Unit - 5
Construction survey & Modern Techniques such as Space Based Positioning System (SBPS)
Establishing Horizontal Control:
When the area is small:
When the area is very large:
When the area is more extensive:
System of horizontal control for large extensive area:
Primary control:
Secondary control:
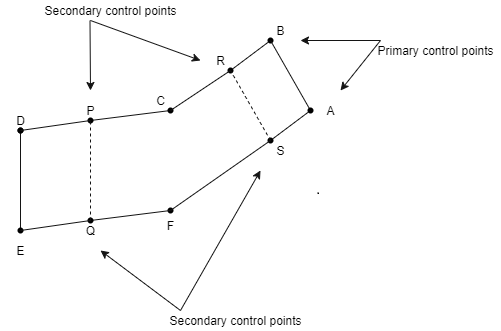
Fig.5.1: Primary and Secondary control
Establishing Vertical Control:
Key Takeaways:
Establishing Horizontal Control: Horizontal controls involve in location of ground control points. These ground controls points cover the complete area to be surveyed.
Establishing Vertical Control: The method of finding the elevations of various ground features is termed as vertical control. The frame work or skeleton of the area is formed by vertical control.
Key Takeaways:
The first stage of construction in a site is a setting out of buildings: Setting out consists of outlining the building structure on the ground. For any new housing scheme or extensions or alterations, mapping out is very important so as to avoid the possible costly errors.
Key Takeaways:
Verticality of the building can be maintained by two plumb bobs at the end of each face of a building, extending upto a fixed height from the base of the tower so that, same reference points are used at all times which give the best result of maintaining verticality of tall buildings.
After map study engineering or field survey are carried out to finalise the highway alignment.
The object of thèse surveys is to locate the alignment of a road which provides maximum transportation facilities with minimum cost of construction and maintenance.
For locating a highway, the following engineering or field survey are undertaken.
Reconnaissance survey:
Preliminary survey:
Objects:
Location survey:
Objects:
Key Takeaways:
For locating a highway, the following engineering or field survey are undertaken.
Key Takeaways:
