Unit II
Checking, Vouching and Audit Report
Test checking:
Meaning
Test checking is the manner of choosing and checking numerous transactions from a huge range of transactions. If the checked access is observed to be accurate, the auditor considers the ultimate entries to be accurate as well. This approach is primarily based totally at the concept of sampling that is generally used as a statistical approach. Checking each transaction that takes place that 12 months is tedious and uneconomical for the auditor. Therefore, the auditor examines and investigates a few consultant transactions which will reap enough and suitable audit proof to assist his opinion. Test tests lessen the workload of the auditor. If the check test unearths that the statistics checked with the aid of using the auditor are accurate, no similarly precise tests could be performed.
Benefits of check checking
Test tests have the subsequent advantages:
1. Reduced workload: The auditor's paintings is extensively decreased due to the fact the auditor tests handiest a small range of transactions. You can use the greater time to be had to consciousness at the regions which might be pretty important.
2. Time and fee savings: Test tests are a manner to store time, fee, and electricity for each auditors and clients.
3. Quick of entirety of audit paintings: Since the auditor tests just a few or a restrained range of transactions, the check test permits the auditor to finish the paintings quickly.
4. Effective checking approach: If the auditor cautiously selects the transactions to be checked, the check test could be effective.
5. Scientific evaluation of chance: The chance of fabric misstatement in monetary statements is classed with the aid of using the auditor in a systematic way with the aid of using taking samples and inspecting them in detail.
6. Role as a manual: Serves as a manual for the auditor to attain conclusions approximately a real and honest view of the commercial enterprise situation.
Disadvantages of check test
Test tests offer the subsequent benefits:
1. No medical technique: This is a conventional auditing approach that doesn't use a systematic technique to pattern selection, so the outcomes depicted there have a tendency to be inaccurate.
2. Risk can't be measured: The quantity of related chance can't be measured.
3. Complex transactions aren't checked: The Audit Assistant selects handiest easy transactions for checking and complicated transactions are left omitted.
4. Carelessness of purchaser workforce: Client workforce are conscious that they may be careless due to the fact the auditor does now no longer test all paintings.
5. Errors and frauds can stay undetected: If the auditor adopts check tests, mistakes and frauds can stay undetected.
6. Inappropriate without inner manipulate system: Auditors can't undertake check tests if right inner and inner manipulate structures aren't in operation.
7. Not appropriate for small commercial enterprise issues: Test tests aren't appropriate for small commercial enterprise issues because of the small range of transactions involved.
Auditor's duties concerning check tests
The following are the auditor's duties or precautions that the auditor has to take while adopting a check test.
1. The access decided on for the check test ought to be consultant of all transactions and the access ought to be randomly decided on for the test.
2. The auditor has to pick out the check independently, no matter the hints of the purchaser workforce.
3. The entries decided on for the check test ought to be cautiously decided on with the aid of using the auditor with the aid of using making use of his intelligence and expert skills.
4. Do now no longer rent check tests while making certain coins and financial institution passbook entries.
5. Auditors have to now no longer rent check tests while checking entries for the primary and final months of the 12 months. You have to additionally very well test each access.
6. Test tests have to be devised to test a big part of the paintings accomplished with the aid of using every employee.
7. The auditor has to bear in mind beyond revel in deciding on the character and length of the pattern to test.
Vouching of Cash Book
Guarantee of cash transactions
For business concerns, cash books are maintained to explain cash receipts and payments. It's an important financial statement for business concerns. Errors and fraud are primarily related to the receipt and payment of cash by misappropriation wherever possible. Therefore, the auditor must check that all receipts are recorded in the cash book and that the payer of the cash book does not see any fictitious payments.
General points to consider when guaranteeing cash transactions
The auditor should consider the following general points when guaranteeing cash transactions:
1. Internal check system
Before starting the cashbook warranty, the auditor should inquire about the internal checking system in operation. Without an organized internal control system, cash misappropriation is more likely. He needs to carefully study the internal check system for cash sales and other receipts. Internal controls need to be reviewed on a regular basis and appropriate modifications have been made to make them more effective.
2. The auditor needs to validate and test the accounting system
Accounting systems need to be tested for the accuracy of cash transaction records. You can commit fraud by curbing cash receipts and payment exaggerations.
3. Examination of test check
Whenever possible, all cash transactions are carefully checked. However, if the auditor is happy to have an efficient internal checking system, he can rely on test checking. In such cases, he may randomly check some items, and if they are all normal and found to be non-irregular, then why he assumes the rest of the transactions are correct I have.
4. Comparison of rough cash book and cash book
Cash receipts are usually first entered into a rough cash book before being entered into the cash book. The auditor should examine the rough cache book and main cache book entries and then compare them to detect any errors or irregularities.
5. Find out a way to deposit your day by day coins receipt
The auditor need to recollect the approach followed to deposit day by day coins receipts with the financial institution. Pay-in slips need to continually be used for this purpose. Receipt accounting need to know no longer be delayed. Coordinating consumer debts with allowances and rebates isn't always definitely allowed. Misappropriation of coins can also additionally arise with inside the scope of the adjustment.
6. Creating a financial institution adjustment assertion
The auditor wishes to create a financial institution reconciliation assertion to test the financial institution balances within side the passbook and passbook to discover the purpose for the distinction among the financial institution balances with inside the passbook and the cashbook.
7. Verification of coins handy
The auditors need to sincerely matter and test the coins handy to look if it fits the stability withinside the coins books.
8. Ensuring right control of receipts
The auditor wishes to ensure that the receipts are well managed. At that time, whether or not all receipts are printed, whether or not counterfoil receipts are used, whether or not a carbon replica device is used, all receipt books and all receipts are numbered one by one and consecutively. You want to test if it's miles there.
He wishes to examine information about dates, amounts, names, etc. with cashbook entries. If you've got particular entries withinside the cashbook for which the receipt becomes issued, you need to cautiously test them. Receipts need to be signed via way of means of the accountable person, now no longer the cashier.
Unused receipts need to be stored secure with the accountable person. Along together along with your coins receipt, you want to recollect the policies for granting coins discounts. If there may be a device wherein receipts accompany coins receipts, such receipts, typically called invoices, need to be well signed and lower back to the consumer.
Verification and Valuation of Assets and Liabilities.
Valuation of business assets and liabilities:
The process of regular checks and guarantees only demonstrates the transactions that occur daily and first confirms the acquisition of assets or the assumption of liabilities, but its value is prepared by the balance sheet.
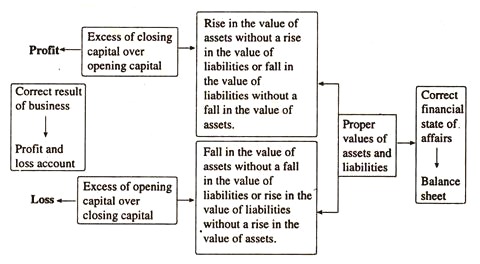
The vital importance of the correct valuation of assets and liabilities for closing purposes is well illustrated in the chart below.
Obviously, in the final analysis, changes in interrelated assets and liabilities are the most important factors in determining profits or losses through their impact on the difference in capital at the beginning and end of a particular accounting period.
Such fluctuations may be the result of real factors that function in the course of normal business activities, or they may be intentionally designed by manipulating or tampering with your account. In addition, improper valuation of assets and liabilities, whether careless or fraudulent, can undermine the financial position of the business by showing the wrong situation on the balance sheet.
Asset Valuation Basics:
Given the importance of valuation, auditors should always carefully check whether an asset is valued to some reasonable and appropriate criteria.
The standard valuation methods commonly followed for different classes of assets are listed below
 .
.
The nature and purpose of the acquisition:
1. FIXED:
It is stable in nature. Obtained for permanent or long-term retention and used in business to earn income.
2. Intangible:
Semi-stable in nature. It is acquired as a non-monetary identifiable asset, for use in business to increase revenue, or as a class of fixed assets that do not have a physical or concrete presence but are all of the same value. Intellectual property of goodwill, or license rights.
3. Fictitious:
A semi-stable or temporary asset with no tangible form. Expenditures or losses of an unusual nature that is usually not feasible with cash. Reserve expenses, loss on issuance of securities or special advertising expenses.
4. Floating:
It is affected by constant movement and change. Obtained as soon as possible for temporary storage and conversion to cash.
Evaluation basis:
1. FIXED:
Consistently appropriate depreciation from the going concern value, ie acquisition cost or initial acquisition cost (including additional adjustments including all costs to bring the asset to a reasonable state or disposal), regardless of market value Depreciation is deducted.
2. Intangible:
It is usually written down on the same basis as fixed assets, that is, according to policies regarding the amortization or fair value of benefits that can be enjoyed in the future. Intangible assets must be amortized within a maximum of 10 years in accordance with ICA's new standards.
3. Fictitious:
The amount of expenses / expenses incurred or their balance, depending on your financial policy, less the amount amortized annually.
4. Floating:
Realizable value, that is, market value (net realizable value) or cost, whichever is lower.
Asset revaluation:
Periodic revaluation of an asset (i.e., book value) by systematic valuation to show a more realistic value of the asset based on the physical condition of the asset and its estimated future useful life, market price trends, etc. Revision) may be made. It should be noted that if there is a reserve created by the revaluation, it will not be available for distribution.
Reassessment can be based on:
(A) Many factors such as technical improvement, replacement costs, productivity and asset efficiency. Also
(B) Acquisition costs do not reflect the true and fair view of the business and have been appropriately modified to show real value.
The reassessment is based on: (A) Replacement cost reduced by accumulated depreciation (net realizable value considering market trends). Or (b) indexing method based on industry indicators. Or (c) Appraisal method, that is, evaluation by an expert appraiser or an appraiser such as an architect, engineer, or certified appraiser.
Accounting Standard AS10, issued by the Association of Certified Accountants of India, recalculates the revaluation of fixed assets by recalculating both the total book value and the accumulated depreciation to calculate the net adjusted book value. It stipulates that it must be displayed in. Redisplays the net book value by adding the net increase in the net book value.
The selective revaluation process above is not available in the instructions for creating assets included in the Schedule VI of the Companies Act 1956. In this instruction, if you want to value the asset, such a written balance sheet.
Auditor's Obligation to Valuate Assets:
The auditor should scrutinize the rationale for the valuation of all assets and liabilities used or adopted by the client before finally passing the item.
