Unit - 3
1D Finite Element Analysis
Introduction:
Engineers use FEA software program application to reduce the extensive form of physical prototypes and experiments and optimize components in their format segment to increase better products, faster on the equal time as saving on expenses.
It is critical to use mathematics to comprehensively understand and quantify any physical phenomena together with structural or fluid behavior, thermal transport, wave propagation, the growth of natural cells, etc. Most of these techniques are described using Partial Differential Equations (PDEs).
However, for a computer to solve the ones PDEs, numerical techniques were superior over the previous couple of a long term and one of the splendid ones, today, is the Finite Element Analysis. Differential equations now not simplest describe natural phenomena but moreover physical phenomena encountered in engineering mechanics.
These partial differential equations (PDEs) are complicated equations that need to be solved a good way to compute relevant quantities of a structure (like stresses ((epsilon)), strains ((epsilon)), etc.) a good way to estimate the structural behavior underneath a given load.
It is important to realize that FEA simplest gives an approximate method to the problem and is a numerical method to get the real give up end result of these partial differential equations. Simplified, FEA is a numerical method used for the prediction of methods a detail or assembly behaves underneath given conditions.
It is used as the idea for current simulation software program application and lets in engineers to find out susceptible spots, areas of tension, etc. in their designs.
The outcomes of a simulation-based absolutely on the FEA method are generally depicted through a satiation scale that shows, for example, the pressure distribution over the object.
Consistent Unit System:
Consistent Units
Generally, any constant device of gadgets includes a few essential gadgets consisting of Length (L), Mass (M) or Force (F), Time (T) as base gadgets and the alternative gadgets named derived gadgets, that are shaped through powers, products, or quotients of the bottom gadgets and are probably limitless in The International System of Units (SI) is an instance of a self-constant set of gadgets. The essential gadgets with inside the SI device are duration in meters (m), mass in kilograms (kg), time in seconds (s), temperature in ranges Kelvin (K), and electric powered modern in Amperes (A). Combinations of base and derived gadgets can be used to explicit different derived gadgets. Definition of derived gadgets is primarily based totally on essential bodily relations:
F = ma
1 force unit = 1 mass unit × 1 acceleration unit
a = 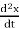
1 acceleration unit = 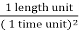
ρ = 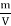
1 density unit = 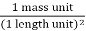
For example, A unit of force in the SI system is called a Newton (N):
1 Newton (N) = 1 (kg) × 1 (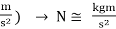
Another example is the unit of energy, called a Joule (J):
1 Joule = 1 Nm = 1 A Volts = 1 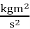
Choosing a appropriate constant machine of devices sometimes the same old devices aren't handy to paintings with. For example, Young’s modulus is regularly laid out in phrases of Mega Pascal’s (MPa) (or, equivalently, N/mm2), in which 1 Pascal = 1 N/m2. In this example the essential devices might be tones (1 tons = one thousand kilograms), millimeters, and seconds.
The exceptional set of devices will depend upon the problem; typically, the maximum correct effects are acquired if the devices are selected such that the price s of the enter portions to the FE simulation are near unity.
Example
Let us see a realistic example: We have modeled a fullerene C60 in Abacus and carried out forces (distributed) to its ends (like a anxiety test). C60 has dimensions on the order of nm (1e-nine m). Our forces also are in nN. E=1.sixteen Tera-Pascal = 1.sixteen e+12 Pa Abacus has no integrated machine of devices. Therefore, earlier than beginning to outline any model, we should determine which machine of devices might be used. For the evaluation effects to be correct or meaningful, all enter facts should be laid out in constant devices. A machine is constant whilst the derived devices (force, stress, energy, power) are effectively expressed in phrases of the selected base devices (length, mass, time, temperature). Some not unusual place structures of constant devices are proven with inside the desk below (supply in manual).
Quantity | SI | SI (mm) | US Unit (ft) | US Unit (inch) |
Length | m | Mm | Ft | In |
Force | N | N | Lbf | Lbf |
Mass | Kg | Tonne (103 kg) | Slug | Lbf s2/in |
Time | s | s | s | s |
Stress | Pa (N/m2) | MPa (N/mm2) | Lbf/ft2 | Psi (lbf/in2) |
Energy | J | MJ (10−3 J) | Ft lbf | In lbf |
Density | Kg/m3 | Tonne/mm3 | Slug/ft3 | Lbf s2/in4 |
Introduction to approaches used in finite element analysis (FEA) such as direct approach and energy approach:
The finite detail approach normally abbreviated as FEM is a numerical approach to achieve approximate approach to bodily troubles.
FEM become at the beginning evolved to observe stresses in complicated plane structures; it has because been prolonged and carried out to the vast area of continuum mechanics, consisting of fluid.
- Because of its functionality to deal with complicated troubles and its flexibility as a evaluation tool, FEM has received a distinguished position in engineering evaluation and design. It should be emphasized that the FEM can handiest provide you with an approximate answer. So it isn't always the maximum favored manner to resolve a bodily trouble.
- Unfortunately, there are numerous realistic conditions wherein the analytical answer is tough to achieve, or an analytical does now no longer exist. For instance, we might also additionally need to decide the drag pressure performing on an arbitrary fashioned frame stored in a viscous waft area.
- To achieve analytical answer, the form of the frame should be recognized in mathematical shape. This is essential to use right boundary conditions. If the form of the frame is irregular, in order that no mathematical illustration may be made, then it's far not possible to resolve the trouble the use of analytical approach.
- Even if the frame has a ordinary form, the governing differential equation of the trouble can be nonlinear. There isn't any any preferred analytical approach to be had for the answer of nonlinear partial differential equations.
- There are numerous methods to achieve a numerical approach to a differential equation. If the governing differential equation is a first-order everyday differential equation, we've got famous techniques which include Euler approach, quite a few Runge-Kutta techniques, or multi-step techniques like Adam-Bash forth and Adam-Molten techniques to achieve numerical answer.
- The direct method is associated with the “direct stiffness approach” of structural evaluation and it's far the perfect to apprehend whilst assembly FEM for the primary time.
- The important benefit of this method is that you may get a experience of primary strategies and the critical idea worried with inside the FEM system without the use of lots of mathematics.
