Unit - 6
Design of Welded Plate Girder
A plate girder is a metal beam this is broadly utilized in bridge production. Depending at the layout necessities and as according to the character of the structure; steel thicknesses for internet, flanges, stiffness, and many others are decided.
The use of the right cloth (metal) having the desired electricity and doing the welding are the 2majorelements to be attended to while growing the plate girder.
A plate girder is used while we want deeper sections having better stiffness to deliver heavy hundreds.
Further, there may be an obstacle in producing a hot-rolled phase while the intensity of the phase is increased. Therefore, we must use built-up sections which could deliver big bending moments and shear forces.
Types of Plate Girders
There may be exclusive classifications relying at the requirements used or relying on the character of the manufacturing of the girders.
There varieties of plate girders.
1. Reverted Plate Girder
2. Welded Plate Girder
Reverted Plate Girder
It is an aggregate of flanges, internet, and different vital stiffness. There are related via way of means of a mechanical method, revert, and plates aren't welded collectively.
- Generally, 90% of the shear is carried via way of means of the internet.
- Connection of the internet and the flange is stabilized via way of means of the angel sections reverted to the flange. Reverts want to be designed for the horizontal shear.
- The reverts that make the relationship among the internet and flange angles want to be designed for horizontal shear and vertical hundreds that carried out to the flange after they switch to the internet.
- Angle sections are used as internet stiffness in revert girders.
Application of Plate Girders
Plate girders are broadly used as assisting systems in exclusive regions. The following regions may be highlighted as key regions of use.
Bridge production
Plate girders are specifically utilized in railway and avenue bridges. Mostly the antique railway bridges may be highlighted as plate girder bridges.
In addition, field girder bridges, beam bridges, navy girder composite bridges, and half – thru plate girder bridges are taken into consideration because it uses.
- Ships
- Gantry beams
- Oil and fuel line platforms
- Load testing
- Cranes
- Lifting systems
Advantages of Plate Girder
- They may be used to hold heavy hundreds
- Speed production
- Grater balance
- High resistance to fatigue failures
- Easy to assemble while as compared with truss kind bridges
- Easy for maintenance
Disadvantages of Plate Girder
- They cannot be used to assist big spans
- Less architectural appearance
- A bit tough to deal within the course of the placement
- Production will be finished strictly according with the layout.
The articles have been written on Steel Beam Design as according to BS 5950 and Steel Beam Design Worked Example [Universal Beam] could be referred for extra facts on metal beam designs.
Further facts on metal beams may be studied from the article Types of metal beams.
Key takeaways:
- They may be used to hold heavy hundreds
- Speed production
- Grater balance
- High resistance to fatigue failures
Welded Plate Girders
Welded plate girders are maximum broadly utilized in production because of the convenience of manufacturing and its miles a far extra green sort of girder.
These sections are specifically utilized in bridge production. The plate girder bridge could be very stiff and it is able to retain very excessive hundred seven as resisting the lateral movements. This movement may be found within side the railway bridges. Further, they may be used to increase the field kind girders.
There are empirical or approximation strategies to decide the general peak of the plate girder and thickness of the flange and internet.
Components of welded Plate Girders
Mainly there are 5additives in a girder. The meeting of that 5-thing is the entire girder. The basic requirement is to make an “I” girder having very excessive bending and shear stiffens similarly to the alternative nearby buckling resistances.
- Web Plate
- Flange
- Stiffeners (bearing, longitudinal, and intermediate)
- Splices for flange and internet
- End Connection
Web Plate
The vertical plate of the girder is called the internet plate.
Its thickness is primarily based totally at the layout necessities and the peak can also be determined primarily based totally at the web page condition and as according to the hundreds carried out at the internet.
The internet typically includes the carried-out hundreds at the flange as shear forces. The impact of the internet isn't always usually taken into consideration while the layout for the bending.
