UNIT - 3
BUILDING CONSTRUCTION AND BUILDING SERVICES
The National Building Code (NBC) of India defines a building as any structure for whatsoever purpose and of whatsoever material constructed and every part thereof whether used as human habitat or not. Tents, shamianas, tarpaulin shelters, etc., erected for temporary and ceremonial occasions are
Not to be considered as buildings.
Classification:
According National Building code of India, 1970 the buildings on the basis of occupancy are classified into following groups
GROUP A: Residential buildings: All those buildings in which sleeping accommodation is provided for residing permanently or temporary with or without looking or dinning or both facilities are termed as residential building Ex: Apartments, Flats, Bungalows, Dormitories, private houses, Hotels, Hostels, Cottages, Hole day camps, clubs, hotels, Inns etc
These buildings are further subdivided into 5 groups
A1 - Lodging Houses
A2 - Family Private Dwellings
A3 - Dormitories
A4 - Flats
A5 - Hotels
GROUP B: Educational buildings: All those buildings which are meant for education from nursery to university are included in this group Ex: schools, colleges, universities, training institutes etc
GROUP C: Institutional Buildings: This group includes any building or part thereof, which is used for the purposes such as medical, health, recovering health after illness, physical or mental diseases, care of infants or aged persons, panel detention etc. These buildings normally provide sleeping accommodation for the occupants.
GROUP D: Assembly Buildings: This group includes any building or part or a building where groups of people assemble or gather for amusement; recreation, social, religious, patriotic or similar purpose for example theatres, cinema halls, museums, gymnasiums, restaurants, places of worship, dance halls, club rooms, passenger stations, public transportation services, open air theatres, swimming pools etc.
GROUP E- Business Buildings: This group includes any building or part or a building which is used for purposes such as transaction of business, keeping of accounts and records etc; dispensaries and clinics, banks, city halls, court halls, libraries etc.
GROUP F – Mercantile Buildings: This group includes any building or part of a building which is used for shops, stores, market, for safe and display of products or waves either whole sale or retail.
GROUP G – Industrial Buildings: This group includes any building or part of a building or structure in which product of different kinds and properties are fabricated, assembled or processed. For example, laboratories, assembly plants, laundries, gas plants, power plants, refineries, diaries etc.
GROUP H – Storage Building: This group includes those building structures which are primarily used for the storage structures which are primarily used for the storage or sheltering of goods, waves or merchandise vehicles or animals, for example warehouses, cold storages, freight depots, store houses, transit sheds, truck terminals, garages etc.
GROUP J – Hazardous Building: This group includes those building structures which are used for the storage, handling, manufacture or processing of materials which are liable to burn with extreme rapidity and prove hazards to health; building or building contents. Hazards may be due to fire; poisonous fumes or gases, explosions, ignitions etc from materials subjected to various operations. Buildings used for storage of gases under high pressure or for storage and handling of highly flammable liquids or explosives, fireworks etc are included in this group.
The building basically consists of three parts namely,
1) Foundation
2) Plinth and
3) Super structure
Plinth: It is the middle part of the structure, above the surface of the surrounding ground up to the surface of the floor immediately above the ground. Its function in the building is same as of sub-structure in the case of the bridge.
Super structure: It is that part of the structure which is constructed above the plinth level (i.e.,) ground level
A building in general made of the following structural components
1. Foundation
2. Plinth
3. Walls and piers in super structure
4. Ground, basement and upper floors
5. Doors and windows
6. Sills, Lintels and weather shades
7. Roofs
8. Steps and stairs
9. Finishes for walls
10.Utility fixtures
Each of these components is an essential part of a building and requires due consideration in design and construction for their functional performance. The basic functional requirements of these components discusses in the following paragraphs.
1. Foundations: The foundation is the most critical part of any structure and most of the failure is probably due to faulty foundations rather than any other cause. The purpose of foundation is to transmit the anticipated loads safety to the soil Basic requirements:
- To distribute the total load coming on the structure over a large bearing area so as to prevent it from any movement.
- To load the bearing surface or area at a uniform rate so as to prevent any unequal or relative settlement.
