Unit-2
Building Byelaws and Introduction to Architectural Drawing
A) Building Byelaws
KEY TAKEWAYS:
In Past years of independence, people started to migrate towards bigger cities for education, jobs and better living conditions. Due to this spurt of movement, the cities were over burdened with population. There was a big fillip in construction activity to accommodate all the migrants. As a result, the cities grown haphazardly and there was big chaos. In order to control this haphazard growth, building bye-laws came into existence.
KEYTAKEWAYS:
To reduce pollution in area by restricting population density in an area there by providing hygienic environment. To ensure that every citizen will receive facilities like water supply, sanitation, ventilation, electric supply, parking and safety. To help architects, engineers in planning and design of every civil engineering construction.
Plot sizes for various zones are as follows:
1. Residential and commercial zones:
Sr.No. | Type of Development | Plot size(m2) or (Sq.m) | Minimum width of frontage(m) |
1 | Row House type building | 50-125 | 4.5 to 8 |
2 | Semi-detached building | 125-250 | 8 to 12 |
3 | Detached Building | Above250 | Above 12 |
2.Industrial zones
3.Other Building
(a) Cinema Assembly halls:
(b) Mangal karyalaya:
(c) Petrol filling station:
30.50 x 15.75 m: Petrol filling station without service bay.
36.5 x 30.5 m: Petrol filling station with service bay.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Plot sizes depends on various zones: Residential zone, Industrial zone, commercial zone, other buildings.
KEYTAKEWAYS:
The approach to the buildings from road/street/internal means of access should be through paved pathways of width not less than 1.5 m provided its length is not more than 20 m from the main/internal mean of access, provided that there is a minimum set back of 2 m between the edge of the pathways and front wall of the building.
On front and rear side – 3m
Side margin – 2m
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Limited lighting and ventilation are basic requirements of rooms, open spaces are also provided inside and around residential buildings. In case of buildings with adjoining streets, open space will provide scope for future widening of streets.
KEYTAKEWAYS:
The floor area ratio (FAR) is a number that denotes the maximum floor space that can be constructed on a given piece of land. In other words, it is a ratio between a building's total constructed floor area and the land area
KEYTAKEWAYS:
V.P.R is the ratio of volume to plot area (VPR). It controls the volume and height of buildings in the specified land use zone. It decides the height and size of building to be constructed.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The open spaces insides and around the building particularly residential type have to provide to carter for the lighting and ventilation requirement. Front open space, Rear open space, Side open space.
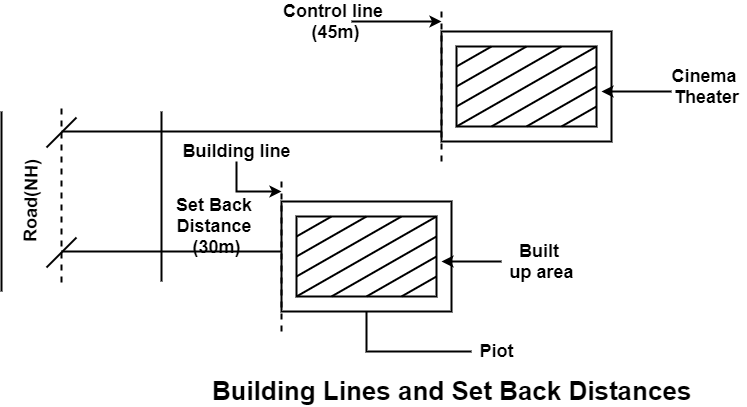
Fig.2.1: Showing Building line
KEY TAKEWAYS:
It is the line up to which the plinth of a building adjoining from the centre of the street or an extension of a street in future may lawfully extend, it is also called as set back or front building line.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
In public building such as cinema halls, factories, commercial buildings which are generally overcrowded attracts large number of vehicles should be set back a further distance apart from the building line. The line up to which such buildings are constructed is known as control line.