- However, through direct method we are able to resolve handiest easy troubles. The first step on this method is to update the machine beneath attention through an equal idealized machine together with man or woman factors. These factors are assumed to be related to every different at particular factors known as nodes.
- Once the factors with inside the machine were defined, you'll be able to use direct bodily reasoning to set up the detail equations in phrases of pertinent variables. In the following step, the man or woman detail equations are mixed to shape the equations for the whole machine and resolve the machine of equations for the unknown nodal variables.
- Since the essential concept of the discretization of the machine (answer region) comes from structural evaluation, we will start our dialogue of finite detail idea through thinking about a easy instance shape this area
Direct Approach:
- In making use of the technique, the machine ought to be modeled as a fixed of simpler, idealized factors interconnected on the nodes.
- The cloth stiffness homes of those factors are then, via matrix mathematics, compiled right into a unmarried matrix equation which governs the behavior of the complete idealized structure.
- The structure’s unknown displacements and forces can then be decided with the aid of using fixing this equation. The direct stiffness technique bureaucracy the idea for maximum business and unfastened supply finite detail software.
- Researchers checked out numerous procedures for evaluation of complicated aircraft frames. These covered elasticity theory, electricity concepts in structural mechanics, flexibility technique and matrix stiffness technique. It changed into via evaluation of those strategies that the direct stiffness technique emerged as a green technique ideally fitted for laptop implementation.
- If are member deformations in place of absolute displacements, then are impartial member forces, and in such case (1) may be inverted to yield the so-referred to as member flexibility matrix, that's used with inside the flexibility technique.
- For a machine with many individuals interconnected at factors referred to as nodes, the individuals' stiffness family members along with Eq.(1) may be incorporated with the aid of using the subsequent observations:
• The member deformations may be expressed in phrases of machine nodal displacements r which will make certain compatibility among individuals. This means that r might be the number one unknowns.
• The member forces assist to the hold the nodes in equilibrium below the nodal forces R. This means that the right-hand-facet of might be incorporated into the right-hand-facet of the subsequent nodal equilibrium equations for the complete machine:
- The machine stiffness matrix K is rectangular for the reason that vectors R and r have the identical size. In addition, it's far symmetric because is symmetric.
- Once the supports' constraints are accounted for in (2), the nodal displacements are discovered with the aid of using fixing the machine of linear equations (2), symbolically: Subsequently, the individuals' feature forces can be discovered from Eq.(1) where may be discovered from r with the aid of using compatibility consideration. The first step while the usage of the direct stiffness technique is to perceive the man or woman factors which make up the structure.
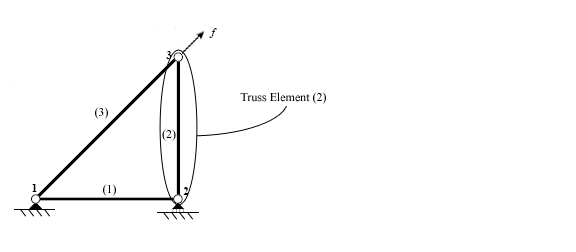
Once the elements are identified, the structure is disconnected at the nodes, the points which connect the different elements together.
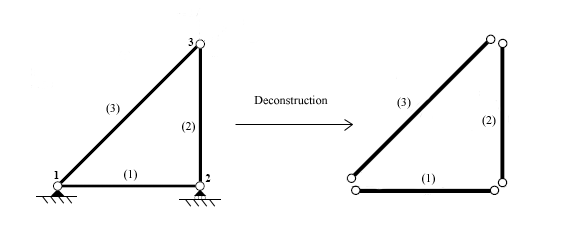
Each detail is then analyzed for my part to increase member stiffness equations. The forces and displacements are associated thru the detail stiffness matrix which relies upon at the geometry and residences of the detail.
A truss detail can simplest transmit forces in compression or tension. This method that during dimensions, every node has tiers of freedom (DOF): horizontal and vertical displacement. The ensuing equation incorporates a 4 with the aid of using 4 stiffness matrix. A body detail is capable of face up to bending moments similarly to compression and tension.
This outcomes in 3 tiers of freedom: horizontal displacement, vertical displacement and in-aircraft rotation.
The stiffness matrix in this situation is six with the aid of using six. Other factors including plates and shells also can be included into the direct stiffness approach and comparable equations need to be developed.
Solution:
Once the worldwide stiffness matrix, displacement vector, and pressure vector had been constructed, the machine may be expressed as a unmarried matrix equation.
f = Ku
Or

For each degree of freedom in the structure, either the displacement or the force is known.

After placing the recognized price for every diploma of freedom, the grasp stiffness equation is entire and prepared to be evaluated. There are numerous one-of-a-kind strategies to be had for comparing a matrix equation which includes however now no longer confined to Cholesky decomposition and the brute pressure assessment of structures of equations.
If a shape isn’t well restrained, the software of a pressure will motive it to transport rigidly and further guide situations need to be added. The approach defined on this segment is supposed as an outline of the direct stiffness approach. Additional reasserts need to be consulted for greater info at the system in addition to the assumptions approximately cloth houses inherent with inside the system.
Applications:
- The direct stiffness approach became evolved in particular too correctly and without problems put in force into pc software program to assess complex systems that include a massive quantity of elements.
- Today, almost each finite detail solver to be had is primarily based totally at the direct stiffness approach. While every application makes use of the identical system, many were streamlined to lessen computation time and decrease the desired memory.
- In order to obtain this, shortcuts were evolved. One of the most important regions to make use of the direct stiffness approach is the sector of structural evaluation wherein this approach has been included into modeling software program.
- The software program permits customers to version a shape and, after the consumer defines the cloth houses of the elements, this system routinely generates detail and worldwide stiffness relationships. When numerous loading situations are implemented the software program evaluates the shape and generates the deflections for the consumer.
Energy Approach:
The minimal overall capacity power precept is a essential idea utilized in physics and engineering. It dictates that at low temperatures a shape or frame shall deform or displace to a function that (locally) minimizes the whole capacity power, with the misplaced capacity power being transformed into kinetic power (particularly heat).
- A unfastened proton and unfastened electron will have a tendency to mix to shape the bottom power kingdom (the floor kingdom) of a hydrogen atom, the maximum strong configuration. This is due to the fact that kingdom's power is 13.6 electron volts (eV) decrease than while the 2 debris separated with the aid of using a limitless distance. The dissipation on this gadget takes the shape of spontaneous emission of electromagnetic radiation, which will increase the entropy of the environment.
