UNIT 3
DESIGN OF BELT CONVEYOR SYSTEM FOR MATERIAL HANDLING
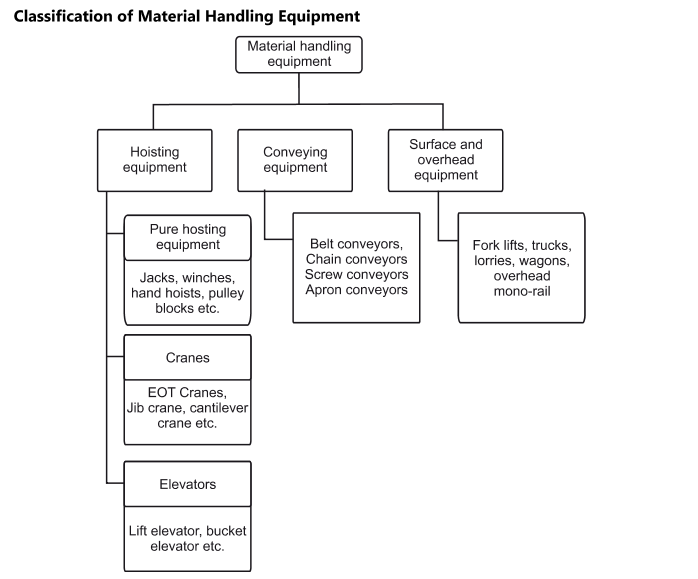
The development of material handling system to move materials from one stage to another stage is very important. Materials handling includes moving, packaging and storing all the materials used by the production unit. Material handling is one of the important management and also in production.
Materials are received and is moved into the plant and transferred to the storeroom. When materials are needed it is moved along the path of manufacturing. Plant layout and, material handling are closely inter-related; it has to be adjusted according to the layout of the plant.
A general definition of the system is a complex unity formed of many diverse parts subjected to a common purpose.
The characteristics of system are called subsystems.
Material handling can also be considered to be a system whose subsystem is
The system concept of material handling means the different types of material handling needed at different parts of an industry. The use of this will reduce overall cost.
The basic objectives of material handling system are:
The types of load handled by a material handling system can be of two types
Bulk load
Unit load
Unit loads are those loads which can be counted by numbers or units
Examples are machine, building block, containers etc...
In this type of conveyor the side belts remain flat supported by cylindrical rollers. These are used for shorter length and suitable for unit loads such as boxes, packages etc. and in manufacturing, assembly operation. These are used for conveyors between workstation and in assembly line for mass production.

In this conveyor wide flat belt is supported on troughed carrying rollers or shaped supporting surface so that the two edges of the active side of the belt are elevated from the middle part to form a trough, it provides a greater carrying capacity than a flat belt of equal width for conveying bulk materials. Such type of conveyors are used in handling bulk material of different classes.

