Unit - 3
Milling
A milling machine is one of the most influential and versatile kinds of machines found in the manufacturing industry. Milling is the most widely used machine used in machine shops and modern manufacturing industries all over the world.
It is a type of machining process in which a cutter having multiple cutting edges is used to remove the material from the work piece. This machine tool makes up about 85 percent of the all-material removal process.
Definition:
The milling machine is a type of machine which removes the material from the work piece by feeding the work past a rotating multipoint cutter. The metal removal rate is higher very high as the cutter has a high speed and many cutting edges. It is the most important machine in the tool room as nearly all the operations can be performed on it with high accuracy.
MRR (Material Removal Rate) can be further increased by increasing the number of teeth on the cutter.
Milling Machine Application:
- Milling Machine is used for Machining flat surfaces, Slotting, Contoured surfaces.
- It is also useful for making Complex and irregular areas, Revolution surface, Gear cutting, Machining external and internal threads.
- Machining helical surfaces of various cross-sections and many more.
- It employed in the metal removing operation on a milling machine is that the work is rigidly clamped on the table of the machine and the revolving cutter which has multiple teeth is mounted on the arbor.
- The cutter revolves at high speed and the work is fed slowly past the cutter.
- The work can be fed in a vertical, longitudinal, or cross direction depending upon the type of milling machine being used.
- As the work proceeds, the cutter-teeth removes the metal from the surface of the job(work piece) to produce the desired shape.
Specification, types, column & knee type milling machine
Milling Machine Types
The various types of milling machines are as follows:
Column and knee type
- Hand milling machine
- Plain or horizontal milling machine
- Vertical milling machine
- Universal milling machine
- Omniversal milling machine
Manufacturing type or fixed bed type
- Simplex milling machine
- Duplex milling machine
- Triplex milling machine
Planer type milling machine
Special Type
- Rotary table milling machine
- Drum milling machine
- Profile milling machine
- Planetary milling machine
- Tracer controlled milling machine
- Pantograph milling machine
- NC/CNC milling machine
Column and Knee Type
- The most used type of milling machine for general shop work is the column and knee type machine. In this the table is mounted on the knee-casting which in turn is mounted on the vertical slides of the main column.
- The knee is vertically adjustable on the column so that the table can be moved up and down to accommodate work of various heights.
- The column and knee type milling machines can be further classified:
- According to the various methods of supplying power to the table.
- Different movements of the table. And
- The different axis of rotation of the main spindle.
1. Hand Milling Machine
- It simplest of all types of milling machine in which table feed is controlled by hand. In this the cutter is mounted on a horizontal arbor and is rotated by power.
- This type of milling machine is small in size and suitable for light & simple milling operations. Example: grooves, machining slots and keyway.
2. Plain Milling Machine
- Plain milling machines are much stronger than hand millers. The table feeding may be done either by hand or power. The plain milling machine with a horizontal spindle is also called as a horizontal spindle milling machine. The table may be fed in a longitudinal, vertical or cross directions.
The feed is:
- Longitudinal – when the table moves at right angles to the spindle.
- Cross – when the table moves parallel to the spindle.
- Vertical – when the table is adjusted in the vertical plane.
3. Universal Milling Machine
- It can be adapted to wide ranges of milling operations. In this the table can be swivelled to any angle up to 45o on either side of the normal position.
- In addition to 3 movements as discussed earlier in a plain milling machine, the table may have the 4th movement when it is fed at an angle to the milling cutter. Helical milling operation can also be performed on this.
- The capacity of this type of machine can be increased by using special attachments such as
- Dividing head or index head.
- Vertical milling attachment.
- Rotary attachment.
- Slotting attachment.
- This machine can produce spur, spiral, twist drill, bevel, reamer, milling cutter. All operations that are performed on a shaper can be performed using a universal milling machine.
4. Ominversal Milling Machine
- In this type of milling machine, the table has four movements of the universal milling machine. It can also be tilted in a vertical plane by providing a swivel arrangement at the knee.
- The additional swiveling arrangement of the table aids in machining spiral grooves in bevel gears and reamers.
5. Vertical Milling Machine
- In this, the position of the spindle is perpendicular to the table. This type of machine is adapted for machining slots, grooves and flat surfaces.
- It may be of plain or universal type and has all the movements of the table for a proper setting & feeding the work.
- The spindle head in this machine is clamped to the vertical column which is swiveled at some angle which allowing the milling cutter fixed on the spindle to work on angular surfaces. In some machines, the spindle can be adjusted up or down relative to the work.
Manufacturing of Fixed Bed Type Milling Machine
- These machines are heavy, large and rigid in construction. These machines can be differentiated from column and knee type milling machines by the construction of its table mounting.
- In this machine the table is mounted directly on the ways of fixed bed and the movement is restricted to reciprocating at a right angle to the spindle axis with no provisions for vertical or cross adjustments.
- It may be classified as simplex, duplex, triplex based on a machine provided with the single, double and triple spindle heads respectively.
- Simplex – single spindle head.
- Duplex – two-spindle head.
- Triplex – three spindle head.
Planer Type Milling Machine
- Planer Type Milling Machine is also called as “Plano-Miller”. It’s a heavy and large machine used for heavy-duty work having adjustable spindle heads in the vertical and transverse direction.
- Similar to a planning machine this machine also has a cross rail capable of being raised or lowered carrying the cutters. It has their heads and saddles, all supported by rigid uprights.
- This arrangement of driving multiple cutter spindles enables a number of surfaces to be machined. Hence, it obtains the great reduction in production time.
- The main difference between a player and a Plano-miller is in the table movement. In a planer, the table moves to give the cutting speed where as in a Plano-milling machine, the table movement gives the feed.
Special Types of Milling Machine
Milling machines of non-conventional design have been developed to suit special purposes. This machine has a spindle for rotating the cutter and provision for moving the tool or the work in different directions. The following special types of machines of interest are described below
1. Rotary Table Milling Machine
- In Rotary table milling machine the table is circular in nature and rotates about a vertical axis. In this machine, cutters are set at different heights resulting in one cutter roughing the workpiece and other one cutter finishing it.
- The advantage of this machine is that continuous loading and unloading of work pieces can be achieved by the operator, while it is in progress.
2. Drum Milling Machine
- It is similar to a rotary table milling machine. But the workpiece supporting table in this machine is called as “DRUM” which rotates in the horizontal axis.
- The face milling cutters that are mounted on 3 or 4 spindle heads rotate in a horizontal axis and removes metal from work pieces supported on both the faces of the drum. The finished machined parts are removed after 1 complete turn of the drum and then the new ones are clamped to it.
3. Planetary Milling Machine
- In this, workpiece is held stationary while the revolving cutter. The cutter moves in a travelling path in order to finish a cylindrical surface on the work piece either externally or internally. This machine is also adapted for milling external and internal threads
4. Pantograph Milling Machine
- A pantograph machine can replicated a job by using a pantograph mechanism. It enables the size of the work piece reproduced to be smaller than, equal to or greater than the size of a template. It is also used for the different model for special purposes.
- A pantograph is a mechanism that is generally consist of four bars or links which are connected in the form of a parallelogram.
- Pantograph machines are available in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional models. The 2-dimensional pantograph is used for engraving letters or other designs. Whereas the 3-dimensional models are employed for copying any shape & contour of the work piece.
5. Profiling Milling Machine
- A profiling machine duplicates the full size of the template attached to the machine. In this, the spindle may be adjusted vertically and the cutter horizontally across the table.
- In this machine, hardened guide pin controls the movement of the cutter. The longitudinal movement of the table & the crosswise movement of the cutter head follow the movement of the guide pin on the template.
6. Tracer Controlled Milling Machine
- This type of machine reproduces irregular and complex shapes of dies, molds by synchronized (matched) movements of the cutter & tracing elements.
- The movement of the stylus energized an oil relay system, which operates the main hydraulic system for the table. This type of arrangement is termed as a servomechanism.
Fixed bed type milling machines
A constant mattress type, as its call hints, is a kind of milling gadget that has an inflexible mattress connected to the gadget. You can't set up the saddle and knee of this milling gadget.
It has a movable spindle head-set up with the spindle of the gadget. The gadget can carry out slicing operations with the aid of using shifting in horizontal and vertical instructions.
1. Simplex Milling Machine
The spindle or the spindle head can journey in a single path only. The maximum not unusual place path wherein it is able to flow is vertical.
2. Duplex Milling Machine
The spindle can flow in each horizontal and vertical instructions.
3. Triplex Milling Machine
The spindle can flow in all 3 instructions i.e. X Y and Z axis.
Production milling machines:
HPSM’ provide a one of a kind variety of SPM Production Milling Machine, that is fabricated from excessive grade uncooked substances.
These machines may be custom designed as in line with our treasured customer’s specifications.
Offered machines are broadly liked through the customers for his or her smooth installation, easy capability and longer carrier life
A milling system is one of the maximum influential and flexible sorts of machines determined with inside the production industry. Milling is the maximum broadly used system utilized in system stores and current production industries all around the world.
It is a sort of machining method wherein a cutter having a couple of reducing edges is used to put off the fabric from the work piece.
This system device makes up approximately eighty five percentage of the all fabric elimination method.
The numerous blessings of Milling are:
- High pace
- Better floor end
- Increase productivity
- High accuracy
High pace: In Milling, the price of metallic elimination may be very excessive because the cutter rotates at a excessive pace and has a couple of reducing edges. Better floor end: The floor end of the substances machined at the milling system is higher due to the multi-reducing edges.
Increased Productivity: CNC Milling Machines are the machines wherein the milling operation is being managed through software. It has expanded the general manufacturing with higher end and accuracy.
High Accuracy: In the milling system, the goods machined are of excessive accuracy particularly with inside the case of the maximum superior shape of milling system that is the CNC Machine.
Huge Application: Indexing head makes it appropriate for such a lot of packages as the precise rotation of the activity is feasible through the usage of it. Milling may be used for machining flat surfaces, abnormal surfaces, contoured surfaces, slotting, tools reducing and plenty of more.
The dangers of the milling system are as follows:
High Flank put on
High author put on
Breaking of carbide
High chatter and chip clogging.
High Flank put on: It has an excessive flank put on price which may be averted through decreasing pace and growing the feed price. Further to keep away from it one need to use tougher carbide with right geometry and sharpened reducing edges. High crater put on: High crater put on is determined which may be tackled through decreasing pace and the usage of tougher carbide.
Breaking of carbide: Sometimes the manufacturing method receives hindered due to the breaking of the carbide. The treatment for this trouble may be the usage of harder carbide, and stress of the cutter, system, and arbor need to be ensured.
High Chatter: This takes place because of negative stress of cutter, system, free arbor, and wrong geometry. This state of affairs may be stepped forward through growing feed, decreasing pace and the usage of unequal pitch cutters.
Chip clogging: The milling system additionally suffers from the trouble of chip clogging which may be decreased through the usage of decreasing the variety of enamel at the cutter and growing pace and chip pockets.
Special purpose milling machines such as thread milling Machines:
Thread Milling
- Thread milling operations are used to produce threads by using a single or multiple thread milling cutters. Thread milling operations are performed in special thread milling machines to produce accurate threads in small or large quantities.
- This operation requires three driving motions in the machine. One for the word, one for the cutter and the third for the longitudinal movement of the cutter.
- When the operation is performed by using a single thread milling cutter, the cutter head is swiveled to the exact helix angle of the thread. The cutter is rotated on the spindle and the workpiece is then revolved slowly about its axis. The thread is complete in one cut by the setting of the cutter to its full depth and then feeding it along the entire length of the workpiece.
- When the thread is cut by multiple thread milling cutter, the cutter axis and the work spindle are always set parallel to each other after adjusting the depth of cut equal to the full depth of the thread. The thread is completed by simply feeding the revolving cutter longitudinally through a distance equal to the pitch length of the thread while the work is rotated through one complete revolution.
Thread milling is a versatile, cost-powerful manner for each person reducing quite a few threads, components and work piece substances at the identical machine.
Our strong carbide thread mills, multi-enamel index able insert cutters and Threading Wizard software program make it smooth to undertake this manner and bring incredible threads with extremely good shape and finish. In general, thread milling generates advanced burr-loose floor finishes and decreases device stock costs.
Shops can use the identical device for each left and right-hand threads in addition to for exceptional thread tolerances.
A vast variety of substances and hollow diameters also can be thread milled with the identical device.
Unlike tapping, threads produced through milling may be machined to complete intensity at excessive accuracy, even in hardened substances.
Gear Milling
The manner
- The spherical work piece is hooked up axially, perpendicular to the axis of the reducing device.
- The device is moved alongside the axis of the work piece and generators out the tools teeth area. The paintings piece is then circled through distance of 1 teeth area and milling is repeated.
- The work piece is processed, step by step till enamel are reduce across the complete work piece.
- To create willing enamel the cutter is angled in the course of the reducing, the work piece is circled slowly whilst the device is moved alongside work piece axis.
- In shape milling, the cutter referred to as a shape cutter travels axially alongside the duration of the tools teeth at the right intensity to supply the tools teeth. After every teeth is reduce, the cutter is withdrawn, the tools clean is circled (indexed), and the cutter proceeds to reduce some other teeth. The manner maintains till all enamel are reduce.
- Each cutter is designed to reduce various teeth numbers. The precision of the shape-reduce teeth profile relies upon at the accuracy of the cutter and the gadget and its stiffness.
- In shape milling, indexing of the tools clean is needed to reduce all of the enamel. Indexing is the manner of lightly dividing the circumference of a tools clean into similarly spaced divisions.
- The index head of the indexing fixture is used for this purpose. The index fixture includes an index head (additionally dividing head, tools reducing attachment) and footstock that is just like the tailstock of a lathe. The index head and footstock connect to the worktable of the milling gadget.
- An index plate containing graduations is used to manipulate the rotation of the index head spindle. Gear blanks are held among facilities through the index head spindle and footstock.
- Work pieces will also be held in a chuck hooked up to the index head spindle or can be geared up immediately into the taper spindle recess of a few indexing fixtures.
Key Takeaways:
- In this machine the table is mounted directly on the ways of fixed bed and the movement is restricted to reciprocating at a right angle to the spindle axis with no provisions for vertical or cross adjustments.
- This arrangement of driving multiple cutter spindles enables a number of surfaces to be machined. Hence, it obtains the great reduction in production time.
