept of relative tool-work motions. Reciprocation of the tool or job and the slow, intermittent transverse feed motions are imparted to the job or tool by the fast straight path cutting motion.
Al the operations done in planning machines can be done in the shaping machine. Stroke length, larger size, and higher rigidity enable the planning machines to do more heavy-duty work on large jobs and their long surfaces.
It produces planes and flat surfaces with a single-point cutting tool. A planer machine is large and massive as compared to a shaper machine. The planer can do machining heavy workpiece, which cannot be done on a shaper surface.
Planer Machine is a machine in which unwanted material is cut from the workpiece to produce a flat surface on the workpiece. Unlike Shaper Machine, in this machine, more than one tool can be set and perform an operation.
Specifications & Description, Type of planner:
The photographic view usually suggests the overall configuration of planning machine. Like shaping machines, planning machines also are essentially used for generating flat surfaces in special planes.
However, the main variations among planning machines from shaping machines are: Though in precept each shaping and planning machines produce flat floor with inside the equal manner through the blended movements of the Generatrix and Directrix however in planing machine, in place of the device, the paintings piece reciprocates giving the short slicing movement and in place of the job, the device is given the gradual feed movement.
Compared to shaping machines, planning machines are an awful lot large and extra rugged and typically used for huge jobs with longer stroke duration and heavy cuts.
In planning machine, the paintings piece is hooked up at the reciprocating desk and the device is hooked up at the horizontal rail which, again, can pass vertically up and down alongside the vertical rails.
Planning machines are extra productive (than shaping machines) for longer and quicker stroke, heavy cuts (excessive feed and intensity of cut) feasible and simultaneous use of some of equipment.
As in shaping machines, in planning machines also;
- The duration and function of stroke may be adjusted
- Only unmarried factor equipment are used
- The short go back persists
- Form equipment are regularly used for machining grooves of curved section
- Both shaping and planning machines also can produce huge curved surfaces through the use of appropriate attachments.
Types of planner:
- Double housing planer
- Open facet planer
- Pit planer
- Edge planer
- Divided head planer
- Size and specification of planner ·
- Distance among columns ·
- Stroke duration of the planer ·
Radial distance among the pinnacle of the desk and the lowest maximum function of the go rail ·
Maximum duration of the desk ·
Power of the motor ·
Range of speeds and feed available ·
Open side planner:
The planer device is much like a shaper device. It supposed to provide aircraft and flat surfaces via way of means of a unmarried-factor slicing device. A planer device could be very massive and big as compared to a shaper device.
It is able to a machining heavy workpiece, which can't be suit on a shaper desk. In a planer, the paintings that's supported at the desk reciprocates over the desk bound slicing device and the feed is furnished via way of means of the lateral motion of the device.
In a shaper, the device that's installed upon the ram reciprocates.
And the feed is given via way of means of the crosswise motion of the desk.
Parts of Planer Machine
Following are the six predominant components of the planer device:
- Bed
- Table Housing or Column
- Cross rail
- Tool head
- Driving and
- Feed Mechanism
Bed
The mattress of a planer is a box-like casting having go ribs. It could be very massive in length and heavy in weight and it helps the column and all different shifting components of the device. The mattress is made barely longer than two times the duration of the desk in order that the whole duration of the desk can be moved on it.
Three or greater guide ways can be furnished on a completely massive extensive device for assisting the desk. The guide ways must be horizontal, actual and parallel to every different.
The approaches are well lubricated and in cutting-edge machines oil beneath stress is pumped into the distinctive components of the guide ways to make sure a non-stop and ok deliver of lubricants
Table
The desk helps the paintings and reciprocates at the side of the approaches of the mattress. The planer desk is a heavy square casting. T-slots are furnished at the whole duration of the desk in order that the paintings and paintings retaining gadgets can be bolted upon it. At every stop of the desk, a hole area is left which acts as a trough for gathering chips.
Long works also can relaxation upon the troughs. In a fashionable planer, the desk is made up of 1 unmarried casting however in a divided desk planer there are separate tables installed upon the bed ways. Hydraulic bumpers are equipped on the stop of the mattress to forestall the desk from overrunning giving cushioning effect.
In a few machines, if the desk overruns, a massive slicing device bolted to the bottom of the desk will take a deep reduce on a replaceable block connected to the mattress, soaking up the kinetic strength of the shifting desk.
Housing
The housings additionally known as columns or uprights are inflexible box-like vertical systems positioned on every aspect of the mattress and are mounted to the perimeters of the mattress. They are closely ribbed to soak up extreme forces because of slicing. The the front face of every housing is as it should be machined to offer precision approaches on which the go rail can be made to slip up and down for accommodating distinctive heights of paintings. Two aspect-tool heads additionally slide upon it. The housing encloses the Cross rail raising screw, vertical and cross feed screws for device heads, counterbalancing weight for the Cross rail, etc. These screws operated both via way of means of hand or strength.
Cross rail
The Cross rail is an inflexible box-like casting connecting the 2 housings. This production guarantees the tension of the device. The Cross rail can be raised or reduced at the face of the housing and may be clamped at any favored function via way of means of manual, hydraulic or electric clamping gadgets. The Cross rail whilst clamped must stay truly parallel to the pinnacle floor of the desk, i.e. it ought to be horizontal no matter its function. Usually, tool heads, are installed upon the Cross rail which might be known as railhead. The Cross rail has screws for vertical and cross feed of the tool heads and a screw for raising the rail. These screws turned around both via way of means of hand or via way of means of strength.
Tool-head
The device head of a planer is much like that of a shaper each in production and operation. The crucial components of a device head are:
Saddle Swivel base
Vertical Slide Apron
Clapper box
Clapper block
Tool post
Down feed screw
Apron clamping bolt, Apron swiveling pin Mechanism for go and down-feed of the device.
1. Standard or Double Housing Planer Machine
The fashionable or double housing planer is the maximum extensively used styles of planer device in workshops. A double housing planer has a protracted heavy base on which a desk reciprocates on correct guide ways.
Standard or Double Housing Planer
The duration of the mattress is little over two times the duration of the desk. Two big vertical housings or uprights are installed close to the center of the base, one on every aspect of the mattress. To make sure the tension of the structure, those housings are linked on the pinnacle via way of means of a solid iron member.
The vertical faces of the 2 housing are as it should be machined in order that horizontal Cross rail sporting device heads can also additionally slide upon it. The device heads which preserve the equipment are installed upon the Cross rail. These equipment can be feed both via way of means of the strength in cross rail or vertical course.
In addition to those device heads, there are different device heads which might be installed upon the vertical face of the housing. They also can be moved both in a vertical or horizontal course to use feed. The planer desk can be pushed both via way of means of mechanical or hydraulic gadgets.
2. Open side Planer Machine
An open side planer has a housing handiest on one aspect of the base. And the cross rail is suspended from the housing as a cantilever. This characteristic of the device permits the massive and extensive workpiece to be clamped at the desk and reciprocated over the slicing device.
One aspect of the planer being opened, massive and extensive jobs can also additionally undertaking out of the desk and reciprocate without being interfered via way of means of the housing. In a double housing planer, the most width of the task which may be machined is restricted via way of means of the gap among the 2 housing. As the unmarried housing has to soak up the whole load, its miles made extra-big to withstand the forces.
3. Pit Planer Machine
A pit kind planer is big in production. It differs from a regular planer. In this the desk is desk bound and the column sporting the cross rail reciprocates on big horizontal rails installed on each aspects of the desk.
This styles of planer device are appropriate for machining a completely massive paintings which can't be supported on a fashionable planer.
This device layout saves plenty of ground area. The duration of the mattress required in a pit kind planer is little over the duration of the desk.
Whereas in a fashionable planer the duration of the mattress is close to two times the duration of the desk.
The uprights and the cross rail are made sufficiently inflexible to soak up the forces even as slicing.
4. Edge or Plate Planer
The layout of a plate or aspect planer is definitely not like that of a regular planer. It is specifically supposed for squaring and beveling the rims of metal plates. Also used for distinctive stress vessels and shipbuilding works.
5. Divided Table Planer
This form of planer has tables at the mattress which can be reciprocated one after the other or together. This form of layout saves plenty of idle time even as placing the paintings. The putting in of a massive quantity of equal work pieces at the planning device desk takes pretty a protracted time. It can also additionally require as plenty time for putting in as can also additionally essential for machining.
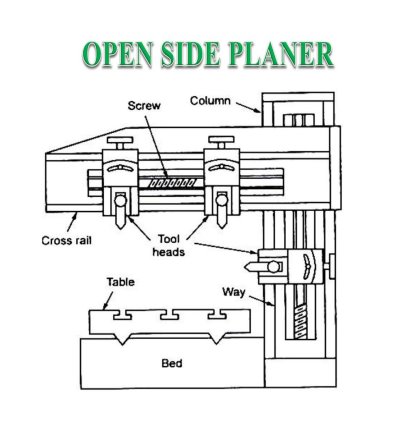
Pit Planner:
- It is rigid in construction. In this, the table is stationary and the column carrying the Cross rail reciprocates on massive horizontal rails mounted on both sides of the table.
- Pit Planer machine are suitable for machining a very large work which cannot be supported on a standard planer.
This varieties of planer device are appropriate for machining a completely massive paintings which cannot be supported on a preferred planer.
This device layout saves plenty of ground space. The duration of the mattress required in a pit kind planer is little over the duration of the desk. Whereas in a preferred planer the duration of the mattress is close to two times the duration of the desk.
The uprights and the cross rail are made sufficiently inflexible to absorb the forces whilst cutting.
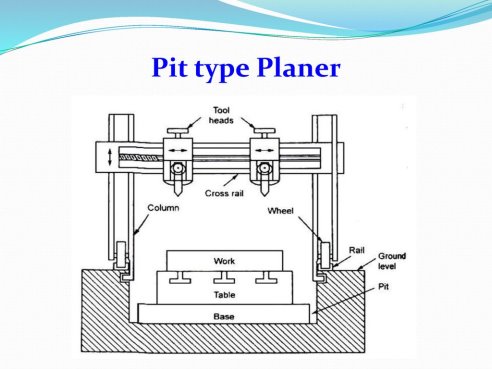
It has a huge creation wherein the desk is stored in a pit and its miles stationary. The column sporting the go rail reciprocates on a horizontal rail hooked up on each facets of the desk as you could see with inside the figure.
The desk of the planer is made a degree with the ground, in order that very heavy paintings may be loaded very easily.
The go rail consists of device heads and those may be moved horizontally and vertically to present the cut. The using screw is used for using the column through a motor.
Key Takeaways:
- It produces planes and flat surfaces with a single-point cutting tool. A planer machine is large and massive as compared to a shaper machine. The planer can do machining heavy workpiece, which cannot be done on a shaper surface.
- Compared to shaping machines, planning machines are an awful lot large and extra rugged and typically used for huge jobs with longer stroke duration and heavy cuts.
Open and Cross Belt Drive Mechanism:
Planer mechanism calls for supplying backward and forward movement to the gadget desk. Quick go back mechanism is likewise hired to present quicker motion all through the idle stroke.
Most planers deliver this machine of open and pass belt power for the short go back of the tables. This mechanism includes belts, one open and one pass working on unfastened and speedy pulleys. The essential riding shaft is supplied under the bed. One cease incorporates the pinion which meshes with the rack supplied below the desk of the gadget. Cross belt is used for ahead or reducing stroke and the open belt is for go back movement. Cross belt is hooked up to speedy pulley and open belt is hooked up to unfastened pulley and it permits sluggish motion of the desk all through ahead stroke. Trip puppies are installed at every cease of the desk imply the cease of the stroke and belt shifter shifts the belts to the unique pulleys. Now open belt is hooked up to the short pulley and the pass belt is hooked up to the unfastened pulley. This permits quicker motion and gives brief go back movement for the gadget desk.
Reversible Motor Drive Mechanism:
Electric motor drives the bull equipment thru equipment trains. Motor is coupled to D.C. Generator. When motor is started, generator substances energy to reversible motor. Reversible motor reasons the planer desk to move. At the cease of stroke, ride canine operates the transfer which reverses the course of desk. Speed of reducing stroke is decreased through regulating the sector modern-day of the generator.
Operations on Planer Machine
Planer operations are similar to those performed on shaper, with a difference that the work pieces are much larger in size.
Planer Operations:
• Planning horizontal surfaces.
• Planning vertical surfaces
• Planning angular surfaces / dovetails
• Planning curved surfaces
• Planning slots & grooves.
Planning Horizontal Surfaces:
• Fix the work properly on the table.
• Set the required cutting speed.
• Give required feed of the tool.
• Give suitable depth of cut for rough cuts.
• Finishing the job by giving less depth of cut.
