Unit-3
Building Components
A) Doors and Windows:
Door:
Function of door :
Window:
Function of window:
KEYTAKEWAYS:
A door may be defined as "an openable barrier or as a framework of wood, steel, aluminium, glass or a combination of these materials secured in a wall opening. A window is defined as vented barrier secured in a wall opening to serve one or more of the functions viz. natural light, natural ventilation and vision.
Basically, a door consists of two parts:
1.Door Frame:
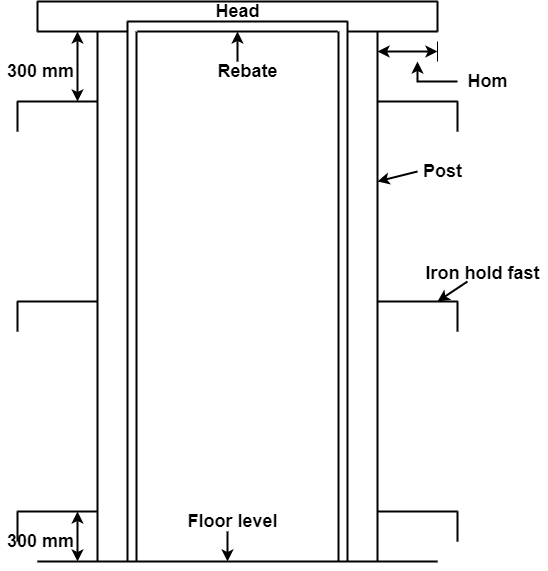
Fig.3.1: Door Frame
2.Door shutter:
Head:
Horn :
Style:
Top rail :
Lock rail
Bottom rail:
Panel :
Hold fasts:
Post or Jamb:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Door frame consist of two parts: Door frame and door shutter. Frame consists of an assembly of horizontal and vertical members which are placed along the top sides and the bottom of an opening thus forming an enclosure to which the shutters are fixed. These are openable parts of a door. It is an assembly of styles, panels, and rails.
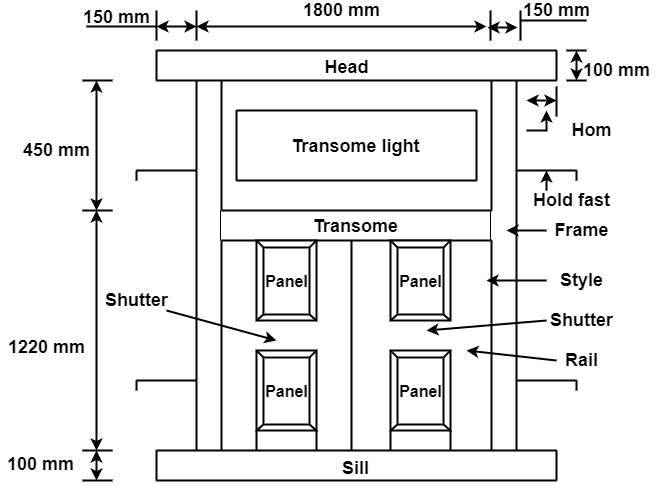
Fig.3.2: Component Parts of Window
Panel:
Horn:
Rail:
Style:
Holdfast:
Head:
Sill:
Transform:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
A window also consists of two main parts: Window frame, secured to the wall opening with the help of hold fast. Window shutters held in position by the window frame.
