Unit 3
Detailed estimation for super structure
- It is accurate estimate of working out quantity for all item of work and finding the cost,
- The dimension of each item are taken from drawings and quantity of each item are calculate, abstract and costing is computed.
- There are two stages of detailed estimate,
1) Detailed of measurements and finding quantity: -
- The details of measurements of each item of work is taken accurate from plan and quantity of each item are calculate in tabular form named as detailed of measurements form.
2) Abstract of estimate cost: -
- The cosy of each item of work is calculate in tabular form quantities that already calculated and total cost is found out in abstract form.
- The rate of different item of work are taken as per schedule rate or present rate.
- Usually 3 to 5 ℅ of estimate cost is added for Contegencies and 2 ℅ of work charge establishment.
- The grand total is estimate cost of work.
Problem: -
1) Work out the following plans quantity upto plinth level of both long wall short wall method and centre line method.
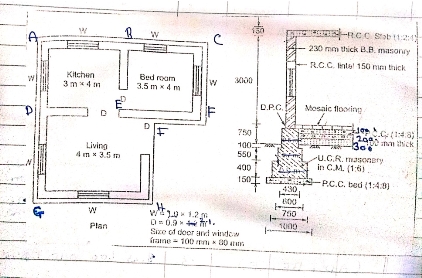
Ans : by long wall short wall method,
Long wall :
(ABC ,DEF) = 6.96m
(GH) = 4.23 m
Short wall :
(AD,BE,CF) = 4.23 m
(DG ,HI) = 3.73 m
1 | Brickwork in superstructure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Long wall |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| (ABC,DEF) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L= 6.96 + 0.23 = 7.19 m | 2 | 7.19 | 0.23 | 3 | 9.93 | 22.76 m3 |
| (GH) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| L= 4.23 + 0.23 = 4.46m | 1 | 4.46 | 0.23 | 3 | 8.08 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Short wall |
|
|
|
|
| |
| (AD,BE,CF) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| l= 4.23 - 0.23 = 4 m | 3 | 4 | 0.23 | 3 | 8.28 | |
| (DG,HI) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| l= 3.3.73 - 0.23 = 3.5m | 2 | 3.5 | 0.23 | 3 | 4.83 | |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door | 3 | 0.9 | 0.23 | 2.1 | 1.3 | |
| Window | 6 | 1 | 0.23 | 1.2 | 1.66 | |
| Lintel over door | 3 | 1.2 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| Lintel over window | 6 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.27 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 | Flooring |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kitchen | 1 | 3 | 4 | _ | 12 | 40 m2 |
| Bed room | 1 | 3.5 | 4 | _ | 14 | |
| Living | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | _ | 14 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 | RCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Lintel over door | 3 | 1.2 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 7.83 m3 |
| Lintel over window | 6 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.27 | |
| RCC slab | 1 | Area = 7.4 x 8.4 - 3.4 x 3.5 = 48.7m | 0.15 | 7.31 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 | External plaster with coarse sand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| External perimetre = 2 x 7.19 +2 x 8.19 = 30.76m | 1 | 30.76 | _ | 3.9 | 119.96 | 115.11 m2 |
| H = 0.75 + 3 + 0.15 = 3.9 m |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (external) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Area = 0.9 x 1.2 = 1.08 m2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 0.95 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Window |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Area 1 x 1.2 = 1.2 m2 | 3 | 1 | _ | 1.2 | 3.6 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 | Internal plaster |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Internal perimetre |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kitchen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| = 2 x 3 + 2 x 4 = 14m | 1 | 14 | _ | 3 | 42 | 163.67 m2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Bed room |
|
|
|
|
| |
| = 2 x 3.5 + 2 x 4 = 15m | 1 | 15 | _ | 3 | 45 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Living |
|
|
|
|
| |
| = 2 x 4 + 2 x 3.5 = 15 m | 1 | 15 | _ | 3 | 45 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Celling |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Kitchen | 1 | 3 | 4 | _ | 12 | |
| Bed room | 1 | 3.5 | 4 | _ | 14 | |
| Living | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | _ | 14 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door ( external) | 0.5 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 0.95 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (internal) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduct full face | 2 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 3.78 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Window | 3 | 1 | _ | 1.2 | 3.6 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
