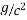UNIT-6
NON-FERROUS MATERIALS
Nonferrous materials: -
Nonferrous material is those which have a metal other than iron as their main constituent such as copper, aluminum, brass, bronzer, tin, silver etc.
Classification of nonferrous material: -
Nonferrous material classified in nine
Study of nonferrous alloys with their designation: -
Numerical system of designation for non-Ferrous metals (weeks off number, catalogue of principal groups 2 and 3) is define by standard DINI 7007, the first digit in designation symbolized the white group of similar materials.
2.0000 to 2.013 - Pure Cu
2.0200 to 2.0599 - Cu Zn alloy
2.0.00 to 2.0699 - Reserved
2.0700 to 2.0799 - Cu, Ni Zn alloy
2.0800 to 2.0899 - Cu, Ni Alloy
2. Zinc, cadmium and its alloy
2.200 to 2.2099 - Pure zinc
2.2100 to 2.2199 - Zinc alloy
2.2200 to 2.2299 - Zinc sheets
2.2300 to 2.2399 - Zinc bare
3. Lead and tin alloy
2.3500 to 2.3509 - Pure tin
2.3510 to 2.3609 - Reserved
2.3610 to 2.3699 - Sn Pb soft solder
4. Aluminum and aluminum alloy
3.0100 to 3.0499 – pure aluminum
3.0500 to 3.0599 - aluminum alloy with Mn, Ir
3.0600 to 3.0699 - aluminum alloy with Pb, Sb, Sn bi, Cd, Ca
3.0700 to 3.0999 - aluminum alloys with Ni, Co
Composition and microstructure of nonferrous metals: -
Hair we have explain some nonferrous material
a) Duralumin
b) Y alloy
c) Magnalium
d) Hindalium
a) It is an important wrought alloy. is composition containing following chemical component
Copper = 3.5 – 4.5 %
Manganese = 0.4 – 0.7%
Magnesium = 0.4 – 0.7%
Aluminum = 94%

b) Y alloy: - Y alloy is also copper aluminum alloy. The addition of copper to pure aluminum increase its strength and machinability. Its composition contents following chemical contents
Copper = 3.5 – 4.5%
Manganese = 1.2 – 1.7%
Nickel = 1.8 – 2.3 %
Silicon, magnesium, iron = 0.5% each
Aluminum = 92.5%
Copper zinc alloys (brasses): -
The various types of brasses composition
Cu = 85%
Zn = 15%
2. Yellow brass: - Also known as Mentz metal, it contains
Cu = 60%
Zn = 40%
3. Admiralty brass: - it contains
Cu = 71%
Zn = 29%
Sn = 1%
4. Naval brass
Cu = 59%
Zn = 40%
Sn = 1%
5. Manganese Brass: -
Cu = 60%
Zn = 38%
Mn = 0.5%
Fe = 1.0%
Sn = 0.5%
Mechanical and other properties for industrial application:
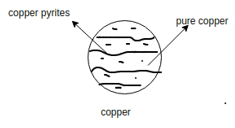
Copper: -
Copper is one of the most widely used nonferrous material in industry. It is extracted from area of copper such as copper glance, copper pyrites, malachite and azurite.
Properties: -
Munts metal is having high strength and high hot workability. It is having tensile strength 38 kg/m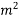 . The percentage elongation of this brass is 45%.
. The percentage elongation of this brass is 45%.
Application: - Yellow brass or munts metal is suitable for hot working by rolling extrusion on 4 stampings. It is utilized for making small various components of machines and electrical equipment such as bolts, rod, tubes, valves, and fuses and also making for pump parts, valves, taps, condensers tubes, sheet form for ship sheathing.
Tin bronze: -
Alloys consists of copper-based material with the major alloy element being tin.
Properties
The percentage of tin provides high Mechanical properties, they pass stronger Mechanical properties.