- To prevent the lateral movement of the structure
- To secure a level or firm natural bed, upon which to lay the courses of masonary and also support the structure.
- To increase the suitability of the structure as a whole, so as to prevent it from overturning or sliding against such as wind, rain, frost etc.
2.Plinth: This is the portion of structure between the surface of the surrounding ground and surface of the floor, immediately above the ground. As per Byelaws, the plinth should not be less than 45cm.
The basic requirements of plinth area
1) To transmit the load of the super-structure to the foundation
2) To act as a retaining wall so as to keep the filling portion below the raised floor or the building
3) To protect the building from damp or moisture penetration into it
4) It enhances the architectural appearance of the building
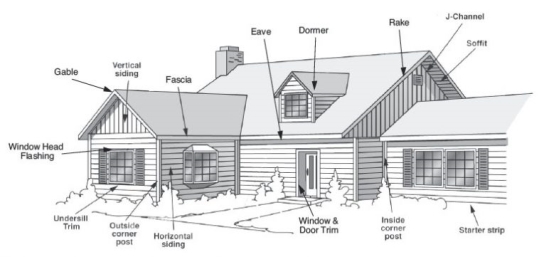
3. Walls and piers in super structure: The primary function of walls is to enclose or liquid space. A load-bearing wall in the super structure should satisfy the following requirements. Strengths, stability, weather resistance, fire resistance, heat insulation, sound insulation, privacy and security.
4. Ground basement and upper floors: The main function of a floor is to provide support of occupants, furniture and equipment of a building and the function of providing different floors is to devoid the building into different levels for the purpose of creating more accommodation within the limited space.
The floor should satisfy the following functional requirements
- Strength and stability
- Durability and dampness
- Heal insulation
- Sound insulation and fire resistance
5.Doors and windows: The main function of doors in a building is to serve us a connecting link between internal parts and also to allow the free movement outside the building. Windows are generally provided for the proper ventilation and lighting of a building. The following are the functional requirements
- Weather resistance
- Sound and thermal insulation
- Damp prevention and terminate-proofing
- Fire resistance and durability
- Privacy and security
6. Sills. Lintels and weather shades: Windowsills are provided between the bottom of window frame and wall below, to protect the top of wall from wear and tear. The actual frame of door or window is not strong enough to support the weight of the wall above the strong enough to support the weight of the wall above the openings and a separate structural element has, therefore to be introduced. This is known as lintel and is similar to a beam. Weather shades on ehhajjas are generally combined with lintels of windows to protect from the weather elements such as sun, rain, frost etc.
7. Roofs: A roof is the uppermost part of the building whose main function is to enclose the space and to protect the same from the effects of weather elements such as rain, sun, wind, heat, snow etc. A good roof is just as essential as a safe
8.Steps and Stairs: A stair is a structural consists of number of steps leading from one floor to another. The main functions of stairs area. To provide means of communication between the various floors for everyday use ii. To escape from upper floors in the case of fire To perform these functions, the stairs should satisfy the following requirements indesign and construction.
- Strength and stability- Strong and stable enough to carry the anticipated loads.
- Fire resistance- The stairs should be made of the fire resisting material and they provide safe means of escape in the event of fire.
- Sound Insulation: If it is necessary to insulate the stairs from the sound either through the proper design and use of insulating materials or separating stair structure from the building structure.
- Weather resistance- The stairs, if exposed to open air, should offer sufficient resistance to weather elements such as rain, heat etc.
- Comfort and convenience: proper design and proper location of steps in a building offer several advantages such as comfort and efficiency in vertical movement, natural light and ventilation; safety in emergency etc.
9.Finishes for walls: The finishes of several types such as pointing, plastering, painting, types such as pointing, plastering, painting, distempering, decorative colour washing etc. applied on the walls.
The main function of these finishes are
a. Protect structure from the sun, rain, snow etc.
b. Provide a true, even and smooth finished surface and also to improve the asthetic appearance of the structure.
c. Rectify rather cover, to some extent, the poor or defective workmanship
d. Cover up the unsound and porous materials used in the construction
10.Utility Fixtures: These are the built in items of an unmovable nature, which add considerably to the utility of a building and hence termed as utility fixtures. The most common of such built-in fixtures are: cupboards, shelves, smokeless chulas etc. These features are generally provided in the recesses for storing valuable articles, clothes etc. The recesses in wall structure reduce its strength, so they are avoided in the modern construction of houses.