By centre line method,
Length centre line plan = 2 x 3.23 +2 x 3.73 +3 x 3.73 +4.23 +2 x 3.73
= 38.3m
Total length = length of centre line plan – n x 0.5 x width
= 38.3 – 4 x 0.5 x width
= 38.3 – 2 x width
1 | Brickwork in superstructure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| L = 38.3 - 2 X 0.23 = 37.84m 1 |
| 37.84 | 0.23 | 3 | 26.11 | 22.76m3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door | 3 | 0.9 | 0.23 | 2.1 | 1.3 | |
| Window | 6 | 1 | 0.23 | 1.2 | 1.66 | |
| Lintel over door | 3 | 1.2 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.12 | |
| Lintel over window | 6 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.27 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 | Flooring |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kitchen | 1 | 3 | 4 | _ | 12 | 40 m2 |
| Bed room | 1 | 3.5 | 4 | _ | 14 | |
| Living | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | _ | 14 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 | RCC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Lintel over door | 3 | 1.2 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.12 | 7.83 m3 |
| Lintel over window | 6 | 1.3 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.27 | |
| RCC slab | 1 | Area = 7.4 x 8.4 - 3.4 x 3.5 = 48.7m | 0.15 | 7.31 | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4 | External plaster with coarse sand |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| External perimetre = 2 x 7.19 +2 x 8.19 = 30.76m | 1 | 30.76 | _ | 3.9 | 119.96 | 115.11 m2 |
| H = 0.75 + 3 + 0.15 = 3.9 m |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (external) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Area = 0.9 x 1.2 = 1.08 m2 | 0.5 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 0.95 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Window |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Area 1 x 1.2 = 1.2 m2 | 3 | 1 | _ | 1.2 | 3.6 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 | Internal plaster |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Internal perimetre |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Kitchen |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| = 2 x 3 + 2 x 4 = 14m | 1 | 14 | _ | 3 | 42 | 163.67 m2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Bed room |
|
|
|
|
| |
| = 2 x 3.5 + 2 x 4 = 15m | 1 | 15 | _ | 3 | 45 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Living |
|
|
|
|
| |
| = 2 x 4 + 2 x 3.5 = 15 m | 1 | 15 | _ | 3 | 45 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Celling |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Kitchen | 1 | 3 | 4 | _ | 12 | |
| Bed room | 1 | 3.5 | 4 | _ | 14 | |
| Living | 1 | 4 | 3.5 | _ | 14 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduction |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door ( external) | 0.5 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 0.95 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Door (internal) |
|
|
|
|
| |
| Deduct full face | 2 | 0.9 | _ | 2.1 | 3.78 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| Window | 3 | 1 | _ | 1.2 | 3.6 | |
| Deduct half face |
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Valuation is art of assessment the present fair value of property a stated time.
- It based on certain fact and only after judicious processing of such fact and indication, so that we can suggest value of fair price of property.
a) Purchase for investment or for occupation: -
- For investment property is purchased and for this valuation property are necessary.
- Such valuation I am depending on income from the property in comparison to money market interest and also possibility of increase in cost.
b) Tax fixation: -
- To fix up municipal tax of property the valuation is essential by municipal authorities which depends upon class of city and trade important.
c) Sale: -
- For sale of property valuation become necessary which depends upon price that can obtain in market and seller considered this amount as reserve price below which any offer us not accept to them.
d) Rent fixation: -
- Valuation of property is necessary to find the rent of property and required for standard rent.
e) Insurance premiums: -
- To fix up the value of property excluding cist of land, valuation is required in order to replace the same and to find out insurance premiums.
f) Mortgage value or security of loans: -
- To raise loan in security of property so that valuation is necessary.
g) Compulsory acquisition: -
- A property is acquired by government for public purpose and in such case compensation against such acquisition is given to owner by government.
