UNIT 3
Insulating materials, properties & applications
Insulating materials are essential for the energy conservation because of they resist the flow of heat. Commonly utilized insulation materials in houses include following are rock wool, glass wool, slag wool cellulose, urethane foam, perlite, wood fiber, vermaiculite and plant fiber. These materials are made to manage the building elements and facilities as long as possible. There are more kinds of insulation materials on the basis of the structure and purpose. Insulation materials are run over the range from the bulky fiber materials like rock and slag wool, fiberglass, natural fibers and cellulose to rigid foam boards to sleek the foils.
Insulating materials have the main characteristics are its heat and insulation resistance. We can measure insulation by insulation strength, ability of the heat resistance of the insulating materials under the high temperature without any changes of dielectric, chemical and mechanical properties. A good insulating material have the following characteristics are-
- Highest insulating resistance
- Higher dielectric strength
- Uniform viscosity- it provides uniform thermal and electrical properties.
- Must be uniform throughput- it contains electric loss as low as potential and electric stress uniform under the high voltage differences.
- Minimum thermal expansion
- While revealed to arcing must be non-ignitable.
- Must be resistance to oils or liquids, acids, gas fumes and alkalis.
- Must have no deteriorating impact on material when in contact with it.
- Loss tangent (low dissipation factor)
- Higher mechanical strength
- Higher thermal conductivity.
- Lower permittivity.
- Higher thermal strength
- To avoid discharges for free from the gaseous (for gases and solids)
- Must be homogeneous to avoid the local stress concentration.
- Must be resistant with the chemical and thermal deterioration.
Insulating materials are classified as follow-
Thermal insulators
Acoustic insulator
Water proofing insulators
Radiation insulators
Electrical insulators
- Thermal insulators- in this we include those materials are which reduce the different forms of heat transfer like conduction, radiation and convection. Insulator repels heat transfer from the out to in or in the opposite direction whether environment temperature is low or high. Thermal insulation has many advantages which isolates the developing from heat and removes energy consumption as well as costs of the operation of the air conditioning. There are many types of thermal insulators. All types of the heat transfer modes such as radiation, convection and conduction. Glass wool is the common thermal insulators polyurethane, polymers, cork and many more materials.
- Acoustic insulators
Acoustic insulators are preventing permeability of the sound and absorb it or attempt to scatter it. Sounds are transfer by the air so this is done differentiate the types of the voices as well as noise. Sounds travel as the waves by the solid objects of the building particular concrete bodies; therefore, it must be isolated to stop transmission of the sound from out of inside or from one place to another place.
Objectives
Avert the transmission of the sound from outside and between partitions by walls and ceilings.
Stop sounds transmission and vibrations of the machines.
Sound absorption inside.
Types
Acoustic tiles made up two sides generally grainy and colored quartz and made through resin.
Glass wool panel that could be wrapped through aluminum foil for absorb sound and reject heat.
Plastic layers which might be pierced face.
Cellulose sheets compressed and pierced face.
Gypsum slabs with possibility of combining glass fibers.
Polymers such as cork, rubber and foam.
Rocks such as perlite.
3. Waterproofing insulators
Mostly buildings require insulation from the rain, groundwater, moisture and surface water because moisture assists to destroy elements of the construction and their materials and free unwanted smells with insects breeding and mice and spread disease.
Types
The common waterproofing materials are flancoat, bitumen, polyethylene white cemen, asphalt, acrylic and asbestos.
4. Radiation insulators
Radiation energy is free from in the form of electromagnetic waves like light, x-rays, UV, infrared and gamma as shown in below figure or small particle like beta and alpha.
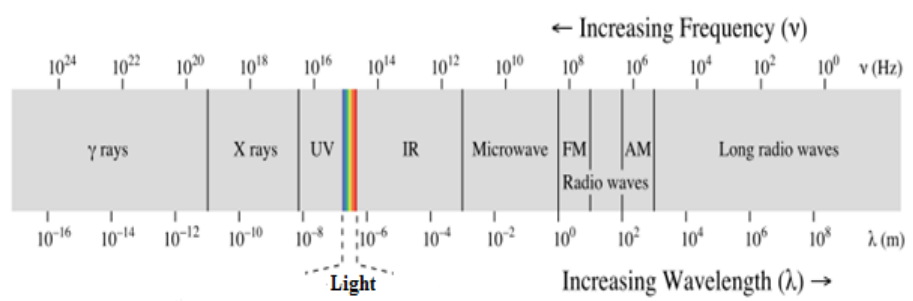
Electromagnetic waves
Radiations are comes from the sun, earth, nuclear reactors, cosmos and different devices or even inside in the body. Radiations which come from the sun such as UV, IR and light and gamma keeps short wave length. With the long wave length named radio waves and microwaves.