The internet is at risk of buckling while thinner and better boom while the hundreds are carried out. Therefore, exclusive varieties of stiffness so as to be discussing on this article, are welded to the internet have its electricity.
Flange
There isn't any distinctiveness aside from using a separate plate for the flange. The flange plate could be welded or related via way of means of different method as mentioned beneath Neath exclusive varieties of plate girders.
Not like rolled sections, we connect the internet and the flange collectively to shape the plate girder.
The flange is layout to hold the bending movement and stiffener or extra plate are furnished as according to the layout necessities.
Stiffeners
Stiffeners are furnished to enhance structural potential heading off the nearby buckling failures. In addition, they may be used to hold the hundreds carried out to the beam till it allotted into the beam.
The following varieties of stiffeners can be found in those varieties of metal elements.
- Bearing stiffeners
- Longitudinal stiffeners
- Intermediate stiffeners
The bearing stiffeners are furnished at assist to distribute the assist response to the internet with none buckling failures. There are jacking stiffness except the bearing stiffeners for installations functions as indicated within side the following figure.
Steel plates welded within side the longitudinal and the transverse instructions also are used to reinforce the internet.
The vertical or the transverse stiffeners may be typically found in maximum of the metal beams that deliver heavy hundreds.
Splices for Flange and Web
It is the splice connection of the internet and the flange of the girder.
When the duration of the girder is less than the span, we must have a splice connection.
This is a second and shear shifting joint which gives beam continuation.
End Connection
End connection is the maximum tough a part of the structural detailing of a metal beam.
When there is continuation or if we are assisting the girder to a few assists, the relationship desires to be designed accordingly.
However, maximum of the time, plate girders are saved as definitely supported on the stop assist. In such situations, we must offer the stiffeners on the stop connection.
A comparable lay out system is followed while designing the endplates and the stiffener furnished vertically connecting the internet and the flange.
Key takeaways:
- Welded plate girders are maximum broadly utilized in production because of the convenience of manufacturing and its miles a far extra green sort of girder.
- These sections are specifically utilized in bridge production.
- The plate girder bridge could be very stiff and it is able to retain very excessive hundred seven as resisting the lateral movements
The minimal duration of an intermittent fillet weld shall be 1-half of in. (forty mm).
Minimum length:
The minimal powerful duration of a fillet weld will be at the least 4 instances the nominal length, or the powerful length of the weld will be taken into consideration now no longer to exceed 25% of its powerful duration
Key Takeaways:
The minimal powerful duration of a fillet weld will be at the least 4 instances the nominal length, or the powerful length of the weld will be taken into consideration now no longer to exceed 25% of its powerful duration
1. Self weight of plate girder
The following imperical formula may be used to access the self weight of the beam
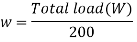
Where,
W= Total factored load
w = Factored self weight
2. Economical depth
Assuming that the moment M is carried out by flange only the economical depth d of girder may be found as given below
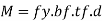
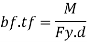
Where bf and tf are width and thickness of the flange
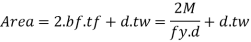
Taking
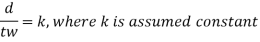
Then
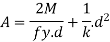
For
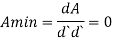
(Differentiate area A w.r.t d and equated to zero)
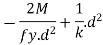
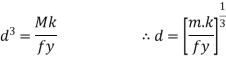
In selecting value of k=d/tw the following codal provision will be useful
1) If 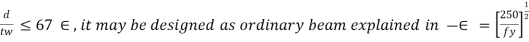
2) Minimum web thickness based on serviceability requirement – cl. 8.6.1.1 (IS 800-2000)
- When transverse stiffeners are not provided