- The advantage of this machine is that continuous loading and unloading of work pieces can be achieved by the operator, while it is in progress.
- A profiling machine duplicates the full size of the template attached to the machine. In this, the spindle may be adjusted vertically and the cutter horizontally across the table.
- The spindle or the spindle head can journey in a single path only. The maximum not unusual place path wherein it is able to flow is vertical.
Hobbing
The quality, performance, service life, safety, and dependability of high-end power transmissions are all determined by high precision gears.
While there are a variety of ways for making these gears, such as milling or grinding, hobbing is the most common.
When compared to grinding, the hobbing technique has the benefit of being more precise and efficient at a cheaper cost.
Though part geometry limits the application of this method, hobbing is still the most productive technique of gear teeth generation for external spur and helical gears.
In the process of gear hobbing indexing movement, three critical parameters must be controlled: feed rate, angle between the axis of the gear blank, and the angle between the axes of the gear hobbing tool (gear hob).
The image shows a schematic diagram of how a gear hobbing machine is set up.
The hob's objectives are placed at an angle equal to the helix angle of the hob with the blank's vertical axis. If a helical gear is to be cut, the hob axis must be adjusted at an angle equal to the sum of the hob's helix angle and the helical gear's helix angle. Feeding the revolving hob till it reaches the desired depth of the gear tooth is how gear hobbing is done.
The method of gear hobbing is classified based on the directions in which the hob is fed for gear cutting, but this should not be confused with the two different techniques for gear cutting that will be explained in the next paragraph. Hobbing with axial feed, radial feed, or tangential feed are the three different forms of gear hobbing. When the hob is fed parallel to the axis and along the face of the blank, it is referred to as axial feed.
This process is used to make spur and helical gears. The hob is fed against the gear blank in a radial direction when the gear blank and hob axes are placed normal to each other. In the production of worm wheels, this type of feed is used.
Tangential feed, which is employed for worms, occurs when the hob is held horizontally with its axis at a right angle to the blank's axis. The hob is set to the tooth's full depth before being fed forward axially. The hob is fed perpendicular to the gear blank's face. Worms are also produced using this procedure.
When it comes to gear hobbing, there are two basic cutting strategies: climb cutting and conventional cutting.
The terms "climb" and "conventional" relate to the direction in which the hob feeds into the workpiece in relation to the table or spindle nose. When possible, it is advised that conventional cutting be employed for optimal stability during cutting. In traditional hobbing, the hob is fed into the piece, moving parallel to the blank axis toward the table or spindle nose.
The hob is fed away from the table or spindle nose, parallel to the blank axis, in climb hobbing.
The three unique motions of the gear hob: tool rotation about its axis, tool axial displacement, and workpiece revolution around its axis must be determined by the direction and axial feed to establish which hobbing strategy should be utilised in a given application.
As a general rule, climb hobbing results in longer tool life and greater precision, but conventional hobbing results in a better finish.
When hobbing, the tool's teeth, or hob's teeth, make simultaneous contact with the workpiece. These teeth generate involute tooth gaps in a generating method, thanks to the constant interaction of the tool and the workpiece rotating motion.
One of the complexities in hobbing is arranging the cutting configuration in a way that will produce the desired tooth profile, whether standard or modified in some way, as long as the cutting configuration corresponds to the selected design structure specifying the geometric and kinematic parameters of the tool's tooth profile such that the tooth trough in the gear is produced in an orderly manner and the cutting configuration corresponds to the selected design structure specifying the geometric and kinematic parameters of the tool's tooth profile such that
Due to the synchronization required to manufacture gear teeth, the kinematics of this complex operation is dependent on three relative motions between the gear and the work gear. The hob tool and the work gear move in a connected revolution ratio when gear hobbing.
These revolutions are coordinated with hob axial-feed and are determined by the cutter's number of starts and the work piece’s number of teeth.
One of the most essential principles in gear hobbling is the generating process. The cutting tool geometry, among other things, can influence cycle times and tool wear in the gear production process.
The hob is essentially a worm with cutting edges created by gashes sliced across it. A hob can alternatively be thought of as a collection of racks arranged around the circle of a cylindrical instrument.
Each subsequent rack is axially adjusted to generate a worm, which is usually a single thread. To create changed tooth shapes, you can customize the shape of a cutting tool. Table 1 shows the benefits of the various modifications:
Modification | Advantages |
Topping Hob | Eliminates the requirement for final turning by reducing the outside diameter of the gear tooth |
Semi-Topping | Softens the transition between the tooth flank and the outer diameter. |
Protuberance | Provides a mix between the hobbed root area and the finished flank Provides a uniform stock for the finishing tool |
- Tool wear is also concept of gear manufacturing that is highly researched as it is very difficult to model and predict due to the generating-rolling principle that governs the hobbing kinematics.
- There are crucial gearing characteristics that might influence the tool life time in a very favorable or negative way when it comes to the wear effects of the tool geometry.
- Modifications to the hob's tooth profile can be made to enhance the manufacturing of a specific workpiece.
- These unique characteristics are frequently employed in industrial applications, but only internal business knowledge is currently available.
- During hobbing, the distinct chip generation on each cutting tooth causes various wear laws, which usually results in unequal wear distribution on the hob teeth.
- Certain faults in the hob will lead to tool wear, such as the simultaneous and intermittent participation of two or more cutting edges of the tool teeth in hobbing.
- As a result, substantial local wear at the tooth tip can occur, resulting in tool life loss. On specific jobs when a custom hob must be manufactured with longer runs, these flaws must be taken into account.
- There are numerous elements to consider while optimising the gear hobbing process; one of the most essential elements is the cutting forces involved in this process, as the cutting forces will contribute to chip formation and tool wear throughout the hobbing process.
- As a result of the tool and machine wear induced by the forces, the pricing of the part in production may be affected. There are several models in which authors have built models to anticipate cutting forces, however due to the complicated nature of the kinematics of gear hobbing, there is currently no means to precisely evaluate cutting forces, tool wear, or the chip generation process. As indicated in Figure 1, cutting forces are often split into small cutting-edge parts.
- Material qualities, in addition to the geometries of the gear workpiece and the hobbing tool, have an impact on the gear hobbing process. High-speed steel and carbide are common materials for hob tools
- The material for the hob is determined by the material of the gear blank and the speeds at which the hobbing procedure will be performed.
- Hobbing tools composed of solid tooling material, such as tungsten carbide, are commonly used to manufacture steel gear work pieces.
- Studies have also demonstrated that matching the substrate with a suitable coating can result in a significant increase in the applied cutting speed. Researchers have proposed new proposals and ways to improve the precision and efficiency of hobbing, such as simulating the kinematics of the hob.
- Machine control and tool development are inextricably linked, ensuring that gear manufacture improves with time.
Machining accuracy
Gear hobbing has a high level of movement precision, yet gear shaping has an excellent profile and surface quality. Because of the following reasons:
1) The mechanical gear shaper's transmission chain is more complicated. The most notable difference is that the tool worm gear pair has one more pair than the gear hobber, implying that there is greater transmission error. The tool spindle's reciprocating motion and the table's moving portion are both easy to wear.
The accumulated error of the pitch of the gear shaper must also be reflected on the gear because the tooth profile of the gear to be machined is obtained when meshing with the gear shaper without clearance, so the kinematic accuracy of the gear shaper is generally lower than that of the gear hobbing. It is important to utilise a gear shaper and a precision gear shaper in order to process gear with high precision.
However, with the widespread usage of gear shapers, this problem has been effectively handled, as the CNC gear shaper's axes are independently controlled, the transmission chain is substantially shorter, and the transmission error is substantially decreased.
2) The circumferential feed, which can be selected, determines the number of tangents to form the profile envelope during gear shaping, whereas the number of tangents to form the involute envelope during gear hobbing is only related to the number of grooves and heads of the helix, and the number of tangents of the envelope cannot be increased or decreased by changing the number of grooves and heads of the helix.
As a result, gear shaping has a far higher surface polish than gear hobbing, and the tooth profile error is also lower.
3) A gear shaper cutter installation fault has little impact on tooth profile error, however a hob installation fault will result in a considerable workpiece tooth profile error.
The gear shaper cutter is shaped like a spur gear or a rack. In comparison to hob, the manufacturing method is simple, making it easier to manufacture more precisely, resulting in improved gear machining precision.
As a result, gears with low kinematic precision can be handled directly by gear shaping, rather than shaving or grinding, from the standpoint of machining accuracy.
Gear and pre-shaving gear, on the other hand, have higher kinematic accuracy requirements (shaving does not improve kinematic accuracy), hence gear hobbing is preferable.
Productivity
In general, gear hobbing has a better productivity than gear shaping. Gear shaping can only compete with gear hobbing when the gear has a compact module, a large number of teeth, and a tiny tooth width.
This is because:
1) The job cuts while rotating, resulting in a faster cutting speed and reduced empty stroke loss. The gear shaper cutter is reciprocating, which restricts the rise in cutting speed, and the actual cutting stroke length accounts for just approximately a quarter of the overall stroke length, resulting in a substantial empty stroke loss.
2) Multiple hobs can be employed to increase rough hobbing efficiency.
3) Gear hobbing moving time is proportional to the number of teeth on the workpiece, but gear shaping moving time is solely dependent on the diameter of the workpiece. Gears having a big diameter and a tiny module, in other words, are suited for gear shaping.
Gear shaping productivity is generally lower than gear hobbing productivity when processing gears with more than 5 modules, due to the necessity to remove a large number of redundant metals.
Key Takeaways:
- These revolutions are coordinated with hob axial-feed and are determined by the cutter's number of starts and the work piece’s number of teeth.
- There are crucial gearing characteristics that might influence the tool life time in a very favorable or negative way when it comes to the wear effects of the tool geometry.
- These unique characteristics are frequently employed in industrial applications, but only internal business knowledge is currently available.
Mechanisms & Attachments for Milling:
Attachments for Milling Machine: The numerous attachments are defined underneath and additionally how they growth the flexibility of the milling system.
1. Vertical Milling Attachment or Swivel Attachment:
This attachment is acceptable on horizontal milling machines for substituting the horizontal spindle through a vertical spindle movement. The attachment is a proper-attitude equipment field having bevel equipment set in ratio of 1 : 1 and the axis of the vertical spindle may also be swiveled through 45°, accordingly permitting the machining of bevels and slanted surfaces. With the assist of this attachment, the operation of milling horizontal surfaces and making grooves and slots with shank kind give up turbines etc. also can be accomplished on horizontal milling system.
The attachment is suited for the column of the system with 4 bolts.
2. High-Speed Milling Attachment:
With the assist of this attachment the velocity of the spindle may be improved 3 to 4 instances in order that the operation with small cutters can be accomplished efficiently. The attachment is established at the column with 4 bolts and may be swiveled additionally at any attitude.
3. Slotting Attachment:
With the assist of this attachment, rectangular holes, slots and a number of jobs may be made on milling system which a rotary device can’t do. This unit is established at the column face and converts rotary movement into reciprocating movement. The traditional variety of linear motion is zero-10 cm with an adjustment for 360 tiers swivel. This attachment lets in the machining of keyways, slots and sure grooves.
4. Universal Dividing Head (Index Head):
This attachment may be very crucial for a milling system. It is used for slicing equipment enamel, slots or grooves at the outer edge of the paintings. With its assist the activity may be circled through genuine tiers and through numerous strategies of indexing (direct, easy or compound), almost any quantity of genuine slots or enamel may be reduce. The indexing can be finished through hand or automatically.
For computerized rotation of activity, the correlation of rotation with feed desk is labored out, and gearing association is furnished on the give up of index head which can be linked to the desk using mechanism.
Thus non-stop movement for indexing of the paintings may be obtained. This energy pressure may be very beneficial for milling such paintings-portions as twist-drill flutes, helical gears, spiral milling cutters and lots of different portions having a helix or comparable geometric form. Swivel Vise
5. Circular Milling Attachment:
This is a type of rotary desk furnished with T-slots. Its circumference is split into tears and can be hand-listed for spacing or finding slots, grooves, or holes. For the motive of milling around arc or groove at the activity, an association may be used to make it energy-operated to offer non-stop movement. Index plates also can be suited for this attachment for acquiring genuine rotation of the activity through any fraction of a circle. With the assist of this attachment, may also profiles may be produced, including immediately or curved slots, grooves, cams and rounded ends on work piece.
6. Rack Milling Attachment:
It is used for milling immediately or willing racks or cross-slotted portions of big lengths on horizontal or usual milling system. It includes a milling unit, a fixture and a rack indexing unit. The milling unit is established at the column face and is supported on the front through an overarm. It has a spindle having its horizontal axis at proper angles to that of the system.
7. Vise:
This is likewise a totally crucial attachment and is bolted to the pinnacle of the desk. It may be fixed to the desk in any function through fastening the T-bolt at the ears on the give up of the vise. It is normally used as useless center to help the activity. It holds the paintings-portions securely and allows in orienting it accurately. Work-piece is held among hardened and floor jaws.
Vises are of 3 kind’s viz., (a) undeniable (b) swivel (Refer Fig. 16.23) device-maker usual . Milling system vises are typically exact in step with the jaw lengths. The widespread metric sizes are 125, 160, 2 hundred and 250 mm. The undeniable vise may be bolted to the desk either parallel or perpendicular to the system spindle. The swivel vise may be swiveled in a horizontal aircraft and may be used for containing paintings to be reduce at attitude.
The usual vise may be swiveled in a horizontal aircraft and also can be hinged up far from the aircraft of the desk for an attitude of zero to ninety tiers, accordingly making it viable to modify the activity in any manner Compound angled surfaces may be milled with this kind of association. However, the scale of the paintings that may be held through the vise is limited.
8. Arbors:
Arbors are used to maintain milling cutter on milling machines. All peripheral milling cutters, shell give up turbines, etc., are established on arbors and held with inside the spindle through a draw bolt association (Refer Fig. 16.26). The cutter is pushed through a key geared up at the arbor. One or greater arbor helps can be furnished to make certain introduced rigidity.
Arbors may be both lengthy or stub. Small shell give up turbines and face turbines and facet and face cutters are established at the front give up of stub arbors. The stub arbor is held with inside the spindle through a draw bolt association, however the arbor being brief isn't supported at its loose give up.
i. Hydraulic Clamping Vice (Fig. 16.27 (a)): Accurate, and without problems adjustable vice. Simple and fast operation through hydraulic action. The clamping strain may be adjusted and controlled. Mechanical coarse adjustment and hydraulic clamping operation.
