Unit-6
Town Planning and Legal Aspects
A) Town Planning and Legal Aspects:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The process of managing land resources. It involves the control of existing and new developments, as well as strategy preparation to ensure manage future requirements. It is a dynamic process that changes in response to policy, development proposals and local needs.
Importance of town planning are as follows:
1. Defective road system resulting in the formation of narrow streets and lanes;
2. Development of slums and squatter settlements;
3. Haphazard location of industries;
4. Heavy traffic congestion during the working/peak hours of the day;
5. Inadequate open spaces, parks and playgrounds can result in unhealthy living conditions;
6. Lack of essential amenities like electricity, water supply and drainage;
7. Noisy atmosphere disturbing the peace of city dwellers;
8. Uncontrolled development of the town;
9. Unhealthy living conditions; etc.
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Objectives Of Development Plan:
Importance Of Development Plan:
Content Of Development Plan:
Method Of Execution of Development Plan:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
It is prepared for improvement of an old city or for a new town to be developed on virgin soil. It is a medium plan generally for 5 years. It contains proposal for socio-economic and spatial development of urban contains indicating the manners in which use of land and overall development of cities under the local authority.
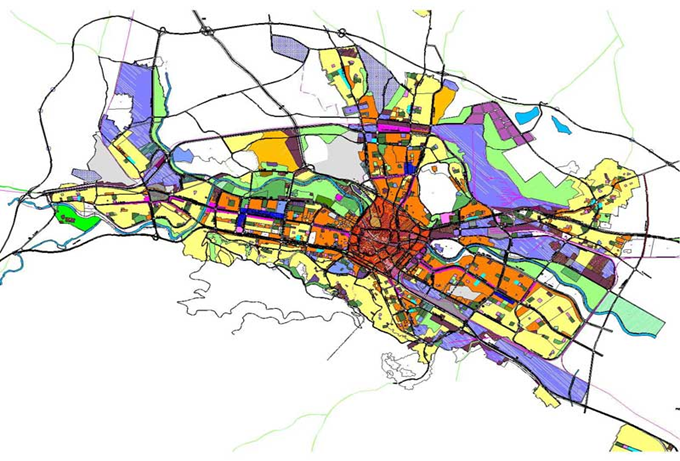
Fig.6.1: Land Use zoning
Zoning:
The term zoning is understood by two aspects:
Importance Of Zoning:
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Land use zoning means it creates land use classifications (i.e. residential, multi-family, commercial) by geographic area, but instead of keeping those uses separate, land use in Indian cities typically builds off of the uses in one zone to create a more integrated approach.
Copy of brief NA order permission
Plan organized through survey branch after subdivision of land withinside the plots, roads, open areas and amenity locations etc.
eight copies of the Architect’s plan
extract of V.F. 7/12 and its four zerox copies and
Copy of the mutation entry (V.F. 6) associated with the brief NA permission.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
N.A sanction procedure is explained in detail above.
Division of land based on its use:
Classification Of Zones –
Requirements Of Various Zones:
(It includes the uses of land for banks, offices, godowns & shops)
Height Zoning:
Advantages:
Density Zoning:
Indirect methods are adopted to have effective density zoning-
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Classification Of Zones –
The zoning is related to the following aspects:
(1) Density zoning
(ii) Height zoning
It is controlling the height of building by considering following factors:
(1) Bulk or cubical content of building
(2) Street width and open spaces
Advantages:
(iii) Use zoning
(1) Residential zone (40-50%)
(2) Commercial zone (2-5%)
(3) Industrial zone (2-25%)
(4) Public semi public zone (15-20%)
(5) Recreational zone (Remaining %)
(6) Transportation
KEY TAKEWAYS:
There are three types of zoning: Density zoning, Height zoning, Use zoning.
In density zoning, the density of population in the residential areas is controlled by means of suitable rules and regulation. It is quite evident that it is not practicable to restrict the number of persons from occupying any residential unit. Hence following indirect measures are adopted to have effective density zoning.
In height zoning, it is controlling the height of building
It is the most important aspect of zoning and it depends on the uses to which various parts of the town will be put.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
It is a revenue documents of ownership mainly for agricultural and rural lands issued by the talathi of the respective village in which property falls.It contains name of owner, description of property i.e. survey no., area of plot and mutation entry no., of any encumbrances by way of loan, charge, protected tenant, etc. and tenure of land.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Village Form VI is a diary of mutations. A record of changes in the record of rights in respect of all the particulars are shown in this form. These particulars are expected to be written in detail as required under Section 148 of the Maharashtra Land Revenue Code and the rules there under.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) is a voluntary, incentive- based program that allows landowners to sell development rights from their land to other interested party who then use these rights to increase the density of development at another designated location.
Documents To Be Submitted:
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Documents to be submitted are:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) Bill turned into brought in 2013 In December 2015, the Union Cabinet of India had authorized 20 predominant amendments to the invoice primarily based totally at the tips of a Rajya Sabha committee that tested the invoice.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
An Act to make provision for making plans the improvement and use of land in Regions set up for that motive and for the charter of Regional Planning Boards therefor; to make higher provisions for the practise of Development plans in order to making sure that metropolis making plans schemes are made in a right way and their execution is made effective; to offer for the introduction of latest cities by way of Development Authorities; to make provisions for the obligatory acquisition of land.
