Unit – 5
Engine Systems and Alternative Fuels
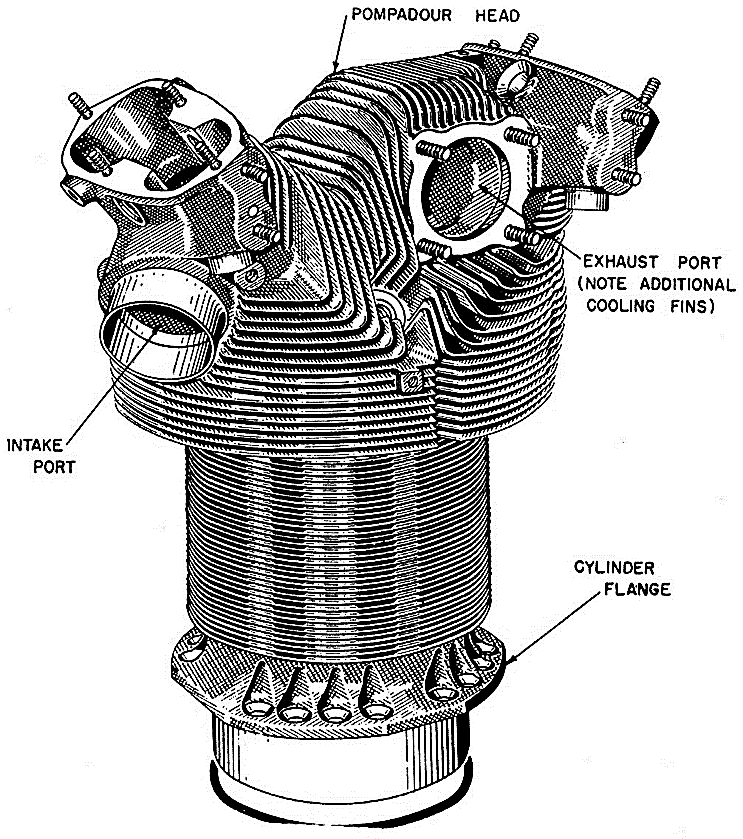
Air cooled engines are those engines, in which heat is conducted from the working components of the engine to the atmosphere directly. The cylinder of an air-cooled engine has fins to increase the area of contact of air for speedy cooling.
The amount of heat dissipated to air depends upon:
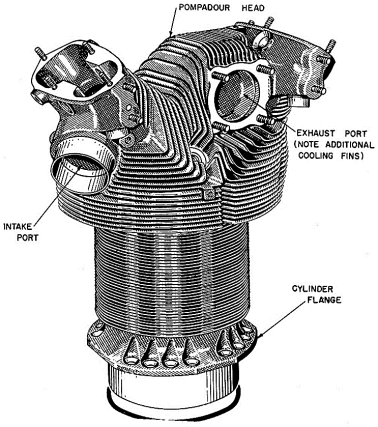
Fig. Air Cooling Fins
Merit & Demerits of Air-Cooling System
MERITS:
DEMERITS:
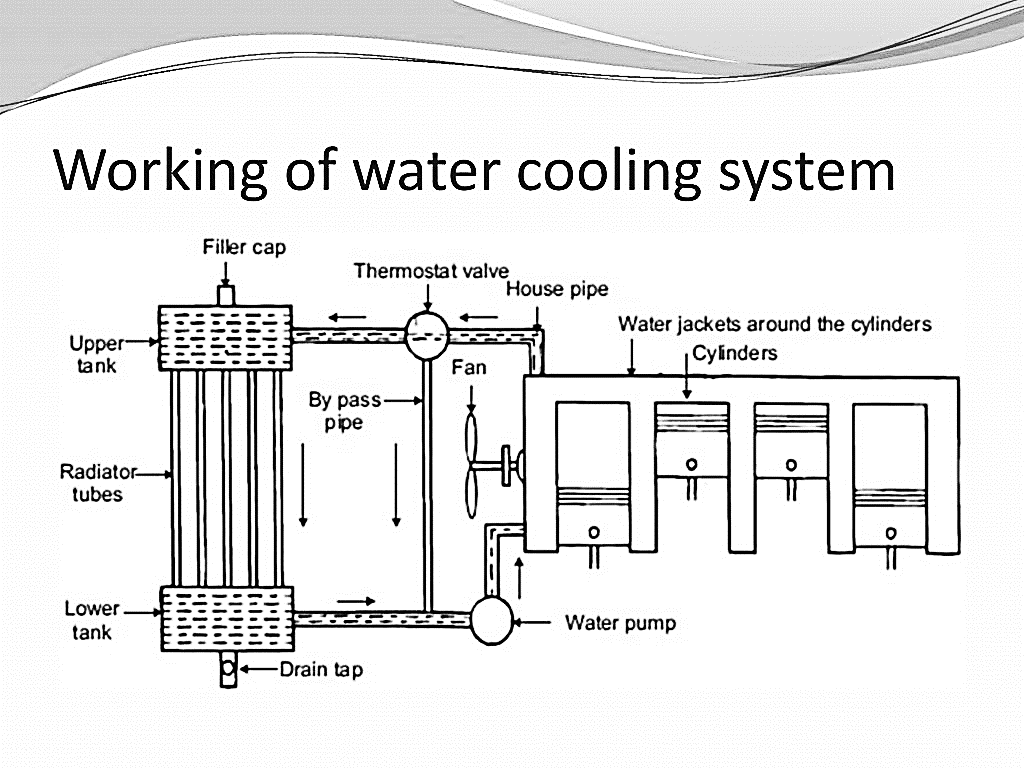
Working of Water-Cooling System:
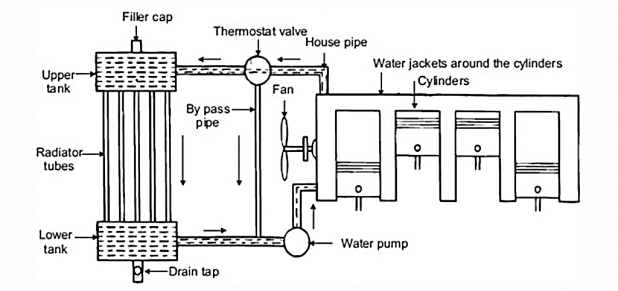
Merits & Demerits of Liquid Water-Cooling System:
MERITS:
DEMERITS:
2. Viscosity Index:
3. Cloud point:
4. Pour point:
5. Flash point and Fire point
6. Specific Gravity:
7. Acidity:
8. Carbon residue:
9. Oiliness:
Mist Lubrication System
1)It causes heavy exhaust smoke, due to busing of lubricating oil partially or fully and also forms deposits on piston crown and exhaust ports which affect engine efficiency.
2)Since the oil comes in close contact with acidic vapors produced during the combustion process gets contaminated and may result in the corrosion of bearing surface.