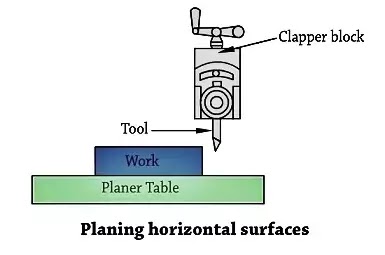
Planning Vertical Surfaces:
• Fix the job on the table firmly.
• Align the surface to be machined properly.
• Vertical slide is adjusted perpendicular to the table
• Swivel the apron away from the job.
• Switch on the machine.
• Rotate down feed screw by hand to give down feed.
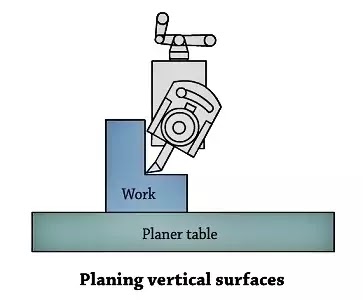
Planning angular surfaces:
• Main angular planning is to make dove tails & V grooves.
• Set the work on the table.
• Swivel the tool head to the required angle.
• Set apron away from work.
• Give down feed as per requirement.
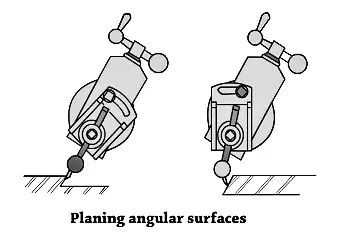
Planning Formed Surfaces:
• Fix up a square nose tool in tool head.
• Required form is obtained by feeding the tool simultaneously in both horizontal
And vertical directions.
• Give suitable depth of cut.
• Set apron away from work.
• This can also be done with the aid of a special fixture.
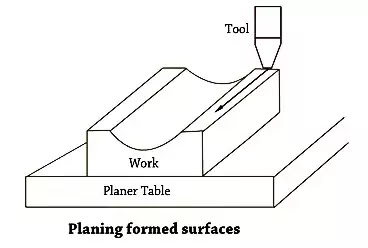
Planning Slots and Grooves:
• Fix up the job on the table suitably.
• Fix slitter tools in tool heads.
• Give feed using down feed screw.
• Move the tool by the required amount to get uniform slots / grooves.
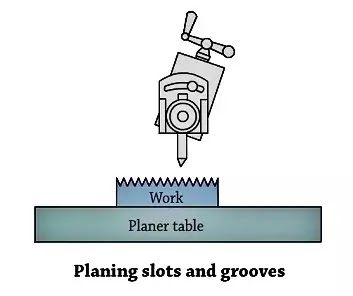
Cutting speed, Feed and Depth of Cut
Cutting Speed:
As in a shaper, the cutting speed of a planer is the rate at which the metal is removed during the forward cutting stroke. The formula, for shaper holds good for a planer also. This is expressed in m/min.
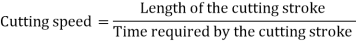
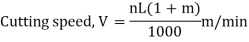
Where,
L = Length of cutting stroke in mm.
m = Ratio between return time to cutting time
n = No of double strokes of the ram/min.
Feed:
The feed in a planing gadget is the gap the device head travels at the start of every reducing stroke.
Depth of Cut:
It is the thickness of metallic eliminated in a single reduce and is measured through the perpendicular distance among the machined and non-machined floor. It is expressed in mm.
Machining Time:
If the reducing pace, feed, duration of reducing stroke, breadth of the activity and quantity of double strokes in step with minute for a planer operation are known, the machining time required for one entire reduce can be calculated through the use of the formula.

The ratio of cutting time to return time usually varies from 2: 1 to 4:1.
Feed mechanisms:
Feeding Mechanism Feed with inside the planer is given on the give up of the ahead stroke or at the start of the backward stroke. The feed is given via the motion of the device. There are sorts of feeds.
- Down feed
- Cross feed
Both those feeds may be given through rotating the feed screws through hand or energy. Down Feed
Down feed is given whilst machining the vertical or angular floor, the down feed screw of the device head is turned around and fed down.
Cross-Feed
Cross feeds are given whilst machining the horizontal floor of a piece keep on a desk.
Table Drive Mechanism For desk force mechanism, short go back mechanism are used. The following techniques are used to gain movement in backward stroke of planer desk and sluggish movement in ahead stroke.
Following are the numerous mechanisms used to run the desk.
- Open and Cross belt force
- DC Reversible Motor
- Hydraulic Drive Open and Cross Belt Drive
Small planners are pushed through open and go belt the usage of speedy and free pulleys.
But such planners can perform simplest at a one slicing velocity and a one go back velocity.
DC Reversible Motor
A DC reversible motor makes use of a motor which can alternate its velocity in line with the feed current.
Power from the motor is transmitted to the desk rack through a discount gearing and a malicious program that mashes with the desk rack. This approach is used to gain desk speeds with inside the range.
Hydraulic Drive Mechanisms for the hydraulic force of the shaper may be utilized in planers with a few modifications.
These force additionally consists of journey puppies alongside the desk to alter the stroke duration and alternate the placement of the desk.
These players aren't used for heavy responsibility paintings as the specified hydraulic energy could be very excessive and the force isn't smooth.
After elements of planer device now we are able to understand sorts of planer device in details.
Planner cutting tools, cutting parameters.
The planer handles paintings weighing as much as numerous tons. Both the shaper and planer typically reduce handiest in a single course, in order that the go back stroke is misplaced time.
However, the go back stroke is made at as much as two times velocity of the reducing stroke.
The Shaper
The shaper is a tremendously easy gadget. It is used pretty regularly with inside the tool room or for machining one or portions for prototype paintings. Tooling is easy, and shapers do now no longer constantly require operator interest whilst reducing. The horizontal shaper is the maximum not unusual place kind, and its foremost additives are proven beneath, and defined as follows:
Ram:
The ram slides to and fro in dovetail or rectangular approaches to transmit electricity to the cutter. The start line and the period of the stroke may be adjusted.
Tool head:
The tool head is mounted to the ram on a round plate in order that it is able to be circled for making angular cuts. The tool head also can be moved up or down through its hand crank for unique intensity adjustments.
Attached to the tool head is the tool holding segment. This has a device publish very just like that used at the engine lathe.
The block maintaining the device publish may be circled some levels in order that the cutter can be nicely placed with inside the reduce.
Clapper Box:
The clapper container is wanted due to the fact the cutter drags over the paintings at the go back stroke.
The clapper container is hinged in order that the reducing too] will now no longer dig in. Often this clapper container is routinely raised through mechanical, air, or hydraulic action.
Table:
The desk is moved left and proper, typically through hand, to place the paintings below the cutter whilst putting in. Then, both through hand or extra regularly routinely, the desk is moved sideways to feed the paintings below the cutter on the quit or starting of every stroke.
Saddle:
The saddle movements up and down (Y axis), typically manually, to set the tough function of the intensity of reduce. Final intensity may be set through the hand crank at the device head. Column: The column helps the ram and the rails for the saddle
Cutting Speed and Feed:
The reducing velocity of the hydraulic shaper is infinitely variable by way of hydraulic controls, as is the move feed. The opposite stroke is made quicker than the electricity stroke due to the smaller place with inside the go back facet of the cylinder, if a steady extent pump is used.
Another approach is to have the feel of fluid float accelerated to hurry up the go back stroke. Speed and feed on a hydraulic shaper are regularly managed through easy dials. Speed is examine at once in ft according to minute and feed is examine at once in decimal inches.
The reducing velocity stays almost steady thru the total stroke.
Vertical Shapers
The vertical shaper, every so often referred to as a Blotter, has a vertical ram, with desk and saddle just like the horizontal shaper. If a rotary desk is established at the ordinary desk, some of slots may be made at pretty correctly spaced intervals. This gadget can paintings either outdoor or interior a part, furnished that the indoors beginning is bigger than the device head.
The Planer
A planer makes the equal sorts of cuts as a shaper. However, it's far a production-- kind gadget for sure sorts of paintings. It can gadget any flat or angular floor, along with grooves and slots, in medium and huge sized work pieces.
Typical paintings could be gadget beds and columns, marine diesel engine blocks, and bending plates for sheet-steel paintings.
These elements are typically huge iron castings or metal elements and can weigh some hundred kilos or numerous tons. The maximum often used form of planer is the double-housing planer.
Frame:
The body is largely heavy columns mounted collectively on the pinnacle with a huge bracing segment and mounted at the lowest to the gadget mattress. This creates a totally strong, inflexible shape with a purpose to deal with heavy hundreds without deflection.
Cross rail:
The cross rail is likewise a heavy container, or comparable construction. It slides up and down on V- or flat approaches, managed through hand or through electricity-operated screws.
These cross rails are so heavy that they're counterweighted, with either solid iron weights or hydraulic cylinders, just so they'll be moved without difficulty and placed correctly. After being placed, they're clamped in place. Railheads: The railheads may be moved left or proper throughout the cross rail, every managed through a separate lead screw, which may be grew to become through hand however typically through electricity feed.
The railhead may be circled, and vertically adjusted for intensity of reduce, similar to the shaper heads. They actually have a clapper container (regularly with electricity lift) just like the shaper.
Side heads:
The side heads are independently moved up or down through hand or through electricity feed and also can be circled and moved in or out for intensity of reduce.
Table:
The desk is a heavy casting which consists of the paintings beyond the reducing heads. It runs on V- or flat approaches. The desk is pushed both through a totally lengthy hydraulic cylinder and through a pinion tools using a rack, that's mounted below the middle of the desk. The motor using the pinion tools is the reversible kind with variable velocity.
Key Takeaways:
- This permits quicker motion and gives brief go back movement for the gadget desk.
- Feeding Mechanism Feed with inside the planer is given on the give up of the ahead stroke or at the start of the backward stroke
- Hydraulic Drive Mechanisms for the hydraulic force of the shaper may be utilized in planers with a few modifications.
References:
1. Manufacturing Engineering & Technology, S. Kalpakjian & S.R. Schmid
2. Technology of Machine Tools, Krar &Oswald
3. Manufacturing Processes, M.Begman
4. Processes & Materials of Manufacture, R.Lindberg
5. Production Technology, HMT
Unit - 2
Lathe
Lathe: Introduction
Lathe Machine is the most widely used lathe machine and still, it is, in every workshop, this machine is present. The operation like Turning, facing, grooving, Knurling, threading and more, such operations are performed on this type of machine.
Centre lathe machine has all the parts such as bed, Saddle, headstock, and tailstock, etc. The headstock of an engine lathe is rigid and tailstock is moveable which is further used to support an operation like knurling. It can easily feed the cutting tool in both directions i.e. longitudinal and lateral directions with the help of feed mechanisms. Center Lathe machines are driven by the gear mechanism or pulley mechanism. It has three types of driven mechanisms, and those are Belt-driven, Motor-driven, gear head type.
The Centre Lathe is used to manufacture cylindrical shapes from a range of materials including; steels and plastics. Many of the components that go together to make an engine work have been manufactured using lathes. These may be lathes operated directly by people (manual lathes) or computer controlled lathes (CNC machines) that have been programmed to carry out a particular task. A basic manual center lathe is shown below. This type of lathe is controlled by a person turning the various handles on the top slide and cross slide in order to make a product / part.
The headstock of a center lathe can be opened, revealing an arrangement of gears. These gears are sometimes replaced to alter the speed of rotation of the chuck. The lathe must be switched off before opening, although the motor should automatically cut off if the door is opened while the machine is running (a safety feature).
The speed of rotation of the chuck is usually set by using the gear levers. These are usually on top of the headstock or along the front and allow for a wide range of speeds.
However, sometimes the only way to set the lathe to a particular speed is to change the gear arrangement inside the headstock. Most machines will have a number of alterative gear wheels for this purpose.
Construction of simple lathe:
i) Basic element:
A lathe machine tool consists of several parts like:
- Headstock
- Bed
- Tailstock
- Carriage
- Saddle
- Cross-slide
- Compound rest
- Tool post
- Apron
- Lead Screw
- Feed rod
- Chuck
- Main spindle
- Leg
1) Head Stock:
Head Stock is situated at the left side of the lathe bed and it is the house of the driving mechanism and electrical mechanism of a Lathe machine tool.
- It holds the job on its spindle nose having external screw threads and internally Morse taper for holding lathe center. And it is rotating at a different speed by cone pulley or all geared drive. There is a hole throughout spindle for handling long bar work.
- Head Stock transmits power from the spindle to the feed rod, lead screw and thread cutting mechanism.
Accessories mounted on headstock spindle:
- Three jaw chuck
- Four jaw chuck
- Lathe center and lathe dog
- Collect chuck
- Faceplate
- Magnetic chuck
A separate speed change gearbox is placed below headstock to reduce the speed in order to have different feed rates for threading and automatic lateral movement of the carriage. The feed rod is used for most turning operation and the lead screw is used for thread cutting operation.