- A rolling ball will grow to be desk bound at the lowest of a hill, the factor of minimal capacity power.
- A protein folds into the kingdom of lowest capacity power. In this case, the dissipation takes the shape of vibration of atoms inside or adjoining to the protein.
- The overall capacity power, , is the sum of the elastic pressure power, U, saved with inside the deformed frame and the capacity power, V, related to the implemented forces
- This power is at a desk bound function while an infinitesimal variant from such function entails no extrude in power
- The precept of minimal overall capacity power can be derived as a unique case of the digital paintings precept for elastic structures challenge to conservative forces.
- The equality among outside and inner digital paintings (because of digital displacements) is:
- This leads to (2) as favored. The variation shape of (2) is frequently used as the idea for growing the finite detail approach in structural mechanics.
The manner finite detail evaluation obtains the temperatures, stresses, flows, or different favored unknown parameters with inside the finite detail version are with the aid of using minimizing a power useful.
A power useful includes all of the energies related to the unique finite detail version. Based at the regulation of conservation of power, the finite detail power useful have to same zero. The finite detail approach obtains the right answer for any finite detail version with the aid of using minimizing the power useful.
The minimal of the useful is determined with the aid of using putting the by-product of the useful with recognize to the unknown grid factor capacity for zero.
This is primarily based totally at the precept of digital paintings, which states that if a particle is beneath equilibrium, beneath a fixed of a gadget of forces, then for any displacement, the digital paintings is zero.
Each finite detail can have its very own specific power useful. At excessive frequency, acoustical and structural wavelengths are brief relative to the scale of the structures of interest. The version length and fee of conventional finite detail fashions grow to be prohibitively massive.
In addition, gadget reaction is particularly touchy to environmental and dimensional variant and deterministic techniques have much less price than statistical techniques for predicting performance. Also, many noise packages are defined in phrases of one–1/3 octave band or octave band metrics. Such analyses are maximum successfully executed the usage of techniques which can be capable of appropriately expect common effects.
To gain a correct and easy mathematical version representing the common power propagation in structures, great attempt has been made to broaden equations that govern the common power go with the drift in non-stop structures.
Belo and Rybak advanced delivery equations using the Green’s characteristic for power go with the drift in limitless vibrating plates, and formulated conduction–like equations for the power go with the drift in ribbed plates. From those equations Nefske and Sung advanced a finite detail approach to expect the power go with the drift in homogeneous finite beams in phrases of power variables.
- The EFEM is complementary to low frequency FEM fashions due to the fact it may use current FEM databases. A finite detail geometric version may be implemented to each low and excessive frequency analyses. The prediction of a spatially various power degree inside a subsystem is anticipated with the EFEM computation.
- The post–processing of EFEM effects additionally gives honest visualization of the power go with the drift in a gadget, that is handy for analysis and manipulate of noise propagation. EFEM may be used to version rather particularly damped or non–uniformly damped substances, and to version disbursed loads in addition to multi–factor electricity input.
- Due to the usage of the finite detail technique, EFEM additionally has the opposite benefits of conventional FEM. It may be effortlessly implemented to abnormal domain names and geometries which can be composed of various substances or blended boundary situations.
- The structural power density and the electricity radiation acquired from an EFEM version may be used as boundary situations of power boundary detail approach (EBEM) to compute the radiated far-area sound pressure. An power boundary detail approach turned into advanced with the aid of using Wang et al.
- Using numerical boundary detail standards and is a beneficial supplement to power finite detail techniques for excessive frequency acoustical evaluation in massive or open spaces. Franzoni et al. Have additionally formulated an acoustic boundary detail approach primarily based totally on time–averaged power and depth variables.
Key Takeaways:
- Differential equations now not simplest describe natural phenomena but moreover physical phenomena encountered in engineering mechanics.
- The finite detail approach normally abbreviated as FEM is a numerical approach to achieve approximate approach to bodily troubles.
- The important benefit of this method is that you may get a experience of primary strategies and the critical idea worried with inside the FEM system without the use of lots of mathematics.
- The machine stiffness matrix K is rectangular for the reason that vectors R and r have the identical size. In addition, it's far symmetric because is symmetric.
Bar and Truss element: Element stiffness matrix:
We will examine the improvement of the matrix structural evaluation technique for the easy case of a shape made best out of truss factors which can best deform in a single direction. This will permit us to get a flavor of ways matrix structural evaluation works while not having to study all the information and complexities which might be found in beam and body systems.
As we are able to see, considering the fact that we've best one-dimensional truss factors, every node with inside the machine best has one viable diploma of freedom (translation alongside the axis of the structural members). In preceding stiffness techniques, every diploma of freedom changed into handled separately.
Then we needed to resolve for the unknown deflections and rotations with the aid of using fixing the machine of equations. In matrix structural evaluation, we are able to become with the identical equations. But we are able to assemble the ones equations the use of matrices that constitute every detail stiffness. Putting those stiffness matrices together, we are able to be capable of assemble a big matrix for the complete shape that represents all the equations that we had formerly with inside the slope-deflection technique.
Since all of our equations might be in matrix form, we will take benefit of matrix techniques to resolve the machine of equations and decide all the unknown deflections and forces. Computers are well-tailored to resolve such matrix problems. The One-Dimensional Truss Element Recall that the deformation of a truss detail can be discovered the use of the subsequent equation:
δ=FLEA
Wherein δδ is the axial deformation, FF is the axial pressure with inside the truss detail, LL is the duration of the detail, EE is the Young's modulus, and AA is the cross-sectional region of the detail. This equation can be rearranged to discover the subsequent courting among axial pressure and axial deformation:
F=(EA/L)δ The term that is multiplied by the deformation to get the force is the axial stiffness:
k=EA/L
With this background, we will study the behavior of a one-dimensional truss detail as proven in Figure 11.1. This truss detail has a steady Young's modulus EE and cross-sectional vicinity AA. It has ends, which we will recall to be linked to 2 separate nodes in our structure, one labelled '1' and one labelled '2' as proven with inside the figure. We can constitute the whole behavior of this whole detail thru the pressure and displacement of the 2 nodes. The pressure at node 1 is labelled Fx1Fx1 and the pressure at node is labelled Fx2Fx2. Displacement of node two is labelled Δx2Δx2.