Installation of door frame :
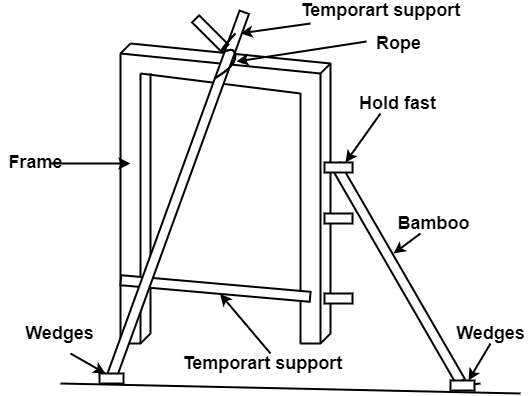
Fig.3.3: Erection of door frame
Installation of Window frame:
Errection of window frame is done under different cases which are explained as under:
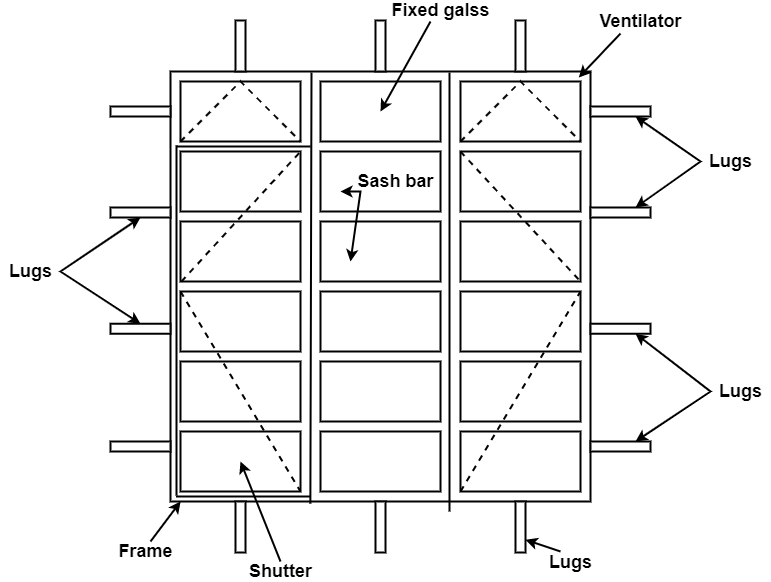
Fig.3.4: Erection of Window frame
KEY TAKEWAYS:
First of all, the frame which is to erected in position is painted with thick coat of coal-tar. Frame is held in position by giving support as shown in Fig. and checked by plumb bob and then masonry work goes on. While doing masonry work, frame is secured to the walls by means of fasts, three iron holdfasts on each post, one at the center and remaining two at 300 mm from the top and bottom of jambs. Holdfasts are embedded into the masonry work and feet of the post are embedded into the finished floor and lime concrete, at level of R.C.C. work.
Fixtures and fastenings of door and windows are classified into the following four heads:
1.Hinge :
(a) Butt hinge :
(b) Back flap hinge :
(c) Garnet hinge:
(d) Nar-madi hinge:
(e) Parliamentary hinge:
(f)Strap hinge:
(g)Rising butt hinge :
(h)Pin hinge :
2.Bolts :
Bolts are of the following types:
3.Handles:
4.Locks:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
There are four types of fixtures and fastenings:
Types of Doors:
Panelled doors:
Battened doors :
Flush doors :
Collapsible doors :
Rolling steel shutters:
Revolving doors :
Types of Windows:
The windows are classified into different types on the basis of several aspects like, nature of shutters, location and manner in which they are fixed.
The windows used in building can be broadly classified as:
Panelled window :
Fixed window:
Casement Windows:
Double hung window :
Metal window:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Types of Doors: Paneled doors, Battened door, flush door, collapsible door, Rolling steel shutters, revolving doors.
Types of Windows: Paneled window, fixed window, Casement window, double hung window, Metal window.

Fig.3.5: Elevation and vertical section of ventilator
Purpose of Ventilators:
Types of Ventilators:
There are three types of natural ventilation occurring in buildings:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Ventilators are windows of small heights generally about 30 to 50 cm below roof levels. Ventilators consists of (1) frame (2) shutter. Ventilation is mainly used to control indoor air quality by diluting and displacing indoor pollutants.
B) Arches and Lintels:
Technical Terms:
The following are the various technical terms used in an arch work.
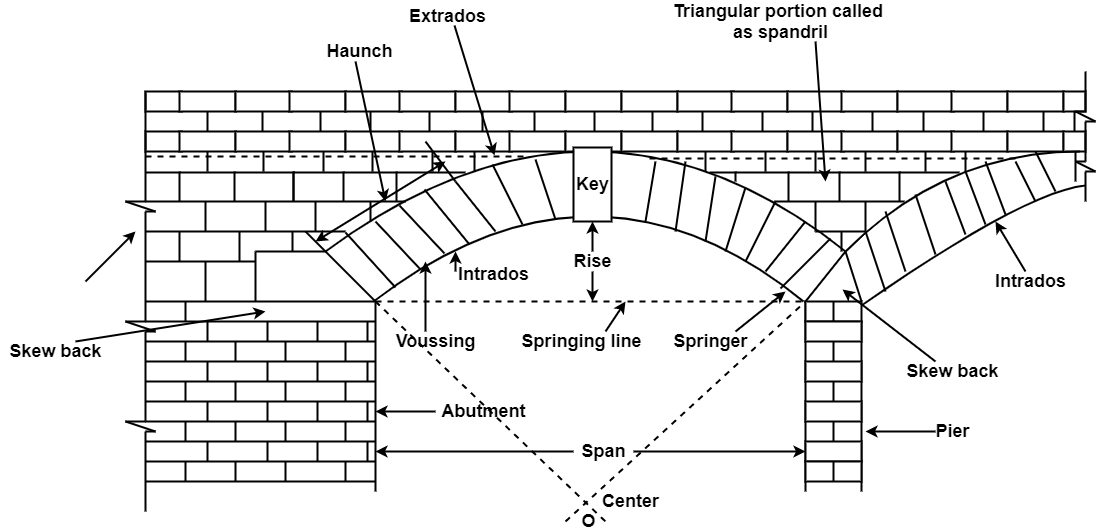
Fig.3.6: Technical terms or Elements of an arch
Intrados:
Extrados:
Crown:
Key:
Soffit :
Voussoirs :
Rise:
Springing points:
Springing line:
Spandril:
Skew back:
Abutment :
Springer:
Pier:
Arcade:
Span:
Haunch :
Bed joints:
Ring :
KEY TAKEWAYS:
A structure which is constructed with the help of wedge- shaped bricks or stone joined together with mortar and forming the curve like portion over the opening to support the weight of the wall above it along with the other super-imposed loads is called as an arch. Due to wedge-shaped portion of bricks or stones, the units support each other and loads makes them more compact and made them possible to transmit the pressure downwards to their supports.
