Unit – 3
SI and CI Engines
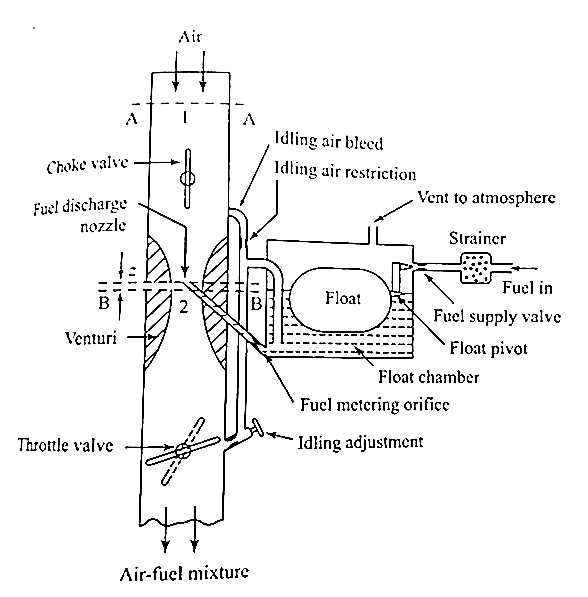
Theory of Carburetion:
Types of carburettors
Updraught carburettor
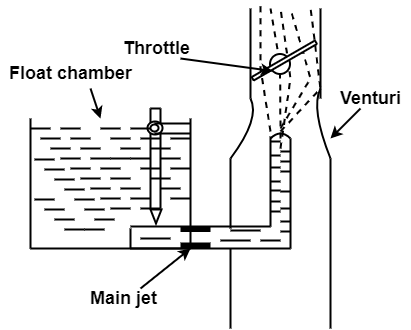
Downdraught carburettor
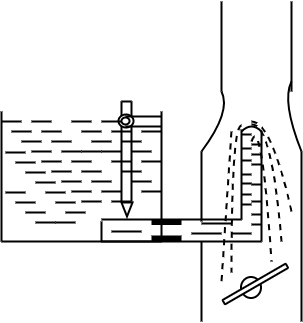
Cross draught carburettor
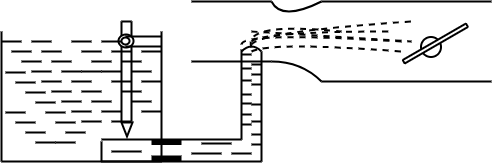
Constant choke carburettor
Constant vacuum carburettor
Multiple venturicarburettor
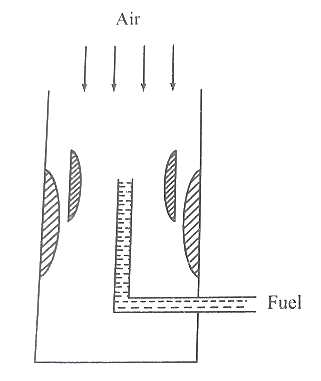
Multi jet carburettor
Multi barrel venturi carburettor
The simple carburettor
Merits of EFI System
Demerits of EFI system
Stages of combustion in SI Engines:
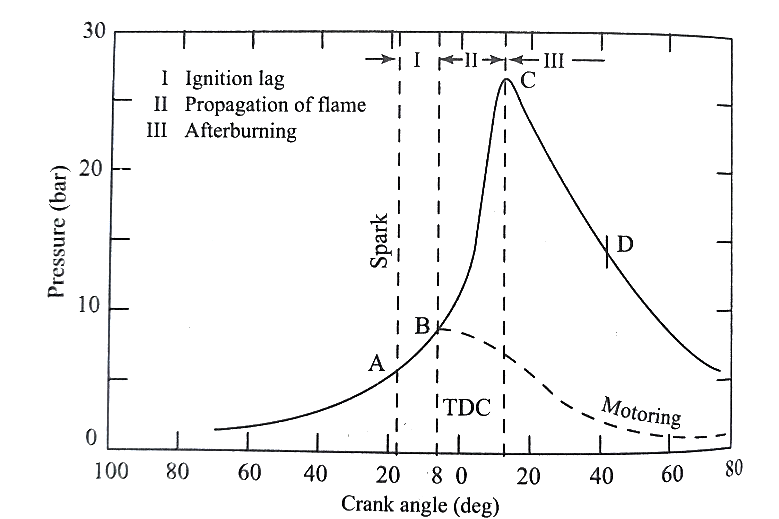
The consequences of this abnormal combustion process are the loss of power, recurring preignition and mechanical damage to the engine.
