Unit - 4
Basics of Estimation and Costing
What is Estimate?
An estimate is the anticipated or tentative, or probable cost of work and is usually prepared before any project work is taken up. It is indeed calculations or computation of various items of an engineering project to have first and knowledge of approximate cost which is likely to be incurred including quantities of various materials required and labor involved for satisfactory completion of work .
OR
Estimation is the technique of calculating or computing the variants quantities and the expected expenditure to be incurred a particular work or project.
Purpose of Estimating and costing
Estimating is necessary as it gives us certainty about the amount of money required, availability of material etc.
In the absence of pre – project and work started without estimating and costing, the work cannot be completed uninterruptedly because it becomes difficult to continue work due to instantaneous shortage of many or unavailability of materials.
Estimator must have the following qualities:
1. Estimator has ability to read and interpret drawings and specifications.
2. Estimator should have good communication skills.
3. He/She should have knowledge of basic mathematics.
4. He/She should have patience.
5. Estimator should have good understandings of fields operations and procedure.
6. He/She should have ability to visualize three dimensional projects by looking at the drawing.
7. He/She should have ability to interpret the risks and then neutralize as much as possible.
8. He/She should have good organizational ability. So that he can communicate his estimate in logical and clear presentation to the client.
9. He/She should have ability to prepare construction schedule.
10. He/She should have ability to anticipate all construction steps in building projects.
11. He/She should have good understanding of labor productivity and equipment performance.
12. He/She should have ability to use the construction company’s job costing system.
13. He/She should have ability to think alternate methods of construction.
14. Estimator should have ability to develop strategy for being successful in bidding and negotiation phase of the project.
15. Estimator should have ability to meet deadlines and still remains calm.
16. He/She should have a solid load of ethics.
17. Estimator should have understanding of contractual relationship.
- Specification of material
- Latest market cost of material
- Price list and net prices
- Calculation of material and labor cost
- Knowledge of purchase system
- Labour cost
It is an invitation from the owner to the contractor to execute some work at specified cost in specified time. It is published in the form of tender notice in newspapers, noticeboards, guests, etc. according to the cost of works.
Guidelines for Inviting Tenders
- Name of the department inviting tender
- Name of work and location
- Designation of officer inviting tender
- Last date and time of receipt of tender
- Period of availability of tender document
- Cost of tender document
- Time of completion and type of contract
- Earnest money deposit to be paid
- Date, time and place of opening the tender
- Designation of the officer opening the tender
Quotation
A quotation is a fixed price offer that can't be changed once accepted by the customer. The manufcturer must adhere to the quotation price even if they carry out more work than expected. If they think this is likely to happen, it makes more sense to give an estimate. They can also specify in the quotation precisely what it covers, and situations that will lead to additional charges.
Price catalogue:
For an upto date estimating and costing, an estimator should always have quotation and a bunch of price lists provided by whole sale quotation and a bunch of price lists provided by whole sale dealers and manufacturers of specific material.
The quotations and price list along with specification of material are called as catalogue .
We can get complete details of all the products of a manufacturing from the catalogue.
An intelligent and experienced estimator can do the job by using the catalogue for prices and other relevant information
The estimator can further save time if the information regarding net price of each item after deducting commission and adding local taxes is available in the catalogue
This information in the form of a catalogue should be available with every estimator.
Determination of labour cost
- To arrive at a final conclusion for determination of labour charge for wiring a particular building is very difficult.
- It is because the labour charges are different at different places.
- For instance, in cities a trained electrician may charge ₹150/- a day but in rural areas an equally trained electrician may be available ₹ 80/- a day.
- The labour charges are decided as under:
(a) As per work duration and work amount i.e. the labour cost is paid to daily wagers
(b) As per unit work basis
(c) As per percentage of material cost
(a) Work duration and work amount
If the wiring work is to be completed on the basis of work duration and work amount, then the skilled workers are employed on daily wages.
The total number of points to be wired is found out, considering the installation of main board as equivalent to 2 points. (Each point is assumed to be at an average distance of 5 m from the switchboard).
The number of days required for one wireman with one helper to complete the work is found out. For this, as an average the number of points which can be installed per day by a wireman with a helper is assumed as 3 points for TW batten wiring, and 2 points for conduit wiring.
Ie., No. Of days required for one wireman with a helper to complete work = 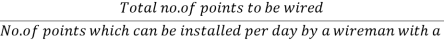
Cost of labour = rate of labour per day X no. Of days required to complete the work.
No. Of points to be wired = 4 + 2 = 6 points.
For TW batten wiring, the no. Of points which can be installed per day by a
Wireman with a helper is 3 points.
No. Of days required for one wireman with onc helper to complete the work = 6/3 = 2 days.
Rate of labour per day for a wireman and helper = Rs. 25.00 + Rs. 20.00 = Rs. 45.00
Cost of labour = Rs. (25 + 20) x2 = Rs. 90.00
The no. Of points which a wireman and his helper are likely to wire, is mentioned in pwd(electrical) work schedule of department.
The labor rates for all categories of labors are also mentioned in the same gazette
The table mentioned below is completed to ascertain the total labor payment
Sr. No | Class of labor | No. Of days | Rate ₹ Per Day | Amount | Total Rs |
1
| Unskilled
| 30 | 80 | 80 x 30 | 2400 |
2
| Skilled | 30 | 150 | 150 x 30 | 4500 |
(b) On unit work Basis
This is very simple and prevalent system to determine this labour charge for a work. In this system, the total no. Of points in the building are counted which includes installation of main board and switch boards.