- To find out property of amount of compensation valuation are necessary.
h) Speculation: -
- When purchased intended for sale of property and to make some profit a short period valuation is necessary for this purpose called as speculative value.
i)Betterment charge: -
- The value of property is increasing as results of making a new road, development and land and provide other amenities.
- To fix up betterment charge of fee, valuation become necessary before and after completing of development.
j) Wealth tax and estate duty: -
- Government fix value like minimum value of property or above which wealthy tax or estate duty to paid by owner of property for valuation of estate is necessary.
k) Gift tax: -
- When property is gifted, valuation of gift property is necessary to pay tax of gift to government by person to whom property has gifted.
l) Capital gains tax: -
- Taxation of capital gains is realized when capital assist is disposed off and process exceed the cost incurred in acquisition the assist.
- There are three type of method of valuation of building: -
1) Book value method.
2) Present land value method.
3) Rental method of valuation.
- Property used for special purpose of general range of commercials as well as residential properties for school, police station or perform non profitable community function where is no direct evidence of income, valuation of such property are made in this method.
- Valuation for under development or owner occupied or vacant possession which is done this method of valuation.
- The basis principle or valuation by this method is final individual market value of land and also individual depreciated buildings.
- Methods are explain as follows: -
1) Book value method: -
- It a simplest method of valuation which adopted for property which not do fetch any rent of owner.
- This method is suitable for recording valuation assist the balance sheet of companies of government office record.
- By know original cost of construction, the depreciation cost for past life is calculated by straight line method.
- Book value is calculated by subtracting depreciation cost from original cost of construction plus original cost of land.
- Book value = original cost of construction – depreciation by straight line method + original cost of land.
- Draw back of this method is value obtain is less than real value and this method are doing not use in practice.
2) Present land value method: -
- Original cost of land is taken for determination the valuation of property this are explain as book value method, but even though the value of building depreciation, the value of land which is building is constructed.
- Time calculate valuation of property, instead of original cost of land, the present market value of land is taken by comparing the land under considering.
- Valuation of property = original cost of construction – depreciation for past life + present market value of land.
3) Rental method of valuation: -
- This method is adopted if building is used on rental basis or when probable rent from building can finally by local enquiry.
- Procedure of rental method explain as follows: -
a) Find out gross rent from property from original rent collection or by making local enquiries in area.
b) Calculate all outgoing to the property is subject.
c) Work out net rent from property by substrate total outgoing from gross rent.
d) Assume suitable rate of interest by comparison with rate of interest is offer by national bank and government security and find out year purchase.
e) Y. P = 100/ assume rate of interest.
f) Find capable value of property by multiplying net income by year purchase.
1) Price: -
- The amount worked out adding the cost of production, interest on investment, reward to producer for his labour and risk.
- Selling price is fixed for commodity.
- For less price demand the selling price have the fixed lower and vice versa.
2) Cost: -
- It means that original cost of construction and can know after accounting all day to day expenditure from very planning stages till construction is complete.
- Cost of old buildings become less due to it age and change in fashion.
- For valuation cost of old buildings is working out from present cost construction of such new building less calculate amount of loss of building due to wear and tear.
3) Value: -
- Value means that the worth or utility.
- Value varies time to time, place to place and depend is largely on supply that particular type property and extend of demand for it.
- The cost construction of building have no relation to value same if sold in open market.
- Value is depend upon,
a) It utility.
b) Scarcity.
c) Events.
- The value of property within short time us more like double than the cost of construction they are more buyers that type property and vice versa.
1) Force of demand and supply: -
- Few buyer as compared to number of property available for sale in locality which results in low prices for property and vice versa.
2) Rise in population: -
- It due to growth of new industry or influx or by multiplication results in heavy demand for land, building and property,
3) Cost of construction: -
- The present cost of construction affects value due to rapid change of price index in comparison with rate of depreciation.
4) Rent control across: -
- Value of property is calculated from it income through rent. But rental value of property in area subject to rent control act may not reflect value similar property unencumbered of tendency as rent are artificial freezer while price land labour and building materials have rising continue.
5) The imposition of control prices of building materials: -
- This cause violent fluctuations in price of building materials.