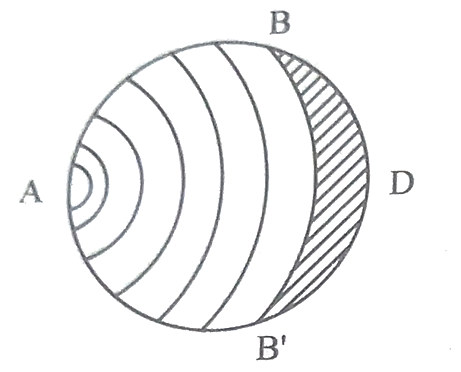
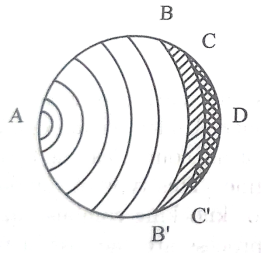
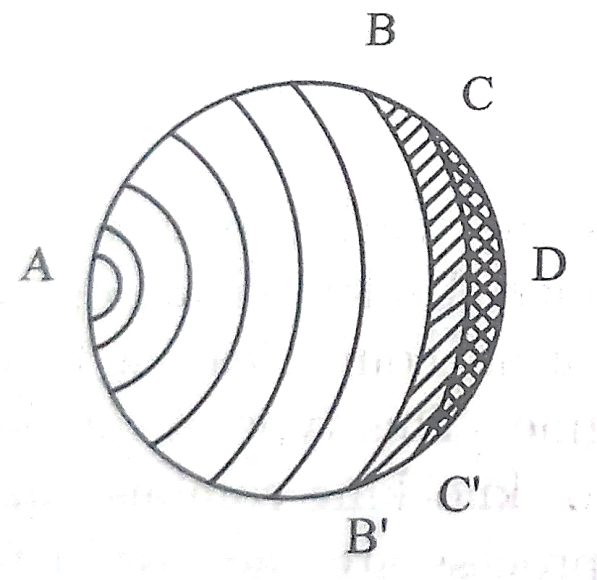
Normal combustion Abnormal combustion
Phenomenon of Detonation in S.I. engine
Effect of engine variables on detonation in SI engines
Intake Temperature:
Increased intake temperature reduces the delay period, therefore increases the detonation tendency. However, it should be noted that the increased temperature also increases the flame speed, thereby reducing the detonation tendency.
But the effect of increased temperature has more pronounced effect on delay period compared to flame speeds due to which the destination tendency is increased with increase in intake temperature.
Intake pressure:
Increased intake pressure increases the density of charge and reduces the delay period but increases the flame speed. The overall effect is to increase the detonation tendency.
Compression ratio:
Increased compression ratio increases both the pressure and temperature and reduces the delay period, hence the tendency to detonation increases.
Ignition advance:
Advancing the Spark timing increases the peak pressures of the cycle and thus reduces the delay period of end part of the gas in the combustion chamber, hence tendency to detonate increases.
Coolant temperature:
Raising the coolant temperature will increase the cylinder wall temperature and reduce the heat transfer rate between gas and cylinder walls.
Increased temperature of the gases would reduce the delay period and increase the detonation tendency.
Engine load:
Higher loads on the engine increases the heating of the engine and reduces the delay period.
Therefore, the increased loads increase the detonation tendency of the engine.
Engine speed:
Increase in engine speed increases the turbulence in the combustion chamber, thereby increasing the flame speed while the effect on the delay period is negligible.
Due to this, the increased speed of the engine reduces the detonation tendency.
Air-fuel ratio:
Engine size:
Combustion chamber design:
Location of spark plug
Type of fuel
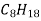
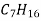
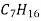
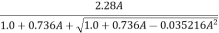
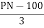
T- head type-

L-head type
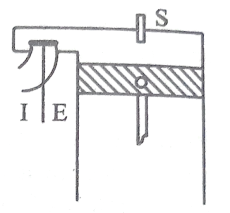

Fig b Fig c
I-head type or overhead valve:
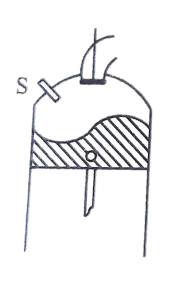
Some of the important characteristics of this type of valves arrangement are-
F-head Type:
Fuel-Injection System is vital to the working and performance of CI engine. This system serves the purpose of initiating and controlling the combustion to meet the demand requirements.
Fuel is injected into combustion chamber towards the end of compression. It is atomized as it enters under high velocity and the droplets get vaporized to form a fuel-air mixture. Due to continued heat transfer from hot air to fuel, the fuel reaches to its self-ignition temperature to ignite spontaneously initiating combustion. Depending upon the demand requirements the fuel injection system continues to deliver the fuel during initial part of combustion.