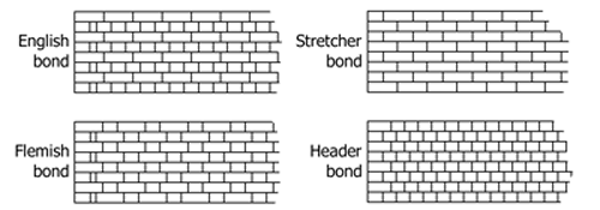
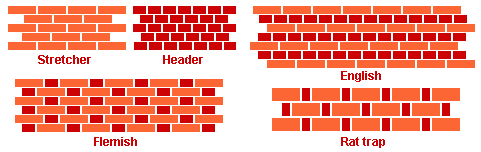
Door
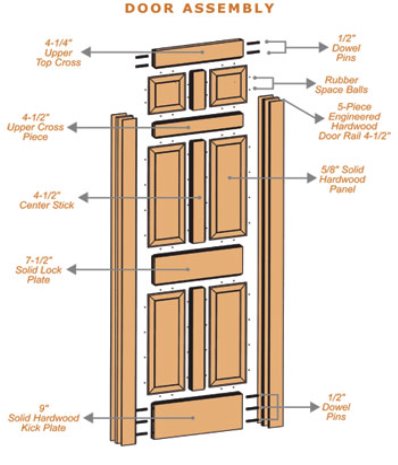
- Window :
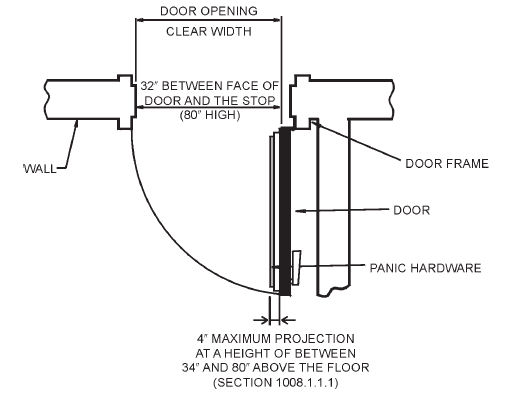
The standard size for an exterior door is 80 inches by 36 inches which is 6 ft, 8 inches by 3 ft. 96 inches or 8 ft. Is now very common for newer homes and stock exterior doors are also commonly available in 30 and 32-inch widths. Some door manufacturers sell doors in 7ft & 8ft heights and door widths from 24 inches to 42 inches. The height for fiberglass or steel doors are fixed at 6 ft. 8 inches tall and 8 ft. Tall. The standard door thickness is 1 ¾ inch.
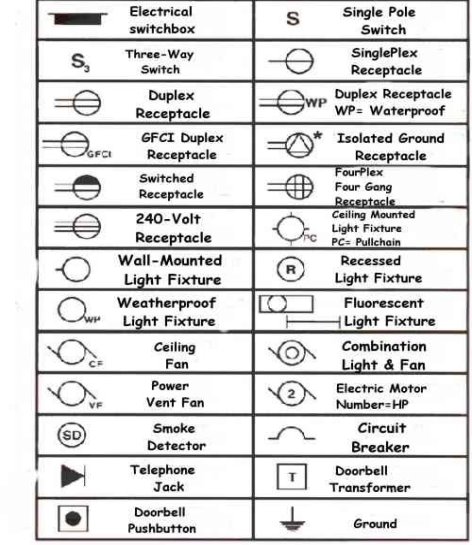
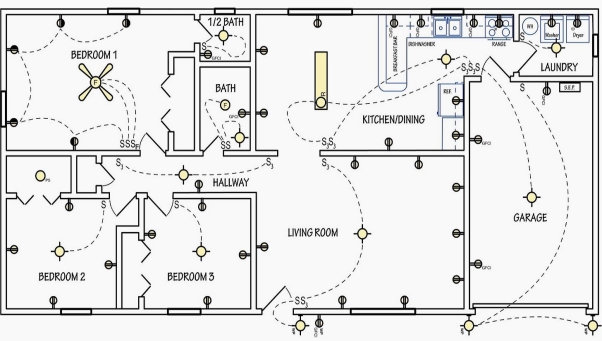
Various types of building services are :
- Plumbing
- Sanitation,
- Water supply
- Drainage system
|
Plumbing :
Plumbing, system of pipes and fixtures installed in a building for the distribution and use of potable (drinkable) water and the removal of waterborne wastes. It is usually distinguished from water and sewage systems that serve a group of buildings or a city.