Ii. Mechanically Operated High Pressure Clamping Vice (Fig. 16.27 (b)): Robust and robust design. Head and clamping slide may be shifted and placed at the decrease slide segment by way of adjustable pins. Basic slides of various lengths may be used and mixed to offer a double appearing vice.
Iii. Universal Precision Vice (Fig. 16.27 (c)): Special, quality grained, grey solid iron. Swiveling of the vice on its cradle through 360o. Swiveling of the cradle on the bottom plate through 360o. Inclination of the vice surface: 90o in a single direction, 30o with inside the different direction.
Cutting parameters:
Milling Process Parameters
The choice of reducing parameters has an immediate impact on machining nice, machining performance, and device lifestyles. The reducing will produce specific outcomes the usage of specific reducing parameters with inside the identical technique circumstance. The technique parameters decided on in milling technique consist of spindle velocity of revolution, reducing intensity, reducing width, and feed price, as proven in Figure.
Process Parameter Vector Spindle Speed of Revolution.
Spindle velocity of revolution determines the rate of reducing area relative to the work piece, namely, reducing velocity. Since reducing velocity has the amazing impact on device lifestyles, the choice of reducing velocity pertains to the sturdiness of device closely.
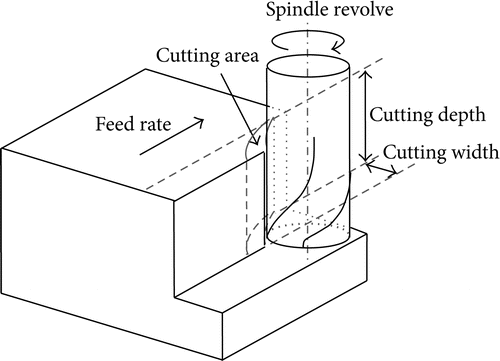
Too low or too excessive reducing velocity will reason the device lifestyles to say no dramatically. Meanwhile, with inside the milling of thin-walled work piece, spindle velocity of revolution has a large impact on the stableness of reducing. Therefore, the spindle velocity of revolution must be decided on discreetly in milling technique.
Cutting Depth and Cutting Width.
Cutting intensity and reducing width are limited via way of means of spindle strength, transmission strength of device, cloth type, device parameters, coolant, machining procedure, and the stiffness of device device-device-work piece system.
Therefore, they must be decided on fairly consistent with machining nice, machining performance, and machining procedure. Generally, machining performance is the primary intention in roughing machining, so a bigger reducing intensity and reducing width must be decided on.
Quality of work piece floor is the principle intention in completing machining, so a much less reducing intensity and reducing width must be decided on.
Feed Rate.
Feed price is the rate of feed circulate of the reducing device relative to work piece in milling technique. Generally, linear feed price is followed in realistic manufacturing and its miles described as feed in keeping with minute.
The feed price of milling will have an effect on the machining accuracy, floor nice, deformation of the work piece, and device lifestyles directly. And it's also limited via way of means of device parameters, work piece cloth, device path, stiffness of device, and overall performance of feed system.
In machining technique, the feed price of milling is chosen consistent with element cloth, geometry features, nice requirements, and the functionality of device.
The process parameters mentioned above can be written in the form of vector, as shown in
Pp={n,ap,we,f},
Wherein these parameters represent spindle speed of revolution, cutting depth, cutting width, and feed rate.
Then, a process parameter vector space consisting of four dimensions is established.
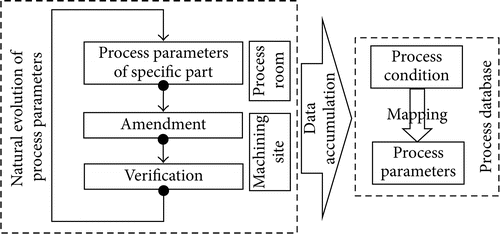
Mapping of Process Condition to Process Parameter
Process parameters are the concrete example of technique expertise with inside the machining of realistic work piece and technique expertise is implicit with inside the technique statistics. Process statistics gathered in realistic manufacturing is used, amended, and established again and again via lengthy time, after which the herbal evolutional technique expertise is achieved.
Therefore, the technique statistics gathered in realistic manufacturing implies a massive quantity of field-confirmed technique expertise.
These statistics must be mined deeply and the technique expertise must be used with inside the choice of technique parameters.
The experiential technique statistics of realistic manufacturing is analyzed and organized consistent with the proposed circumstance vector and technique parameter vector, after which those statistics are gathered into technique database.
The technique parameter vectors are matched with the circumstance vectors, and the mapping of circumstance vector area to technique parameter vector area is constituted. The technique of herbal evolution of technique parameters and accumulation of statistics is proven in Figure 3.
Types of milling operations:
Slot Milling
In this method, the width of the cutter is much less than the width of the work piece: it's far used to make a slot with inside the work piece. Thin cutters make for skinny slots. To reduce the piece in, a completely skinny slot may be made to undergo the intensity of the work piece. Another call for this method might be “noticed milling.”
Vertical Milling
The maximum not unusual place device utilized in vertical milling is the cease mill or a flat-bottomed cutter. In a few cases, it is able to talk over with spherical-nosed cutters as well.
Horizontal Milling
A horizontal milling gadget is excellent for forming flat surfaces, dovetails, keyways, and gears. These machines are excellent operated via and up milling method wherein the metallic is fed into the cutter towards its rotating route. Compared to vertical milling, horizontal milling can exert most pressure towards the jaw conserving the work piece.
Side Milling
When the intention is to supply a flat vertical floor with inside the work piece, aspect milling is the operation to choose. The intensity of the reduce may be manipulated with the aid of using rotating the vertical feed screw of the desk.
Gang Milling
When or extra milling cutters are used collectively on one arbor whilst reducing horizontal surfaces that is called gang milling. The regular technique is to mount the milling cutters of various diameters, shapes, and/or widths on an arbor. The capacity combos of cutters are limitless and are decided in every case with the aid of using the desires of the job.
Straddle Milling
When you want or extra parallel vertical surfaces machined in an unmarried reduce, straddle milling is what you want. The method is completed with the aid of using mounting aspect milling cutters at the equal arbor, set aside such that they straddle the work piece.
Up (and Down) Milling
Also called traditional milling, up milling is whilst the cutter rotates towards the route of the desk feed. Contrast this with down milling, wherein the cutter rotates alongside the route of the desk feed. The difference? In up milling, the chip load on tooth will increase progressively whilst in down milling, the chip load at the tooth decreases.
Form Milling
The shape milling method lets in for machining unique contours composed of curves and directly lines—or probably most effective curves—in a unmarried reduce. This is completed with fashioned cutters, the ones fashioned to the contour of the reduce, or with a fly cutter floor mainly for the job. More not unusual place shape milling includes milling half-spherical recesses at the work piece.
Face Milling
In face milling, the scale and nature of the work piece determines the kind and length of the cutter required. The tooth at the outer edge of the cutter does maximum of the work, however, if the cutter is nicely floor, the face tooth dispose of a small amount of inventory that's left due to the springing of the work piece or cutter, generating a higher finish.
Turret Milling
Turret milling is completed with the aid of using drilling, reducing, and shearing. The spindle is desk bound at some stage in the milling method, whilst the desk movements alongside the X and Y axes. This method is regularly used for “lighter” operations.
Types of milling cutters
Some Cutters with Description
1. Roughing End Mill
This kind of cutter is used if you have to get rid of extra quantity of fabric from the paintings piece. By the usage of roughing cease turbines, we attain a difficult floor finishing. Roughing cease turbines also are well-known as “ripper” cutters.
They are extra useful commercially and are utilized in numerous business applications.
2. Slab Mill
This kind of cutter is used if you have to get rid of extra quantity of fabric from the paintings piece. They are extra useful commercially and are utilized in numerous business applications.
3. End mill
These sorts of milling cutters have the reducing tooth at the each sides. We use cease mill extra with inside the vertical milling processes. High velocity metallic or the cemented carbide are used to create cease turbines. High velocity metallic is likewise referred to as HS or HSS.
The excessive velocity metallic doesn’t unfastened its hardness while the temperature increases. Hence, because of higher hardness the excessive velocity metallic is used to make cease turbines. The cease turbines are in most cases utilized in plunging, tracer milling, face milling, etc. Torus cutters, etc.
4. Hollow Mill
They also are referred as hole milling cutters. They appear to be a pipe having thicker walls. You will discover the reducing tooth of the whole turbines at the interior surfaces. Hollow milling cutters are used with inside the screw machines.
5. Ball Mill Cutter
Ball cutters also are well-known as ball nosed cutters. You may be effortlessly discover as ball cutters as their cease is hemispherical in shape. Ball cutters are used to lower the pressure attention and also are referred to as ball cease turbines. Whenever there may be want of reducing 3 dimensional shapes then, there may be a use of ball cutters to flawlessly reduce the ones 3-dimensional shapes.
Tool geometry & their specifications:
1. Shank:
It is that a part of an unmarried factor reducing device which is going into the device holder. Or in easy language shank is used to preserve the device.
2. Flank:
It is the floor beneath and adjoining to the reducing edges. There are flank surfaces, the primary one is most important flank and the second is minor flank. The most important flank lies beneath and adjoining to the aspect reducing facet and the minor flank floor lies beneath and adjoining to the give up reducing facet.
3. Base:
The part of the shank that lies contrary to the pinnacle face of the shank is known as base.
4. Face:
It is the pinnacle part of the device alongside which chips slide. It is designed in this sort of manner that the chips slide on it in an upward direction.
5. Cutting facet:
The facet at the device which eliminates substances from the paintings piece is known as reducing edges. It lies at the face of the device.
The unmarried factor reducing device has edges and those are
(i) Side reducing facet: The pinnacle fringe of the most important flank is known as aspect reducing facet.
(ii) End reducing facet: The pinnacle fringe of the minor flank is known as give up reducing facet.
6. Nose or reducing factor:
The intersection factor of most important reducing facet and minor reducing facet is known as nose.
7. Nose radius:
It is the radius of the nose. Nose radius will increase the existence of the device and presents higher floor finish.
8. Heel:
It is a curved component and intersection of the bottom and flank of the device.
Angles of Single Point Cutting Tool
The diverse angles of the unmarried factor reducing device have top notch importance. Each attitude has its very own characteristic and specialty.
1. End Cutting Edge Angle:
The attitude fashioned in among the give up reducing facet and a line perpendicular to the shank is known as give up reducing facet attitude.
2. Side Cutting Edge Angle:
The attitude fashioned in among the aspect reducing facet and a line parallel to the shank.
3. Back Rack Angle:
The attitude fashioned among the device face and line parallel to the bottom is known as again rake attitude.
4. End Relief Angle:
The attitude fashioned among the minor flank and a line every day to the bottom of the device is known as give up remedy attitude. It is likewise called the front clearance attitude. It keep away from the rubbing of the work piece in opposition to device.
5. Lip Angle/ Wedge Angle:
It is described because the attitude among face and minor flank of the unmarried factor reducing device.
Key Takeaways:
- The cutter is pushed through a key geared up at the arbor. One or greater arbor helps can be furnished to make certain introduced rigidity.
- Since reducing velocity has the amazing impact on device lifestyles, the choice of reducing velocity pertains to the sturdiness of device closely.
- Cutting intensity and reducing width are limited via way of means of spindle strength, transmission strength of device, cloth type, device parameters, coolant, machining procedure, and the stiffness of device device-device-work piece system.
- In machining technique, the feed price of milling is chosen consistent with element cloth, geometry features, nice requirements, and the functionality of device.
Indexing
- Indexing is the operation of dividing the periphery of a workpiece into numbers of equal parts. Example; if you want to make a hexagonal bolt. Head of the bolt is given hexagonal shape. You need to do indexing to divide circular workpiece into six equal parts and all the six parts are then milled to an identical flat surface. If you want to cut “n‟ number of teeth in a gear blank then the circumference of gear blank is divided into “n‟ number of equal parts and teeth are made by milling operation one by one. The main component used in indexing operation is the universal dividing head.
Universal Dividing Head
- It is most common and the popular type of indexing arrangement. As indicated by name itself “universal”, it can be used to do all types of indexing on a milling machine. Universal dividing head can set the workpiece in vertical, horizontal, or in inclined position relative to the worktable.
Construction and Working of Universal Dividing Head
- Universal Dividing Head/ Indexing Head consist of a robust body & a worm drive is enclosed in it. It has a worm and worm wheel arrangement as shown in fig.
In this, the dividing head spindle carries a worm wheel that meshes with the worm.
- This worm always carries a crank at its outer end. The index pin works inside the spring-loaded plunger, which can easily slide radially along a slot provided in the crank.
- This plunger can slide and adjust the pin position along a desired whole circle on the index plate.
- The index plate is mounted on the same spindle as the crank, but on a sleeve, so the crank and worm spindle can move independently on the index plate.
- To set a particular distance along the desired whole circle, sector arms are used. Sector arms are of detachable type and can be set at the required angles with one another. The index plates are available in a set of 2 or 3, with a number of whole circles generally on both sides.
Simple Indexing (Plain Indexing)
- Indirect Indexing is basically used when the index number does not permit direct indexing.
- The worm shaft, attached to the crank, should be engaged with the worm wheel on the indexing spindle. The index plate is secured to the head housing and has no motion during simple indexing
- The indexing spindle is rotated by the index crank, over a worm gear set with a single thread worm & worm gear wheel with 40 teeth.
- Since there are 40 teeth on the worm wheel, one complete turn of the index crank will cause the spindle as well as the work to rotate 1/40 of a turn.
- Similarly, 40 turns of the crank will rotate the work 1 complete turn.
- In order to calculate the indexing data or the number of turns of the crank for most division, it is necessary only to divide 40 by the number of divisions to be cut.
- Indexing crank movement = 40 N
N-number of required divisions
- Indexing plates which are available:
- Plate 1 16, 30, 33, 36, 39, 51, 57, 63
- Plate 2 22, 24, 27, 29, 37, 43, 49, 59
- Plate 3 23, 25, 28, 31, 41, 47, 53, 61
Problem 1:
Calculate indexing required to cut 60 slots of the workpiece.
Indexing crank movement = 40 N = 40 60
= 2 3
= 12/18
(Means, 12 holes on 18 hole circle.)