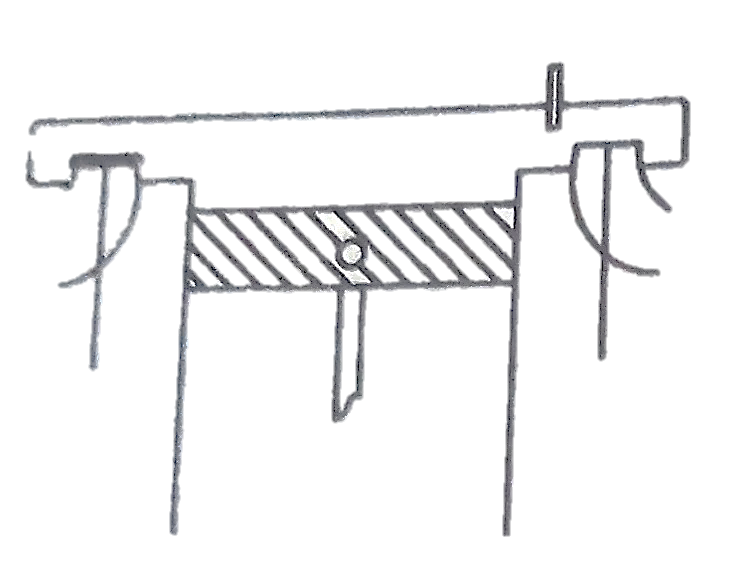
The plunger is driven by a cam and tappet mechanism at the bottom. The plunger reciprocates in the barrel. There are as many plungers as the number of cylinders in the engine. The plunger has a rectangular vertical groove.
The delivery valve is lifted off its seat under the pressure of the fuel against the spring. The fuel from the delivery valve goes to the injector. When the plunger is at the bottom of its stroke, the supply port and spill are uncovered, the fuel from a low-pressure pump after filtration is forced into the barrel.
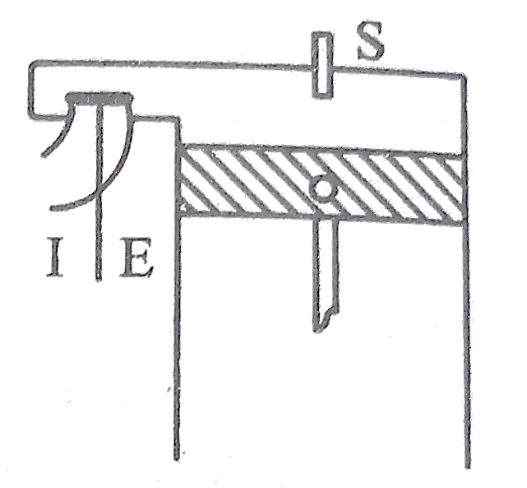
Nozzle:
Nozzle is that part of injector through which the liquid fuel is spread into the combustion chamber
There are essentially four different types of nozzles
Pressure variation along with crank angle in CI engine Stages of combustion in CI engine:
1. Ignition delay period
2. Pre-mixed burning
3. Mixing controlled combustion
4. Tail region / After burning
Ignition delay period:
a) Physical Delay: Since the time of the injection to the beginning of chemical reactions is called physical delay. In this period fuel is atomized, vaporized and mixed with air and raised to self-ignition temperature.
b) Chemical Delay: In the chemical delay, reactions start slowly and then accelerate until inflammation takes place. It depends various factors like temperature, property of the fuel.
Pre-mixed burning:
Mixing controlled combustion:
Tail region / After burning:
The combustion does not stop with the completion of injection process because unburned and partially burnt fuel particles start burning as soon as they come in contact with oxygen. This burning may continue in expansion stroke up to 70 to 80% of crank travel from TDC.
Factors affecting delay period in CI engine:

There are different types of combustion chamber used in CI Engine are as follows:
DIRECT INJECTION COMBUSTION CHAMBERS: -
Shallow Depth Chamber:
Hemispherical Chamber:
Cylindrical Chamber:
Toroidal Chamber:
INDIRECT INJECTION COMBUSTION CHAMBERS: -
Swirl Chamber:
Pre-ignition Chamber:
Air-Cell Chamber:
Reference:
1) V. Ganesan: Internal Combustion Engines, Tata McGraw-Hill
2) M.L. Mathur and R.P. Sharma: A course in Internal combustion engines, Dhanpat Rai
3) H.N. Gupta, Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engines, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.