Sr. no. | Width of street | Height of the building |
|
|
|
1. | ‘W’ | Height = 1.5W + front open space(general criteria) |
2. | Up to 8m | 1.5 x width of street |
3. | 8m to 12m | 12m |
4. | Above 12m | Width of street and in no case more than 21 |
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Height of building depends on the width of the road.
Habitable Rooms:
Size:
Height:
Kitchen:
Size:
Other requirements:
Every room to be used as Kitchen shall have:
Bath Rooms and Water Closets
Size:
Height:
Other requirements:
Every bath room or water-closet shall:
Loft
Store Room
Size:
Height:
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Room sizes for Habitable room, kitchen, store room, loft, Bathroom, WC closet are given above.
1. BUILT UP AREA/ PLINTH AREA:
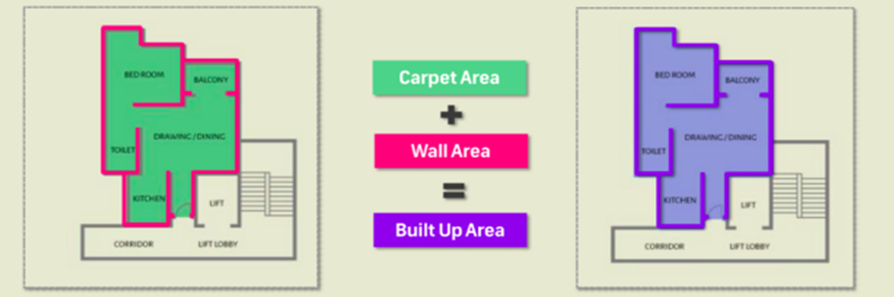
Fig.2.2: showing built-up area
2. CARPET AREA :
3. SET BACK AREA:
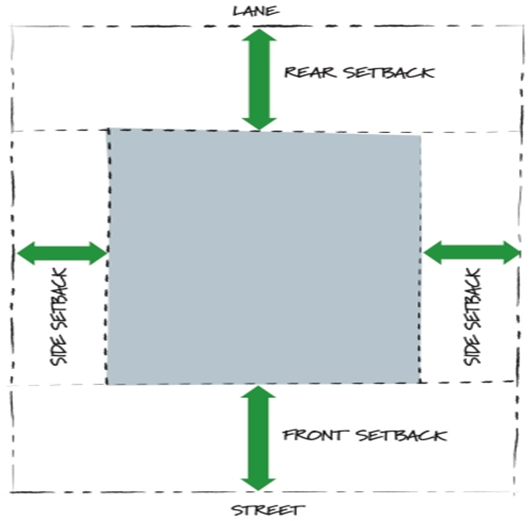
Fig.2.3: Showing Setback area
4. SUPER BUILT-UP AREA:
5. PLOT AREA:
KEYTAKEWAYS:
There are five types of areas which explained above:
The rate of ventilation by natural means through windows or other openings depends on:
Min. area for opening –
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The rate of ventilation by natural means through windows or other openings depends on: Direction and speed of wind currents outside, and size & disposition of openings. Convection effects arising from temperature of vapor pressure difference between inside & outside the room and the difference in height between the inlet and outlet openings (stack effect).
Natural Light:
Artificial Light:
Principles Of Lighting:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Lighting is also known as Illumination. The use of light to achieve aesthetic effect. There are two types of light: Natural light and artificial light
DIRECTION | USE |
HORIZONTAL CIRCULATION affected by columns, furniture layouts, trees, or topographic changes. In hallways, paths, entries, exists.
| PUBLIC CIRCULATION is the area of a building which is used widely and access easily. Like Lobby, atrium, gallery where crowd is high. |
VERTICAL CIRCULATION includes stairs, lifts, escalators, ladders, ramps to move from one floor to another.
| PRIVATE CIRCULATION requires a degree of privacy. eg. Back door in houses. |
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The movement of people and goods between interior spaces in buildings and to entrances and exits. To simplify further, architects divide their thinking according to different types of circulation, which overlay with one another and the overall planning
The planning, design, construction and installation of water supply, drainage and sanitation and gas supply systems shall be in accordance with the Part-IX. Plumbing Services-Section-1-Water Supply, Section-2-Drainage and Sanitation and Sections 3-Gas Supply of national building code of India 2005.