3) This system calls for a through mixing for effective lubrication. This requires either separate mixing prior to use or use of some additive to give the oil good mixing characteristics.
4) During closed throttle operation as in the case of the vehicle moving down the hill, the engine will suffer from insufficient Lubrication as the supply of fuel is less.
Wet sump Lubrication System
i) Splash System:
ii) The Splash and Pressure Lubrication System:
iii) Pressure Feed System:
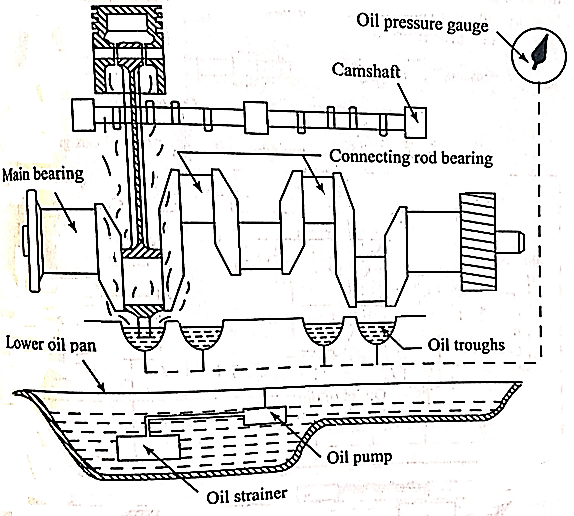
Fig. Pressure Feed System
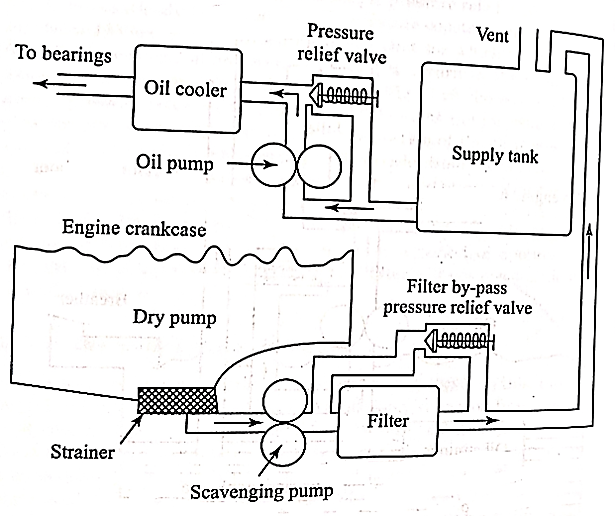
Dry sump Lubrication system
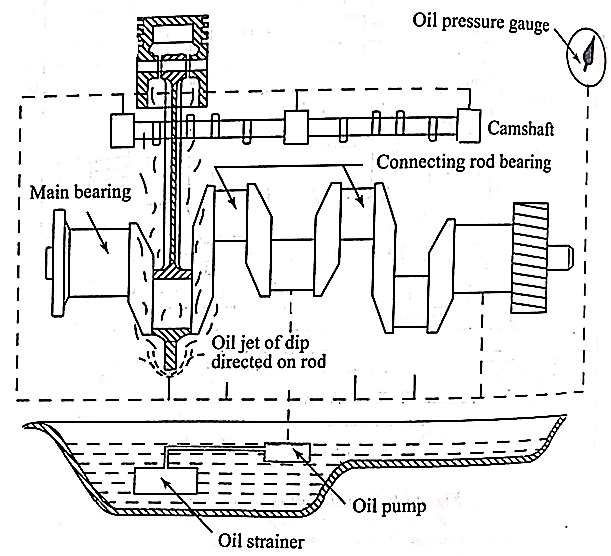
Fig. Dry sump lubrication system
This system is an internal-combustion engine that produces the spark to ignite the mixture of fuel and air which includes
Construction:
It consists of the following parts:
Working:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
The purpose of an ignition system is to provide sufficient electrical voltage to discharge a spark plug at precisely the right time to ignite highly compressed air-fuel mixture.
Magneto Ignition systems provide current for ignition without any outside primary source of electricity.
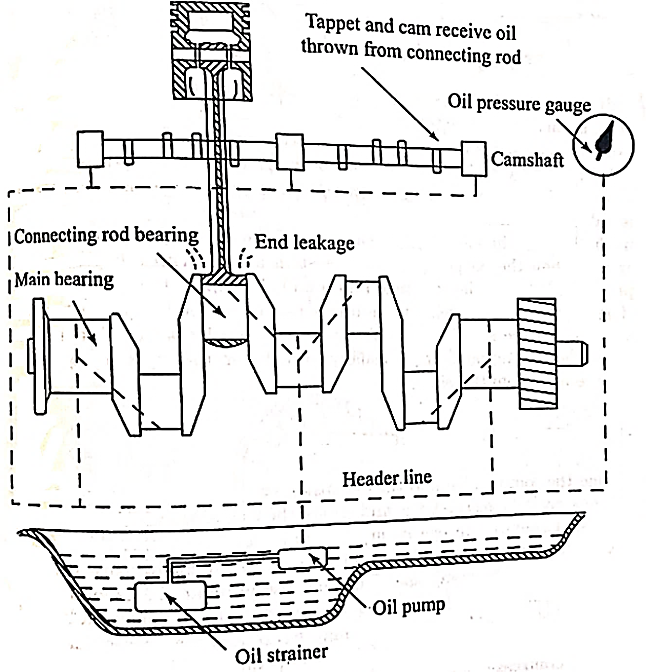
Fig. Magneto Ignition system
The magneto is the source of energy generation in the magneto ignition system. it’s typically a small generator that works on electricity as it produces a voltage when rotated by the engine. This is to say, the higher the rotation, the greater the voltage produced by the system. The system has no external source of energy and does not need one to start it, the magneto itself is a source for generating energy.
The winding in the system is of two types which include;
Depending on the engine rotation, the magneto is of three types;
The difference between the three is just their source of rotation. In the magnet type, the armature is stationary while the magnets rotate around the armature. Whereas in the armature type, the armature rotates between the stationary magnet. Finally, in the polar inductor type, both the magnet and the windings remain stationary but the voltage is generated when the flux field is reversing. This is achieved with the help of soft iron polar projections which is known as inductors.
Distributor:
The distributor components used in the magneto ignition system can also be found in the multi-cylinder engine. This multi-cylinder engines are used for the regulation of spark in the right sequence in the spark plug. It causes the surge of the ignition to be distributed uniformly among the spark plugs.