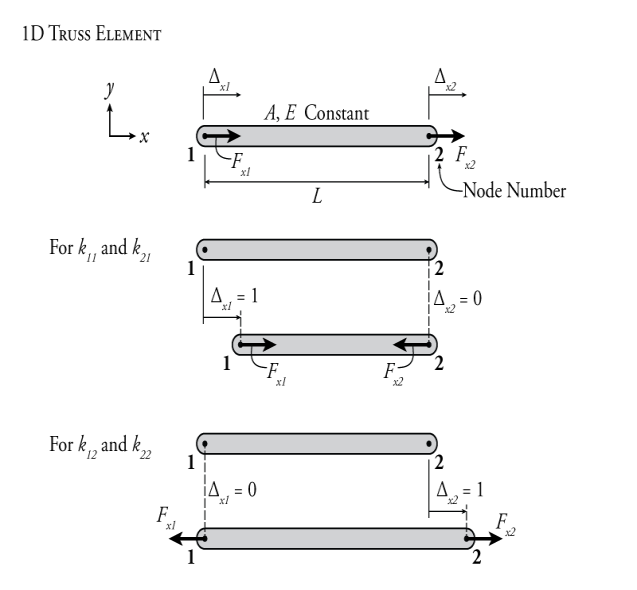
Figure: One-Dimensional Truss Element
We can relate the forces to the displacements at the 2 ends of the member the use of the stiffness time period from equation (3) (3); however, we want to narrate the stop displacement to the bar deformation (those aren't the identical thing). For, example, if each the left and proper facets flow through 1.zero unit positive (to the proper), then the complete bar actions to the proper as a inflexible body, neither increasing or contracting, so the deformation could be zero. The deformation may be associated with the stop node displacements as follows:
δ=Δx2−Δx1(4)
F=(EA/L)(Δx2−Δx1)
If the inner pressure from equation (5)(5) is positive, the bar is in tension, so the pressure at the left (Fx1Fx1) should factor to the left (negative), and the pressure at the right (Fx2Fx2) should factor to the right (positive). So:
Fx1 = - 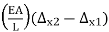
Fx2 = - 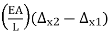
These equations outline the pressure/deflection behavior of the truss at each nodes simultaneously. They are simplest a characteristic of displacements of the nodes (the nodal displacements) and the forces carried out to the nodes (the nodal forces). We can effortlessly explicit those equations in a matrix shape as follows:
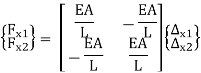
Wherein the matrix at the left of the same signal is referred to as the pressure vector, the massive valuable matrix is referred to as the stiffness matrix and the smaller matrix at the proper with the displacements is referred to as the displacement vector. The time period vector simply method a matrix with simplest one column. If we multiply the massive valuable matrix with the aid of using the vector of displacements at the proper, we get:
Fx1 = 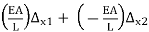
Fx2 = 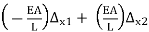
That are similar to equations (6)(6) and (7)(7). This matrix equation constitutes a whole version for the behavior of a one-dimensional truss detail. The massive matrix with inside the center is referred to as the stiffness matrix of the detail as it consists of all the stiffness terms. It consists of the maximum critical statistics for the version, and its miles beneficial to consider it as a separate detail:
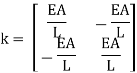
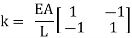
This is the stiffness matrix of a one-dimensional truss detail. Other sorts of factors have distinct sorts of stiffness matrices. For a truss detail in 2D space, we might want to do not forget greater tiers of freedom according to node in addition to the rotation of the detail in space. Beam factors that encompass axial pressure and bending deformations are greater complicated still. For actual bodily systems, stiffness matrices are constantly rectangular and symmetric approximately the diagonal axis of the matrix.
Another manner to consider the development of a stiffness matrix is to discover the forces at both cease of the detail if the detail reviews a unit deformation at every cease (separately). This works due to the fact the stiffness is described because the pressure according to unit deformation. If we do not know the stiffness matrix, we are able to determine it out via way of means of first beginning with the overall shape of the stiffness matrix for our detail:
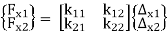
Wherein k11k11, k12k12, k21k21 and k22k22 are the character phrases in the stiffness matrix that we need to discover. The first wide variety with inside the subscript is the row with inside the matrix wherein the stiffness time period is located, and the second one wide variety is the column with inside the matrix wherein its miles located. So let's personally set every displacement to 1.zero at the same time as putting the opposite to 0 to calculate the stiffness phrases. This procedure is proven in Figure 11.1.
If we set Δx1=1Δx1=1 and Δx2=0Δx2=zero, we get:
Fx1=k11(1)+k12(0)
Fx2=k21(1)+k22(0)
So, while Δx1=1Δx1=1 and Δx2=0Δx2=zero, Fx1=k11Fx1=k11 and Fx2=k21Fx2=k21. So, to discover the stiffness phrases k11k11 and k21k21, we simply want to discover what the pressure is with inside the truss detail at every cease while Δx1=1Δx1=1 and Δx2=0Δx2=zero. This scenario is proven with inside the center of Figure 11.1. When the left facet of the truss movements to the proper via way of means of 1.zero and the proper facet stays with inside the equal place, the truss detail is in compression with a complete deformation δ=−1.0δ=−1.zero. This method that the pressure on the left cease of the bar is:
Fx1=(EA/L)
Which is positive because it points to the right for tension, as shown in the figure. This means that:
k12= Fx1 = −EA/L
k22= Fx2 = EA/L
If we now take all of these solved stiffness terms and construct the stiffness matrix of the element, we get:
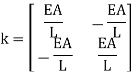
Which is the same stiffness matrix that we derived previously in equation (12)
Load Vector:
The load vector f consists of the outside nodal forces as targeted with inside the enter record and of the meeting of the detail masses. These detail masses may be subdivided into the subsequent components
1. Equivalent nodal forces because of thermal results, results as a consequence of distinction in attention and preliminary strains. Summing those results effects in an equal preliminary strain, which may be converted to nodal masses.