2) Bed:
It is the base of the lathe machine. It is made of single piece casting of Semi-steel (Chilled Cast Iron). The bed consists of two heavy metal slides running lengthwise, with ways or ‘V’ formed upon them and rigidly supported with cross girths.
- It is sufficiently rigid and good damping capacity to absorb vibration.
- It prevents the deflection produced by the cutting forces.
- It supports the headstock, tailstock, carriage and other components of the lathe machine.
3) Tail Stock:
Tail Stock is situated on the right side above the lathe bed. It is used for:
- Support the long end of the job for holding and minimizes its sagging.
- It holds the tool for performing different operations like drilling, reaming, tapping, etc.
And it is also used for a small amount of taper for a long job by offsetting the tailstock
4) Carriage:
The carriage is used for support, guide and feed the tool against the job when the machining is done.
- It holds moves and controls the cutting tool.
- It gives rigid supports to the tool during operations.
- It transfers power from feed rod to cutting tool through apron mechanism for longitudinal cross-feeding.
- It simplifies the thread cutting operation with the help of lead screw and half nut mechanism.
It consists of:
- Saddle
- Cross-slide
- Compound rest
- Tool post
- Apron
It provides three movements to the tool:
- Longitudinal feed-through carriage movement
- Cross feed-through cross slide movement
- Angular feed-through top slide movement
5) Saddle:
Generally, it is made up of ‘H’ shaped casting and it has a ‘V’ guide and a flat guide for mounting it on the lathe bed guide ways.
6) Cross-slide:
It is assembled on the top of the saddle. The top surface of the cross-slide is provided with T-slot.
7) Compound rest:
It supports the tool post and cutting tool in its various positions. It can be swiveled at any desired position in the horizontal plane. It is necessary for turning angles and boring short tapers.
8) Tool post:
It is the topmost portion of the carriage and it is used to hold various cutting tools or tool holders. There are three types of tool post commonly used and those are:
- Ring and rocker tool post
- Square head tool post
- Quick change tool post
9) Apron:
An apron is a house of the feed mechanism. It is fastened to the saddle and hangover in front of the bed.
10) Lead screw:
A lead screw is also known as a power screw or a translation screw. It converts rotational motion to linear motion. Lead Screw is used for Thread Cutting operation in a lathe machine tool.
11) Feed Rod:
Feed rod is used to move the carriage from the left side to the right side and also from the right side to the left side.
12) Chuck:
Chuck is used to holding the work piece securely.
There are generally 2 types of chucks:
- 3 jaw self-cantering chuck
- 4 jaw independent chuck
13) Main Spindle:
The spindle is a hollow cylindrical shaft in which long jobs can pass through it.
It is designed so well that the thrust of the cutting tool does not deflect the spindle.
14) Leg:
Legs are carrying an entire load of a lathe machine tool and transfer to the ground. The legs are firmly secured to the floor by the foundation bolt.
Types:
There are varieties of alternative lathe varieties, temporary descriptions of that are given here.
Bench Lathes:
Because the name suggests, these lathes are placed on a bench or a table. They need low power, are sometimes operated by hand feed, and are accustomed machine little work pieces. Tool room lathes have high exactitude, enables the machining of components to shut dimensional tolerances.
Special-purpose Lathes:
These lathes are used for applications (such as railroad wheels, gun barrels, and rolling-mill rolls) with piece of work sizes as giant as 1.7 m in diameter by eight m long and capacities of 450 kilowatt
Tracer Lathes:
These lathes have special attachments that are capable of turning components with varied contours. Conjointly known as a duplicating lathe or contouring lathe, the cutting implement follows a path that duplicates the contour of a template, like a pencil following the form of a plastic stencil. However, operations generally performed on a tracer lathe are replaced mostly by numerical-control lathes and turning centers.
Automatic Lathes:
Lathes became more and more machine-controlled over the years; manual machine controls are replaced by varied mechanisms that modify machining operations to follow a definite prescribed sequence. In an exceedingly absolutely automatic lathe, components are fed and removed mechanically, whereas in semi-automatic machines, these functions are performed by the operator. (The cutting remains automatic.) Automatic lathes could have a horizontal or vertical spindle and are appropriate for medium- to high-volume production. Lathes that don't have tailstocks are known as chucking machines or checkers. They used for machining individual items of normal or irregular shapes and are either single- or multiple-spindle varieties. In another kind of automatic lathe, the bar stock is fed sporadically into the lathe and an area is machined and discontinue from the top of the bar stock.
Automatic Bar Machines:
Conjointly known as automatic screw machines, these machine tools are designed for high-production-rate machining of screws and similar rib components. All operations on these machines are performed mechanically with tools connected to a special turret. When every half or screw is machined to finished dimensions, the bar stock is fed forward mechanically through the outlet within the spindle then discontinue. Automatic bar machines are also equipped with single or multiple spindles. Capacities vary from 3- to 150-mm diameter bar stock. Long stock is supported by special fixtures because it enters the spindle hole.
Single-spindle automatic bar machines are like turret lathes and are equipped with varied cam-operated mechanisms. There are 2 forms of single spindle machines. In Swiss-type-automatic the cylindrical surface of the solid-bar stock is machined with a series of tools that move radially and within the same plane toward the piece of work. The bar stock is clamped near to the support spindle, that minimizes deflections thanks to cutting forces. These machine tools are capable of high-precision machining of small-diameter components. The opposite single-spindle machine (called the American type) is comparable to a tiny low automatic turret lathe. The turret is on a vertical plane, and every one motions of the machine parts are controlled by cams. Automatic bar machines are currently equipped with laptop numerical management, eliminating the employment of cams, and also the operation is programmed for a selected product.
Multiple-spindle automatic bar machines generally have from four to eight spindles organized in an exceedingly circle on an outsized drum, with every carrying a personal piece of work. The cutting tools are organized in varied positions within the machine and move in each axial and radial direction. Every half is machined little by little because it moves from one station to successive. As a result of all operations is meted out at the same time, the cycle time per half is reduced.
Turret Lathes:
These machine tools are capable of activity multiple cutting operations, comparable to turning, boring, drilling, thread cutting, and facing. Many cutting tools (usually as several as six) are mounted on the polygonal shape main turret, that is turned when every specific cutting operation is completed. The lathe sometimes includes a sq. Turret on the cross-slide, mounting as several as four cutting tools. The piece of work (generally an extended, spherical bar stock) is advanced a planned distance through the chuck. When the half is machined, it does discontinue by a tool mounted on the sq. Turret that moves radially into the piece of work. The rod then is advanced identical planned distance, and also the next half is machined. Turret lathes (either the bar kind or the chucking type) are versatile, and also the operations is also meted out either by hand, victimization the gate (capstan wheel), or mechanically. Once found out properly, these machines don't need extremely experienced operators.
Vertical turret lathes are available; they're additional appropriate for brief, significant work pieces with diameters as giant as 1.2 m. The turret lathe shown in figure is understood as a ram-type turret lathe-one during which the ram slides in an exceedingly separate base on the saddle. The short stroke of the turret slide limits this machine to comparatively short work pieces and lightweight cuts in each small- and medium-quantity production. In another vogue (called the saddle type), the most turret is put in directly on the saddle, that slides on the bed. The length of the stroke is proscribed solely by the length of the bed. This kind of lathe is made additional heavily and is employed to machine giant work pieces. As a result of the significant weight of the parts, saddle-type lathe operations are slower than ram type operations.
Computer-controlled Lathes:
Within the most advanced lathes, movement and management of the machine and its parts are achieved by laptop numerical control (CNC). These lathes typically are equipped with one or additional turrets and every turret are supplied with a spread of tools and perform many operations on totally different surfaces of the piece of work. Work piece diameters is also the maximum amount as one m. To require advantage of latest cutting-tool materials, computer-controlled lathes are designed to work quicker and have higher power obtainable compared with alternative lathes. They’re equipped with automatic tool changers (ATCs). Their operations are faithfully repetitive, maintain the required dimensional accuracy, and need less experienced labor (once the machine is about up). They’re appropriate for low- to medium volume production.
Mechanism and attachments for various operations:
To carry out distinctive lathe system operations on a lathe, the work piece can be supported and pushed via way of means of any individual of the subsequent strategies:
- Work piece held among centers and device pushed via way of means of companies and capture plates.
- Work piece hung on a mandrel that's supported among centers and pushed via way of means of companies and capture plates. Held and pushed via way of means of chuck with the alternative quit supported at the tailstock center.
- Held and pushed via way of means of a chuck or a faceplate or a perspective plate.
- The above strategies of conserving the paintings can be categorized beneath heading: Work piece held among centers.
- Work piece held via way of means of a chuck or some other fixtures. A lathe system is usually utilized in metalworking, steel spinning, woodturning, and glass working.
- The diverse operations that it could carry out encompass the subsequent: sanding, slicing, knurling, drilling, and deforming of gear which might be hired in growing items that have symmetry approximately the axis of rotation.
- Some of the maximum not unusual place merchandise of the lathe system are crankshafts, camshafts, desk legs, bowls, and candlestick holders.
- The first lathe system that changed into ever advanced changed into the -man or woman lathe system which changed into designed via way of means of the Egyptians in approximately 1300 BC.
- Primarily, there are matters which might be completed on this lathe system set-up.
- The first is the turning of the timber running piece manually via way of means of a rope; and the second one is the slicing of shapes with inside the timber via way of means of using a pointy device.
- As civilizations progressed, there were steady changes and upgrades over the authentic -man or woman lathe system, most significantly at the manufacturing of the rotary movement.
The manufacturing of the rotary movement consequently developed in keeping with the subsequent procedures: the Egyptians guide turning via way of means of hand; the Romans addition of a turning bow; the creation of the pedal with inside the Middle Ages; using the steam engines at some point of the Industrial Revolution; the employment of person electric powered vehicles with inside the nineteenth and mid twentieth centuries; and the contemporary of that's the adaption of numerically managed mechanisms in controlling the lathe
For the lathe system to characteristic and carry out its operations, diverse critical elements are included together.
These necessities elements make up the lathe system.
Machine specifications:
Machine tools are defined as machines used for carrying out the metal cutting processes and surface finish processes by removing the material from the work piece in the form of chips.
A lathe is one of the oldest & most important machine tools ever developed. The job to be machined is rotated & the cutting tool is moved relative to the job. That is why, it’s also called as “Turning Machine”. A Lathe was basically developed to machine cylindrical surfaces. But many other operations can also be performed on lathes. E.g.-facing, parting, necking, knurling, taper turning & forming. We also can perform operations of other machine tools on a lathe, e.g. Drilling, reaming, milling & drilling operation etc. lathe is called the mother of the entire machine tool family. The lathe can be defined as a machine tool which holds the work between two rigid & strong centers, or in a chuck or face plate while the latter revolves. The cutting tool is rigidly held & supported in a tool post & feed against the revolving work.
Planer and shaper:
Planning and shaping are similar operations, which differ only in the kinematics of the process. Planning is a machining operation in which the primary cutting motion is performed by the work piece and feed motion is imparted to the cutting tool. In shaping, the primary motion is performed by the tool, and feed by the work piece.
Milling
Milling is a process of producing flat and complex shapes with the use of multi-point (or multi-tooth) cutting tool. The axis of rotation of the cutting tool is perpendicular to the direction of feed, either parallel or perpendicular to the machined surface. Milling is usually an interrupted cutting operation
Since the teeth of the milling cutter enter and exit the work piece during each revolution.
Drilling
Drilling is a process of producing round holes in a solid material or enlarging existing holes with the use of multi-point cutting tools called drills or drill bits. Various cutting tools are available for drilling, but the most common is the twist drill.
Basis for selection of cutting speed:
1. Cutting velocity is described because the velocity (commonly in ft in keeping with minute) of a device while its miles slicing the paintings.
2. Feed price is described as device’s distance travelled in the course of one spindle revolution.
3. Feed price and slicing velocity decide the price of fabric elimination, strength requirements, and floor finish.
4. Feed price and slicing velocity are broadly speaking decided with the aid of using the fabric that’s being cut. In addition, the deepness of the cut, length and circumstance of the lathe, and stress of the lathe must nonetheless be considered.
5. Roughing cuts (0.01 in. To 0.03 in. Intensity of cut) for maximum aluminum alloys run at a feedrate of .1/2 inches in keeping with minute (IPM) to 0.02 IPM even as completing cuts (0.002 in. To 0.012 in. Intensity of cut) run at 0.002 IPM to 0.004 IPM.
6. As the softness of the fabric decreases, the slicing velocity increases.
Additionally, because the slicing device fabric will become stronger, the slicing velocity increases.
7. Remember, for every thousandth intensity of cut, the diameter of the inventory is decreased with the aid of using thousandths.
A lathe paintings slicing velocity can be described because the price at which a factor at the paintings circumference travels beyond the slicing device.
Cutting velocity is constantly expressed in meters in keeping with minute (m/min) or in ft in keeping with minute (ft/min.) enterprise needs that machining operations be finished as fast as possible; consequently modern slicing speeds ought to be used for the sort of fabric being cut.