Application
Their uses include heavy load, low-speed service application. Their alloys are the premier alloy for long life under heavy loads and used for piston pin and linkage bushing, valves guides. Many types of bearing including rolling mill, worm and pilot for the machine tool industry.
Beryllium bronze: -
Beryllium bronze is a copper bar alloy contains
Cu = 97.5%
Br = 2.5%
Applications
Beryllium bronze a is particularly suitable material for making springs, tubes, diaphragms and electrical contacts, heavy duty electrical switches, cams and bushings.
Properties: -
It possesses higher tensile strength than other bronze. It possesses excellent corrosion resistance. It is having high yield point and high fatigue limit. It is having good but cold assistance.
Aluminum alloy: -
The aluminum may be easily alloyed with other elements like copper, magnesium, zinc, manganese, silicon, nickel to improve various properties.
LM5: - The aluminum alloy confirms to BS 1490: 1988 LM5
Chemical composition
Copper = Max 0.1
Iron = Max 0.6
Zinc = Max 0.1
Titanium = Max 0.2
Magnesium = 3.0 – 6.0
Manganese = 0.3 – 0.7
Lead = 0.5 max.
Aluminum = remainder
Silicon = max 0.3
Tin = max 0.05
Nickel = max 0.1
Mechanical properties
Here we have explained some properties
Properties | Sand casting | Gravity casting |
0.2 % proof stress (N/ | 90 - 110 | 90 - 120 |
Tensile strength | 140 – 170 | 17 0-2 80 |
Elongation (%) | 3 | 5 |
Impact resistance 1200 (Nm) | 7.9 | 12.6 |
Brinell hardness | 50 – 70 | 60 - 70 |
Modulus of elasticity | 71 | 71 |
Shear strength | 140 | - |
Application: -
LM5 is used where very high resistance to corrosion from sea water or Marine atmosphere is required for equipment used for the manufacture of foodstuffs, cooking, utensils and chemical plant and application include, for example door furnitures, car fittings and trim. Similar aluminum casting. LM5 is mainly used for sand casting, for gravity the casting.
Duralumin:- It is unimportant wrought alloy. Its composition contains following chemical components
Copper = 3.5 - 4.5 %
Manganese = 0.4 – 0.7%
Magnesium = 0.4 days 0.7%
Aluminum = 94%
Properties
Duralumin can be very easily forged casted and worked because it possesses low melting point. It has high tensile strength, compare with mild steel combined with the characteristic lightness of aluminum. It is light in weight as compared to its strength in comparison to other metal.
Application
Duralumin is used in wrought conditions for forging, stampings, bars, sheets, tubes, bolts and rivals. It is also employed in surgical and orthopedic work, nonmagnetic work and measuring instrument parts constructing work.
Y alloy: - Y alloy is also called copper aluminum alloy. The addition of copper to aluminum increase its strength and machinability. It contains following chemical compositions.
Copper = 3.5 – 4.5 %
Manganese = 1.2 – 1.7%
Nickel = 1.8 – 2.8%
Silicon, magnesium, iron = 0.6% each
Aluminum = 92.5%
Properties
The addition of copper in aluminum increases its strength and machinability. Y alloy can be easily cast and hot worked. Like aluminum alloy is heat treated and age hardened.
Hinduminum: - Is a common trade name of aluminum alloy. It is an alloy of aluminum, magnesium, manganese, chromium and silicon etc.
Property
Disallowed are strong and hard, easily cleaned, low cost than stainless steel having fine finish, having good scratch resistance.
Application
It is mainly used for manufacture anodized utensils. Utensils manufactured by this alloy are strong and hand easily clean.
Nickel and its alloy: -
The important nickel alloy is Monel metal, invan, nomonic.
Invan:- Invan also known generally as Fe Ni 36 is a nickel iron alloy notable for its uniquely low coefficient of thermal expansion. The name Invar comes from the word 'Invaniable' referring to its relative lack of expansion or contraction with temperature changes. It contains around 86% nickel and 64% iron.