He must be completely satisfied that they have been properly valued or revalue on the basis of scientific principles in order to represent true fair value to the business on the balance sheet date. However, valuing an asset or liability yourself is not part of the auditor's normal obligation.
The work is usually done by the person responsible for the business or an independent expert witness, and in such situations the auditor's liability is limited to the receipt of a certificate of value from management or the expert in some cases. Of course, he will be subject to appropriate personal investigation by himself to prove that the value seems reasonable given the nature of the business and the associated assets or liabilities.
In either case, the auditor is not responsible for the valuation of assets and liabilities, subject to reasonable skills and care in scrutinizing the rationale for the valuation (Kingston in the case of London & General Bank). For Cotton Mills, for Westminster Road Construction).
Verification of business assets and liabilities:
Asset validation means demonstrating the actual existence of an asset under the client's legal and / or ownership on the balance sheet date. This is as important as valuing an asset, but nothing more. The balance sheet should only include items that the client truly owns, and the auditor must not pass on the asset unless he is completely satisfied with the client's good faith ownership of the asset.
Responsibility verification:
Debts are usually valued at face value. Debt verification is as important as asset verification. Because its underestimation or omission has a significant impact on business performance and financial position. Debts are usually small in number and inherently more or less fixed, so they are less difficult to give to auditors than assets.
The auditor properly accounts for all truly unpaid liabilities or obligations on the closing date, even if accidentally or intentionally omitted, and all credit balances shown in the books are the actual liabilities. And you need to make sure that there are no operations related to it.
The auditor must be convinced that the liabilities recorded on the books are real and, if any, the obligation omissions are accounted for and properly disclosed. In fact, if the auditor does not detect a lack of liability, the auditor will be liable for negligence [Westminster Road Construction Co. In the case of. Audit reports must be subject to liability omissions.
The important points regarding liability verification are listed below. However, keep in mind that most of such verifications have already been done at the time of regular checks and guarantees of the books. As an additional safeguard, the auditor may obtain a certificate from the responsible person indicating that all responsibilities have been fully considered.
Contingent debt:
Contingent liability is contingent or contingent on the occurrence of a particular event. There is an element of uncertainty in this liability group that may or may not occur. Such liability entails future payments of money if it eventually occurs.
The main types of contingent debt are:
(i) Liability for invoices that have been discounted or received on behalf of another party but has not matured.
(ii) Liability under warranties or warranty arrangements in favour of others.
(Iii) Liability under an incomplete contract, which may or may not be required to be paid under a forward contract.
(iv) Liability under disputed proceedings, claims, or tax appeals.
(v) Liability for unpaid calls on partially paid-in shares held.
(vi) Responsibility for cumulative delinquent dividends on cumulative preferred stock.
(vii) Liability for claims not recognized as debt.
(viii) Responsibility of members of the warranty limited Liability Company.
(ix) Possible personal liability of a company partner.
(x) Liability under guarantee for loans made by others.
(xi) Other uncertain financial liability.
If the liability under the above responsible person does not actually occur on the balance sheet date, it should be compulsory for the company and, if possible, otherwise stated as a separate note on the balance sheet liability side. I have. But the numbers should not be extended to the money column.
The maturity of contingent debt can result from either the acquisition of an asset or the occurrence of a loss. However, if any of these liabilities are expected to cause an actual loss, sufficient reserves must be provided.
These items are usually found during a regular check and warranty process. It's also useful for checking contracts, notices, lawyer invoices, minutes, bank letters, correspondence, and discussing with clients.
As an additional measure, the auditor obtains details of the proceedings, claims, appeals, etc. from the client's solicitor, legal adviser, or tax consultant and obtains a schedule of contingent liabilities authorized by the responsible person. All possible debts under this head can be validated because the auditor may not be able to gain knowledge about all items of contingent debt during the normal audit process has been taken into account. The auditor must ensure that the appropriate notes on contingent liabilities are incorporated into the balance sheet.
The above exercises by the auditor ensure that the income statement and balance sheet disclose a "true and fair view" of the company's profits and losses and circumstances.
(Ii) Auditor's obligations re: Contingent liability:
(1) Collect the schedule of contingent liabilities certified by the responsible person.
(2) Check the items in the list using the notes taken during the regular check and warranty process.
(3) Collect a copy of the discounted invoice from the bank or other parties, if any.
(4) Check the bill receivable book entered in the bank passbook.
(5) Confirm payment for partially paid shares.
(6) For contingent liabilities, state inadequate reserves, if any, in the report
(7) Check the calculation and reason for the accrued dividend of cumulative preferred stock.
(8) Confirm all facts, legitimacy, and contingent liability amount of the proceedings in dispute.
(9) Confirm the letter and certificate from the lender of the solicitor regarding the contingent liability based on the loan guarantee.
(10) In the case of a company, confirm compliance with the provisions of Schedule VI of the Companies Act 1956.
(11) Confirm the disclosure of contingent liabilities on the balance sheet.
Auditor's obligations for events that occur after the balance sheet date:
1. Analyze all related events to find the event related to the date on the balance sheet in question.
2. Eliminate events that are not related to the balance sheet date.
3. According to the concept of “materiality”, modify the balance sheet to incorporate changes in the value of assets and liabilities due to events that occur after the balance sheet date.
4. Adjust the income statement appropriately by changing the allowances and reserves for events that occur after the balance sheet date.
5. Create and authenticate a special settlement statement that covers the above points.
Valuation and validation of specific assets:
In accordance with the general principles of valuation and verification above, the auditor should always give due consideration to the special points regarding the valuation and verification of individual items of an asset, based on the exact nature and usefulness of the asset.
Cash, books and debt, and equity transactions make up three important assets that need great attention. Therefore, these valuation and validation aspects are detailed below, followed by a tabular list of points related to other assets.
(I) Cash balance:
There can be no individual valuation criteria for cash balances; except that the actual balances on hand must be the same as those shown in the cashbook. In other words, the auditor needs to confirm the existence of cash balances on hand on the closing date.
To this end, issues are treated separately for different types of cash balances, such as:
(A) Bank cash:
The balance remains in the bank and cannot be physically verified. Only written verification needs to be done. For this purpose, you need to compare the bank balance shown in the "Bank Column" of your cash book with the corresponding number in your bankbook.
You should also check your bank's reconciliation statement. If the discrepancy still persists, you can check the cast and balance of the passbook itself. It is advisable to obtain a certificate or confirmation from the bank for the balance held by the bank. For fixed deposits, you need to check the deposit receipt from the bank. If such a receipt is pledged, you will need to obtain a certificate from the pledge.
(B) Cash on hand, including petty cash:
Physical verification is the only effective verification method. That is, if possible, the cash on hand should actually be counted by the auditor on the closing date. However, it is not practical to attend all client offices on the deadline, so for this purpose validation is usually done after that date.
In such cases, the auditor should attend as soon as possible after closing, carefully guarantee cash transactions from the closing date to the visit date, and count the actual cash on hand on the latter day. If your bankbook provides the only reliable source of verification, you may follow a system that deposits your closing cash balance with your bank on the closing date and withdraws it the next day.
If an organization such as a bank always holds a large amount of cash, a complete physical check is not feasible and a test check should be adopted if a system with good internal control is in operation. I have. A bunch of notes may be counted by checking some of them in detail. Bullions or coins can be identified by taking the average weight of the bag containing the coin and counting some of the bags actually picked up randomly.
The auditor must insist on the generation of all cash balances at once to prevent substitution, in order to cover up the defamation. According to the London Oil Storage Co. Ruling, the auditor will be liable for negligence if he fails to check his cash balance.
(C) Cash held by officers:
The auditor should generally not accept a certificate from an employee regarding the large amount of cash he holds. If such practice is unavoidable, the auditor will find that it is properly approved, absolutely necessary for the true purpose of the business, the balance is within fixed limits and no officers involved. You need to make sure that you are not allowed to stay on time.
(D) Cash with branches and agents, or cash in transit:
Auditors cannot personally count cash balances in transit at different branches or lying with different agents. Therefore, he must be content with the appropriate documentation.
If you follow the system of depositing branch or agency balances in a bank on the last business day of the fiscal year, the auditor must check your bank passbook and obtain a certificate from the relevant bank for the balance held by the bank. For cash in transit, you should scrutinize each piece of advice from your branch or agency.
(Ii) Book debt:
The auditor's main duty is to ensure that the book value of the miscellaneous debtors is confirmed correctly. The basis of the valuation should be the net realizable value after deducting bad debt and suspicious debt.
The schedule of the debtor's account, extracted from the debtor's ledger and certified by management, should be compared to the balance of the debtor's account in the general ledger when the self-balancing system is running. Checking the items listed in the debtor's schedule above on a separate financial statement or checking the balance received from the customer is also a useful method of verification.
A very important issue regarding the verification of book debt is the adequacy or other checks of the allowance for doubtful accounts.
In this regard, the auditor needs to obtain a certified schedule of bad debts and suspicious debts from management and should thoroughly check the same with special attention to the following:
(A) Confirm the year-end balance and its subsequent realization.
(B) The age of the debtor's balance. Check to see if you have debt that has already expired or is nearing the end of the time limit.
(C) Whether regular payments are made in accordance with the terms of the permitted credit. Pay particular attention to late payments.
(D) If the customer's check or invoice is disgraced.
(E) If there is a history of bankruptcy or attachment of the debtor's funds and assets.
(F) When it is necessary to file a proceeding against the debtor in order to collect the membership fee.
(G) Is the balance of individual debtors stable, increasing or decreasing?
(H) Check reserves, discounts, bad debts and suspicious debt, if any.
(I) Check the debtor's ledger trial balance using Control A / cs.
(J) Inquire specifically about the restraint of sales that leads to the restraint of debtors.
After careful consideration of the above information, the auditor should estimate the possibility of bad debt or suspicious debt and compare it with management's regulations. If you are not satisfied with the rules, you should first discuss it thoroughly with management and try to convince them to correct your position, but if you fail, you should state that fact in your report.
Arthur E. Green & Co. The proceedings clearly proved that the auditor would be liable for negligence if he accepted the bad debt schedule and could not detect the time-limited debt contained therein.
The Westminster Road Construction Co. Ltd. Proceeding proved that the auditor could neglect his duties if he received a certificate from management such as: According to the decision in the McKesson & Robins case in the United States, auditors are expected to witness the actual inventory and see for themselves.
Key takeaways:
- Test checking is the manner of choosing and checking numerous transactions from a huge range of transactions
- The auditor's paintings is extensively decreased due to the fact the auditor tests handiest a small range of transactions.
