Unit - 5
Serial port Structure in 8051
The format of the SCON register is shown
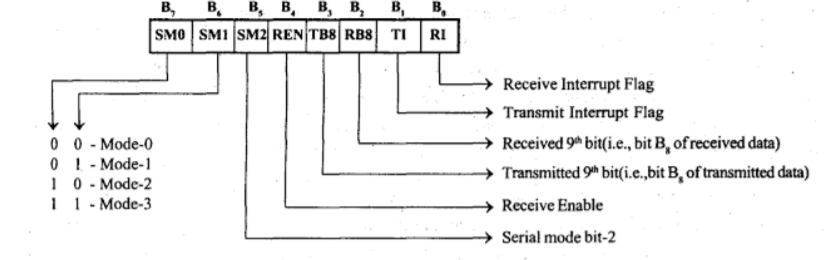
Figure 1: SCON register
o In this mode the serial port function as a half-duplex serial port with a fixed baud rate.
o The 8- bit serial data is received and transmitted through the RxD pin and the controller output the shift clock through TxD pin during reception and transmission.
o The baud rate is fixed at 1 / 12 of the oscillator frequency.
o In this mode the serial port function as a full-duplex serial port with variable baud rate.
o In this mode one data consists of 10 bits, which includes one start bit, eight data bit and one stop bit. During reception the stop bit is stored as RB8 in SCON register.
o Baud rate in mode-1 depends on the value of SMOD bit in PCON register and the timer1overflow rate.
o In this mode the serial port function as a full-duplex serial port with a baud rate of either 1/32 or 1/64 of the oscillator frequency.
o In this mode one data consists of 11 bits which includes one start bit, eight data bit, a programmable 9th data bit and one stop bit.
o During transmission the TB8 of SCON register is added as 9th data bit and during reception the 9th data bit is stored as RB8 in SCON register.
o The baud rate depends on the value of SMOD bit in PCON register.
o The mode-3 is same as mode-2, except the baud rate. o In mode-3, the baud rate is variable. The baud rate depends on the value of the SMOD bit in the PCON register and the Timer- 1 overflow rate.
The serial mode bit-2 (SM2) has no effect in mode-0 and when programmed for mode-0, the SM2 should be equal to zero.
In mode-1, SM2 is used to check a valid stop bit during the reception.
In mode-1, if SM2 = 1, then receive interrupt (RI) is activated only when a valid stop bit is received.
In mode-2 and mode-3 the SM2 bit is used to enable multiprocessor communication.
In multiprocessor communication the serial port of a number of microcontrollers can be connected to a common serial bus. One controller will act as a master and all other controller will act as slave.
A unique 8-bit address is assigned to each slave and the SM2 bit in all the slaves is set to 1.
When SM2 bit is one, the slaves will consider the received byte as address and when SM2 bit is zero the slaves will consider the received byte as data. • For communication with a slave the master will first send as address byte and then a data byte.
The master initiates communication with a slave by sending the address of the slave on the bus. All the slaves will receive the address byte. Since SM2 = 1 initially in all the slaves, the received byte will be considered as address and the slaves will verify whether the received address matches with assigned address. The slave whose assigned address matches with the received address will clear its SM2 bit. Now SM2 bit of only one of the slaves will be zero.
Next the master will send a data byte which is also received by all the slave, but the data byte is accepted by the slave whose SM2 = 0 and so the receive interrupt is activated only in one of the slave whose SM2 = 0.
After reading the received data from SBUF register, the SM2 bit of the slave should be set to one again to receive next data.
The REN bit of SCON register can be used to enable or disable the serial reception. When REN = 1, the serial reception is enabled and when REN = 0, the serial reception is disabled.
The bits TI and RI of SCON register are transmitting interrupt flag and receive interrupt flag respectively.
The controller will set the TI bit during the transmission of stop bit of a data character in mode 1 to 3 and during the transmission 0 bit of a data character in mode-0.