2. Equivalent nodal forces as a consequence of preliminary stresses.
3. Equivalent nodal forces as a consequence of masses on detail boundaries.
4. Equivalent nodal forces as a consequence of acceleration results (useless weight).
Equilibrium
Invoking the theory of the digital displacements, the equilibrium equations of the detail assemblage are
Ku = f (29.35)
Where the matrix K is the stiffness matrix of the element assemblage
K = 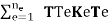 (29.36)
(29.36)
And the vector f is the right hand side vector
f = fg + ft + f ε0 – f σ0 + fc (29.37)
With
fg = 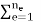 TeT
TeT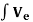 NTge dV
NTge dV
The contribution of the element body forces.
ft = 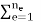 TeT
TeT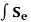 NTte dS
NTte dS
The contribution of the element surface tractions.
f ε0 = 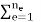 TeT
TeT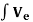 BTD𝛆0 dV
BTD𝛆0 dV
The effect of the element initial strains.
f σ0 = 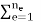 TeT
TeT  BT𝛔0 dV
BT𝛔0 dV
The effect of the element initial stresses.
fc
The contribution of the concentrated nodal forces.
Stress and reaction forces calculations:
Principal FEA Stresses
In the previous article we focused on the Cartesian stresses SX, SY and SXY. We saw that for a specific coordinate device those had been the stresses with inside the neighborhood X, Y path and XY plane, respectively. We turned around the strain device from the simple XY coordinate device to 2 different coordinate structures to study neighborhood ‘cut’ directions.
In fact, we are able to rotate the strain nation to any coordinate device we want. It is crucial to realize that we're constantly describing the equal strain nation, however simply viewing it from a distinctive angle. Fig. 2 suggests the equations that may be used to calculate the strain in a neighborhood coordinate device, with the aid of using the use of a rotation via an angle.
These are precisely the equal equations so one can be utilized by your put up processor to turn from one coordinate device to another. You can also additionally take into account having to plan those alterations with the aid of using hand the use of the Mohr’s circle construction.
It became very handy to do it this manner earlier than digital calculators got here along. (I will check Mohr’s circle in greater element in a later article).
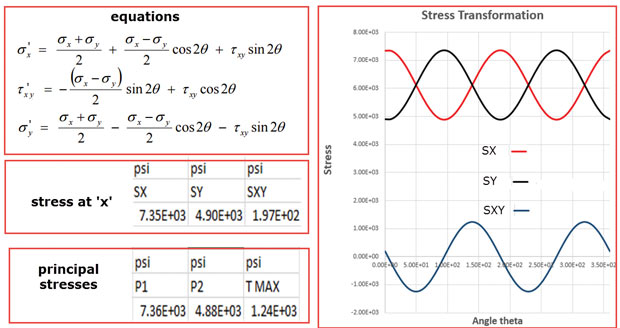
Fig. 2D stress transformations
We’re going to select out a datum factor at the structure, adjoining to the pinnacle proper hand nook lug. This is proven in Fig. 3, in which we additionally see the strain contours for Cartesian SX, SY and SXY stresses.If we alternative those values into the equation in Fig. 2 then we are able to plot the version strain on the datum factor as we rotate round all of the feasible nearby coordinate systems.
The ensuing plot is proven in Fig. 2. Looking at Fig. 2 we are able to see that the strain varies in a cyclic way as we rotate round the overall 360°. There are a few different exciting rotation angles we are able to see on this plot. The direct stresses SX and SY top collectively on the identical rotation perspective. At this rotation perspective the shear strain SXY drops to zero.
The largest and smallest direct stresses we discover at this precise perspective are referred to as the foremost stresses. The values are proven in Fig. 2. In a 2D strain nation, those are categorized as P1 and P2.
There is an in addition perspective in which the shear strain SXY is a most. This fee is referred to as most shear strain. We certainly have a 3-d strain nation on this structure, even though the dominant responses are with inside the XY plane. For a 3-d strain nation the foremost stresses come to be P1, P2 and P3. Usually, P2 is a completely small strain and we're handiest worried with the values of P1 and P3. The menu choice for 3-d contour strain plotting typically incorporates P1 and P3 foremost strain components.
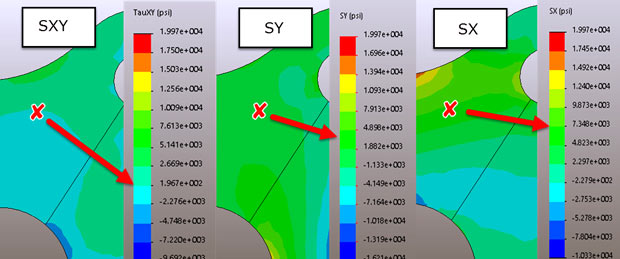
Fig. Stresses at the datum point x
Fig. Suggests pressure contour plot of the most fundamental pressure P1. This is a beneficial manner of seeing the most important tensile pressure go with the drift direction. I even have clipped the contour at across the 0 pressure line so tensile stresses dominate.
If the P1 pressure degree is compressive then it approach that the pressure country is continually compressive, regardless of what attitude we pick out for a neighborhood coordinate system.
So, a brief eyeball of this shape suggests that the pinnacle member is absolutely in anxiety all through its depth. The transverse member (pinnacle left to backside proper) has a small tensile pressure go with the drift. The proper hand vertical member has localized tensile regions that are truly the high-quality facet of the bending distribution.
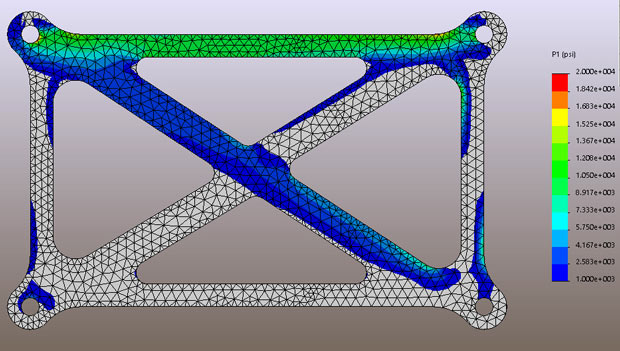
Fig. P1 stress distribution for the overall structure
The contour plot in Fig. Shows the P3 distribution through the structure. Again, I genuinely have clipped this plot so most effective compressive stresses are established.These regions are genuinely with inside the grayed out quarter. The plots in Figs. Are complementary: They show, respectively, the zones of tensile and compressive dominated structure.