Rules for Sanitation:
There are some rules and regulations for 6 minimum requirements. For water supply and sanitation for different types of buildings.
1. Residential Building
2.Commercial shops and offices
3.Hotels
4.Educational Building
KEY TAKEWAYS:
There are some rules and regulations for 6 minimum requirements. For water supply and sanitation for different types of buildings.
Types of parking –
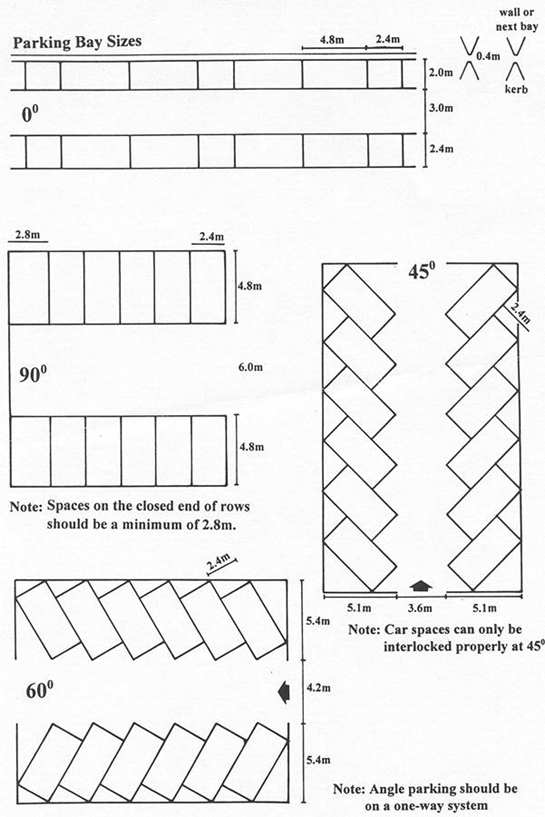
Fig.2.4: Showing Parking of vehicles
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Types of parking are angle parking, perpendicular parking, parallel parking.
Where, t = Thickness of wall immediately above basement level (Not less than 200 mm )
j = offset of concrete (Not less than 100 mm)
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Plinth area should be a minimum of 1.2 times the floor area of the building. Minimum width of footing = 2t + 2j.Thickness of the damp proof courses 20 mm to 25 mm. Thickness of cement concrete floor is a minimum of100 mm plus floor finish. Ceiling height should be 3000 to 3600mm.
B) Introduction to Architectural Drawing:
1. Aspect:
2. Prospect
3. Privacy:
4. Roominess:
5. Grouping:
6. Circulation:
7. Elegance:
8. Sanitation:
9. Orientation:
10.Economy:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Principles of Planning for Building are as follows:
1. Function/utility
2. Form
3. Aesthetics
4.Unity
KEY TAKEWAYS:
There are four principles of architectural design: Form, Function, Aesthetics, Unity. The planning and design of building needs a proper process/program at each stage from sketch plane to the construction of building. Hence principles of architectural planning are essential.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The word utility means the purpose of the entire layout; the infrastructure provided within the layout are also outside the layout. The layout of the area indicates the approach roads, internal roads, positioning of the other buildings, marginal distance etc. Also other important features within the layout are location of security office, water storages, drainage facilities, electric substation and supply, gas connections etc.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Usually proportioning systems as adopted in architecture go beyond the functional and technical details of architectural form and space and provide a different dimension called as "Aesthetics". Aesthetic experience from a built form is that we know something is beautiful when we see it or when we think of it. we experience a pleasing sensation.
For ex. Line plans for public building: Bank-details of units
1.Entrance ad moving space:2m wide |
2.Counter(minimum 4 no.):Height 1.5m to 1.8m Width:0.5m to 0.75m Length:1.2m |
3.Working space behind counter:3m wide |
4.Agent’s room:3m |
5.Cashier’s cage:1.5m |
6.Safe deposit vault:20m2 |
7.Manager’s room:12m2 |
8.Accounting room:9.5m2 |
9.Staff room/pantry:9.5m2 |
10.Sanitary block:1 WC/1WB for male and female |
11.Parking space: |
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Line Plan show the outside wall line (for exterior walls). For interior walls the line would represent the center of the wall. Also called as SINGLE LINE PLAN.