Types
There is proper shield for every kind of radiation shown below figure-
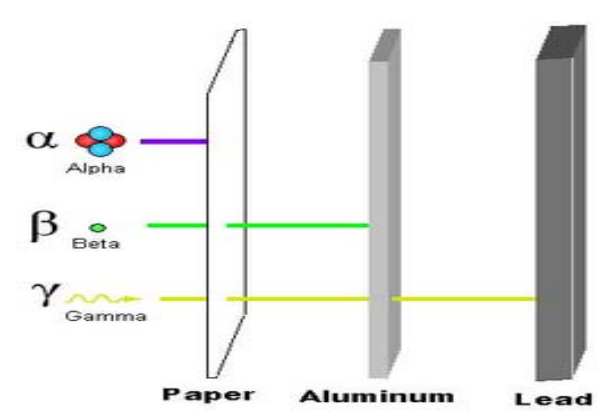
Shielding for some types of radiation
5. Electrical insulators
Any insulators or substances keeps many numbers of atoms. These atoms has some electrons in outer orbit named “free electrons”. This is simple to expel free electrons from external orbit and develop it move to other atoms. When the electron is flow from one to other atoms are called electrical current. Some of the substances or materials do not allow the electric current flow \, called insulators like wood, ceramic and plastic. The main reason of the current flow restriction is they have less free electros. These substances have the separation between electrical charges produces the dipole and corresponding procedures named polarization.
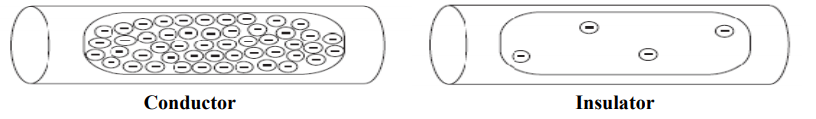
There are many kinds of insulators in the electrical systems for different uses and purposes. Like plastic is utilized for covering the electrical wires to provide protection against the electrical shock. Other example like wood, ceramics, paper, glass and oils etc.
These are made from the organic, inorganic fibres (glass asbestos) and synthesis fibres. The paper manufacture for utilization as an insulant needs cellulose fibers of the high degree of the chemical purity and having higher mechanical strength. Cellulose has the high molecular material, its formula is (C6H1OO5)n, where n=very large number. For paper manufacture utilized as insulating material, constitution of the wood fibers are main ingredient. Normally, soft wood fiber is utilized. card board and paper is made from the alkaline cellulose is powerful mechanically and much heat resistant, that is extremely essential in the engineering applications. But paper is made from raw material sometimes other than wood like cotton, linen, rags and different kinds of hemp. For using paper to be its best for applications mostly, it must have a fix minimum moisture content. Paper must be hygroscopic, is impregnated and dried with the impregnates. The most common impregnates are the mineral oils and vegetable oils.
3.4.1 Press-boards
When we compare with paper, these are denser, thick and less flexible. It is utilized to developing slot wedges and liners for the rotor and stator core stacks, in transformer winding saperator and slot lining. The press-boards and paper are utilized for the winding and cable conductor insulation, backing for mica insulation, primary dielectric in the capacitors, transformer insulation and electrical machines for slot insulation etc.
3.4.2 Fibrous materials
There are some essential fibres are available at present like silk, cotton, wool, jute rayons, acetate, nylon, Terylene, fibre glass, Teflon and many more. The benefits of these materials are high mechanical strength, cheapness and simple processing and flexibility. The limitations are hygroscopicity and lower electrical strength. Properties of these materials are increased by the impregnation. Vulcanized fibre paper is treated with the zinc chloride is utilized for the bushings, low voltage insulation and washers.