Properties
Invar have a coefficient thermal expansion of about 1.2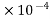 while ordinary Steel have any around 11-15 ppm though display high dimensional stability over a range of temperature.
while ordinary Steel have any around 11-15 ppm though display high dimensional stability over a range of temperature.
Application
Invar is used where high dimensional stability is required such as precision instrument, clocks, siesmic creep gauge, television shadow mask frames, valves in engines and large aerostructure moulds
Inconel :- it contains
Ni = 80%
Cr = 14%
Fe = 6%
Properties
it has high resistance to corrosion and oxidation at elevated temperature. It can be readily cold worked and hot worked. But does not respond to heat treatment. It contains high Mechanical properties, Coupled corrosion and resistance property. It can be cast, forged, rolled and cold down. Its specific gravity is 8.55 and melting point 1395 degree Celsius. It's Brinell hardness is about 160 BHN.
Application
It is used for making springs, exhaust main fold of aircraft engines, machinery for food processing industries especially milk and milk products. It is widely used for processing uranium and for sheeting for high temperature heating element.
Titanium alloy: -
Titanium alloy are alloys that contain a mixture of titanium and other chemical components. Such alloy has very high tensile strength and toughness. Here we discuss two main titanium alloy

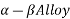
Properties
Generally, it contains predominant Lee Alpha phase and temperature well above 40 degree Celsius. Alpha rich boy is more resistance to high temperature creep and Alpha alloys exhibit little strengthening from heat treatment and they have good workability.
Cobalt: -
Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27.
Cobalt and its alloy: -
Cobalt based super alloys have historically consumed most of the Cobalt produced. Here we have discussed.
1) Stellite alloy:- Stellite alloys are a group of Cobalt chromium “super alloys” consisting of complex carbides in an alloy matrix. Predominantly design for high wear resistance and super chemical and corrosion performance in hostile environment therefore it is possible to group stellite alloys as follows: -
High carbon= design for high wear applications
Low carbon = for high temperature
Loss carbon/ higher chromium to combat corrosion
It consists of
Cobalt = 57%
Chromium = 28.3 %
Tungsten = 11.30%
Carbon = 2.3%
Silicon = 1.2%
Iron = 1%
Nickel = 1%
Other = 1.50%
Properties: - The properties of steel alloys are
Property | Metric | Imperial |
Density | 8.69 | 0.314 Ib/i |
Hardness Rockwell | 50 - 58 | 50 – 58 |
Tensile strength | 1195 MPa | 173 Ksi |
Yield strength | 1050 MPa | 152 Ksi |
Modulus of elasticity | 2304 MPa | 33.4×106 Psi |
Application: -
Saw teeth, hand facing and acid resistance, machine parts, poppet valves, seats and exhaust valve of Application: - engine, M2HB machine gear and machine gun barrel, turning tool for lathe.
2) Alnico: - The composition of alnico alloys is typically
Aluminum= 8-12%
Co = 5-24%
Ni = [15-26%
Properties: -
Alnico alloys can be magnetized to produce strong magnetic field. It has a high coercivity, thus making strong permanent magnets. Alnico alloys have some of the highest Curie temperature off any magnetic material, they are only magnets that have useful magnetism even when heated red hot. the property as well as its brittleness and high melting point.
Application
Alnico magnets are widely used in industrial and application where strong permanent magnets are needed. Examples are electric motor, electric guitar pickups, microphones, sensors, magnetron tubes and cow magnets.
Bearing alloy: -
A bearing alloy commonly possesses good wearing quality, low coefficient of friction, high thermal conductivity, good casting qualities, non-corrosive properties, ability to withstand high pressure and impact low shrinkage after coating and less cost various bearing metal are
Lead based alloy: -
Lead is very soft and ductile. It is normally used commercially as lead alloys. Antimony, tin, arsenic and calcium are the most common alloys.