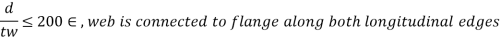
b. When transverse stiffeners are provided
- When
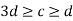
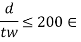
2. When 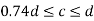

3. When 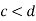
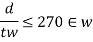
4. When c>3d the web shall be considered unstiffened
c. When transverse stiffeners and longitudinal stiffeners at one level only are provided (0.2d from compression flange)
- When
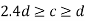
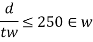
2. When 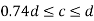

3. When 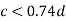
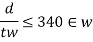
d. When a second longitudinal stiffeners (located at neutral axis is provided)
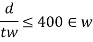
3) Minimum web thickness based on compression flange buckling requirement (cl.8.6.1.2)
To avoid buckling of compression flange into the web the thickness shall satisfy the following
- When transverse stiffeners are not provided
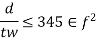
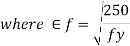
2. When transverse stiffeners are provided an
- When
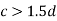

2. When 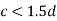
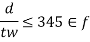
3.Size of flanges
Assuming moment of resisted by flange only and using material safety factor for a plastic section
(Af.fy.d)/1.1 = M
Hence area of flange Af may be found. (IS 800-2000)
1. Curtailment of Flange plate
In beam B.M is very less near to the simple support therefore, no need to provide same size of flange plate. To achieve economy flange thickness are curtailed near to the support called curtailment of flange.
Its position from support is calculating by equating the B.M at that section to the design bending strength at the section.
2. Load bearing
The load carrying of the stiffeners Fpsd is given by
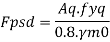
Where
Aq= Area of stiffeners in contact with flange
Fyq= yield stress of the stiffener
In safe design Fspd> Reaction
3. Intermediate stiffeners
The design requirement for intermediate stiffener is covered in cl. 8.7.2 and they are given below
1) They may be provided on one or both sides of the web
2) The spacing of stiffeners depends upon the web thickness
3) Outstand of stiffeners should not be more than 20tq.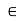 . The core outstand is more than 14.tq.
. The core outstand is more than 14.tq.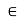 and less than 20tq.
and less than 20tq.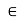 the section width is to be considered 14.tq.
the section width is to be considered 14.tq.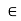 only.
only.
4) Minimum moment of inertia should satisfy the following requirement
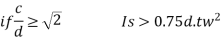
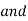

Where
d = depth of web
Tw= minimum required web thickness for spacing using tension field action
c= Actual stiffeners spacing
5) Stiffeners not subjected to external loads or moments should be checked for a stiffeners force
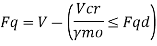
6) Intermediate stiffeners subjected to external loads should be designed as bearing stiffeners. In addition, they should satisfy the following interaction formula
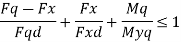
4. End bearing
a. Local capacity of the web
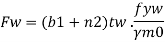
b. Check for buckling of the stiffener
Design strength Pd = Ae.fcd
c. Check for bearing capacity of stiffener
Bearing strength
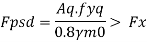
e. Check for torsional resistance provided by end bearing stiffener
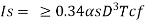
1. Design of connection between flange and web plate
If v is the shear force acting on the section, then shear stress at the function is
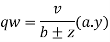
Shear force per unit length
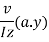
Where
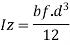
If weld of throat thickness te is provide on both sides, then strength of shop weld per unit length
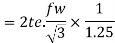
Equating force to strength we get
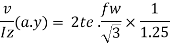
From throat thickness size of weld computed as s= te/0.7