3.4.3 Ceramics
The ceramic is utilized as the dielectric may be widely explained as the clay keeping alumina, porcelains and ceramics talc keeping titanates and steatites (barium titanat). There are many different types of composition of the ceramics, which are suitable for the electric utilization are made from combination including alumina (Al2O3), silica (SiO2), titania (TiO2), boron oxide (B2O3), magnesia (MgO) or zirconia (ZrO2).
There are various classification of the ceramics are-
Porcelain
Steatite
Alumina
Titanite
3.4.4 Mica
Mica contains different properties and many uses. Cause of the high thermal resistance, it has an excellent industrial insulation material. It gives offers to the resistance to the electricity, moisture and light, these all are making this ideal for a range of the applications over various sectors. Mica is the high temperature insulation specialist, so manufacture various mica products like mica sheets and mica roll and utilize mica in different thermal management solutions and another industrial applications.
In mica 37 layered group minerals which are chemically and physically similar.
The chemical formula of the mica is-
X2Y4-6Z8O2O(OH, F)4
3.4.5 Asbestos
This insulator has been utilized since old time to develop fireproof cloths for burial shrouds of the kings and tablecloth of wealthy landholders, however modern asbestos industry did not arise till machinery of industrial revolution developed a huge need for the insulation materials. There are many types of asbestos insulation on the basis of the thermal insulation can be categorized into 4 major types are-
- Loose-fill asbestos insulation
- Asbestos insulation wrappings
- Asbestos block insulation
- Spray on asbestos insulation
3.4.6 Resins (Polymers)
Resins or polymers are the organic materials with the very high molecular weight. These are accessible in the nature and made artificially as well as. Purpose of the electrical insulating, natural resins these days have been returned by the synthetic resins. Synthetic resins are named sometimes plastics and made an essential category of the insulating materials. These synthetic polymers are classified on the basis of their behavior like heat, as thermosetting resins and thermoplastic resins. Various types of resins are-
- Polyethylene
- Polystyrene
- Polyvinyl chloride (P.V.C)
- Natural resins
- Polyester resins
- Epoxy resins
- Silicon resins
- Phenolic resins
- Polyamide resins (nylons)
- The acrylic resins (polymethyl methacrylate)
- Polytetrafluorethylene (Teflon)
- Resins derived from the cellulose
3.5.1 Transformer oil
Insulating oil or transformer oil, this is a specific type of oil that has excellent electrical insulating qualities or properties and is stable at the high temperature. This oil is utilized in oil filled electrical power transformer for insulating, corona discharge and stop arcing, dissipate to heat of transformer and work as coolant. Transformer oil is utilized for preservation of the transformer winding and core and another property which is important for insulating oil is its ability to stop oxidation of cellulose made paper insulation.
There are two types transformer oil utilized in transformer are-
- Paraffin based transformer oil
- Naphtha transformer oil
Properties of the transformer oil are
Some significant properties of the insulating oil must be considered to fix the serviceability of oil. Properties are :
Electrical properties
Specific resistance, dielectric dissipation factor and strength.
Chemical properties
Acidity, sludge content, water content
Physical properties
Viscosity, flash point, pour point and interfacial tension.
3.5.2 Varnish
This is a liquid insulator which coats winding glues and wires, the wires are together when curd, improper varnish selection can provide opposite impact through improving thermal degradation of magnet wire, this is leading to turn the insulation failure and breakdown. Varnish is utilized for following purposes, for sealing all hygroscopic materials in winding against absorption of the moisture. For bonding the complete winding, insulation and wires mechanically, into the solid cohesive mass, therefore which it is build more resistant to the shcok, mechanical stress and vibration.
3.5.3 Askeral
This is the relatively higher dielectric constant of askeral aids in the transferring dielectric stress to solid components. Askeral has the limited capability to recover the after dielectric overstress, and so the strength is controlled in non-uniform dielectric fields.
3.5.4 Insulating gases
Insulating gases like air and SF6 provide excellent insulation as an insulating gas. It is more suitable for different climate situations due to its lower boiling point (-64 degree C).
SF6- sulphur hexafluoride gas (SF6) is engaged as insulation in all parts of installation, or in the circuit breaker for arc quenching. This gas is electronegative gas, its atmospheric pressure for dielectric strength 3 times that of the air.