The term plumbing fixture embraces not only showers, bathtubs, lavatory basins, and toilets but also such devices as washing machines, garbage-disposal units, hot-water heaters, dishwashers, and drinking fountains.
The water-carrying pipes and other materials used in a plumbing system must be strong, noncorrosive, and durable enough to equal or exceed the expected life of the building in which they are installed. Toilets, urinals, and lavatories usually are made of stable porcelain or vitreous china, although they sometimes are made of glazed cast iron, steel, or stainless steel. Ordinary water pipes usually are made of steel, copper, brass, plastic, or other nontoxic material; and the most common materials for sewage pipes are cast iron, steel, copper, and asbestos cement.

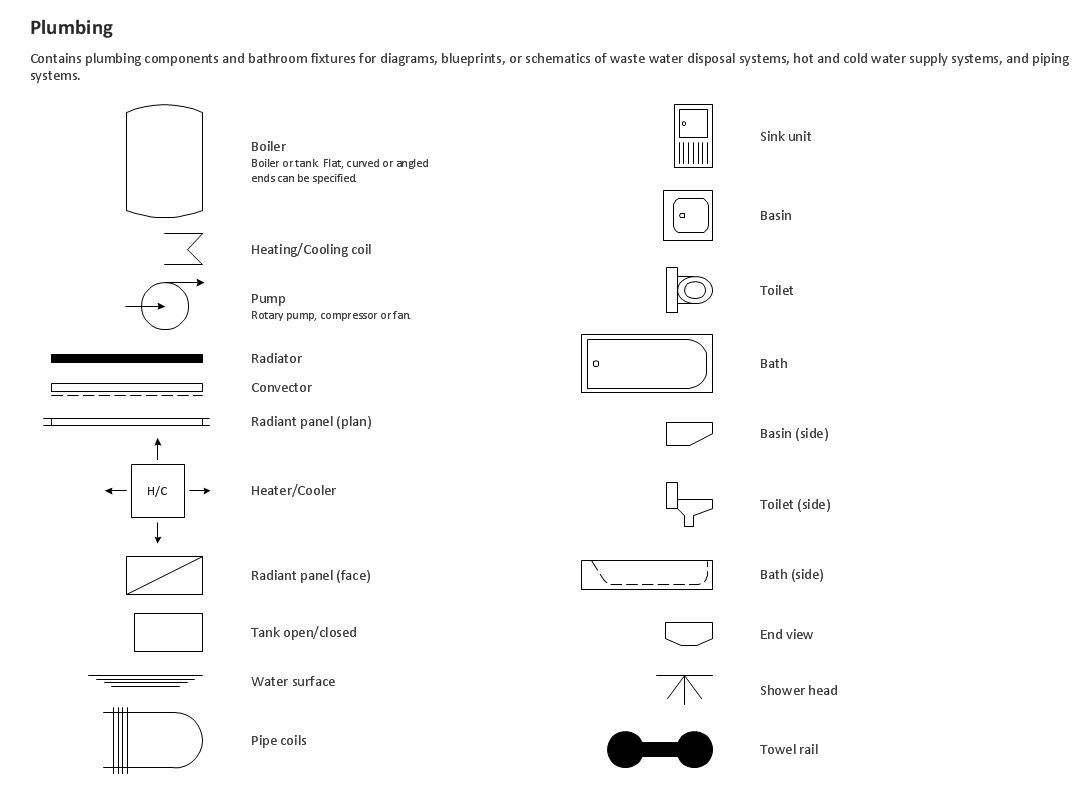
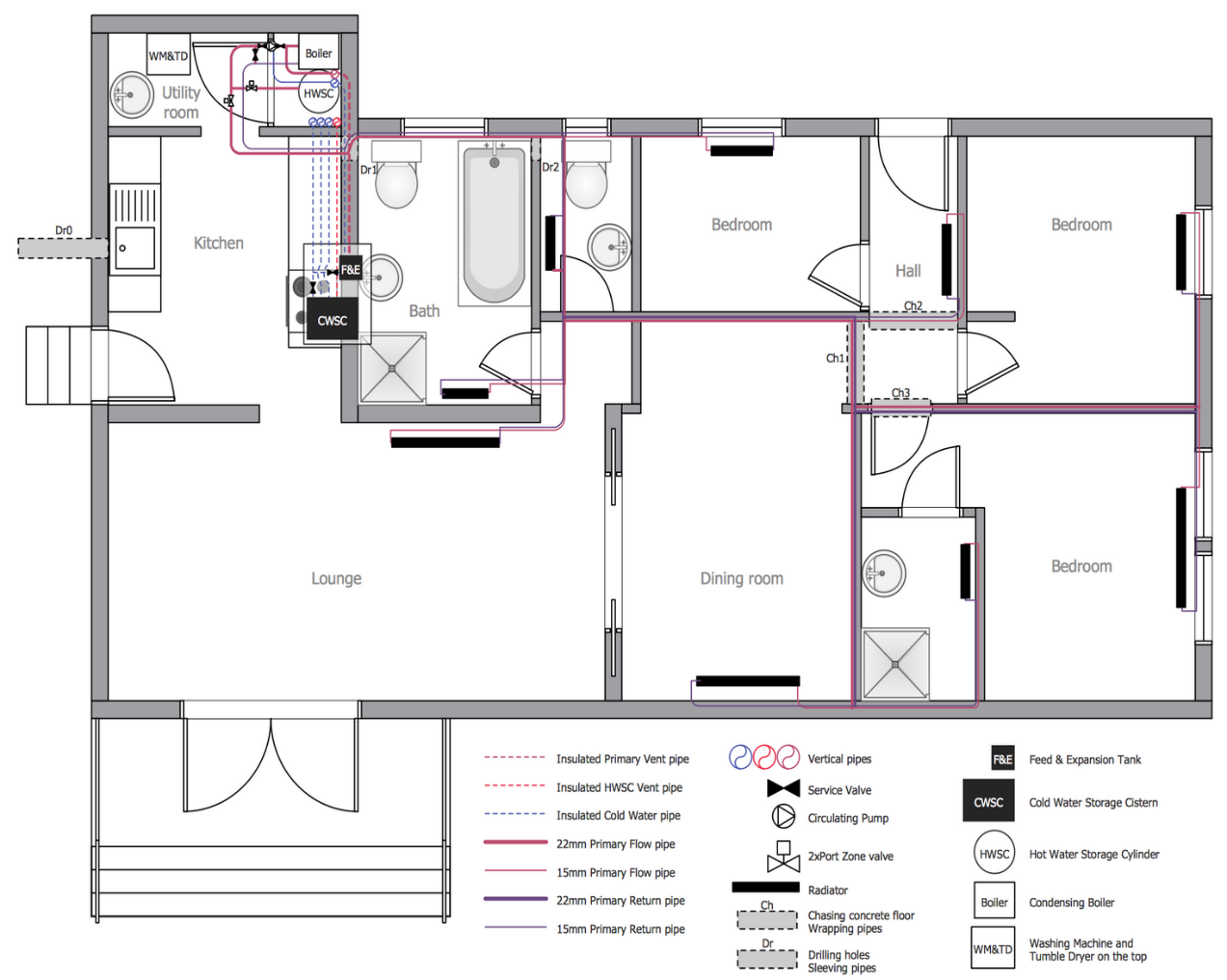
Sanitation :
Sanitation refers to public health conditions such as drinking clean water, sewage treatment, etc. All the effective tools and actions that help in keeping the environment clean come under sanitation.