Problem 2:
Calculate indexing required to cut 23 slots of the workpiece.
Problem 3:
Calculate indexing required to cut 35 slots of the workpiece.
- If, however, it was necessary to mill 7 slots, then the indexing data would be:
- Indexing data = 40 N = 40 7 = 5 5/7 turns of the index crank
- Five complete turns of the crank are easily made, however, the 5/7 of a turn involves the use of the index plate and sector arms. To get 5/7 of a turn, choose any whole circle which is divisible by the denominator 7, such as 28.
- Then, take 5/7 of 28 = 20 (means, 20 holes on a 28 whole circle plate).
- Therefore, the indexing data for 7 slots would be 40/7 = 5 5/7 turns or 5 complete turns plus 20 holes on 28 hole circle plate.
Compound indexing:
- When none of the indexed plate has a whole circle which enables the work to be divided by simple indexing method we can use compound indexing.
The procedure is explained as;
Let;
z = no. Of division needed
Crank rotations for each indexing= 40/z
- Write z above and 40 below a straight line and factorized them
- Select 2 numbers representing 2 whole circles in the same plate.
- Write these numbers below 40 and factorized them.
- Write their difference above z and factorize it. These whole numbers are to be chosen in such a manner that all the factors above the line gets cancelled out.
Let these holes number be N1 and N2
Let n1 be the numbers of holes indexed in N1 whole circle, and n2 the number of holes to be indexed in N2 hole circle.
Then;
n 1/N1 +/- n 2 /N2 = 40/z
n1 and n2 are found by hit and trail method.
Example Let z=77
Steps;
- 77=11x7
40=2 x 2 x 2 x 5 - Let N1= 21 and N2 = 33
Difference 12= 2 x 2 x 3
Therefore
77 = 11 x 7
40 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 5
21 = 7 x 3
33 = 11 x 3
Since all the factors above the line get cancelled out, therefore, selection of N1 and N2 is correct.
Now;
n1 /21 +/- n 2/33 = 40/77
Values of n1 and n2 would be determined by hit and trail method.
Differential Indexing
- When it is not possible to calculate the required indexing by the indirect indexing method, that is, when the fraction 40/N cannot be reduced to a factor of one of the available whole circles, it is required to use differential indexing.
- With this method of indexing, the index plate is unlocked leaving it free to turn either backward or forward a part of a turn to attain the proper indexing or spacing
- A gear train is set-up to join the outer end of the spindle to the worm shaft. When index crank is turned to move the spindle, the gear train will cause the index plate to turn at the same time.
- The rotation of the plate can be either in the same direction (positive) or in the opposite direction (negative) of the index crank. This change of rotation is effected by an idler gear or gears in the gear train.
- When it is required to calculate the indexing data for a required number of divisions by the differential methods, a number is chosen close to the required divisions which may be indexed by indirect indexing.
- To illustrate the principle of differential indexing, assume that the index crank has to be rotated 1/9 of a turn, and there is only 8 whole circle available.
- If the crank is be moved by 1/8 of a turn, the index pin will contact the plate at a spot after the first 1/9 turns.
- The exact position of this spot would be the difference between 1/8 and 1/9 of a revolution of the crank. This would be 1/8 – 1.9 = (9-8)/72 = 1/72 of a turn more than 1/9 of a turn.
- As, there is no hole at this point into which the pin could engage, it is necessary to cause the plate to rotate backwards by means of change gears 1/72 of a turn in order that the pin will engage in a hole using an arrangement
- At this point, the index crank will be locked at exactly 1/9 of a turn. The method for the calculation of the change that gears required to rotate the plate the proper amount is as follows:
- Change gear ratio = (A – N) x 40/A
= Driver (work spindle gear) / Driven (worm shaft gear)
A – Approximate number of divisions (selected number)
N – Required number of divisions
- When the approx. Number of divisions is larger than the required number the resulting fraction is plus and the index plate must move in the same direction as the crank (clockwise).
- However, if the approx. Number is smaller than the required number the resulting fraction is minus and the index plate must move in a counter clockwise direction.
- The numerator of the fraction shows the driving (work spindle) gear or gears, while the denominator shows the driven (worm shaft) gear or gears.
Procedure:
Let z = no. Of divisions required to be indexed
k = number very nearly equals to z
No. Of crank turns for each simple indexing
n = 40/k
No. Of crank turns needed for z indexing
N = 40z/k
- If N >40, then(N-40) turns have to be subtracted
- If N < 40 , then (40-N) turns indexed plate should rotate in same direction as of crank.
The gear ratio will be:
I=40(k-z)/k
Example: Do differential indexing for 93 divisions
Solution;
z = 93, therefore,
Let k = 90, which can be simple indexed each indexing = 40/90 =4/9 =8/18, i.e., 8 holes in an 18 holes circle.
For 93 indexing’s,
N = 8/18 x 93 = 41 1/3
Since N>40, the indexed plate must rotate 4/3 backward
I=40(k-z)/k= 40/90 x 3 =4/3
In brown and sharp dividing head, the gears supplied are 24,28,32,40,44,48,56,64,72,86,100
Slotter: Introduction
Slotter device is described as a device makes use of fore casting off undesirable fabric chips from the work piece to make splines, grooves and more.
Here the Ram (Tool connected) movements reciprocating, while in shaper the ram movements horizontally. This is a reciprocating kind of Machine device.
Application of Slotter Machine
Slotter device is used to provide slots, keyways, and equipment teeth.
It is used for machining inner and outside flat surfaces and round surfaces.
If there's a want for shaping outside and inner varieties of profiles then slotter is the satisfactory choice.
It is used for machining abnormal surfaces, blind holes, dies and punches, outside and inner equipment teeth.
Advantages of Sotter Machine
It is a light-weight device and may be without problems transportable.
It makes use of an unmarried factor slicing device that is economical.
It offers you can correct floor finish.
The price of this device is low in comparison with different machines on this category.
Disadvantages of Slotter Machine
A Very Skilled employee is needed to function the slotter.
Working Principle of Slotter Machine:
The running of the Slotter device is just like the shaper device do however the predominant distinction among them is the Shaper device works horizontally while Slotter machines paintings vertically.
As we've got studied all of the components in detail. Now the ram is attached to the crank and crank linked to the gears.
So what came about right here is whilst we boom or lower the tools velocity, the rotation of crank will increase and decreases.
And as in step with those, the ram movements up and down. We have connected the work piece into the paintings desk and manually we carry the ram close to the work piece and in line with the ram we alter the worktable after which we must clamp it.
Now we deliver the electricity as in step with tools the crank rotates and the crank is attached to the ram so ram movements up and down.
During down (ram movements down) the reducing stroke takes region and at the same time as shifting up or go back stroke there's no reduce.
If we must reduce on the special sections then manually we deliver feed to the paintings desk and as in step with requirement, it cuts.
Types of drives for slotter:
Drive Mechanism of Slotting Machine:-
In slotting machine, the metallic is reduce in the course of the upward stroke and no metallic is eliminated in the course of the downward stroke.
So, the time taken in downward stroke may be decreased to enhance the operating pace of the machine. So, brief go back mechanism is used to pressure the ram of the slotting machine.
Quick go back mechanism is an apparatus to supply a reciprocating movement wherein the time taken in go back stoke is much less than time taken in ahead stroke. There are 3 kinds of brief go back mechanism which may be utilized in slotter machine:-
Slotted disc mechanism
It is the most effective of all of the ram power mechanisms and may be very normally utilized in length slotting machines. In this mechanism, the using pinion receives power from a pulley which runs via belt with the aid of using motor. The pinion rotates the tools which in flip rotates the slotted using disc.
The rotation of the slotted disc is transformed into the vertical reciprocating movement ram with the assist of connecting rod. The duration of stroke of ram may be modified with the aid of using moving the crank pin in the direction of or from the middle of the slotted using disc. Position of the stroke is adjusted with the assist of hand lever furnished for adjustment.
Variable pace reversible motor power
Such a power is utilized in big modem slotting machines. Slotting machines have a connected or enclosed motor power with a multi pace tools field to present various speeds to the ram. A traditional variety could be forty to one hundred fifty strokes or cycles in step with minute.
Hydraulic power
Hydraulic power is utilized in big-modem slotted machines. The power is much like that hired for the shapers. In this power, the hydraulic cylinder is in vertical direction. Both consistent stress and consistent quantity kind drives are used.
Types of Slotter Machine:
Slotter Machines are may be categorized in those four-types.
- Punch Slotter
- Precision Tool room slotter
- Production Slotter and
- Special Purpose Slotter Machine
Let me provide you with a quick know-how of those four sorts of Slotter Machine.
Punch Slotter:
This is a heavy and inflexible kind of device. This device designed for the elimination of a massive quantity of metallic from cast or forged fabric. The period of the puncher slotter is massive it can be as long as 1800 to 2000 mm.
How does Punch Slotter paintings?
The ram is commonly pushed with the aid of using a spiral pinion meshing with the rack tooth reduce on the bottom of ram.
The pinion is pushed with the aid of using a variable velocity reversible electric powered motor just like that of a planer device. The Feed is managed with the aid of using electric tools.
Precision Tool room Slotter:
The device room slotter works with top device velocity and produces an correct floor finish.
Production Slotter:
This kind of slotter is used for machining tapered jobs with the aid of using ram swivel to ten to 30 degrees.
Special Purpose Slotter Machine
This kind of slotter machines provide an excessive quantity of manufacturing at low cost, additionally it offers extra accuracy too. Keys eater is one of the unique functions of slotter machines.
It is used for machining keys at the wheel and tools hub
Slotter Machine Specification:
The specifications of a Slotter Machine is depended on the several factors some of these are:
- Power Input
- Type of drive
- Maximum table drive
- The maximum length of ram stroke
- Number of speed
- Number of feed
- Table feed
- Floor space required
- The diameter of the Work Table in MM
- KW of motor
A slotter machine is a machine tool in which material is removed for producing desired shapes. It is used for producing Machining cylindrical surfaces and flat surfaces.
Puncher Slotter Machine:
The puncher slotter is a rigid and heavier machine designed mainly for the removal of a large amount of metal from large castings or forgings. The length of the puncher slotter is sufficiently large which may be as long as 1800 to 2000 mm.
The ram of the slotter is driven by a spiral pinion meshing with the rack teeth cut on the underside of the ram and the pinion is driven by a variable speed reversible electric motor which is similar to the planer.
The feed is also controlled by electrical gears.
Production slotter:
Production Slotter is a heavy-obligation slotter including a heavy solid base and heavy body and is normally made in parts.
It’s in particular used for preferred manufacturing work. A slotted disc with a connecting rod is used for reciprocating the motion of the ram.
A flywheel is used on this slotter to save you stroke on the give up of the stroke. A slotter gadget is a manufacturing gadget.
This is a totally vintage form of the gadget and became invented with the aid of using BRUNEL.
The slotting gadget is just like a verticle shaper.
The ram sporting the slotting device reciprocates in a verticle guide-manner of the gadget.
This form of slotter is used for machining tapered jobs with the aid of using ram swivel to ten to 30 degrees. This form of slotter machines provide an excessive extent of manufacturing at low cost, additionally it offers extra accuracy too.
Keys eater is one of the unique functions of slotter machines. It is used for machining keys at the wheel and tools hub.
Tool room slotter:
Tool room slotter is precision kind with is locate for extremely unique machining. It is lighter system and is perform at excessive speeds.
By use unique jigs system can take care of some of same works on a manufacturing basis.
The major characteristic of a slotting system is to eliminate metallic from a bit of a piece to carry it to the desired form and size.
This is performed with the aid of using protecting the paintings rigidly at the system and a reciprocating unmarried factor device established on device head.
The unmarried factor device movements alongside a vertical axis over the paintings piece.
The pinion that's in mesh with the principle equipment receives its force from a pulley through a belt with the aid of using motor.
The equipment is coupled to the slotted disc. The round movement of slotted disc is transformed into the reciprocating one with the assist of connecting rod.
The crank pin may be officially set with inside the slot of slotted disc at one-of-a-kind distances from the center for verifying the duration of the ram stroke. The role of the stroke is adjusted with the assist of hand lever supplied for the stroke adjustment.
Slotting system is typically supplied with horizontal round worktable, however coordinate tables also are supplied a few times.
The desk is established at once over a mattress casting and heavy paintings can be located on it.
The round desk may be revolved with the aid of using hand or electricity fed.
It is graduated round its outer edges and paintings can for this reason be established and grew to become to a predetermined role, relying upon the characteristic for which slotter is designed.
Slotter Tools:
KIT-STO-825
KIT of 8 REV insert-carrier tools to execute keyway seatings on slotting machine.
It is comprised of:
• 8 insert-carrier tools with a diameter of 25 mm (UT-03,04,05,06,08,10,12,14/16)
• 1 square adapter AD-35
• 18 inserts (2 for each tool size with tolerance class from standard catalogue selection)
• 4 re-sharpeners (RF-1, RF-2, RF-3,RF-4)
• 1 painted steel tool-carrier base
• 3 Torx screwdrivers (T08, T15, T20).
KIT-STO-825-L
KIT of 8 REV insert-carrier tools to execute keyway seatings on slotting machine.
It is comprised of:
• 8 insert-carrier tools long line with a diameter of 25 mm (UT
03,04,05,06,08,10,12,14/16)
• 1 square adapter AD-35
• 18 inserts (2 for each tool size with tolerance class from standard catalogue selection)
• 4 re-sharpeners (RF-1, RF-2, RF-3,RF-4)
• 1 painted steel tool-carrier base
• 3 Torx screwdrivers (T08, T15, T20).
Key Takeaways:
- The ram is commonly pushed with the aid of using a spiral pinion meshing with the rack tooth reduce on the bottom of ram.
- This kind of slotter machines provide an excessive quantity of manufacturing at low cost, additionally it offers extra accuracy too. Keys eater is one of the unique functions of slotter machines.
- The ram of the slotter is driven by a spiral pinion meshing with the rack teeth cut on the underside of the ram and the pinion is driven by a variable speed reversible electric motor which is similar to the planer.
References:
1. Manufacturing Engineering & Technology, S. Kalpakjian & S.R. Schmid
2. Technology of Machine Tools, Krar &Oswald
3. Manufacturing Processes, M.Begman
4. Processes & Materials of Manufacture, R.Lindberg
5. Production Technology, HMT
Unit - 3
Milling
A milling machine is one of the most influential and versatile kinds of machines found in the manufacturing industry. Milling is the most widely used machine used in machine shops and modern manufacturing industries all over the world.