Necessity of Lintel:
Types of Lintel:
Timber lintel:
Brick lintel:
Steel lintel:
Reinforced concrete lintels (R.C.C Lintel):
KEY TAKEWAYS:
A horizontal structural member which is placed across the opening viz door, windows, etc. to support the structure over the opening is known as lintel. Lintel is used to support the structure over the opening like door, windows etc. Lintels are usually rectangular in shape, the width of which is equal to the width of the wall and the ends of which are built into the wall.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
A chhajja is an overhanging eave or roof overlaying observed in Indian architecture. It is characterized with massive aid brackets with distinct creative designs.
Following points shows the essential requirements of a floor :
KEY TAKEWAYS:
A floor should be capable to support the occupants, equipment, internal partitions, furniture involved in a building. A floor should have adequate strength and stability so as to support the live loads. A floor should have a good sound insulation or it should be sound proof.
Shahabad:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Kotah:
Marble:
Granite :
Kadappa:
Mosaic tiles :
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Types of flooring are as follows: Shahabad, Kotah, Marble, Granite, Kadappa, Mosaic tiles.
Brick flooring:
Granolithic flooring:
Terrazzo flooring:
Marble flooring:
Timber flooring:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Types of flooring are as follows:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Roll roofing materials based on bitumen and tar (tar paper) are most commonly used. Roll roofing materials are relatively inexpensive and easy to install, and they provide a light and thin roof covering on almost any type of roof. Bituminous roll materials last for ten to 15 years; tar-based materials are good for no more than five to six years (tar materials are generally used for temporary structures).
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Galvanized iron (GI) sheets are essentially metallic sheets that have been lined with zinc. These sheets consist of a number warm dip galvanized and electro-galvanized metallic sheet. The zinc coating affords a non-stop barrier which does now no longer permit moisture and oxygen to attain the metallic. It reacts with the surroundings to offer the bottom metallic a safety.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Fiber Tech Roof Sheets may be used in conjunction with asbestos cement, Galvanized or commercial corrugated roof sheets to permit uniform subtle light. Fiber Tech roof offer alternative of sizes, colours, opacity, and corrugations. Flat FRP sheet with easy and wrinkled floor is likewise to be had for ornamental purpose
Pitched roof:
Flat roof :
Shells and domes :
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Types of roof construction are as follows: Pitched roof, Flat roof, Shells and domes. Shell is a roof structure resembling the shell of an egg. Pitched roofs are covered by covering material like Mangalore pattern tiles, Country tiles, Galvanized iron sheet, Asbestos cement sheet. Flat roofs can be constructed using mud terrace roof, brick concrete terrace roof or reinforced cement concrete roof.
Step 1: Laying of trusses and bracing
Step 2: Laying of wall plates
Step 3: Laying of ridge piece and purlins
Step 4: Laying of rafters
Step 5; Laying of battens
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Step 1: Laying of trusses and bracing
Step 2: Laying of wall plates
Step 3: Laying of ridge piece and purlins
Step 4: Laying of rafters
KEY TAKEWAYS:
To conceal the defective workmanship. To preserve and protect the surface from atmospheric influences by acting as a protective coating. To fill the joints formed in masonry work. To cover inferior quality material.
References:
1.Building Materials by S.K.Duggal, New Age International Publishers.
2.Building Construction by S.C.Rangwala, Charotdar Publications.
3.Building design and construction by Frederick Merrit, Tata McGraw Hill.
4.IS 962-1989 code for Practice for Architectural and Building drawings