Unit-1
Introduction to Building Construction and Masonry
KEY TAKEWAYS:
There are many construction practices or processes which are applied in the construction of residential building, commercial building, public buildings. And the process which takes place in construction is given in detail above.
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Any structure for whatsoever purpose and of whatsoever materials constructed is called as Building.
• According to the NBC of India i.e. National constructing code of India, homes are labeled into numerous agencies which can be primarily based totally on occupancy, are referred to as follows:
1. Group A - Residential Building:
2. Group B - Educational Building:
3. Group C - Institutional Building:
4. Group D - Assembly Building:
5. Group E-Business Building:
6. Group F - Mercantile Building:
7. Group G - Industrial Building:
8. Group H-Storage Building:
9. Group I- Hazardous Building:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Types of building are as follows:
Any building structure can be divided into two basic components i.e. substructure and superstructure.
1.Substructure
2. Superstructure
1.Substructure:
2.Superstructure:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
A part of the structure lying below the ground surface such as foundation of any type is known as substructures. Superstructure denotes part of the structure lying above the ground surface.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Automation of production addresses diverse and severe troubles associated with production for example, low first-rate of very last product, shortages of professional labor, protection of labor, negative climate condition, and quick production length which in recent times are capabilities of project.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Masonry is essentially a wall material which should have sufficient strength and stability. To efficiently perform the functional requirements of a wall, masonry form of construction is done for a wall.
Stone Masonary:
The selection of stone for masonry depends upon :
Brick Masonary:
Definitions of some common terms broadly used in brick masonry are stated below: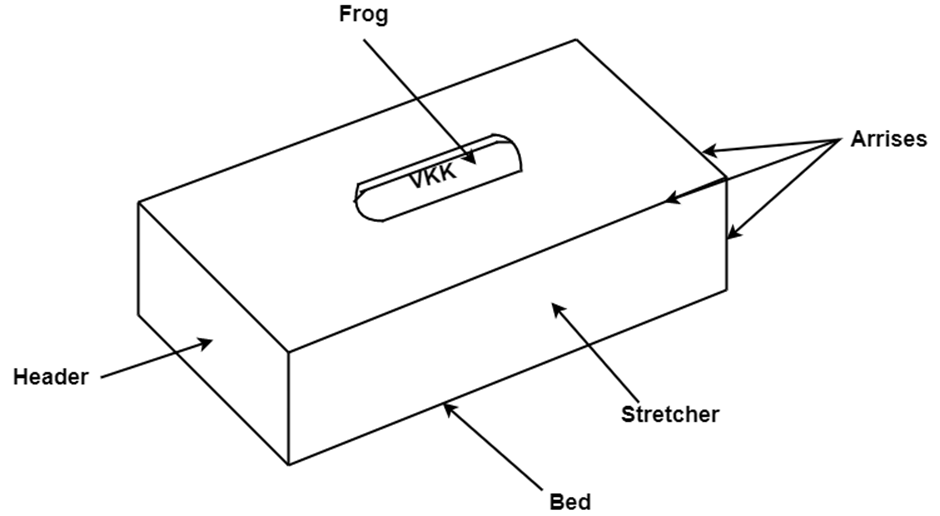
Fig.1.1: showing Brick with technical terms.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
It is the art of building the structures in stones. Stones are abundantly available in nature. These stones when cut and dressed to the proper shapes, prove to be an economical material for the construction.
Laying of bricks bonded together with mortar is known as brick masonry. The strength of brick masonry depends upon the bonding material and method of bonding adopted. Mortar acts as a binding material but also gives strength to the masonry work.
Following factors offers the requirement of exact brickwork:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Building brick should be tough, well burnt, free from chemicals, having perfect frog.