- Serves as a manual for the auditor to attain conclusions approximately a real and honest view of the commercial enterprise situation.
- : If the auditor adopts check tests, mistakes and frauds can stay undetected.
- The access decided on for the check test ought to be consultant of all transactions and the access ought to be randomly decided on for the test.
- For business concerns, cash books are maintained to explain cash receipts and payments.
- Before starting the cashbook warranty, the auditor should inquire about the internal checking system in operation.
- Cash receipts are usually first entered into a rough cash book before being entered into the cash book.
- The auditor wishes to create a financial institution reconciliation assertion to test the financial institution balances within side the passbook and passbook to discover the purpose for the distinction among the financial institution balances with inside the passbook and the cashbook.
- The process of regular checks and guarantees only demonstrates the transactions that occur daily and first confirms the acquisition of assets or the assumption of liabilities, but its value is prepared by the balance sheet.
- A semi-stable or temporary asset with no tangible form.
- The amount of expenses / expenses incurred or their balance, depending on your financial policy, less the amount amortized annually.
- ) Acquisition costs do not reflect the true and fair view of the business and have been appropriately modified to show real value.
- Asset validation means demonstrating the actual existence of an asset under the client's legal and / or ownership on the balance sheet date.
- The auditor must be convinced that the liabilities recorded on the books are real and, if any, the obligation omissions are accounted for and properly disclosed.
- The important points regarding liability verification are listed below
- If the liability under the above responsible person does not actually occur on the balance sheet date, it should be compulsory for the company and, if possible, otherwise stated as a separate note on the balance sheet liability side.
- In accordance with the general principles of valuation and verification above, the auditor should always give due consideration to the special points regarding the valuation and verification of individual items of an asset, based on the exact nature and usefulness of the asset.
- The balance remains in the bank and cannot be physically verified. Only written verification needs to be done.
- If an organization such as a bank always holds a large amount of cash, a complete physical check is not feasible and a test check should be adopted if a system with good internal control is in operation.
- Arthur E. Green & Co. The proceedings clearly proved that the auditor would be liable for negligence if he accepted the bad debt schedule and could not detect the time-limited debt contained therein.
Types of Audit Report
The audit report commented on the financial statements as to whether the auditor faithfully presented the company's financial position, financial performance, and cash flows in accordance with applicable financial reporting frameworks such as US GAAP, IFRS, and local GAAP. This is a report to express.
The purpose of the auditor is to express an appropriate opinion as to whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. Similarly, there are four types of audit reports based on this perspective. 4 types of audit reports
These four types of audit reports include:
a) Inappropriate audit report
b) Eligible audit report
c) Unfavourable audit report
d) Opinion Audit Report Disclaimer
- Inappropriate audit report
A non-qualified audit report is a report in which the auditor expresses his opinion that there are no material misstatements in the financial statements. In this case, the financial statements are prepared according to the applicable accounting standards.
Of the four types of audit reports, non-qualified audit reports are those normally issued by the auditor. This is because non-qualified audit reports are only reports that state that the financial statements are okay (no material misstatements).
Similarly, if there is a material misstatement, the auditor usually proposes adjustments to the client's management for correction. And, in most cases, adjustments are made, resulting in the auditor issuing a non-qualified audit report.
In this type of audit report, the auditor usually says, "In our opinion, the financial statements give a true and fair view in all important respects ..." or "In our opinion, the financial statements. Is presented fairly in all important respects ... "
For example, the auditor issues an ABC Limited non-qualified audit report following IFRS. In this case, the extracted non-qualified audit report * typically looks like this:
* This is an extracted report because the audit report has several sections other than opinions, such as the section of management responsibility and the section of auditor responsibility.
b. Eligible audit report
A qualified audit report is a report in which the auditor gives a qualified opinion on the financial statements. In this case, the financial statements contain material misstatements that can be separated as part of the financial statements.
In other words, misrepresentation is important, but not widespread. It does not affect the overall financial statements.
In this type of audit report, the auditor states that there is a problem with the financial statements, but the problem is less serious.
The problem in this case is one of the following:
The auditor finds that there is a material misstatement in an account or balance in the financial statements, or
The auditor does not have sufficient evidence to ensure that a particular account or balance is free of material misstatement.
In a qualified audit report, the auditor typically states: "In our opinion, the financial statements fairly represent the true and fair present in all important respects, except as stated in the grounds for eligibility ..."
For example, the extracted qualified audit report issued by the auditor to ABC Limited's financial statements following IFRS is as follows:
Auditors use the phrase "exclude" in the opinion paragraph to point out issues that lead to eligibility. Similarly, a separate paragraph, Eligible Opinion Basis, is needed to explain the eligibility of an opinion.
c. Unfavourable audit report
An unfavourable audit report is a report issued by the auditor that has material misstatements and affects the overall financial statements. In this case, misrepresentation is important and widespread.
In the unfavourable audit report, the auditor expresses the opinion that the financial statements contain serious problems, that is, the financial statements are unreliable.
Similarly, this type of audit report usually indicates that the financial statements are unreliable and that the integrity of the client's management can be questionable.
Auditors usually state in unfavourable audit reports that "financial statements do not provide a true and fair view" or "financial statements are not presented fairly."
d. Opinion Audit Report Disclaimer
Rejection of Opinion An audit report is an audit report in which the auditor is unable to express his or her opinion on the financial statements. This is usually due to the auditor's lack of adequate audit evidence to form an opinion on the financial statements.
Also, in this type of audit report, transactions or balances for which the auditor could not obtain evidence are significant and widespread. Such issues affect the financial statements as a whole and cannot be separated.
Similarly, auditors may disagree in the face of situations with significant uncertainty or lack of independence. However, this usually happens only in rare situations.
Audit Certificate
An auditor certificate (also known as an audit opinion in a business environment) is a statement issued after a company undergoes a professional audit. Auditors spend days or weeks conducting audits and testing company financial information. When this process is complete, the auditor publishes an opinion for use by internal and external business people. The information contained in the auditor certificate provides a brief statement as to whether the auditor approves the company's financial information. There are four types of certificates: unqualified, qualified, disclaimer, or dissenting.
An auditor certificate containing an unqualified opinion indicates that the auditor does not have protracted questions or doubts about the company's financial information. Informally, this is known as the "Clean Health Bill" and mimics the statement doctors give to healthy individuals. The unconditional opinion assures business stakeholders that the financial statements comply with national accounting standards, that internal controls are in place, and that there are no restrictions throughout the audit process.
A qualified opinion means that the auditor has problems applying national accounting standards or that there are other problems as a result of the audit. This may include failure to disclose important information related to the company, unfair representation of the company's finances, or failure to properly apply accounting standards. This auditor certificate typically requires a company to undergo a corrective audit in order to retest financial information when amendments are made.
The third judge certificate is a disclaimer opinion. The auditor issues this statement if it has not completed a complete audit of the company's financial statements or financial information. This opinion is often related to professional accounting services, such as review contracts, where accountants may provide companies with a rough review of financial information rather than a full-fledged audit. As expected, this opinion is significantly less important than the others.
1) Certified Public Accountant (CPA)
A certified public accountant is a person who has a CPA license. There are several artwork traces collectively with consulting, forensic accounting, internal accounting, tax and financial modelling and planning.
This course has the widest range for auditors as it permits them to showcase their capabilities right now in the most important markets. The CPA evaluates and tests the awesome of financial disclosures to make sure those organizations / humans examine usually common accounting principles.
Certified accountants are known as the oldest and most respectable accounting designation withinside the profession. CPA certification is considered the gold standard.
Certified accountants are licensed thru America U.S government and may comment on the financial statements of listed companies. A certified accountant can also sign a tax audit document and represent the patron withinside the front of the IRS, America tax department. CPA can perform all duties that unique certifications can perform.
To end up a Certified Public Accountant, you want to fulfil the requirements of U.S education and artwork experience, and take and by skip all four additives of the AICPA Unified Certified Public Accountant Exam. Each of us has a passing standard.
2) Certified Fraud Examiner
Certified Fraud Examiners are legal thru the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE). The fraud inspector's duty is to prevent and select out out fraud.
This characteristic requires humans with accounting research information with jail and criminology skillets. CFE learns how fraud is 2d only to no.
They take a look at the books for signs and symptoms and signs and symptoms of fraud and disclose the suspect. CFE's artwork includes auditing and accounting, fraud-related criminology / sociology, fraud investigations, fraud law, code of ethics, and more.
To end up a CFE, you need to earn a bachelor's degree in related fields collectively with business company control and accounting, and assemble a foundation for CFE from there.
3) Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
CISA guarantees that your IT enterprise machine is nicely checked, controlled, and protected. This function makes use of accounting, auditing, and laptop ability sets.
CISA uses the auditor's knowledge in the IT <vulnerability assessment line while implementing technology control in a corporate environment.
CISA certification requires five years of work experience in the areas of information systems auditing, control, warranty, or security. The CISA exam is very difficult and takes 4 hours to complete.
CISA holders are required to train 20 hours a year, 120 hours in 3 years to maintain their certification. You must also maintain ISACA auditing standards and comply with ISACA Professional Ethics Code.
4) Certified Management Accountant (CMA) Certified
CMA specializes in corporate accounting management. This certification covers aspects that CPA does not cover either. Therefore, these candidates are ideal for corporate internal control and executive level roles. They may retain their position as COO or CFO.
For certified accountants, this certification is not that great. It does not train applicants for audits and drafting of audit reports. It has a strict focus on the management aspects of the company.
CMA courses are half the size of CPA and are regulated by the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA).
To become a CMA, you must have a bachelor's degree with the appropriate amount of educational credits in a particular subject. You must also have at least two years of work experience to be certified.
5) Certified Internal Auditor (CIA) certified
This certification is for compliance personnel and auditors only. The CIA usually works for companies with larger structures.
They perform audit procedures and help independent auditors do their job. To become a CIA, you must have a bachelor's degree and years of relevant years of experience in the fields of auditing and accounting.
Auditor’s certificate sample

We, the undersigned, being the auditors of the company hereby certify that so much of this report as related to the shares allotted, the cash received in respect of such shares and the receipts and payments of the company are correct.”