The controller will set the RI bit during the reception of stop bit of a data character in mode 1 to 3 and during the reception of 8th bit of a data character in mode- 0.
Key Takeaways:
Serial data communication uses two methods:
-Synchronous methods transfer a block of data at a time.
-Asynchronous method transfers a single byte at a time.
Programming the 8051 to transfer data serially
In programming the 8051 to transfer character bytes serially, the following steps must be taken.
1 in mode 2 (8-bit auto-reload) to set the baud rate.
serial data transfer (assuming XTAL = 11.0592 MHz).
where an 8-bit data is framed with start and stop bits.
Programming the 8051 to receive data serially
In the programming of the 8051 to receive character bytes serially, the following steps must be taken.
1.TMOD register is loaded with the value 20H, indicating the use of timer 1 in mode 2 (8-bit auto-reload) to set the baud rate.
2. The TH1 is loaded with one of the initial values to set baud rate for serial data transfer (assuming XTAL = 11.0592 MHz).
3. The SCON register is loaded with the value 50H, indicating serial mode 1, where an 8-bit data is framed with start and stop bits
4. TR1 is set to 1 to start timer 1.
5. TI is cleared by CLR TI instruction.
6. The character byte to be transferred serially is written into the SBUF register.
7. The TI flag bit is monitored with the use of instruction JNB TI, xy to see if the character has been transferred completely.
8. To transfer the next byte, go to step 5.
Write a C program for 8051 to transfer the letter “A” serially at 4800 baud continuously. Use 8-bit data and 1 stop bit.
#include<reg51.h>
void main(void)
{
TMOD = 0x20;
TH1= 0xFA;
SCON = 0x50;
TR1=1;
while(1)
{
SBUF = ‘A’
while(TI==0)
TI=0;
}
}
Program in 8051C to receive bytes of data serially and put them in P1. Set the baud rate at 4800 8-bit data and 1 stop bit.
#include<reg51.h>
void main(void)
{
unsigned char mybyte;
TMOD =0x20;
TH1=0xFA;
SCON =0x50;
TR1=1;
while(1)
{
while(RI==0)
mybyte=SBUF;
P1=mybyte;
RI=0;
}
}
Key Takeaways:
The 8051 transfers and receives data serially at many different baud rates. Serial communications of the 8051 are established with PC through the COM port.
GSM stands for (Global System for Mobile Communications) which is basically a modem which accepts SIM card and works in GSM network provided by the operator just like mobile phone. The GSM module can be controlled by a computer or microcontroller to do different tasks in the network such as calling, sending messages, accepting messages, sending FAX, etc.
The GSM module usually communicates with the parent hardware through serial communication. If the parent hardware is a personal computer, the communication is usually done through the serial port (RS232) and if the parent system is microcontroller based, the communication is through the TTL pins Rx and Tx.
Advanced GSM modules may have Bluetooth or Wi-Fi connectivity. Common applications of GSM module are message delivery/reception systems, mobile-based appliance control systems or simply any data communication application which is supported by the GSM network provider and the GSM module.