If a slicing velocity is just too excessive, the slicing device side breaks down rapidly, ensuing in time misplaced recondition the device.
With too gradual a slicing velocity, time may be misplaced for the machining operation, ensuing in low manufacturing rates. Based on studies and trying out with the aid of using metal and slicing device manufacturers, see lathe slicing velocity desk beneath.
The slicing speeds for excessive velocity metal indexed beneath are encouraged for green steel elimination rates.
These speeds can be numerous barely to shift elements including the circumstance of the machine, the sort of paintings fabric and sand or difficult spots with inside the steel.
Feed and depth of cut:
1. Cutting velocity is described because the velocity (commonly in ft in keeping with minute) of a device while its miles slicing the paintings.
2. Feed price is described as device’s distance travelled in the course of one spindle revolution.
3. Feed price and slicing velocity decide the price of fabric elimination, strength requirements, and floor finish.
4. Feed price and slicing velocity are broadly speaking decided with the aid of using the fabric that’s being cut. In addition, the deepness of the cut, length and circumstance of the lathe, and stress of the lathe must nonetheless be considered.
5. Roughing cuts (0.01 in. To 0.03 in. Intensity of cut) for maximum aluminum alloys run at a feedrate of .1/2 inches in keeping with minute (IPM) to 0.02 IPM even as completing cuts (0.002 in. To 0.012 in. Intensity of cut) run at 0.002 IPM to 0.004 IPM.
6. As the softness of the fabric decreases, the slicing velocity increases. Additionally, because the slicing device fabric will become stronger, the slicing velocity increases.
7. Remember, for every thousandth intensity of cut, the diameter of the inventory is decreased with the aid of using thousandths. A lathe paintings slicing velocity can be described because the price at which a factor at the paintings circumference travels beyond the slicing device.
Cutting velocity is constantly expressed in meters in keeping with minute (m/min) or in ft in keeping with minute (ft/min.) enterprise needs that machining operations be finished as fast as possible; consequently modern slicing speeds ought to be used for the sort of fabric being cut.
If a slicing velocity is just too excessive, the slicing device side breaks down rapidly, ensuing in time misplaced recondition the device.
With too gradual a slicing velocity, time may be misplaced for the machining operation, ensuing in low manufacturing rates.
Based on studies and trying out with the aid of using metal and slicing device manufacturers, see lathe slicing velocity desk beneath.
The slicing speeds for excessive velocity metal indexed beneath are encouraged for green steel elimination rates.
These speeds can be numerous barely to shift elements including the circumstance of the machine, the sort of paintings fabric and sand or difficult spots with inside the steel.
The RPM at which the lathe must be set for slicing metals is as follows: To decide the RPM of the lathe even as appearing techniques on it:
The following are the lathe machine formula commonly used to calculate in turning operations:
Depth of Cut
Depth of cut = (d1 – d2)/2
The depth of cut (t) is the perpendicular distance measured from the machined surface to the uncut surface of the work piece. In a lathe machine, the depth of cut is shown as follows:
Where,
- d1 – diameter of the work piece surface before machining.
- d2 – diameter of the machined surface.
Another factor remaining fixed, the depth of cut changes inversely as the cutting speed. For general purpose, the ratio of the depth of cut to the feed varies from 10:1
The cutting speed (v) of a tool is the speed at which the metal is removed by the tool from the workpiece. In a lathe, it is the peripherical speed of the work past the cutting too
Time estimation for turning operations such as facing:
Facing is a turning operation wherein the work piece is machined to its middle.
It entails transferring the slicing device perpendicular to the work piece’s axis of rotation.
This operation may be finished at a steady floor pace (sfm, m/min.), that is recommended, or at a steady rotational pace (rpm), which isn't recommended.
Facing at a steady rpm decreases the slicing pace, due to the fact the diameter of the going through floor steadily decreases through the quantity of a feed in keeping with revolution.
The nearer a slicing device is to the middle of a work piece, the decrease the slicing pace. It processes 0 on the middle of a work piece.
A low slicing pace can purpose built-up edge.
Time required = Length of cut / Feed X RPM
Step turning, taper turning, threading, knurling:
Step turning:
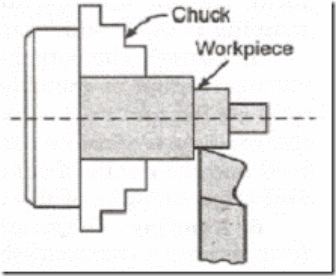
Step turning is a turning procedure wherein collection of steps having exclusive diameters is produced with the lathe gadget.
Procedure
- Fix the cylindrical work piece into the chuck and stable it nicely. Select the device and stable the device with inside the device submit.
- Bring the tailstock in advance and take a look at if the tooltip middle aligns with the middle of the lifeless middle.
- Adjust the device submit in order that most effective the reducing factor of the device comes in touch with the work piece.
- Set the rate of the spindle and route of rotation.
- Start the motor and take a look at if the work piece is rotating nicely and now no longer wobbling because it rotates.
- First, perform the going through operation via way of means of adjusting the device submit (rotate approximately 30-60 stages approx.) touching the tooltip to the face of the work piece, and use the pass feed spindle to provide intensity of reduce radial to the work piece.
- If the task is lengthy and slim then drill a hollow and makes use of the tailstock lifeless middle to help the work piece.
- Once going through operation is done, perform the turning operation in order that the work piece is flawlessly cylindrical.
- Then degree the diameter of the work piece, determine the step lengths and dia of the steps.
- Start the gadget, contact the tooltip to the flat round face of the task then mark the primary dia of the step. Bring the device radially out.
- Stop the gadget, take a Venire caliper and mark the step duration onto the task practice a few chalk in order that the mark is without problems seen whilst it begins off evolved rotating with inside the chuck.
- Then begin the gadget simply contact the tooltip on that mark, to have step one duration seen.
- Carry at the turning procedure as much as that marked duration from the quilt of the work piece to create step one, hold a watch at the device because the dia of the work piece reduces and is ready to attain the marked diameter at the flat round face of the work piece.
- Use hard reduce to take away most fabric then completing cuts may be given because the device processes marked diameter. Once step one is created.
- You may also word that on the nook of the step i.e. on the junction in which the small dia of the step meets the bigger dia has a few radius or wedge form which may be corrected via way of means of feeding the device to the wedge and getting rid of the fabric grade by grade till a great step is formed.
- Mark the second one dia and duration of the step and keep on the procedure till the preferred range of steps are formed.
Key Takeaways:
- This kind of lathe is made additional heavily and is employed to machine giant work pieces.
- As civilizations progressed, there were steady changes and upgrades over the authentic -man or woman lathe system, most significantly at the manufacturing of the rotary movement.
- Feed price is described as device’s distance travelled in the course of one spindle revolution.
Introduction to Capstan:
Capstan and Turret Lathe:
A capstan and turret lathe are used to manufacture any number of identical work pieces in less time. These lathes are the next step in the evolution of engine lathes. Pratt and Whitney invented the capstan lathe for the first time in 1860.
The capstan and turret lathe consists of:
1. Bed
2. Headstock with all gears
3. A saddle with a four-station tool post that can hold four different tools.
4. A tool-post attached to the carriage's back. It inverts the position of a parting tool. The tool post on the cross slide is manually indexed.
5. Instead of a tailstock, this machine has a hexagonal turret positioned on a slide that rests on the bed.
Working of Capstan and Turret Lathe
The turret's six faces can each contain six or more different tools. Each tool can be brought in line with the lathe axis in a regular succession by automatically indexing the turret. Collets or chucks are used to hold the work pieces.
The Capstan or Ram Type Lathe
The figure depicts a capstan or ram type lathe. The hexagonal turret is carried on ram or a short slide by this mechanism.
The ram is mounted longitudinally on a saddle that is attached to the lathe bed ways. This machine is made of lightweight materials and is ideal for processing smaller diameter bars.
The tools are installed on the hexagonal turret's six faces and the square turret's six faces.
When the ram moves from left to right, the feeding movement is obtained. The turret indexes automatically when the ram is shifted backwards. The tool mounted on the next face then goes to work.
Adjustable stops govern the longitudinal and cross feed movement of the turret saddle and cross slide.
Different tools set at different stations are enabled by these stops. To move by a preset amount in order to perform different operations on repeating work pieces without having to measure the length or diameter of the machined surface in each case.
A capstan and turret lathe's unique properties allow it to execute a variety of tasks, including:
1. Turning.
2. Drilling.
3. Boring.
4. Cutting the thread
5. Reaming.
6. Necking.
7. Chamfering.
8. Cutting-off.
9. And a slew of other procedures performed in a predictable order to generate a huge number of similar components in a short period of time.
The Turret or Saddle Type Lathe
Another sort of lathe machine is the turret lathe. It is used for repetitive production of same duplicate parts, which by the nature of their cutting process are usually replaceable. The hexagonal turret as depicted in the illustration.
It is directly installed on a saddle, and the entire unit slides back and forth on the bed ways to apply feed.
The construction of this sort of turret lathe machine is more substantial. It's especially well-suited to chucking and larger-diameter bar work. Longer work pieces can be fed into the machine than a capstan lathe can.
Principle Parts of Capstan and Turret Lathes
Except for the turret, the turret lathe has essentially the same components as the engine lathe. It also has a complicated mechanism that makes it appropriate for large production tasks.
Following are the main parts of a capstan and turret lathe,
- Bed.
- Headstock.
- Cross slide and saddle.
- The turret saddle and auxiliary slide.
1. Bed
The carriage and turret saddle are installed on the bed, which is a large box-like casting with precise guide ways. Under heavy-duty conditions, the bed is designed to ensure strength, rigidity, and alignment stability.
2. Headstock
The headstock is constructed from massive castings. It's at the far end of the bed, on the left. The following are the various types of headstocks used in capstan and turret lathes:
- Step cone pulley driven headstock.
- Direct electric motor driven headstock.
- All geared headstock.
- Preemptive or preselected headstock.
1. Step Cone Pulley Driven Headstock
Small capstan lathes are fitted to this style of headstock, which is the most basic. When the lathe is used to process work pieces with a tiny and nearly constant diameter. Only three or four steps of the pulley can meet the machine's requirements.
Unlike an engine lathe, where the machine spindle may be started, stopped, and reversed by pushing a foot pedal, the machine requires a unique countershaft.
2. Electric Motor Driven Headstock
Both the machine's spindles and the motor's armature shaft are one and the same in an electric motor-driven headstock.
Direct control of the motor allows for any speed differential or reversal. Three or four are available, and the machine is designed for work pieces with smaller diameters that revolve at high speeds.
3. All Geared Headstock
The headstocks on larger lathes are geared, and a separate mechanism is used to change the speed by actuating levers. The machine was not stopped while the speed was changed.
4. Preemptive or Preselected Headstock
It's an all-geared headstock with features like speedy stopping, starting, and speed charging for various tasks, as well as the ability to push a button or pull a lever.
The spindle speed must alter for different activities and for turning different diameters. The next operation's needed speed is chosen ahead of time. And the speed-changing lever has been set to the desired setting.
A button or a lever is simply actuated when the initial operation is completed. And, without stopping the machine, the spindle begins rotating at the set speed for the second operation. Friction clutches have an impact on this innovative mechanism.
5. Cross-Slide and Saddle
Hand-operated cross slides are secured on the lathe bed at the desired position in small capstan lathes. Larger lathes and heavy-duty turret lathes are frequently supplied with two carriage configurations.
- Conventional type carriage
- Side hung type carriage
1. The Conventional Type Carriage
The traditional carriage spans the distance between the front and back bed-ways. It also has four station tool posts in the front and one rear tool post at the back of the cross slide.
2. The Side-hung Type Carriage
The saddle rides on the top and bottom guide ways on the front of the lathe bed on the side-hung type carriage, which is usually equipped with heavy-duty turret lathes. The design allows for the swinging of a bigger diameter work piece without the cross-slide interfering. Hand or power feeding can be used to feed the saddle and cross slide longitudinally or across.
Stop-bars or shafts can be used to control the longitudinal movement of each tool. It's positioned against the bed's and carriage's halt. These stops are placed such that each tool feeds into the work to the desired length, allowing the job to be duplicated without having to check the machining length for each operation.
These act as a dead-stop for small head-operated tool movement to complete the cut after stopping the first trip out the feed. To synchronize with the tool's indexing, the stop bars are indexed by hand.
The tools are fixed on the tool post, and the correct heights are achieved with the help of a rocking or parking piece.
The Turret Saddle and Auxiliary Slide
The turret saddle spans the gap between two bed-ways in a capstan lathe. Furthermore, the top face is precisely cut to serve as a bearing surface for the auxiliary slide. On the lathe bed-ways, the saddle is adjusted and clamped in the desired position. The auxiliary slide holds the hexagonal turret.