Property:
Antimony generally is used to give greater hardness and strength as in storage battery. It has high density and easy workability. It has very good resistance to corrosion. It is the softest and heaviest of all common material. It is very malleable and may be readily formed into cell.
Application
It is used in battery grids, sheets, pipe and casting and used in safety plug in boiler and cable sheathing.
Tin based alloy: -
3-piece chalk is also known as Babbitt metal which contains
Sn = 88%
Sb = 8%
Cu=4%
Properties
Babbitt battle possesses excellent antifriction properties and sufficient mechanical strength. It can be easily casted. It is expensive because of high tin contents.
Application
Because of the above properties babbitt metal is the most common Bearing metal with cast iron boxes. Where the bearing are subjected to Bering high pressure load application.
Age hardening: Age hardening also known as precipitation hardening is a type of heat treatment that is used to impart strength to metals and their alloys. It is called precipitation hurting as it makes use of solid impurities or precipitate for the strengthening process. The metal is aged by either heating it or keeping it stored at lower temperature so that precipitates are formed.
Advantage: -
Some of the advantages that each hardening offers
Application
Some of the application of age hardening are: -
Additive manufacturing processes are gradually increasing in their practical application and engineers are starting to figure out where, when and how they could be most useful.
Metals: -
Industrial machinery has the ability to use metals. We have some metals
a) Stainless steel
b) Steel
c) Titanium
d) Gold
e) Silver
a) Stainless steel: - Here we have discussed composition, properties and application
C = 0.030
Mn= 2%
P = 0.04
S = 0.03
Si = 0.75
Cr = 18.0-20.00%
Ni = 8.00 – 10.00%
Al = 0.1%
Properties
Density = 0.29 lb./i
And modulus of elasticity in tension = 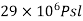
Good thermal conductivity and formability also good. It's corrosion resistance alloy.
Application
Architecture, building and construction, cutlery and kitchen ware, power generation, food production, automotive and medical application etc.
Titanium: -
Here we have discussed chemical composition of (Ti-4 Al-4V)
Ti = 90%
Al = 6%
V = 4%
C= less than 0
O = less than 0.20%
N = less than 0.05%
Fe= less than 0.3%
Properties
It contains both alpha and beta phase crystalline structure, the high strength grade can be e use at cryogenic temperature to about 800-degree Fahrenheit.
Application
In the aerospace industry the alloy is commonly used in fan blades, fan disks, compression blades, front compressor cases and multistage disk and airframe forging in the annealed or heat-treated conditions.
Thermoplastics
Thermoplastics all polymers are amongst the cheapest material that can be used. The main thermoplastic being used is
a) Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
b) Poly lactic acid (PLA)
c) Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)
d) Poly carbonate
ABS in the type of polymers which is the most widespread and can most easily be described as the type of plastic used for making bricks.
PLA. is however starting to rise in popularity because of its flexibility being available in both rigid and soft finishes and third type of PLA provides a rubber refinish remaining flexible.
PVA is used as a material to create supports within the additive manufacturing processes and is entirely dissolvable.
Polycarbonate is a material which is still in development as it requires a high temperature nozzle but holds possibilities for the future.
Unusual material
Polymers and metals are the most common type of material used and can be used to produce modulus and functioning components. They are particularly efficient for low volume manufacturing and minimize waste.
Glass
Ground down into a powder so it can be layered thinly as required glass can be used in additive manufacturing processes.
Questions
Q1. How do you classify nonferrous metals?
Q2. What is brass? Describe the composition, properties and uses of important types of brasses?
Q3. Explain the various types of aluminum alloys giving their composition, properties and uses?
Q4. Discuss the various type of nickel alloys?
Q5. How will you select the suitable engineering materials for particular applications?
Q6. Discuss the properties and uses of following nonferrous metal
Q7. What is age hardening and explain also advantage and application?
Q8. What is bearing alloy and describe the composition, properties and explain application.
Q9. Describe the Cobalt alloy properties, application and also composition?
Q10. What is titanium alloy? Describe the composition, properties and uses.