B) Safety Aspects and Services:
Fire load = ((combustibles in kg) x (calorific value in kcal/kg))/ Floor area in square meters
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Formula for calculating fire load is -
Fire load = ((combustibles in kg) x (calorific value in kcal/kg))/ Floor area in square meters
Grade 1…………………… 6 hours
Grade 2…………………… 4 hours
Grade 3…………………… 2 hours
Grade 4…………………… 1 hours
Grade 5…………………… 0.5 hours
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Grading of the occupancies by fire load are-
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The occupants inside the fire site often only have a few minutes to evacuate, which is referred to as the golden evacuation time. In this study, total evacuation time was divided into waiting time, response time, and moving time.
Fire Alarms
Emergency Lights and Exit Signs
Fire Extinguishers
Fire Sprinkler/Standpipe Systems
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Fire escaping elements are as follows:
Principles Of Earthquake Resistant Building:
Rules For Building Design:
Seismic Design for Buildings:
Seismic Effects on Structure:
Inertia forces in structures
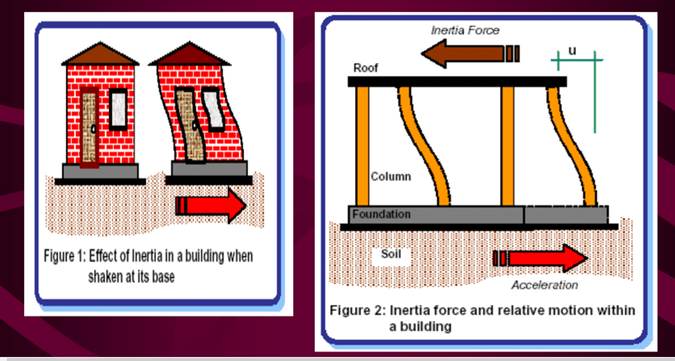
Fig.6.2: Horizontal and vertical shaking
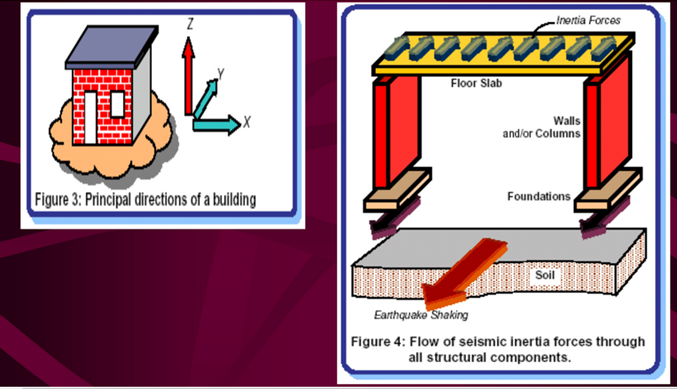
Fig.6.3: Principal direction of building and flow of seismic inertia forces.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Need for Earthquake Resistant Structures is-
Noise:
Effects are:
Acoustics:
Acoustical Defect:
1.Echo:
2.Sound Foci:
3.Dead Spot:
4.Insufficient Loudness:
5.Outdoor Nuisance/ Exterior Noise:
6.Reverberation:
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Unwanted sound is called as noise. Man’s vocal cord, vibrating loudspeaker, running engine, an operating machine tool and so on. Acoustics is defined as the study of sound which includes the effect of reflection, absorption, refraction, diffraction and interference and so on.
Sound insulating materials-
Constructional Measures-
KEYTAKEWAYS:
Sound insulating materials-
Rock wool, Foam panels, Green glue, Glass wool, Glass insulation, Mass loaded vinyl, Gypsum board, Thermocol, cork sound insulation.
Following may be the possible defects due to reflected sound:
1. Deflection time of reverberation
2. Echo formation
3. Sound foci
4. Dead spots
5. Loudness of sound
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Acoustical defects are as follows-
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Reverberation time is the time required for the sound to “fade away” or decay in a closed space. Reverberation reduces when the reflections hit surfaces that can absorb sound such as curtains, chairs and even people.
Porous Absorber-
Membrane (Panel) Absorber-
Resonance Absorbers-
This openings act as bottleneck which traps the sound and lock behind it.
KEY TAKEWAYS:
This materials convert the sound energy into heat energy i.e. only minimal part of sound is reflected back. They are non-porous and non-rigid material. Consist of an acoustical oscillation system, which have solid plate on the front with tight air space behind it.
The following are the conditions which will affect acoustic properties in an auditorium.
1. The sound should be clear and distinct
2. The sound should be evenly distributed
3. The sound should reach the audience in the same pitch and tone as it is produced
KEY TAKEWAYS:
Good Acoustics are:
The process of supplying air or removing by natural or mechanical means to and from a space.
Necessity-
KEY TAKEWAYS:
The process of supplying air or removing by natural or mechanical means to and from a space. To create air movement, remove the vitiated air. To prevent body odor, dust, fumes and other industrial product.
Natural Ventilation-
a) Wind effect-
A = free area of inlet openings, m2
V = wind speed, m/s
b) Stack effect-
Q=CA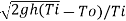
Q=Stack effect draft/draught flow rate(m3/s)
A=flow area(m2)
C=Distance coefficient (usually taken to be from 0.65 to 0.70)
g=Gravitational acceleration (9.81m/s2)
h=height of distance(m)
Ti=average inside temperature(k)
To=outside air temperature(K)
KEY TAKEWAYS:
There are two types of ventilation:
References:
1. Building Materials by S.K.Duggal, New Age International Publishers.
2. Building Construction by S.C.Rangwala, Charotdar Publications.
3. Building design and construction by Frederick Merrit, Tata McGraw Hill.
4. IS 962-1989 code for Practice for Architectural and Building drawings