In a turret, the top of the saddle is directly attached on the turret, and any movement of the saddle affects the turret. The turret's mobility can be controlled by hand or by power. The turret is a tool storage with a hexagonal design that can accommodate six or more tools.
Each turret face is meticulously machined. Each face has precisely bored holes through the center OD to accommodate shanks of various tool holders.
When aligned with the headstock spindle, the center line of each hole aligns with the lathe's axis. In addition to these holes, each face of the turret has four tapped holes for fastening various tool holding attachments.
There is a clamping mechanism in the center of the turret on the top of it that locks the turret to the saddle.
The saddle is equipped with six stop bars.
For duplicating work pieces, this restricts the movement of each tool installed on each face of the turret to a set amount.
The turret is moved away from the spindle nose when one operation is accomplished. A device on the bed and in the turret saddle automatically indexes the turret. So that the tool on the following face is parallel to the work.
Difference between Capstan and Turret Lathe Machine:
The following 17 Point is the Difference between Capstan and Turret Lathe Machine:
Sr. No. | Capstan Lathe Machine | Turret Lathe Machine |
1. | The capstan lathe is a light-duty equipment that can be used for a variety of tasks. | This is a powerful machine. |
2. | In The tool head is mounted in the ram, and the ram is positioned on the saddle of the capstan lathe. | The saddle is where the tool head is affixed. |
3. | To This ram movement necessitates the provision of nourishment. | It is necessary to supply feed saddle movement here. |
4. | Because ram movement is limited for small type work pieces, this is employed. | And because the ram movement is not limited or set, this one is employed for larger work pieces. |
5. | Because of the light construction, this is a quick form of work. | This is a machine that works slowly. |
6. | A Because of the non-rigid design, a hefty cut is not possible. | In Turret lathe, turret lathe, turret lathe Because to the robust design, heavy cutting is not possible. |
7. | It is a horizontal lathe of some sort. | However, this one can be used for both horizontal and vertical tasks. |
8. | Crosswise movement of the turret head is not possible. | The turret head can be moved crosswise here. |
9. | In The turret head on the capstan lathe is easy to move because it glides over the ram. | It It's tough to move the turret head and saddle at the same time. |
10. | To The collect is used to retain the workpiece. | A jaw chuck is utilized to hold the workpiece here. |
11. | This machine can only machine work pieces up to 60mm in diameter. | This machine can only machine work pieces with a diameter of 60mm. |
12. | This lathe machine has a smaller lengthwise movement. | There's more. |
13. | The head of the turret can be moved manually. | The head of the turret cannot be moved manually. |
14. | Because there is a certain amount of feed and cut depth, machining is constrained compared to a turret lathe. | Machining can be improved by increasing the feed rate and cutting depth. |
15. | Construction is lighter. | The construction is substantial. |
16. | There is no such facility as a turret lathe here. | In The ability to move the turret at a right angle to the lathe axis is provided by a turret lathe. |
17. | Both can be mass-produced in large quantities. | Both can be mass-produced in large quantities. |
Shaper: Introduction, types, specification, description of machines, cutting parameters
Introduction:
- A shaper is a sort of gadget device that makes use of linear relative movement among the work piece and a single-factor slicing device to gadget a linear tool path.
- Its reduce has similarities to that of a lathe, besides that it is (archetypally) linear in preference to helical.
- A single-factor slicing device is rigidly held with inside the device holder, that's established at the ram. The paintings piece is rigidly held in a vice or clamped at once at the desk.
- The desk can be supported on the outer quit. The ram reciprocates and the slicing device, held with inside the device holder, actions backwards and forwards over the paintings piece.
- In a fashionable shaper, slicing of fabric takes location at some point of the ahead stroke of the ram and the go back stroke stays idle. The go back is ruled via way of means of a short go back mechanism.
- The intensity of the reduce increments via way of means of transferring the work piece, and the work piece is fed via way of means of a pawl and ratchet mechanism.
- The work piece mounts on a rigid, field-fashioned desk in the front of the gadget. The top of the desk may be adjusted to healthy this workpiece, and the desk can traverse sideways under the reciprocating device, that's established at the ram.
- Table movement can be managed manually, however is commonly superior via way of means of an automated feed mechanism performing at the feeds crew. The ram slides backward and forward above the paintings.
- At the front quit of the ram is a vertical device slide that can be adjusted to both facet of the vertical aircraft alongside the stroke axis.
- This device-slide holds the clapper field and device post, from which the device may be located to reduce a straight, flat floor at the pinnacle of the workpiece.
- The device-slide allows feeding the device downwards to deepen a reduce.
- This flexibility, coupled with the usage of specialized cutters and device holders, allow the operator to reduce inner and outside tools teeth.
Types:
1. Bases on the Type of Driving Mechanism
Following are the distinct varieties of shaper machines primarily based totally at the sort of using mechanism
1. Crank Type Shaper Machine
These are very not unusual place varieties of shaper machines, that's the usage of to keep the workpiece at the desk.
The device is reciprocating in movement same to the duration of the stroke favored even as the paintings is clamped in role on an adjustable desk. In construction, the crank shaper employs a crank mechanism to alternate the round movement of a massive equipment called “bull equipment” integrated with inside the device to the reciprocation movement of the ram.
It makes use of a crank mechanism to transform the round movement of the bull equipment into the reciprocating movement of the ram. The ram includes a device head at its cease & offers the reducing movement.
2. Gear Type Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the ram is reciprocating. The ram is affecting because of reciprocating movement with the rack and pinion.
The rack enamel are reduce without delay under the ram mesh with the spur equipment. The pace and the route wherein the device will traverse rely on the quantity of gears with inside the equipment train. This sort of shaper device isn't broadly the usage of in any industry.
3. Hydraulic Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the reciprocating movement of the ram is supplied with the aid of using the hydraulic mechanism. The Hydraulic shaper makes use of the oil beneath excessive strain.
The cease of the piston rod is hooked up to the ram. The excessive-strain oil first acts on one aspect of the piston after which on the opposite inflicting the piston to reciprocating and the movement is transmitted to the ram.
The major benefits of this sort of shaper device are that the reducing pace and pressure of the ram pressure are constant.
From begin to cease of the reduce without making noise and operates quietly.
2. Based on Ram Travel
Following are the distinct varieties of shaper machines primarily based totally on ram travel
1. Horizontal Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the ram is reciprocating. The ram conserving the device on a horizontal axis and reciprocate.
This sort of shaper is the usage of for the manufacturing of flat surfaces, outside grooves, keyways, etc.
2. Vertical Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the ram reciprocating with inside the vertical plane
. In this, the desk holds the workpiece. Vertical shapers perhaps crank driven, rack-driven, screw-driven, or hydraulic power-driven.
The vertical shaper could be very handy for machining inner surfaces, keyways, slots, or grooves. The workpiece can flow in any given route including the cross, longitudinal or rotary movements. This sort of shaper is appropriate for machining inner surfaces, slots & keyways.
3. Based on the Table Design
Following are the distinct varieties of shaper machines primarily based totally at the desk design
1. Standard Shaper Machine
In this sort of shaper device, the desk has handiest movements, vertical and horizontal, to provide the feed. That’s why it's far called a well-known shaper device. Here the desk isn't assisting on the outer cease.
2. Universal Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, further to the 2 moments i.e. vertical and horizontal, the desk may be transferring on a willing axis, and additionally it could swivel on its personal axis.
Since the workpiece hooked up at the may be adjusted in distinct planes, the shaper is appropriate for a distinct sort of operations and is given the name “Universal”. This sort of shaper is generally the usage of the device room works.
4. Based on Cutting Stroke
Following are the distinct varieties of shaper machines primarily based totally on reducing stroke
1. Push reduce Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the steel is eliminated with inside the ahead movement of the ram. These are generally used varieties of shaper machines.
2. Draw reduce Shaper Machine
In those varieties of shaper machines, the steel is eliminated with inside the backward movement of the ram. In this shaper, the device is constant with inside the device head with inside the opposite route in order that it offers the reducing movement with inside the opposite stroke of the ram.
Specifications of shaper machine:
Technical Specification of Shaping Machine
Model | JF-SH-24 and 26 | JF-SH-30 | JF-SH-32 | JF-SH-36 | JF-SH-42 |
Capacity |
|
|
|
|
|
Length of ram stroke | 610 mm / 660 mm | 762 mm | 815 mm | 915 mm | 1070 mm |
Length of ram | 1325 mm | 1400 mm | 1536 mm | 1640 mm | 2135 mm |
Length X width of ram bearing | 995 mm x 280 mm | 995 mm x 280 mm | 1145 mm x 300 mm | 1145 mm x 300 mm | 1600 mm x 405 mm |
Max / min Distance from table to ram | 485 mm / 109 mm | 485 mm / 109 mm | 521 mm / 140 mm | 521 mm / 140 mm | 521 mm / 140 mm |
Table |
|
|
|
|
|
Working surface of table | 610 mm x 330 mm | 762 mm x 370 mm | 810 mm x 387 mm | 915 mm x 387 mm | 1050 mm x 562 mm |
Max. Horizontal table travel | 665 mm | 670 mm | 762 mm | 865 mm | 1070 mm |
Max. Vertical table travel | 432 mm | 435 mm | 381 mm | 381 mm | 457 mm |
Angular movement of table | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. | Fix | Fix | Fix |
Tool Head |
|
|
|
|
|
Max. Tool shank size | 38 mm x 21 mm | 38 mm x 21 mm | 38 mm x 21 mm | 38 mm x 21 mm | 38 mm x 25 mm |
Max. Vertical travel of tool slide | 152 mm | 152 mm | 152 mm | 228 mm | 305 mm |
Max. Swivel of tool head | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. | +/- 60 deg. |
Speeds & feeds |
|
|
|
|
|
Diameter of clutch pulley | 311 mm | 311 mm | 405 mm | 405 mm | 405 mm |
Number of ram speeds / strokes | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
Range of ram strokes per minute | 12-72 | 12-72 | 12-67 | 12-67 | 10-60 |
Range of table feeds / stroke | 0.22 – 0.88 | 0.22 – 0.88 | 0.22 - 0.88 | 0.22 – 0.88 | 0.22 – 0.88 |
Tool head feed | Hand feed | Hand feed | Hand feed | Hand feed | Hand feed |
Electric equipment |
|
|
|
|
|
Main motor drive 960 rpm | 3 hp | 3 hp | 5 hp | 5 hp | 7.5 hp |
V belt section | B – 57 | B – 58 | b-72 | b-72 | b-85 |
Motor starter | 5 amp | 5 amp | 15 amp | 15 amp | 15 amp |
Description:
Shaper Machine Parts:
Shaper Machine includes following components:
- Base
- Column Table
- Cross rail
- Ram
- Clapper Box
- Elevating Screw
- Shaper Machine
Let’s recognize one with the aid of using one, Base: The base is the maximum essential a part of the shaper as it holds all of the hundreds of the machine. It is made of solid iron. It absorbs vibration and different forces that arise even as acting shaping operations.
Column: The column is established at the base. It is likewise made of solid iron. Column helps the ram this is transferring ahead and backward for operation. It additionally acts for masking the power mechanism.
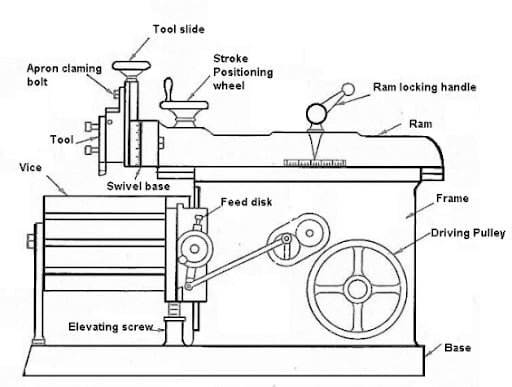
Table: It is established at the saddle. It is likewise one of the essential components of the machine. The desk may be moved crosswise with the aid of using rotating the cross feed rod and additionally for vertical with the aid of using rotating the raising screw. It is a box-like casting with an as it should be machined facet and pinnacle surfaces. These surfaces having T-Slots for clamping the work. In heavier kind shaper machines, the desk clamped with desk assist to make it extra rigid.
Cross rail: It is likewise established at the column on which the saddle is established. The vertical motion and Horizontal motion is given to the desk with the aid of using elevating or decreasing the go rail the use of the raising screw and with the aid of using transferring the saddle the use of the go feed screw.
Ram: The Ram reciprocates and it includes the device head wherein unmarried factor slicing device is attached. The device head is with inside the clapper box, which reasons slicing movement simplest in an ahead stroke of the ram. The feed or intensity of reduce of the device is given with the aid of using down feed screw.
Shaper Machine Working:
In short, the shaper works at the precept of the Quick go back movement mechanism. Let’s recognize in intensity, Shaper Machine As you could see the above diagram of Shaper machine, the device is preserve with the aid of using Ram and work piece is constant over desk.