It is a type of machining process in which a cutter having multiple cutting edges is used to remove the material from the work piece. This machine tool makes up about 85 percent of the all-material removal process.
Definition:
The milling machine is a type of machine which removes the material from the work piece by feeding the work past a rotating multipoint cutter. The metal removal rate is higher very high as the cutter has a high speed and many cutting edges. It is the most important machine in the tool room as nearly all the operations can be performed on it with high accuracy.
MRR (Material Removal Rate) can be further increased by increasing the number of teeth on the cutter.
Milling Machine Application:
- Milling Machine is used for Machining flat surfaces, Slotting, Contoured surfaces.
- It is also useful for making Complex and irregular areas, Revolution surface, Gear cutting, Machining external and internal threads.
- Machining helical surfaces of various cross-sections and many more.
- It employed in the metal removing operation on a milling machine is that the work is rigidly clamped on the table of the machine and the revolving cutter which has multiple teeth is mounted on the arbor.
- The cutter revolves at high speed and the work is fed slowly past the cutter.
- The work can be fed in a vertical, longitudinal, or cross direction depending upon the type of milling machine being used.
- As the work proceeds, the cutter-teeth removes the metal from the surface of the job(work piece) to produce the desired shape.
Specification, types, column & knee type milling machine
Milling Machine Types
The various types of milling machines are as follows:
Column and knee type
- Hand milling machine
- Plain or horizontal milling machine
- Vertical milling machine
- Universal milling machine
- Omniversal milling machine
Manufacturing type or fixed bed type
- Simplex milling machine
- Duplex milling machine
- Triplex milling machine
Planer type milling machine
Special Type
- Rotary table milling machine
- Drum milling machine
- Profile milling machine
- Planetary milling machine
- Tracer controlled milling machine
- Pantograph milling machine
- NC/CNC milling machine
Column and Knee Type
- The most used type of milling machine for general shop work is the column and knee type machine. In this the table is mounted on the knee-casting which in turn is mounted on the vertical slides of the main column.
- The knee is vertically adjustable on the column so that the table can be moved up and down to accommodate work of various heights.
- The column and knee type milling machines can be further classified:
- According to the various methods of supplying power to the table.
- Different movements of the table. And
- The different axis of rotation of the main spindle.
1. Hand Milling Machine
- It simplest of all types of milling machine in which table feed is controlled by hand. In this the cutter is mounted on a horizontal arbor and is rotated by power.
- This type of milling machine is small in size and suitable for light & simple milling operations. Example: grooves, machining slots and keyway.
2. Plain Milling Machine
- Plain milling machines are much stronger than hand millers. The table feeding may be done either by hand or power. The plain milling machine with a horizontal spindle is also called as a horizontal spindle milling machine. The table may be fed in a longitudinal, vertical or cross directions.
The feed is:
- Longitudinal – when the table moves at right angles to the spindle.
- Cross – when the table moves parallel to the spindle.
- Vertical – when the table is adjusted in the vertical plane.
3. Universal Milling Machine
- It can be adapted to wide ranges of milling operations. In this the table can be swivelled to any angle up to 45o on either side of the normal position.
- In addition to 3 movements as discussed earlier in a plain milling machine, the table may have the 4th movement when it is fed at an angle to the milling cutter. Helical milling operation can also be performed on this.
- The capacity of this type of machine can be increased by using special attachments such as
- Dividing head or index head.
- Vertical milling attachment.
- Rotary attachment.
- Slotting attachment.
- This machine can produce spur, spiral, twist drill, bevel, reamer, milling cutter. All operations that are performed on a shaper can be performed using a universal milling machine.
4. Ominversal Milling Machine
- In this type of milling machine, the table has four movements of the universal milling machine. It can also be tilted in a vertical plane by providing a swivel arrangement at the knee.
- The additional swiveling arrangement of the table aids in machining spiral grooves in bevel gears and reamers.
5. Vertical Milling Machine
- In this, the position of the spindle is perpendicular to the table. This type of machine is adapted for machining slots, grooves and flat surfaces.
- It may be of plain or universal type and has all the movements of the table for a proper setting & feeding the work.
- The spindle head in this machine is clamped to the vertical column which is swiveled at some angle which allowing the milling cutter fixed on the spindle to work on angular surfaces. In some machines, the spindle can be adjusted up or down relative to the work.
Manufacturing of Fixed Bed Type Milling Machine
- These machines are heavy, large and rigid in construction. These machines can be differentiated from column and knee type milling machines by the construction of its table mounting.
- In this machine the table is mounted directly on the ways of fixed bed and the movement is restricted to reciprocating at a right angle to the spindle axis with no provisions for vertical or cross adjustments.
- It may be classified as simplex, duplex, triplex based on a machine provided with the single, double and triple spindle heads respectively.
- Simplex – single spindle head.
- Duplex – two-spindle head.
- Triplex – three spindle head.
Planer Type Milling Machine
- Planer Type Milling Machine is also called as “Plano-Miller”. It’s a heavy and large machine used for heavy-duty work having adjustable spindle heads in the vertical and transverse direction.
- Similar to a planning machine this machine also has a cross rail capable of being raised or lowered carrying the cutters. It has their heads and saddles, all supported by rigid uprights.
- This arrangement of driving multiple cutter spindles enables a number of surfaces to be machined. Hence, it obtains the great reduction in production time.
- The main difference between a player and a Plano-miller is in the table movement. In a planer, the table moves to give the cutting speed where as in a Plano-milling machine, the table movement gives the feed.
Special Types of Milling Machine
Milling machines of non-conventional design have been developed to suit special purposes. This machine has a spindle for rotating the cutter and provision for moving the tool or the work in different directions. The following special types of machines of interest are described below
1. Rotary Table Milling Machine
- In Rotary table milling machine the table is circular in nature and rotates about a vertical axis. In this machine, cutters are set at different heights resulting in one cutter roughing the workpiece and other one cutter finishing it.
- The advantage of this machine is that continuous loading and unloading of work pieces can be achieved by the operator, while it is in progress.
2. Drum Milling Machine
- It is similar to a rotary table milling machine. But the workpiece supporting table in this machine is called as “DRUM” which rotates in the horizontal axis.
- The face milling cutters that are mounted on 3 or 4 spindle heads rotate in a horizontal axis and removes metal from work pieces supported on both the faces of the drum. The finished machined parts are removed after 1 complete turn of the drum and then the new ones are clamped to it.
3. Planetary Milling Machine
- In this, workpiece is held stationary while the revolving cutter. The cutter moves in a travelling path in order to finish a cylindrical surface on the work piece either externally or internally. This machine is also adapted for milling external and internal threads
4. Pantograph Milling Machine
- A pantograph machine can replicated a job by using a pantograph mechanism. It enables the size of the work piece reproduced to be smaller than, equal to or greater than the size of a template. It is also used for the different model for special purposes.
- A pantograph is a mechanism that is generally consist of four bars or links which are connected in the form of a parallelogram.
- Pantograph machines are available in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional models. The 2-dimensional pantograph is used for engraving letters or other designs. Whereas the 3-dimensional models are employed for copying any shape & contour of the work piece.
5. Profiling Milling Machine
- A profiling machine duplicates the full size of the template attached to the machine. In this, the spindle may be adjusted vertically and the cutter horizontally across the table.
- In this machine, hardened guide pin controls the movement of the cutter. The longitudinal movement of the table & the crosswise movement of the cutter head follow the movement of the guide pin on the template.
6. Tracer Controlled Milling Machine
- This type of machine reproduces irregular and complex shapes of dies, molds by synchronized (matched) movements of the cutter & tracing elements.
- The movement of the stylus energized an oil relay system, which operates the main hydraulic system for the table. This type of arrangement is termed as a servomechanism.
Fixed bed type milling machines
A constant mattress type, as its call hints, is a kind of milling gadget that has an inflexible mattress connected to the gadget. You can't set up the saddle and knee of this milling gadget.
It has a movable spindle head-set up with the spindle of the gadget. The gadget can carry out slicing operations with the aid of using shifting in horizontal and vertical instructions.
1. Simplex Milling Machine
The spindle or the spindle head can journey in a single path only. The maximum not unusual place path wherein it is able to flow is vertical.
2. Duplex Milling Machine
The spindle can flow in each horizontal and vertical instructions.
3. Triplex Milling Machine
The spindle can flow in all 3 instructions i.e. X Y and Z axis.
Production milling machines:
HPSM’ provide a one of a kind variety of SPM Production Milling Machine, that is fabricated from excessive grade uncooked substances.
These machines may be custom designed as in line with our treasured customer’s specifications.
Offered machines are broadly liked through the customers for his or her smooth installation, easy capability and longer carrier life
A milling system is one of the maximum influential and flexible sorts of machines determined with inside the production industry. Milling is the maximum broadly used system utilized in system stores and current production industries all around the world.
It is a sort of machining method wherein a cutter having a couple of reducing edges is used to put off the fabric from the work piece.
This system device makes up approximately eighty five percentage of the all fabric elimination method.
The numerous blessings of Milling are:
- High pace
- Better floor end
- Increase productivity
- High accuracy
High pace: In Milling, the price of metallic elimination may be very excessive because the cutter rotates at a excessive pace and has a couple of reducing edges. Better floor end: The floor end of the substances machined at the milling system is higher due to the multi-reducing edges.
Increased Productivity: CNC Milling Machines are the machines wherein the milling operation is being managed through software. It has expanded the general manufacturing with higher end and accuracy.
High Accuracy: In the milling system, the goods machined are of excessive accuracy particularly with inside the case of the maximum superior shape of milling system that is the CNC Machine.
Huge Application: Indexing head makes it appropriate for such a lot of packages as the precise rotation of the activity is feasible through the usage of it. Milling may be used for machining flat surfaces, abnormal surfaces, contoured surfaces, slotting, tools reducing and plenty of more.
The dangers of the milling system are as follows:
High Flank put on
High author put on
Breaking of carbide
High chatter and chip clogging.
High Flank put on: It has an excessive flank put on price which may be averted through decreasing pace and growing the feed price. Further to keep away from it one need to use tougher carbide with right geometry and sharpened reducing edges. High crater put on: High crater put on is determined which may be tackled through decreasing pace and the usage of tougher carbide.
Breaking of carbide: Sometimes the manufacturing method receives hindered due to the breaking of the carbide. The treatment for this trouble may be the usage of harder carbide, and stress of the cutter, system, and arbor need to be ensured.
High Chatter: This takes place because of negative stress of cutter, system, free arbor, and wrong geometry. This state of affairs may be stepped forward through growing feed, decreasing pace and the usage of unequal pitch cutters.
Chip clogging: The milling system additionally suffers from the trouble of chip clogging which may be decreased through the usage of decreasing the variety of enamel at the cutter and growing pace and chip pockets.
Special purpose milling machines such as thread milling Machines:
Thread Milling
- Thread milling operations are used to produce threads by using a single or multiple thread milling cutters. Thread milling operations are performed in special thread milling machines to produce accurate threads in small or large quantities.
- This operation requires three driving motions in the machine. One for the word, one for the cutter and the third for the longitudinal movement of the cutter.
- When the operation is performed by using a single thread milling cutter, the cutter head is swiveled to the exact helix angle of the thread. The cutter is rotated on the spindle and the workpiece is then revolved slowly about its axis. The thread is complete in one cut by the setting of the cutter to its full depth and then feeding it along the entire length of the workpiece.
- When the thread is cut by multiple thread milling cutter, the cutter axis and the work spindle are always set parallel to each other after adjusting the depth of cut equal to the full depth of the thread. The thread is completed by simply feeding the revolving cutter longitudinally through a distance equal to the pitch length of the thread while the work is rotated through one complete revolution.
Thread milling is a versatile, cost-powerful manner for each person reducing quite a few threads, components and work piece substances at the identical machine.
Our strong carbide thread mills, multi-enamel index able insert cutters and Threading Wizard software program make it smooth to undertake this manner and bring incredible threads with extremely good shape and finish. In general, thread milling generates advanced burr-loose floor finishes and decreases device stock costs.
Shops can use the identical device for each left and right-hand threads in addition to for exceptional thread tolerances.
A vast variety of substances and hollow diameters also can be thread milled with the identical device.
Unlike tapping, threads produced through milling may be machined to complete intensity at excessive accuracy, even in hardened substances.
Gear Milling
The manner
- The spherical work piece is hooked up axially, perpendicular to the axis of the reducing device.
- The device is moved alongside the axis of the work piece and generators out the tools teeth area. The paintings piece is then circled through distance of 1 teeth area and milling is repeated.
- The work piece is processed, step by step till enamel are reduce across the complete work piece.
- To create willing enamel the cutter is angled in the course of the reducing, the work piece is circled slowly whilst the device is moved alongside work piece axis.
- In shape milling, the cutter referred to as a shape cutter travels axially alongside the duration of the tools teeth at the right intensity to supply the tools teeth. After every teeth is reduce, the cutter is withdrawn, the tools clean is circled (indexed), and the cutter proceeds to reduce some other teeth. The manner maintains till all enamel are reduce.
- Each cutter is designed to reduce various teeth numbers. The precision of the shape-reduce teeth profile relies upon at the accuracy of the cutter and the gadget and its stiffness.
- In shape milling, indexing of the tools clean is needed to reduce all of the enamel. Indexing is the manner of lightly dividing the circumference of a tools clean into similarly spaced divisions.
- The index head of the indexing fixture is used for this purpose. The index fixture includes an index head (additionally dividing head, tools reducing attachment) and footstock that is just like the tailstock of a lathe. The index head and footstock connect to the worktable of the milling gadget.
- An index plate containing graduations is used to manipulate the rotation of the index head spindle. Gear blanks are held among facilities through the index head spindle and footstock.
- Work pieces will also be held in a chuck hooked up to the index head spindle or can be geared up immediately into the taper spindle recess of a few indexing fixtures.
Key Takeaways:
- In this machine the table is mounted directly on the ways of fixed bed and the movement is restricted to reciprocating at a right angle to the spindle axis with no provisions for vertical or cross adjustments.
- This arrangement of driving multiple cutter spindles enables a number of surfaces to be machined. Hence, it obtains the great reduction in production time.