According to clause 8.7.2.6 the web should be designed to transfer a shear equal to difference between the reaction and the shear carried by the web plus a shear between each component of the stiffener and web not less than 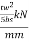
Where,
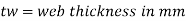
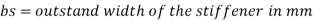
The shear carried by the web may be found as explained below (cl.8.7.3.1)
- Effective length KL= 0.7d
- Area of cross section= (b1+n1).tw
- M.I of section
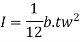
4. Radius of gyration
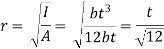
5. Slenderness ratio
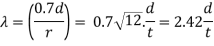
6. Design compressive stress fcd can be found from table 9 (c) of code. (IS 800-2007)
7. Then buckling resistance= b.t.fcd
2. Design of connection between web plate & stiffeners
There will be two weld length along the depth of weld on each side of stiffener plates bs
Tension capacity of plate
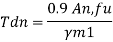
Strength of weld per unit length
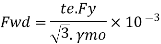
1. Check for shear buckling of web
For a web it is necessary to check the shear resistance of web for buckling IS 800-2007, Clause 8.4.2 specifies that this check is necessary when:

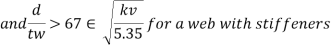
Where,
Kv= 5.35 when transverse stiffeners provided at support
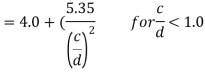
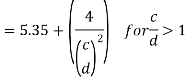
Where c and d are the spacing of transverse stiffeners and depth of the web resp. The normal shear strength vn= vcr may be calculated by any one of the following two method
- Simple post critical method
- Tension field method
2. Shear capacity of end panel and serviceability
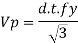
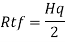
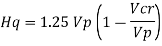
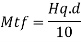
The end panel to be check as a beam spanning between the flange to resist Rft and Mft
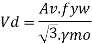
End panel can carry the shear due to anchoring force
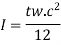
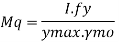
Examples:
Q.1 A simply supported welded plate girder of an effective span of 24 m subjected to uniformly distributed load of 35 kn/m throughout the span excluding the self weight of plate girder assume compression flange laterally supported throughout the span and yield stress of steel is 250 MPa Design cross section of plate girder stiffeners.
Solution:
1. Maximum bending moment and shear force
- Self weight of plate girder
Factored load = 35x 1.5 = 52.5 kN/m
Self weight of plate girder
W1= W/200 = 6.3 kN/m
Total uniformly distributed load on plate girder
w = 58.8 KN/m
b. Maximum bending moment
M= 58.8 x 24^2 /8 = 4233.6 kN/m
c. Maximum shear force
V= 58.8 x 24/2 = 705.6 kN
2. Initial sizing of plate girder
- Design of web plate
If stiffener spacing c is in between d and 3d, where d is depth of web the serviceability requirement is
K = d/tw< 200 considering k=190
Economical depth
S = [ Mk/fy]^(1/3) = 1473.29 mm= 1500mm
Tw = 1500/190 = 8 mm
Provide 1500 mm deep and 8 mm thick web plate.
Provide intermediate stiffeners at a spacing of 2000 mm center to center (3d>c<d)
b. Design of flange
Assuming the flange resist the moment
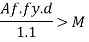
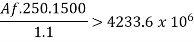
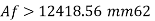
Maximum width = d/3 = 15000/3 = 500mm
Provide 400 mm width of flange
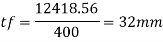
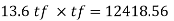
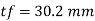
Provide 32 mm thick flange plate
3. Check for shear buckling of web
Using simple post critical method as per cl.8.4.2.2 of IS 800-2007
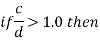
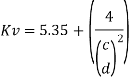
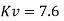
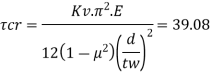
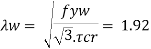
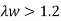
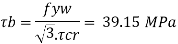
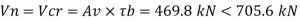
4. Shear capacity of end panel
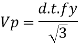
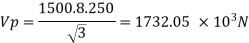
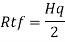
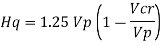
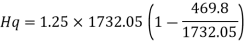
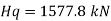
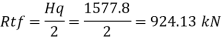