Capacity of belt conveyor (Q):
The material which is carried out by conveyor system is called capacity of the conveyor.
Q = C x b2 x V m3/sec
where, b = Storage material width in m = (0.9 B – 0.05)
B = Width of the belt in m
Q = Capacity of conveyor m3/sec
M = Mass capacity of conveyor
V = Speed of belt
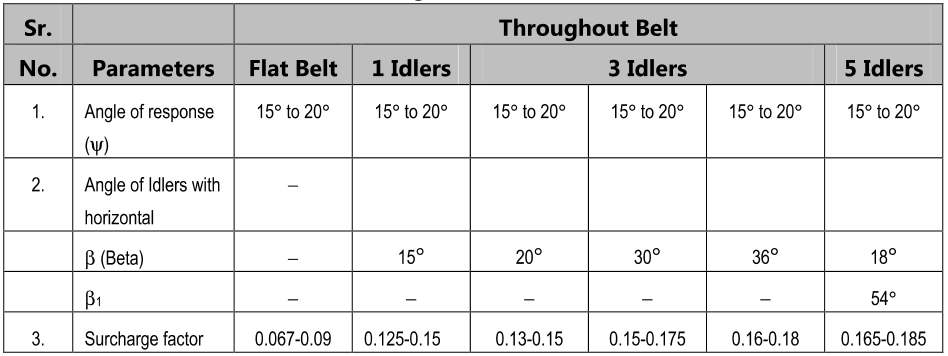
Horizontal belt conveyor capacity :
Q = C x b2 x V
Q = C(0.92B – 0.05)2 V m3/sec
where C = Surge factor
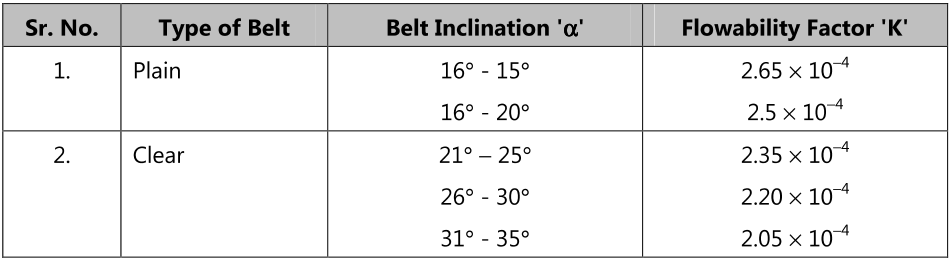
Capacity of inclined Belt Conveyors :
Q = K x b2 x V m3/sec
Q = K (0.9B – 0.05)2 V m3/sec
Q = K (0.9B – 0.05)2 V x 3600mi3/sec
Mass capacity of inclined conveyor
M = ρQ
K = Flow ability Factor
ρ = Density of material
Conveyor belt speed :
The running conveyor belt travels at speed which is called as conveyor speed
The speed depend on
The weight of material is fine and light in order to prevent slippage
The wider belts are operated at higher speeds
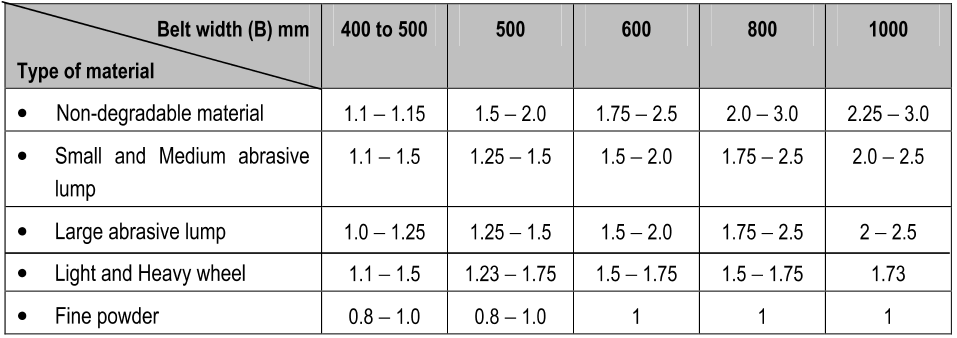
Standard belt width used for the conveyor belts are:
400, 450, 500, 600, 750, 800, 900, 1000, 1200, 1400, 1600, 1800, 2000, 2200, 2400 mm.
Synthetic rubber is in use for belts. Combination of synthetic and natural rubber have been found satisfactory. Synthetics are superior under special circumstances eg, neoprene for flame resistance and resistant to petroleum based oils, Buna N for resistance to vegetable, animal and petroleum oils, and butyl for resistance to heat.
Fabric Ply Belts :
The most common carcass design is made up of layers or piles of woven fabrics bonded together. The fabric is made from a variety of materials. Some of these are listed below with characteristics.
Material | Characteristics |
Cotton(Natural Cellulose Composition) | This is the only natural fibre carcass used excessively in conveyor belts. Its strength increases when it is wet but the absorption of moisture results in poor dimensional stability. It is also susceptible to mild dew attacks. |
Rayon (Regenerated Cellulose Composition) | Slightly stronger that cotton, but tensile strength is lowered by water. High absorption reduces the dimensional stability. Chemical resistance is similar to cotton and is Susceptible to mildew attack. |
Glass | Very high strength compared to rayon. Low elongation, mainly used in high temperature applications. It has poor flex life and has a limited use. |
Nylon (Polyamide) | High strength, high elongation, good resistance to abrasion, fatigue and impact. Moisture absorption not as high as cotton but it reduces the dimensional stability. |
Polyester | High strength, exceptionally good abrasion and fatigue resistance. Extremely low moisture absorption and is unaffected by mildew and is used extensively for conveyor belts (70 to 75% of all conveyor) |
Kevlar (Aramid) | Aramid has twice the strength of steel, with stretch characteristics roughly half wave between steel and polyester. It is significantly lower in weight that steel and will not rust. The belts made from this are extremely expensive and are used only in special circumstances. |
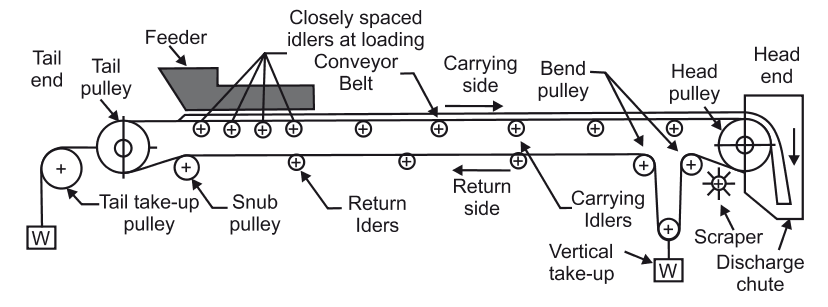
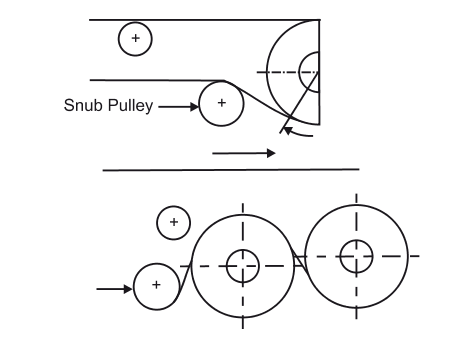
The conveyor arrangement uses the following types of pulleys
Driving pulley (Head and Tail pulley)