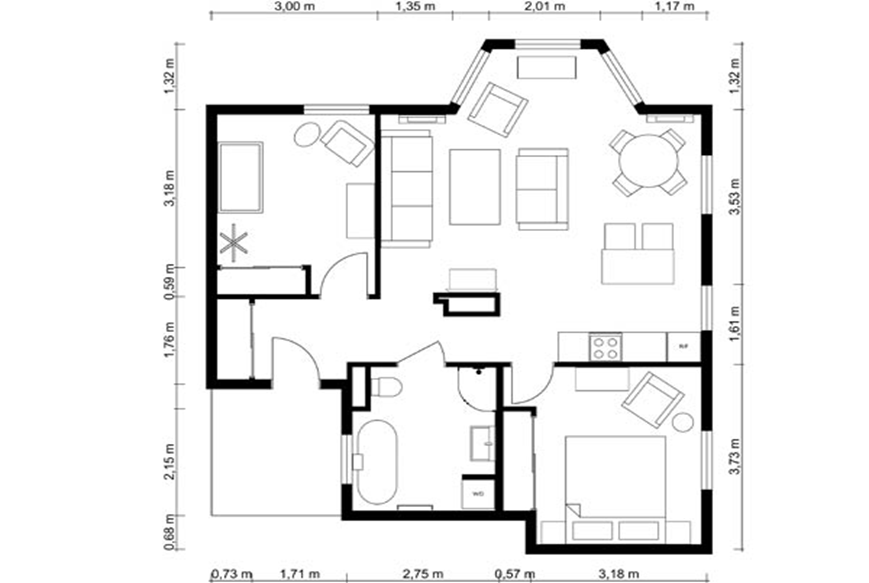
Fig.2.5: Developed Plan
KEY TAKEWAYS:
It is a horizontal section cut through a building showing walls, windows and door openings and other features at that level. The plan view includes anything that could be seen below that level: the floor, stairs, fittings and sometimes furniture. Objects above the plan level (e.g. beams overhead) can be indicated as dashed lines. Also called as FLOOR PLAN.
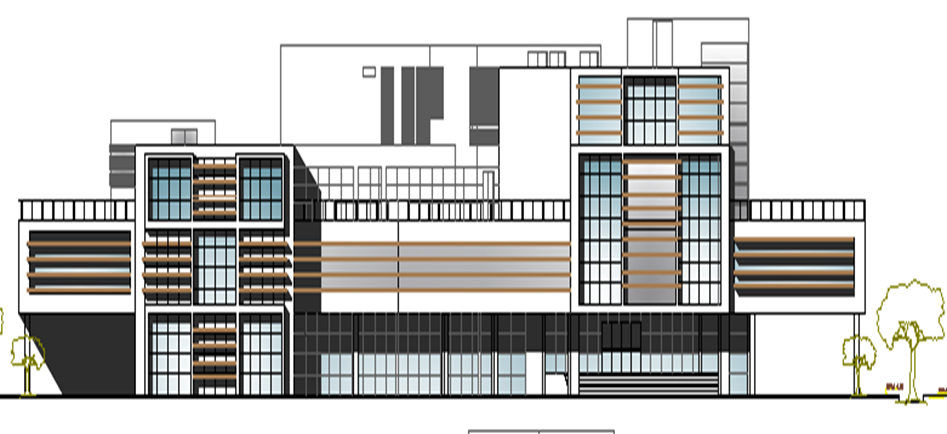
Fig.2.6: Elevation
KEY TAKEWAYS:
An elevation is a view of side of a building. Usually there are 4 main elevations - North, South, West, & East. Elevation shows the building height, length, width, placement of windows, etc.