6) Rent restrictions act: -
- Value of property is calculated from probable annual income rent and due to certain enactment of rent restrictions act, by government it may cause slump in property values.
7) Interest on schedules bank or government security: -
- By lowering of schedule bank interest or government security higher may be interest of make more money available for investment in property and vice versa.
8) Abnormal conditions: -
- Due to insecure conditions like riot, war trend etc, value may drop and remain so for consistent period.
1) Scrap value: -
- It is the value of dismantled materials of property at end of it utility period and absolutely useless except for sale as scrap.
- Scrap value is considered the 10℅ of cost of construction.
- It also known as junk value or demolition value.
- In rare case, scrap value may be zero or even negative if cost dismantling or removal become equal or more than scrap value.
2) Salvage value: -
- It estimates value of built up property at end of it useful life without being dismantled.
- This general account by deduction depreciation from it new cost.
3) Market value: -
- Market value of property at which it can sold in open market at particular time.
- In open market means that the property is offer for sale by advertising in daily newspaper and all necessary steps are adopted so that person who desires to purchase the same can make an offer.
4) Book value: -
- The value of property show in account book in particular year like original cost less the total depreciation till that year.
- The book value property gradually reduce constant amount year after year upto limit of scrap value.
5) Distress value: -
- If property is sold at lower price than the market value at time, it said to have distress value such as following reason: -
A) Financial difficulties of seller.
B) Court decree.
C) Insufficient knowledge of seller.
D) Quarrel among partners.
E) Panic due to war or riot or civil commotion.
6) Replacement value:-
- It is present value of property or portion ,there of it replaced at current market rate.
7) Potential value: -
- When property is capable of fetching more return due to it alternatively use or advantage planning by providing some development work, such value of property called as potential value.
8) Sentimental value: -
- When property is sold or purchased at higher value than market value due to play of sentiment in mind of owner is called sentimental value. This are have following reason,
A) The owner is attach that demand fancy price.
B) The situation and class of property suit prospective purchase. It may ideal for his purpose and may have special value to him.
9) Speculative value: -
- Speculation in agriculture land, ripe for building development will cause value to rise, even before road are made and service installed.
- Speculation purchase such property at low prices as far as possible know as speculative value.
10) Capitalized value: -
- The capitalized value of property is sum or amount interest on which highest prevailing rate equal to net income out of property.
- A freehold property is in absolute possession of it owner for period of indefinite duration who has right to use the property at his free will subject only to low of land.
- The freeholder in inherently the absolute owner of property, he holds it without any payment in nature of rent.
- He may sell the property divide it, develop it or donate it on lease his sweet it.
- Being the legal estate a freehold can only transfer on execution of deed.
- The duration at letting like lease may be for quite short period yearly or 3 year. But occupation lease for term such 15,21,25 or 50 year are common practice.
- When lease is grant for 99 year it knows as long term lease and when for 999 year it said to perpetuity.
- At expiry of lease, the lessor get back absolute possession of property.
- The leasehold is known as lessee and hold the physical possession of property for definition period under term and conditions specified in lease documents.
- The lessee is used to pay an annual rent to lessor and observe content in lease.
- There are different type of lease as follows: -
1) Building lease: -
- In case of owner of freehold open plot of land let our his land on lease to some person called lessee on agrees amount of premium or ground rent or both combined.
- The lease holder can erect building up to specified amount in specific period and he maintain the property and reside income through such property.
- The rent which paid by leaseholder for use of land usually for purpose and privilege of building on another man land called as ground rent.
2) Life lease: -
- When duration of lease for property is given until death of person this is called as life lease.
3) Occupation lease: -
- In case of this lease is grant premium or rent or combination of two by owner of property consist of land and building or other structures for occupancy for fixed period to another person.
- The leaseholder does not have to spend money to construction of building and such lease is generally granted for short term as 7,14,21 year
- The leaseholder maintain the property according to term and condition or lease.
4) Sub lease: -
- A leaseholder have tender sub lease of his leasehold property to other person subject to term and condition In original lease and allow by local regulations or court of law.