- The advantage of this machine is that continuous loading and unloading of work pieces can be achieved by the operator, while it is in progress.
- A profiling machine duplicates the full size of the template attached to the machine. In this, the spindle may be adjusted vertically and the cutter horizontally across the table.
- The spindle or the spindle head can journey in a single path only. The maximum not unusual place path wherein it is able to flow is vertical.
Hobbing
The quality, performance, service life, safety, and dependability of high-end power transmissions are all determined by high precision gears.
While there are a variety of ways for making these gears, such as milling or grinding, hobbing is the most common.
When compared to grinding, the hobbing technique has the benefit of being more precise and efficient at a cheaper cost.
Though part geometry limits the application of this method, hobbing is still the most productive technique of gear teeth generation for external spur and helical gears.
In the process of gear hobbing indexing movement, three critical parameters must be controlled: feed rate, angle between the axis of the gear blank, and the angle between the axes of the gear hobbing tool (gear hob).
The image shows a schematic diagram of how a gear hobbing machine is set up.
The hob's objectives are placed at an angle equal to the helix angle of the hob with the blank's vertical axis. If a helical gear is to be cut, the hob axis must be adjusted at an angle equal to the sum of the hob's helix angle and the helical gear's helix angle. Feeding the revolving hob till it reaches the desired depth of the gear tooth is how gear hobbing is done.
The method of gear hobbing is classified based on the directions in which the hob is fed for gear cutting, but this should not be confused with the two different techniques for gear cutting that will be explained in the next paragraph. Hobbing with axial feed, radial feed, or tangential feed are the three different forms of gear hobbing. When the hob is fed parallel to the axis and along the face of the blank, it is referred to as axial feed.
This process is used to make spur and helical gears. The hob is fed against the gear blank in a radial direction when the gear blank and hob axes are placed normal to each other. In the production of worm wheels, this type of feed is used.
Tangential feed, which is employed for worms, occurs when the hob is held horizontally with its axis at a right angle to the blank's axis. The hob is set to the tooth's full depth before being fed forward axially. The hob is fed perpendicular to the gear blank's face. Worms are also produced using this procedure.
When it comes to gear hobbing, there are two basic cutting strategies: climb cutting and conventional cutting.
The terms "climb" and "conventional" relate to the direction in which the hob feeds into the workpiece in relation to the table or spindle nose. When possible, it is advised that conventional cutting be employed for optimal stability during cutting. In traditional hobbing, the hob is fed into the piece, moving parallel to the blank axis toward the table or spindle nose.
The hob is fed away from the table or spindle nose, parallel to the blank axis, in climb hobbing.
The three unique motions of the gear hob: tool rotation about its axis, tool axial displacement, and workpiece revolution around its axis must be determined by the direction and axial feed to establish which hobbing strategy should be utilised in a given application.
As a general rule, climb hobbing results in longer tool life and greater precision, but conventional hobbing results in a better finish.
When hobbing, the tool's teeth, or hob's teeth, make simultaneous contact with the workpiece. These teeth generate involute tooth gaps in a generating method, thanks to the constant interaction of the tool and the workpiece rotating motion.
One of the complexities in hobbing is arranging the cutting configuration in a way that will produce the desired tooth profile, whether standard or modified in some way, as long as the cutting configuration corresponds to the selected design structure specifying the geometric and kinematic parameters of the tool's tooth profile such that the tooth trough in the gear is produced in an orderly manner and the cutting configuration corresponds to the selected design structure specifying the geometric and kinematic parameters of the tool's tooth profile such that
Due to the synchronization required to manufacture gear teeth, the kinematics of this complex operation is dependent on three relative motions between the gear and the work gear. The hob tool and the work gear move in a connected revolution ratio when gear hobbing.
These revolutions are coordinated with hob axial-feed and are determined by the cutter's number of starts and the work piece’s number of teeth.
One of the most essential principles in gear hobbling is the generating process. The cutting tool geometry, among other things, can influence cycle times and tool wear in the gear production process.
The hob is essentially a worm with cutting edges created by gashes sliced across it. A hob can alternatively be thought of as a collection of racks arranged around the circle of a cylindrical instrument.
Each subsequent rack is axially adjusted to generate a worm, which is usually a single thread. To create changed tooth shapes, you can customize the shape of a cutting tool. Table 1 shows the benefits of the various modifications:
Modification | Advantages |
Topping Hob | Eliminates the requirement for final turning by reducing the outside diameter of the gear tooth |
Semi-Topping | Softens the transition between the tooth flank and the outer diameter. |
Protuberance | Provides a mix between the hobbed root area and the finished flank Provides a uniform stock for the finishing tool |
- Tool wear is also concept of gear manufacturing that is highly researched as it is very difficult to model and predict due to the generating-rolling principle that governs the hobbing kinematics.
- There are crucial gearing characteristics that might influence the tool life time in a very favorable or negative way when it comes to the wear effects of the tool geometry.
- Modifications to the hob's tooth profile can be made to enhance the manufacturing of a specific workpiece.
- These unique characteristics are frequently employed in industrial applications, but only internal business knowledge is currently available.
- During hobbing, the distinct chip generation on each cutting tooth causes various wear laws, which usually results in unequal wear distribution on the hob teeth.
- Certain faults in the hob will lead to tool wear, such as the simultaneous and intermittent participation of two or more cutting edges of the tool teeth in hobbing.
- As a result, substantial local wear at the tooth tip can occur, resulting in tool life loss. On specific jobs when a custom hob must be manufactured with longer runs, these flaws must be taken into account.
- There are numerous elements to consider while optimising the gear hobbing process; one of the most essential elements is the cutting forces involved in this process, as the cutting forces will contribute to chip formation and tool wear throughout the hobbing process.
- As a result of the tool and machine wear induced by the forces, the pricing of the part in production may be affected. There are several models in which authors have built models to anticipate cutting forces, however due to the complicated nature of the kinematics of gear hobbing, there is currently no means to precisely evaluate cutting forces, tool wear, or the chip generation process. As indicated in Figure 1, cutting forces are often split into small cutting-edge parts.
- Material qualities, in addition to the geometries of the gear workpiece and the hobbing tool, have an impact on the gear hobbing process. High-speed steel and carbide are common materials for hob tools
- The material for the hob is determined by the material of the gear blank and the speeds at which the hobbing procedure will be performed.
- Hobbing tools composed of solid tooling material, such as tungsten carbide, are commonly used to manufacture steel gear work pieces.
- Studies have also demonstrated that matching the substrate with a suitable coating can result in a significant increase in the applied cutting speed. Researchers have proposed new proposals and ways to improve the precision and efficiency of hobbing, such as simulating the kinematics of the hob.
- Machine control and tool development are inextricably linked, ensuring that gear manufacture improves with time.
Machining accuracy
Gear hobbing has a high level of movement precision, yet gear shaping has an excellent profile and surface quality. Because of the following reasons:
1) The mechanical gear shaper's transmission chain is more complicated. The most notable difference is that the tool worm gear pair has one more pair than the gear hobber, implying that there is greater transmission error. The tool spindle's reciprocating motion and the table's moving portion are both easy to wear.
The accumulated error of the pitch of the gear shaper must also be reflected on the gear because the tooth profile of the gear to be machined is obtained when meshing with the gear shaper without clearance, so the kinematic accuracy of the gear shaper is generally lower than that of the gear hobbing. It is important to utilise a gear shaper and a precision gear shaper in order to process gear with high precision.
However, with the widespread usage of gear shapers, this problem has been effectively handled, as the CNC gear shaper's axes are independently controlled, the transmission chain is substantially shorter, and the transmission error is substantially decreased.
2) The circumferential feed, which can be selected, determines the number of tangents to form the profile envelope during gear shaping, whereas the number of tangents to form the involute envelope during gear hobbing is only related to the number of grooves and heads of the helix, and the number of tangents of the envelope cannot be increased or decreased by changing the number of grooves and heads of the helix.
As a result, gear shaping has a far higher surface polish than gear hobbing, and the tooth profile error is also lower.
3) A gear shaper cutter installation fault has little impact on tooth profile error, however a hob installation fault will result in a considerable workpiece tooth profile error.
The gear shaper cutter is shaped like a spur gear or a rack. In comparison to hob, the manufacturing method is simple, making it easier to manufacture more precisely, resulting in improved gear machining precision.
As a result, gears with low kinematic precision can be handled directly by gear shaping, rather than shaving or grinding, from the standpoint of machining accuracy.
Gear and pre-shaving gear, on the other hand, have higher kinematic accuracy requirements (shaving does not improve kinematic accuracy), hence gear hobbing is preferable.
Productivity
In general, gear hobbing has a better productivity than gear shaping. Gear shaping can only compete with gear hobbing when the gear has a compact module, a large number of teeth, and a tiny tooth width.
This is because:
1) The job cuts while rotating, resulting in a faster cutting speed and reduced empty stroke loss. The gear shaper cutter is reciprocating, which restricts the rise in cutting speed, and the actual cutting stroke length accounts for just approximately a quarter of the overall stroke length, resulting in a substantial empty stroke loss.
2) Multiple hobs can be employed to increase rough hobbing efficiency.
3) Gear hobbing moving time is proportional to the number of teeth on the workpiece, but gear shaping moving time is solely dependent on the diameter of the workpiece. Gears having a big diameter and a tiny module, in other words, are suited for gear shaping.
Gear shaping productivity is generally lower than gear hobbing productivity when processing gears with more than 5 modules, due to the necessity to remove a large number of redundant metals.
Key Takeaways:
- These revolutions are coordinated with hob axial-feed and are determined by the cutter's number of starts and the work piece’s number of teeth.
- There are crucial gearing characteristics that might influence the tool life time in a very favorable or negative way when it comes to the wear effects of the tool geometry.
- These unique characteristics are frequently employed in industrial applications, but only internal business knowledge is currently available.
Mechanisms & Attachments for Milling:
Attachments for Milling Machine: The numerous attachments are defined underneath and additionally how they growth the flexibility of the milling system.
1. Vertical Milling Attachment or Swivel Attachment:
This attachment is acceptable on horizontal milling machines for substituting the horizontal spindle through a vertical spindle movement. The attachment is a proper-attitude equipment field having bevel equipment set in ratio of 1 : 1 and the axis of the vertical spindle may also be swiveled through 45°, accordingly permitting the machining of bevels and slanted surfaces. With the assist of this attachment, the operation of milling horizontal surfaces and making grooves and slots with shank kind give up turbines etc. also can be accomplished on horizontal milling system.
The attachment is suited for the column of the system with 4 bolts.
2. High-Speed Milling Attachment:
With the assist of this attachment the velocity of the spindle may be improved 3 to 4 instances in order that the operation with small cutters can be accomplished efficiently. The attachment is established at the column with 4 bolts and may be swiveled additionally at any attitude.
3. Slotting Attachment:
With the assist of this attachment, rectangular holes, slots and a number of jobs may be made on milling system which a rotary device can’t do. This unit is established at the column face and converts rotary movement into reciprocating movement. The traditional variety of linear motion is zero-10 cm with an adjustment for 360 tiers swivel. This attachment lets in the machining of keyways, slots and sure grooves.
4. Universal Dividing Head (Index Head):
This attachment may be very crucial for a milling system. It is used for slicing equipment enamel, slots or grooves at the outer edge of the paintings. With its assist the activity may be circled through genuine tiers and through numerous strategies of indexing (direct, easy or compound), almost any quantity of genuine slots or enamel may be reduce. The indexing can be finished through hand or automatically.
For computerized rotation of activity, the correlation of rotation with feed desk is labored out, and gearing association is furnished on the give up of index head which can be linked to the desk using mechanism.
Thus non-stop movement for indexing of the paintings may be obtained. This energy pressure may be very beneficial for milling such paintings-portions as twist-drill flutes, helical gears, spiral milling cutters and lots of different portions having a helix or comparable geometric form. Swivel Vise
5. Circular Milling Attachment:
This is a type of rotary desk furnished with T-slots. Its circumference is split into tears and can be hand-listed for spacing or finding slots, grooves, or holes. For the motive of milling around arc or groove at the activity, an association may be used to make it energy-operated to offer non-stop movement. Index plates also can be suited for this attachment for acquiring genuine rotation of the activity through any fraction of a circle. With the assist of this attachment, may also profiles may be produced, including immediately or curved slots, grooves, cams and rounded ends on work piece.
6. Rack Milling Attachment:
It is used for milling immediately or willing racks or cross-slotted portions of big lengths on horizontal or usual milling system. It includes a milling unit, a fixture and a rack indexing unit. The milling unit is established at the column face and is supported on the front through an overarm. It has a spindle having its horizontal axis at proper angles to that of the system.
7. Vise:
This is likewise a totally crucial attachment and is bolted to the pinnacle of the desk. It may be fixed to the desk in any function through fastening the T-bolt at the ears on the give up of the vise. It is normally used as useless center to help the activity. It holds the paintings-portions securely and allows in orienting it accurately. Work-piece is held among hardened and floor jaws.
Vises are of 3 kind’s viz., (a) undeniable (b) swivel (Refer Fig. 16.23) device-maker usual . Milling system vises are typically exact in step with the jaw lengths. The widespread metric sizes are 125, 160, 2 hundred and 250 mm. The undeniable vise may be bolted to the desk either parallel or perpendicular to the system spindle. The swivel vise may be swiveled in a horizontal aircraft and may be used for containing paintings to be reduce at attitude.
The usual vise may be swiveled in a horizontal aircraft and also can be hinged up far from the aircraft of the desk for an attitude of zero to ninety tiers, accordingly making it viable to modify the activity in any manner Compound angled surfaces may be milled with this kind of association. However, the scale of the paintings that may be held through the vise is limited.
8. Arbors:
Arbors are used to maintain milling cutter on milling machines. All peripheral milling cutters, shell give up turbines, etc., are established on arbors and held with inside the spindle through a draw bolt association (Refer Fig. 16.26). The cutter is pushed through a key geared up at the arbor. One or greater arbor helps can be furnished to make certain introduced rigidity.
Arbors may be both lengthy or stub. Small shell give up turbines and face turbines and facet and face cutters are established at the front give up of stub arbors. The stub arbor is held with inside the spindle through a draw bolt association, however the arbor being brief isn't supported at its loose give up.
i. Hydraulic Clamping Vice (Fig. 16.27 (a)): Accurate, and without problems adjustable vice. Simple and fast operation through hydraulic action. The clamping strain may be adjusted and controlled. Mechanical coarse adjustment and hydraulic clamping operation.