Place and date
Difference between Audit Report and Audit Certificate
Points | Audit Report | Audit Certificate |
1.Nature | It is an expression of opinion approximately the account. | Confirmation of accuracy and accuracy of a few matters. |
2. Audit Basis | This file is primarily based totally on assumptions and assumptions. | The certificate is primarily based totally on actual numbers and facts. |
3.Criticism | There can be complaint approximately the complaint file. | There isn't anyt any complaint of the certificates. |
4. Range | The variety of the file is wide. | Its variety is limited. |
5. Scope of advice | The scope of recommendation is the scope of giving positive recommendation to the company. | For certificates, there's no scope of positive recommendation. |
6. Time of issue | An annual file is needed after the crowning glory of every accounting. | . Certificates aren't required each year. |
7. Liability of auditor | The file is simply an opinion and, if wrong, the auditor won't be liable. | The auditor is liable for any wrong certificates. |
8. Guarantee | The audit report is not a guarantee of the absolute correctness and accuracy of the books of accounts. | Auditor serves as a guarantee of the absolute correctness and accuracy of the books of accounts.
|
9.Responsibility | An auditor can be held responsible if the audit report is later on found to be wrong since he just gave an opinion. | But a duly signed certificate is found wrong, he will be held responsible.
|
10. Facts | The audit report is based on facts, estimates and assumptions. | The auditor's certificate is based on actual facts.
|
Key takeaways:
- The audit report commented on the financial statements as to whether the auditor faithfully presented the company's financial position, financial performance, and cash flows in accordance with applicable financial reporting frameworks such as US GAAP, IFRS, and local GAAP.
- A non-qualified audit report is a report in which the auditor expresses his opinion that there are no material misstatements in the financial statements.
- A qualified audit report is a report in which the auditor gives a qualified opinion on the financial statements.
- In a qualified audit report, the auditor typically states:
- An unfavourable audit report is a report issued by the auditor that has material misstatements and affects the overall financial statements.
- Auditors usually state in unfavourable audit reports that "financial statements do not provide a true and fair view" or "financial statements are not presented fairly."
- An auditor certificate (also known as an audit opinion in a business environment) is a statement issued after a company undergoes a professional audit.
- A qualified opinion means that the auditor has problems applying national accounting standards or that there are other problems as a result of the audit.
- A certified public accountant is a person who has a CPA license.
- CISA guarantees that your IT enterprise machine is nicely checked, controlled, and protected.
- CMA courses are half the size of CPA and are regulated by the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA).
AAS1-Basic principles for managing audits
The following is the text of the Audit and Guarantee Standards (AAS) 1 * "Basic Principles for Managing Audits" issued by the Council of Chartered Accountants of India. This standard should be read in conjunction with the "Introduction to the Statement on Standard Audit Practices" issued by the Institute.
Preface
- This standard defines the professional responsibilities of the auditor and describes the basic principles that must be adhered to each time an audit is conducted.
- Auditing is the independence of financial information of any entity, whether profit-oriented or not, regardless of its size or legal form, when such an investigation is conducted for the purpose of expressing an opinion. It is a survey. [2] In this standard, the term "financial information" includes financial statements.
- Other audit and assurance standards issued by the Institute detail the principles contained in this document to provide guidance on audit procedures and reporting practices.
- Adherence to the basic principles requires the application of audit procedures and reporting practices that are appropriate for the particular situation.
Honesty, objectivity, independence
The auditor must be candid, honest and honest in his approach to professional work. He must be fair and must not allow prejudice or prejudice to defeat his objectivity. He needs to maintain a fair attitude and appear to have no interest that could be considered incompatible with honesty and objectivity, whatever its actual effect.
Confidentiality
Auditors respect the confidentiality of information obtained in the course of their business and disclose such information to third parties without specific authority or unless there is a legal or professional obligation to disclose it.
Skills and abilities
The audit should be carried out and the report should be prepared with due professional attention by a person with sufficient training, experience and ability in the audit.
Judges are professionals gained through a combination of general education, technical knowledge gained through research, and formal courses completed by qualification exams recognized for this purpose and work experience under appropriate supervision. Requires good skills and abilities.
In addition, auditors require continued awareness of the ICAI's announcement of accounting and audit matters and progress, including relevant regulatory and statutory requirements.
Work done by others
If the auditor delegates work to an assistant or uses work performed by other auditors or professionals, the auditor remains responsible for forming and expressing opinions on financial information. However, you have the right to rely on the work done by others unless you have sufficient skill and attention and know why you believe you should not rely on it. Audit reporting in the case of an independent statutory appointment to perform the work that the auditor must rely on in forming an opinion, as in the case of the work of a branch auditor appointed under the Companies Act of 1956. The book is explicitly the fact of such trust.
The auditor should carefully direct, supervise, and review the work delegated to the assistant. The auditor must obtain reasonable assurance that the work performed by other auditors or professionals is appropriate for his purposes.
Documentation
The auditor must document important matters in providing evidence that the audit was conducted in accordance with the basic principles.
Plan
Auditors need to plan their work so that they can perform effective audits efficiently and in a timely manner. The plan should be based on the client's business knowledge.
Above all, you need to plan to cover:
(A) Acquire knowledge of client accounting systems, policies, and internal control procedures.
(B) Establish the reliability expected to be placed in internal control.
(C) Determine and program the nature, timing, and scope of the audit procedure to be performed.
(D) Coordinate the work to be performed.
The plan needs to be further developed and revised as needed during the audit process.
Audit evidence
Auditors need to obtain adequate audit evidence through compliance and substantive steps so that they can draw reasonable conclusions based on financial information.
Compliance procedures are tests designed to provide reasonable assurance that audit-dependent internal controls are in effect.
Substantial procedures are designed to obtain evidence of the integrity, accuracy, and validity of the data generated by the accounting system.
There are two types of them.
There are varieties of them.
(I) Testing transaction and stability details.
(Ii) Analysis of vast proportions and trends, consisting of investigations on account of unusual fluctuations and items.
Accounting gadget and inner manipulate
Management is liable for retaining the perfect accounting gadget that includes diverse inner controls to the volume suitable for the dimensions and nature of the commercial enterprise. The auditor has to fairly make certain that the accounting gadget is in region and that each one accounting data that need to be recorded is clearly recorded. Internal controls generally make a contribution to such guarantees.
Auditors want to apprehend the accounting gadget and associated inner controls and check out and examine the operations of inner controls that they need to consider in figuring out the nature, timing, and scope of different audit procedures.
If the auditor concludes that he can depend on a selected inner manipulate, his major steps are generally much less considerable than in any other case required and can fluctuate of their nature and timing. I have.
Audit conclusions and reports
The auditor need to overview and examine the audit proof acquired and the conclusions drawn from the entity's understanding of the commercial enterprise as a foundation for expressing an opinion on economic data. This overview and score entails drawing universal conclusions about:
(A) Financial data is produced the use of ideal accounting guidelines which are constantly applied.
(B) Financial data complies with applicable regulatory and statutory requirements.
(C) Where applicable, according with statutory requirements, there can be suitable disclosure of all fabric subjects referring to the right presentation of economic data.
The audit document have to consist of a clean opinion on economic data, and if the shape or content material of the document is stipulated or stipulated in an settlement or decree or regulation, the audit document will do so. Must follow requirements. The ineligible opinion is, in a few cases, the auditor's pleasure in all fabric respects with recognize to subjects that can be treated, mounted or stipulated beneath the applicable agreement or decree or regulation. .
If a certified opinion, a negative opinion or a denial of opinion is made, or if an opinion is reserved at the issue, the audit document need to kingdom the reason.
Powerful date
This audit and guarantee general is powerful for all audits associated with accounting durations starting on or after April 1, 1985.
AAS2-Purpose and scope of economic announcement audit
Preface
- This general describes the general motive and scope of an unbiased auditor's audit of a company's preferred economic statements.
- According to Section three. Three of the Preface of Accounting Standards 2 issued with the aid of using the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, the term "preferred motive economic statements" consists of stability sheets, earnings statements, and different statements and explanations. .. Some of them had been issued to be used with the aid of using shareholders / members, creditors, employees, and the overall public. "
- References to economic statements on this general need to be construed as regarding preferred-motive economic statements.
Purpose of audit
The motive of auditing economic statements organized in the framework of identified accounting guidelines and practices and associated statutory requirements (if any) is to permit auditors to specific their perspectives on such economic statements.
The auditor's opinion enables decide a real and honest view of a company's economic role and overall performance. However, customers need to now no longer anticipate that the auditor's opinion is assure of the company's destiny viability or the performance or effectiveness of management's overall performance of the company's commercial enterprise.
Responsibility for economic statements
The auditor is liable for forming and expressing reviews at the economic statements, however the obligation for the auditor's practise is the obligation of the company's management. Management obligations consist of retaining exact accounting statistics and inner controls, deciding on and making use of accounting guidelines, and shielding company assets. Auditing economic statements does now no longer lessen the manipulate of that liability.
Scope of audit
The scope of auditing monetary statements is decided via way of means of the reason and scope of auditing monetary statements SA 200A. The auditor considers the phrases of the contract, applicable prison requirements, and laboratory announcements.
However, the phrases and situations of the settlement can not restrict the scope of the audit with admire to subjects stipulated via way of means of regulation or the assertion of the institute.
The audit have to be prepared to thoroughly cowl all factors of the business enterprise as lengthy because it pertains to the monetary statements being audited. To touch upon the monetary statements, the auditor is fairly happy that the facts contained withinside the underlying accounting data and different supply information is dependable and enough as the idea for the practise of the monetary statements. Is needed. When forming an opinion, the auditor ought to additionally decide, if applicable, whether or not the applicable facts is nicely disclosed withinside the monetary statements situation to statutory requirements.
The auditor assesses the reliability and sufficiency of the facts contained withinside the underlying accounting data and different supply information withinside the following ways:
(A) Investigate and compare the accounting structures and inner controls he desires to believe and check the ones inner controls to decide the character, scope and timing of different audit tactics. When
(B) Perform such different trying out, inquiry and different verification tactics for accounting transactions and account balances, if he deems it suitable in a selected situation.
The auditor determines whether or not the applicable fact is nicely disclosed withinside the monetary statements withinside the following ways:
(A) Compare the monetary statements with the underlying accounting data and different supply information to make certain that they thoroughly summarize the transactions and activities recorded therein.
(B) Consider the choices made via way of means of control whilst making ready monetary statements. Therefore, the auditor evaluates accounting coverage alternatives and regular application, facts class methods, and disclosure adequacy.