Fig.2.7: Section
KEY TAKEWAYS:
This drawing can reveal the relationship between the different parts of the building that might not be apparent on plan drawings. Plan drawings are in fact a type of section, but they cut through the building on a horizontal rather than vertical plane.
When drawings are made in this way they are called as scale drawing.
The main scales or ratios to be used in construction drawings are:
Sr.no. | Scale | Use |
1 | 1:200 or 1:100 or 1:50 | For submission and working drwaing |
2 | 1:20 or 1:10 | For large scale drawings like door and window details. |
3 | 1:5 or 1:2 or 1:1 | For enlarge details. |
KEY TAKEWAYS:
SCALES - It is impossible to draw the actual size of building, plot, window and door sizes, etc. on drawing paper. So they are reduced to smaller sizes. The size they are reduced will be to a ratio of the real object.
Elements of dimensioning-
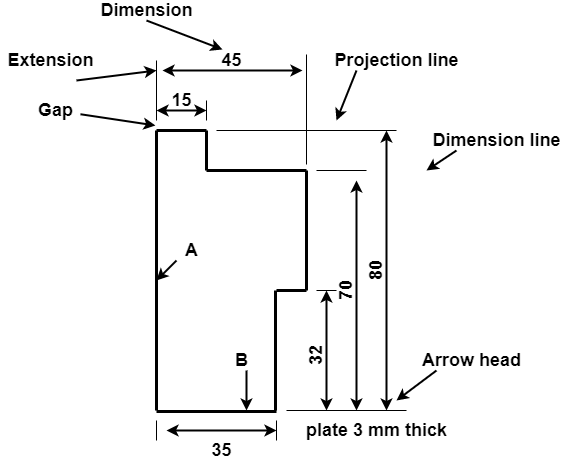
Fig.2.8: showing dimension parameter
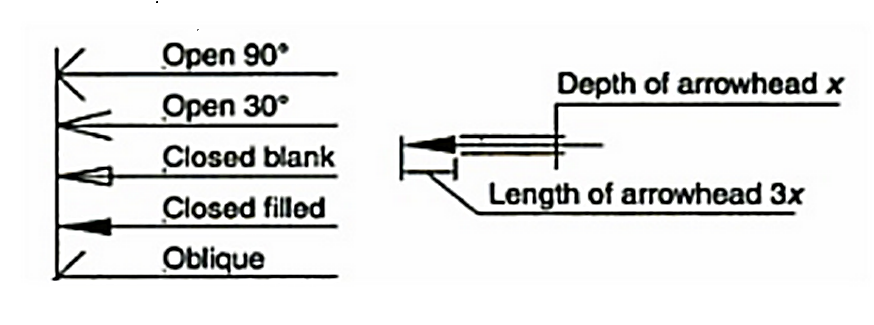
Fig.2.9: showing Arrow head
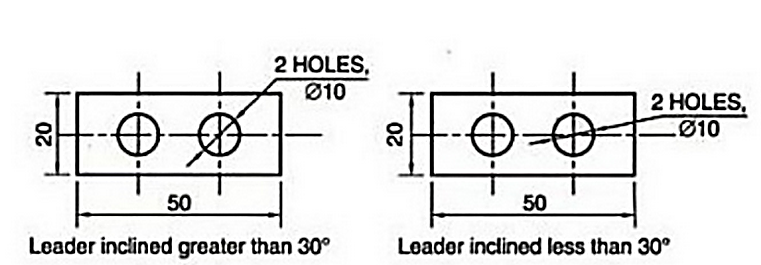
Fig.2.10: Showing Leader line
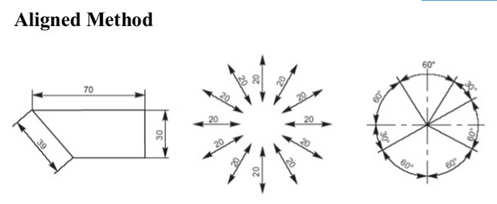
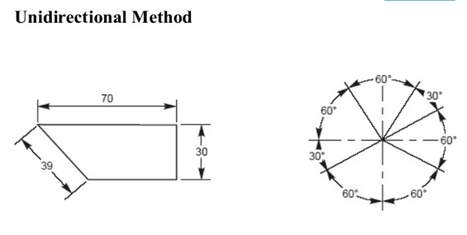
Fig.2.11: Showing Method of dimensioning
Rules For Dimensioning-
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Elements of dimensioning- dimension line, extension line or projection line, arrow heads, leader line.