When we turn on the electricity the ram reciprocates with recognize to the desk meaning the slicing device cuts work piece cloth with inside the ahead route and while transferring go back there may be no reduce.
The slicing system take region at low velocity of ram and go back stroke take region at excessive velocity. With using hand transverse wheel we are able to do up and down of the desk.
Cutting parameters:
The shaper is a reciprocating system device (see fig.1) supposed to provide flat surfaces (like horizontal, vertical, or willing surfaces).
Generally, the shaper can produce flat floor via way of means of the usage of brief go back mechanism. Modern shapers can generate contoured floor.
The steel operating shaper became advanced via way of means of James Nesmith an, Englishman in 1836.
Shaper Operation: Cutting Gears/Spines Machining irregularity curved floor Machining Horizontal/Vertical Surface Machining Angular Surface Machining V/ Keyway in block A shaper operates via way of means of shifting a hardened slicing device ahead and backwards throughout the work piece.
On the go back stroke, Tool is lifted clean of the work piece, decreasing the slicing motion to at least one course only.
By adjusting of ram and mechanism, stroke can be adjusted and stroke duration also can be adjusted.
It movements quicker at the go back (non-slicing) stroke than at the ahead (slicing stroke). This motion is through a slotted hyperlink or Whitworth hyperlink brief go back mechanism.
Photographic view of shaper system Material and method Aluminum alloy 6061 is one of the maximum drastically used of the 6000 collection aluminum alloys.
It is an in general warmth treatable extruded alloy with medium to excessive power capabilities.
Aluminium | 98.8 |
Magnesium | 0.8-1.2 |
Silicon | 0.4-0.8 |
Iron | Max 0.7 |
Copper | 0.15-0.4 |
Zinc | Max 0.25 |
Titanium | Max 0.15 |
Manganese | Max 0.15 |
Chromium | 0.04-0.35 |
Others | 0.05 |
Key Takeaways:
- Each turret face is meticulously machined. Each face has precisely bored holes through the center OD to accommodate shanks of various tool holders.
- Its reduce has similarities to that of a lathe, besides that it is (archetypally) linear in preference to helical.
- These are very not unusual place varieties of shaper machines, that's the usage of to keep the workpiece at the desk.
Quick Return Mechanism: Definition, Types, Working Principle, Applications, Advantages, Disadvantages:
A quick return motion mechanism is used in the shaper and slitter machine in which the circular motion is converted into reciprocating motion so that the slider moves forward and backwards. The cutting process occurs in the forward motion, but there is no corresponding cutting in the reverse direction.
- Quick Return Mechanism Types:
Quick return mechanisms come in three varieties:
- Whitworth Quick Return mechanism
- Crank and Slotted Link Mechanism and
- Hydraulic Drive
- Whitworth Quick Return Mechanism:
The oscillatory motion is created by converting the rotating motion. The bull gear is utilized in this device, which features a crank pinion.
The connecting rod connects the pin at one end to the ram at the other end of the connecting rod, which slides over the crankpin and into the slot of a crank plate.
The pinion is driven by the electric motor shaft, which rotates the gear. The bull gear now rotates in tandem with the crankpin, and the sliding block moves into the crank plate's groove.
As a result of this operation, the connecting rod causes the ram to travel up and down.
- Crank and Slotted Link Mechanism:
Whitworth devised this system in the 1800s. A slider, crank, fixed link, slotted lever, connecting rod, and ram make up the mechanism.
The slider and fixed link are connected to the crank. When the cranks begin to rotate, the connecting rod pushes the ram forward and backward.
From rotational motion, the motion is translated to linear motion here.
Please see the diagram for a better understanding.
Crank and slotted link mechanisms are commonly employed in shaping machines such as slitters and shapers to produce flat surfaces on work pieces.
In this mechanism, the return stroke is substantially faster than the forward stroke.
- Hydraulic Drive:
The hydraulic drive has a reciprocating piston inside the hydraulic cylinder. Between the ram and the piston lies the piston rod. As a result, the piston reciprocates with the ram.
There are two entries at the cylinder's end, as shown in the diagram. A control valve with four passages is installed below it.
The remaining two entries from the cylinder to the control valve are connected through a reservoir.
Quick Return Mechanism Working Principle:
There are four links in the diagram, and they are Slider, Crank, Frame, and Slotted Lever. It is also linked by a pair, which are as follows:
- Frame and Slotted lever: Changing the Pair
- Now Frame and Crank: Changing the Pair
- Crank and Slider: Changing the Pair
- Now Slider and Slotted lever: Sliding Couple
- There are three turning Pairs and one sliding pair. It is also known as the Inversion of the Single slider crank chain mechanism. The connecting rod is fixed here.
1. The slider is free to slide in the slotted lever, and the slotted lever's upper end is linked to the shaper machine's ram by a linkage.
2. At points A and B, the crank and slotted lever are attached to the frame.
3. The crank and slotted lever are connected to each other via a slider.
When the power is turned on, the crank begins to rotate, and the motion is transferred to the slider, which is fitted inside the slotted lever and therefore begins to oscillate.
Now, when the ram moves ahead, it creates an angle of beta, which is registered, and it creates an angle of alpha, which is also documented.
The beta angle is greater than the alpha angle, as shown in the diagram. As a result, cutting strokes take longer than returning strokes.
Applications of Quick Return Mechanism:
These are the following applications of Quick return mechanism:
1. It is used to flatten the workpiece in the shaper machine.
2. The same machine is utilized in the Slitter and Planer.
3. It’s also found in the Screw press, the Mechanical Actuator, and the Rotary Internal Combustion Engine.
Advantages of Quick Return Mechanism:
These are the advantages of Quick return mechanism:
1. The procedure is fully automated.
2. The mechanism's construction isn't overly sophisticated.
3. It can cut, flatten, and slot the workpiece, among other tasks.
4. Because of the quick return stroke, the idle time is reduced.
Disadvantages of Quick Return Mechanism:
Disadvantages of Quick return mechanism are:
1. Because there is no contact with the work during the returning stroke, no cutting occurs, and the process takes a long time to complete.
2. In comparison to the return stroke, the forward stroke takes a long time.
3. Performing procedures requires more electricity.
4. Friction exists between the slider and the piston.
5. Continuous Because of the heat generated inside the piston, it will not work, and wear and tear may occur.
6. Linkage balancing is a serious issue because this device is also related to links.
Table feed mechanism, attachments for shaper, work holding devices, shaper operations:
The computerized feed mechanism of the desk could be very simple.
This is finished via way of means of rotating a ratchet wheel, installed on the cross feed screw.
This permits a corresponding same rotation of the cross feed screw after every stroke.
Arrangement of parts It includes a slotted disc, which includes a T-slot, as proven with inside the figure.
In this slot is geared up an adjustable pin and to that is connected a connecting rod. The different cease of the connecting rod is hooked up to the decrease cease of the rocker arm of the pawl mechanism.
The rocker arm swings approximately the screw C, and at its higher cease includes a spring-loaded pawl, as proven. Working Note, that the decrease cease of the pawl is beveled on one side.
This association allows the electricity feed to perform in both direction, however the identical ought to be set to perform for the duration of the go back stroke only.
If otherwise, the mechanism can be subjected to intense stress. In a few ultra-modern kinds of shapers, can pushed feed mechanisms are supplied that are extra green and offer a much broader variety of feed.
Variation with inside the feed may be supplied via way of means of various the space R among the disc center and the center of the adjustable pin.
Larger the stated distance more can be the feed and vice versa.
The quantity of feed to take delivery of relies upon the kind of end required at the job.
For difficult machining, heavier cuts are hired, and thus, a rough feed is needed. Against this, a finer feed is hired in completing operations
. The slotted disc at its returned includes a spur tools that's pushed via way of means of the bull tools. As the disc rotates thru this tools the adjustable pin, being eccentric with the disc center.
This reasons the connecting rod to reciprocate. This, in turn, makes the rocker arm to swing approximately the screw C to transport the pall over one or extra teeth.
Thus transmit an intermittent movement to the cross feed screw which movements the desk.
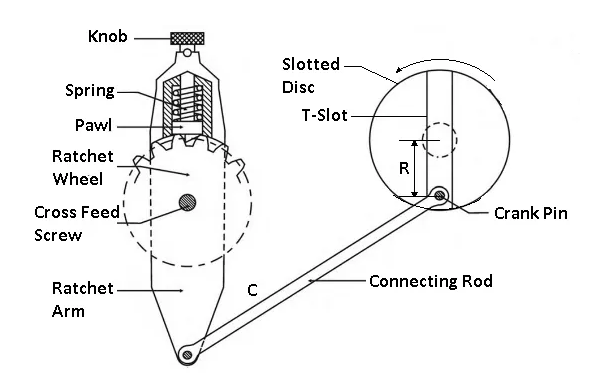
Work holding devices:
Carriers and seize plates
These are in preferred used for riding the paintings piece whilst it's miles held in among facilities particularly head inventory and tail inventory. Carriers also are known as because the riding dogs. These are connected to the paintings piece with the aid of using the assist of setscrews. Where because the seize plates are pinned to the headstock.
Face plates
Faceplates are used for containing the ones paintings pieces, which can't be held each with the aid of using facilities and with the aid of using chucks.
The production of the faceplates could be very simple. It includes a middle bore and undeniable and radial slots thru the plate for facilitating the conserving of the paintings piece. The relevant bore has a radius same to that of the radius of the spindle of the lathe. And the apparent and radial slots offer a wholesome platform for containing the roles with the aid of using the usage of T-bolts and clamps.
Angle plates
These are used in conjunction with faceplates for preserving the given paintings piece horizontal i.e. perpendicular to the device used. Angle plates encompass faces, that are enormously machined, and those additionally have the supply of holes for the clean clamping of the paintings piece to it.
Mandrels
This sort of paintings conserving gadgets are hired for containing formerly drilled or bored hollow so that it will facilitate powerful outer floor machining.
The paintings is loaded over the mandrels among the facilities. The ends of the mandrels are made barely smaller than the authentic diameter. This is executed for powerful gripping of the mandrel with inside the chuck or every other conserving device. In preferred the fabric used for the producing of the mandrels is obvious carbon steel. Various styles of mandrels are in usage
Chucks
A chuck is a piece conserving device. It is used for containing paintings over a lathe machine, that's having massive duration and small diameter, and additionally for jobs, that are not able to mount on among the facilities i.e., head inventory and tail inventory facilities.
A chuck is likewise hired whilst a non-axis symmetrical item is to be installed over the lathe. The chucks are maximum typically used paintings conserving gadgets.
These are constant without delay to the spindle of the lathe with the aid of screws and an again plate. In preferred there are numerous styles of chuck, that have their personal significance and particular applications
Rests
Rest is a piece conserving device, that's used to keep the paintings piece whilst the paintings piece of very lengthy duration are to be held. In preferred whilst a protracted piece is to be held it could have without delay held then there arises deflection with inside the paintings piece due its personal weight. So to save you the deflection with inside the paintings piece rests of numerous sorts are used.
Shaper Operations:
1. Machining of horizontal floor
Crossfade to the desk is given to start with via way of means of hand till the reduce starts. After that electricity feed may be employed. After the reduce is finished, the gadget is stopped and the paintings inspected. If greater cloth is to be removed, the system is repeated till the preferred floor is obtained.
A unique precaution is needed in putting the device for horizontal slicing. The device must be held vertically in any such manner that it’s slicing side factors in a course barely far from the paintings, as moves, because of the slicing pressure, it'll pass far from the paintings in place of digging into it.
2. Machining Vertical Surfaces
A vertical reduce is made at the same time as machining the cease of a workpiece, squaring up a block or slicing a shoulder. The paintings is hooked up with inside the vice or without delay at the desk and the floor to be machined is cautiously aligned with the axis of the ram. A facet slicing device is ready at the device put up and the location and duration of stroke are adjusted.
The vertical slide is ready as it should be at 0 role. This is vital to allow the device to transport upwards and far from the paintings throughout the go back stroke. This prevents the facet of the device from dragging at the planed vertical floor throughout the go back stroke. The down–feed is given via way of means of rotating the down feed screw via way of means of hand.
The feed is set 0.25mm given on the cease of every go back stroke. Both roughing and completing cuts are completed to finish the job.
3. Machining Angular Surface
Shaper gadget operation - Machining of Angular Surface In this shaper gadget operation, an angular reduce is completed at any perspective apart from a proper perspective to the horizontal or to the vertical plane. The paintings is ready at the desk and the vertical slide of the teeth head is swiveled to the specified perspective both closer to the left or closer to proper from the vertical role.
The apron is then similarly swiveled far from the paintings in order that the device will clean the paintings throughout the go back stroke. The down feed is given via way of means of rotating the down feed screw. The angular floor also can be machined in a well-known shaper or via way of means of the usage of a well-known vice without swiveling the device head.