The auditor's paintings involves, for example, figuring out the scope of the audit system and exercise judgments made via way of means of control in making ready monetary statements and assessing the rationality of estimates. In addition, a great deal of the proof to be had to the auditor can permit the auditor to attract best affordable conclusions from it. Due to those factors, absolutely the actuality of an audit is not often achieved.
Audit Declaration Handbook-SA200A
When commenting on monetary statements, auditors comply with tactics designed to persuade themselves that the monetary statements mirror a real and truthful view of a business enterprise's monetary role and performance. Auditors have the unavoidable danger that a few fabric misstatements can also additionally stay undiscovered because of the character of the audit's trying out and different inherent barriers, in addition to the inherent barriers of the inner manage system. I am conscious that there is. Often, control's discovery of fabric misstatement frequently takes place in the course of an audit, however such discovery isn't the primary reason of the audit, however due to the auditor's discovery. It is likewise now no long in particular designed paintings program. Therefore, the audit cannot be relied upon to make certain the invention of all fraud or errors, however that the auditor can also additionally have encountered any fraud or mistakes that would result in severe misrepresentation. If indicated, the auditor has to enlarge the process to verify or dispel his suspicions.
Auditors are more often than not interested by critical objects associated with the enterprise of a business enterprise, both personally or as a group. However, it's far hard to set clean standards for figuring out importance. Important objects are objects which can have an impact on the choices of customers of monetary statements3. It is an issue of creating choices primarily based totally at the auditor's expert revel in and judgment.
The auditor isn't predicted to carry out obligations outdoor his capabilities. For example, the expert abilities required of an auditor do now no longer consist of the technical expert abilities to decide the bodily circumstance of a selected asset. 13. Restrictions at the scope of auditing monetary statements that impair the auditor's cap potential to specific unconditional reviews on monetary statements have to be said in his document and, if necessary, certified reviews. Or a denial of opinion has to be expressed.
Powerful date
This auditing fashionable is legitimate for all audits associated with accounting intervals starting on or after April 1, 1985.
AAS3-Document
The following is the textual content of the Audit and Guarantee Standards (AAS) 3 * "Documents" issued via way of means of the Council of Chartered Accountants of India. This widespread have to be study alongside the "Introduction to the Statement on Standard Audit Practices" issued via way of means of the Institute.
Preface
Audit and Assurance Standards (AAS) 1 “Basic Principles for Managing Audits” (paragraph 11) states that “auditors want to file critical topics in offering proof that audits had been performed according with the primary principles. There is. “The motive of this widespread is to increase the above primary principles.
Documents for the functions of this widespread talk over with operating papers organized or received via way of means of the auditor and held via way of means of the auditor in reference to the behaviour of the audit.
Working paper:
-Supports audit making plans and implementation.
-Supports audit paintings supervision and review. When
-Provide proof of audit paintings executed to aid the auditor's opinion.
Form and content material
- The operating paper have to report the audit plan, the nature, timing, scope of audit strategies executed, and the conclusions drawn from the proof received.
- The layout and content material of the operating paper is stricken by the subsequent issues:
-The nature of engagement.
-Audit document layout.
-The nature and complexity of the client's business.
-The nature and country of the client's facts and their reliance on inner control.
-Specific situational desires for instructions, supervision, and opinions of the paintings executed
By an assistant.
- The operating paper should be designed and well prepared to satisfy the reputation of every audit and the auditor's desires for it. Standardization of operating papers (checklists, pattern letters, widespread shape of operating papers, etc.) improves the performance of operating paper manufacturing and review. It additionally allows delegation of labour even as offering a method of controlling the pleasant of labour.
- The operating paper should be whole and distinct sufficient for the auditor to benefit a typical expertise of the audit. The scope of documentation is an issue of professional judgment, as it's miles neither important nor sensible for all observations, opinions or conclusions to be documented via way of means of the auditor in his operating paper.
- All cloth topics that require the exercising of judgment have to be protected withinside the operating paper, together with the auditor's conclusions.
- To enhance audit performance, auditors usually gain and use client-created schedules, analyzes, and different operating papers. In such situations, the auditor has to make sure that those operating papers are well organized. An instance of this type of operating paper is an in depth evaluation of critical sales debts, debts receivable, etc.
- For normal audits, a few operating paper documents can be categorized as everlasting audit documents. These documents are presently up to date with facts that stays critical to next audits, not like contemporary audit documents, which incorporate on the whole audit-associated facts.
Persistent audit documents usually include:
1. Information approximately the felony and organizational shape of an entity. For companies, this consists of a memorandum and articles of incorporation. For felony entities, this consists of the legal guidelines and guidelines beneath which the felony entity works.
2. Excerpts or copies of critical felony documents, agreements, and mins associated with the audit.
3. Records of investigations and tests of inner controls associated with the accounting system. This may be with inside the shape of explanations, questionnaires, flowcharts, or an aggregate thereof.
4. A replica of the audited economic statements of preceding years.
5. Analysis of critical ratios and trends.
6. A replica of the control letter issued via way of means of the auditor (if any).
7. A report of verbal exchange with the retired auditor (if any) earlier than accepting the appointment as Audit & Supervisory Board Member.
8. Notes on critical accounting policies.
9. Early critical audit observations.
Current documents normally include:
1. Communication concerning reputation of annual reappointment.
2. Excerpts of crucial topics withinside the mins of the board of administrators and the overall assembly associated with the audit.
3. Evidence of the audit and programmed audit making plans process.
4. Transaction and stability analysis.
5. A document of the nature, timing, scope of audit processes accomplished and the consequences of such processes.
6. Evidence that the paintings accomplished through the assistant has been supervised and reviewed.
7. A reproduction of conversation with different auditors, experts, and different 0.33 parties.
8. A reproduction of a letter or memo concerning the audit topics communicated or mentioned to the client, which include the phrases of engagement and sizable weaknesses of associated inner controls.
9. Statement or affirmation letter acquired from the client.
10. Conclusions reached through the auditor with appreciate to crucial elements of the audit, which include how any exceptions and anomalous troubles disclosed through the audit system had been resolved or dealt with.
11. A reproduction of the suggested economic statistics and related audit report.
Ownership and garage of running paper
The running paper is the assets of the auditor. The auditor might also additionally, at his discretion, make a few or excerpts of his running paper to be had to clients.
The auditor has followed affordable processes for the garage and confidentiality of running papers, and for duration enough time to fulfil the wishes of his enterprise and to fulfil the applicable prison or expert necessities for document keeping.
Powerful date
This audit and assurance well known is legitimate for all audits associated with accounting durations starting on or after 1 July 1985.
AAS4-Auditor's obligation to don't forget fraud and blunders in auditing economic statements
Preface
The cause of this Audit and Assurance Standard (AAS) is to set up a well known for auditors' legal responsibility to don't forget fraud and blunders in auditing economic statements. This AAS specializes in the auditor's obligation for fraud and blunders; however the number one obligation for fraud and blunders prevention and detection lies with the individual chargeable for each governance and entity control. In this well known, the term "economic statistics" includes "economic statements." In a few circumstances, sure legal guidelines and policies might also additionally require the auditor to take steps further to the ones set forth on this AAS.
When making plans and executing audit processes and assessing and reporting the consequences, the auditor ought to don't forget the chance of cloth misstatement of economic statements because of fraud or blunders.
Fraud and mistakes and their characteristics
Misstatement of economic statements can end result from fraud or blunders.
The term "blunders" refers to accidental misstatement in economic statements, which include the omission or disclosure of quantities such as:
• Incorrect series or processing of the information from which the economic statements are prepared.
• False accounting estimates on account of oversights or misunderstandings of facts.
• Incorrect utility of accounting standards associated with measurement, recognition, classification, presentation, or disclosure.
The term "fraud" refers back to the planned behavior of 1 or extra executives, governance, personnel, or 0.33 celebration accountable persons, which include using fraud for fraudulent or unlawful gains. Although fraud is a huge prison concept, auditors are interested by fraud that reasons cloth misstatement in economic statements. Misstatement of economic statements might not be the cause of a few frauds. The auditor makes no prison judgment as to whether or not the fraud definitely occurred. Fraud concerning one or extra executives or governors is called "control fraud." Fraud concerning simplest personnel of an entity is called "worker fraud." In both case, collusion might also additionally arise with a 3rd celebration outdoor the entity.
Two kinds of planned misstatement are related to auditor assessment of fraud.
(A) Fraudulent economic reporting and
(B) Misappropriation of property and liabilities.
Fraudulent economic reporting consists of intentional misstatement or omission or disclosure of quantities in economic statements to mislead customers of economic statements. Fraudulent economic reporting may also include:
- Manipulation, falsification, falsification, or different deception of the accounting file or assisting report from which the economic statements are organized.
- Misrepresentation or intentional omission of events, transactions, or different essential data withinside the economic statements.
- Intentional misuse of accounting standards associated with measurement, recognition, classification, presentation, or disclosure.
Asset misappropriation consists of robbery of company property. Asset misappropriation may be completed in lots of ways, consisting of embezzlement of receipts, robbery of bodily or intangible property, or having agencies pay for items or offerings that they've now no longer received. Often observed with the aid of using fake or deceptive information or files to cover the truth that property is missing.
Fraud consists of motivation to dedicate fraud and diagnosed possibilities to do so. Individuals may be influenced with the aid of using beside the point property, as an example, due to the fact they stay past their very own means. Management is expected (and possibly unrealistic) from outside or inner reasserts of the enterprise, mainly if the effect on control is in all likelihood to be extensive if economic dreams aren't achieved. Fraudulent economic reporting is viable because of stress to attain sales targets. Fraudulent economic reporting or misappropriation of property whilst an character believes that inner manipulate can be circumvented, as an example due to the fact the character is in a reputable role or is aware of sure weaknesses withinside the inner manipulate device. There can be diagnosed possibilities for.
The element that distinguishes fraud from mistakes is whether or not the underlying movement that consequences withinside the misstatement of economic statements is intentional or unintentional. Unlike errors, fraud is intentional and commonly calls for the records to be intentionally hidden. The auditor can be capable of become aware of possibilities for fraud, however the auditor intends, mainly in subjects associated with control's judgment, together with accounting estimates and the right utility of accounting standards. Judgment is difficult, if now no longer impossible.
Responsibilities of Governance and Administration Officers
The number one duty for fraud and mistakes prevention and detection lays with each the individual liable for company governance and control. The obligations of all and sundry liable for governance and control can range from entity to entity. Management oversees governance officers, takes suitable attitudes, creates and continues a subculture of integrity and excessive ethics, and establishes suitable controls to save you and stumble on fraud and mistakes in the enterprise.