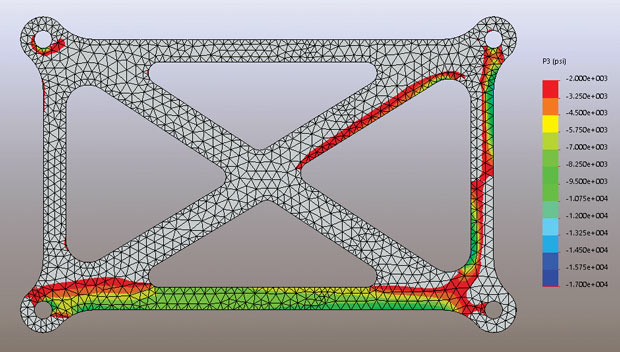
Fig. P3 stress distribution for the overall structure
Figs. Show, respectively, contours of maximum and minimum number one stresses P1 and P3 for the close by lug place. The insert XY graphs show tensile number one stress on foot along the top lug fillet radius and compressive number one stresses on foot throughout the factor fillet radius. These figures illustrate how useful the number one stresses are. By definition, along a free ground, the stresses want to be tangential and will certainly form number one stress directions. Running a line plot along the ground will show the distribution of top stress. This in fact is the most effective way that this can be visualized and it is a powerful studies tool.
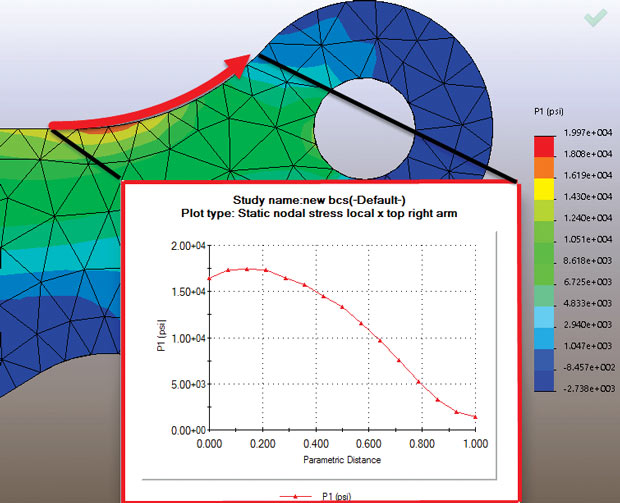
Fig. Tensile principal stress running around the top lug fillet radius
I find out that contour plotting of number one stresses segregated into tensile and compressive dominant regions is a useful approach. However, the greater regular way of imparting principle stresses is thru a vector plot. Fig. Shows a vector plot of the P1 number one stresses on foot throughout the lug place.
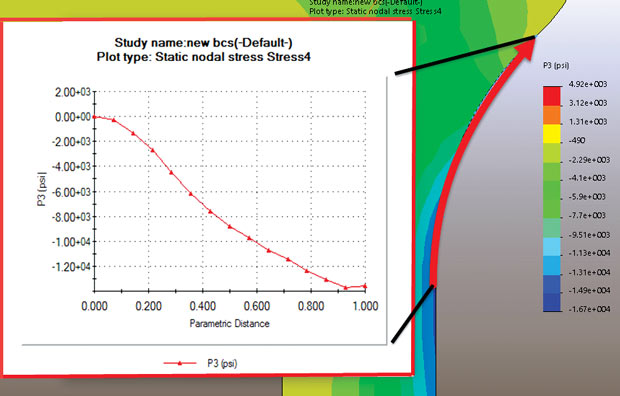
Fig. Compressive principal stress running around the side lug fillet radius
Both are further valid representations; some analysts choose plots that distinguish P1 and P3 greater clearly, some choose to have a mixed plot. Whichever we use, there can be no question that the vector plots offer a exquisite instance of the go together with the glide of the stress. This is one of the most useful additives of number one stress plotting. The main difficulty is that the small P1 stresses in a compressive quarter and the corresponding massive P3 values with inside the compressive quarter can also ruin the visualization (what I genuinely have described as “fizzling out”). I choose to segregate the two plots and control the clipping of the vector values carefully to aid visualization.
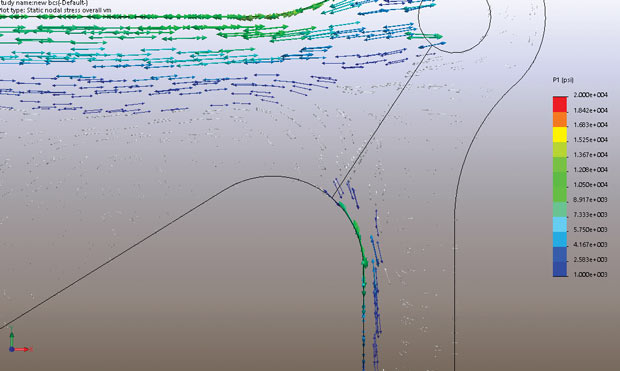
Fig. P1 principal tensile stresses running around the fillet radii of the lug region
P1 number one stresses are useful even as considering fatigue and fracture. The most damaging orientation can be at 90°. We can use the P1 number one stress as an pinnacle sure estimate for the biggest tensile stress we're capable of ever see for the duration of the crack in this place. In a similar way, a crucial compressive stress can be positioned thru manner of method of the use of the P3 number one stress. In the place liable to buckling it can be difficult to assess the relative orientation most of the slenderest direction (this is most liable to buckling) and the dominating compressive stress. By assuming a rate P3 for stress, then we have got defined the worst case.