4. Machining Irregular Surfaces Machining of Irregular floor
A shaper also can produce a contoured floor, i.e. a convex or concave floor or a aggregate of any of the above surfaces. To manufacture a small contoured floor a forming device is used. If the curve is large, electricity go feed at the side of guide down feed is so adjusted that the wool will hint the specified contour. If the contour (workpiece shape) has too many ups and downs each the feeds are operated via way of means of hand.
For machining abnormal surfaces a spherical nostril device is used. For a shallow reduce the apron can be set vertical however if the curve is pretty sharp, the apron in swiveled closer to the proper or left far from the floor to be reduce.
The determine suggests the machining of a concave floor the usage of a spherical nostril device.
5. Cutting Slots and Keyways
Machining of External keyway with appropriate tools, a shaper can very effectively gadget slots or grooves on paintings or reduce outside keyways on shafts and inner keyways on pulleys or gears. For slicing slots or keyways on shafts and inner keyways on pulleys or gears.
For slicing keyways or slots a rectangular nostril device much like a parting device is used. External keyways are made on a shaft via way of means of first drilling a hollow on the blind cease of the keyway.
The diameter of the hollow must be 0.five to 0.8mm oversize than the width of the keyway and the intensity must be approximately 1.5mm large than the intensity of the keyway. This is critical to depart clearance at the device on the cease of the stroke.
The duration and role of stroke are cautiously adjusted in order that the stroke will terminate precisely on the clearance hollow.
The pace is decreased at the same time as slicing keyways. Internal keyways are reduce via way of means of protecting the device on a unique device holder in order that the device put up will now no longer hit in opposition to the paintings on the cease of the stroke.
The clapper block is locked with inside the clapper field to save you the device from lifting throughout the go back stroke. Lubrication is vital at the paintings to save you the slicing fringe of the device shape put on because of dragging.
6. Machining Splines or Cutting Gears
This varieties of shaper gadget operations completed via way of means of the usage of an index center, illustrated in a tools or similarly spaced splined can be reduce. The paintings is positioned among centers, and a spline is reduce much like the slicing of a keyway.
After the primary spline is reduce, the paintings is circled via a predetermined quantity via way of means of the usage of the index plate and index pin.
The outer edge of a tools clean is divided, and similarly spaced grooves are reduce the usage of an index plate having right hollow circles. While slicing tools a forming device is used.
Key Takeaways:
- The paintings is loaded over the mandrels among the facilities.
- The ends of the mandrels are made barely smaller than the authentic diameter.
- The paintings is ready at the desk and the vertical slide of the teeth head is swiveled to the specified perspective both closer to the left or closer to proper from the vertical role.
The principle of the planner machine is the concept of relative tool-work motions. Reciprocation of the tool or job and the slow, intermittent transverse feed motions are imparted to the job or tool by the fast straight path cutting motion.
Al the operations done in planning machines can be done in the shaping machine. Stroke length, larger size, and higher rigidity enable the planning machines to do more heavy-duty work on large jobs and their long surfaces.
It produces planes and flat surfaces with a single-point cutting tool. A planer machine is large and massive as compared to a shaper machine. The planer can do machining heavy workpiece, which cannot be done on a shaper surface.
Planer Machine is a machine in which unwanted material is cut from the workpiece to produce a flat surface on the workpiece. Unlike Shaper Machine, in this machine, more than one tool can be set and perform an operation.
Specifications & Description, Type of planner:
The photographic view usually suggests the overall configuration of planning machine. Like shaping machines, planning machines also are essentially used for generating flat surfaces in special planes.
However, the main variations among planning machines from shaping machines are: Though in precept each shaping and planning machines produce flat floor with inside the equal manner through the blended movements of the Generatrix and Directrix however in planing machine, in place of the device, the paintings piece reciprocates giving the short slicing movement and in place of the job, the device is given the gradual feed movement.
Compared to shaping machines, planning machines are an awful lot large and extra rugged and typically used for huge jobs with longer stroke duration and heavy cuts.
In planning machine, the paintings piece is hooked up at the reciprocating desk and the device is hooked up at the horizontal rail which, again, can pass vertically up and down alongside the vertical rails.
Planning machines are extra productive (than shaping machines) for longer and quicker stroke, heavy cuts (excessive feed and intensity of cut) feasible and simultaneous use of some of equipment.
As in shaping machines, in planning machines also;
- The duration and function of stroke may be adjusted
- Only unmarried factor equipment are used
- The short go back persists
- Form equipment are regularly used for machining grooves of curved section
- Both shaping and planning machines also can produce huge curved surfaces through the use of appropriate attachments.
Types of planner:
- Double housing planer
- Open facet planer
- Pit planer
- Edge planer
- Divided head planer
- Size and specification of planner ·
- Distance among columns ·
- Stroke duration of the planer ·
Radial distance among the pinnacle of the desk and the lowest maximum function of the go rail ·
Maximum duration of the desk ·
Power of the motor ·
Range of speeds and feed available ·
Open side planner:
The planer device is much like a shaper device. It supposed to provide aircraft and flat surfaces via way of means of a unmarried-factor slicing device. A planer device could be very massive and big as compared to a shaper device.
It is able to a machining heavy workpiece, which can't be suit on a shaper desk. In a planer, the paintings that's supported at the desk reciprocates over the desk bound slicing device and the feed is furnished via way of means of the lateral motion of the device.
In a shaper, the device that's installed upon the ram reciprocates.
And the feed is given via way of means of the crosswise motion of the desk.
Parts of Planer Machine
Following are the six predominant components of the planer device:
- Bed
- Table Housing or Column
- Cross rail
- Tool head
- Driving and
- Feed Mechanism
Bed
The mattress of a planer is a box-like casting having go ribs. It could be very massive in length and heavy in weight and it helps the column and all different shifting components of the device. The mattress is made barely longer than two times the duration of the desk in order that the whole duration of the desk can be moved on it.
Three or greater guide ways can be furnished on a completely massive extensive device for assisting the desk. The guide ways must be horizontal, actual and parallel to every different.
The approaches are well lubricated and in cutting-edge machines oil beneath stress is pumped into the distinctive components of the guide ways to make sure a non-stop and ok deliver of lubricants
Table
The desk helps the paintings and reciprocates at the side of the approaches of the mattress. The planer desk is a heavy square casting. T-slots are furnished at the whole duration of the desk in order that the paintings and paintings retaining gadgets can be bolted upon it. At every stop of the desk, a hole area is left which acts as a trough for gathering chips.
Long works also can relaxation upon the troughs. In a fashionable planer, the desk is made up of 1 unmarried casting however in a divided desk planer there are separate tables installed upon the bed ways. Hydraulic bumpers are equipped on the stop of the mattress to forestall the desk from overrunning giving cushioning effect.
In a few machines, if the desk overruns, a massive slicing device bolted to the bottom of the desk will take a deep reduce on a replaceable block connected to the mattress, soaking up the kinetic strength of the shifting desk.
Housing
The housings additionally known as columns or uprights are inflexible box-like vertical systems positioned on every aspect of the mattress and are mounted to the perimeters of the mattress. They are closely ribbed to soak up extreme forces because of slicing. The the front face of every housing is as it should be machined to offer precision approaches on which the go rail can be made to slip up and down for accommodating distinctive heights of paintings. Two aspect-tool heads additionally slide upon it. The housing encloses the Cross rail raising screw, vertical and cross feed screws for device heads, counterbalancing weight for the Cross rail, etc. These screws operated both via way of means of hand or strength.
Cross rail
The Cross rail is an inflexible box-like casting connecting the 2 housings. This production guarantees the tension of the device. The Cross rail can be raised or reduced at the face of the housing and may be clamped at any favored function via way of means of manual, hydraulic or electric clamping gadgets. The Cross rail whilst clamped must stay truly parallel to the pinnacle floor of the desk, i.e. it ought to be horizontal no matter its function. Usually, tool heads, are installed upon the Cross rail which might be known as railhead. The Cross rail has screws for vertical and cross feed of the tool heads and a screw for raising the rail. These screws turned around both via way of means of hand or via way of means of strength.
Tool-head
The device head of a planer is much like that of a shaper each in production and operation. The crucial components of a device head are:
Saddle Swivel base
Vertical Slide Apron
Clapper box
Clapper block
Tool post
Down feed screw
Apron clamping bolt, Apron swiveling pin Mechanism for go and down-feed of the device.
1. Standard or Double Housing Planer Machine
The fashionable or double housing planer is the maximum extensively used styles of planer device in workshops. A double housing planer has a protracted heavy base on which a desk reciprocates on correct guide ways.
Standard or Double Housing Planer
The duration of the mattress is little over two times the duration of the desk. Two big vertical housings or uprights are installed close to the center of the base, one on every aspect of the mattress. To make sure the tension of the structure, those housings are linked on the pinnacle via way of means of a solid iron member.
The vertical faces of the 2 housing are as it should be machined in order that horizontal Cross rail sporting device heads can also additionally slide upon it. The device heads which preserve the equipment are installed upon the Cross rail. These equipment can be feed both via way of means of the strength in cross rail or vertical course.
In addition to those device heads, there are different device heads which might be installed upon the vertical face of the housing. They also can be moved both in a vertical or horizontal course to use feed. The planer desk can be pushed both via way of means of mechanical or hydraulic gadgets.
2. Open side Planer Machine
An open side planer has a housing handiest on one aspect of the base. And the cross rail is suspended from the housing as a cantilever. This characteristic of the device permits the massive and extensive workpiece to be clamped at the desk and reciprocated over the slicing device.
One aspect of the planer being opened, massive and extensive jobs can also additionally undertaking out of the desk and reciprocate without being interfered via way of means of the housing. In a double housing planer, the most width of the task which may be machined is restricted via way of means of the gap among the 2 housing. As the unmarried housing has to soak up the whole load, its miles made extra-big to withstand the forces.
3. Pit Planer Machine
A pit kind planer is big in production. It differs from a regular planer. In this the desk is desk bound and the column sporting the cross rail reciprocates on big horizontal rails installed on each aspects of the desk.
This styles of planer device are appropriate for machining a completely massive paintings which can't be supported on a fashionable planer.
This device layout saves plenty of ground area. The duration of the mattress required in a pit kind planer is little over the duration of the desk.
Whereas in a fashionable planer the duration of the mattress is close to two times the duration of the desk.
The uprights and the cross rail are made sufficiently inflexible to soak up the forces even as slicing.
4. Edge or Plate Planer
The layout of a plate or aspect planer is definitely not like that of a regular planer. It is specifically supposed for squaring and beveling the rims of metal plates. Also used for distinctive stress vessels and shipbuilding works.
5. Divided Table Planer
This form of planer has tables at the mattress which can be reciprocated one after the other or together. This form of layout saves plenty of idle time even as placing the paintings. The putting in of a massive quantity of equal work pieces at the planning device desk takes pretty a protracted time. It can also additionally require as plenty time for putting in as can also additionally essential for machining.
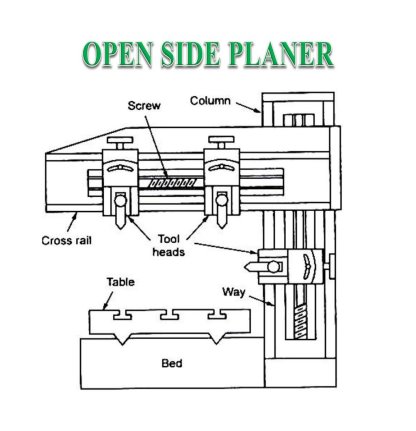
Pit Planner:
- It is rigid in construction. In this, the table is stationary and the column carrying the Cross rail reciprocates on massive horizontal rails mounted on both sides of the table.
- Pit Planer machine are suitable for machining a very large work which cannot be supported on a standard planer.
This varieties of planer device are appropriate for machining a completely massive paintings which cannot be supported on a preferred planer.
This device layout saves plenty of ground space. The duration of the mattress required in a pit kind planer is little over the duration of the desk. Whereas in a preferred planer the duration of the mattress is close to two times the duration of the desk.
The uprights and the cross rail are made sufficiently inflexible to absorb the forces whilst cutting.
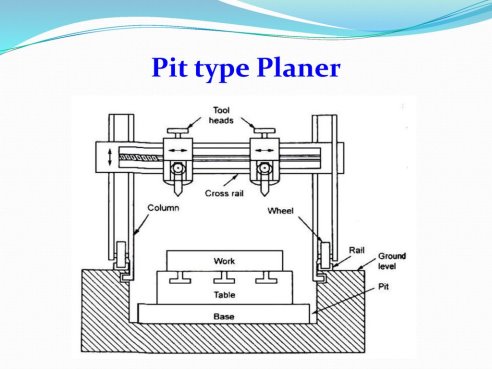
It has a huge creation wherein the desk is stored in a pit and its miles stationary. The column sporting the go rail reciprocates on a horizontal rail hooked up on each facets of the desk as you could see with inside the figure.