Through control oversight, making sure the integrity of a company's accounting and economic reporting device and making sure that right control is in place, consisting of hazard monitoring, economic control and compliance, is company governance. It is the duty of the individual in rate of.
The operator of the entity is liable for setting up a control surroundings and retaining rules and strategies to assist reap the goals of making sure the orderly and green implementation of the entity's commercial enterprise as a whole lot as viable. This legal responsibility consists of the implementation and guarantee of the continued operation of accounting and inner manipulate structures designed to save you and stumble on fraud and mistakes. Such structures reduce, however do now no longer eliminate, the hazard of misrepresentation, whether or not because of fraud or mistakes. Therefore, control is liable for the final risks.
Auditor duty
As said in AAS 2 “Purpose and Scope of Financial Statement Audit”, the cause of economic announcement audit organized in the framework of diagnosed accounting rules and practices and associated statutory requirements (if any) is , Is to allow auditors. Express your opinion on such economic statements. Audits carried out according with typically typical auditing requirements in India are designed to moderately make sure that the whole economic statements are freed from fabric misstatement, whether or not because of fraud or mistakes. I am. The truth that an audit is carried out may also act as a deterrent, however the auditor isn't and isn't liable for the prevention of fraud or mistakes.
Specific limits of auditing
The auditor cannot acquire absolute guarantee that cloth misstatements withinside the monetary statements can be detected. Due to the inherent obstacles of audits, the unavoidable danger that a few cloth misstatements in monetary statements will now no longer be detected, although the audits are nicely deliberate and performed according with usually commonplace auditing requirements in India. Audits are all cloth falsehoods because of elements which include using judgment, using tests, the inherent obstacles of inner controls, and the reality that a lot of the proof to be had to auditors isn't always conclusive and convincing. We do now no longer assure that the show can be detected. For those reasons, the auditor can best acquire affordable guarantee that cloth misstatements withinside the monetary statements can be detected.
The auditor's opinion on monetary statements is primarily based totally at the idea of acquiring affordable guarantees. Therefore, in audits, the auditor does now no longer assure that cloth misstatements can be detected, no matter fraud or mistakes. Therefore, next discoveries of cloth misstatement of monetary statements because of fraud or mistakes do now no longer, via way of means of themselves, indicate:
(A) When an inexpensive assure cannot be obtained
(B) Poor making plans, performance, or judgment,
(C) Lack of expert cap potential and right care, or
(D) Not in compliance with usually commonplace auditing requirements in India.
This is particularly genuine within side the case of positive varieties of planned misrepresentations. Audit processes consist of control, governance, employees, or third-celebration personnel, or tampered files. Whether an auditor conducts an audit according with usually commonplace auditing requirements in India is decided via way of means of the adequacy of the audit processes executed in that state of affairs and the suitability of the audit record primarily based totally at the consequences of those processes.
Expert scepticism
Auditors plan and perform audits with expert scepticism. This mindset is vital for the auditor to pick out and nicely assess:
- Matters that boom the danger of cloth misstatement of monetary statements because of fraud or mistakes (e.g., control traits and control environment, enterprise conditions, and effect on control traits and monetary stability).
- A state of affairs that makes the auditor suspects that the monetary statements are significantly misunderstood.
- Evidence obtained (such as auditor understanding from proceeding audits) that casts doubt at the credibility of control representatives.
However, the auditor has the proper to just accept the facts and files as real until the audit well-known shows proof of opposition. Therefore, audits performed according with usually commonplace auditing requirements in India are not often meant to certify files, and auditors are educated or predicted to be specialists in such certification.
Discussion approximately the plan
When making plans an audit, the auditor must speak with different contributors of the audit group the company's susceptibility to cloth misstatement of monetary statements because of fraud or mistakes.
Such discussions consist of, for example, thinking about the context of a selected entity this is probable to motive a mistakes and the way fraud may be committed. Based on those discussions, contributors of the audit group had been requested approximately the opportunity of cloth misstatement of monetary statements because of fraud or mistakes in a selected location of the assigned audit, and the way the consequences of the audit manner are. When executed, it is able to have an effect on different components of the audit. You also can make choices approximately which contributors of the audit group carry out particular inquiries or audit processes and the way to percentage the consequences of these inquiries and processes.
Inquiries from control
When making plans an audit, the auditor must touch control.
(A) Obtain the subsequent information:
(I) Management's evaluation of the danger that monetary statements can be significantly misunderstood because of fraud. When
(Ii) Accounting and inner manipulate machine controls are in vicinity to deal with such risks.
(B) Gain understanding of control's information of accounting and inner manipulate structures applied to save you and discover errors.
(C) Determine if control is privy to any acknowledged fraud that has affected the entity or suspected fraud that the entity is investigating. When
(D) Determine if control has determined a severe mistakes.
The auditor supplements management's knowledge of the company's business by contacting management regarding its own assessment of the risk of fraud and the systems in place to prevent and detect it. In addition, the auditor contacts management about the accounting and internal control systems in place to prevent and detect errors. Management is responsible for the accounting and internal control systems of the company and the preparation of financial statements, so it is appropriate for the auditor to ask management how they are fulfilling these responsibilities. The following items may be discussed as part of these inquiries:
(A) Whether there are specific subsidiary locations, business segments, transaction types, account balances, or financial statement categories that are likely to be in error or have fraud risk factors, and they How is it dealt with by management?
(B) Whether the business of the company's internal audit function and whether internal audit has identified fraudulent or material weaknesses in the internal control system. When
(C) How management communicates its views on responsible business practices and ethical behavior to employees through ethical policies and codes of conduct.
The nature, scope and frequency of management's assessment of such systems and risks vary from entity to entity. For some entities, management may make detailed assessments annually or as part of ongoing oversight. For other entities, management assessments may be informal and infrequent. The nature, scope and frequency of management's assessment is related to the auditor's understanding of the corporate control environment. For example, the fact that management does not assess the risk of fraud may indicate that management does not focus on internal control.
It is also important for auditors to understand the design of accounting and internal control systems within the enterprise. When designing such a system, management makes informed decisions about the nature and scope of the management procedures that it chooses to implement and the nature and scope of the risks that it chooses to undertake. As a result of these inquiries to management, the auditor may find, for example, that management has consciously chosen to accept the risks associated with the lack of separation of duties. The information from these queries identifies fraud risk factors that may affect the auditor's risk assessment that the financial statements may contain material misstatements caused by fraud.
It is also important for the auditor to ask management's knowledge of the fraud that has affected the entity, the alleged fraud under investigation, and the material errors found. Such queries may indicate potential weaknesses in the control procedure, for example, if a large number of errors are found in a particular area. Alternatively, such a query may indicate that the control procedure is working effectively because the anomaly is being identified and investigated quickly.
Inquiries to the management of the auditor may provide useful information regarding the risk of material misstatement of financial statements due to employee fraud, but such inquiries may result in management fraud. It is unlikely to provide useful information about the risk of material misstatement of the resulting financial statements. Therefore, follow-up of fraud risk factors by auditors is especially important in relation to management fraud.
Discussion with Governance Officer
The person responsible for corporate governance is responsible for overseeing systems for risk monitoring, financial management, and legal compliance. If corporate governance practices are well developed and the governance client plays an active role in monitoring the performance of management responsibilities, the auditor governs the adequacy of accounting and internal control. It is encouraged to seek the opinion of the client in charge of. Systems are in place to prevent and detect fraud and error, fraud and error risk, and management capabilities and completeness. Such inquiries may, for example, provide insight into a company's susceptibility to management fraud. Auditors may have the opportunity, for example, at meetings with the Audit Committee to discuss the general approach and overall scope of auditing and seek the views of governance officers in eliciting the views of independent directors. I have. This discussion may also provide governance officials with the opportunity to draw the auditor's attention to concerns.
Since the duties of the individual accountable for governance and control can range from entity to entity, auditors have to recognize the character of those duties in the entity to make certain that the above inquiries and communications are directed to the proper individuals.
In addition, the auditor considers whether or not there may be a governance situation to speak about with the individual accountable for company governance following control inquiries. Such troubles include, for example:
- Concerns approximately the character, scope and frequency of control checks of accounting and control structures carried out to save you and locate fraud and errors, and the dangers that monetary statements can be misunderstood.
- Management did not competently cope with the substantial weaknesses in inner controls diagnosed in the course of the preceding audit.
- Auditor's evaluation of a company's control environment, inclusive of questions on control competence and integrity.
- Impact of the above on the overall audit method and common scope, inclusive of extra steps that the auditors have to perform.
Audit hazard
In Section three of AAS 6 (Revised) “Risk Assessment and Internal Control”, “audit hazard” is the hazard that the auditor will provide an irrelevant audit opinion if the monetary statements are substantially incorrect. Such misrepresentations may be because of both fraud and error. AAS 6 (revised) additionally offers steerage on the way to perceive and check the 3 additives of audit hazard: inherent hazard, manage hazard, and detection hazard.
Inherent dangers and control dangers
When assessing precise dangers and manage dangers according with AAS 6 (Revised) “Risk Assessment and Internal Control”, how auditors can severely misunderstand monetary statements due to fraud or error. When thinking about the hazard of fabric misstatement because of fraud, the auditor have to recollect whether or not there are fraud hazard elements that imply the capacity for fraudulent monetary reporting or misappropriation of assets.
AAS 6 (Revised) “Risk Assessment and Internal Control” describes the auditor's evaluation of inherent and manage dangers and the way the ones checks have an effect on the character, timing, and scope of audit procedures. I am. In making those checks, the auditor considers how monetary statements may be extensively misunderstood due to fraud or error.
The truth that scams are normally hidden may be very hard to locate. Nevertheless, the auditor can also additionally use the auditor's expertise of the commercial enterprise to perceive activities or situations that offer an opportunity, motivation, or method to dedicate fraud, or that fraud can also additionally have already occurred. It can also additionally imply that. Such activities or situations are called "fraud hazard elements." For example, lacking documentation, out-of-stability widespread ledger, or evaluation steps do not make sense. However, those situations may be the end result of non-fraud situations. Therefore, fraud hazard elements do now no longer always imply the life of fraud, however they frequently exist withinside the context of fraud. The presence of fraud hazard elements can have an effect on the auditor's evaluation of inherent or manage hazard.