Carbon brush type distributor:
In the gap type distributors, the electrode of the rotor arm is close to the distributor cap but is in contact. This eliminates the occurrence of wear in the electrode. While in the carbon brush type, the rotor arm sliding over the metallic segment carries the carbon brush that is placed inside the distributor cap or molded insulating material. With this, an electric connection is created with the spark plug.
Spark plug:
The spark plug is a device that is powered by the ignition system to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the cylinder. It has two electrodes that are parted from each other which allow a high voltage to flow through it. These electrodes are made of steel shell and an insulator. The central electrode is attached to the supply of the ignition coil and an outer steel shell. It’s grounded insulating them.
Capacitor:
A capacitor is also a component in the magneto ignition system. it’s just like the conventional electrical capacitor with two metal plates separated by an insulating material with a distance. Air is commonly used as insulating material on this system, but to reach a particular technical requirement, a high-quality insulating material is employed. The function of this capacitor is to store charge.
Different Types of Magneto ignition system:
Capacitive Discharge Ignition:
Advantages to TCI:
Transistor Controller Ignition:
Advantages to TCI:
If start of combustion is too early work is done against piston and if too late then peak pressure is reduced. The optimum spark timing that gives the maximum brake torque, called MBT timing occurs when these two opposite factors cancel.
Purpose of spark advance:
Supercharging
Method of supercharging
2. Ram effect of supercharging.
3. Under piston supercharging.
4. Kadenacy system of supercharging
Effects of supper charging
Turbo charging
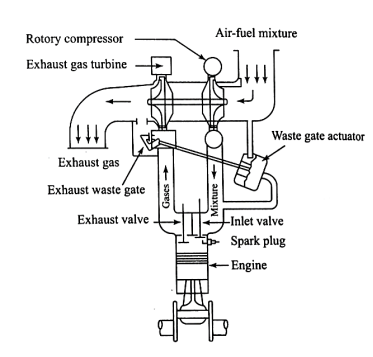
Fig. Turbo charging
Bio-diesel
Biodiesel refers to a non-petroleum-based diesel fuel consisting of short chain alkyl (methyl or ethyl) esters, made by Transesterification of vegetable oil or animal fat, which can be used (alone, or blended with conventional petrol-diesel) in unmodified diesel-engine vehicles.
"Biodiesel" is standardized as mono-alkyl ester.
Ethanol
LPG
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) or Auto Gas is a generic name for mixtures of hydrocarbons (Generally Combination of the gas is 70% butane (C4H10), 30% propane (C3h8)) which exists as vapor under ambient conditions and can be changed into liquid state by applying moderate pressures.
When stored under pressure it becomes a dense liquid allowing large quantities of gas to be stored in a relatively small space. Energy content similar to gasoline. Inherently clean burning characteristics.
LPG, known world over as Auto gas, gives you a new life as it brings along multiple benefits. Auto gas is the 3rd most popular automotive fuel and the number # 1 clean fuel alternative in the world.
2 C4H10 + 13 O2 → 8 CO2 + 10 H2O + heat C3H8 + 5 O2 → 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + heat
CNG and Hydrogen: Compressed Natural Gas (CNG)
PREPARATION:
It is made by compressing the natural gas(composed of methane) to less than 1% of the volume at standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored in hard cylindrical containers at a pressure of 200-280 bars.
IMPORTANCE:
ADVANTAGES:
Hydrogen:
Hydrogen has three naturally occurring isotopes, denoted 1H, 2H, and 3H. Other, highly unstable nuclei (4H to 7H) have been synthesized in the laboratory but not observed in nature.
Hydrogen burns readily in air at a very
The enthalpy of combustion is −286 kJ/mol
2 H2 + O2 → 2 H2O + 572 kJ
Hydrogen/oxygen mixtures are explosive and ignites spontaneously in air, is 560 °C
Hydrogen gas (dihydrogen) is highly flammable and will burn in air at a very wide range of concentrations between 4% and 75% by volume. The enthalpy of combustion for hydrogen is −286 kJ/mol:
2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(l) + 572 kJ (286 kJ/mol)
Hydrogen/oxygen mixtures are explosive across a wide range of proportions. Its autoignition temperature, the temperature at which it ignites spontaneously in air, is 560 °C (1,040 °F).
1) V. Ganesan: Internal Combustion Engines, Tata McGraw-Hill
2) M.L. Mathur and R.P. Sharma: A course in Internal combustion engines, Dhanpat Rai
3) H.N. Gupta, Fundamentals of Internal Combustion Engines, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.