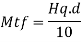
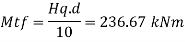
The end panel to be check as a beam spanning between the flange to resist Rft and Mft
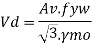

End panel can carry the shear due to anchoring force

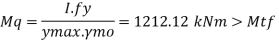
Hence end panel can carry the bending moment due to anchor force
5. Design of end stiffeners
Reaction at ends= 705.6 kN
Compressive force due Mtf
Mtf/c= 118.33 kN
Total compression = 705.6 +118.33 = 824kN
Strength of the stiffeners as per clause8.7.2.2 IS 800-2000
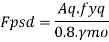
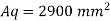
Provide 180 mm wide and 10 mm thick flats on either side of web Then Aq provided is
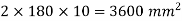
Check for outstand
It should not be more than 20 tq
Since it is more than 14 tq, 14 x10 = 140 mm
Core area of each stiffener = 140 x10 = 1400 mm^2
6. Design of intermediate stiffeners
As the shear force reducing towards mid span the first stiffener from end is critical. Since first intermediate stiffener is at c=2m from end
Shear force on the stiffeners V
R-2w= 705.6 – 2x58.8 = 588 kN
The ratio c/d = 200/15000= 1.33<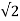
Hence required minimum moment of inertia
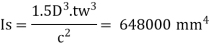
Provide intermediate stiffener of size 120 mm wide and 10mm thick which satisfy the condition of outstand
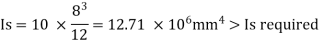
Hence o.k
Checking for buckling
Shear buckling resistance of web alone
Vcr= 469.8 kN
Shear strength of stiffener alone required
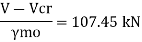
Buckling resistance of intermediate stiffener as per clause 8.7.1.5 of IS 800-2007
Considering
20 tw= 160 mm width of web on both sides along with stiffener
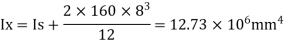
Area = A= (2x120x10+2x160x8) = 4960mm^2
r= 50.66mm
KL/r= 20.72
From Is 9c of IS 800-2007
Fcd= 223.87mpa
Buckling resistance
223.78 x 4960/1000= 1109.97>107.45
Hence Safe.
Case Study
Plate Girder
In a plate girder bridge, the plate girders are generally I-beams made up from separate structural metallic plates (in preference to rolled as an unmarried cross-section), which can be welded or, in older bridges, bolted or riveted collectively to shape the vertical internet and horizontal flanges of the beam. In a few cases, the plate girders can be fashioned in a Z-form in preference to I-form. The first tubular wrought iron plate girder bridge turned into constructed in 1846-forty-seven with the aid of using James Millholland for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad.
Plate girder bridges are appropriate for quick to medium spans and might assist railroads, highways, or different traffic. Plate girders are commonly prefabricated and the period restriction is often set with the aid of using the mode of transportation used to transport the girder from the bridge save to the bridge site.
Anatomy of a plate girder
Generally, the intensity of the girder isn't any much less than 1⁄15 the span, and for a given load bearing capacity, an intensity of round 1⁄12 the span minimizes the burden of the girder. Stresses at the flanges close to the centre of the span are more than close to the quit of the span, so the pinnacle and backside flange plates are often strengthened within side the center part of the span. Vertical stiffeners save you the internet plate from buckling below shear stresses. These are generally uniformly spaced alongside the girder with extra stiffeners over the helps and anywhere the bridge helps focused loads
References:
- Design of Steel Structure, N Subramanian, Oxford University Press, New Delhi
- Limit State Design in Structural Steel, M. R. Shiyekar, PHI, Delhi
- Fundamentals of structural steel design, M L Gambhir, Tata McGraw Hill Education Private limited, New Delhi.
- Limit State Design of Steel Structure, Ramchandra & Gehlot, Scientific Publishers, Pune
- Analysis and Design: Practice of Steel Structures, Karuna Ghosh, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd. Delhi
- Structural Design in Steel, Sarwar Alam Raz, New Age International Publisher
- Limit State Design of Steel Structure, V L Shah & Gore, Structures Publication, Pune
- IS Codes: IS 800-2007: Code of practice for general construction in steel, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delh