Ii. Mechanically Operated High Pressure Clamping Vice (Fig. 16.27 (b)): Robust and robust design. Head and clamping slide may be shifted and placed at the decrease slide segment by way of adjustable pins. Basic slides of various lengths may be used and mixed to offer a double appearing vice.
Iii. Universal Precision Vice (Fig. 16.27 (c)): Special, quality grained, grey solid iron. Swiveling of the vice on its cradle through 360o. Swiveling of the cradle on the bottom plate through 360o. Inclination of the vice surface: 90o in a single direction, 30o with inside the different direction.
Cutting parameters:
Milling Process Parameters
The choice of reducing parameters has an immediate impact on machining nice, machining performance, and device lifestyles. The reducing will produce specific outcomes the usage of specific reducing parameters with inside the identical technique circumstance. The technique parameters decided on in milling technique consist of spindle velocity of revolution, reducing intensity, reducing width, and feed price, as proven in Figure.
Process Parameter Vector Spindle Speed of Revolution.
Spindle velocity of revolution determines the rate of reducing area relative to the work piece, namely, reducing velocity. Since reducing velocity has the amazing impact on device lifestyles, the choice of reducing velocity pertains to the sturdiness of device closely.
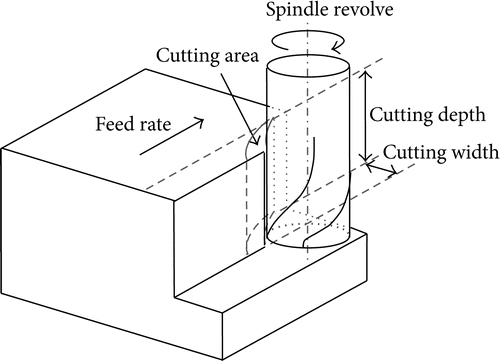
Too low or too excessive reducing velocity will reason the device lifestyles to say no dramatically. Meanwhile, with inside the milling of thin-walled work piece, spindle velocity of revolution has a large impact on the stableness of reducing. Therefore, the spindle velocity of revolution must be decided on discreetly in milling technique.
Cutting Depth and Cutting Width.
Cutting intensity and reducing width are limited via way of means of spindle strength, transmission strength of device, cloth type, device parameters, coolant, machining procedure, and the stiffness of device device-device-work piece system.
Therefore, they must be decided on fairly consistent with machining nice, machining performance, and machining procedure. Generally, machining performance is the primary intention in roughing machining, so a bigger reducing intensity and reducing width must be decided on.
Quality of work piece floor is the principle intention in completing machining, so a much less reducing intensity and reducing width must be decided on.
Feed Rate.
Feed price is the rate of feed circulate of the reducing device relative to work piece in milling technique. Generally, linear feed price is followed in realistic manufacturing and its miles described as feed in keeping with minute.
The feed price of milling will have an effect on the machining accuracy, floor nice, deformation of the work piece, and device lifestyles directly. And it's also limited via way of means of device parameters, work piece cloth, device path, stiffness of device, and overall performance of feed system.
In machining technique, the feed price of milling is chosen consistent with element cloth, geometry features, nice requirements, and the functionality of device.
The process parameters mentioned above can be written in the form of vector, as shown in
Pp={n,ap,we,f},
Wherein these parameters represent spindle speed of revolution, cutting depth, cutting width, and feed rate.
Then, a process parameter vector space consisting of four dimensions is established.
Mapping of Process Condition to Process Parameter
Process parameters are the concrete example of technique expertise with inside the machining of realistic work piece and technique expertise is implicit with inside the technique statistics. Process statistics gathered in realistic manufacturing is used, amended, and established again and again via lengthy time, after which the herbal evolutional technique expertise is achieved.
Therefore, the technique statistics gathered in realistic manufacturing implies a massive quantity of field-confirmed technique expertise.
These statistics must be mined deeply and the technique expertise must be used with inside the choice of technique parameters.
The experiential technique statistics of realistic manufacturing is analyzed and organized consistent with the proposed circumstance vector and technique parameter vector, after which those statistics are gathered into technique database.
The technique parameter vectors are matched with the circumstance vectors, and the mapping of circumstance vector area to technique parameter vector area is constituted. The technique of herbal evolution of technique parameters and accumulation of statistics is proven in Figure 3.
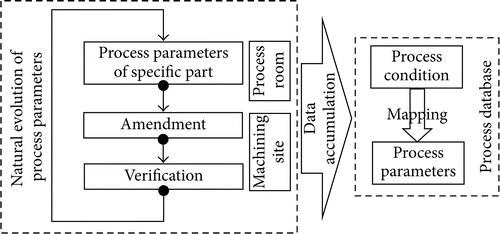
Types of milling operations:
Slot Milling
In this method, the width of the cutter is much less than the width of the work piece: it's far used to make a slot with inside the work piece. Thin cutters make for skinny slots. To reduce the piece in, a completely skinny slot may be made to undergo the intensity of the work piece. Another call for this method might be “noticed milling.”
Vertical Milling
The maximum not unusual place device utilized in vertical milling is the cease mill or a flat-bottomed cutter. In a few cases, it is able to talk over with spherical-nosed cutters as well.
Horizontal Milling
A horizontal milling gadget is excellent for forming flat surfaces, dovetails, keyways, and gears. These machines are excellent operated via and up milling method wherein the metallic is fed into the cutter towards its rotating route. Compared to vertical milling, horizontal milling can exert most pressure towards the jaw conserving the work piece.
Side Milling
When the intention is to supply a flat vertical floor with inside the work piece, aspect milling is the operation to choose. The intensity of the reduce may be manipulated with the aid of using rotating the vertical feed screw of the desk.
Gang Milling
When or extra milling cutters are used collectively on one arbor whilst reducing horizontal surfaces that is called gang milling. The regular technique is to mount the milling cutters of various diameters, shapes, and/or widths on an arbor. The capacity combos of cutters are limitless and are decided in every case with the aid of using the desires of the job.
Straddle Milling
When you want or extra parallel vertical surfaces machined in an unmarried reduce, straddle milling is what you want. The method is completed with the aid of using mounting aspect milling cutters at the equal arbor, set aside such that they straddle the work piece.
Up (and Down) Milling
Also called traditional milling, up milling is whilst the cutter rotates towards the route of the desk feed. Contrast this with down milling, wherein the cutter rotates alongside the route of the desk feed. The difference? In up milling, the chip load on tooth will increase progressively whilst in down milling, the chip load at the tooth decreases.
Form Milling
The shape milling method lets in for machining unique contours composed of curves and directly lines—or probably most effective curves—in a unmarried reduce. This is completed with fashioned cutters, the ones fashioned to the contour of the reduce, or with a fly cutter floor mainly for the job. More not unusual place shape milling includes milling half-spherical recesses at the work piece.
Face Milling
In face milling, the scale and nature of the work piece determines the kind and length of the cutter required. The tooth at the outer edge of the cutter does maximum of the work, however, if the cutter is nicely floor, the face tooth dispose of a small amount of inventory that's left due to the springing of the work piece or cutter, generating a higher finish.
Turret Milling
Turret milling is completed with the aid of using drilling, reducing, and shearing. The spindle is desk bound at some stage in the milling method, whilst the desk movements alongside the X and Y axes. This method is regularly used for “lighter” operations.
Types of milling cutters
Some Cutters with Description
1. Roughing End Mill
This kind of cutter is used if you have to get rid of extra quantity of fabric from the paintings piece. By the usage of roughing cease turbines, we attain a difficult floor finishing. Roughing cease turbines also are well-known as “ripper” cutters.
They are extra useful commercially and are utilized in numerous business applications.
2. Slab Mill
This kind of cutter is used if you have to get rid of extra quantity of fabric from the paintings piece. They are extra useful commercially and are utilized in numerous business applications.
3. End mill
These sorts of milling cutters have the reducing tooth at the each sides. We use cease mill extra with inside the vertical milling processes. High velocity metallic or the cemented carbide are used to create cease turbines. High velocity metallic is likewise referred to as HS or HSS.
The excessive velocity metallic doesn’t unfastened its hardness while the temperature increases. Hence, because of higher hardness the excessive velocity metallic is used to make cease turbines. The cease turbines are in most cases utilized in plunging, tracer milling, face milling, etc. Torus cutters, etc.
4. Hollow Mill
They also are referred as hole milling cutters. They appear to be a pipe having thicker walls. You will discover the reducing tooth of the whole turbines at the interior surfaces. Hollow milling cutters are used with inside the screw machines.
5. Ball Mill Cutter
Ball cutters also are well-known as ball nosed cutters. You may be effortlessly discover as ball cutters as their cease is hemispherical in shape. Ball cutters are used to lower the pressure attention and also are referred to as ball cease turbines. Whenever there may be want of reducing 3 dimensional shapes then, there may be a use of ball cutters to flawlessly reduce the ones 3-dimensional shapes.
Tool geometry & their specifications:
1. Shank:
It is that a part of an unmarried factor reducing device which is going into the device holder. Or in easy language shank is used to preserve the device.
2. Flank:
It is the floor beneath and adjoining to the reducing edges. There are flank surfaces, the primary one is most important flank and the second is minor flank. The most important flank lies beneath and adjoining to the aspect reducing facet and the minor flank floor lies beneath and adjoining to the give up reducing facet.
3. Base:
The part of the shank that lies contrary to the pinnacle face of the shank is known as base.
4. Face:
It is the pinnacle part of the device alongside which chips slide. It is designed in this sort of manner that the chips slide on it in an upward direction.
5. Cutting facet:
The facet at the device which eliminates substances from the paintings piece is known as reducing edges. It lies at the face of the device.
The unmarried factor reducing device has edges and those are
(i) Side reducing facet: The pinnacle fringe of the most important flank is known as aspect reducing facet.
(ii) End reducing facet: The pinnacle fringe of the minor flank is known as give up reducing facet.
6. Nose or reducing factor:
The intersection factor of most important reducing facet and minor reducing facet is known as nose.
7. Nose radius:
It is the radius of the nose. Nose radius will increase the existence of the device and presents higher floor finish.
8. Heel:
It is a curved component and intersection of the bottom and flank of the device.
Angles of Single Point Cutting Tool
The diverse angles of the unmarried factor reducing device have top notch importance. Each attitude has its very own characteristic and specialty.
1. End Cutting Edge Angle:
The attitude fashioned in among the give up reducing facet and a line perpendicular to the shank is known as give up reducing facet attitude.
2. Side Cutting Edge Angle:
The attitude fashioned in among the aspect reducing facet and a line parallel to the shank.
3. Back Rack Angle:
The attitude fashioned among the device face and line parallel to the bottom is known as again rake attitude.
4. End Relief Angle:
The attitude fashioned among the minor flank and a line every day to the bottom of the device is known as give up remedy attitude. It is likewise called the front clearance attitude. It keep away from the rubbing of the work piece in opposition to device.
5. Lip Angle/ Wedge Angle:
It is described because the attitude among face and minor flank of the unmarried factor reducing device.
Key Takeaways:
- The cutter is pushed through a key geared up at the arbor. One or greater arbor helps can be furnished to make certain introduced rigidity.
- Since reducing velocity has the amazing impact on device lifestyles, the choice of reducing velocity pertains to the sturdiness of device closely.
- Cutting intensity and reducing width are limited via way of means of spindle strength, transmission strength of device, cloth type, device parameters, coolant, machining procedure, and the stiffness of device device-device-work piece system.
- In machining technique, the feed price of milling is chosen consistent with element cloth, geometry features, nice requirements, and the functionality of device.
Indexing
- Indexing is the operation of dividing the periphery of a workpiece into numbers of equal parts. Example; if you want to make a hexagonal bolt. Head of the bolt is given hexagonal shape. You need to do indexing to divide circular workpiece into six equal parts and all the six parts are then milled to an identical flat surface. If you want to cut “n‟ number of teeth in a gear blank then the circumference of gear blank is divided into “n‟ number of equal parts and teeth are made by milling operation one by one. The main component used in indexing operation is the universal dividing head.
Universal Dividing Head
- It is most common and the popular type of indexing arrangement. As indicated by name itself “universal”, it can be used to do all types of indexing on a milling machine. Universal dividing head can set the workpiece in vertical, horizontal, or in inclined position relative to the worktable.
Construction and Working of Universal Dividing Head
- Universal Dividing Head/ Indexing Head consist of a robust body & a worm drive is enclosed in it. It has a worm and worm wheel arrangement as shown in fig.
In this, the dividing head spindle carries a worm wheel that meshes with the worm.
- This worm always carries a crank at its outer end. The index pin works inside the spring-loaded plunger, which can easily slide radially along a slot provided in the crank.
- This plunger can slide and adjust the pin position along a desired whole circle on the index plate.
- The index plate is mounted on the same spindle as the crank, but on a sleeve, so the crank and worm spindle can move independently on the index plate.
- To set a particular distance along the desired whole circle, sector arms are used. Sector arms are of detachable type and can be set at the required angles with one another. The index plates are available in a set of 2 or 3, with a number of whole circles generally on both sides.
Simple Indexing (Plain Indexing)
- Indirect Indexing is basically used when the index number does not permit direct indexing.
- The worm shaft, attached to the crank, should be engaged with the worm wheel on the indexing spindle. The index plate is secured to the head housing and has no motion during simple indexing
- The indexing spindle is rotated by the index crank, over a worm gear set with a single thread worm & worm gear wheel with 40 teeth.
- Since there are 40 teeth on the worm wheel, one complete turn of the index crank will cause the spindle as well as the work to rotate 1/40 of a turn.
- Similarly, 40 turns of the crank will rotate the work 1 complete turn.
- In order to calculate the indexing data or the number of turns of the crank for most division, it is necessary only to divide 40 by the number of divisions to be cut.
- Indexing crank movement = 40 N
N-number of required divisions
- Indexing plates which are available:
- Plate 1 16, 30, 33, 36, 39, 51, 57, 63
- Plate 2 22, 24, 27, 29, 37, 43, 49, 59
- Plate 3 23, 25, 28, 31, 41, 47, 53, 61
Problem 1:
Calculate indexing required to cut 60 slots of the workpiece.
Indexing crank movement = 40 N = 40 60
= 2 3
= 12/18
(Means, 12 holes on 18 hole circle.)