The desk of the planer is made a degree with the ground, in order that very heavy paintings may be loaded very easily.
The go rail consists of device heads and those may be moved horizontally and vertically to present the cut. The using screw is used for using the column through a motor.
Key Takeaways:
- It produces planes and flat surfaces with a single-point cutting tool. A planer machine is large and massive as compared to a shaper machine. The planer can do machining heavy workpiece, which cannot be done on a shaper surface.
- Compared to shaping machines, planning machines are an awful lot large and extra rugged and typically used for huge jobs with longer stroke duration and heavy cuts.
Open and Cross Belt Drive Mechanism:
Planer mechanism calls for supplying backward and forward movement to the gadget desk. Quick go back mechanism is likewise hired to present quicker motion all through the idle stroke.
Most planers deliver this machine of open and pass belt power for the short go back of the tables. This mechanism includes belts, one open and one pass working on unfastened and speedy pulleys. The essential riding shaft is supplied under the bed. One cease incorporates the pinion which meshes with the rack supplied below the desk of the gadget. Cross belt is used for ahead or reducing stroke and the open belt is for go back movement. Cross belt is hooked up to speedy pulley and open belt is hooked up to unfastened pulley and it permits sluggish motion of the desk all through ahead stroke. Trip puppies are installed at every cease of the desk imply the cease of the stroke and belt shifter shifts the belts to the unique pulleys. Now open belt is hooked up to the short pulley and the pass belt is hooked up to the unfastened pulley. This permits quicker motion and gives brief go back movement for the gadget desk.
Reversible Motor Drive Mechanism:
Electric motor drives the bull equipment thru equipment trains. Motor is coupled to D.C. Generator. When motor is started, generator substances energy to reversible motor. Reversible motor reasons the planer desk to move. At the cease of stroke, ride canine operates the transfer which reverses the course of desk. Speed of reducing stroke is decreased through regulating the sector modern-day of the generator.
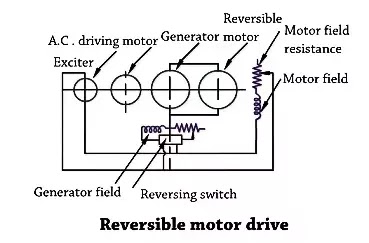
Operations on Planer Machine
Planer operations are similar to those performed on shaper, with a difference that the work pieces are much larger in size.
Planer Operations:
• Planning horizontal surfaces.
• Planning vertical surfaces
• Planning angular surfaces / dovetails
• Planning curved surfaces
• Planning slots & grooves.
Planning Horizontal Surfaces:
• Fix the work properly on the table.
• Set the required cutting speed.
• Give required feed of the tool.
• Give suitable depth of cut for rough cuts.
• Finishing the job by giving less depth of cut.
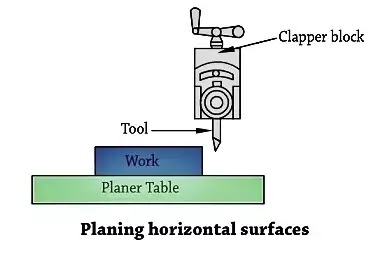
Planning Vertical Surfaces:
• Fix the job on the table firmly.
• Align the surface to be machined properly.
• Vertical slide is adjusted perpendicular to the table
• Swivel the apron away from the job.
• Switch on the machine.
• Rotate down feed screw by hand to give down feed.
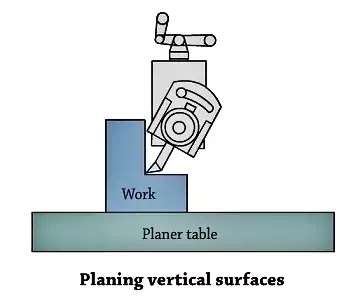
Planning angular surfaces:
• Main angular planning is to make dove tails & V grooves.
• Set the work on the table.
• Swivel the tool head to the required angle.
• Set apron away from work.
• Give down feed as per requirement.
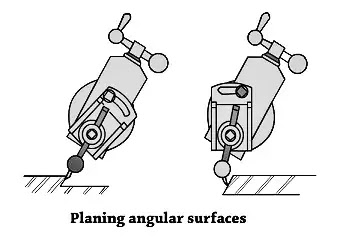
Planning Formed Surfaces:
• Fix up a square nose tool in tool head.
• Required form is obtained by feeding the tool simultaneously in both horizontal
And vertical directions.
• Give suitable depth of cut.
• Set apron away from work.
• This can also be done with the aid of a special fixture.
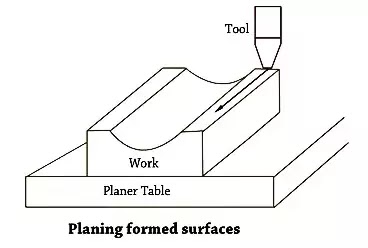
Planning Slots and Grooves:
• Fix up the job on the table suitably.
• Fix slitter tools in tool heads.
• Give feed using down feed screw.
• Move the tool by the required amount to get uniform slots / grooves.
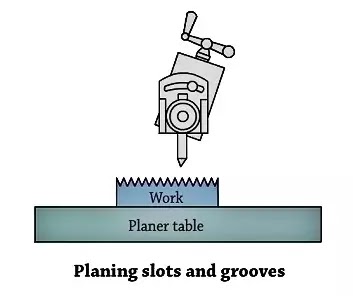
Cutting speed, Feed and Depth of Cut
Cutting Speed:
As in a shaper, the cutting speed of a planer is the rate at which the metal is removed during the forward cutting stroke. The formula, for shaper holds good for a planer also. This is expressed in m/min.
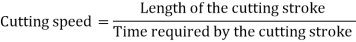
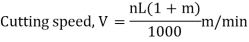
Where,
L = Length of cutting stroke in mm.
m = Ratio between return time to cutting time
n = No of double strokes of the ram/min.
Feed:
The feed in a planing gadget is the gap the device head travels at the start of every reducing stroke.
Depth of Cut:
It is the thickness of metallic eliminated in a single reduce and is measured through the perpendicular distance among the machined and non-machined floor. It is expressed in mm.
Machining Time:
If the reducing pace, feed, duration of reducing stroke, breadth of the activity and quantity of double strokes in step with minute for a planer operation are known, the machining time required for one entire reduce can be calculated through the use of the formula.

The ratio of cutting time to return time usually varies from 2: 1 to 4:1.
Feed mechanisms:
Feeding Mechanism Feed with inside the planer is given on the give up of the ahead stroke or at the start of the backward stroke. The feed is given via the motion of the device. There are sorts of feeds.
- Down feed
- Cross feed
Both those feeds may be given through rotating the feed screws through hand or energy. Down Feed
Down feed is given whilst machining the vertical or angular floor, the down feed screw of the device head is turned around and fed down.
Cross-Feed
Cross feeds are given whilst machining the horizontal floor of a piece keep on a desk.
Table Drive Mechanism For desk force mechanism, short go back mechanism are used. The following techniques are used to gain movement in backward stroke of planer desk and sluggish movement in ahead stroke.
Following are the numerous mechanisms used to run the desk.
- Open and Cross belt force
- DC Reversible Motor
- Hydraulic Drive Open and Cross Belt Drive
Small planners are pushed through open and go belt the usage of speedy and free pulleys.
But such planners can perform simplest at a one slicing velocity and a one go back velocity.
DC Reversible Motor
A DC reversible motor makes use of a motor which can alternate its velocity in line with the feed current.
Power from the motor is transmitted to the desk rack through a discount gearing and a malicious program that mashes with the desk rack. This approach is used to gain desk speeds with inside the range.
Hydraulic Drive Mechanisms for the hydraulic force of the shaper may be utilized in planers with a few modifications.
These force additionally consists of journey puppies alongside the desk to alter the stroke duration and alternate the placement of the desk.
These players aren't used for heavy responsibility paintings as the specified hydraulic energy could be very excessive and the force isn't smooth.
After elements of planer device now we are able to understand sorts of planer device in details.
Planner cutting tools, cutting parameters.
The planer handles paintings weighing as much as numerous tons. Both the shaper and planer typically reduce handiest in a single course, in order that the go back stroke is misplaced time.
However, the go back stroke is made at as much as two times velocity of the reducing stroke.
The Shaper
The shaper is a tremendously easy gadget. It is used pretty regularly with inside the tool room or for machining one or portions for prototype paintings. Tooling is easy, and shapers do now no longer constantly require operator interest whilst reducing. The horizontal shaper is the maximum not unusual place kind, and its foremost additives are proven beneath, and defined as follows:
Ram:
The ram slides to and fro in dovetail or rectangular approaches to transmit electricity to the cutter. The start line and the period of the stroke may be adjusted.
Tool head:
The tool head is mounted to the ram on a round plate in order that it is able to be circled for making angular cuts. The tool head also can be moved up or down through its hand crank for unique intensity adjustments.
Attached to the tool head is the tool holding segment. This has a device publish very just like that used at the engine lathe.
The block maintaining the device publish may be circled some levels in order that the cutter can be nicely placed with inside the reduce.
Clapper Box:
The clapper container is wanted due to the fact the cutter drags over the paintings at the go back stroke.
The clapper container is hinged in order that the reducing too] will now no longer dig in. Often this clapper container is routinely raised through mechanical, air, or hydraulic action.
Table:
The desk is moved left and proper, typically through hand, to place the paintings below the cutter whilst putting in. Then, both through hand or extra regularly routinely, the desk is moved sideways to feed the paintings below the cutter on the quit or starting of every stroke.
Saddle:
The saddle movements up and down (Y axis), typically manually, to set the tough function of the intensity of reduce. Final intensity may be set through the hand crank at the device head. Column: The column helps the ram and the rails for the saddle
Cutting Speed and Feed:
The reducing velocity of the hydraulic shaper is infinitely variable by way of hydraulic controls, as is the move feed. The opposite stroke is made quicker than the electricity stroke due to the smaller place with inside the go back facet of the cylinder, if a steady extent pump is used.
Another approach is to have the feel of fluid float accelerated to hurry up the go back stroke. Speed and feed on a hydraulic shaper are regularly managed through easy dials. Speed is examine at once in ft according to minute and feed is examine at once in decimal inches.
The reducing velocity stays almost steady thru the total stroke.
Vertical Shapers
The vertical shaper, every so often referred to as a Blotter, has a vertical ram, with desk and saddle just like the horizontal shaper. If a rotary desk is established at the ordinary desk, some of slots may be made at pretty correctly spaced intervals. This gadget can paintings either outdoor or interior a part, furnished that the indoors beginning is bigger than the device head.
The Planer
A planer makes the equal sorts of cuts as a shaper. However, it's far a production-- kind gadget for sure sorts of paintings. It can gadget any flat or angular floor, along with grooves and slots, in medium and huge sized work pieces.
Typical paintings could be gadget beds and columns, marine diesel engine blocks, and bending plates for sheet-steel paintings.
These elements are typically huge iron castings or metal elements and can weigh some hundred kilos or numerous tons. The maximum often used form of planer is the double-housing planer.
Frame:
The body is largely heavy columns mounted collectively on the pinnacle with a huge bracing segment and mounted at the lowest to the gadget mattress. This creates a totally strong, inflexible shape with a purpose to deal with heavy hundreds without deflection.
Cross rail:
The cross rail is likewise a heavy container, or comparable construction. It slides up and down on V- or flat approaches, managed through hand or through electricity-operated screws.
These cross rails are so heavy that they're counterweighted, with either solid iron weights or hydraulic cylinders, just so they'll be moved without difficulty and placed correctly. After being placed, they're clamped in place. Railheads: The railheads may be moved left or proper throughout the cross rail, every managed through a separate lead screw, which may be grew to become through hand however typically through electricity feed.
The railhead may be circled, and vertically adjusted for intensity of reduce, similar to the shaper heads. They actually have a clapper container (regularly with electricity lift) just like the shaper.
Side heads:
The side heads are independently moved up or down through hand or through electricity feed and also can be circled and moved in or out for intensity of reduce.
Table:
The desk is a heavy casting which consists of the paintings beyond the reducing heads. It runs on V- or flat approaches. The desk is pushed both through a totally lengthy hydraulic cylinder and through a pinion tools using a rack, that's mounted below the middle of the desk. The motor using the pinion tools is the reversible kind with variable velocity.
Key Takeaways:
- This permits quicker motion and gives brief go back movement for the gadget desk.
- Feeding Mechanism Feed with inside the planer is given on the give up of the ahead stroke or at the start of the backward stroke
- Hydraulic Drive Mechanisms for the hydraulic force of the shaper may be utilized in planers with a few modifications.
References:
1. Manufacturing Engineering & Technology, S. Kalpakjian & S.R. Schmid
2. Technology of Machine Tools, Krar &Oswald
3. Manufacturing Processes, M.Begman
4. Processes & Materials of Manufacture, R.Lindberg
5. Production Technology, HMT