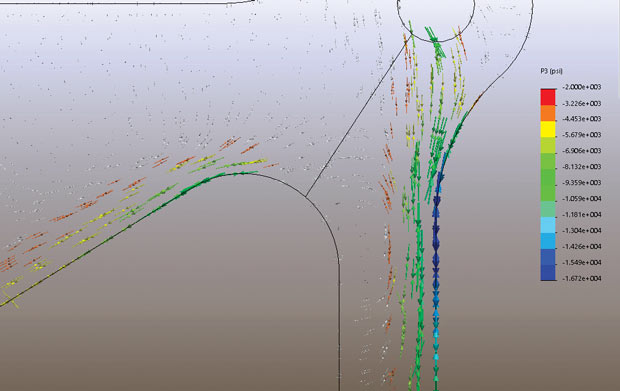
Fig.P3 principal compressive stresses flowing around the fillet radii of the lug region
Originally, laptop structures have been designed to treatment matrix equations. Numerical techniques have been superior during the last severe a few years with the aim of solving linear and nonlinear matrix equations. Today, one may want to say that linear systems can without a doubt be solved. However, the identical can't be assumed for a nonlinear device of equations. In addition, one of the additives of inexperienced meshing includes task of node numbers such that the complete bandwidth of the matrix is reduced to a minimum. Thus, equation systems are normally stored in “Sparse” formats. For greater data on sparse matrices and solvers, the blog article on “Direct and iterative solvers” is a advocated reading. An entire branch of accomplished mathematics is dedicated to improving solvers and algorithms for solving nonlinear device of equations.
The Process of FEA
So far, its miles understood that FEM converts a PDE right into a gadget of equations. This gadget of equations (in matrix shape) is solved the use of complex algorithms and solvers.
The query stays as to what's one fixing for? Is one fixing for displacements or velocities or traces or stresses or forces? In short, we're typically fixing for unknowns on the nodes.
In mechanical issues, those unknowns are usually displacements, and in thermal issues, the unknown is commonly temperature. Further portions like strain and pressure are acquired most effective as a part of post-processing. The normal system of FEA may be divided into numerous steps:
• Preparation of geometry
• Pre-processing
• Post-processing for outputs
• Analysis
In the approaching section, every step worried in an FEA software and while/how strain and pressure are calculated may be mentioned in greater detail. The normal method stays the same, regardless of the software program used.
Preparation of Geometry the coaching of geometry is known as improvement of a CAD version. Most frequently, CAD fashions may be acquired thru on line systems like Grab CAD. The taken into consideration CAD version wishes to be an excellent consultant of the reality.
It is critical to be cautious, as among the fashions acquired from such boards have engravings. The unique authors frequently engrave their call at the CAD version, and the presence of such engravings can purpose troubles with computerized mesh generators, which results in extraordinarily small or distorted meshes and in the end mistakes with inside the solution.
Pre-Processing includes numerous critical troubles, which begin from meshing. Timescale gives computerized mesh generators, which include the opportunity for mesh refinements in layers or at areas round feasible singularities.
The mesh introduction is a crucial a part of arrangements for the answer system. Meshing additionally implies to deciding on an interpolation function.
For example, as mentioned with inside the weblog article on “Modeling Elastomers Using FEM: Do’s and Don’ts,” second-order interpolation features are desired over first-order—especially for modeling hyperplastic materials. In contrast, the use of first-order tetrahedrons may be disastrous! Hence, deciding on the proper mesh and interpolation kind governs the accuracy.
In addition, pre-processing additionally includes deciding on the correct boundary conditions, fabric properties, and constraints while deciding on a mesh.
Solution Process the PDE governing the physics has been transformed to a crucial shape and later changed into transformed right into a matrix shape. The matrix contribution of every detail is calculated and assembled right into an international gadget of equations
This international equation is subsequently dispatched to a solver, which takes the equation for nodal displacements and reactions.
While in linear issues, the solver solves for the displacements and reactions in a single step, at the same time as the nonlinear issues want numerous iterations to resolve for the same.
Once the nodal displacements were solved, it's time to calculate the stresses which are proven for plotting. A flag is typically used to tell the habitual that the answer system is whole and stresses are being calculated for plotting.
Key Takeaways:
- Putting those stiffness matrices together, we are able to be capable of assemble a big matrix for the complete shape that represents all the equations that we had formerly with inside the slope-deflection technique.
- The deformation may be associated with the stop node displacements as follows:
- The time period vector simply method a matrix with simplest one column. If we multiply the massive valuable matrix with the aid of using the vector of displacements at the proper, we get:
- The load vector f consists of the outside nodal forces as targeted with inside the enter record and of the meeting of the detail masses.
- We turned around the strain device from the simple XY coordinate device to 2 different coordinate structures to study neighborhood ‘cut’ directions.
Temperature effect on bar element:
The finite-detail have a look at of the impact of temperature version on plain-jointed concrete pavements is offered. Temperature version reasons curling and thermal-growth stresses. Curling stresses end result from temperature gradients thru a slab intensity.
Thermal-growth stresses are prompted because of uniform modifications in temperature that reason the slab to make bigger. The advanced 3-dimensional (3D) version includes 4 slabs separated via way of means of longitudinal and transverse joints. The interplay among the floor and the concrete slab at the side of interplay on the joints have been modeled the usage of interface factors. These factors gave the version the functionality to clear up for partial touch among curled slabs.
The first-rate correlation became received with JSLAB. The version became used to carry out parametric research on curling and thermal-growth stresses to have a look at the impact of superposition of each stresses and to deal with the impact of uniform temperature modifications on joint opening.
The consequences of the parametric research are offered and in comparison with different solutions. The mathematics addition of nice curling stresses and thermal-growth stresses have been much less than the ones stresses received via way of means of superposition. In a few cases, the calculated joint openings have been better than the allowable joint opening.
Nonlinear temperature distribution induced better tensile stresses than the linear distribution of temperature. The distinction in tensile stresses among the 2 distributions became about 3–thirteen of the modulus of rupture of concrete.
Metals are factors or compounds with extraordinary conductivity for each strength and heat, making them beneficial for a extensive variety of sensible purposes. The periodic desk presently consists of ninety one metals, and every has its personal precise homes. The electrical, magnetic and structural homes of metals can extrude with temperature and thereby offer beneficial homes for technological devices.
Thermal Expansion
A boom with inside the temperature results in a small boom with inside the duration, vicinity and quantity of a metal, referred to as thermal growth. The value of the growth relies upon the precise metal. Thermal growth consequences from the boom of atomic vibrations with temperature, and attention of thermal growth is crucial in a whole lot of applications. For example, while designing pipework in bathrooms, producers want to keep in mind seasonal modifications with inside the temperature to keep away from bursting pipes.
All substances concern to a temperature extrude will make bigger or settlement proportional with their duration and temperature distinction. Some substances will make bigger or settlement extra than others; the qualitative belongings that suggests how a good deal will they make bigger is referred to as the Linear Thermal Expansion Coefficient (α), measured in m/(m ºC) or (in/in ºF). Also gadgets like 1/ºC or 1/ºF may be used.