Snub Pulley
These are used to increase the angle of wrap of the belt and overall for all the necessary changes in belt direction in the areas of counterweight tensioner, mobile unloader etc.
The choice of the optimum conveyor system and its project design and rationalization depends on full knowledge of the construction characteristics and the forces involved that apply themselves to all the system components.
16) BELT TAKE UP ARRANGEMENT
Idlers
Idlers
The efficiency of belt conveyor is mainly dependent on idlers. For higher efficiency of conveying systems, the idlers must be accurately made and provide a rigid framework. This will maintain a permanent, well balanced smooth running alignment.
There are, in general, three kinds of belt carrying idlers used in handling of bulk materials. The type of idlers affects the cross-sectional load on the belt.
There are two basic types of belt conveyor idlers:
Carrying idlers which support the loaded run of the conveyor belt; and
Return idlers which support empty return run of the conveyor belt.
Carrying Idlers
Carrying idlers
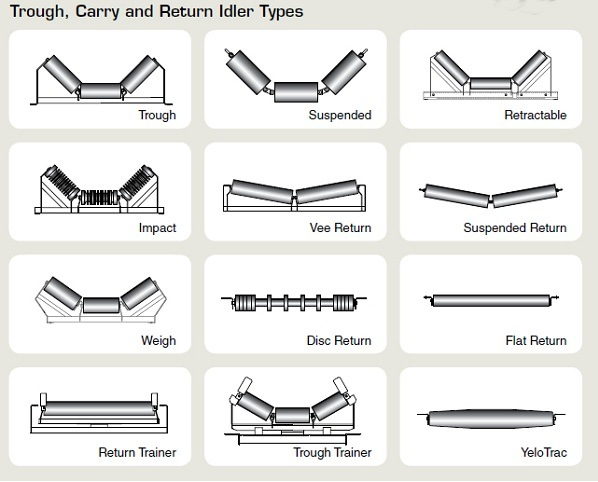
Return Idlers
Rollers
Main functions of take up are:
Two types of belt take up devices are generally used:
Fixed take-up devices that are adjusted periodically
Automatic take-up devices (constant load type)
Fixed take-up devices that are adjusted periodically
In this type of take-up devices, the take-up pulley remains fixed between successive periodic adjustments.
Take-ups of this type generally used are:
Automatic take-up devices
In this system, take-up pulley is mounted on slides or on a trolley and travels freely while a constant tension is automatically maintained to ensure normal conveyor operation in all cases. The most frequently used type is gravity weight operated take-up device. Hydraulic, pneumatic or electrical take-up devices of
Various types are also used. All types of automatic take up devices shall include a system for adjusting belt tension. Automatic take-up has following features:
The power requirement of belt conveyor is
Let, Q = Conveyor capacity m3/sec
ρ = Mass density of material kg/ m3
h = Natural trough which is to be lifted ‘h’ m
L = Length of belt m
Co = Specific factor
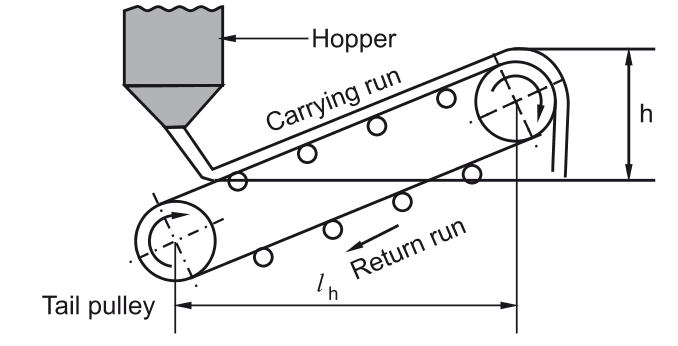

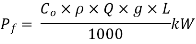
Total power required (P)
P =  +
+ 

Determine the resistance offered by a single carrying and return idler for the conveyer having the following data
Capacity of the conveyer = 400tph
Belt speed = 2m/sec
Mass of belt = 16kg/m
Mass of idler = 25.1 kg
Carrying side pitch = 2 m
Return side pitch = 2 m
Coefficient of friction between the idler and the pulley = 0.02
Coefficient of friction between the roller pin and idler = 0.5
Belt Inclination = 15o