Setting out of bridge consist of following points:
There are two methods for locating piers for a bridge:
Two methods for locating plers for a bridge
1. By finding the length of the centre line of the bridge
Method I
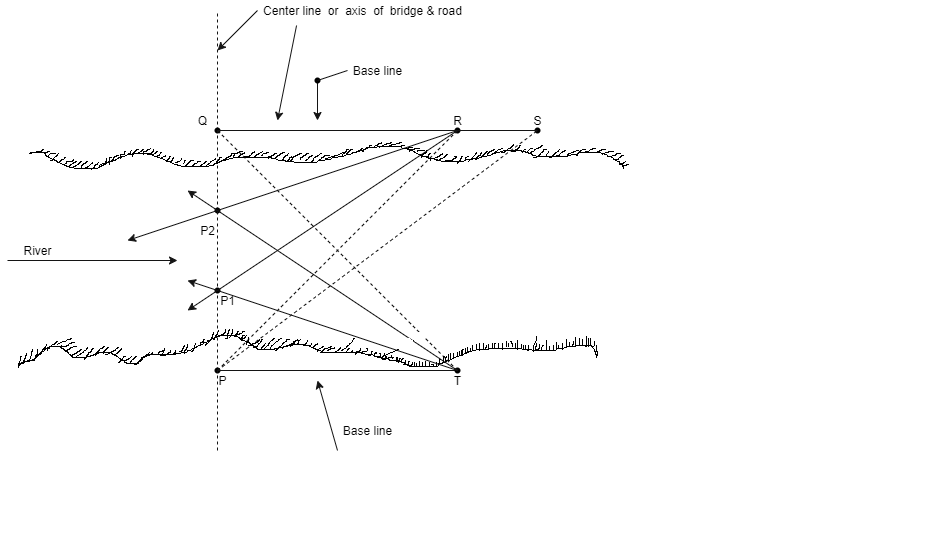
Fig.5.2: Locating piers for bridge by method 1
∴1 (PQ) = PR tan 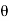
Method II
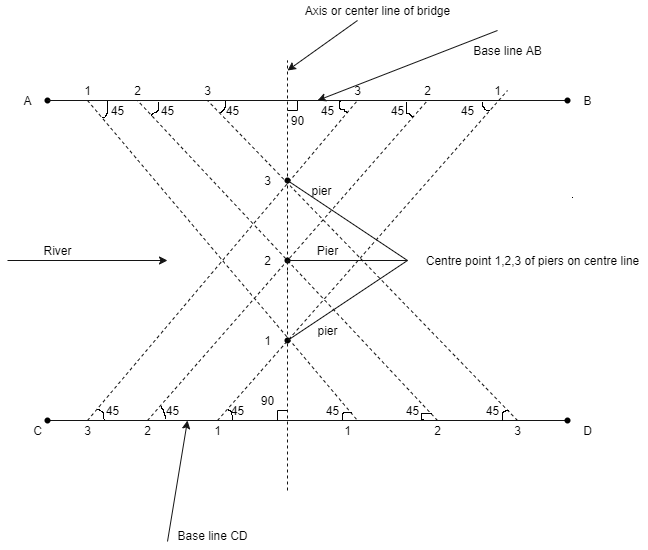
Fig.5.3: Locating piers for a bridge by method 2
Advantage and disadvantage of this method
Method III
Method IV
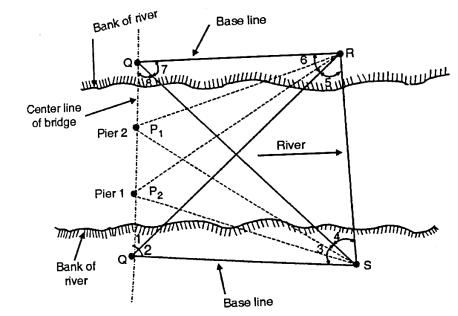
Fig.5.4: Locating piers for a bridge by method 4
2. By locating the central point for each pier
Key Takeaways:
Two methods for locating piers for a bridge:
Definition: The process of setting out the alignment of the tunnel on the ground and then transferring the same to inside of the tunnel through shafts is called tunnel surveying.
The survey work of a tunnel involves the following operations:
Locating centre line of the tunnel on ground:
Constructing the shaft over the centre line:
Transferring the alignment to inside of the tunnel:
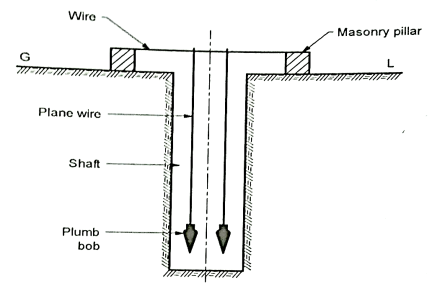
Fig.5.5: Transferring the alignment at the bottom of the shaft
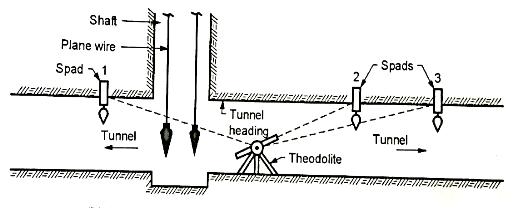
Fig.5.6: Transferring the alignment to inside of the tunnel
Key Takeaways:
The survey work of a tunnel involves the following operations:
Key Takeaways:
Spaced based positioning system (SBPS) technology is a fast and accurate method of determining the location of any point of interest anywhere on the face of earth of any time during the day or night.
Working System of GPS with SBPS:
Types of GPS:
There are the basic types of survey grade systems in GPS.
Single Frequency:
This type of surveying with a single frequency system is called as 'static mode' GPS surveying.
Dual Frequency:
Dual frequency systems only require post processing when operating in static or fast static.