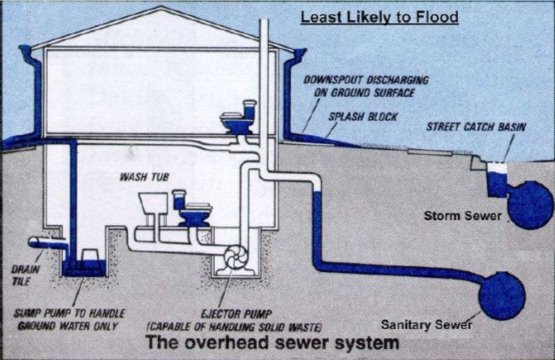
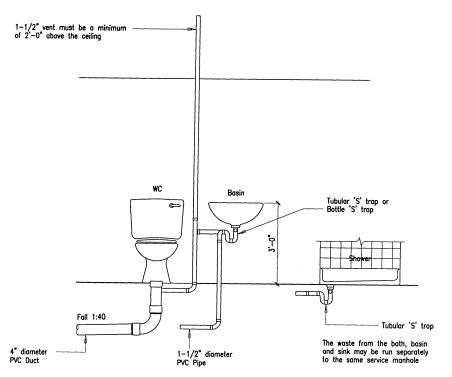
Water supply:
The objective of a public protected water supply system is to supply safe and clean water in adequate quantity , conveniently and as economically as possible . The planning may be required at national level for the country as a whole , or for the state or region or community Though the responsibility of the various organizations incharge of planning of water supply systems in each of these cases is different , they still have to function within the priorites fixed by the national and state governments , taking into consideration , the areas to be provided with water supply and the most economical way of doing it , keeping in view the overall requirements of the entire The water supply projects formulated by the various state authorities and local bodies at present do not contain all the essential clenients for appraisal and when projects are assessed for their cost benefit ratio and for institutional or other funding , they are not amenable for comparative study and appraisal Also , different guidelines and norms are adopted by the central and state agencies , for example , assumptions regarding per capita water supply , design porod , population forecast , measurement of flow , water treatment , specifications of materials , etc. Therefore , there is a need to specify appropriate standards , planning , and desiga criteria to avoid empirical approach.
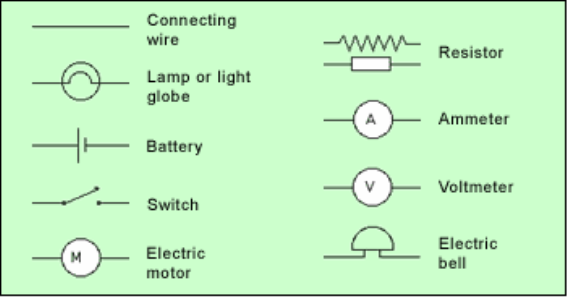
Symbols used for water supply:

Drainage system:
A drainage system is an arrangement to move liquids away from where they are not required for disposal in appropriate locations. A ‘drainage system’ can include anything from gutters and drains in houses to remove rain water, storm water systems to drain rainwater from roads into roadside drains and drainage systems to remove sewage from houses into municipal ‘sewers’ for disposal. Within the medical industry, ‘drainage systems’ can mean methods to drain unwanted fluids from the body, such as pus from wounds, colostomy bags to remove body wastes and fluids from internal abscesses and ulcers. Within engineering it can mean systems for removing spent oil, coolant liquids and by-products from industry referred to as ‘industrial waste’.