It is non-toxic, incombustible and chemically inert with the arc-quenching properties 3 to 4 times which better than air at similar pressure. SF6 commercially available is not dangerous and this is not hazardous materials order or technical regulations on hazraouds substances (TRGS).
3.6.1 Power and distribution transformers
Insulation of the transformer is based on basic impulse insulation level and together with the voltage rating. Materials which are used in insulations and their applications.
Insulating oil
Insulating oil plays a too important role in transformer insulation system. In the low voltage transformer, transformers are utilized in the range of the 12 to 1000V or low power ratings transformers so there is no requirement of the insulating oil in these transformers. In low voltage transformers heat dissipation is very low. Transformer oil is used as a coolant. And it takes place in a tank in that core of transformer is placed.
Insulating paper
Paper is fabric which is made from vegetables fibers that are felted to the form a sheet or web. The raw materials of the fibrous are acquired from the plants involving hemp, cotton, straw, manila and coniferous trees. It reaches a high value of the electric strength while combined in the oil under vacuum. “craft insulating paper of the medium air permeability” is utilized in the layer winding insulation, oil impregnated busing condenser core. This paper is utilized for covering over the rectangular copper conductor and regularly transposed copper conductor. “crepe kraft paper” is utilized for covering across flexible copper cable insulation of the winding lead.
Pressboard
Pressboard is broadly utilized insulating substances for building a variety of elements utilized in the mechanical, electrical and thermal design of the transformers. ID of the pressboard made from the vegetable’s fibers, cells of these keeps more cellulose. The more typical practical insulation in the power transformer happen at the last of windings and lead outs from windings. Pressboard shaped elements can be developed to any type of shape required. Angle caps and rings are broadly utilized shaping. There are many types of pressboard utilize in the high voltage transformers but “ soft pressboard-laminated” is utilized in the 11KV transformers as a block washer, support and terminal gear cleat and spacer etc.
Wood
Laminates which are made from the wood are manufactured form the chosen veneers acquired from different timbers. The veneers are fully impregnated and dried with the natural phenomenon. The areas that are required high mechanical and low electric strength, laminated wood densities is utilized for developing a insulation variety elements such as cleat, coil clamping ring, core, support and yoke etc.
3.6.2 Insulating materials used in rotating machines
Conductor
Enamel baked cotton combination of both (class A) fiber glass coated with the organic varnish,
(Class B) fiber glass coating with the silicon varnish (class H).
Slot liner
Fiber glass, cotton tapes, synthesis resin fabric tapes are utilized as binders to general finishing and paper baked mica.
The insulations are impregnated with the thermosetting synthetic organic varnishes or the silicon varnishes after the windings.
For the high voltage generators, conductor and turn insulation is generally type of mica tape. The ground insulation of coil keeps of mica flakes bonded through resins.
3.6.3 Capacitors insulating materials
Different types of capacitors are utilized significantly for the DC applications. For paper capacitors, paper with impregnates such as castor oil, minerals oil, synthetic oils and polyesters etc. electrolytic capacitors are with the aluminum or tantalum, ceramic capacitors with the variety of the ceramic bodies like tubular, blocking and disc etc. and film dielectric capacitors like Teflon, polystyrene and polyethylene etc.
3.6.4 Cables
Liquids are utilized as impregnates to the insulation of the solid type of cables and as filing for the hollow core, gas pressurized cables and liquid cooled. Liquid acts as dielectric and as coolant also. Low permittivity liquids, high dielectric, low dielectric dissipation factor, strength and gas absorbing qualities are desirable and all kinds of the hydrocarbons insulating liquids are utilized. gases are filled cables utilizes sulfur hexafluoride as gas.
3.6.5 Line insulators and switch gears
In insulators lines porcelain has been utilize a most acceptable insulation medium for the transmission lines. In high voltage systems weight has been proved to the major constraints. In insulators lines glass insulators are used.
Switchgear
The MCB (miniature circuit breakers that operate on very high currents and high voltage utilize both the gases and liquids arc interrupting coolant medium. In the oil filled breakers, petrol is utilized in transformer is utilized.
Reference book
Mahmood, S. Behavior of Lap Shear Connections with Thermally Insulating Filler Plates.
PC Technology Center. (2020). Thermotechnical properties of the fire-extinguishing powder for extinguishing materials based on magnesium alloy chips.