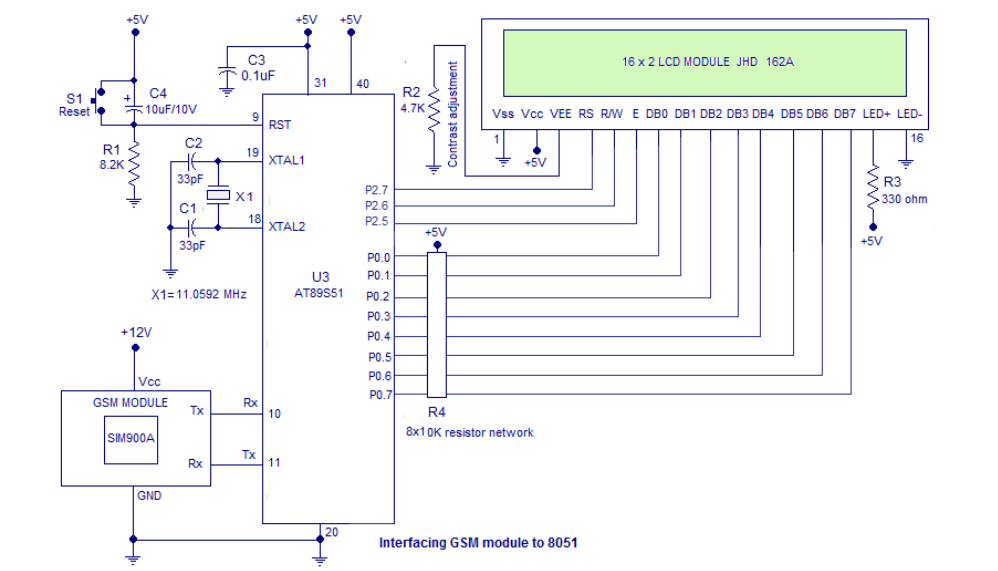
Figure 2. Interfacing of GSM with 8051.
Interfacing of GSM with 8051 microcontroller
Here the GSM module and the microcontroller communicates in between using serial communication. Rx pin of the 8051 is connected to Tx pin of the GSM module and Tx pin of the 8051 is connected to the Rx pin of the GSM module. The LCD module is involved in this project to give an indication message when the SMS is sent.
Switch S1, capacitor C4 and resistor R2 are associated with the reset circuit of the microcontroller. Capacitor C1, C2 and crystal X1 are associated with clock circuit. C3 is just a noise by-pass capacitor. Resistor R2 is used to set the contrast of the LCD. Resistor R3 limits the current through the backlight LED.
Key Takeaways:
The 8051 transfers and receives data serially at many different baud rates. Serial communications of the 8051 are established with PC through the COM port.
The parent hardware (PC or uC) does different tasks with the GSM module by sending different commands and the data to the module in a suitable order and format.
The task in the module is to send a message to a mobile phone The commands and their format required for this application are
AT- to check the modem.
AT+CMGF=1 to configure the GSM module to SMS mode.
AT+CMGS=” mobile number“ to send the mobile number to the GSM module.
CTRL+Z to send the message.
Program.
ORG 000H
MOV TMOD,#00100001B
MOV TH1,#253D
MOV SCON,#50H
SETB TR1
RS EQU P2.7
RW EQU P2.6
E EQU P2.5
MAIN: ACALL DINT
MOV A,#"A"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"T"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#0DH
ACALL SEND
ACALL DELAY1
MOV A,#"A"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"T"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"+"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"C"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"M"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"G"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"F"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"="
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"1"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#0DH
ACALL SEND
ACALL DELAY1
MOV A,#"A"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"T"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"+"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"C"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"M"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"G"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"S"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"="
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#34D
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"+"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"9"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"1"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"9"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"5"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"4"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"4"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"3"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"4"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"0"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"0"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"7"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"7"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#34D
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#0DH
ACALL SEND
ACALL DELAY1
MOV A,#"H"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"E"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"L"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"L"
ACALL SEND
MOV A,#"O"
ACALL SEND
ACALL DELAY1
MOV A,#1AH
ACALL SEND
ACALL DELAY1
ACALL DINT
ACALL TEXT1
ACALL DELAY1
HERE1:SJMP HERE1
SEND: CLR TI
MOV SBUF, A
WAIT: JNB TI, WAIT
RET
DELAY1:MOV R6,#15D
BACK: MOV TH0,#00000000B
MOV TL0,#00000000B
SETB TR0
HERE: JNB TF0, HERE
CLR TR0
CLR TF0
DJNZ R6, BACK
RET
DELAY: CLR E
CLR RS
SETB RW
MOV P0,#0FFh
SETB E
MOV A, P0
JB ACC.7, DELAY
CLR E
CLR RW
RET
DISPLAY:MOV P0,A
SETB RS
CLR RW
SETB E
CLR E
ACALL DELAY
RET
CMD: MOV P0,A
CLR RS
CLR RW
SETB E
CLR E
ACALL DELAY
RET
DINT:MOV A,#0FH
ACALL CMD
MOV A,#01H
ACALL CMD
MOV A,#0CH
ACALL CMD
MOV A,#06H
ACALL CMD
MOV A,#81H
ACALL CMD
MOV A,#3CH
ACALL CMD
RET
TEXT1: MOV A,#"S"
ACALL DISPLAY
MOV A,#"E"
ACALL DISPLAY
MOV A,#"N"
ACALL DISPLAY
MOV A,#"T"
ACALL DISPLAY
MOV A,#" "
ACALL DISPLAY
MOV A,#" "
ACALL DISPLAY
MOV A,#" "
ACALL DISPLAY
RET
END
About the program.