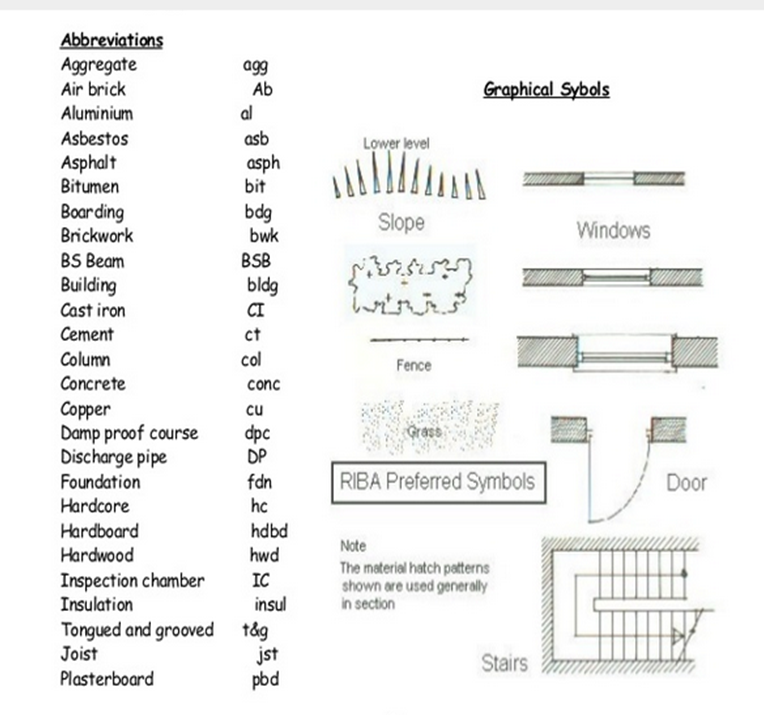
Fig.2.12: showing abbreviations
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Abbreviations have to be used in the context eg. M.S. for Mild Steel in context of construction but could be an abbreviation for some other word to another situation.
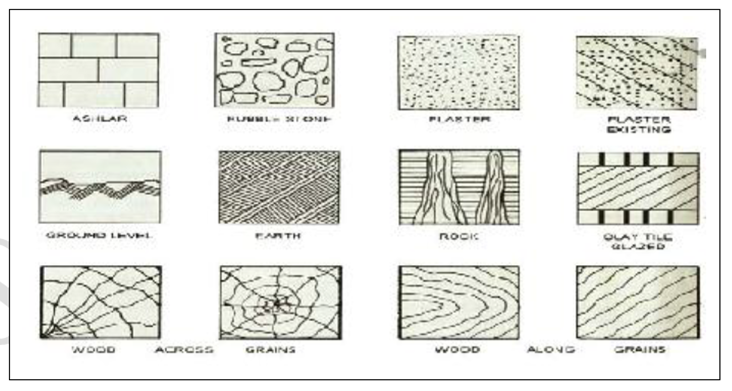
Fig.2.13: showing symbols as per IS962
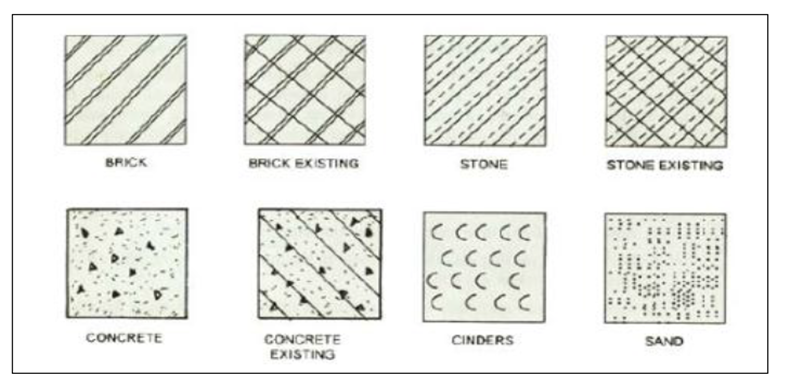
Fig.2.14: showing symbols as per IS962
KEY TAKEWAYS:
These are used to represent the particular item like stone masonry, brick masonry, concrete etc. in the section of drawing. (i.e.) when the materials are cut by any imaginary plane. Conventional symbols are provided to indicate doors, windows, their fixing, and movement of shutters.