Problem 2:
Calculate indexing required to cut 23 slots of the workpiece.
Problem 3:
Calculate indexing required to cut 35 slots of the workpiece.
- If, however, it was necessary to mill 7 slots, then the indexing data would be:
- Indexing data = 40 N = 40 7 = 5 5/7 turns of the index crank
- Five complete turns of the crank are easily made, however, the 5/7 of a turn involves the use of the index plate and sector arms. To get 5/7 of a turn, choose any whole circle which is divisible by the denominator 7, such as 28.
- Then, take 5/7 of 28 = 20 (means, 20 holes on a 28 whole circle plate).
- Therefore, the indexing data for 7 slots would be 40/7 = 5 5/7 turns or 5 complete turns plus 20 holes on 28 hole circle plate.
Compound indexing:
- When none of the indexed plate has a whole circle which enables the work to be divided by simple indexing method we can use compound indexing.
The procedure is explained as;
Let;
z = no. Of division needed
Crank rotations for each indexing= 40/z
- Write z above and 40 below a straight line and factorized them
- Select 2 numbers representing 2 whole circles in the same plate.
- Write these numbers below 40 and factorized them.
- Write their difference above z and factorize it. These whole numbers are to be chosen in such a manner that all the factors above the line gets cancelled out.
Let these holes number be N1 and N2
Let n1 be the numbers of holes indexed in N1 whole circle, and n2 the number of holes to be indexed in N2 hole circle.
Then;
n 1/N1 +/- n 2 /N2 = 40/z
n1 and n2 are found by hit and trail method.
Example Let z=77
Steps;
- 77=11x7
40=2 x 2 x 2 x 5 - Let N1= 21 and N2 = 33
Difference 12= 2 x 2 x 3
Therefore
77 = 11 x 7
40 = 2 x 2 x 2 x 5
21 = 7 x 3
33 = 11 x 3
Since all the factors above the line get cancelled out, therefore, selection of N1 and N2 is correct.
Now;
n1 /21 +/- n 2/33 = 40/77
Values of n1 and n2 would be determined by hit and trail method.
Differential Indexing
- When it is not possible to calculate the required indexing by the indirect indexing method, that is, when the fraction 40/N cannot be reduced to a factor of one of the available whole circles, it is required to use differential indexing.
- With this method of indexing, the index plate is unlocked leaving it free to turn either backward or forward a part of a turn to attain the proper indexing or spacing
- A gear train is set-up to join the outer end of the spindle to the worm shaft. When index crank is turned to move the spindle, the gear train will cause the index plate to turn at the same time.
- The rotation of the plate can be either in the same direction (positive) or in the opposite direction (negative) of the index crank. This change of rotation is effected by an idler gear or gears in the gear train.
- When it is required to calculate the indexing data for a required number of divisions by the differential methods, a number is chosen close to the required divisions which may be indexed by indirect indexing.
- To illustrate the principle of differential indexing, assume that the index crank has to be rotated 1/9 of a turn, and there is only 8 whole circle available.
- If the crank is be moved by 1/8 of a turn, the index pin will contact the plate at a spot after the first 1/9 turns.
- The exact position of this spot would be the difference between 1/8 and 1/9 of a revolution of the crank. This would be 1/8 – 1.9 = (9-8)/72 = 1/72 of a turn more than 1/9 of a turn.
- As, there is no hole at this point into which the pin could engage, it is necessary to cause the plate to rotate backwards by means of change gears 1/72 of a turn in order that the pin will engage in a hole using an arrangement
- At this point, the index crank will be locked at exactly 1/9 of a turn. The method for the calculation of the change that gears required to rotate the plate the proper amount is as follows:
- Change gear ratio = (A – N) x 40/A
= Driver (work spindle gear) / Driven (worm shaft gear)
A – Approximate number of divisions (selected number)
N – Required number of divisions
- When the approx. Number of divisions is larger than the required number the resulting fraction is plus and the index plate must move in the same direction as the crank (clockwise).
- However, if the approx. Number is smaller than the required number the resulting fraction is minus and the index plate must move in a counter clockwise direction.
- The numerator of the fraction shows the driving (work spindle) gear or gears, while the denominator shows the driven (worm shaft) gear or gears.
Procedure:
Let z = no. Of divisions required to be indexed
k = number very nearly equals to z
No. Of crank turns for each simple indexing
n = 40/k
No. Of crank turns needed for z indexing
N = 40z/k
- If N >40, then(N-40) turns have to be subtracted
- If N < 40 , then (40-N) turns indexed plate should rotate in same direction as of crank.
The gear ratio will be:
I=40(k-z)/k
Example: Do differential indexing for 93 divisions
Solution;
z = 93, therefore,
Let k = 90, which can be simple indexed each indexing = 40/90 =4/9 =8/18, i.e., 8 holes in an 18 holes circle.
For 93 indexing’s,
N = 8/18 x 93 = 41 1/3
Since N>40, the indexed plate must rotate 4/3 backward
I=40(k-z)/k= 40/90 x 3 =4/3
In brown and sharp dividing head, the gears supplied are 24,28,32,40,44,48,56,64,72,86,100
Slotter: Introduction
Slotter device is described as a device makes use of fore casting off undesirable fabric chips from the work piece to make splines, grooves and more.
Here the Ram (Tool connected) movements reciprocating, while in shaper the ram movements horizontally. This is a reciprocating kind of Machine device.
Application of Slotter Machine
Slotter device is used to provide slots, keyways, and equipment teeth.
It is used for machining inner and outside flat surfaces and round surfaces.
If there's a want for shaping outside and inner varieties of profiles then slotter is the satisfactory choice.
It is used for machining abnormal surfaces, blind holes, dies and punches, outside and inner equipment teeth.
Advantages of Sotter Machine
It is a light-weight device and may be without problems transportable.
It makes use of an unmarried factor slicing device that is economical.
It offers you can correct floor finish.
The price of this device is low in comparison with different machines on this category.
Disadvantages of Slotter Machine
A Very Skilled employee is needed to function the slotter.
Working Principle of Slotter Machine:
The running of the Slotter device is just like the shaper device do however the predominant distinction among them is the Shaper device works horizontally while Slotter machines paintings vertically.
As we've got studied all of the components in detail. Now the ram is attached to the crank and crank linked to the gears.
So what came about right here is whilst we boom or lower the tools velocity, the rotation of crank will increase and decreases.
And as in step with those, the ram movements up and down. We have connected the work piece into the paintings desk and manually we carry the ram close to the work piece and in line with the ram we alter the worktable after which we must clamp it.
Now we deliver the electricity as in step with tools the crank rotates and the crank is attached to the ram so ram movements up and down.
During down (ram movements down) the reducing stroke takes region and at the same time as shifting up or go back stroke there's no reduce.
If we must reduce on the special sections then manually we deliver feed to the paintings desk and as in step with requirement, it cuts.
Types of drives for slotter:
Drive Mechanism of Slotting Machine:-
In slotting machine, the metallic is reduce in the course of the upward stroke and no metallic is eliminated in the course of the downward stroke.
So, the time taken in downward stroke may be decreased to enhance the operating pace of the machine. So, brief go back mechanism is used to pressure the ram of the slotting machine.
Quick go back mechanism is an apparatus to supply a reciprocating movement wherein the time taken in go back stoke is much less than time taken in ahead stroke. There are 3 kinds of brief go back mechanism which may be utilized in slotter machine:-
Slotted disc mechanism
It is the most effective of all of the ram power mechanisms and may be very normally utilized in length slotting machines. In this mechanism, the using pinion receives power from a pulley which runs via belt with the aid of using motor. The pinion rotates the tools which in flip rotates the slotted using disc.
The rotation of the slotted disc is transformed into the vertical reciprocating movement ram with the assist of connecting rod. The duration of stroke of ram may be modified with the aid of using moving the crank pin in the direction of or from the middle of the slotted using disc. Position of the stroke is adjusted with the assist of hand lever furnished for adjustment.
Variable pace reversible motor power
Such a power is utilized in big modem slotting machines. Slotting machines have a connected or enclosed motor power with a multi pace tools field to present various speeds to the ram. A traditional variety could be forty to one hundred fifty strokes or cycles in step with minute.
Hydraulic power
Hydraulic power is utilized in big-modem slotted machines. The power is much like that hired for the shapers. In this power, the hydraulic cylinder is in vertical direction. Both consistent stress and consistent quantity kind drives are used.
Types of Slotter Machine:
Slotter Machines are may be categorized in those four-types.
- Punch Slotter
- Precision Tool room slotter
- Production Slotter and
- Special Purpose Slotter Machine
Let me provide you with a quick know-how of those four sorts of Slotter Machine.
Punch Slotter:
This is a heavy and inflexible kind of device. This device designed for the elimination of a massive quantity of metallic from cast or forged fabric. The period of the puncher slotter is massive it can be as long as 1800 to 2000 mm.
How does Punch Slotter paintings?
The ram is commonly pushed with the aid of using a spiral pinion meshing with the rack tooth reduce on the bottom of ram.
The pinion is pushed with the aid of using a variable velocity reversible electric powered motor just like that of a planer device. The Feed is managed with the aid of using electric tools.
Precision Tool room Slotter:
The device room slotter works with top device velocity and produces an correct floor finish.
Production Slotter:
This kind of slotter is used for machining tapered jobs with the aid of using ram swivel to ten to 30 degrees.
Special Purpose Slotter Machine
This kind of slotter machines provide an excessive quantity of manufacturing at low cost, additionally it offers extra accuracy too. Keys eater is one of the unique functions of slotter machines.
It is used for machining keys at the wheel and tools hub
Slotter Machine Specification:
The specifications of a Slotter Machine is depended on the several factors some of these are:
- Power Input
- Type of drive
- Maximum table drive
- The maximum length of ram stroke
- Number of speed
- Number of feed
- Table feed
- Floor space required
- The diameter of the Work Table in MM
- KW of motor
A slotter machine is a machine tool in which material is removed for producing desired shapes. It is used for producing Machining cylindrical surfaces and flat surfaces.
Puncher Slotter Machine:
The puncher slotter is a rigid and heavier machine designed mainly for the removal of a large amount of metal from large castings or forgings. The length of the puncher slotter is sufficiently large which may be as long as 1800 to 2000 mm.
The ram of the slotter is driven by a spiral pinion meshing with the rack teeth cut on the underside of the ram and the pinion is driven by a variable speed reversible electric motor which is similar to the planer.
The feed is also controlled by electrical gears.
Production slotter:
Production Slotter is a heavy-obligation slotter including a heavy solid base and heavy body and is normally made in parts.
It’s in particular used for preferred manufacturing work. A slotted disc with a connecting rod is used for reciprocating the motion of the ram.
A flywheel is used on this slotter to save you stroke on the give up of the stroke. A slotter gadget is a manufacturing gadget.
This is a totally vintage form of the gadget and became invented with the aid of using BRUNEL.
The slotting gadget is just like a verticle shaper.
The ram sporting the slotting device reciprocates in a verticle guide-manner of the gadget.
This form of slotter is used for machining tapered jobs with the aid of using ram swivel to ten to 30 degrees. This form of slotter machines provide an excessive extent of manufacturing at low cost, additionally it offers extra accuracy too.
Keys eater is one of the unique functions of slotter machines. It is used for machining keys at the wheel and tools hub.
Tool room slotter:
Tool room slotter is precision kind with is locate for extremely unique machining. It is lighter system and is perform at excessive speeds.
By use unique jigs system can take care of some of same works on a manufacturing basis.
The major characteristic of a slotting system is to eliminate metallic from a bit of a piece to carry it to the desired form and size.
This is performed with the aid of using protecting the paintings rigidly at the system and a reciprocating unmarried factor device established on device head.
The unmarried factor device movements alongside a vertical axis over the paintings piece.
The pinion that's in mesh with the principle equipment receives its force from a pulley through a belt with the aid of using motor.
The equipment is coupled to the slotted disc. The round movement of slotted disc is transformed into the reciprocating one with the assist of connecting rod.
The crank pin may be officially set with inside the slot of slotted disc at one-of-a-kind distances from the center for verifying the duration of the ram stroke. The role of the stroke is adjusted with the assist of hand lever supplied for the stroke adjustment.
Slotting system is typically supplied with horizontal round worktable, however coordinate tables also are supplied a few times.
The desk is established at once over a mattress casting and heavy paintings can be located on it.
The round desk may be revolved with the aid of using hand or electricity fed.
It is graduated round its outer edges and paintings can for this reason be established and grew to become to a predetermined role, relying upon the characteristic for which slotter is designed.
Slotter Tools:
KIT-STO-825
KIT of 8 REV insert-carrier tools to execute keyway seatings on slotting machine.
It is comprised of:
• 8 insert-carrier tools with a diameter of 25 mm (UT-03,04,05,06,08,10,12,14/16)
• 1 square adapter AD-35
• 18 inserts (2 for each tool size with tolerance class from standard catalogue selection)
• 4 re-sharpeners (RF-1, RF-2, RF-3,RF-4)
• 1 painted steel tool-carrier base
• 3 Torx screwdrivers (T08, T15, T20).
KIT-STO-825-L
KIT of 8 REV insert-carrier tools to execute keyway seatings on slotting machine.
It is comprised of:
• 8 insert-carrier tools long line with a diameter of 25 mm (UT
03,04,05,06,08,10,12,14/16)
• 1 square adapter AD-35
• 18 inserts (2 for each tool size with tolerance class from standard catalogue selection)
• 4 re-sharpeners (RF-1, RF-2, RF-3,RF-4)
• 1 painted steel tool-carrier base
• 3 Torx screwdrivers (T08, T15, T20).
Key Takeaways:
- The ram is commonly pushed with the aid of using a spiral pinion meshing with the rack tooth reduce on the bottom of ram.
- This kind of slotter machines provide an excessive quantity of manufacturing at low cost, additionally it offers extra accuracy too. Keys eater is one of the unique functions of slotter machines.
- The ram of the slotter is driven by a spiral pinion meshing with the rack teeth cut on the underside of the ram and the pinion is driven by a variable speed reversible electric motor which is similar to the planer.
References:
1. Manufacturing Engineering & Technology, S. Kalpakjian & S.R. Schmid
2. Technology of Machine Tools, Krar &Oswald
3. Manufacturing Processes, M.Begman
4. Processes & Materials of Manufacture, R.Lindberg
5. Production Technology, HMT