- In this case original lease holder is named as assignment of lease and sub lease holder called sub lease.
5) Perpetual lease: -
- When lease of property is given for number of year providing condition that lease in renewable time to time, even for endless time according to desire of lease holder called as perpetual lease.
Estimation |
Valuation
|
An estimation to calculation of quantities required and expenditure like to incurred in construction work
| Valuation is process estimating the cost of property based on present condition. |
An estimate is the probable cost of work and find out by mathematical calculation based on plan drawing and current rate | Properties may be immovable properties like land , building, quarries, etc and movable properties like coal, oil, steel, cement and sand etc
|
- It loss in value of property due to it use, life, wear, tear, decay, and obsolescence.
- This is about assessment of physical wear and tear of building or property and it depends upon its original conditions, quality of maintenance and mode of use
- The value of building or property decrease gradually upto utility period due to depreciation.
There have three type of method explain as follows: -
a) Straight line method: -
- This method of property is assuming to lease value by constant amount at every year and fixed amount of original cost is written off every year so, that at end at term when asset is worm our, only scrap value removal.
- Annual depreciation = ( original cost – scrap value) / life in year.
b) Constant percentage method / declining balance method: -
- In this method the property which can assume to lose value annually at constant percentage of it value.
- By constant percentage method at end of first year the value of property,
= C ( 1 – P) at end of 2nd year.
= C ( 1- p) ( 1- p) = C ( 1- p) ^2 and so on.
- Hence at end of n year value of property became ultimately scrap value
= C ( 1 – p) ^ n
- Or
- P = 1- (sc / C) ^ (1/n).
- Above formula does not hold good when scrap value is zero.
c) Quantities survey method: -
- In this method, the property is studied in details and extend of physical deterioration work out in endeavours to calculate depreciation.
- Sinking fund is an amount which has to set aside at fixed intervals of time our gross income so that the end useful life of building or property the fund should accumulate to initial cost of property.
- A building is subject to normal wear and tear it value goes on decreasing with age
- Sinking fund to be calculate depend on following factor: -
1) Life of building.
2) Rate of interest on bank deposit or government security.
3) Scrap value of building which assumes as 0.1 time cost of construction at end of it useful life
- Annual sinking fund = I / ( 1 + I) ^n -1.
- It defined as capital sum required to invested in order to receive a net annual income as annuity of Rain 1/- at certain rate of interest.
- Year purchase is found by education,
- Y. P = 100 / rate of interest.
- The property of value becomes less that date in style, in structure, in design, this is called as obsolescence,
- An older structure like massive wall so that arrangements of room not suited now a day and structure is doing the, obsolete even it maintains in very good condition.
- The obsolescence of structures is due to progress in addition, change in fashion, planning idea new invention and improvement of techniques.
Problem: -
1) A person has purchased an old building at cost Rs, 90,000/- on the basis cost of land is Rs, 50,000/- and cost of building structure is Rs, 40,000/-.consider future life of building is 20 years. Workout amount of annual sinking fund at 4℅ interest when scrap value is 10℅ of cost of building structure.
Ans: -
Scrap value = 10 ℅ of cost of building
= 0.1 x 40,000
= Rs. 4000/-
Total amount of sinking fund is accumulated= 40,000 – 4000 = Rs, 36,000/-
Annual sinking fund for re- equipment of Rain, 36000/- in 20 year,
I = si / ( 1 + I) ^n – 1
= 36000 x 0.04/ ( 1 + 0.04) ^20 – 1
= Rs. 1209.60/-
2) A person wish to sell his building at Rs, 15 lakhs. The life of building is considered as 80 year and scrap value as 10℅, find the depreciation value on building if current age of but us 20 year, also at what prices the building which is purchased.
Ans: -
Present cost of construction = 15 lakhs.
Scrap value = 10 ℅ = 1.5 lakh
Life =80℅
Total depreciation = 15 – 1.5 = 13.5 lakh.
Value of building = present cost – depreciation cost
= 1500000 – 0.16875 x 20
= 1499996.62