The exceptional checks on bricks are completed are as follows:
1. Porosity:
2. Crushing power:
3. Hardness:
4. Soundness:
5. Water-absorption test:
6. Efflorescence test:
7. Dimensional balance:
8. Structure:
9.Impact test:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The test taken on bricks are as follows:
Bricks are made for unique motive and therefore they may be categorised as follows:
1. Acid resistant bricks :
2. Engineering bricks :
3. Silica bricks :
4. Refractory bricks :
5. Sand-lime bricks:
6. Blue bricks:
7. Coloured bricks :
8. Perforated bricks :
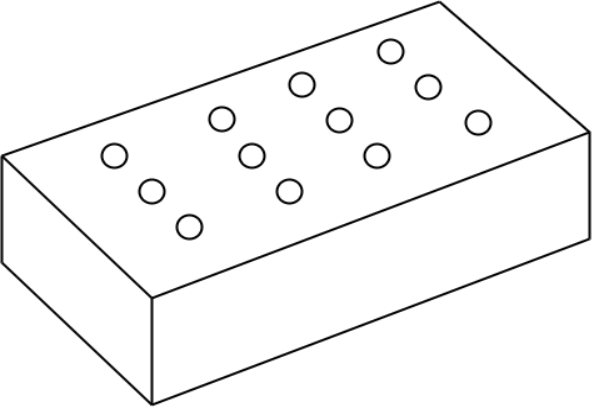
Fig.1.2: Showing Perforated brick
9. Fire bricks:
10. Hollow Bricks or Hollow Blocks:
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Bricks are made for unique motive and therefore they may be categorised as follows:
There are a lot of bonds used for exclusive varieties of works:
1. English bond
2. Flemish bond
3. Header bond
4. Stretcher bond
1. English bond:
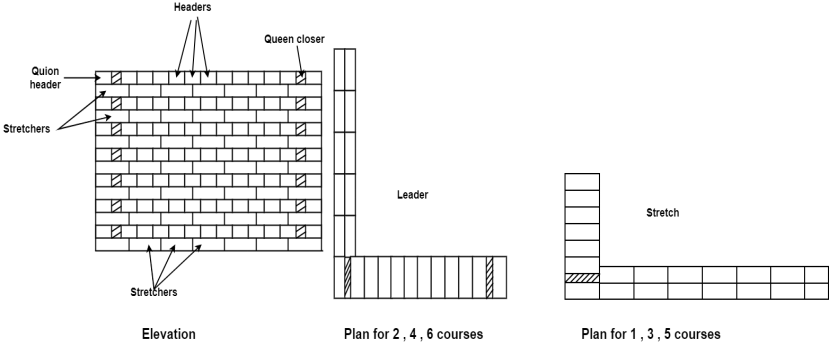
Fig.1.3: showing One Brick wall English bond
2. Flemish bond:
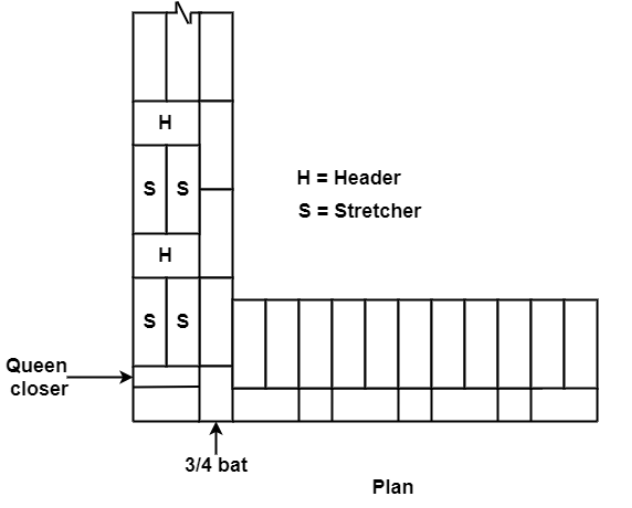
Fig.1.4: Single Flemish Bond(1&1/2 brick wall)
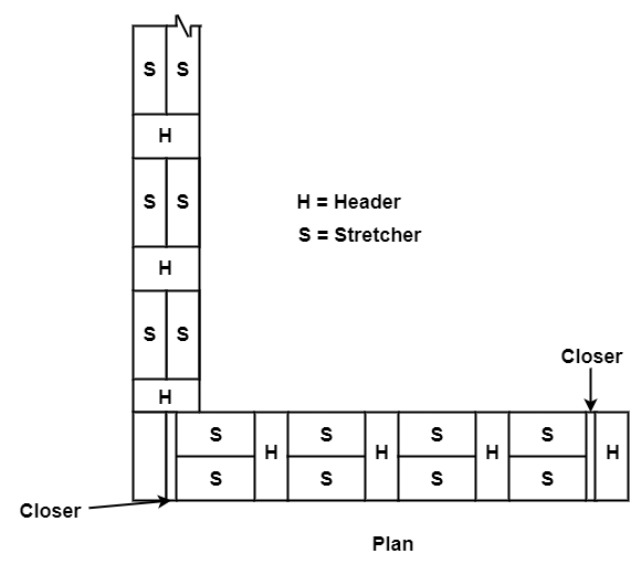
Fig.1.5: Double Flemish Bond of one brick wall
3. Header Bond:
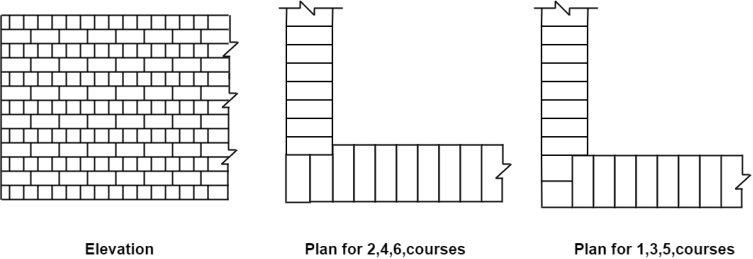
Fig.1.6: Header bond
4. Stretcher bond:
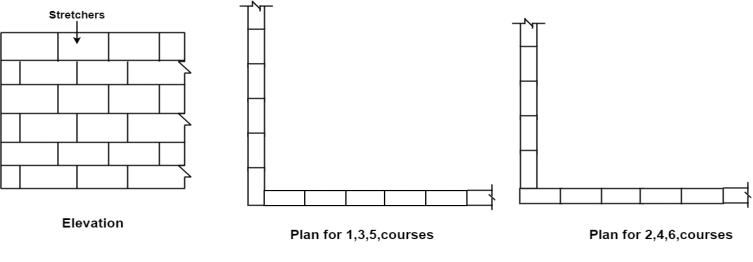
Fig.1.7: Stretcher Bond
KEYTAKEWAYS:
There are four types of bond: Header bond, Stretcher bond, English bond and Flemish bond.