The extrude in duration because of thermal growth is calculated with:
∆L ( or δ ) = ∝ × L × ∆T
Wherein δ is the alternate in length, L is the unique length (makes positive each are with inside the identical units) and ΔT is the temperature difference.
For instance if metal has a thermal enlargement coefficient of 11.7×10-6 1/ºC it approach that a 1 m lengthy bar difficulty to a temperature growth of 1ºC will enlarge 11.7×10-6 m, or 0.0117 mm.
This may be very critical for the piping designers due to the fact they should permit for this enlargement or element it with inside the pressure calculations.
One alloy is used to face up to corrosion, at the same time as the opposite is frequently an accepted stress vessel material.
Typical packages for composite tubes are steam boilers with corrosive conditions, such as:
• Black liquor healing boilers (BLRB)
• Syngas coolers
• Waste warmness boilers
• Waste-to-electricity boilers
Thermal Expansion –
Axial Force Calculator Linear enlargement because of alternate in temperature may be expressed as
Dl = α lo dt (1)
Where
Dl = elongation (m, in)
α = temperature expansion coefficient (m/mK, in/in oF)
lo = initial length (m, in)
Dt = temperature difference (oC, oF)
The strain - or deformation - for an unrestricted expansion can be expressed as
ε = dl / lo (2)
Where
ε = strain - deformation
The Elastic modulus (Young's Modulus) can be expressed as
E = σ / ε (3)
Where
E = Young's Modulus (Pa (N/m2), psi)
σ = stress (Pa (N/m2), psi)
Thermal Stress
When restricted expansion is "converted" to stress - then (1), (2) and (3) can be combined to
σdt = E ε
= E dl / lo
= E α lo dt / lo
= E α dt (4)
Where
σdt = stress due to change in temperature (Pa (N/m2), psi)
Axial Force
The axial force acted by the restricted bar due to change in temperature can be expressed as
F = σdt A
= E α dt A (5)
Where
F = axial force (N)
A = cross-sectional area of bar (m2, in2)
Example - Heated Steel Pipe - Thermal Stress and Force with Restricted Expansion
A DN150 Std. (6 in) steel pipe with length 50 m (1969 in) is heated from 20oC (68oF) to 90oC (194oF). The expansion coefficient for steel is 12 10-6 m/mK (6.7 10-6 in/inoF). The modulus of elasticity for steel is 200 GPa (109 N/m2) (29 106 psi (lb/in2)).
Expansion of unrestricted pipe:
Dl = (12 10-6 m/mK) (50 m) ((90oC) - (20oC))
= 0.042 m
If the expansion of the pipe is restricted - the stress created due to the temperature change can be calculated as
σdt = (200 109 N/m2) (12 10-6 m/mK) ((90oC) - (20oC))
= 168 106 N/m2 (Pa)
= 168 MPa
The outside diameter of the pipe is 168.275 mm (6.63 in) and the wall thickness is 7.112 mm (0.28 in). The cross-sectional area of the pipe wall can then be calculated to
A = π ((168.275 mm) / 2)2 - π ((168.275 mm) - 2 (7.112 mm)) / 2)2
= 3598 mm2
= 3.6 10-3 m2
The force acting at the ends of the pipe when it is restricted can be calculated as
F = (168 106 N/m2) (3.6 10-3 m2)
= 604800 N
= 604 kN
Compare force and weight
The calculation in Imperial units
Expansion of unrestricted pipe:
Dl = (6.7 10-6 in/inoF) (1669 in) ((194oF) - (68oF))
= 1.4 in
Stress in restricted pipe:
σdt = (29 106 lb/in2) (6.7 10-6 in/inoF) ((194oF) - (68oF))
= 24481 lb/in2 (psi)
Cross sectional area:
A = π ((6.63 in) / 2)2 - π ((6.63 in) - 2 (0.28 mm)) / 2)2
= 5.3 in2
Axial force acting at the ends:
F = (24481 lb/in2) (5.3 in2)
= 129749 lb
Example - Thermal Tensions in Reinforced or Connected Materials
When two materials with different temperature expansion coefficients are connected- as typical with concrete and steel reinforcement, or in district heating pipes with PEH insulation etc. - temperature changes introduces tensions.
This can be illustrated with a PVC plastic bar of 10 m reinforced with a steel rod.
The free expansion of the PVC bar without the reinforcement - with a temperature change of 100 oC - can be calculated from (1) to
DlPVC = (50.4 10-6 m/mK) (10 m) (100 oC)
= 0.054 m
The free expansion of the steel rod with a temperature change of 100 oC - can be calculated from (1) to
Dlsteel = (12 10-6 m/mK) (10 m) (100 oC)
= 0.012 m
If we assume that the steel rod is much stronger than the PVC bar (depends on the Young's modulus and the areas of the materials) - the tension in the PVC bar can be calculated from the difference in temperature expansion with (4) as
σPVC = (2.8 109 Pa) (0.054 m - 0.012 m) / (10 m)
= 11.8 106 Pa
= 11.8 MPa
The Tensile Yield Strength of PVC is approximately 55 MPa
Key Takeaways:
- Temperature version reasons curling and thermal-growth stresses. Curling stresses end result from temperature gradients thru a slab intensity.
- The consequences of the parametric research are offered and in comparison with different solutions.
- For instance if metal has a thermal enlargement coefficient of 11.7×10-6 1/ºC it approach that a 1 m lengthy bar difficulty to a temperature growth of 1ºC will enlarge 11.7×10-6 m, or 0.0117 mm.
References:
1. K. J. Bathe, Finite Element Procedure, Prentice-Hall of India (P) Ltd., New Delhi, 1996.
2. Cook R. D., Finite Element Modeling for Stress Analysis, John Wiley and Sons Inc, 1995.
3. G.R. Liu S. S. Quek, The Finite Element Method- A Practical Course, Butterworth Heinemann, 2013.
4. Fagan M. J., Finite Element Analysis Theory and Practice, Harlow Pearson/Prentice Hall, 2012.
5. S. Moaveni, Finite element analysis, theory and application with Ansys, Pearson, Third Edition, 2011.
6. David V. Hutton, Fundamental of Finite Element Analysis, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2017.