Fraud hazard elements cannot be without problems ranked so as of significance or blended with a powerful forecast model. The significance of fraud hazard elements varies greatly. Some of those elements are found in entities wherein positive situations do now no longer display a substantial hazard of misstatement. Therefore, the auditor will, at its discretion, recollect the hazard elements for fraud for my part or in combination, and whether or not there are precise controls that mitigate the hazard.
Auditors use professional judgment to evaluate the significance and relevance of fraud hazard elements and to decide the proper audit response.
The size, complexity, and possession traits of an entity have a substantial effect at the attention of applicable fraud hazard elements. For example, for massive entities, auditors usually recollect elements that usually constrain control's fallacious behaviour, which includes the effectiveness of governance employees and inner audit capabilities. The auditor additionally considers what steps were taken. Enforce the effectiveness of a proper code of behaviour and budgeting system. For smaller entities, a few or all of those issues won't be relevant or can be much less important. For example, small groups won't have a written code of behaviour, however instead, a lifestyle that emphasizes the significance of integrity and moral conduct thru verbal exchange and control examples. It can also additionally were developed.
Management control by a single individual in a small entity generally does not, by itself, indicate a proper attitude and communication failure by management regarding internal control and the financial reporting process. In addition, fraud risk factors considered at the business segment's business level may provide insights that differ from those considered at the enterprise level.
The presence of fraud risk factors may indicate that the auditor is unable to assess control risk below a high level for a particular financial statement assertion. On the other hand, auditors may be able to identify internal controls designed to mitigate fraud risk factors that auditors can test to support high or lower control risk assessments.
Detection risk
Based on the auditor's assessment of inherent and control risk (including the results of control testing), the auditor reduces the risk of misstatement due to fraud and error material to the financial statements to an acceptable low level. Substantial steps to reduce need to be designed. Not detected as a whole. When designing the substantive procedure, the auditor must address the fraud risk factors that the auditor has identified as present.
In AAS 6 (Revised) “Risk Assessment and Internal Control”, the auditor's control risk assessment, along with the inherent risk assessment, is the nature of the substantive steps taken to reduce the detection risk to an acceptable low level. , Timing, and range are affected. .. When designing the substantive procedure, the auditor addresses the fraud risk factors that the auditor identifies as present. The auditor's reaction to these factors is influenced by their nature and importance. In some cases, even if it is confirmed that a fraud risk factor exists, the auditor's judgment is that the audit procedure, which includes both control testing and already planned substantive procedures, addresses the fraud risk factor. You may decide that it is sufficient.
In other situations, the auditor may conclude that the nature, timing, and scope of substantive procedures need to be changed to address existing fraud risk factors. In such situations, does the auditor require an assessment of the risk of material misstatement to be an overall response, a response specific to a particular account balance, a class of transaction or assertion, or both types of response? I will consider it. The auditor considers whether changing the nature of the audit procedure, rather than the scope, is more effective in addressing the identified fraud risk factors.
Procedure when the situation indicates the possibility of misrepresentation
If the auditor encounters a situation that could indicate that the financial statements are materially misrepresented due to fraud or error, the auditor takes steps to determine if the financial statements are substantially false.
During the course of the audit, the auditor may encounter situations that indicate that the financial statements may contain material misstatements due to fraud or error.
If the auditor encounters such a situation, the nature, timing, and scope of the procedure performed will determine the type of fraud or error indicated, the likelihood of its occurrence, and the particular type of fraud or error financial. It can have a significant impact on the tables. In general, the auditor can take sufficient steps to confirm or dispel any suspicion that the financial statements are substantially misidentified as a result of fraud or error. If not, the auditor considers the impact on the audit report.
The auditor cannot assume that the fraud or error case is a single occurrence and must revise the audit risk component assessments made during the audit planning prior to the end of the audit. Whether it should be considered and the nature, timing, and scope of the auditor's other procedures need to be revisited. {See “Risk Assessment and Internal Control” in AAS 6 (Revised Edition). For example, the auditor considers the following:
- Substantial procedure nature, timing, and scope.
- Assessment of the effectiveness of internal control when the control risk is assessed below high.
- Assign audit team members that may be appropriate in your situation.
Considering whether or not the diagnosed misstatement can be a signal of fraud
If the auditor identifies a misstatement, the auditor have to recollect whether or not such misstatement can also additionally suggest fraud, and if there are such signs, the auditor of the audit Other aspects, particularly control expressions.
If the auditor determines that the misstatement is or can be the end result of fraud, the auditor assesses the effect, particularly the effect managing the organizational function of the events worried. For example, fraud related to the misappropriation of coins from a small coins fund is commonly of little significance to the auditor in assessing the threat of cloth misstatement because of fraud. This is due to the fact each fund control and length have a tendency to restriction capacity losses, and control of such finances is commonly outsourced to much less legal employees. Conversely, if the problem includes a better stage of authority control, the quantity itself isn't always vital to the economic statements, however it could suggest a broader issue. In such situations, the auditor revisits the credibility of formerly received proof as it could query the integrity and truthfulness of the statements made and the authenticity of the accounting information and files. Auditors additionally recollect the opportunity of collusion related to employees, control, or 0.33 events while reviewing the credibility of proof. If control, particularly pinnacle control, is worried in fraud, the auditor won't have the proof wanted to finish the audit and record the economic statements.
Evaluation and disposal of misstatements and their effect on audit reports
The auditor have to recollect the effect at the audit if it reveals that the economic statements are notably misidentified due to fraud or error, or if it's miles not able to attain a conclusion. AAS 13 “Audit Importance” and AAS 28 “Auditor's Report on Financial Statements” offer steerage at the evaluation and disposition of misstatements and their effect at the auditor's record. In the occasion of a fabric fraud, or if the character answerable for governance commits the fraud, the auditor have to recollect the want for disclosure of the fraud withinside the economic statements. If right disclosure isn't always made, the auditor have to recollect the want for correct disclosure withinside the record.
Documentation
The auditor need to record the fraud threat elements diagnosed as being gift throughout the auditor's evaluation method and the auditor's reaction to such elements. If, throughout an audit, fraud threat elements that persuade the auditor that extra audit processes are diagnosed are diagnosed, the auditor files the lifestyles of such threat elements and the auditor's reaction to them. Is wanted.
The auditor need to record vital subjects in imparting proof to aid the audit opinion, and the operating paper have to encompass the auditor's inferences and audits on all vital subjects that require the auditor's judgment. You want to encompass the character's conclusions. Due to the significance of fraud threat elements in assessing the inherent threat of cloth misstatement or control threat, the auditor files the diagnosed fraud threat elements and the moves deemed suitable with the aid of using the auditor. (AAS 3, "Documents" may want to be referenced).
Management representative
(A) Recognize obligation for the implementation and operation of accounting and inner manipulate structures designed to save you and discover fraud and error.
(B) We trust that the effect of misstatement of those unadjusted economic statements aggregated with the aid of using the auditor throughout the audit isn't always massive to the economic statements as a whole, for my part and as a whole. A precis of such gadgets have to be blanketed or connected to the written representation.
(C) Disclosure to the auditor all cloth data associated with fraud or suspected fraud regarded to control that could have affected the entity. When
(D) Disclosure to the auditor of the effects of the threat evaluation that the economic statements may be notably misidentified due to fraud.
AAS 11 “Management Statements” gives steerage for acquiring suitable statements from control in audits. In addition to spotting legal responsibility for economic statements, it's miles vital for control to well known obligation for accounting and inner manipulate structures designed to save you and discover fraud and errors.
Because control is accountable for adjusting the monetary statements to accurate fabric misstatements, the auditor stated that uncorrected misstatements as a consequence of both fraud and blunders are in my view in control's opinion. And it's miles critical to attain a written declaration from control that it isn't always critical as a whole. Such statements aren't an alternative choice to acquiring enough and suitable audit proof. In a few circumstances, control won't agree with that a number of the misstatements within side the unadjusted monetary statements compiled through the auditor all through the audit are misstatements. Therefore, control is recommended to feature a declaration consisting of "For [explaining the reason], the items ... And ..... Do now no longer comply with represent a misrepresentation."
The auditor can specify a quantity that doesn't want to build up misstatements. This is due to the fact the auditor does now no longer assume the build up of such quantities to have a sizeable effect at the monetary statements. In doing so, the auditor takes under consideration the reality that the materiality dedication entails qualitative and quantitative considerations, but a fairly small quantity of misstatement may have a sizeable effect at the monetary statements. The précis of uncorrected misstatements contained or connected to the written illustration does now no longer want to encompass such misstatements.
Due to the character of the fraud and the problems that the auditor encounters in detecting fabric misstatements of monetary statements because of injustice, the auditor has disclosed to the auditor all statistics associated with the fraud. It is critical to attain a written declaration from control to confirm. Alternatively, control the consequences of control's hazard evaluation of suspected fraud, spotting that it could be affecting the company, and the capacity for sizeable false impression of monetary statements due to fraud.
Verbal exchange
If the auditor identifies fraud, or suspected fraud, or misrepresentation because of blunders, the auditor communicates that statistics to control, governors, and, in a few cases, as required through regulation and regulation. You want to keep in mind the duty of the auditor to do so. Also to regulatory and enforcement authorities.
Timely verbal exchange of fraud, suspected fraud, or misrepresentation because of mistakes to the proper degree of control is critical due to the fact it may take the essential actions. Determining what degree of manipulate is suitable is an issue of professional judgment and is situation to elements consisting of the character, scale and frequency of alleged misrepresentation or fraud. Appropriate stages of manipulate are generally as a minimum one degree above the individual believed to be worried withinside the alleged misrepresentation or fraud.
Determining which subjects the auditor communicates to the governing officer is an issue of professional judgment and is likewise motivated through the parties' knowledge of which subjects to talk. Such troubles commonly encompass:
- Questions approximately manageability and completeness.
- Fraud, which includes control.
- Other frauds that bring about fabric misstatement of monetary statements.
- Significant misstatement because of blunders.
- False warning signs of sizeable weaknesses in inner controls, which includes layout or inner controls
- Operation of a company's monetary reporting process.
- Misstatements that may result in misstatements in destiny monetary statements.
Communicating misrepresentations because of mistakes to control and governors
If the auditor identifies a fabric misstatement because of an blunders, the auditor need to keep in mind the want to well timed talk the misstatement to the ideal degree of control and record it to governance personnel.