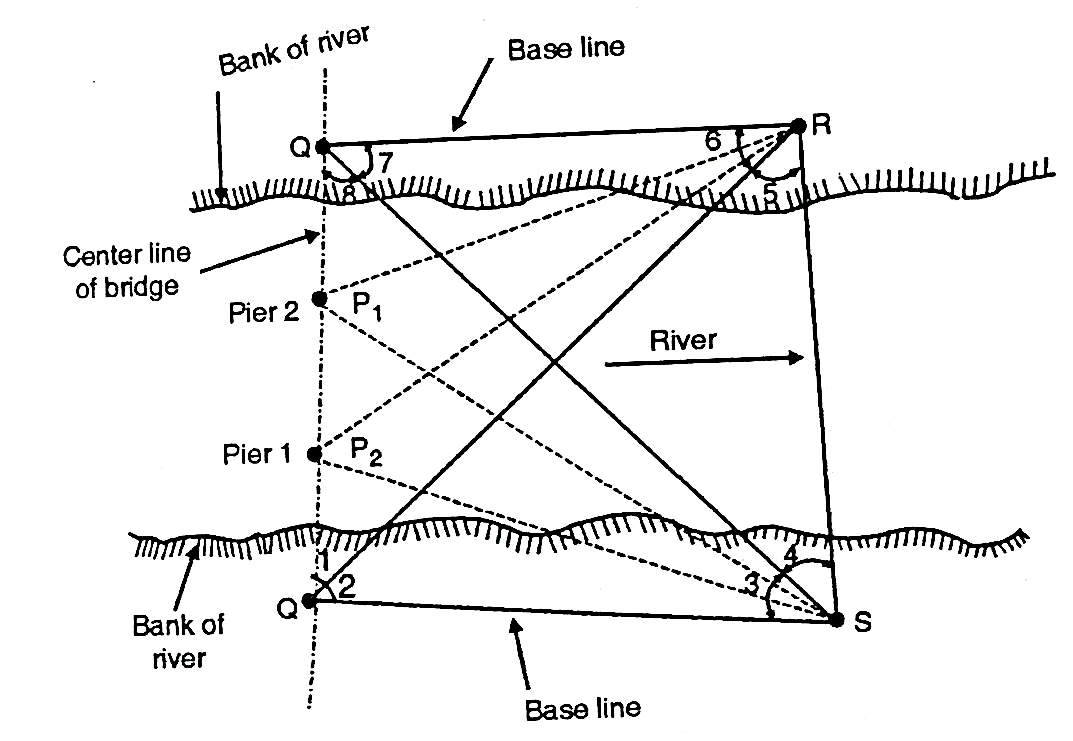
Fig.5.7: Configuration of GAGAN Satellite
Key Takeaways:
GAGAN system is jointly developed by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Airports Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPS) as established by the GNSS Panel (i.e., Global Navigation Space System)
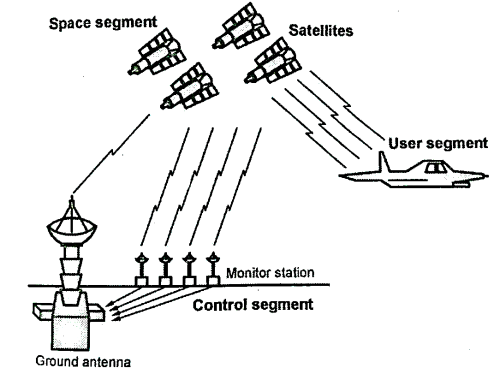
Fig.5.8: System segmentation
Space Segment (SS):
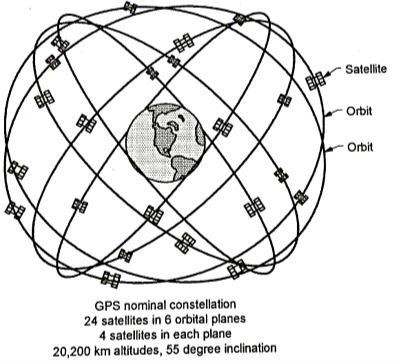
Fig5. 9: Details of Space segment
Control Segment
User Segment
Importance and Role of Space Segment, Control Segment and user Segment in SBPS:
Space segment
Control segment
User’s segment
Key Takeaways:
There are three types of segments:
References: