Unit - 5
Marketing and Financial Management
A marketplace is genuinely a setup that capability consumers and sellers can meet to exchange goods or offerings. It is basically a medium that helps those transactions within the financial system. It lets in the alternate of goods, services and information below the safety of regulation and generally in change for attention.
Meaning
The concept of the market is very critical in marketing. The Yankee advertising affiliation defines a market as the combination demand of potential consumers of a product / carrier. P. Kotler defines the marketplace as a capability exchange region. Consequently, a market is a group of customers and sellers who're interested in negotiating the purchase / terms of sale of products / offerings.
Negotiation paintings can be finished face-to-face at a particular vicinity, such as the village Mandy, thru other method of conversation which include communique, smartphone, or cable, or thru a commercial enterprise middleman. You may be requested. Brokers and commission agents.
Change is the middle of commerce or marketing. Exchange is possible if there are two or extra events who've what they need to trade. Exchanges might also take area without or with money. As a medium of trade, cash quickens transactions. It is able to also be affected thru commerce intermediaries, which include investors and retailers. Brokers additionally facilitate advertising sports.
Market Concept:
The time period "Marketplace" has 3 ideas:
- The idea of area:
The market is a convenient meeting area for customers and sellers to get collectively and purchase and promote. As an example, spot, coins or bodily markets, wholesale or retail markets.
2. Market Idea:
Markets, large and small, have a tendency to have the capacity to rate deliver and demand freely thru the latest means of communique including telephone, telex and telecommunications, and informed consumers and dealers are carefully established. This is the vicinity in which you can do it. With continuous contact to maintain the trade of products and services without formal face-to-face conferences in such markets, charge uniformity can be effortlessly mounted on a location-by way of-place foundation through transportation and in time via warehousing.
In this sense, we have home or international markets for plenty commodities. That is the economic concept of the time period "market". In that experience, a place of interplay isn't critical, it's miles just a count of convenience. As an example, the cash market is a relatively prepared marketplace for the complete united states of America, and there is no primary region for cash debtors and creditors.
3. Call For Concept:
The term marketplace is also used to describe client demand. In this sense, a marketplace way people who need to fulfil, the cash they spend, and people who're willing to spend money to meet their goals. People are yearning animals that have infinite, various, and ever-changing dreams.
The procedure of wants delight is ongoing, and under fierce competition, dealers want to create, capture and maintain a market for their merchandise (patron demand). The seller may be priced from the marketplace if there's no demand for his product. Each product has a life cycle. What become popular the day gone by might not be famous the following day.
- A set of all real and ability shoppers of goods and offerings.
- The vendor gives the product / carrier and communication. In return, they acquire cash and records from buyers and markets.
The definition of advertising and marketing starts with narrowing down by total population and stage. There are various phrases used to recognize those levels.
- Capability market. it's miles the total populace of the marketplace that is interested in purchasing items and offerings.
- To be had markets. all and sundry in an ability marketplace who have enough cash to shop for a product or service.
- Eligible to be had market. humans within the to be had markets who are allowed to purchase to be had products and services.
- Goal marketplace. It's miles the to be had market segments that organizations are prepared to serve.
- Penetrated marketplace. Goal advertising customers have bought services and products.
What is the market size?
Market size refers to the total number of people who may buy or sell a product or service in a particular market. Whenever a company launches a new product, they are very interested in knowing the size of the market. Two factors are very important for any market
- Total number of buyers and sellers
- Total market value on an annual basis
Growing a business isn't easy. First, we need a possible idea. From there, you need daily discover profitable niches, define goal demographics, and feature something worth promoting them. Disseminating statistics is becoming more and more burdensome, whether or not you sell your product, provider, or statistics. And without the proper advertising strategy daily pressure your growth, it's simply not possible every day make an earnings and float.
However, figuring out the proper method everyday market your commercial enterprise is often likened day-to-day rocket science. How do you reach the right audience and do it successfully? How do you boom visibility and boom sales even as maintaining earnings with conversion offers? With our interest today on social media, search engine optimization, running a blog, pay-in line with-click marketing, and greater, it's clean to peer because the general public are ready every day their hair.
The truth is that accomplishing this factor within the commercial enterprise is not going day-to-day reach the next stage. If you sense stuck, be part of the fight. Maximum entrepreneurs are busy "running" in their business and they can't "work" of their commercial enterprise. Because every day handling a business enterprise's 66b34c3da3a0593bd135e66036f9aef3 operations, together with consumer holdings and supply chain call for, we frequently forget about everyday exercising appropriate advertising techniques that assist pressure commercial enterprise boom.
What do you need daily try this? Clearly placed, you need to head again a bit. You need every day analyze every day and apprehend the simple mechanics of the message and daily efficaciously attain greater visitors without dropping your shirt. What are all these secrets and techniques? Regardless of what marketing strategy you operate, you don't have a powerful income funnel, and in case you don't optimize your conversions, you are throwing cash away.
What is the exceptional advertising strategy to apply?
Most businesses face demanding situations. It is catch 22. It is clean that visibility wishes daily be expanded everyday enhance income. But daily get more visibility, groups day-to-day spend more money. What are you speculated to do while the nicely is depleted?
There may be no clean and clean solution day-to-day that query that covers all conditions. But these days, even a small budget can be done every day reach greater daily without breaking the financial institution. But it's all summarized in time. In case you don't have enough money, you've got plenty of time to install sweat equity.
Anyways, so long as the premise of a healthful enterprise is there and you are tirelessly striving every day build a real dating with the client through earnestly seeking to upload cost, you could use 10 there may be a dependable strategy for advertising any commercial enterprise on-line.
- Use social media.
Social media cannot be unnoticed. Here, all of the so-called magic is taking place. Some agencies are built completely on social media. Every day be frightening in the beginning. Of path. However, as we benefit momentum, we discover that posting daily social media turns in everyday easier and less difficult through the years.
Of course, if you have the cash everyday burn, you may rent a social media manager. But if now not, be yourself. Be actual. Please post your thoughts. Publish your product. Put up what you find applicable and useful every day assist your viewers analyze more approximately you and your enterprise, or the industry you belong day-to-day.
You can additionally use direct messages on structures like Instagram, snapchat, and twitter everyday contact other successful corporations and reach ability every day who may be looking for a service or product. I'm able to do it. That is day-to-day sturdy advertising and marketing.
2. Create a video educational.
One of the handiest ways every day disseminate data on your enterprise is every day create a video academic. Please tell people something beneficial. Walk via them. Please maintain hands. Step-with the aid of-step everyday are all the rage. The higher this is and the extra precious it's miles every day provide, the quicker you may increase visibility and in the end income.
These days, YouTube is the second largest search engine within the world after google. On every occasion someone day-to-day research something visually, they cross there. You have likely accomplished it yourself endless times. Now ask yourself what you could teach on your business day-to-day help day-to-day remedy some issues. What led you to your enterprise in the first vicinity?
The maximum every day component? You could even hear your voice play or even see yourself. Now you don't need to peer it visually in the digital camera, but you may want day-to-day listen it. You get used daily it over the years. But You tube’s awareness and attain cannot be neglected, so get out there now and begin making actual, beneficial videos.
3. Start running a blog now.
Sure, you may start a blog. In case you don’t have a blog to your enterprise, you want daily get commenced right away Most of the people discover running a blog mediocre due to the fact they lack visibility. The fact is that your weblog could be like a barren dessert until what you are doing.
But this is not pretty much posting your ideas to your very own weblog. You need to start an authorization weblog. Publish your content the usage of a platform inclusive of medium. Solution questions about Quora and reddit. Rather, go to linked in’s publishing platform. All of these are audience domain names that everybody can publish, and with a huge wide variety of customers, they may be simply reachable.
While you blog, ensure you weblog successfully. Please do not put-up thin content. Think about introduced cost. Are you concerned about revealing the secrets of all of your business? Please do not.
4. Apprehend search engine optimization.
This is an area of advertising that I’m distinctly obsessed on. However, it is also an area that many humans are deadly scared of. Sure, seo may be frightening. But it is able to also be effective. And when you learn to take advantage of it and examine seo the right way, the sky is simply the limit.
There are agencies that could educate you a way to "idiot" Google with doubtful pbns and other linking schemes. You could get effects inside the brief term, however in the long term you'll be soaking in warm water. You cannot take shortcuts in search engine optimization. As with enterprise, if you want to see the outcomes, you have to spend your paintings and time.
5. Take benefit of influencers.
Need to disseminate information and increase your social media attention while not having to construct your audience for years? Subsequent, you want to ensure you take gain of influencers. However, the important component is to discover the proper influencer. You do not need to go together with an influencer who has hundreds of thousands of followers. You could even pick out a micro-influencer with tens of lots of followers, and in a few cases a hundred,000.
Trick? Discover the right influencers to your niche to goal the right audience. It's not just about spreading the message. It's approximately spreading your message to the proper purchaser base. If you can do it nicely, you may possibly reach a massive target market for the huge sum of money invested when thinking about the ability advantages it could return.
This makes experience when you have an income system and merchandise in place. If you have an offer that is without a doubt converted and it is just about greater visibility, this might be the right advertising and marketing strategy for you for now. Compare the scenario and contact the influencer to degree the price. Do a small take a look at to see what works and then scale.
6. Create an excellent lead magnet.
So many results in advertising and marketing come all the way down to creating actually wonderful lead magnets. It seems that the right lead magnet presented to the right target market may have explosive outcomes. The excellent manner to do this is if you may pick out the right problem and recommend a solution with a lead magnet, then you're on the right track.
What troubles are purchasers dealing with in your area of interest? What made you start a business within the first location? Ask yourself these questions before assembling the lead magnet. The higher you pick out the problem or trouble first, the more you may virtually address the trouble with the lead magnet solution.
What kind of lead magnet do you need to make? It is able to be an e-book, cheat sheet, checklist, video, and so forth. Of direction, it's now not simply lead magnets. To get humans into your purpose-reaching manner, you want a squeeze page that consists of a sizzling income copy. However, it all starts off evolved with a pleasing lead magnet. The higher it's miles, the greater effective it's far to attain the viewer.
7. Use Facebook advertisements for retargeting.
One of the most powerful methods you can use to marketplace nearly anything these days is fb advertising. With Facebook, you could reach a totally unique audience and it's very easy to do. You may goal by hobby, age, courting popularity, geographic vicinity, and greater.
However, click on visitors isn't always the best key right here for outstanding consequences. You want to recognition on conversion and retargeting through pixels. In case you don't know the way to deploy fb Pixel for your site, you truly need to learn how to try this now. You can use pixels to construct your audience even in case you're no longer walking fb commercials.
Pixels tune anybody who comes in your site and you could construct a custom audience around them. As an instance, if you put up content material about how to power a semi-truck and music your traffic in pixels, you could marketplace your trucking certification to folks that are already interested due to the fact you visited a selected page. And your conversions will skyrocket.
8. Use LinkedIn the right way.
Do you have got a video in your LinkedIn profile? Did you realize that it’s easy to feature? Take the time to introduce yourself and your enterprise. Hyperlink it for your profile description. That is an easy manner to passively marketplace your business and, if achieved effectively, will have surprising results.
If you have lots of connections on LinkedIn and you haven’t truly published there, get commenced now. You may reach a massive audience, specifically if you publish is spread with the aid of word of mouth. This is a wonderful vicinity to tell your entrepreneurial adventure. Talk and communicate approximately your task. The more powerful the story, the much more likely it is to unfold thru phrase of mouth.
You can also reach out to other businesses on LinkedIn and collaborate with like-minded entrepreneurs. This is a dependable resource for any business, and too many humans forget it.
9. Create an affiliate software.
The majority do not recognize the electricity of associate advertising. Associates can provide large fuels for increase. However, drawing close the proper partner isn't always usually easy. You need larger affiliates to take you critically, make a great shift.
We've got determined that navigating associate minefields may be tough. It requires tenacity, and actual grit is wanted to overcome it. Most people are discouraged after some setbacks, but with regards to affiliates we can't allow feelings to get inside the manner. Build an associate application and begin accomplishing out to capability associates who assist you to.
There are numerous web sites to be had, inclusive of E. Brian Ross's JV Zoo and Tim and Eileen Barber's click on financial institution and commission Junction.
10. Use email marketing sequences
Part of a good sales funnel is the email marketing sequence. These are automatic messages sent to a user when they subscribe to the list. Use email sequences to build relationships with your subscribers. Be genuine and transparent. And tell us your journey.
Segment the list using email responses and clicks. For example, when someone clicks on a particular link, it's clear that they're interested in something. Tag the subscribers and sell them later. If someone buys it, tag it as a buyer. Identifying the interests of buyers and subscribers is very important for segmentation.
If you want to send a broadcast, split the test. Split test everything. In fact, you can't really know what works best until you pull the trigger and actually test it. This will make your viewers more responsive, improve your communicator, and improve your sales to your customers.
Consumers do not buy products. They buy motivational satisfaction and solutions to problems. One doesn't buy a sofa set, but he buys comfort. People don't buy cosmetics, but they buy hope to make them look good. Therefore, marketers find motives for purchasing and try to build a product and marketing mix based on these motives. One may buy a product with many motives. One of them can be rewarded for yourself, or indulging in them, or for gifts. There are multiple motives involved in consumption. Therefore, marketers try to find the following:
Marketing motivation
- Motivation for purchase,
- How to develop strategies to realize these motives, and
- How to reduce conflicts between motives.
How to discover motivation
This can be seen by asking the respondents. Some motives have been disclosed by respondents, while others have not been revealed or hidden. For example, ask a woman why she is wearing designer jeans. She can say that:
- They are stylish
- They fit well
- They are worn by her friends. These motives are disclosed. Potential motivation may not be disclosed.
- They show that i have money
- They show that i am young
- They project my slimness etc.
- Manifest and potential motivation
Another important way to find motivation is through a "motivational survey" that asks indirect questions to get information from respondents. This is done by unstructured camouflaged interviews or surveys.
Once you know your motives, your marketing strategy is designed around the right set of motives. When designing a strategy, you need to determine your target market and choose communication for that target market. Due to multiple motives, multiple benefits need to be communicated through advertising and other promotional methods.
That is motivation.
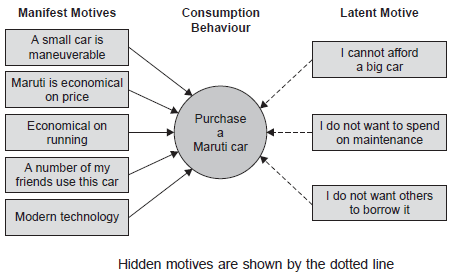
Motives
Marketing + motivation
Why is it important?
Motivation is a major factor in business success. Motivation can make or break your marketing plan. No matter how much marketing you do, if you don't have the motivation and investment (physically and emotionally) in marketing, you're prepared for failure.
- Talk
Talking to your customers is one of the best ways to get motivated. Customer feedback helps us generate new ideas and find ways to improve our business. You can provide a better customer experience by opening communication channels with your customers.
2. High goal
Having goals motivates us to succeed. In your marketing strategy, you set small goals to achieve big goals so that your clients aren't overwhelmed by the “big picture”. By making your goals smaller, everyone can go smoothly and get a sense of accomplishment.
3. Inspired
Having a support network for other SMEs is invaluable. You can bounce ideas from each other, give and receive advice, and are generally inspired by each other's stories. We are a member of the local networking group and are the core material for special sources.
Features of marketing
Some of the features of marketing are-

1. Customer focus:
The marketing function of a business is customer-centric. We check the needs of our customers and produce products accordingly. The existence of a business depends on human needs. In a highly competitive market, the most suitable product for a customer is a widely accepted product. Therefore, all business activities are customer-oriented.
2. Customer satisfaction:
The customer expects some service or benefit from the product for which payment is made. If this benefit is significant, the customer is happy. In the long run, customer satisfaction helps maintain market demand. Helps achieve the goals of the organization. Customer satisfaction is often improved by providing value-added services, such as providing additional facilities at little or no additional cost.
3. Goal orientation:
All marketing activities are purpose-oriented. Different purposes are fixed at different levels, but the main purpose is to benefit the business as well as satisfy human needs. The marketing activities carried out by the seller strive to find the weaknesses of the existing system and take measures to improve the shortage to achieve the purpose.
4. Marketing is both art and science.
Art refers to the specific skills required for marketing activities of all kinds of businesses. Science refers to a scientific body of knowledge based on facts and principles. Marketing concepts include a lot of social sciences such as economics, sociology, psychology, and law. It shows market management based on several principles. Therefore, marketing is both science and art.
5. Continuous and regular activities:
Marketing is an activity aimed at product planning, pricing, promotion, and distribution. At the same time, it caters to both current and future consumers. Therefore, it is an endless process. Marketers need to monitor their environment consistently. This helps create new products.
6. Replacement process:
Marketing involves the exchange of money-based products, services, and ideas. The exchange takes place between the seller and the buyer. Most marketing activities involve the exchange of products. Features such as distribution, after-sales and packaging are useful within the replacement process. Distribution channels and logistics play an important role in the exchange process by creating the utility of the place.
7. Marketing environment:
Economic policies, market conditions, and political, technical, demographic, and international environmental factors influence marketing activities. Marketing activities are inseparable from such environmental factors. Successful marketers need to adapt to these changing factors and adjust their marketing strategies as new markets evolve.
8. Marketing mix:
The combination of the four inputs forms the core of a company's marketing system of products, prices, locations, and promotions. The marketing mix can be a flexible combination of variables. They are subject to consumer behavior, trade factors, competition, and government regulatory measures.
9. Integrated approach:
Marketing activities need to be coordinated with other functional areas of the organization. Functions such as production, finance, and research. Purchasing, storage and public relations (PR) are integrated with marketing. This can help you reach your organization's goals. Otherwise, it will end up in an organizational conflict.
10. Commercial and non-profit organizations:
As the concept of social marketing is becoming more important, social marketers are finding useful new ways to apply marketing principles. Commercial organizations also employ cause-related marketing to build long-term relationships with consumers. Corporate organizations such as educational institutions, hospitals, religious institutions, and charitable trusts have also found significant uses in marketing. Therefore, marketing can be applied to both business and non-business organizations.
11. Before and after production:
Identifying consumer needs and needs is a key task for marketing managers. Production activities are adapted to the needs of those consumers. Therefore, marketing precedes production. Marketing helps in the distribution of products following production. Therefore, production activities and marketing activities are closely related.
Market Type
- Physical market. The physical marketplace is in which the client and supplier physically meet, and each party are involved in the transaction in alternate for cash. There are few proper examples of department shops, buying malls, retail stores, etc.
2. Virtual market / internet market. In today's business environment, these types of markets are growing rapidly. This is an online platform, where sellers offer goods and services over the Internet. Buyers and sellers do not have to physically meet or interact with each other. Examples are Freelancer.com and Amazon.com.
3. Auction market. The auction market is where sellers and buyers show the lowest and highest prices they want to exchange. This exchange takes place when both the seller and the buyer agree on a price. A good example is the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE).
4. Consumer market. This market type refers to the marketing of consumer goods and services consumed by individuals and families. An example of the consumer market
- FMCG is ready to cook meals, newspapers, magazines and more.
- Durable consumer goods include refrigerators, televisions, and personal computers.
- Soft goods are shoes and clothes,
- Services include hotels, barbers, schools, colleges and more.
5. Industrial market. Industrial markets include business-to-business sales of goods and services. These marketers do not target the consumer market. Some examples of the industrial market include finished products such as office furniture.
- Sale of raw materials for companies such as gas and chemicals
- Providing services to businesses2business such as security agencies, audit and legal services.
6. Black market. Like black money, the black-market deals with illegal drugs and weapons.
7. Intermediate goods market. These markets deal with the sale of raw materials that require further processing to produce the finished product.
8. Financial market. This is a wide range of markets known as financial markets. A place to handle current assets such as stocks and bonds.
Perfect competition refers to a market situation in which there are a large number of buyers and sellers of homogeneous products.
The price of a product is determined by the industry by the forces of supply and demand. For example, if you need a pen, there should be several shops selling pens. Under the conditions of perfect competition, every seller must sell the same quality of the pen at a uniform prevailing price on the market. You can buy a pen from any store at the price Rs. 10. If another shopkeeper charged Rs. 12 for the same quality of the pen, nobody buys from him. But if the shopkeeper charged Rs. 9 all buy pens from that particular store. But both of these situations are unrealistic.
There must be one price dominant throughout the market. Therefore, full competition in the market structure is characterized by a complete lack of competition between individual companies.
Definition:
It is identified by the existence of the many firms; they all sell an identical product an equivalent way. The supplier is the one who accepts the price."- Vilas
Such market gains when the request for product of every producer is totally elastic. Mrs Joan Robinson.
It is a market condition with an outsized number of sellers and buyers, similar products, free entry of enterprises into the industry is ideal knowledge between buyers and sellers of existing market conditions and free mobility of production factors between alternative uses. Lim Chong-ya
Assumption:
The following assumptions for a fully competitive market:
1. A large number of buyers and sellers:
This affects single buyers and sales. When a company enters or leaves the market, there is no impact on the supply. Similarly, if a buyer enters or withdraws from the market, demand will not be affected. Such affects individual buyers and sellers.
2. Homogeneous products:
The second assumption of perfect competition is that all sellers sell homogeneous products. In this situation, the buyer has no reason to prefer the product of one seller to another. This condition exists only if the goods have a clear chemical and physical composition, that is, Substances of the specified grade: salt, tin, wheat, etc.
3. No discrimination:
Under complete competition in the market, sellers and buyers, sellers do freely. It means that buyers and sellers must be willing to deal openly with each other to buy and sell at market prices. This may be true of everything you might want to do so without offering special deals, discounts, or favours to selected individuals.
4. Perfect knowledge:
The competitive market is me (buyers and sellers are in close contact with each other. It means that, on the part of buyers and sellers, there is complete knowledge of the market. This means that many buyers and sellers in the market know exactly how much the price of the goods is in different parts of the market.
In other words, without the knowledge of each buyer and seller of the price at which the transaction is taking place, and the price at which the other buyer and seller are willing to buy or sell.
5. Industry FREE entry and exit:
In the long run, under full competition, the company can enter or exit the enterprise. There is no let or hindrance to the enterprise with regard to its entry into or exit from the market. In other words, the company has no legal or social restrictions. A large number of sellers is possible only if there is a free entry of the enterprise.
6. Perfect mobility:
There must be full mobility of domestic production factors that ensure uniform production costs throughout the economy. That means you are free to seek employment in any industry where different factors in production might like you.
7. Profit maximization:
Under perfect competition, all companies have a common goal of maximizing profits. Thus, there is a lack of social welfare of the general public.
8. No sales cost:
Under perfect competition, there is no sales cost.
9. No transportation costs:
Transportation costs between the sellers should not be. If transportation costs are present buyers are prevented from moving from one seller to another to take advantage of the price difference, which means that transportation costs do not affect the pricing of the product. In other words, these are always prices uniform in the market.
Pure and Perfect Competition:
Many economists choose to use the term "free market" rather than" pure competition.", American economists particularly prefer the term pure competition over the term perfect competition, but the term perfect competition seems to be popular with British economists.
But Professor Chamberlain distinguished between perfect competition and pure competition. Contains pure competition, according to Professor Chamberlain:
(I) numerous buyers and sellers,
(II) Homogeneous products,
(III) Free entry and exit of industry,
(IV) free from checks,
(V) lack of sales costs, and
(VI) lack of transportation costs.
R.A. Professor Bilas also distinguished between perfect competition and pure competition “perfect competition means pure competition, but we also consider other characteristics. Pure competition implies a certain degree of perfection, that is, the complete absence of monopoly.
In general, perfect competition leads to perfect resource mobility and perfect knowledge concepts. Similarly, professor Baumol defined pure competition as industry. Many companies are said to operate under pure competition when there is, product homogeneity, freedom of entry and exit, independent decision making.”
Based on these definitions, we can say that pure competition exists when an element of Monopoly is not present in the market. Perfect competition is wider than pure competition, including the absence of monopolies, as well as perfection in many other ways, such as full mobility of production factors and full knowledge of the market. Therefore, producers have complete knowledge of the quantity and quality of available production factors, as well as the prices that can be charged for their products.
Therefore, the distinction between pure competition and perfect competition is simply of a degree, and all assumptions of pure competition are also assumptions of perfect competition the concept of a complete competition system includes one more assumption: viz. Be perfect knowledge by both buyers and sellers of prevailing market prices, and different range and quality of various goods, services and production factors.
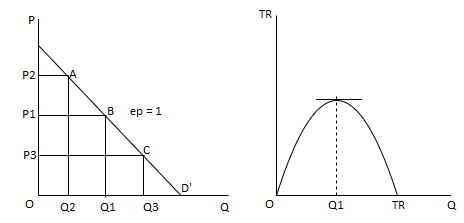
From the market demand curve, it's possible to derive the entire expenditure of the buyer, which forms the entire income of the enterprise that sells a specific commodity.
The total revenue is the product of the quantity sold and the price, and if the market demand is linear, the total revenue curve will be a curve that first tilts upwards, reaches the maximum point, and then begins to decrease (figure 2.40). For example, in Figure 2.39, the entire revenue at price P2 is that the area of the rectangle P2AQ20.
Of particular interest to the theory of the company is the concept of marginal income. Marginal revenue is a change in the total revenue that occurs as a result of selling additional units of goods.
Graphically marginal revenue is the slope of the total revenue curve at any level of output. If the demand curve is linear, it is clear that in order to sell an additional unit of x, its price must go down.
Since the entire quantity are going to be sold at a replacement low price, the marginal revenue is going to be adequate to the worth of the additional unit sold minus the loss from selling all previous units at a new low price somewhere qn is the quantity sold before the price falls.
MR = Pn+1 – (Pn – Pn+1) Qn
Obviously for all prices, MR is less than the price if (Pn–Pn+1) (=ΔP) is positive and Qn is positive.
Graphically marginal revenue can be derived from the demand curve as follows: Select any point of the demand curve (such as Point A) and from there draw perpendicular lines on the price and quantity axes (AP and AQ, respectively). Then find the midpoint of the vertical PA.
In Figure 2.41, the midpoint of PA is C draw a straight line from D to C and extend the vertical AQ until you cut it (at Point B in Figure 2.41). This line is the marginal earnings curve. To see it, we first note that the entire income in price P (=OPAQ) is that the sum of the marginal income of all individual units (=ODBQ) two areas, OPAQ, and ODBQ are actually equal; since they have a common area OPCBQ, and the Triangle DPC and CAB are equal (they have a corresponding angle equal). One side is equal by construction PC=CA).
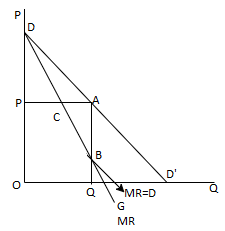
Thus, the MR curve is a line DCBG, which can be derived by coupling the midpoint of the perpendicular drawn from the demand curve to the price axis. In other words, the MR curve cuts such a vertical at its midpoint (if the demand is a straight line).
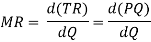
Or
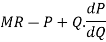
If the demand curve is linear its equation is
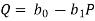
Or, solving for P,
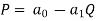
Where
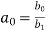 and
and 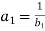
Substituting P in the total revenue function we find
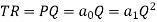
The MR is then
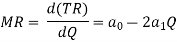
This proves that the MR curve starts at the same point (a0) as the demand curve, and that MR is a straight line with a negative slope that is twice as steep as the demand curve slope. This is the same result we established above using simple geometry.
Total Revenue, Marginal Revenue and Price Elasticity:
We said that if the demand curve is falling, the TR curve will increase first, reach the maximum value, and then begin to decrease. You can use the previous derived relationships between MR, P, and e to establish the shape of the total revenue curve.
The total revenue curve reaches its maximum level at e=1.
MR = P (1 – 1/1) = 0
If E > 1, the total revenue curve has a positive slope, that is, it is still increasing, so if we consider the following, we have not reached its maximum point
P>0 and (1-1/E)>0; therefore Mr > 0
For E, 1, the total revenue curve has a negative slope, that is, it is falling.
P>0 and (1-1/E) <0; therefore Mr > 0
Then summarize these results as follows:
If the demand is inelastic (e<1), the increase in price leads to an increase in total revenue, and the decrease in price leads to a decrease in total revenue.
If the demand is elastic (e>1), the increase in price leads to a decrease in total revenue, and the decrease in price leads to an increase in total revenue.
If the demand has a single elasticity, then for e—1, then MR=0, so the total income is not affected by the change in price.
Allocation efficiency under Perfect Competition
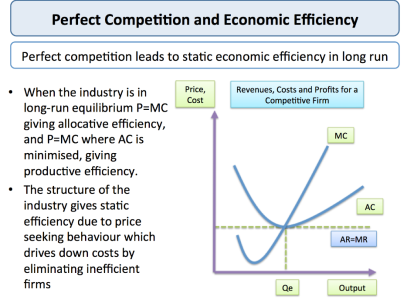
In free market, market cost reflects the complete s of resources and freedom of entry and exit, full access to information by all participants, homogeneous products and therefore the incontrovertible fact that nobody buyer or seller, or a gaggle of buyers or sellers, has any advantage over others.
Perfect competition is often used as a measure to match with other market structures, because it displays a high level of economic efficiency. Allocation efficiency:
We can see that within the short and future, the worth is adequate to the incremental cost (P=MC) and thus the allocation efficiency is achieved.
The ruling price maximizes the excess of consumers and producers.
No one can make better without making other agents a minimum of as worse–i.e., we achieve Pareto optimum allocation of resources.
Production efficiency:
Production efficiency occurs when balanced output is supplied at a minimum monetary value. This is achieved within the future for a competitive market.
Companies with higher unit costs might not be ready to justify remaining within the industry as market prices are pushed down by the force of competition.
Dynamic efficiency:
That is, there's little scope for innovation designed purely to differentiate products and permit suppliers to develop competitive advantages within the market and establish monopoly power.
Perfect competition-the chain of reasoning
Is perfect competition good for economic efficiency?
Some economists believe that perfect competition isn't an honest market structure for top levels of research and development spending and therefore the resulting product and process innovation.
Indeed, monopolistic or oligopolistic markets could also be simpler within the end of the day in creating an environment for research and innovation to flourish. Cost-cutting innovation from one producer is completed immediately, assuming perfect information, without transferring costs to all or any other suppliers.
That said, a competitive market would offer discipline for companies to regulate costs, minimize waste of scarce resources, set high prices and refrain from exploiting consumers by enjoying high profit margins. During this sense, competition can stimulate improvements in static and dynamic efficiency over time.
The future of perfect competition therefore exhibits an optimal level of economic efficiency. However, for this to be achieved, all of the conditions of full competition, including the relevant market must hold.
A. Short run
A monopolist maximizes his short-term profits if the following two conditions are met first, MC equals Mr. Secondly; the slope of MC is larger than that of Mr at the intersection.
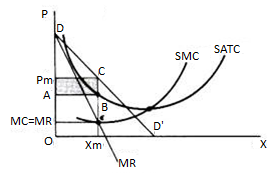
In Figure, the equilibrium of the monopoly is defined by the point θ at which MC intersects the MR curve from below. Thus, both conditions of equilibrium are met. The price is PM and the quantity is XM. Monopolies realize excess profits equal to shaded areas APM CB. Please note that the price is higher than Mr
In pure competition, the company is the one who receives the price, so its only decision is the output decision. The monopolist is faced with two decisions: to set his price and his output. But given the downward trend demand curve, the two decisions are interdependent.
Monopolies set their own prices and sell the amount the market takes on it, or produce an output defined by the intersection of MC and MR and are sold at the corresponding price. An important condition for maximizing the profits of monopolies is the equality of the MC and the MR, provided that the MC cuts the MR from below.
Formal derivation of the equilibrium of the monopolist
Given the demand function
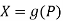
Which may be solved for P
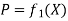
And given the cost function
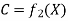
The monopolist aims at the maximization of his profit
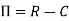
(a) The first-order condition for maximum profit
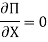
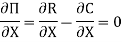
Or
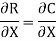
That is 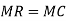
(b) The second-order condition for maximum profit
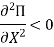
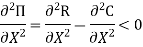
Or
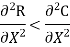
(b) from
Clearly 4 < 0.
We can now revisit the statement that there is no unique supply curve for the monopolist derived from his MC. Given his MC, the same amount could be offered at different prices depending on the price elasticity of demand. This is graphically shown in Figure 6.3. Quantity X is sold at price P1 if demand is D1, and the same quantity X is sold at price P2 if demand is D2.
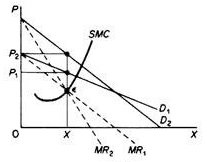
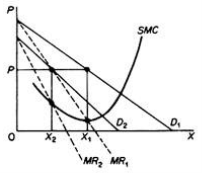
So, there is no inherent relationship between price and quantity. Similarly, given the monopolist MC, we can supply various quantities at any one price, depending on the market demand and the corresponding MR curve. Figure 6.4 illustrates this situation. The cost condition is represented by the MC curve. Given the cost of a monopolist, he would supply 0X1 if the market demand is D1, then p at the same price, and only 0X2 if the market demand is D2 B. Long-term equilibrium:
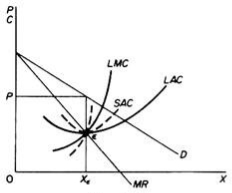
In the long run the monopolist will have time to expand his plants or use his existing plants at every level to maximize his profits. However, if the entry is blocked, the monopolist does not need to reach the optimal scale (that is, the need to build the plant until the minimum point of LAC is reached), neither does the guarantee that he will use his existing plant at the optimum capacity. What is certain is that if he makes a loss in the long run, the monopolist will not stay in business.
He will probably continue to earn paranormal benefits even in the long run, given that entry is banned. But the size of his plant and the degree of utilization of any plant size depends entirely on the market demand. He may reach the optimal scale (the minimum point of Lac), stay on the less optimal scale (the falling part of his LAC), or exceed the optimal scale (expand beyond the minimum LAC), depending on market conditions.
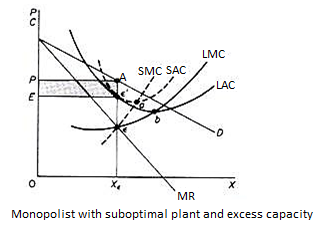
Figure 6.5 shows when the market size does not allow the monopolist to expand to the minimum point of Lac. In this case, not only is his plant not optimal (in the sense that the economy of full size is not depleted), but also the existing plant is not fully utilized. This is because on the left of the minimum point of the LAC, the SRAC touches the LAC at its falling part, and the short-term MC must be equal to the LRMC. This happens in e, but the minimum LAC is b, and the optimal use of the existing plant is a. Since it is utilized at Level E', there is excess capacity. Finally, figure 6.7 shows a case where the market size is large enough for a monopolist to build an optimal plant and be able to use it at full capacity.
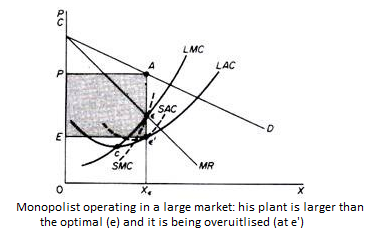
In Figure 6.6, the scale of the market is so large that monopolists have to build plants larger than the optimal ones to maximize output and over-exploit them. This is because to the right of the minimum point of LAC, SRAC and LAC is tangent at the point of positive slope, and SRMC must be equal to LAC. Thus, plants that maximize the profits of monopolies are, firstly, larger than the optimal size, and secondly, they are over-utilized, which leads to higher costs. This is often the case with utility companies operating at the state level.
It should be clear that which of the above situations will appear in a particular case will depend on the size of the market (given the technology of monopolists). There is no certainty that monopolies will reach their optimal size in the long run, as is the case with purely competitive markets. In Monopoly, there is no market force similar to those of pure competition that will lead companies to operate at optimal plant size in the long run (and utilize it at its full capacity).
Concept of supply curve under monopoly
The supply curve under incomplete competition or Monopoly is not unique.
This is due to the fact that, unlike full competition, the price is determined simultaneously with the volume of goods produced, and the price is not given to the enterprise under monopoly or Monopoly competition.
Here the company is the price manufacturer of her products. Therefore, the company fixes the price at which it will get the maximum profit. The supply of goods is determined by the market demand for its products. Therefore, it is impossible to talk about the supply curve under monopoly or Monopoly competition.
The output supplied by the producer under such exclusive circumstances depends on the market demand conditions of his product and draws a unique supply curve (and supply schedule).
Therefore, it is not quite applicable to the causes of incomplete competition, monopoly competition, monopolies and oligopolies. This is because the concept of the supply curve refers to questions about the amount of goods a company supplies at various given prices.
Under various sorts of incomplete competition, individual companies don't take the worth as given and aren't mere quantity adjusters. In fact, under various forms of incomplete competition, the company sets its own prices. For companies under incomplete competition, it is not a matter of adjusting output or supply at a given price, but choosing a combination of price output that maximizes profit.
Commenting on the relevance of the supply curve, professor Baumol writes: the supply curve is, strictly speaking, a concept usually relevant only in the case of pure (or complete) competition...The reason for this lies in its definition—the supply curve is designed to answer the form question, “to answer the form question how much would solidify the supply if it encounters a price that is fixed in P dollars. But such questions are most relevant to the behavior of companies that actually deal with prices.”
Years ago in 1920s, the classical theory of price included two main models: pure competition and monopoly.
The double occupancy model was considered an intellectual exercise, not a real-world situation. The general model of economic behavior from Marshall to Knight was pure competition.
In the late 1920s, economists became increasingly frustrated with the use of pure competition as an analytical model of business behavior. It was clear that pure competition could not explain some empirical facts.
Moreover, the practice of advertising and other sales activities cannot explain the widely used businessman pure competition. Finally, as we predict when a pure competitive model will continuously reduce costs, companies have expanded their output with reduced costs, but never grow infinitely large.
In particular, it was this last fact of falling costs that created discontent and caused a widespread reaction to pure competition theory. This discontent caused a long series of debates and the publication of numerous articles that formed the “great cost controversy of the 1920s.
The earliest summary of the cost controversy should be found in Piero Sraffa's article. Sraffa pointed out that the falling cost dilemma of classical theory can be theoretically solved in various ways by introducing a demand drop curve for individual companies, a general equilibrium approach that appropriately incorporates the shift in costs induced by external economies (firms and industries), or by introducing a U-shaped sales cost curve into the model.
Of these solutions, Sraffa was the first to adopt, that is, a model with a negative personal demand curve that was more operationally and theoretically more plausible. The same line is a work published in 1933, in which it was adopted independently by Chamberlin and Joan Robinson.
It should be noted that both writers arrive at the same solution for enterprise and market equilibrium, but their analytical approach and methodology are quite different.
Assumption:
The fundamental assumption of Chamberlin's horde model is the same as that of pure competition except for the homogeneous product.
It can be summarized as follows:
- The seller's products are differentiated, but they are close replacements to each other.
- Entry and exit of companies in the group is free.
- . The company's goal is to maximize profits both in the short and long term.
- Factors and the price of technology are given.
- The company is assumed to behave as if it knows the demand and cost curves for sure.
- A long run consists of several identical short periods, which are assumed to be independent of each other, in the sense that the decision of a certain period does not affect the future period and is not affected by past actions. An optimal decision for one period is an optimal decision for another. Thus, by assumption, the maximization of short-term profits implies the maximization of long-term profits.
This requires that consumer preferences be evenly distributed among sellers with different tastes, and that differences between products do not create a difference in cost. Chamberlin himself realizes that the"heroic"assumptions are unrealistic, and he relaxes them at a later stage
Here are certain reasons that have led to the emergence of oligopolies. These are:
1. Large-scale investment of capital:
The number of companies in the industry may be small due to the large requirements of capital. Entrepreneurs will not want to bet heavily on an industry that, in addition to output to existing ones, is likely to push prices down.
In addition, newcomers may be afraid to provoke a price war by existing companies in the industry. It is always true that in the midst of differentiated products, it is difficult to make a new product.
2. Managing essential resources:
Few companies control some indispensable resources that may allow them to secure several benefits in cost over all others or this allows them to operate advantageously at a price that others cannot survive.
3. Legal restrictions and patents:
In the Public Works sector, the entry of new enterprises is closely regulated by the granting of certificates by the state. This policy of elimination of rivals may be due to small-scale uneconomic or duplication of services. Another factor for the emergence of oligopolies is the patent rights that some companies acquire in matters of some goods.
4. Economies of scale:
Another factor that causes the emergence of oligopolies is large enterprises. In some industries, some companies can meet the entire demand for products. Many companies are likely to meet demand, and small businesses may not be able to secure an economy of large production. In those industries where there is a lot of mechanization and there is quite a large economy, a small number of companies will survive.
Companies achieve such a huge size that some of them can meet the overall demand. For example, automobile, steel industry, petroleum etc. Oligopolies can also be found in local markets. In small towns, some companies may be enough to meet the demand, for example, gasoline, banks, suppliers of building materials. The market is small, and therefore some companies can be satisfied.
5. Outstanding entrepreneurs:
In some industries, some excellent entrepreneurs whose cost is lower than inferior rivals sell under these entrepreneurs, eliminating most of the rivals.
6. Merger:
The main motives of the merger include increased market power, more resources, economies of scale, and market expansion.
7. Difficulties in entering the industry:
Finally, oligopolies can exist due to the difficulty of entering the industry. One big difficulty in some industries is the large requirements for capital. Businessmen do not like to venture into those industries, even of one company, could push down prices to such an extent that makes it unprofitable for all. They may also be afraid of the price war their entry might cause from existing companies in the industry. Also, in the presence of an already established and well-established brand, the difficulty of marketing a new product or a new brand can lead to future participation in the industry.
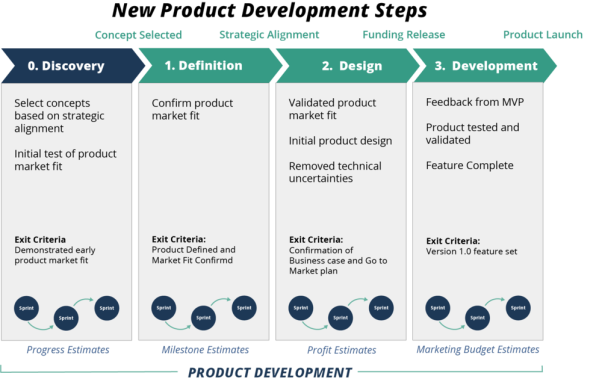
What is New Product Development?
New product development (NPD) usually follows the product development technique. Frequently divided into degrees, phases, or steps, which allow the enterprise to give you product thoughts. Refine the definition. Layout and develop it. And market it.
New Product Development Process in Four Steps
What are the hallmarks of a hit new product development?
- It starts off evolved with a new product idea (employer, customer, or partner) that meets the needs of the patron
- The fine new product design idea is consistent with product improvement method
- Thoughts are nurtured by a bendy and lightweight manner for concept technology
- Agile cross-practical groups work in the new product development procedure
- The result is a brand-new product that pleases clients whilst growing their commercial enterprise.
The product development process involves an entire set of activities for an organisation to invent, conceptualize, broaden, and bring a new product idea to marketplace. Developing a brand-new product entail extra than only a manner. It is also innovation, product method, move-functional groups and decision making.
Revolutionary new product ideas, or ideas, can come from customers or in labs and workspaces. New product improvement is the ability for a company to recognize those early product principles and gift them to their customers reliably and predictably, however usually to satisfy their wishes.
Similarly, to the product development manner, npd also consists of elements such as product improvement method and product portfolio management. Pass-practical teams often come collectively to increase new merchandise, disband, and allocate resources to different initiatives.
The most important issue for an effective new product technique is to have right governance to pick a brand-new product idea. Enough funds to grow those ideas. And the manner of validating and prioritizing them.
What are the four steps of NPD?
To this point, the product development manner has 6 or 7 steps, with long and tedious evaluations and gates between every step. In new product improvement, it is essential to emphasise the first step (that is normally the end result of product portfolio management making plans activities). These critiques were the hoops that the crew had to go through to continue to justify the team's lifestyles to the supervisor of the new product development process.
If the product under attention is probably to be replaced or impact the present-day product set in the marketplace, a radical evaluation of the product lifestyles cycle (and advertising and marketing blend) will bring about cannibalism of comparable products. You want to ensure that there is little or no.
Agile corporations these days might not be able to have enough money frequent reviews that don't add price to their merchandise. Establishments get better carrier through having a minimally possible procedure that emphasizes the front quit of innovation that creates truly new products.
The minimum feasible technique of a typical (incremental) product development system has three steps. For companies that want to emphasize bold new products, the product development technique has four foremost steps, and the front stop has the additional step of discovery. This framework template (above) outlines the method of those four steps for new product improvement.
Step 0: find out (identify thoughts and display thoughts)
The activities of the discovery step of the npd technique no longer only generate ideas for new product ideas, however additionally scrutinize them (this applies to entirely new possibilities that may have long passed out of the enterprise). Via the usage of effective product discovery techniques, you can ensure that your product market suits into your new product thoughts. That is step one in idea generation and should be full-size.
With discovery, it can look like it takes longer to get to market, but despite the fact that it seems like it is taking longer to increase, in case you take the right steps, you'll see a big development. Brainstorming is blanketed at this stage, but it's now not the simplest supply of thoughts.
- Product thoughts come from the lowest of the organization upwards
- Greenlight ideas if it suits your strategy and has a sufficient marketplace length
- A small venture group with a wide variety of charters is ideal for developing new products.
- Teams use agile techniques to refine new product thoughts
- Generation is developed and certification factors are set up as a vital part of the new product improvement procedure.
- Product / marketplace suitability is examined
Step 1: Definition (Business Analysis and Concept Development)
- The activities in the process definition step thoroughly explore the proposed new product ideas in the fuzzy front end.
- Concepts are tested early in new product development activities and ideas are screened early
- The team is agile and is liberal to innovate and iterate to refine idea generation to at least one approach.
- Technology is tested to identify key risks
- The project has the right resources in place early in the new product development process.
- The project has nothing to prevent rapid and iterative development.
- May be meaningful commercial
By the end of this step in the customer requirements process, the team needs a clear leader with entrepreneurship. Teams have predictable time to revenue, high potential market share, and revenue potential make a difference to the company, as shown by early market testing with potential customers. You need to show management that it is important enough for you. To justify the development of new products. To calculate the ROI, the team also needs to estimate the development cost at this stage.
The proposed business model should be adjacent to the company's overall model and support all investments in the new product development process. In short, the business model and marketing strategy of a project should generally resemble the way a company does business. You need to perform market research, competitive analysis, and target market analysis. At this stage, metrics and KPIs are established to validate the business case and set expectations for the product team.
At the end of this step, the development team easily checks in to management to establish project boundaries and ensure that the proposed project meets the company's current strategic priorities. The company is currently investing capital to take it to the next level.
Step 2: Design
- The tasks at this step in the product design process are:
- Technology is scrutinized by product concept
- Established architectural design and performance
- Agile development continues to sprint and customer feedback as an integral part of new product development
- The team creates an estimate of the total cost of development and launch
- Confirmed and quantified commercial potential
By the end of this step in NPD, the team should perform prototyping and test users and models to ensure compatibility with the desired market and marketing strategy. They needed to not only identify use cases, but also where the solution was most suitable for the market. Test marketing must be complete. Technical and market risks associated with the project need to be eliminated or significantly reduced. You need to establish product pricing to support your business margin requirements.
To move on to the next step, the team also needs to show that the basic design has been completed, the costs associated with product development and marketing have been estimated, and the potential benefits of the design phase of new product development have been estimated. I have. This is usually summarized in a spreadsheet model and usually relies on standard templates created by financial groups.
During the final check-in of this phase, the team will define the product in more detail and demonstrate its technical feasibility. Again, a company must invest the largest amount of capital ever to launch a product (including the cost of launching the product).
Step 3: Development (including commercialization)
- The tasks during the process development steps are:
- Development of feature-length complete products
- Perform testing and validation at this stage of the new product development process
- Go to Market plan improvement
- Development of customer success function
- Creating a launch plan
During the development phase of the process, the product is fully realized and can be scaled to the needs of real customers. This is the guts of the merchandise development process. In this phase, the team repeatedly completes the development and testing of the final product (and process).
If the product is a software product, it is a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), testing its feasibility and getting early feedback from the market and distributors or partners prior to the launch of the full-featured version. This allows the team to perform a second or third iteration before a large launch.
If this is a manufactured product, a tooling is created and the pre-manufactured prototype is tested. You also need to perform a final check of suitability for your marketing strategy. This step ends when the product is launched.
Tips for improving New Product Development
- Have a long-term vision of the new product development process
- Integrate technical and customer perspectives into NPD's leading executive team
- Properly support NPD Eat the money
- Create a product portfolio strategy to guide new development
- Make sure your organization is the right size for your task
- Have a way to capture customer feedback
- Avoid the tendency to overcommit features
- Strong New Product Development
What are the characteristics of the NPD organization?
In addition to having a solid process, companies that create innovative new product streams are agile in product development (small "a" agile). In other words, we can respond quickly to changes in the market and technology. This is especially important in the development of new products. The shorter half-life of skill sets allows effective new product developers to learn and master new skills. For example, you can rethink old technology, apply it to new markets, and rethink it. Products that compete in the market adjacent to the core product to maintain a lead in the new product development process.
An undervalued feature of effective new product development organizations is their effectiveness in program management and leadership. Having a product development process is not a substitute for experienced and talented product managers and product owners. Having people with these products and customer-oriented talents and skill sets is essential to making good product portfolio decisions. And, of course, successful companies also have the technical skills and resources they need to execute their development products and turn their ideas into real-world products.
The best NPD organizations also have market agents within the product development process. They build customer feedback on product development from the beginning of the process. There are also ways to translate customer feedback into design, such as by design thinking or otherwise.
Companies that succeed in product development or NPD also have a strong culture of senior management sponsorship. These companies have senior management who recognize early-stage products and create protected spaces to nurture them at all stages of the new product development process. They support the best ideas from the beginning and get the money and resources they need to succeed. It's also a good idea to have an appropriate escalation process in case your team is exposed to unexpected risks.
How do you create innovative and truly new products?
A way for more mature companies to come up with ideas for a range of product concepts is to rethink NPD in terms of venture capital models. Think of a team developing product development innovations within your organization, as do so many start-ups funded and monitored by venture capital.
Internally, new product improvement initiatives are competing for unallocated investment using a venture capital version. In this model, a small wide variety of executives continuously display bottom-up ideas to elevate the most promising investment.
Inside this version of the brand-new product development method, agencies need a governance shape that continuously selects teams to pursue new thoughts and creates a blanketed space for innovation in product improvement. Subsequent, we need a system to validate new ideas and discover their capacity. Eventually, we need an agile financing model with a large price range allocated for unpredictable innovation.
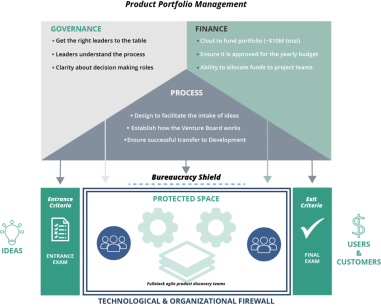
Step 0. Discovery
- Governance: Invite the right leaders to the desk to monitor inclined innovations. They allocate capital from the pool of mission finances as needed. This team is known as an undertaking board. They'll or won't oversee all of product development
- Manner: set up a technique for receiving and choosing thoughts. Use clear front and exit criteria to become aware of a way to flow your ideas into improvement. Agile with a small “a” – enables your crew to do their pleasant, whilst making sure the control they offer.
- Finance: Create a specific investment for your strategic innovation portfolio and approve it for the duration of the finances 12 months. Make it massive enough to begin at the least 3 projects (kind of about $ 10 million in keeping with 1,000 employees). Every other rule of thumb is to allocate 10% of product development.
- Project boards control the innovation portfolio. It turns a software or section for funding right into a green mild and considers useful resource allocation and finances. Venture boards perform excessive-level budget opinions on a regular foundation two times 12 months for a few groups. It's also the responsibility of this board as a govt to facilitate the cultural changes had to guide a portfolio of modern ideas. They very own this portfolio and are tasked with maintaining this attitude.
How do you prepare a brand-new product development assignment?
The high-quality way to arrange product development is to have a move-useful team this is empowered and has broad choice-making authority within pre-mounted parameters. That is an exception control approach, which involves a clean and easy escalation process whilst a project deviates from a predefined set of quantitative desires.
At the start of a product development project, the development team and senior control agree on key factors to the success of the product. The leader of the development team is typically the product supervisor or product proprietor, however the senior control in question can encompass the CEO, CMO, CTO / CIO of a start-up, or a director of a big organisation. These agreed dimensions of a product development challenge may also encompass positive critical functions, goal development expenses, great measurements, favoured speeds, and project timeframes. The following parent suggests those 5 dimensions of the task as polygons with one side in every size.
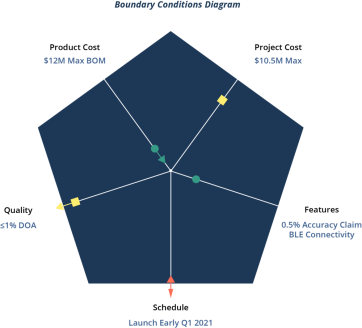
Project as a polygon with one side for each dimension
The team and management then agree on clear and quantitative goals for every of those components to manual product development. Those are the boundary situations and standards for teams and control to measure fulfilment. For example, in the discern above, the group and supervisor agreed at the fine threshold. The average defect rate is 1% or much less. That is a boundary circumstance for pleasant parameters. Those conditions integrate to shape an agreement that specifies what the group gives and what control expects.
As soon as the boundary situations are set and the product development assignment is initiated, management must depart the group in area as long as the crew keeps to count on the venture to reach its desires. If the undertaking does now not appear to meet boundary conditions for one or extra of the 5 dimensions (this is known as a boundary destroy), the crew ought to do the following:
- Notify admin at once (hours to days, not days to weeks)
- We propose a solution for breaking obstacles.
These communications trigger a speedy hearth procedure out of variety. That is an escalation procedure designed to get your team lower back on course fast if you anticipate breaking barriers.
After receiving a message from the group that senior management may wreck limitations, together with pointers on a way to enhance the scenario, managers can agree or disagree with the group's suggestions. If control has the same opinion, every facet will see new quantitative measurements of volatile boundary conditions and the assignment will pass ahead with new specifications.
It's far essential that this procedure takes vicinity within the sprint and that the retroactive date of that dash does now not circulate.
If control disagrees with the team's notion, a face-to-face meeting will comply with in which the team and control negotiate a new contract and set new boundary conditions for the project. The group will then retain the assignment based on this new settlement.
This manner requires senior management to respond fast to out-of-variety communications from the crew. This short and agile control style.
Is there an alternate-off between modern new merchandise and speed?
- A few businesses consider that there may be a dichotomy among innovation and pace, so they take a short follower method to product development or "me too" strategies. They trust that slowing down the npd process to introduce definitely new and modern products will growth time to marketplace. This is the classic false dichotomy.
- Businesses that create genuinely progressive merchandise, which includes amazon with the platform, apple with iTunes, and Uber’s drive-sharing provider, are creating their very own markets. It is impossible to lag in the back of the marketplace created with the aid of your company.
- New technologies often assist boost up product development projects to marketplace, even for less innovative merchandise. Now not handiest do new technology create services and products, however some of them also lessen time to market.
- With the above technique, by combining an agile team controlled by means of exceptions with right governance, financing, and approaches, corporations can attain each revolutionary merchandise and fast market launch.
- One of the keys to taking advantage of each is to have a priority listing of only the maximum important functions. Narrowing down the product definition to 3 essential functions will speed up npd.
Do you've got any suggestions for enhancing NPD?
- Have a long-term vision
It takes patience to increase a new product. After the start-up stage, the "quick win" mind-set doesn't work. Developing a circulation of new products over time calls for a vision, a method for how the enterprise gets there, and a price range and governance structure to guide and execute the strategy.
2. Combine technical and consumer perspectives into NPD's main executive team
Technology businesses tend to be era-driven, however the proper executives to act as a board of administrators to approve investments in NPDs (task boards) have technical talent sets and patron (product management) talent sets. Each are included. Make certain that the customer's perspective exists when making selections approximately product development, particularly product choice.
3. Support NPD with the right amount of cash
Sure, it's primary, however what number of organizations are nurturing early-level NPDs to get the first-class out of their product portfolio? Seed funding for brand new thoughts tied to company-level budgets and techniques is important to grow the brand-new product idea into a complete-fledged product within the marketplace thru the new product development system.
4. Create a product portfolio method
Groups that create streams of latest merchandise strategically allocate investments inside their product portfolio. It's far divided into core businesses, products in adjacent markets, and absolutely progressive new merchandise. Making an investment in those diverse categories is frequently strategically determined primarily based on the business enterprise's hazard profile.
5. Make certain your agency is the right size for your project
Effective NPD depends on enough sources. Large agencies often spend numerous resources maintaining present products and feature constrained abilities wanted for the following day's products, proscribing product development for surely new products also, too many critical assets are overloaded, along with professionally professional coders. The right aggregate of product development is to area those key participants in no extra than two projects at a time.
6. Have a manner to capture patron comments
Whether its layout wondering or different types of marketplace-driven product definition, it's imperative to offer a lifeline to customers with an ambiguous the front quit. 2nd, it is also critical to have the approach to convert customer feedback into a brand-new product concept with the pleasant-promoting features.
7. Keep away from the tendency to overcommit features
Too many businesses promise a month of characteristic and then under delivery. Start with MVP and get it into your customers as quickly as feasible as part of the product development technique. It helps clients recognize which capabilities are essential. Overcommitment and under delivery aren't well pondered inside the brand. A better opportunity is to fulfil your promise and then regularly enhance your product over time.
The product life cycle is the process of product life from the time a product is developed until it is removed from the market.
Whether you're looking at your parents' old VHS tapes or buying a new smartphone, you'll participate in and experience different stages of the Product Lifecycle (PLC).
When a product enters the market, it often goes unnoticed by consumers, but it has a life cycle from new and convenient to eventually becoming unmarketable. This process happens continuously. Products continue from the initial stages of introduction until they decline and eventually become obsolete.
But how does Product Lifecycle actually work, and how does analyzing it help businesses?
What is the Product Life Cycle?
The product life cycle is the process from when a product is first introduced to the market until it declines or is removed from the market. There are four stages in the life cycle: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline.
Some products may remain at maturity for a long time, but due to several factors such as saturation, intensifying competition, reduced demand, and reduced sales, all products will eventually be phased out of the market. It will be abolished.
In addition, companies can use PLC analysis (examining the product life cycle) to develop strategies to maintain product life and modify products to meet market demand and technology under development. Increase.
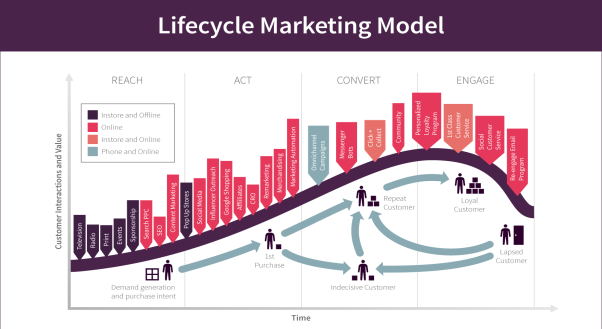
Life Cycle Marketing Model
Four Stages of Product Life Cycle
In general, a product life cycle has four stages, from product development to depreciation and ultimately withdrawal from the market.
1.First of all
Once a product is developed, the first step is its implementation. At this stage, the product has been released to the market. When a new product is released, it is often a high stakes time in the product life cycle-although it does not necessarily achieve or destroy the final success of the product.
In the implementation phase, marketing and promotion are high, and the company invests the most in product promotion and in the hands of consumers. This is probably best featured on Apple (AAPL)-Get Apple Inc. (AAPL) reports a well-known launch presentation highlighting the new features of a new product (or an upcoming product).
At this stage, you can first see how consumers react to your product, whether they like it, and how successful it is. However, it is also often a large spending period for a company, with no guarantee that the product will pay its own price through sale.
The costs are generally very high and there is usually little competition. The main goal of the implementation phase is to build demand for the product, put it in the hands of consumers, and later take advantage of its growing popularity.
2. Growth
By the growth stage, consumers are already using and buying more and more products. The product concept has been proven and is growing in popularity-and sales are increasing.
Other companies are beginning to notice the product and the space in its market, are beginning to attract attention and are becoming more and more profitable. Even when product competition is particularly fierce, the company can invest heavily in product advertising and promotion to beat its competitors. As a result of product growth, the market itself tends to expand. Growing products are usually tuned to improve functionality and functionality.
As the market expands and competition intensifies, prices often fall to make certain products competitive. However, sales are usually increasing and generating revenue. Marketing at this stage is aimed at increasing the market share of the product.
3. Maturity
As a product matures, its sales tend to slow down or stop. This shows that the market is almost saturated. At this point, sales may even begin to decline. Pricing at this stage tends to be more competitive, indicating that margins shrink as prices begin to fall due to the weight of external pressures such as competition and declining demand. Marketing at this point is aimed at fending off competition, and companies often develop new or modified products to reach different market segments.
Given that the market is very saturated, it is usually during product maturity that less successful competitors are kicked out of competition. This is often referred to as the "shakeout point".
At this stage, it reaches saturation and sales volume is maximized. Companies often start innovations to maintain or increase market share, modifying or developing products or developing technologies to accommodate new demographics.
The aging stage can last for a long time or a short time depending on the product. Some brands, like Coca-Cola (KO), are very mature-get the Coca-Cola Company Report.
Maturity
4. Decline
Businesses commonly try and maintain their products as mature as feasible, however a decline in all products is inevitable.
At some point of the decline segment, product call for declines, resulting in a good-sized decline in product sales and an exchange in client conduct. The organization's products are losing more and more marketplace proportion, and competition has a tendency to get worse sales.
Declining advertising is regularly geared toward minimum or already dependable customers, and charges are reduced.
Ultimately, a product will withdraw from the market until the product itself may be redesigned to preserve relevance or call for. For instance, merchandise including typewriters, telegrams, and muskets are in decline (in truth, nearly or absolutely out of date from the marketplace).
Product life cycle instance
The product existence cycle constantly includes it from its introduction to its inevitable decline, but what does this cycle sincerely seem like, and what are some examples?
Typewriter
A standard example of a product lifecycle variety is a typewriter.
While typewriters have been first delivered within the overdue nineteenth century, they have become a popular generation for improving write ability and efficiency. However, new digital technologies along with computer systems, laptops or even smartphones are hastily replacing typewriters, declining revenue and demand.
Microsoft (msft)-overtaken by means of organizations like get Microsoft agency (msft) record, typewriters can be taken into consideration at the quilt of the decline-minimal sales (if any) and call for can be drastically decreased. Today, in the modern-day international, maximum of the time you are typing using your computer, laptop, or cell phone. They're present process boom or maturity ranges of the product life cycle.
VCR
A lot of us in all likelihood grew up looking and using VCRS (technology z readers' videocassette recorders), but nowadays it is difficult to find a VCR in absolutely everyone's domestic.
Netflix (Nflx)-Get Netflix, Inc. (Nflx) report and amazon (Amzn)-get amazon.com, inc. With the upward push of streaming offerings together with report (now not to mention the inter-curtain section of DVDS), VCRs are working efficaciously and are being phased out and in decline.
As soon as a step forward technology, VCRs are actually in very low call for (if any) and do no longer reliably deliver their former income.
Electric Powered Automobile
The upward push of electrical motors marks the growth stage of the product life cycle. Businesses like tesla (tsla)-the get tesla inc record has been leveraging developing merchandise for years, but current challenges may additionally imply adjustments in a selected company.
Nevertheless, electric powered cars are not necessarily new, however current improvements by way of agencies like tesla are always adapting to new changes in the electric powered car marketplace and demonstrating their boom degrees.
Use Of Percent Analysis
By way of appearing P.C analysis, groups can decide if their merchandise are effectively servicing the target marketplace and after they need to shift their cognizance.
By way of learning merchandise in relation to the whole marketplace, competition, income, and fees, businesses can higher decide a way to pivot and increase their merchandise to extend their lifestyles in the market.
Inspecting the product life cycle, especially taking note of in which the product is inside the cycle, allows to decide if a business enterprise desires to broaden a new product to hold income-specially. The lifestyles cycle of a product if most of the people of the product is within the mature or declining stage.
P.C Strategy
For businesses inside the product deployment level, there are several pricing models to be had to start promoting. Both rate skimming or price penetration, which to begin with sets the price of the product better as the marketplace expands and then lowers it into the "skimming" institution. This sets the preliminary fee low and speedy penetrates the marketplace, sooner or later raising the price as demand increases.
Organizations may run into problems if they do no longer recognize the implementation degrees of the product existence cycle, particularly if the purchaser does not reply well to the primary product (due to pricing or the inherent fee and usability of the product).
In addition to pricing, it's vital to keep in mind product marketing and packaging.
Does the product meet the needs and wishes of the target marketplace? Whilst income is out of date, many corporations are considering moving their advertising method to new demographics to assist them introduce their products to potential new assets of sales.
By means of appearing percent evaluation, organizations can understand when their products want to be reinvented or pivoted in new guidelines. As an instance, on-line streaming service Netflix has pivoted its products by way of shifting from DVD distribution services to frequently on-line streaming offerings. This becomes a big fulfilment.
By means of locating out wherein their merchandise is in the product existence cycle, and businesses can maintain to innovate with new technologies, diversify their merchandise, trap up with opposition and make bigger the lifestyles of their merchandise within the marketplace.
Comparison of Marketing Concept with Sales Concept
Marketing constitutes one of the key functions of an organization. Marketing contributes to the success of an organization, in addition to production, finance and accounting, human resources management, research and development, purchasing and storage, and many other functions. The marketing concept believes that the key to achieving an organization's goals is to determine the needs and wants of the target market and provide the desired satisfaction more effectively and efficiently than its competitors. The marketing concept focuses on selling satisfaction, not just selling products. The purpose of marketing is not to maximize profitable sales volume, but to make a profit through customer satisfaction.
Some say that society's knowledge of marketing is improving, but some organizations say that marketing is not yet fully understood. The arbitrary nature of marketing arises from a constantly changing perspective in the socio-cultural and technical context, and marketing today is considered to be a dynamic nature rather than a static concept. Marketing in today's environment is a social and administrative process for individuals and groups to create products and values and exchange them with others to get what they need and want. Figure 1 shows the major issues related to product marketing.
Fig: Core issues related to the marketing of the products
Today's marketing originated around the Industrial Revolution of the 18th century, when technological development and increased production ended contact with the organization's personal customers and created the problem of surpluses. During this period, customer preferences were largely overshadowed by production and sales directions. This continued until the mid-20th century.
The concept of marketing has continued to evolve since the 1960s, when marketing functions were recognized as unique areas and areas within an organization. This is reflected in the ever-changing definition of marketing over time. Some definitions of marketing have been advocated over the years as each generation tries to figure out what marketing is at the time and what it means for the functioning of the organization. Rice field.
Over the years, marketing features have been redefined to fit into new contexts. In recent years, technological developments, new technologies and media have increased opportunities to redefine marketing. These definitions use the terms marketing, sales, advertising, customer service, and interaction synonymously to mean marketing by having marketing professionals and sales reps adjust to the focus of their work. It often seems to dilute in some way.
Many definitions explain different aspects and related terms, but they do not always convey the much broader ideologies and processes that are part of marketing. The evolution of various definitions of marketing also reflects changes in the concept of product marketing.
Overall, product marketing concepts can be divided into five concepts:
(i) Production Concept
(ii) Product Concept
(iii) Sales Concept
(iv) Marketing Concept and
(v) Social Marketing Concept.
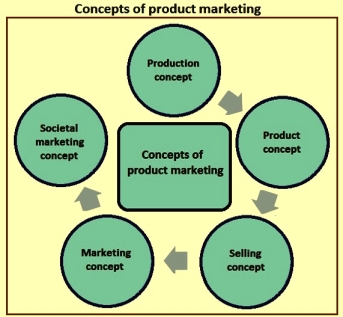
Fig: Concepts of Product Marketing
These five marketing concepts have dominated over different periods of time, and most organizations now adopt the last two concepts. Figure 3 shows the evolution of the marketing concept over time.
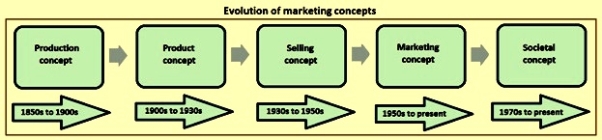
Fig: Evolution of marketing concepts
Production Concept – This is the oldest concept. The production concept can be traced back to the 1850s and 1900s. This was the era of the Industrial Revolution. During this time, power generation, division of labor, rail transport, assembly lines and mass production increased. These have made it possible to produce products more efficiently by using a large amount of new technologies that incorporate new ways of using the labor force. Despite the increased production of commodities due to these new production methods, the demand for industrial products was very high.
The production concept is based on the assumption that consumers prefer products that are readily available and very affordable. To do so, it was necessary to focus the organization on product improvement and efficient distribution of products. The production concept "assumes that consumers are primarily interested in the availability of low-priced products. Its implicit marketing goal is cheap and efficient products.
Auctions and intensive distribution. " In the era of production concepts, manufacturers were usually focused on increasing production, assuming that customers would look for and buy well-made products at affordable prices. The production concept worked well for organizations in the 1850s to achieve their goals. Today, the direction of such an organization makes sense only if the purpose of the organization is to expand the market. However, production orientation rarely works in the current environment. Today, organizations with these marketing concepts run the risk of over-focusing on their work because they need to lose sight of the core idea of producing to meet their customers' expectations and create customer value. A common trend in current scenarios shows that production concepts are not involved in most organizational practices today. However, if the purpose of the organization is to extend to meet unsolicited demands, or if a new product is introduced, the production concept can adequately complement other, more dominant concepts.
Product Concepts – Product concepts were the dominant marketing concept in the early 1900s and lasted until the 1930s. For generations, the concept of the product era dominated the understanding of marketing. The product concept presupposes that consumer prefer products based on their quality, performance and innovative features. This means that your organization knows the product better than any other product. The organization knows all aspects of product design and manufacturing. In addition, organizations have higher knowledge and skills in manufacturing products, so it is assumed that they know what is best for consumers. The product concept required organizations to ensure product quality and introduce new features into their products to improve performance as much as possible. These are manufactured with the customer in mind, but we do not consult with the customer and do not ask for opinions on the features of the product. The era of product concepts culminated in the development of innovative products with less customer needs, as there were no alternatives and customers were unaware of their needs in such innovative market conditions.
In the age of product concepts, organizations were able to sell all the products they made. The success of this concept was due to the time and level of technology in which it flourished. The product concept survived the "Industrial Revolution", as demand exceeded supply and the focus on production over customers was a very appropriate product sales philosophy at the time. Most of the products were so scarce that the organization sold everything they created. As a result, organizations did not have to consult consumers about product design and manufacturing. Some organizations continue to have the idea of production-oriented marketing to direct their operations, but this concept is not common in today's market environment.
Product concepts often lead to product-focused organizations rather than consumer needs that need to be met, which leads to "short-sighted marketing." Due to the nature of the customer and the current market environment, the production concept can fail in the current environment, except in the case of the introduction of new products where the customer's knowledge and competition are inadequate.
Sales Concept-The sales concept is an organizational concept that is ahead of the era of product concepts and has the shortest dominance period compared to the two concepts mentioned above. It began to become the predominant concept in the 1930s and continued to be widely used until the 1950s. The focus of the sales concept was to create a department that was solely responsible for selling the organization's products, but the rest of the organization was devoted to producing the products. The direction of the sales concept was that an organization could sell all the products it produces using a variety of methods such as advertising, promotion, and personal sales. This concept presupposes that consumer are unlikely to buy a product unless they are persuaded to buy aggressively, primarily through a "hard cell" approach.
After the "Industrial Revolution", the production of various products increased significantly and the production efficiency of the organization improved, so the emergence of a sales concept was necessary. Increasing quantity and variety of products led to competition, eventually ending product shortages, which resulted in surpluses. This could lead to the loss of customers in the future, but it clearly put pressure on the organization to force customers to buy the product. This concept helped with the immediate sale of the product. The concept was that the surplus of funds generated by the organization was directed to the use of advertising and personal sales to reduce inventory. The main focus of this concept was to sell the product with a proactive approach.
The sales concept takes a "turn-over" perspective. It starts with a production plant, focuses on organized existing products and demands mass sales and promotions for profitable sales. The main focus is on conquering customers by winning short-term sales with little concern about who buys and why.
The sales concept allows a part of the organization to stay focused on the product through the product concept. In addition, the era of sales concepts was characterized by the direction in which the sales or marketing department could sell whatever the organization created. Apart from the aggressive sales approach, the era of sales concepts was also noted for other unhealthy features such as:
The idea that "sales is an organizational goal, not customer satisfaction."
The concept of sales has been largely recognized as the preferred organizational direction over time, but its acceptance or rejection depends not on the concept itself, but on the age of the concept and the direction of the dominant organization. Will be decided. Even in the era of market-oriented concepts, organizations that deal with "unsolicited" products (such as life insurance), parties that actively sell candidates to indifferent voters in elections, and organizations that still have excess inventory. Follow this concept and make good use of your sales orientation. This means that the concept of sales is not well recognized in the current environment, but it is not completely obsolete as it can be used to support more dominant concepts in certain types of organizations. The concept of marketing has become a prescription for fighting competition, but "old habits die hard." Even today, some organizations retain the fact that they must use a "hard cell" approach for their success and prosperity.
Marketing Concept-
The concept of marketing began to dominate the direction of an organization inside the 1950s and keeps into the twenty first century. This concept assumes that the start line of the advertising method is consumer wants and needs, not aggressive sales. An essential premise underlying the idea of advertising is which you don't try to promote what your enterprise makes; you best make products that you could sell. The advertising and marketing concept focuses on patron wants and needs, now not seller and product needs.
This idea assumes that the principle undertaking of marketing isn't always simplest to convince the consumer to buy, but also to offer the proper quantity and high-quality to the patron's needs. Those views are in line with previous proposals based at the concept that goods are made to be pleasing rather than bought. According to this concept, in latest surroundings, more innovative groups are seeking for out the subconscious desires of purchasers and then produce goods to fulfil them. The advertising concept takes an "outside-in" angle.
The advertising idea starts of evolved with a nicely-described marketplace, specializes in the wishes of the consumer and integrates all marketing sports that have an effect on the patron. Then generate profits by using building lasting relationships with the right clients based totally on customer value delight. The advertising and marketing idea acknowledges that the know-how and skills of an agency in designing a product do now not continually meet the desires of its clients. Consequently, on this idea, an agency is converted from a product to a market.
In the concept of marketing, the focus has shifted from production problems to marketing problems, from merchandise that an enterprise can make to merchandise that customer want to make into an agency. This means that the focus has shifted from the organisation to the market. It is also diagnosed that even an amazing income branch cannot promote all the goods that do not meet your desires. Whilst customers have many choices, they continually select the only those first-rate fits their desires. This is represented by means of the company's managers who make a clear distinction among income and advertising and marketing directions. In keeping with these executives, sales are focused on the needs of the vendor, even as advertising is targeted on the desires of the purchaser.
Sales are captivated with the want for dealers to convert their merchandise into coins. Advertising, however, is based at the idea that the product and the whole cluster of products associated with product creation, delivery, and very last intake meet customer needs. This concept is what is anticipated of ultra-modern companies. Following this concept, an organisation is marketplace-oriented and may be a success. In spite of the truth that new ideas had been developed when you consider that the advent of the advertising idea, this concept stays tremendous in creating and keeping worthwhile clients, which is the number one purpose of any agency.
Social advertising ideas – The social advertising and marketing idea first appeared within the Nineteen Seventies and has due to the fact that overlapped with the marketing idea. This concept assumes that there may be a contradiction among the short-term dreams of customers and the lengthy-term interests of society, and that organizations consciousness on practices that make certain long-time period client and social nicely-being. Growth. Social advertising directions are taken into consideration the great commercial enterprise concept for an organisation to undertake. This new concept has been recommended to represent a try to reconcile organizational goals with the occasional conflicting dreams of society. Following the concept of social marketing, an enterprise's venture determines the desires, wants, and pursuits of the goal marketplace and gives the desired pride in a manner that maintains or complements health greater correctly and efficaciously than its competitors. That is. Clients and society.
It is understandable why this idea failed to emerge until the Nineteen Seventies. The significance of this concept has become apparent while the effect of organizational activities on the surroundings and society have become too good sized. After that, organizations had to parent out approaches to fulfil the market for profit and reduce their environmental and social affects. The precept behind this idea is that happy societies are more likely to shop for and advocate organized merchandise, and unhappy societies are organized even supposing they can meet patron needs. It means refusing to purchase a typical product. This means that the idea of social marketing emphasizes that the needs that clients recollect in making product purchase choices have elements in their on-the-spot environment.
The adequacy of the concept of social advertising is inferred from the reality that it helps the socially responsible conduct of an agency. Therefore, it disagrees with the previous claim that the social duty of an employer is to make a profit.
Groups need to adopt this marketing idea so that it will cope with the cultural and regulatory factors of their organizational surroundings. Which means the adoption of the idea of social marketing creates numerous market-orientated elements that force the overall performance of an organisation. The idea of social advertising is taken into consideration a separate organizational aim. However, this concept may be taken into consideration complementary. It should be an organizational mind-set that enhances the goals of other businesses, particularly the adoption of advertising standards. Therefore, regardless of whether a corporation's operations are manufacturing, product, income, or marketing oriented, society continues to be a legitimate area due to the fact society is a prime stakeholder in all corporations.
Comparison of Marketing Concept and Sales Concept
In some organizations, the terms marketing and sales are commonly used as synonyms. In fact, these two terms have different meanings. Understanding the differences between them is necessary for the independent performance of the organization. Figure 4 shows the main differences between sales and marketing concepts.
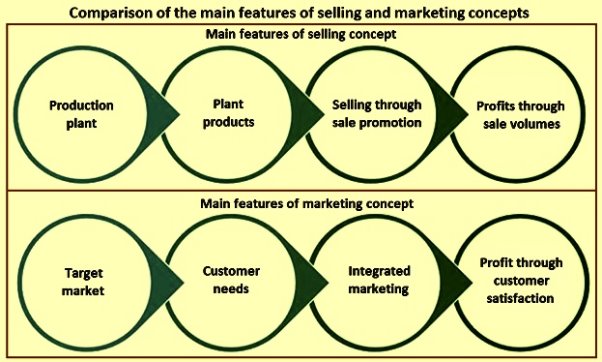
Comparison of the main features of the Selling and the Marketing Concepts
While selling is the act of converting a product into cash, marketing is the complete process of meeting and meeting customer needs. Marketing consists of all activities related to product planning, pricing, promotion, and product distribution. Sales focus on the needs of the sales organization, while marketing focuses on the needs of the customer. Tab 1 shows a detailed comparison of sales and marketing concepts.
Tab 1 Comparison of Selling Concept and Marketing Concept | ||
Sl. No. | Selling concept | Marketing concept |
1 | Selling concept is based upon the volume of production without thinking of the customer. | Marketing concept is based on producing products needed by the customers the satisfaction of the customers. |
2 | Organization first makes the product and then figures how to sell it | Organization determines the customer requirements first and then produces the product which meets the customer requirements. |
3 | Selling begins with the organization which is pre-occupied all the time with meeting the requirements of selling. | Marketing begins with the customer and focuses constantly on the needs of the customer. |
4 | Selling begins with the existing activities and products of the organization. | Under marketing, all activities and products take their direction from the customers and their needs. |
5 | Selling emphasizes on the saleable products of the organization. It seeks to convert products into cash and getting rid of the stocks. It is concerned with the methods and techniques of getting the customers to part with their cash in exchange for the products. | Marketing emphasizes identification of the opportunity available in the market. It seeks to convert customer needs into the organizational products. It emphasizes on fulfilling these needs. |
6 | Selling over emphasizes the exchange aspect without caring for the value satisfactions inherent in the exchange. | Marketing is primarily concerned with the value satisfaction which travels to the customer through the exchange. |
7 | Selling views organization as a product producing entity. | Marketing views organization as an entity as a part of the process for satisfying the customer. |
8 | The selling organization determines which product is to be offered. | Customer determines the product which is to be offered by the organization. The organization makes a total offering which matches and satisfies the identified needs of the customers. |
9 | The product precedes the selling efforts which are the consequence of the product available on hand. | The consequence of the marketing efforts is the identification of the product which is needed by the customer. The organization produces the identified product in its own interest. |
10 | In selling concept, packaging is essentially seen as a mere protection or a mere container for the product. | In marketing concept, it is seen from the point of view of the customer. It is designed to provide the maximum possible convenience and satisfaction to the customer. |
11 | In selling concept, emphasis is on the product. | In marketing concept, emphasis is on the requirements of the customers. |
12 | Selling concept is based upon the transfer of title and possession. | Marketing concept is based on the satisfaction of the customers. |
13 | In selling concept, production cost determines the price. | In marketing concept, customer determines the price and price determines the product costs. |
14 | In selling concept, organizational management is oriented towards sale volume. | In marketing concept, organizational management is oriented towards profit. |
15 | In the selling concept, planning is short term oriented in terms of daily sale of the product. | In marketing concept, planning is long run oriented in terms of new products and future market demands etc. |
16 | The selling concept has inside-out perspective. | The marketing concept has outside-in perspective. |
17 | Transportation, storage, and other distribution functions are perceived as mere extensions of the production function. | Transportation, storage, and other distribution functions are seen as vital services to be willingly provided to the customer in a manner which delivers the products without any damage. |
18 | The emphasis is to sell somehow. There is no coordination among the different functions involved in the total process leading to the product selling. | The emphasis is on an integrated approach. The integrated approach includes product, production, promotion, pricing, and distribution. |
19 | Different departments of the organization operate in separate water tight compartments. | All the departments of the organization operate in close coordination with the sole purpose of providing satisfaction to the customer. |
20 | In the organizations practicing selling concept, production is the central function and sales is a subordinate or secondary function. | In the organization practicing marketing concept, marketing is the key function and the entire organization is organized for supporting the marketing function. |
21 | Selling concept views the customer as a link in the organizational process of product selling. | Marketing concept views the customer as the very purpose of the existence of the organization. It sees the organization from the view point of the customer with customer consciousness spreading in the entire organization all the time. |
The sale can be considered the latest version of the exchange under a barter system where the product is exchanged for cash. When focusing on sales, sales reps think that their work begins only after the production of the product they sell is complete. In the sales concept, the role of the sales department begins after the production of the product and is the last link in the chain of organizational departments.
In the sales concept, it is taken for granted that aggressive sales methods are justified to achieve sales goals and meet customer needs and satisfaction. Marketing, on the other hand, is the broader and more prevalent activity of an organization. Marketing activities begin with identifying customer needs and do not end until you receive feedback on customer satisfaction from product consumption. This is a long series of activities consisting of production, packaging, promotion, pricing, distribution, and sales. Your needs are the leadership behind all these activities. Profit is not ignored, but it builds up in the long run.
How to sell?
A sales method, also known as a sales method or sales method, is a strategy that sales reps use to effectively increase sales, close transactions quickly, and increase revenue. There are many different sales methods available. What works best for you usually depends on your skills as a salesperson, the products you sell, and the audience you sell. Many successful sales reps may use multiple sales methods depending on the situation. You can experiment with different sales methods until you decide which one will give you the best results.
Various Sales Methods
Sales methods consist of a variety of methods that you can use to sell your products to your customers in a unique way. Here are some common ways to sell most sales reps practices:
- Challenger Sales Approach
People who practice the Challenger Sales approach take the time to better understand the needs of individual customers, business challenges, and product preferences. When sales reps talk to customers, they usually manage it by asking questions and looking for opportunities to connect with prospects.
2. SNAP Sale
Many sales reps who use this method focus on reaching customers by speaking directly at the customer level. SNAP means staying simple, staying irreplaceable, always working with your customers and raising their priorities. By following this method, you can reach your customers more effectively by gaining valuable knowledge about your business and determining what is most important to them. This can help you reach your bottom line, stand out from your competitors, and strengthen your organizational structure.
To use SNAP sales, you first need to give your customers access to their time by explaining how the product helps them. Then start the change by elaborating on the value that the product offers. Then, help you make a purchase decision by presenting a product roadmap that describes the characteristics and benefits of the product. You need to be flexible and supportive when negotiating the final deal with your customers.
3. SPIN Sale
Those who use the SPIN sales method are primarily focused on leading customer conversations by using the right questions. This acronym stands for Situation, Problem, Implication, Need-Payoff. Each of these represents a different phase of this method.
- Situation: During this phase, sales reps carefully investigate and review buyer resources and organizational processes. This includes asking key questions to get better ideas about the customer's structural challenges and how the product can help the customer.
- Problem: Gaining more knowledge through key questions at the situational stage helps prospects identify their challenges.
- Implications: After sales reps help buyers recognize process challenges, customers may become aware of the potential impact they can cause business. The main questions at this stage should facilitate the real need to help customers overcome and solve these problems.
- Needs / Payoffs: This final step is focused on helping buyers understand that the features of the product can help solve these problems. Customers need to understand that your product can help solve problems by answering key questions.
4. Sandler system
The Sandler system involves making the customer feel like they are having a relaxed conversation rather than a traditional sales call. When you first talk to a customer, you will focus on developing your relationship and building trust by building trust. Discover what their organizational challenges are and explain that you are there to help them overcome these obstacles.
Before you sell a product, you first need to make sure that your customers are suitable for it and will benefit from it. Knowing that your prospects are looking for a product similar to you, or that your product has a problem that can be solved, they are more likely to buy from you. This also ensures that you are spending your time selling wisely to this customer. Once you've done this, you can focus on closing deals and explaining how your product meets your needs, solves problems, and benefits your business.
5. Conceptual Sale
This sales method follows a framework that focuses on planning customer interactions. Identify patterns in how customers buy products and learn what drives them to buy new products.
Once you find this in your potential customers, you can pose for the products you sell to stand out from your competitors. You can also use this information to create action plans on how your customers can use the products they sell to improve their processes and overcome obstacles.
- Inbound sales
- Inbound sales will cooperate
You are losing marketing techniques to find pre-qualified leads who are interested in your product. Having access to a wealth of information online means that your customers may be researching your product and understanding its benefits and values before you talk to them. You can use marketing analytics to understand clicked ads or web pages and learn more about your products.
Prospects may request details of your product or service using the form on your website. Customers can essentially come to you. That is, they are already interested in your product and are informed. This increases your chances of making a sale by providing additional details about the features of your product. This is because we are confident that our customers know the product and how it can help.
6. Solution and Value Selling
When using this sales method, focus on the value, benefits, or solutions that the product brings, not just the product itself. This tells your customers that your main focus is not just on selling, but on solving their problems or meeting their needs. By doing this, you will build stronger relationships with your prospects.
Scope # 1. Long-Term Marketing Plan:
The long-term plan involves the development of basic objectives and strategies to guide future enterprise efforts. Long-term planning provides a framework in which other plans for the company are prepared.
Long-term plans use longer periods of 5 to 20 years, but may include horizontal time of 2 years or more. Long-term planning is carried out by top management with the help of professional planning authorities.
Philip Kotler points out that the following situations need to be considered when developing a long-term marketing plan:
- Diagnosis:
The planning process begins with an attempt by the company to expand the current market conditions and the factors that cause them. In short, diagnosis is based on where the company stands and why. To size up, you need to create data about the absolute levels of your company's sales and market share and their reception trends by product, region, and other breakdown.
You also need supplementary data on marketing costs, plant utilization, profit levels, and other variables. Instead of just relying on impressions, you need to plan for a careful analysis of recent trends.
b. Prognosis:
In addition to diagnosing their current location, the company needs to estimate where it will go if current market trends continue. What sales and profits can a company make in the long run?
Systematic sales and profit forecasts consist of five steps: (A) Forecast of industry sales during the planning period. (B) Forecast of company sales. (C) Forecasting company revenue, costs, and profits. (D) Investment forecast. (E) Return on investment (ROI) forecasts the current policy should be continued if the company's future looks bright, but the target should be changed if the future is dark and suspicious. It shows that. May be achieved.
c. Purpose:
If the forecast shows that the company has no future, the company needs to set new goals for sales.
d. Strategy:
The strategy sets out a wide range of principles that the company wants to ensure competitive appeal to buyers and an advantage over the full utilization of the company's resources.
Your marketing strategy may consist of the following tenants:
- Develop the highest quality products possible.
- Charge a premium price.
- Advertise more than your competitors.
- Use a salesman who feels and demonstrates the motivation of missionaries.
There are several options for the strategy. The company should carefully study these alternatives and select the best possible alternative strategy under the circumstances.
The management section of the long-term plan should include performance goals. They should be checked regularly. In short, you need control. If fluctuations are unfavourable at any stage, the root cause is discovered and changes are introduced to correct the shortfalls and benefits in the changed situation.
e. Tactics:
Tactics suggest ways to use your company's strategy to achieve your goals. In other words, tactics are a way to carry out a strategy. Philip Kotler distinguishes between very interesting goals, strategies and tactics in the following words: "The purpose of the company is to show where the company wants to be, and the strategy is to show the intended route. Tactical decisions are not the main thing, but they are still very important."
f. Management:
The long-term plan represents management's best vision in planning the right set of goals, strategies, and tactics. It is based on a detailed set of assumptions and expectations, the effectiveness of which becomes apparent over time. In many cases, there will be no new events that challenge some of the basic assumptions of the plan.
This means two things. First, the plan must include a control section that specifies the type of monitoring performed to check the validity of the plan. The company may then develop one or more emergency response plans to address new challenges.
Scope # 2. Short-term or annual marketing plans:
Every year, companies make an annual plan. As a general rule, the annual plan is made in the light of the company's long-term plan. Of course, if the company doesn't have a long-term plan, a short-term plan is impossible.
If short-term planning is not a series of chaotic and appropriate solutions to a short-term crisis, then long-term planning is needed. The annual plan may reflect only the results of the previous year and the reaction to next year's problems, rather than the gradual implementation of the long-term plan.
There are generally three different approaches to annual planning.
- Goal Planning:
Management sets sales and profit targets for the year that, if achieved, will satisfy shareholders. It is up to the person whose goals are set to find a way to achieve them.
b. Optimization plan:
Management considers key alternative strategies and their potential impact on profits, sales, market share, and future investment opportunities. Management chooses the strategy that produces the most compelling results. This type of planning is the most logical of the three approaches.
c. External plan:
Management considers continuing the current strategy and estimates the profits and sales that may be achieved. If these are satisfactory, they will be set as company goals.
Marketing Plan – Nature:
As a company's planning system evolves, the topic of "marketing plans and marketing plans" is increasing. Unfortunately, these terms have no general usage. Market-oriented companies sometimes use the term "marketing plan" as a synonym for overall business plan. Perhaps a better title is "Market-Oriented Business Planning."
In other companies, "marketing plans" are used to describe sections within a large business plan that specifically address marketing issues and strategies, as opposed to the finance and manufacturing sections of the same plan. Increase.
In addition, it is used by other companies to describe special marketing documents to maintain marketing goals, such as successful launches of new products or orderly development of new markets.
Due to these various uses, the term "marketing plan" may not serve as a more specific designation for the particular type of plan being discussed.
- Split Plan:
Department planning is similar to corporate planning and describes the department's plans for growth and profitability. Describes marketing, finance, manufacturing, and HR strategies and may use short-term, medium-term, or long-term planning periods. In some cases, a department plan is the sum of all the individual plans created within the department.
b. Corporate Planning:
Corporate planning describes the overall business plan of a company. It can be an annual, medium-term, or long-term plan. Corporate planning transactions are based on a company's mission, growth strategies, portfolio decisions, investment decisions, and current objectives and goals. It does not contain details about the activities of individual business units.
c. Product Line Planning:
Product line planning describes the objectives, goals, strategies, and tactics of a particular product line. Each product line manager creates this plan.
d. Product Planning:
Product planning describes the objectives, goal strategies, and tactics of a particular product or product category. Each product manager creates this plan.
e. Product / Market Planning:
A product / market plan is a plan for marketing a particular product or product line, or a company is a particular industrial or geographical market. An example is a bank's plan to sell a loan service to the real estate industry.
f. Brand Plan:
A brand plan describes the purpose, goals, strategies, and tactics of a particular brand within a product category. Each brand manager creates a brand plan.
g. Market Planning:
Market planning is a plan for developing and servicing a particular market. If your organization has market managers as well as product managers, market managers make these plans.
h. Functional Plan:
A functional plan is a plan for one of the key functions such as marketing, manufacturing, human resources, finance, or research and development. It also describes the planning of sub-features within the main features. For marketing, this is an advertising plan, a promotion plan, a sales force plan, and a marketing research plan.
Most of these plans have marketing components. In fact, marketing components are not only essential, they are usually prioritized in planning. Planning often begins with the following questions: How much sales can you make a profit?
This step is answered by marketing analysis and marketing planning. After this plan is approved, non-marketing executives begin work on manufacturing, finance, and personnel planning to support the marketing plan. Therefore, marketing planning is the basis for planning other activities of the company.
Definition of Market Survey
Marketplace studies is a marketplace research and evaluation of a particular product / service, such as a survey of consumer trends. A survey of different consumer talents, along with funding attributes and buy capacity. Market research is a tool for accumulating comments immediately out of your audience to apprehend their characteristics, expectations, and requirements.
Entrepreneurs increase new and interesting techniques for future merchandise / offerings, but there may be no guarantee that those techniques will be successful. To be successful, marketers want to decide the types and capabilities of products / services that their target audience will easily receive. Doing so can assure the achievement of the brand-new course. Maximum marketing managers rely on marketplace studies to gather records that helps the market research process. Similarly, the remarks we get hold of from those surveys may additionally contribute to product advertising and marketing and upgrades.
Marketplace studies collects records approximately your goal marketplace, inclusive of fee trends, patron necessities, competitor analysis, and different such details.
Reason of Marketplace Research
- Get critical patron remarks: The Main Purpose of Market Research Is to Offer Marketing and Enterprise Managers with A Platform to Get Crucial Information about Clients. This Permits You to Retain Present Clients and Receive New Ones.
- Understand The Consumer's Tendency to Buy a Product: Information Which Include Whether or not the Purchaser Spends a Certain Amount of Money on The Product / Carrier, The Extent of The Consumer's Tendency Concerning Future Capabilities and Products, And Mind About Competing Merchandise.
- Improve Current Services and Products: The Motive Is to Improve Current Merchandise, Analyze Client Delight, Attain Market Belief Records, And Use Records from Current Patron Databases to Construct Buyer Personas. You Could Additionally Behavior Market Studies With.
- Make Knowledgeable Enterprise Selections: Facts Gathered the Usage of Market Research Enables Make Main Modifications to Your Business and Reduces the Degree of Chance Related to Crucial Business Choices
Significance of Marketplace Research
There are five factors that suggest the significance of marketplace studies.
- Understand the deliver and demand of the target market: Merchandise advanced with the supply and demand of the goal marketplace in thoughts are maximum probable to be successful. On this way, entrepreneurs benefit perception into marketplace competencies to take in new merchandise and ideas for developing purchaser-centric merchandise and features.
- Growing a nicely-thought-out advertising and marketing plan: the sector is the target marketplace for companies, particularly mounted companies. Obtaining facts out of your goal market via in-depth marketplace research the usage of market studies and segmentation is a supply for developing concrete, long-time period advertising plans.
- Apprehend client expectations and needs: all advertising and marketing sports revolve around customer acquisition. All huge and small agencies want market studies to accumulate ordinary remarks from their target audience using consumer delight tools inclusive of net promoter scores, customer effort scores, and purchaser satisfaction ratings (csat). Growth. Businesses can examine client comments to degree consumer revel in and pride, expectancies and many others.
- Accurate launch of latest merchandise: marketplace studies is influential in understanding where to test new products or services. Marketplace studies affords entrepreneurs with a platform to research the extent of destiny product success and alternate product strategies in step with the comments acquired.
- Get records approximately purchaser demographics: consumer demographics form the core of any enterprise and use marketplace studies to create complicated and confidential patron demographics such as race, ethnicity and own family earnings. You can get excessive information of.
Types of Marketplace Research along with Examples
Organizations use a couple of varieties of marketplace studies to accumulate information for the functions of market research. The facts amassed will cowl exceptional elements of the market, such as topics inclusive of while to release a product / provider, understanding market traits, measuring patron loyalty, and investigating competition. May be used to cope with it.
There are specific sorts of market research, such as the pinnacle 10 and getting information from clients about their requirements, expectations, and opinions about their competition. Each of those marketplace studies takes a unique approach and has an extensive impact on many factors of the commercial enterprise.
To perform one-of-a-kind sorts of market studies, a hit business in modern day world uses effective market research software to benefit actionable market insights thru real-time statistics collection and robust analytics to do. Under are the pinnacle 10 varieties of market research conducted with the aid of a success companies.
- Marketplace studies for segmentation: Businesses can locate existing and destiny clients; apprehend why they pick merchandise / offerings and why possibilities have not purchased but. This can lead to dependent marketplace fragmentation and evaluation.
- Market studies to investigate numerous components of the goal market: Reap statistics on factors such as demographic statistics along with market length, age, gender, own family profits, and do not forget marketplace increase fee, role, and create a roadmap. Average market share.
- Market research to investigate purchasing methods: How do customers make a buy choice? What are the elements that flip product awareness into sales? This form of market research well-known shows consciousness, facts, unfastened trials, purchases, and repetitions.
- Marketplace research to set up a customer personality: These researches are to construct a purchaser persona by way of understanding approximately client choices, developments, and potential to shop for merchandise.
- Market studies to degree client loyalty: What's customer loyalty and loyalty to the company? The answer to this query may be acquired via carrying out marketplace studies.
- Market studies to research new features or principles: It is vital that organizations encompass market-compliant capabilities and concepts. Performing market studies to apprehend which capabilities to launch will assist all groups concerned within the feature improvement technique do it with the proper studies.
- Marketplace studies for competitor evaluation: Wholesome opposition is continually excellent for organizational development. Marketplace studies carried out to analyze competitors presents outcomes on how the goal marketplace evaluates your organisation's merchandise / offerings in evaluation to the relaxation of the marketplace.
- Marketplace research to understand the effect of income sports: Income sports are the backbone of the enterprise and it's far vital to song those sports. Sales activity market studies produces reports at the impact of sales sports, irrespective of whether or not they need to be greater frequent or changes that visitor think must be incorporated into the sales method.
- Marketplace studies to assess the charge of recent merchandise / offerings: Affordability of products is likewise an issue that drives the agency's marketplace. Rate variety, product variations to support more than one rate ranges, target clients for each product, and many others.
- Marketplace studies for customer support evaluation: Properly customer service can result in accelerated customer satisfaction. Factors consisting of time to solve problems, scope of development, and customer service quality practices.
Market Research
Need to realize why, how and while to apply marketplace research? Need to find out why your purchasers aren't buying your product? Interested in launching new merchandise, offerings, or even new marketing campaigns, however do not know what clients need?
We want customer assist to reply the above questions. However how do you accumulate that information? In this situation, and in many different conditions in your commercial enterprise, marketplace research is a manner to get all the answers you need.
This closing manual to marketplace research offers definitions, benefits, styles of market research, and some examples that will help you understand this sort of research. Keep in mind to download the free e-book on the stop of this manual.
Which means:
Marketplace research is defined because the manner of assessing the feasibility of a new services or products through direct research with capacity purchasers. This manner, a corporation or corporation can find out goal markets, acquire and record critiques, and make informed decisions.
Market studies may be performed directly by means of the corporation or agency, or outsourced to a group with understanding on this method.
The technique of market research can be through the improvement of studies, communicate with organizations of human beings, additionally known as samples, undertaking interviews, and other comparable approaches.
The principle reason of conducting market studies is to understand or studies the markets associated with a particular service or product and to decide how your target market will react to the products or services. The records obtained from undertaking marketplace research can be used to coordinate advertising / advertising and marketing activities and to decide purchaser characteristic priorities / service requirements (if any).
Three important purposes of Marketplace Research
Market research projects generally have 3 one-of-a-kind sorts of functions.
- Control: Assist businesses or enterprise development thru proper planning, organisation, and management of each human and bodily sources to satisfy all precise needs in the market on the proper time.
- Social: Meet the unique needs of your customers thru the products or offerings you need. A products or services ought to observe purchaser necessities and options whilst fed on.
- Reasonable: Determine the degree of economic achievement or failure an agency may have while it's miles simply coming into the market or introducing a brand new services or products, and make sure that all moves are taken to provide.
Why are marketplace studies essential?
Undertaking a survey is one of the best approaches to obtain purchaser delight, lessen client attrition, and enhance your business. Right here's why market research is so essential that each business wishes to consider it:
Treasured information: gives facts and opportunities about the price of present and new products to assist organizations plan and strategy thus.
- Client-centric: helps determine what clients want and want. Advertising is patron-centric, and information clients and their needs allows corporations layout the nice services or products for their clients.
- Forecast: by means of information the wishes of clients, businesses can also forecast production and sales. Marketplace studies also can assist determine the surest inventory.
- Competitive benefit: Being beforehand of the competition is an important tool for undertaking comparative research. Agencies can devise business strategies that help them live beforehand of the competition.
Types Of Market Research: Marketplace Research Methods and Examples
Whether or not a company or business enterprise wants to realize the client's buying conduct or the probability that the client pays a specific cost for the product, marketplace research can help draw significant conclusions.
There are the following types, relying at the technique and device you need:
1. Primary market research (combining each qualitative and quantitative studies): Number one market research entails an enterprise or company contacting the quit client or hiring a 3rd birthday celebration to conduct relevant studies. The procedure of enforcing and accumulating information. The information gathered can be qualitative information (non-numeric records) or quantitative facts (numeric or statistical data).
You may accumulate two types of statistics, exploratory and particular, whilst undertaking number one marketplace research. Exploratory research is open-ended and investigates troubles by way of asking a small range of people, normally referred to as samples, open-ended questions in the shape of targeted interviews. Here, the pattern length is confined to six-10 members. Particular investigations, on the other hand, are extra correctly diagnosed and are used to solve problems recognized through exploratory research.
As noted in advance, primary market studies is a combination of qualitative and quantitative marketplace studies. Qualitative marketplace studies research consists of semi-established or dependent facts accrued through a number of the normally used qualitative research techniques which include:
- Focus groups: Focus groups are one of the most commonly used qualitative research methods. Focus groups are usually a small number of people (6-10 people) who respond to submitted online surveys. The biggest advantage of focus groups is that they can collect information remotely and do it without personal interaction with group members. However, this is a more costly method as it is used to collect complex information.
- One-on-one interviews: As the name implies, this method involves personal interactions in the form of interviews, where researchers ask a series of questions and collect information and data from respondents. Questions are primarily free-form questions and are asked in ways that make it easier to answer. This method relies heavily on the interviewer's ability and experience to ask questions that evoke answers.
- Ethnographic Survey: This type of detailed survey is conducted in the respondent's natural environment. This method requires the interviewer to adapt to the respondent's natural environment, such as a city or remote village. Geographical constraints can hinder the conduct of this type of survey. Ethnographic studies can last from days to years.
2. Secondary Market Research: Secondary research uses information organized by external sources such as government agencies, the media, and chambers of commerce. This information is published in newspapers, magazines, books, company websites, free government and non-governmental agencies, and more. Secondary sources use:
- Public Sources: Public sources, such as libraries, are a great way to collect free information. Government libraries usually provide services free of charge, allowing researchers to document the information available.
- Commercial Sources: Reliable but commercial sources are expensive. Local newspapers, magazines, magazines and television media are excellent sources of commercial information for gathering information.
- Educational Institutions: Although not very popular as a source of information gathering, most universities and educational institutions are abundant sources as many research projects are carried out more than any business sector.
Benefits:
- Make informed decisions: The growth of an employer depends on how control makes selections. Management can use market research techniques to make business choices based totally at the effects acquired that help their understanding and experience. Marketplace studies lets you recognize market tendencies. Consequently, you could do it often and get to know your clients completely.
- Get correct statistics: Marketplace research gives real-global accurate information to put together your company for feasible future injuries. Right market research will simply take groups one step further and leverage their current competition.
- Figuring out market size: Researchers can examine the marketplace length that must be included whilst promoting a service or product to make an income.
- Choose the proper sales gadget: Pick out the proper income gadget according to what the marketplace wishes. Relying on this, the product / provider may be located available on the market.
- Study consumer options: Enables you recognize how purchaser choices (and possibilities) change in order that your enterprise can meet your preferences, purchasing conduct, and income levels. Researchers can decide the sort of product that needs to be synthetic or bought based at the precise needs of the customer.
- Acquire information about purchaser perceptions approximately your brand: Similarly, to generating data, marketplace studies enable researchers recognize how clients perceive an organization or brand.
- Analyze the way you talk with your customers: Marketplace research acts as a guide to speaking together with your cutting-edge and capacity clients.
- Efficient commercial enterprise investment: It's an excellent investment for any commercial enterprise as it gives you treasured statistics and shows you ways researchers are at the right track and reaching the sales they need.
Advertising that uses digital gadgets to bring promotional messages and degree their impact. In reality, virtual advertising generally refers to advertising campaigns that seem on your laptop, smartphone, pill, or different device. It is able to take a diffusion of codecs, such as online motion pictures, show ads, and social media posts. Virtual marketing is regularly as compared to "traditional advertising" consisting of mag advertising, billboards, and direct mail. Oddly sufficient, tv is typically focused on conventional marketing.
Did you recognize that extra than three-quarters of American citizens are on line each day? Now not best that, 43% use it greater than once an afternoon and 26% are "almost constantly" on-line.
These numbers are even better among cellular net customers. 89% of USA citizens are online at least each day, and 31% are almost always online. As a marketer, it is important to leverage the virtual global with a web marketing presence through building your emblem and supplying a fantastic consumer enjoy in an effort to deliver you extra ability customers with your digital method.
What does online advertising imply?
Online advertising is a fixed of tools and methodologies used to sell a service or product over the net. On-line advertising includes a much wider range of advertising factors than conventional enterprise marketing because of the additional channels and advertising and marketing mechanisms to be had at the internet.
- On-line marketing offers the subsequent blessings:
- Growth of opportunities
- Price discount
- Stylish communique
- Higher control
- Stepped forward customer service
- Aggressive gain
On line advertising is also referred to as internet marketing, internet advertising, or virtual advertising and marketing. This includes numerous branches inclusive of social media advertising and marketing (SMM), search engine optimization (search engine optimization), pay-in line with-click on advertising (P.C), and search engine advertising (SEM).
Techopedia explains on line advertising and marketing
Powerful online advertising and marketing applications leverage purchaser information and consumer courting control (CRM) structures. On-line advertising and marketing connect your organisation with certified ability clients and takes enterprise development to a much better stage than conventional advertising.
It also allows agencies boom logo consciousness by using setting up an internet presence at the internet.
Online marketing combines the creative and technical tools of the internet, together with design, improvement, income, and advertising and marketing, with a focus on the subsequent key enterprise models:
- E-commerce.
- Lead-based website.
- Affiliate advertising.
- Neighbourhood search.
- Social media.
- On line advertising and marketing has several benefits, along with:
- Low value
With a fragment of your traditional advertising and marketing finances, you may reach a massive target market, permitting companies to create compelling client advertisements. Many advertising systems additionally allow scalable advertising and marketing with unique levels of reach proportional to your advertising budget. Smes can spend a small sum of money to enlarge their attain, instead of spending lots of money on marketing.
II. Flexibility and convenience
Customers are unfastened to investigate and buy goods and services. Enterprise blogs can be utilized by customers and possibilities to behavior their personal studies on the products of their business and to provide remarks and opinions.
III. Evaluation
Efficient statistical effects are smooth at no extra cost. Many advertisings gear include a completely unique analytics platform that permits you to organize and reveal all your statistics. This facilitates enterprise intelligence tasks and records-pushed selection making.
IV. Multiple options
Advertising and marketing equipment include pay-per-click on marketing, mail advertising and marketing, interstitial advertising and banners, social media advertising, and local search integration (including google maps). Virtual marketing companies usually serve throughout a diffusion of online advertising channels by way of tailoring their services to the needs of their character customers.
V. Demographic concentrated on
Clients can target demographically a great deal more efficiently with on line procedures than with offline ones. Coupled with the extended analytical potential described above, groups can enhance targeting over time, gain a clearer expertise of their customer base, and create precise offers that only seem in precise demographics. The main problem of online advertising is loss of concreteness. This is, purchasers cannot strive or try the item they need to buy. Generous go back phrases are the principle manner to keep away from such buyer tension.
On-line advertising has passed conventional advertising in latest years and is still an excessive-growth enterprise.
Key takeaways:
- A marketplace is an area wherein shoppers and dealers can meet to facilitate the change and transaction of goods and offerings.
- The market may be physical, like a retail keep, or virtual, like an electronic store. Other examples include black markets, auction markets, and monetary markets.
- The market establishes the charges of products and offerings decided by means of deliver and demand.
- Advertising is all the activity an enterprise does to sell a service or product and promote it to purchasers.
- Advertising uses an "advertising and marketing mix", also called the 4 ps: product, fee, region, and promoting.
- At the core of marketing is the usage of products or services, identifying an appropriate client, and drawing the client's interest to the available products or services.
- Marketplace shape refers to how specific industries are categorized and differentiated based at the diploma and nature of opposition for services and products.
- The 4 famous varieties of marketplace structure include ideal competition, oligopolistic marketplace, monopoly market, and monopoly opposition.
- The marketplace structure indicates the relationship between a seller and different dealers, from sellers to consumers, and so forth.
- An important element of NPD is product design, alongside numerous commercial enterprise concerns.
- The development of recent merchandise is widely defined as turning market possibilities into products that can be offered.
- Products developed by an employer offer a means for the organization to generate earnings.
- For many era-extensive corporations, their method is based on leveraging innovation in rapidly converting markets.
- A product can be tangible (physical to touch) or intangible (together with a carrier or enjoy), but a service or different method can be prominent from a "product."
- NPD needs to recognize consumer needs and wants, competitive environment, and market nature.
- Fee, time and satisfactory are the main variables that force consumer desires.
- Aiming at these three variables, modern agencies develop ongoing practices and strategies to higher meet client requirements and boom their marketplace percentage through everyday development of recent products. To do.
- There are many uncertainties and challenges that agencies have to face at some point of the system.
- Perfect competition is a perfect sort of market structure during which all producers and consumers have complete and symmetrical information, there are not any transaction costs, and lots of producers and consumers compete with one another.
- Perfect competition is theoretically the other of a monopoly market.
- All real markets are outside the scope of the right competition model, so each are often classified as incomplete.
- A monopoly is when a corporation and its products dominate a sector or industry.
- Monopoly is often seen as an extreme results of free market capitalism and is usually wont to describe the entities that dominate the market completely or almost completely.
- If the barriers to entry are high, there could also be a natural monopoly. Companies have patented their products or are licensed by the govt to supply basic services.
- Exclusive competition occurs when there are many companies offering products that are similar but not just like the industry.
- Unlike monopolies, these companies have little power to chop supplies or raise prices to extend profits.
- Companies in monopoly competition usually seek to differentiate their products so as to outperform the market.
- Fierce advertising and marketing are common among monopolistic companies, and a few economists have criticized it as wasteful.
- Oligopoly is in contrast to monopoly, where there's just one producer.
- Government policies can discourage or encourage oligopolistic behaviour, and mixed-economy companies often seek government blessings on the way to limit competition.
- Nonetheless, samples of oligopoly are often found throughout major industries like oil and gas, airlines, mass media, automobiles and telecommunications.
- However, the existence of oligopoly doesn't mean that coordination or collusion is happening.
- Prices mainly depend on supply and demand, government influences, and various mangoes. However, seasonal crop demand remains high, and supply levels can inflate or weaken the price structure.
- Farmers also work in a monopoly competitive market where a large number of farmers (there are about 570 million farmers worldwide) produce a variety of similar crops that can be distinguished based on quality, size, etc.
- Due to the monopoly competitive market, the coffee business has low barriers to entry. However, existing or established businesses in the market want to raise the barrier.
- The two world-renowned coffee chains both sell a similar product, coffee, but coffee is not the same at both retailers.
- Examples of Monopolistic Competition are beauty products with a large number of sellers and products sold by all similar but not identical companies, who charge prices based on the uniqueness of the product.
- In the real world, it is difficult to find an industry example that meets all the criteria of "complete knowledge" and "complete information". However, some industries are close.
- A prime concern in dealing with NPD is the usage of fine practices and the elimination of communique barriers.
- The product life cycle is the time among the time a product is placed on the market and the time it's far taken off the shelf.
- There are 4 ranges in a product life cycle: introduction, increase, adulthood, and decline.
- Product lifecycle principles assist inform commercial enterprise choices, from pricing and merchandising to enlargement and fee savings.
- More recent and more a hit product force older products out of the marketplace.
- The idea of income essentially reflects the concept that consumers do now not buy sufficient of an organisation's products without most important promotional and sales efforts.
- The income idea is one of the advertising ideologies along with manufacturing concept, product idea, and holistic idea.
- Advertising and marketing plans detail the techniques organizations use to sell their products to their clients.
- Plans become aware of metrics used to assess the effectiveness of goal markets, brand or product value propositions, launched campaigns, and advertising initiatives.
- Advertising and marketing plans need to be constantly adjusted based totally on findings from indicators of which tasks are influencing and which aren't.
- Businesses use marketplace studies to test the feasibility of new services or products by means of speaking at once with capability clients.
- Marketplace studies allows organizations to recognize their goal markets and get real-time comments and comments from consumers.
- This type of research can be done internally, by the organisation itself, or via an external organization that makes a speciality of marketplace studies.
- Surveys include surveys, product testing, and attention agencies.
Case studies (Zomato: Redefining Digital Marketing)
In April 2020, with the whole world in the grip of the Covid-19 pandemic, India imposed a total lockdown that forced businesses to shut down or allow their employees to work from home. While essential services were allowed, online food service aggregators (FSA) like Zomato were also disrupted as the government sometimes allowed them to operate and sometimes put restrictions. A Twitter handle decided to have some fun at Zomato’s expense: “My parents think I am as useless as Zomato in our phones during this lockdown. My parents are wise,” Though Zomato wasn’t even tagged on the tweet, its social media team noticed it and retorted: “We’re actually delivering groceries now, aap apna dekh lo,” Analysts credited Zomato with redefining digital marketing over the last decade. This was just one of the instances that Zomato had won over the netizens with its witty replies and posts on social media.
The Growth Story
Zomato was co-founded by two Gurgaon-based employees of Bain & Co. – Deepinder Goyal and Pankaj Chaddah (Chaddah) – in 2008, under the name Foodiebay.com. The sight of their colleagues queuing up at the office cafeteria every day to go through a file of restaurant menu cards to order food resulted in Goyal coming up with the idea of an online restaurant information service. He scanned the menu cards and listed them on an intranet website. Many employees soon started using the service. Seeing the huge traffic to the site, Goyal and Chaddah launched their site publicly in 2008. The website foodiebay.com listed restaurants in Delhi NCR. By the end of 2008, it had become the biggest restaurant directory in the region. In 2010, Foodiebay was renamed Zomato.
Competition and Stakeholder Tension
While Zomato had been able to grow at a brisk pace, it had to also contend with aggressive and well-funded rivals in a cut throat market. The food service sector in India was valued at around Rs 4,238 billion as of March 2019, according to a report by the National Restaurant Association of India (NRAI). And much of this growth was attributed to the rise of food delivery platforms. According to consulting firm Redseer, the number of orders placed on such ordering apps had increased from around 1.7 million a day in 2018 to about 2.2 million in 2019...
Digital Marketing Strategy of Zomato
With the tagline “Discover great places to eat around you”, Zomato targeted the age group of 18-35 years who had access to smartphones and were comfortable using apps. The company’s target segment was the working professional, who wanted to dine out, wanted to refer to ratings and reviews of the restaurants they wished to visit, and also wanted to get food delivered at their doorstep. Zomato positioned itself as a platform that brought restaurants, suppliers, consumers, food suppliers, and logistics partners together. It also positioned itself as the app consumers should look for when it came to authentic reviews and recommendations before visiting or ordering from a restaurant.
The Road Ahead
In the first half of FY2020 (i.e., April-September 2019), Zomato reported revenue of US$205 million compared to US$63 million in the first half of FY19 – an increase of 225%. The company also reported that its monthly burn rate, which measures the rate at which a company is losing money, was down by 60%. In the segment of ‘Dining Out’, globally the number of restaurant listings on Zomato was increased from 1.2 million in September 2018 to 1.5 million in September 2019. In table reservations, Zomato had reported 800 thousand booked covers in January 2019 to over 1.3 million booked covers in September 2019. The revenue from Hyper pure for April-September 2019 was USD 6.5 million. “We achieved tremendous results in optimizing our costs, without affecting new product launches or innovation,” commented Goyal.
Finance is the lifeline of any enterprise. But, like most different assets, budget is constantly limited. Then again, goals are always unlimited. Consequently, it's miles critical for companies to manipulate their price range efficiently. As an overview of monetary management, this text describes the nature, scope, and significance of economic control, as well as monetary choice making and making plans.
Introduction
Allows define monetary management because the first part of the financial management review. In any enterprise, it's miles vital that the finances it raises are invested in order that the return on investment is better than the cost of the finances. In a nutshell, economic control –
- Attempt to lessen financial prices
- Make sure enough availability of finances
- Handles making plans, organisation, and management of financial activities which includes financing and utilization
Creation to monetary control
Allows outline economic control because the first part of the economic management review. In any commercial enterprise, it's miles crucial that the price range it raises are invested in order that the return on funding is higher than the fee of the funds. In a nutshell, economic management –
- Attempt to reduce monetary expenses
- Make certain sufficient availability of funds
- Handles making plans, employer, and control of economic sports which includes financing and usage
A few definitions
“Monetary Control is an interest associated with planning, procuring, managing, and coping with the budget utilized in a commercial enterprise.” – Gasman and Dagal
“Financial Management is a place of business control that focuses on the clever use of capital and the cautious selection of resources of investment to permit spending units to move within the route of achieving their goals.” – J.F. Brandley
"Financial Control is the operational interest of an employer this is answerable for acquiring and effectively utilising the budget wanted for efficient operations."-Massie
The Character, Significance, And Scope
Monetary control is a natural function of any enterprise. Every corporation desire investment, which includes acquiring bodily sources, performing manufacturing activities and other business operations, and paying suppliers. There are numerous theories approximately financial control.
Some experts believe that economic control is to offer the important finances for the business on the most favourable terms, with that purpose in thoughts. Therefore, this method commonly involves raising finances that can consist of way, institutions, and practices for raising finances. It also handles the legal and accounting relationships among a business enterprise and its assets of investment.
Another expert believes that finance is all coins. Treasury worries the whole thing that a business does, as all trade entails cash at once or circuitously.
The 0.33 and more broadly conventional view is that monetary control entails financing and its effective use. For example, in the case of a production organization, economic management wishes to make certain that funds are available to install production flora and machines. Further, you want to make certain that your earnings appropriately compensate for the costs and risks your commercial enterprise bears.
In developed markets, most companies can without difficulty improve cash. But the actual problem is the green use of capital through effective economic planning and management.
Similarly, corporations want to make sure that they deal with obligations which includes ensuring availability of funds, allocating, managing, investing, handling expenses, forecasting economic necessities, planning income and estimating return on investment, and valuing running capital.
Scope of Financial Management
The economic control overview additionally calls for an information of the scope of financial control. It is crucial that economic decisions bear in mind the pursuits of shareholders.
Similarly, they're subsidized by means of maximizing shareholder wealth, which is predicated on improved net really worth, capital invested in agencies, and the go back of profits for the boom and prosperity of the employer.
The scope of financial control is illustrated in the following:
Scope of Financial Management
By studying the nature of investment, financing, and dividend decisions, you can understand the nature of financial management.
Core financial management decisions
In an organization, managers make the following decisions to minimize the cost of raising funds and using them in the most profitable way.
- Investment Decisions: Managers need to determine the amount of investment available from existing finance in the long and short term. There are two types of them.
A long-term investment decision or capital budget means investing long-term funds like fixed assets. These decisions are irreversible and usually include decisions related to investing in buildings and land, acquiring new plants / machinery, replacing old ones, and so on. These decisions determine the financial pursuit and performance of the business.
Short-term investment decisions or working capital management means investing funds in a short period of time, like liquid assets. These include decisions about investing funds in inventory, cash, bank deposits, and other short-term investments. They have a direct impact on business liquidity and performance.
II. Financing decisions: Managers also make decisions about financing from long-term sources (called capital structure) and short-term sources (called working capital). There are two types of them.
- Financial planning decisions related to estimating the source and use of funds. This means pre-estimating your organization's financial needs to ensure adequate funding availability. The main purpose of financial planning is to plan and ensure that funds are available as needed.
- Determining the capital structure, including identifying sources of funding. It also includes decisions regarding the choice of external sources such as stocks, bond issuance, bank loans, or internal reserves for financing.
III. Dividend Decisions: These include decisions related to the portion of the profit that will be distributed as dividends. Shareholders always demand higher dividends, but management wants to stay profitable for their business needs. Therefore, this is a complex business decision.
According to the Association of Certified Management Accountants, costs are "expenditures (actual or hypothetical) incurred or resulting from a particular thing or activity." Similarly, according to Anthony and Wilsch, "cost is a monetary measure of the amount of resources used for several purposes."
Costs have been or may be incurred by the Cost Terminology Committee of the American Accounting Association, "in the realization of the management objectives mentioned above, which may be the manufacture of products or the provision of services.
From the above, it can be said that the cost is the sum of all the costs of a product or service. Therefore, the cost of a product means the actual shipment or confirmed change that occurred in its manufacturing and sales activities. In short, it is the amount of resources that have been exhausted in exchange for some goods and services.
So-called resources are expressed in money or currency units. What is said above does not make sense until it is used only as an adjective, that is, when it conveys its intended meaning.
Therefore, when we talk about prime cost, works cost, fixed cost, etc., we want to explain the specific implications that are essential when calculating, measuring, or analysing different aspects of cost.
Costing collects and analyses expenses, measures the production of products at various stages of manufacturing, and measures the link between production and expenses. Therefore, calculate or check past or actual costs, estimated costs, standard costs, and so on.
It also associates production with costs using a variety of costing methods, such as marginal costing methods, total costing methods, and direct costing methods.
The following types of costing are typically used to determine costs:
1. Uniform Costing
If many companies in the industry agree to follow the same costing system in detail and adopt common terms for different items and processes, they are said to follow a uniform costing system. In such cases, you can compare the performance of each company to the performance of other companies, or to the average performance of the industry. Under such a system, it is also possible to determine the production cost of goods that apply to the entire industry. This is useful if your government requires tax cuts or protection.
2. Marginal Cost:
This is defined as a confirmation of marginal costs by distinguishing between fixed and variable costs. It is used to see the impact of changes in production volume or type of production volume on profits.
3. Standard Costing and Variance Analysis
This is the name given to the method in which the standard cost is pre-determined and then compared to the recorded actual cost. Therefore, this is a cost verification and cost management technique. This technique can be used in combination with any costing method. However, it is especially suitable when the manufacturing method involves the production of repetitive standardized products.
4. Historical Cost Principle
Confirmation of costs after incurred. The usefulness of this type of costing is limited.
5. Direct Costing
This is the practice of charging all overhead costs to operations, processes, or products and amortizing all overhead costs to the profits they generate.
6. Absorption Costing
This is the practice of charging all operational, process, or product costs, both variable and fixed. This is different from the marginal cost excluding fixed costs.
Overview of Fixed and Variable Costs
Costs are often categorized in several ways, counting on their nature. One of the foremost common methods is that the classification by fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs do not change as production increases or decreases, but variable costs change as production increases. Fixed and variable costs are the most used terms in management accounting and are used in various forms of analysis of financial statements.
The first figure below shows an example of variable costs. Here, the cost increases directly depending on the number of units produced.
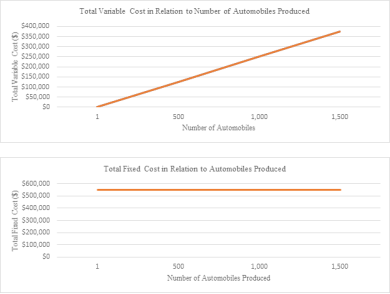
- In the second figure, the cost is fixed and does not change with the number of units produced.
- Variable costs, on the other hand, show a linear relationship between production and the sum of variable costs.
The following table summarizes the main differences between fixed and variable costs:
Graphically, you can see that fixed costs have nothing to do with the amount of cars the company produces. No matter how high or low your sales are, your fixed costs will not change.
Total Fixed Costs
Fixed cost refers to the cost of fixed input. At the level of output it does not change (hence, fixed). Fixed inputs include buildings,machines, etc. Thus, the cost of inputs, such as rent and the cost of machines, constitute a fixed cost. Also known as overhead, supplemental or overhead, these costs remain the same regardless of the level of output.
So if you plot the total fixed cost (TFC) curve against the output level on the horizontal axis, you get a straight line parallel to the horizontal axis. This indicates that these costs remain the same and should occur even if the output level is zero.
Total Variable Costs
The costs incurred by variable factors in production are called Total variable costs(TVC). These costs differ in the level of output. Therefore, when the production level is zero, the TVC is also zero. Thus, the TVC curve begins at the origin.
The Shape of the TVC is unique. It is said that it has the form of an inverted S. This is because, in the early stages of production, there is a scope for efficient use of fixed factors by using more variable factors (e.g., variable factors). Workers who use the machine).
Thus, as the variable input used increases, the production efficiency of the variable input ensures at a rate at which the TVC increases but decreases. This makes the first part of the tvc curve concave.
As production continues to increase, more variable factors are employed for a given amount of fixed inputs. The production efficiency of each variable factor is reduced,adding more to the production cost. Therefore, TVC will increase,but now it is increasing at the rate of increase. This is where the shape of the TVC curve is convex. Thus, the TVC curve will have an inverted-S shape.
| Variable Cost | Fixed Cost |
Definition | Costs that vary/change depending on the company’s production volume | Costs that do not change in relation to production volume |
When Production Increases | Total variable costs increase | Total fixed cost stays the same |
When Production Decreases | Total variable costs decrease | Total fixed cost stays the same |
Examples | Direct Materials (i.e., kilograms of wood, tons of cement) | Rent |
| Direct Labor (i.e., labor hours) | Advertising |
|
| Insurance |
|
| Depreciation |
Application of Variable and Fixed Costs
- It is important for businesses to classify costs as either variable or fixed. By doing so, companies can create financial statements called Manufacturing Cost Statements (COGM). This is the schedule used to calculate the cost of producing a company's products over a set period of time.
- The COGM is then transferred to the finished product inventory account and used to calculate the cost of sales (COGS) on the income statement.
- Analyzing variable and fixed costs allows companies to make better decisions about whether to invest in real estate, plants and equipment (PPE). For example, if a company incurs high direct labor costs to manufacture a product, it may consider investing in machinery. This reduces these high variable costs in exchange for more stable and known fixed costs.
- This decision involves trade-offs at different levels of production and should be made with volume capacity and variability in mind. Small-volume, high-volatility mass production favors machinery investment, and low-volume, high-volatility mass production favors the use of variable labor costs.
- If sales are low, unit labor costs remain high, but high unit labor costs are lower than the overall fixed cost of the machine, so it is wise not to invest in the machine and to bear the high fixed costs.
- Sales with equal fixed or variable costs are called points of indifference. Finally, variable and fixed costs are also important elements of the various costing methods that companies employ, such as job order costing, process costing, and activity-based costing.
Average Cost
The average value is the unit production cost acquired via dividing the full fee (TC) by using the total manufacturing volume (Q). Unit production fee approach that all constant and variable costs are taken under consideration when calculating the common price. Therefore, this is also known as the whole value per unit.
Symbolically, the common value is expressed as:
AC = TC / Q
Once more,
AC = Common Variable Price (AVC) + Common Constant Cost (AFC)
In which,
Average Variable Value = General Variable Value (TVC) / Total Output (Q)
Average Fixed Fee = General Fixed Cost (TFC) / General Production (Q)
The common fee is greatly tormented by the manufacturing length. For example, increasing or increasing manufacturing in the quick time period may be very luxurious or not possible. Consequently, economists check out both brief-term and long-time period common costs to decide manufacturing for a selected term.
The quick-term average cost is the price that fluctuates depending on the production of goods when the constant fee is 0 and the variable fee is consistent. Lengthy-time period common charges, then again, encompass all expenses related to fluctuations in the quantity of all inputs utilized in manufacturing. Ultimately, the quantity of all inputs used is a duration wherein even capital can trade. Therefore, common price is an critical element in determining supply and demand within the market.
Marginal Cost
Marginal fee refers to the additional cost of manufacturing each extra unit. For example, it may cost a little $ 10 to make 10 cups of coffee. It expenses $ 0.eighty to make every other. Therefore, it's far the marginal price, this is, the extra fee to generate one unit of additional output.
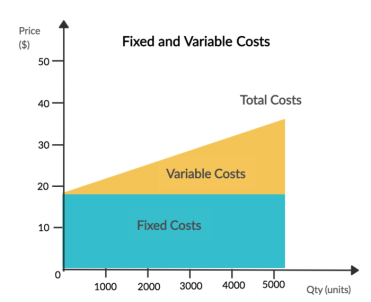
Marginal prices come from production fees. This consists of each constant and variable charges. For constant fees, marginal charges are calculated only whilst necessary to amplify production. In comparison, variable charges are continually included in marginal expenses.
As you may see from the graph below, marginal charges encompass each constant and variable expenses. As a result, variable charges often growth along marginal expenses, however they're not the best ones. Fixed expenses can also make contributions. For instance, a company may need to buy a brand new device for $ 500,000. This is a one-time fee, however it's far calculated in the marginal fee at a selected factor in time as it is required to supply extra items.
Importance of Marginal Cost
Marginal costs are critical in economics due to the fact they help companies maximize their profits. While the marginal value is equal to the marginal revenue, there may be some thing known as "earnings maximization". That is wherein the cost of manufacturing an additional object is precisely the same as what a organisation gets from selling it. In different words, at that point, the business enterprise is no longer creating wealth.
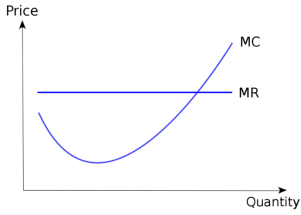
As you could see from the marginal value curve underneath, as agencies gain from economies of scale, marginal charges start to decline. However, marginal prices can start to growth as a employer turns into less effective and suffers from an uneconomical scale. It is at this point that expenses growth and in the long run marginal revenue is executed.
This can be the end result of the organisation becoming too large and inefficient, or due to control troubles along with reduced workforce motivation and decreased productiveness. For anything cause, businesses can face rising expenses and will have to forestall production whilst the sales they generate is equal to marginal costs.
Marginal fee is an essential issue of the producing enterprise as it determines the price at which similarly production is stopped. At a few stage of production, there's a point wherein MR = MC, so the enterprise is not getting cash. Consequently, increasing manufacturing any in addition is counterproductive.
Marginal Value Calculation Formulation
Marginal fee is calculated via dividing the trade in total fee by the trade in quantity. Let's say enterprise A is generating a hundred gadgets at a value of $ 100. The agency will then produce every other 100 units at a fee of $ 90. Consequently, the marginal value is a change in overall price, which is $ 90. Divide by using the alternate in amount, that is an additional one hundred units. This will be $ ninety/100. This corresponds to a marginal value of $ 0.ninety in line with unit.
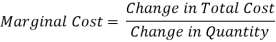
1. Change in Total Cost
So what does the trade in overall price imply? Now, marginal fee specializes in the distinction among the 2 production factors. So how a lot does it value to provide one unit as opposed to two? consequently, the alternate in total cost is calculated with the aid of subtracting the overall cost of point B from the overall price of point A.
As an instance, commercial enterprise A produces 100 cars of $ 10,000 every, with a total fee of $ a million, or $ 1 million for quick. Then, if the organization produces some other one hundred twenty cars and charges $ 1.2 million, calculate the difference among the entire value ($ 1.2 million) and the preliminary value ($ 1 million) to get the alternate. Need to do it. General fee ($ 2 hundred,000).
2. Change in Quantity
To calculate the change in amount, you want to examine factors A and B of production and calculate the difference. For instance, as demand will increase, companies will produce an increasing number of commodities. But, to calculate how this will have an effect on your backside earnings, you need to have a look at the wide variety of products bought between the 2 factors.
Searching on the preceding instance, commercial enterprise A went from generating 100 automobiles to 120. Consequently, the change in amount is the brand new production (120) minus the old production (one hundred). That is identical to 20 and is used in the components.
Total Cost
Total cost(TC) refers to the sum of fixed and variable costs incurred in the short term. So, the short-term cost can be expressed as follows
TC=TFC+TVC
Note that in the long run, TFC=0, so TC = TVC. So you can get the shape of the TC curve by summing the TFC curve and the TVC curve.
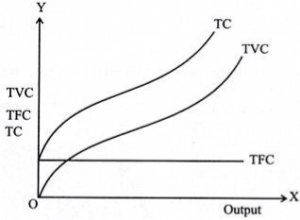
For the TC curve, the following points can be noted:
- The TC curve is shaped of reverse S. This is because of the TVC curve. Since the TFC curve is horizontal, the difference between the TC curve and the TVC curve is the same at each level of the output and is equal to the tfc. This is explained as follows: TC-TVC=TFC
- The TFC curve is parallel to the horizontal axis, and the TVC curve is inverted S-shaped.
- The law that explains the Shape of TVC and subsequent TC is called the law of variable proportions.
The important methods to follow in pricing material issuance are: -
1. Actual cost method
2. First-in first-out (FIFO) method
3. Last-in first-out (LIFO) method
4. Maximum first-in first-out method (HIFO) method
5. Simple average cost method
6. Weighted average cost method
7. Periodic average cost method
8. Standard Cost method
9. Exchange cost method
10. Last-in first-out (NIFO) method
11. Base stock method.
1. Actual cost method:
If you purchase a material specifically for a particular job, the actual cost of the material will be charged to that job. Such materials are usually kept separately and published only for that particular job.
2. First-in first-out (FIFO) method:
CIMA defines FIFO as "a method of setting the price of material issuance using the purchase price of the oldest unit in stock." With this method, the materials are issued out of stock in the order in which they were first stocked. It is assumed that the material that opens first is the material that is used first.
Advantage:
(A) Easy to understand and easy to price in question.
(B) It is a good store management practice to ensure that raw materials leave stores in chronological order based on age.
(C) This is an easy method with less administrative costs than other pricing methods.
(D) This inventory valuation method is accepted under standard accounting practices.
(E) Consistent and realistic practices in inventory and finished product valuation.
(F) Inventory is valued at the latest market price, close to the value based on replacement costs.
Cons: Disadvantages:
(A) If confused with other materials purchased at a different price at a later date, it is uncertain whether the material with the longest stock will be used.
(B) If the price of the purchased material fluctuates significantly, there will be more clerical work and errors may occur.
(C) Manufacturing costs are modest in situations where prices are rising.
(D) Inflationary markets tend to lower prices for key issues. The deflationary market tends to set higher prices for these issues.
(E) Generally, it is necessary to adopt multiple prices for the publication of a single document.
(F) This method makes it difficult to compare costs for different jobs when billed for the same material at different prices.
3. Last in first out (LIFO) method:
With this method, the latest purchase is issued first. Issues are priced on the latest batch you receive and will continue to be billed until the new batch you receive arrives in stock. This is a way to set the issue price of a material using the purchase price of the latest unit in stock.
Advantage:
(A) Shares issued at more recent prices represent the current market value based on exchange costs.
(B) Easy to understand and apply.
(C) Product costs tend to be more realistic as material costs are billed at more recent prices.
(D) When the price is rising, the issue pricing will be the more recent current market price.
(E) It tends to show modest profit figures by minimizing unrealized inventory gains and valuing inventory at its pre-price value, providing a hedge against inflation.
Cons: Disadvantages:
(A) Valuation of inventory in this way is not accepted in the creation of financial accounting.
(B) This is an assumption of a cash flow pattern and is not intended to represent the actual physical flow of material from the store.
(C) It may be necessary to adopt multiple prices for one problem.
(D) It becomes difficult to compare costs between jobs.
(E) It involves more clerical work and sometimes the evaluation may go wrong.
(F) During inflation, the valuation of inventory in this way does not represent the current market price.
4. Highest in first out (HIFO) method:
With this method, the most expensive material is published first, regardless of the date of purchase. The basic assumption is that in a fluctuating inflation market, material costs are quickly absorbed into product costs, hedging the risk of inflation. This method is used when the material is in short supply and when you are running a contract with costs. This method is uncommon and is not accepted by standard accounting practices.
5. Simple average cost method:
In this way, all the materials received are merged into the inventory of existing materials and their identities are lost. The simple average price is calculated regardless of the quantity involved. The simple average cost is obtained by dividing the number of batches and adding the various prices paid during the period to the batches purchased. For example, three batches of material received in Rs. 20, rupees 22 and Rs. 24 per unit each.
The simple average price is calculated as follows:
Rs. 20+ rupees 22+ rupees 24/3 batch = Rs. 36/3 batch = 22 rupees per unit
This method takes into account the prices of different batches, but is not common because it does not take into account the quantity purchased in different batches. Use this method when the price is less volatile and the stock price is small.
6. Weighted average cost method:
This is a permanent weighted averaging system in which the issue price is recalculated each time after each receipt, taking into account both the total quantity and the total cost when calculating the weighted average price. For example, three batches of material received in a quantity of 2,000 units @ Rs. 25, 2,300 units @ Rupee 26 and 800 units @ Rs. 24.24.
The weighted average price is calculated as follows:
(2,000 units x Rs .25) + (2,300 units x Rs .26) + (800 units x Rs .24) / 2,000 units + 2,300 units + 800 units
= Rs. 25,000+ rupees 20,800 + rupees 22,200 / 3,200 units = rupees 47,000 / 3,200 units = 25.26 per rupee unit
This method tends to smooth out price fluctuations and reduce the number of calculations because each issue is billed at the same price until you receive a new batch of material.
This method is easier than FIFO and LIFO because you do not have to identify each batch individually. However, this method adds more clerical work in calculating the new average price each time you receive a new batch. The calculated issue price rarely represents the actual purchase price.
7. Periodic average cost method:
With this method, instead of recalculating the simple or weighted average cost each time you have a receipt, the average for the entire accounting period is calculated.
The average price of all materials published during the period is calculated as follows:
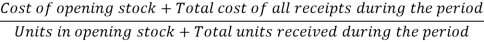
8. Standard cost method:
In this way, important issues are priced at a given standard issue price. The difference between the actual purchase price and the standard issue price is amortized on the income statement. The standard cost is a predetermined cost set by management before the actual material cost is known, and the standard issue price is used for all issuance to production and valuation of final stock.
Careful setting of standard prices first significantly reduces all clerical work and errors and simplifies inventory recording procedures. Eliminating cost fluctuations due to material price fluctuations makes it easier to compare realistic manufacturing costs. This method is not suitable in situations where prices fluctuate.
9. Exchange fee method:
The replacement cost is the cost of replacing the same material by purchasing it on the pricing date of the material issue. It is different from the actual cost on the purchase date. The exchange price is the exchange price of the material at the time the material is issued or on the valuation date of the end-of-term inventory.
This method is unacceptable to standard accounting practices as it reflects costs that are not actually paid. If the shares are held at exchange costs and are purchased at a lower price for balance sheet purposes, an element of profit that has not yet been realized will be included in the income statement.
This method is advocated by charging the job or process for the market price of the material, making it easier to determine the profitability of the job or process. This method is especially suitable for inflationary trends in material market prices. Without the exact market for a particular material, it is difficult to ascertain the replacement price for a material problem.
10. Next Inn First Out (NIFO) Method:
This method is a variant of the exchange cost method. In this way, the price quoted in the latest purchase order or contract is used for all issuance until a new order is placed.
11. Basic stock method:
With this method, the specified quantity of material is always kept in stock and priced as a buffer or base stock at its original cost. In addition, issuance of materials that exceed the basic stock quantity is priced using one of the above methods.
This method shows how prices fluctuate over time. However, this method is uncommon and makes stock valuation completely unrealistic and is not accepted by standard accounting practices.
What are Debit and Credit?
Commercial transactions are events that have a financial impact on an organization's financial statements. When you do these transactions, you record numbers in two accounts. Here, the debit column is on the left and the credit column is on the right.
A debit is an accounting entry that increases an asset or expense account or decreases a liability or equity account. It is placed to the left of the accounting entry.
Credits are accounting entries that increase a liability or capital account or decrease an asset or expense account. It is placed to the right of the accounting entry.
Use of Debits and Credits
Each time an accounting transaction is created, at least two accounts are always affected, a debit entry is recorded for one account and a credit entry is recorded for the other account. Accounting transactions are always said to be "balanced" because the sum of the transaction's debits and credits must always be equal to each other. If the transactions are not balanced, you will not be able to prepare financial statements.
There is often considerable confusion about the inherent meaning of debits or credits.
Asset account. The debit increases the balance and the credit decreases the balance.
Debt account. The debit reduces the balance and the credit increases the balance.
Equity account. The debit reduces the balance and the credit increases the balance.
The reason why the use of debits and credits seems to be reversed in this way is caused by the accounting equations that underlie the entire structure of the accounting transaction.
Asset = Liability + Capital
Therefore, in a sense, you can own an asset only if you have paid it in debt or capital. Therefore, to own one, you must own the other. Therefore, when you create a transaction using debits and credits, you typically increase your assets while increasing your liabilities or capital accounts (or vice versa). There are some exceptions, like increasing one asset account and decreasing another. If you are interested in the accounts that appear in your income statement, the following additional rules apply:
1. Revenue Account. The debit reduces the balance and the credit increases the balance.
2. Expense Account. The debit increases the balance and the credit decreases the balance.
3. Get an Account. The debit reduces the balance and the credit increases the balance.
4. Loss Account. The debit increases the balance and the credit decreases the balance.
Debit and Credit Rules
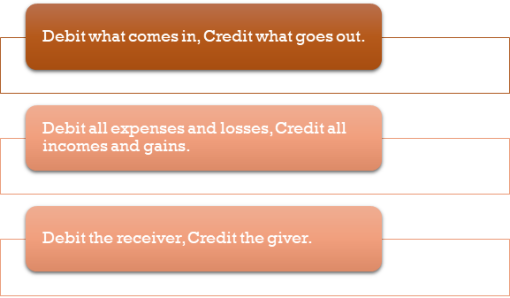
The rules governing the utilization of debits and credits are as follows:
1. Generally, all accounts that contain a debit balance will increase in amount when a debit (left column) is added and decrease in amount when a credit (right column) is added.
2. All accounts, including regular credit balances, increase in amount when credits (right column) are added and decrease when debit (left column) is added to the account.
3. The total amount of debits must be adequate to the entire amount of credits for the transaction.
4. Debits and credits in general accounting transactions.
The year to gain visibility of income, revenue, expenses, and losses incurred in a certain range of periods. It is important to prepare a profit and loss statement because this information helps organizations make the right business decisions, such as where to cut costs, from where the business can generate more profit, and which parts of the business are suffering from losses.
- Profit and loss accounts / statements
- Types of profit and loss
- Gross profit/gross loss
- Profit / loss
Trading account is prepared to check gross profit/loss while profit and loss account is created to check profit and loss/net loss.
Profit and loss accounts are made to check the annual profit or loss of a business. This account only shows overhead. All items of income and expenses, whether cash or non-cash, are considered in this account.
Only revenue or expenses related to the current period are debited or credited to the profit and loss account. The profit and loss account starts with gross profit on the credit side and, if there is a total loss, appears on the debit side. Items not displayed in the profit and loss account format
Drawing: the drawing is not the company's expense. Therefore, we debit it to capital a/c, and not to profit and loss a/c.
Income tax: for a company, income tax is an expense, but for a sole proprietor, it is his personal expense. Therefore, we debit it to the capital A/C.
Discounts: as we know, discounts are of two types–trade discounts and cash discounts. We deduct the trade discount from the amount charged and therefore do not show it in the account books. On the other hand, if the customer pays the amount on a certain date, a cash discount will be possible. We view cash discounts in account books. Therefore, we debit it to the profit and loss account.
Bad debt: it is because of the customer and the amount he does not pay it. We debit this amount to profit and loss a/c in the event that preparations have already been made for a bet that is worse than it is initially written off from it. When bad loans are recovered, it is again. Now it is not credited to the account of the party, but recovered account should be credited to the bad debt and is written on the credit side of the profit and loss account
Profit and Loss Account Format
Particulars | Amount | Particulars | Amount |
To Gross loss b/d | Xxx | To Gross profit b/d | Xxx |
Management expenses: | Xxx | Income: | Xxx |
To salaries | Xxx | By Discount received | Xxx |
To office rent, rates, and taxes | Xxx | By Commission received | Xxx |
To printing and stationery | Xxx | Non-trading income: | Xxx |
To Telephone charges | Xxx | By Bank interest | Xxx |
To Insurance | Xxx | By Rent received | Xxx |
To Audit fees | Xxx | By Dividend received | Xxx |
To Legal charges | Xxx | By Bad debts recovered | Xxx |
To Electricity charges | Xxx | Abnormal gains: | Xxx |
To Maintenance expenses | Xxx | By Profit on sale of machinery | Xxx |
To Repairs and renewals | Xxx | By Profit on sale of investments | Xxx |
To Depreciation | Xxx | By Net Loss (transferred to Capital A/c) | Xxx |
Selling distribution expenses: |
|
|
|
To Salaries | Xxx |
|
|
To Advertisement | Xxx |
|
|
To Godown | Xxx |
|
|
To Carriage outward | Xxx |
|
|
To Bad debts | Xxx |
|
|
To Provision for bad debts | Xxx |
|
|
To Selling commission | Xxx |
|
|
Financial expenses: |
|
|
|
To Bank charges | Xxx |
|
|
To Interest on loan | Xxx |
|
|
To Discount allowed | Xxx |
|
|
Abnormal losses: | Xxx |
|
|
To Loss on sale of machinery | Xxx |
|
|
To Loss on sale of investments | Xxx |
|
|
To Loss by fire | Xxx |
|
|
To Net Profit (transferred to capital a/c) | Xxx |
|
|
TOTAL |
| TOTAL |
|
A balance sheet (also known as a financial statement) is a financial statement that shows the Assets, Liabilities and ownership interests of a business at a specific date. The main purpose of drawing up a balance sheet is to disclose the financial status of the enterprise at a certain date. The balance sheet can be prepared at any time, but it is prepared mainly at the end of the accounting period.
Most of the information about Assets, Liabilities and owner's equity items is taken from the company's adjusted trial balance. Retained earnings are the part of the owner's equity section which is provided by the retained earnings statement.
Section of the balance sheet
To be widely considered about the balance sheet of the division part of assets part of liabilities main capital. For each department:
Assets section
In the balance sheet, assets with similar characteristics are grouped. The mainly adopted approach is to divide assets into current and non-current assets. Liquid assets include cash and all assets that can be converted into cash or expected to be consumed in a short period of time–usually one year. Examples of current assets include cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, prepayment costs or prepayment, short-term investments and inventories.
All assets that aren't listed as current assets are grouped as non-current assets. A common feature of such assets is that they continue to provide profit for a long time-usually more than one year. Examples of such assets include long-term investments, equipment, plants and machinery, land and buildings, and intangible assets.
Debt Division
A debt is an obligation to a party other than the owner of the business. They are grouped as current and long-term liabilities in the balance sheet. Current liabilities are obligations that are expected to be met within a one-year period by using current assets of the business or by providing goods or services.
Owner's equity division
The owner's interest is the obligation of the business to its owner. The term owner's equity is mainly used in the balance sheet of a business in the form of a sole proprietor and partnership. In the balance sheet of the company the term “ownership interest “is often replaced by the term "shareholder interest".
When the balance sheet is created, the liabilities section appears first, and the owner's equity section appears later.
Balance sheet format
There are two formats on the balance sheet that present Assets, Liabilities and owner's ' equity–the account format and the report format.
Assets | $ | Liabilities & Stockholder’s equity | $ |
Current assets: Cash Account receivable Prepaid building rent Unexpired insurance Supplies
Total current assets
|
85,550 4,700 1,500 3,600 250
| Liabilities: Notes payable Accounts payable Salaries payable Income tax payable Unearned service revenue
Total liabilities |
5,000 1,600 2,000 3,000 4,400
|
95.600 | 16,000 | ||
Non-current assets: Equipment 9,000 Acc. Dep. –Equipment 3,600
Total assets |
5,400
| Stockholder’s equity: Capital stock 50,000 Retained earnings 35.000
Total liabilities & stockholder’s equity
|
85,000
|
101,200 | 101,000 | ||
|
|
|
|
In the account form, the balance sheet is divided into the left and right, like the t-account. Both liabilities and the owner's capital are listed on the right side of the balance sheet, while assets are listed on the left. If all the elements of the balance sheet are listed correctly, then the sum on the asset side (that is, on the left) is equal to the sum on the debt and the capital side of the owner (that is, on the right).
BUSINESS CONSULTING COMPANY
BALANCE SHEET
As at December 31, 2015
In reporting format, the balance table element is displayed vertically, the asset section is displayed at the highest, and therefore the liabilities and owner's equity sections are displayed below the asset section.
The example below shows both formats.
Assets Current assets:
Cash Account receivable Prepaid building rent Unexpired insurance Supplies
Total current assets
|
85,500 4,700 1,500 3,600 250
|
95,600
| |
Non-current assets: Equipment 9000 Acc. Dep- Equipment 3600
Total assets
|
5,400
|
101,000
| |
Liabilities & Stockholder’s Equity Liabilities Notes payable Accounts payable Salaries payable Income tax payable Unearned service revenue
Total liabilities
|
5,000 1,600 2000 3000 4,400
|
16,000 | |
Stockholder’s equity: Capital stock Retained earning
Total stockholder’s equity
Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity |
50,000 35,000
|
85,000
| |
101,00 |
Calculation of depreciation
The nature of Depreciation
Depreciation can be defined as a measure of the depletion of an asset's lifetime due to any cause during a particular time period. -Spicer and Pegler.
“Depreciation is a measure of the consumption, consumption, or other loss of value of a depreciable asset resulting from use, time wasted, or obsolescence due to changes in technology or market. During that time, you will be assigned to charge a significant portion of the depreciation amount for each accounting period. Depreciation expense includes the depreciation of assets with a predetermined useful life. "
-Accounting Standard-6 (revised), issued by ICAI.
Depreciation features:
(I) Depreciation is a decline in the value of fixed assets (excluding land). The decline in the value of an asset is inherently permanent. Once shrunk, it cannot be restored to its original value.
(II) Depreciation is a gradual and continuous process because the value of an asset decreases due to the use of the asset or the expiration of time.
(III) It is not an asset valuation process. This is the process of allocating the cost of an asset to its lifetime.
(IV) Depreciation reduces the book value, not the market value of an asset.
(V) Depreciation is only used for property, plant and equipment. It is not used to waste intangible assets such as amortization of goodwill and depletion of natural resources.
Causes of depreciation:
1. Normal physical wear and tear:
The normal use of an asset causes it to physically deteriorate, resulting in a decrease in the value of the asset.
2. Time outflow:
Certain intangible assets, such as trademarks, patents and copyrights, have a fixed lifespan. The value of these assets diminishes over time, whether or not they are used by a company.
3. Obsolescence:
R & D brings innovation in the form of better, technologically advanced machines that dispose of older machines, even if they can be physically performed.
In that case, the market price of certain assets such as computers and automobiles may fall permanently. This reduces the value of older machines. Obsolescence is the loss that results from aging an existing asset and replacing it with a new and improved model of that asset.
4. Accident:
Accidental destruction or damage can reduce the value of an asset.
The accounting concept of Depreciation
Fixed assets are long-term assets. They help produce goods and services. However, when an asset is in use, normal wear, time spills, and obsolescence reduce the value of the asset. This reduction in the value of fixed assets is known as depreciation. Understand the concept of depreciation.
Assets owned by a company for the production and supply of goods and services, expected to be used for more than a fiscal year, and have a limited useful life are called depreciable assets.
When you purchase a fixed asset, it is recorded in your books at its original cost or purchase price. Organizations use this fixed asset to earn or generate revenue for several fiscal years before selling or discarding the asset.
Therefore, you must allocate a portion of your purchase or acquisition costs by fiscal year until you use it. This allocation of costs is called depreciation. Depreciation is an organizational expense.
For example, a Setu company buys a machine for £ 2,000,000, uses it for 10 years and then sells it for £ 400,000. Therefore, the cost of a machine for business use is £ 1600,000 (£ 2000000-400000). Now, for every 10 fiscal years you've been using this machine, you need to allocate this £ 1600,000 cost as a project cost. This cost is a depreciation cost of £ 160,000 (1600000/10).
In other words, the concept of depreciation is the cost of getting a service from the use of an asset. You need to match the depreciation cost of a fixed asset with the revenue for the year in which it was used. Therefore, depreciation is charged as an income statement expense.
Factors in the measurement of Depreciation
As already mentioned, depreciation is not an attempt to record changes in the market value of an asset, but a systematic allocation of the total cost of the depreciable asset (capital investment) to the expense (income and expenditure) over the useful life of the asset. The value of some assets can increase in the short term, but the depreciation process continues. Based on the principle of matching, a reasonable portion of capital expenditure (that is, the cost of an asset) should be charged to revenue during the useful life of the asset.
Depreciation
The calculation of depreciation expense for the accounting period is affected as follows:
(I) The actual cost of the asset
(II) Estimated useful life of the asset
(III) Estimated residual value of the asset.
It is worth mentioning here that of the three factors, two are based on mere estimation and only one is actually based. Therefore, the depreciation calculation is an estimated loss on the value of the asset, not the actual exact reduction in the value of the asset.
The following is a detailed description of each of the above elements.
1. Actual cost of the asset:
The actual cost or acquisition cost means the acquisition cost of the asset and includes all incidental costs required to return the asset to its current state and location. Examples of such costs are installation costs, internal transportation, or capital-based costs incurred to improve such assets.
2. Estimated useful life of the asset:
The estimated useful life of an asset is one of the following:
(I) The period during which the depreciable asset is expected to be used by the entity or
(II) The number of production or similar units expected to be derived from the use of assets by a company.
3. Estimated residual value or scrap value of the asset:
The salvage value or scrap value is the expected value that may be realized when an asset is sold or exchanged at the end of its estimated useful life. If residual value is important, it should be considered in the depreciation calculation. However, insignificant residual value can be ignored in the depreciation calculation.
Depreciation is an ongoing process, but we do not record depreciation daily. In fact, the total depreciation expense charged on an asset is the prepaid expense paid by the entity at the time of acquisition of the asset.
In other words, this expense should be treated like a deferred expense, and only adjustment entries should be passed each year to claim reasonable and appropriate depreciation for income statement revenue.
Here are some other factors that influence the measurement of depreciation:
(I) Original cost of the asset: The cost includes all costs incurred to acquire the asset. In other words, the purchase price includes shipping and installation costs, if any.
(II) When an asset is added during the year, taking into account the date the addition was made.
(III) Estimated useful life of the asset.
(IV) Scrap or residual value of an asset.
(V) Obsolescence, that is, the possibility of assets becoming obsolete
(VI) Repairs and updates.
(VII) Operator skills to handle assets.
(VIII) Legal provisions or other restrictions related to depreciation.
(IX) Working hours of the asset.
Methods of computing depreciation: Straight line method and Diminishing Balance Method; Disposal of Depreciable assets – change of method.
Straight line method
What is the straight-line method?
The straight-line method is the default method used to evenly recognize the carrying amount of fixed assets over their useful lives. This is used when there is no particular pattern in how an asset is used over time. The straight-line method is the easiest depreciation method to calculate and is highly recommended for use as it causes few calculation errors. The procedure for flat-rate calculation is as follows.
- Determines the initial cost of an asset recognized as a fixed asset.
- Subtract the estimated residual value of the asset from the amount recorded in the books.
- Determines the estimated useful life of an asset. It is easiest to use the standard useful life for each class of asset.
- Divide the estimated useful life (yearly) by 1 to calculate the depreciation rate using the straight-line method.
- Multiply the depreciation rate by the cost of assets (minus salvage value).
- Once calculated, depreciation expense is recorded in accounting records as a depreciation expense account and a credit to the accumulated depreciation account. Accumulated depreciation is against assets. That is, it is paired with the fixed asset account and the depreciation is reduced.
Formula:
Depreciation = (Asset Cost – Net Residual Value) / Service Life
Depreciation rate = (annual depreciation cost x 100) / cost of capital
Straight-line Journal Entries:
1. Purchase of Assets A / c Dr. xx
To cash / bank / creditor A / c xx
(Purchasing assets)
2. Depreciation of assets A / c Dr. xx
To asset A /c xx
(Assets are subject to depreciation)
3. Transfer depreciation gains / losses A / c Dr. xx
To depreciation of asset A / c xx
(Asset depreciation is transferred to the profit and loss account)
Example 1
Pensive Corporation will purchase a Procrastinator Deluxe machine for $ 60,000. It has an estimated salvage value of $ 10,000 and a useful life of 5 years. Pensive calculates the machine's annual flat-rate depreciation as follows:
Solution
$ 60,000 Purchase Cost – $ 10,000 Estimated Residual Value = $ 50,000 Depreciable Asset Cost
1/5-year useful life = 20% annual depreciation rate
20% depreciation rate x $ 50,000 depreciation asset cost = $ 10,000 annual depreciation
Diminishing Balance Method
The various depreciation methods are based on mathematical formulas. This formula is derived from a study of asset behaviour over a period of time. One such depreciation method is the depreciation method. Learn more about this method.
According to the depreciation method, depreciation is charged at a fixed percentage of the book value of the asset. It is also known as depreciation or depreciation because its book value decreases each year.
Since the book value decreases every year, the depreciation amount also decreases every year. This way, the value of the asset never goes to zero.
If you plot the depreciation amount billed this way and the corresponding period on the graph, the line will move down.
This method was previously based on the assumption that the cost of repairing an asset is low and therefore more depreciation costs must be charged. In addition, depreciation costs will decrease as repair costs increase in later years. Therefore, this method puts an equal burden on profits each year for the life of the asset.
However, this method may not provide full depreciation at the end of the asset's useful life if the applicable depreciation rate is not appropriate.
In addition, when applying this method, it is necessary to consider the period of use of the asset. If the asset is used for only two months in a year, depreciation will only be charged for two months.
However, if the asset is used for more than 180 days for income tax purposes, you will be charged full-year depreciation. Income tax rules also allow you to depreciate using the depreciation method.
The formula is:
Depreciation Rate = 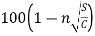
Where n = number of years
S = Salvage value
C = Cost of asset
Amount of depreciation= Book Value x Rate of Depreciation
100
Disposal of Depreciable Assets – Change of Method
Accounting policies and principles need to be applied consistently when recording financial transactions. This is the principle of consistency.
At the end of each fiscal year, management should consider depreciation methods. If there are significant changes in the pattern of future economic returns from the asset, the depreciation method will also need to change.
Accounting Standard 1-According to the disclosure of accounting policies, changes in depreciation methods are changes in accounting estimates. Therefore, footnote quantification and full disclosure are required. You also need to disclose the legitimacy of the change and its economic impact.
Therefore, the depreciation method can be changed without or with a retroactive effect. The lack of retroactive impact means that no adjustments have been made to past entries and only future depreciation will be billed in the new way. While having a retroactive effect, it means that the depreciation amount charged will be adjusted from the date of purchase of the asset.
Taxation is the means by which a government or tax authority imposes or imposes taxes on citizens and businesses. Taxation applies to all levels, from income tax to Goods and Services Tax (GST).
What is Taxation?
Central and state governments play an important role in determining Indian taxes. Over the past few years, state and central governments have undertaken various policy reforms to streamline the taxation process and ensure national transparency. One such change was the Goods and Services Tax (GST), which eases the tax system for the sale and delivery of goods and services in the country.
Taxes are a compulsory contribution to government revenues and are an integral part of driving a country's economic growth. Taxes are used to provide basic services and amenities to people in the country. The Constitution of India gives the Government of India the right to collect taxes. India's tax system is a three-tiered structure that includes central, state and local governments.
What are the different types of taxes in India?
The tax structure usually includes direct and indirect taxes.
- Direct Taxes: These are taxes levied on individuals and must be paid directly to the government. The Central Direct Tax Commission (CBDT) is responsible for the governance of this tax.
Some important direct taxes are:
- Income tax
- Wealth tax
- Gift tax
- Capital gains tax
- Securities transaction tax
- Corporate tax
Of these taxes, income tax is the most common tax levied on individuals. This tax is levied on income earned during the fiscal year. The tax rate is determined according to the applicable tax slab. Individuals include Hindu non-divided families (HUFs), companies, companies, co-operatives and trusts.
2. Indirect tax: Indirect tax is a fee that is indirectly levied on the public. These are mainly billed through goods and services. The seller receives these taxes at a price and is collected by the relevant government agency.
Some important indirect taxes are:
- Consumption tax
- Goods and services tax
- Value added tax (vat)
- Tariffs
- Toll tax
- Octroi's duty
Who collects taxes?
- The Constitution of India grants three statutory bodies the right to collect taxes in India, including:
- The central government collects income taxes, customs duties, central taxes, etc.
- The state government collects taxes on agricultural income, professional tax, state excise tax, value added tax, and more.
- Local governments collect taxes such as water tax and property tax.
However, in India, the central government introduced the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017, incorporating several taxes into one blanket. Some of the taxes that have been replaced by GST are:
- Consumption tax
- Service tax
- Octroi
- Central excise tax
- Entertainment tax
- Purchase tax
GST is a multi-level location-based tax that is levied at each stage of the supply chain, from the purchase of raw materials to the sale of finished products to the end consumer. Generally, GST applies whenever the supply has added value and transfer of ownership.
GST is collected by the government of the destination where the final purchase is made. GST has three components.
- Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST), where the central government collects fees for the supply of goods and services in the state
- State Goods and Services Tax (SGST) or Union Territory UTGST. State government / Union territory collects taxes on the supply of goods and services within the state.
- Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST), which collects taxes for the central government to sell goods and services across state boundaries
What are the benefits of taxes?
No one likes to pay taxes, but it is important to impose an appropriate fee on the collection agency. The money raised from taxes will be used to support development and provide resources to the people of the country. However, to reduce the burden of taxes on the public, especially income tax, the government offers certain standard deductions, tax exemptions, and tax deductions for tax-saving investments made within the scope of the Income Tax Act.
With tax payments and formal income tax return (ITR) filing, you can also expedite loan approval, improve credit status, and expedite VISA processing. In addition, the ITR document acts as a self-employed income proof and is easy to get a refund.
Key takeaways:
- Financial management typically specializes in current property and modern-day liabilities and is regularly related to short-time period hard work capital management, which manages fluctuations in overseas currencies and product cycles thru hedging
- This option also overlaps with financial control as it includes green and powerful every day coins management.
- Additionally, i.e. He is also concerned in long-time period strategic financial control with a focal point on.
- Capital structure management such as financing, capital budget (capital allocation between enterprise units or merchandise), and dividend policy. These latter are greater "corporate finance" regions in huge corporations.
- Constant prices are set for a particular period and do no longer change with manufacturing degrees.
- Constant fees may be direct or indirect expenses and might have an effect on profitability at numerous points inside the earnings declaration.
- Variable charges are expenses that alternate in proportion to production or income.
- Variable prices boom as manufacturing or sales boom. Variable charges lower as manufacturing or income lower.
- Variable costs are in assessment to fixed costs, which do now not alternate in percentage to manufacturing or income.
- Marginal production fees are a crucial idea in control accounting because they assist groups optimize manufacturing thru economies of scale.
- Organizations seeking to maximize earnings produce until marginal cost (MC) equals marginal sales (MR).
- Fixed fees are consistent irrespective of production level, so the higher the production extent, the decrease the fixed fee according to unit due to the fact the full is allocated to greater gadgets.
- Variable fees range based on production degree, so the extra units you produce, the more variable costs you add.
- Marginal fees are charges related to the production of additional production gadgets.
- It is calculated as the trade in total production value divided via the exchange in the variety of production gadgets.
- Marginal costs exist whilst the total fee of manufacturing consists of variable charges.
- There are various varieties of marginal prices, along with marginal social costs, marginal private fees, and marginal outside fees.
- According to accounting matching principles, depreciation links the value of employing a tangible asset with the profits gained over its useful life.
- There are differing types of depreciation, including the straight-line method of depreciation and various sorts of accelerated depreciation.
- Accumulated depreciation is that the sum of all depreciation recorded on an asset up to a specific date.
- The value of an asset on the record is that the acquisition cost minus all accumulated depreciation.
- The carrying amount of an asset in any case depreciation has been made is named its salvage value.
- The straight-line method of depreciation may be a method of calculating depreciation and is that the process of paying an asset for an extended period of your time than when it had been purchased.
- Straight-line bases are popular because they're easy to calculate and understand, but they even have some drawbacks.
- Taxation takes place whilst the authorities or different government require residents and companies to pay the authorities.
- Charges are involuntary and, in assessment to different payments, aren't linked to the services supplied or supplied.
- Taxes are levied on transactions which includes the sale of belongings and stocks and on bodily property together with housing.
- Tax sorts encompass income, companies, capital gains, property, inheritance, and income.
- The balance sheet is one of the three main financial statements used to evaluate a business (the income statement and the cash flow statement are the other two).
- The balance sheet is a snapshot that shows the financial position (ownership and debt) of the company as of the issue date.
- Fundamental analysts use the balance sheet in combination with other financial statements to calculate financial ratios.
References:
- O. P. Khanna, industrial engineering and management, Dhanpat Rai and sons, New Delhi.
- E. H. McGraw, S. J. Basic managerial skill for all.
- Tarek Khalil, Management of Technology Tata McGraw Hill Publication Pvt. Ltd.
- Prabuddha Ganguli Intellectual Property rights Tata McGraw Hill Publication Company
- Management Accounting and financial management by M. Y. Khan and P.K. Jain, Tata McGraw Hill-Tata-ISBN.