The auditor have to notify the Governance Officer of any uncorrected misstatements that had been aggregated through the auditor all through the audit and decided through control to be unimportant in my view or as a whole.
Uncorrected misstatements communicated to the governing officer want now no longer encompass misstatements underneath the desired quantity.
Communicating misrepresentations as a consequence of fraud to control and governors
If the auditor has:
(A) Identified fraud irrespective of whether or not the monetary statements had been materially misrepresented.
(B) Obtained proof that fraud may also exist (even supposing the capacity effect on monetary statements isn't always sizeable).
Auditors must don't forget the want to talk those problems to the proper degree of control in a well timed way and file such problems to governance officials.
When an auditor obtains proof that fraud exists or might also additionally exist, it's far critical to attract the eye of the precise degree of control to the issue. This is genuine even supposing the trouble is taken into consideration non-essential (as an instance, a minor dropout through a low-degree worker of the entity's organization). Determining what degree of manage is suitable is likewise motivated through the ability for collusion or the involvement of control individuals in those conditions.
If the auditor determines that the misstatement is or can be the end result of fraud and the effect can be substantial to the economic statements, or check whether or not the effect is substantial. If now no longer, the auditor does the following:
(A) Discuss problems and procedures to in addition research with suitable degree managers, as a minimum one degree above stakeholders, and pinnacle degree managers. When
(B) We propose that control seek advice from a attorney if essential.
Communicating substantial weaknesses in inner manage
The auditor ought to talk to control the substantial weaknesses of inner manage associated with the prevention or detection of fraud and mistakes which have attracted the auditor's interest because of carrying out the audit. The auditor become additionally knowledgeable of substantial weaknesses in inner manages associated with fraud prevention and detection that have been observed through control or recognized through the auditor all through the audit. You must be satisfied with that. ..
When the auditor identifies substantial inner manage weaknesses associated with fraud or blunders prevention or detection, she or he communicates those substantial inner manage weaknesses to control. It is likewise critical to inform governance employees of such deficiencies, as substantial weaknesses in inner controls associated with fraud prevention and detection have severe implications.
When the integrity or integrity of control or governance officials is suspected, auditors commonly don't forget looking for criminal recommendation to help in making suitable path of movement decisions.
Contacting regulatory and enforcement authorities
The auditor's expert duty to keep the confidentiality of patron statistics commonly removes reporting fraud or mistakes to events outdoor the patron entity. However, the auditor's legal responsibility might also additionally vary, and in positive instances the law, law, or courtroom docket might also additionally revoke confidentiality. For example, beneath the regulatory framework of non-financial institution economic companies, auditors are obliged to file any dangers or dangers to the file to the Reserve Bank of India. In such conditions, the auditor might also additionally don't forget looking for criminal recommendation.
Auditor not able to finish engagement
If the auditor concludes that it isn't viable to preserve the audit because of fraud or misrepresentation because of suspected fraud, the auditor ought to:
(A) Consider the expert and criminal legal responsibility relevant to the situation, consisting of whether or not the auditor has made the audit appointment or, in a few instances, desires to be pronounced to the regulatory agency.
(B) Consider the opportunity of taking flight from engagement. When
(C) If the auditor withdraws:
(I) Discuss withdrawal from and withdrawal from auditor involvement with suitable degree control and governance officials.
(Ii) Consider whether or not the person that appointed the audit, or in a few instances the regulatory agency, has the expert or criminal requirement to file the withdrawal from the auditor's involvement and the cause for the withdrawal.
Auditors might also additionally stumble upon super conditions that query the auditor's cap potential to preserve auditing, as an instance withinside the following conditions:
(A) The entity does now no longer take corrective movement concerning fraud that the auditor deems essential withinside the situation, even supposing fraud isn't substantial to the economic statements.
(B) Auditor issues and audit take a look at outcomes concerning the chance of fabric misstatement because of fraud suggest a substantial and sizable chance of fraud.
(C) Auditors have severe worries approximately the abilities or integrity of control or the ones accountable for governance.
Due to the variety of situations that can occur, it is not possible to clearly explain whether withdrawal from engagement is appropriate. Factors that influence the auditor's conclusions are the impact of the involvement of management or the governing authority (which may affect the credibility of management's representatives) and the ongoing relationship with the entity.
The auditor has professional and legal responsibilities in such situations, and these responsibilities may vary from situation to situation. For example, an auditor may have, or may be required, to make a statement or report to one or more persons who appointed an audit, or in some cases, to a regulatory agency. Given the exceptional nature of the situation and the need to consider legal requirements, the auditor will provide legal advice in deciding whether to withdraw from the contract and in deciding on an appropriate course of action. Consider asking.
Communication with the host auditor
Section 8 of Part I of the 1st Schedule of the Chartered Accountant Act of 1949 is actually held by another Chartered Accountant without the Chartered Accountant first contacting him if he accepts his position as an Auditor. If so, it is stipulated that you will be guilty of professional illegal acts. In writing. The existing auditor, who is inquired by the next auditor, should advise if there is a professional reason why the next auditor should not accept the appointment. If the client denies the existing auditor's permission to discuss its work with the next auditor, or limits what the existing auditor can say, that fact should be disclosed to the next auditor. ..
The auditor may be contacted by the next auditor asking if there is a professional reason for the next auditor not to accept the appointment. The responsibilities of existing and upcoming auditors are set out in the Code of Ethics issued by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India.
The extent to which an existing auditor can discuss the client's business with the next auditor depends on whether the existing auditor has the client's permission and the professional and legal liability associated with such disclosure.Given the constraints arising from these responsibilities, the existing auditor advises the next auditor if there is a professional reason not to accept the appointment, provides details of the information, and is relevant to the next auditor and the appointment. Feel free to discuss everything you need to do. If fraud or suspected fraud was a factor in withdrawing from the involvement of existing auditors, be careful that existing auditors state only the facts related to these issues (not his or her conclusions).
Effective date
This audit and warranty standard is valid for all audits related to accounting periods beginning on or after April 1, 2003.
Key takeaways:
- Adherence to the basic principles requires the application of audit procedures and reporting practices that are appropriate for the particular situation.
- Auditors respect the confidentiality of information obtained in the course of their business and disclose such information to third parties without specific authority or unless there is a legal or professional obligation to disclose it.
- If the auditor delegates work to an assistant or uses work performed by other auditors or professionals, the auditor remains responsible for forming and expressing opinions on financial information.
- Auditors need to obtain adequate audit evidence through compliance and substantive steps so that they can draw reasonable conclusions based on financial information.
- Management is liable for retaining the perfect accounting gadget that includes diverse inner controls to the volume suitable for the dimensions and nature of the commercial enterprise.
- Financial data complies with applicable regulatory and statutory requirements.
- The auditor is liable for forming and expressing reviews at the economic statements, however the obligation for the auditor's practise is the obligation of the company's management.
- The auditor's paintings involves, for example, figuring out the scope of the audit system and exercise judgments made via way of means of control in making ready monetary statements
- Audit and Assurance Standards (AAS) 1 “Basic Principles for Managing Audits” (paragraph 11) states that “auditors want to file critical topics in offering proof that audits had been performed according with the primary principles.
- Excerpts or copies of critical felony documents, agreements, and mins associated with the audit.
- Evidence of the audit and programmed audit making plans process.
- The term "fraud" refers back to the planned behavior of 1 or extra executives, governance, personnel, or 0.33 celebration accountable persons, which include using fraud for fraudulent or unlawful gains.
- The auditor cannot acquire absolute guarantee that cloth misstatements withinside the monetary statements can be detected.
- The person responsible for corporate governance is responsible for overseeing systems for risk monitoring, financial management, and legal compliance.
- If the auditor encounters a situation that could indicate that the financial statements are materially misrepresented due to fraud or error, the auditor takes steps to determine if the financial statements are substantially false.
- The auditor need to record the fraud threat elements diagnosed as being gift throughout the auditor's evaluation method and the auditor's reaction to such elements.
- The auditor ought to talk to control the substantial weaknesses of inner manage associated with the prevention or detection of fraud and mistakes which have attracted the auditor's interest because of carrying out the audit.
- The extent to which an existing auditor can discuss the client's business with the next auditor depends on whether the existing auditor has the client's permission and the professional and legal liability associated with such disclosure.
Reference:
- Practical Auditing Spicer and Peglar Allied, 1975, H.F.L., 1978
- A Handbook of Practical Auditing B.N. Tondon S Chand & Co Ltd
Case Study:
You are an audit manager at RMT & Co. And you are considering a number of ethical issues which have arisen on some of the firm’s long-standing audit clients. ABC Ltd. RMT & Co is planning its external audit of ABC Ltd. Yesterday, the audit engagement partner, Ramesh, discovered that a significant fee for information security services, which were provided to ABC Ltd. By RMT & Co., is overdue. Mr. R hopes to be able to resolve the dispute amicably and has confirmed that he will discuss the matter with the finance director, Mr. Keshav, at the weekend, as they are both attending a party to celebrate the engagement of Ramesh’s daughter and Keshav’s son. XYZ (P) Ltd. RMT & Co is the external auditor of XYZ (P) Ltd. And also provides other non-audit services to the company. While performing the audit for the current year, the audit engagement partner was taken ill and took an indefinite leave of absence from the firm. The ethics partner has identified the following potential replacements and is keen that independence is maintained to the highest level: Mr. Pankaj Garg who is also the partner in charge of the tax services provided to XYZ (P) Ltd.
Mr. Mohit Taneja who was the audit engagement partner for the preceding five years.
Mr. Chetanya Garg who introduced XYZ (P) Ltd. As a client when he joined the firm as an audit partner
five years ago. Mr. Nikunj Garg who is also the partner in charge of the payroll services provided to XYZ (P) Ltd.
MN Ltd. MN Ltd. Is a large public company, and has been an audit client of RMT & Co. For several years. Aadish Jain, a partner of RMT & Co, has acted as the engagement quality control reviewer (EQCR) on the last two audits.
At a recent meeting, he advised that he can no longer be EQCR on the engagement as he is considering accepting appointment as a non-executive director and will sit on the audit committee of MN Ltd. The board of directors has also asked RMT & Co. If they would be able to provide internal audit services to the company. PQR Ltd. PQR Ltd., a listed company, is one of RMT & Co’s largest clients. Last year the fee for audit and other services was ₹1.2 Cr. And this year it is expected to be ₹1.5 Cr. Which represents 18% and 19.6% of RMT & Co’s total income respectively.