Timer 1 of the 8051 is configured Mode 2 for serial communication. Timer 0 of the 8051 is configured as Mode 1 timer for creating few delays used in the program. TMOD register is loaded with 00100001B for this purpose. TH1 is loaded with 253D for setting the baud rate to 9600. The relevant equation is TH1 = 256 – ((Crystal / 384) / Baud) where crystal frequency is in Hz. The crystal used is 11.0592 MHz and the baud rate we need is 9600. When substituting these values in the above equation, we get TH1=256-((11.0592/384)/9600)=253. SCON register is loaded with 50H for setting the serial port mode to Mode1 and receiver enabled.
The next part is controlling the GSM module for performing our task which is to send a predetermined message to a given mobile number. For this, first you need to send the command AT to the GSM module for checking the status. The format is AT/r.This is done by sending the ascii code of A, then ascii code of T, and ascii code of /r ( carriage return) to the GSM module one by one. The ascii code of carriage return is 0DH.
Next, you have to send the command AT+CMGF=1 to the GSM module for configuring the GSM module in the SMS mode. The format is AT+CMGF=1/r.This is done by sending the ascii code of A, then ascii code of T, then ascii code of +, then ascii code of c, then ascii code of M, then ascci code of G, then ascii code of F, then ascii code of =, then ascci code of +, then ascii code of 1 and finally the ascci code of /r.
Next, you have to send the command AT+CMGS=” mobile number” to the GSM module for sending the target mobile number to the GSM module. The format is AT+CMGS=” mobile number”/r. GSM module for configuring the GSM module in the SMS mode. The format is AT+CMGF=1/r.This is done by sending the ascii code of A, then ascii code of T, then ascii code of +, then ascii code of c, then ascii code of M, then ascii code of G, then ascii code of s, then ascii code of =, then ascii code of “, then ascii code of each of the mobile number one by one, then the ascii code of” and finally the ascii code of /r.
Then you need to send the message text to the GSM module. This is done by sending the ascii code of each letters in the text to the GSM module one after another. Finally the ascii code of CTRL+Z (substitute) is send to the GSM module for sending the message. The ascii code of CTRL+Z in HEX format is 01AH. A delay of 1 second has to be introduced between each commands for giving the GSM module enough time to accept and execute each commands. The entire procedure can be simply written as given below.
AT/r
1S delay.
AT+CMGF=1/r
1S delay.
AT+CMGS="mobile number"/r
1S delay.
message text.
1S delay.
CTRL+Z
1S delay.
Key takeaway:
GSM module is used to send and receive a text from a handheld device to instruct operations that 8051 needs to perform.
References:
1. The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems using Assembly and C by Muhammad Ali Mazidi.
2. The 8051 Microcontroller by I. Scott Mackenzie, Raphael C.W Phan
8051 Microcontrollers: Internals, Instructions, Programming, and Interfacing Book by Subrata Ghoshal
3. 8051 Microcontroller Based Embedded Systems Textbook by MANISH K PATEL
4. 8051 Microcontrollers: An Applications Based Introduction Book by David Calcutt, Frederick Cowan, and G. Hassan
5. Advanced PIC Microcontroller Projects in C Book by Dogan Ibrahim