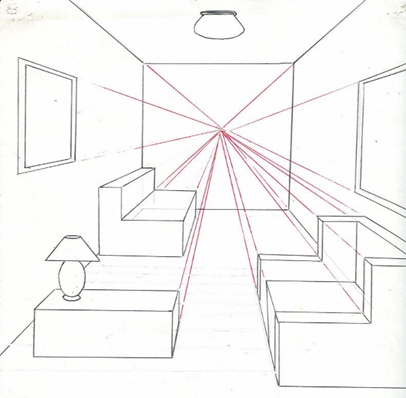
Fig.2.15: One- point perspective
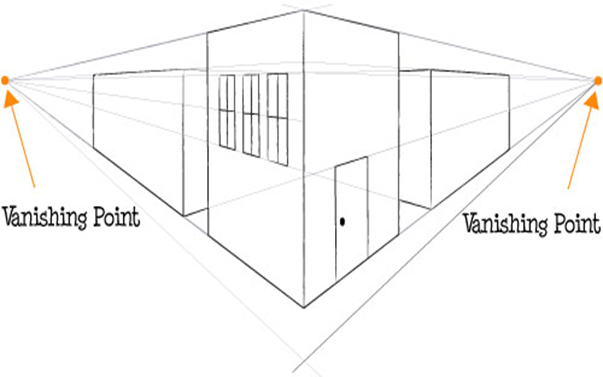
Fig.2.16: Two Point Perspective
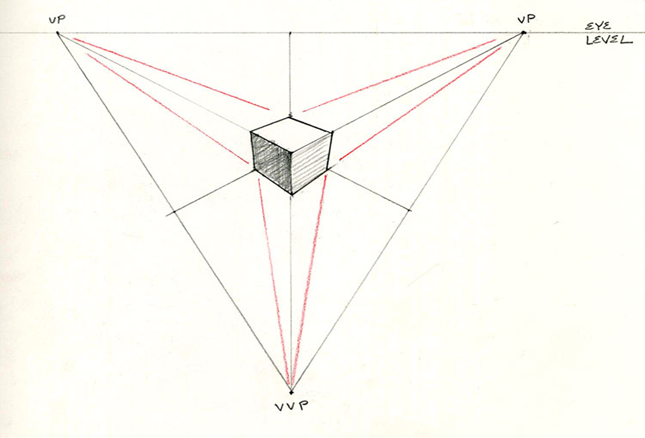
Fig.2.17: Three Point Perspective
KEY TAKEWAYS:
There are three types of perspective: One point, Two point, Three point perspective It is illusion which is different from actual form of object. It is useful to architects, engineers, designers, public and artists. It is used for printing brochures & advertisement.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
In this form of angle, we've a vanishing factor, that is continually at the horizon line. This vanishing factor is wherein all of the traces converge to (that’s why it is known as a 1-factor angle). When we draw an interior, we see 3 walls: one this is parallel to the photograph plane (frontal wall) and aspect walls.
References:
1.Building Materials by S.K.Duggal, New Age International Publishers.
2.Building Construction by S.C.Rangwala, Charotdar Publications.
3.Building design and construction by Frederick Merrit, Tata McGraw Hill.
4.IS 962-1989 code for Practice for Architectural and Building drawings