Installation of main board and switch boards.
The labour rate per unit is paid to an approved contractor in the case of govt. Buildings and to an individual trained wireman in case of private building. The total payment can be calculated from the table mentioned below:
Sr. No | Description of unit work conduit | No. Of points | Rate Rs P | Total Payment |
1 | Main points installation | 4 | 20. 00 | 80. 00 |
2 | Total Points light fan socket | 46 | 20. 00 | 920. 00 |
| Total labour charges |
|
| Rs. 1000. 00 |
(c) Material cost
As per percentage of Material cost in this system a fixed percentage of the total material cost is counted towards labour payment. This percentage may be 15% , 20% or 25% depending upon type of wiring, the payment of labor is calculated from table give below:
Sr. No | Description of Material | Rate | Amount | |
Cost | % of total material | |||
1 | Total cost of wiring Material | 6115 | 15% | 917. 25 =920 |
A schedule or list of rates of various items is prepared after the analysis of rates of these items. Such a document is known as the schedule of Rates or S.O.R. It is prepared by large concerns or public bodies such as Central Public Works Department (CPWD), State Governments etc. It becomes very useful, especially in the preparation of estimate and also in deciding the rate of an extra item, carried out by the contractor. Normally a clause in the conditions of the contract is inserted, stating that, any extra item that might occur during the execution of work shall be paid as per rate in the SOR.
Important Points to be remembered:
In some cases, the contractor may be asked to submit his tender by simply quoting the percentage above or below the S.O.R for carrying out the construction work.
The schedule of rates consists of groups of items such as demolishing items, excavation items, concrete items, RCC works, brickwork items etc. and also information regarding the present wages of labour and prices of different items, is given in it.
As the rates of items mentioned in the schedule of rates are likely to vary because of continuous changes in the market rate of materials, wages of labour, cost of carriage etc., Thus schedule of rates is periodically revised, usually after two years.
The CPWD is the premier construction organization of the Govt. Of India and it has been responsible for the planning and design, construction and maintenance of a variety of building projects. Hence, the SOR serves as an important document for the CPWD.
The CPWD schedule of rates contains the basic rates of materials, labour, carriage etc. of about more than 2500 items and the finished rates of about 3000 items of works covered under different subheads like Building work, Wiring work, water supply etc.
SOR is prepared for both Civil Works and Electrical & Mechanical Works.
Estimation
Electrical Installation work is a highly competitive business and contracts are usually given to firm that submit the lowest estimate. If the prices of a contractor are too high, he will secure no business, if too low, it will land him in a loss. As a result, correct estimating is a very important part of a running business. Thus we know that estimating is an art of calculating the quantities of various items and cost of the material and labour involved in executing the work.
To estimate the cost involved, first quantities of materials required are calculated. A price list is prepared, labour charges are calculated and overhead charges and contingencies are calculated.
Price List
To prepare a price list, a market survey is carried out and quotations are collected from different manufacturers in the market. The approximate costs of differenr materials is prepared in the form of price list.
Labour Charges
Labour is the most difficult and variable item to assess. It is affected by so many factors such as site condition, skill and technical training, physical fitness etc. By vast experience, and proper records of time sheets, an intelligent estimator will be able to obtain labour values by the system of man-hour constant.
Overhead Charges
Overhead charges include general ollice expenses, rent, rates of lighting and heating, depreciation of furniture and office equipment. Overheads should be ascertained annually and a percentage figure obtained can be included in the estimate.
Contingencies
Contingencies include unexpected expenditure due to increase in cost rate of the matcrial, loss due to floods or any other reasons etc.
The total cost is calculated by adding together the cost of material and cost of labour. To the total cost, overhead charges and contingencies charges are added, and thus the final cost of carrying out the installation is estimated.
Profit Purchase System
The estimate of material as prepared, enables the engineer in charge of the works to procure all the items required for the installation. Purchasing of different items has to be done profitably. Enquirics are to be sent to the different manufacturers and quotations are collected from them, A compara-live statement is prepared, so that the prices of the different manufacturer’s can be compared qualitatively also. Then the best suitable product is selected ratewise or quality wise. The supply order is sent to the manufacturer along-with an advance payment. The actual payment is done on producing the bills after the supply of materials. Such a system of purchase can be called as profit purchase system.
References:
1. P.S. Pabla –Electric Power Distribution, 5th edition, Tata McGraw Hill.
2. S. L. Uppal, Electrical Wiring and Costing Estimation, Khanna Publishers, New Delhi.
3. Surjit Singh, Electrical wiring, Estimation and Costing, Dhanpat Rai and company, New Delhi.
4. Raina K.B. And Bhattacharya S.K., Electrical Design, Estimating and Costing, Tata McGraw Hill, New Delhi
5. B.D. Arora-Electrical Wiring, Estimation and Costing,- New Heights, New Delhi.
6. M.V. Deshpande, Elements of Power Station design and practice, Wheelers Publication.
7. S. Sivanagaraju and S. Satyanarayana, Electric Power Transmission and Distribution, Pearson Publication .