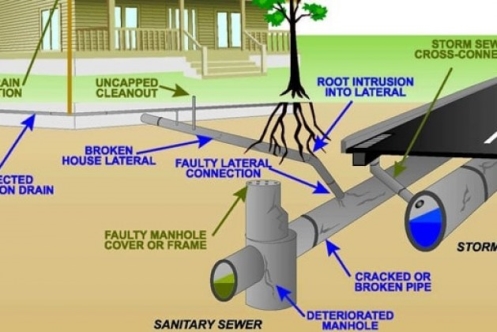
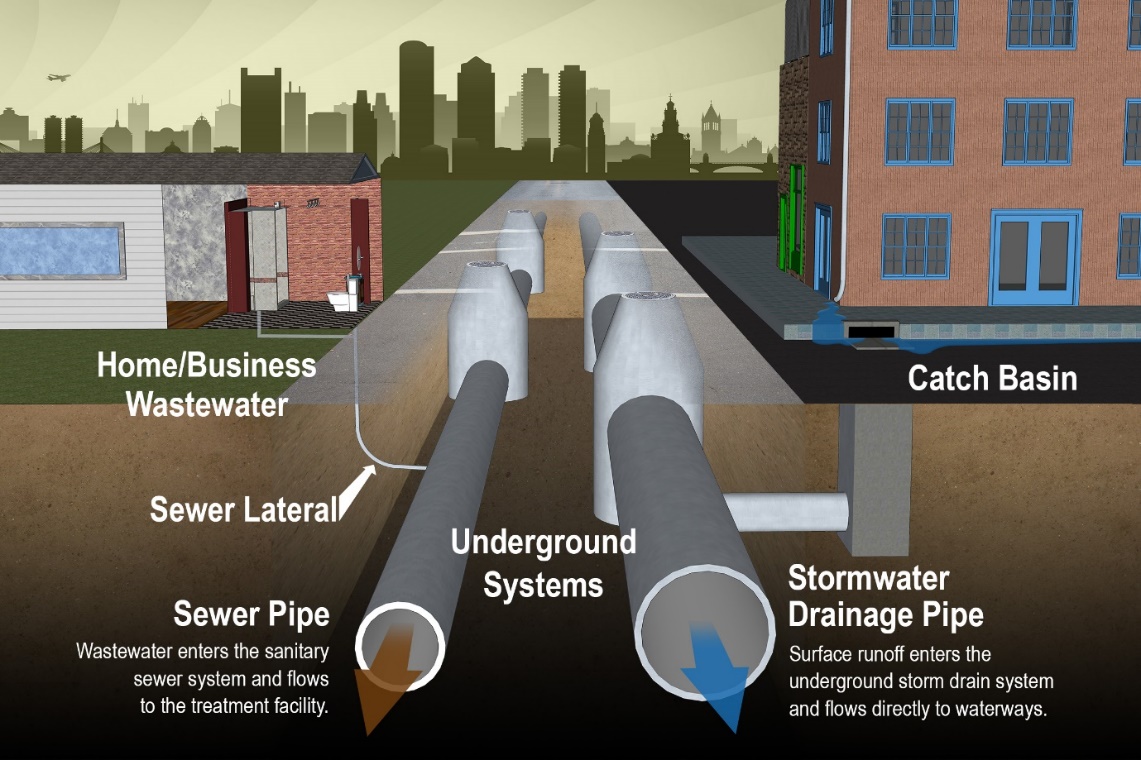
Building finishes:
HVAC stands for Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning.
HVAC refers to the different systems used for moving air between indoor and outdoor areas, along with heating and cooling both residential and commercial buildings. They are the systems that keep you warm and cozy in the winter and feeling cool and fresh in the summer. They also are the systems that filter and clean indoor air to keep you healthy and maintain humidity levels at optimal comfort levels.
The purpose of an HVAC system is more than just warming or cooling a space. Instead, it serves to improve indoor air quality and provide comfort for everyone inside a building. While there are several different types of HVAC systems, they all begin with the same essentials.
Mechanical ventilation uses a mechanical system--the V in HVAC--to move air in and out. In the past, there was plenty of natural ventilation in most homes from gaps and cracks in the construction along with opening and closing of doors. However, modern construction is creating homes that are far more tightly sealed so ventilation is becoming an increasingly important component in home HVAC systems. Once the air is brought in, it is drawn into an air handling unit where the work begins. Here, air is drawn through filters to remove dirt, dust, allergens, and other particles. Next up is comfort. Air is either sent to be heated or sent to be cooled and have excess humidity removed.
Reference books
1.Dr.B.C. Punamia, “Building Construction”
2. M. S. Palanichamy, “Basic Civil Engineering”