Laying of brick must be executed very systematically with recognize to right bonding, jointing and ultimate finishing. Hence professional masons are required for correct laying of bricks into the masonry paintings.
Following are the critical steps for laying the brickwork for wall production:
Also, wetting of bricks washes the dirt from them and a smooth brick will produce a higher joint and bond with mortar.
Bricks are soaked in water earlier than laying due to the fact dry brick quick take in water from the mortar. This is risky due to the fact while the use of cement mortar sufficient water will now no longer be to be had for the manner known as as warmness of hydration and in the long run it impacts at the strength.
Then the bricks are taken and tied through line dori or wire or string after which those bricks are suspended in such manner that the road dori or mason cords get stretched on each the faces of wall and among the 2 quit of the wall with the intention to deliver the similarly masonry paintings in right alignment.
Perpends must be stored vertical. Bricks with one frog must be laid with its frog on its pinnacle face to make certain that they may be absolutely full of mortar or now no longer.
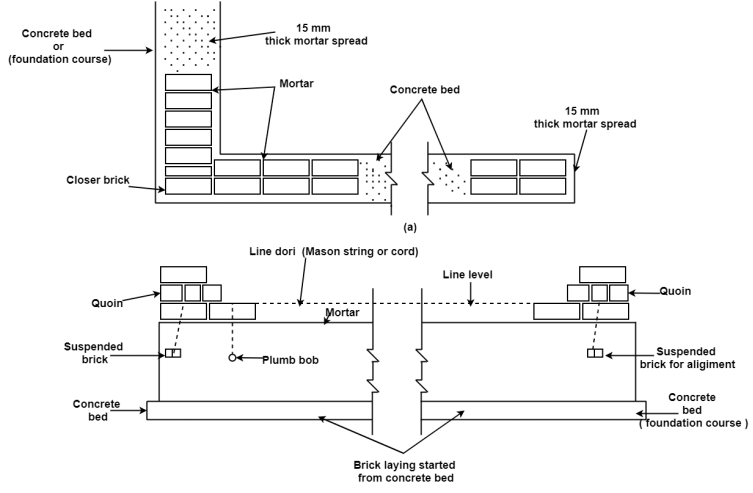
Fig.1.8: Laying of Brick
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Laying of brick must be executed very systematically with recognize to right bonding, jointing and ultimate finishing.
Following are the critical precautions and are to be taken into consideration in brick paintings:
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Brick should be well burnt, reddish in colour, sound and hard. There are lot of precautions are taken during supervision.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
There are lot of trends in light weight structure. Developments with inside the nanotechnology and nano materials are probably to offer worthwhile opportunities to the global manufacturing organization with inside the near future.
1. Mould or platform:
2. Support device or centering:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The moulds made up from a few inflexible cloth including wooden or metal plates wherein concrete is positioned and wherein it's far harden are called "formwork”. There are two parts of formwork- Mould and Support device.
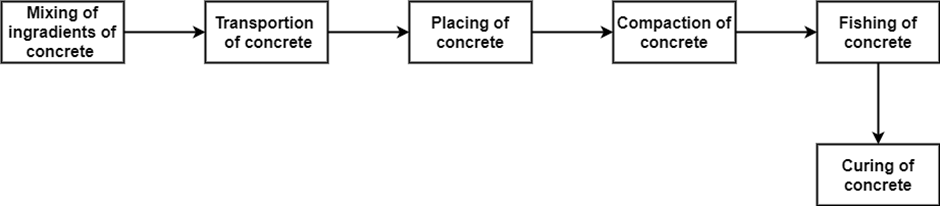
Fig.1.9: Showing Casting procedure of concrete
Modes of Transportation of Concrete :
Precautions to be Taken During Transportation and Placing of Concrete in Formwork:
Following Precautions Should be Taken During Placing of Concrete in Formwork:
Compaction of Concrete:
Methods of Compaction :
Finishing of Concrete:
Curing of Concrete:
Necessity of Curing:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Casting procedure for reinforced concrete columns, R.C.C beams and R.C.C Slabs consist of following things: Transportation, placing, compaction, mixing, Finishing of concrete and curing.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Slip formwork is extensively used for building the massive towers or bridges. It is likewise used for building the silos and grain elevators.
Underpinning:
Methods of under pinning :
Scaffolding:
Purpose of Scaffolding:
Components Parts:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Underpinning is the system of presenting new basis under the prevailing basis without negative the stableness of present shape. These transient shape or platform built very near the wall, is with inside the shape of tiss or metallic framework, generally referred to as scaffolding
References:
1.Building Materials by S.K.Duggal, New Age International Publishers.
2.Building Construction by S.C.Rangwala, Charotdar Publications.
3.Building design and construction by Frederick Merrit, Tata McGraw Hill.
4.IS 962-1989 code for Practice for Architectural and Building drawings