Unit 4
Computer Basics and Hardware
Generations of Computer
Introduction:
A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data.
Nowadays, a computer can be used to type documents, send email, play games, and browse the Web. It can also be used to edit or create spreadsheets, presentations, and even videos. But the evolution of this complex system started around 1940 with the first Generation of Computer and evolving ever since.
There are five generations of computers.
1. FIRST GENERATION
- Introduction:
- 1946-1959 is the period of first generation computer.
- J.P.Eckert and J.W.Mauchy invented the first successful electronic computer called ENIAC, ENIAC stands for “Electronic Numeric Integrated And Calculator”.
- Few Examples are:
- ENIAC
- EDVAC
- UNIVAC
- IBM-701
- IBM-650
……..
- Advantages:
- It made use of vacuum tubes which are the only electronic component available during those days.
- These computers could calculate in milliseconds.
- Disadvantages:
- These were very big in size, weight was about 30 tones.
- These computers were based on vacuum tubes.
- These computers were very costly.
- It could store only a small amount of information due to the presence of magnetic drums.
- As the invention of first generation computers involves vacuum tubes, so another disadvantage of these computers was, vacuum tubes require a large cooling system.
- Very less work efficiency.
- Limited programming capabilities and punch cards were used to take inputs.
- Large amount of energy consumption.
- Not reliable and constant maintenance is required.
2. SECOND GENERATION
- Introduction:
- 1959-1965 is the period of second-generation computer.
- 3.Second generation computers were based on Transistor instead of vacuum tubes.
- Few Examples are:
- Honeywell 400
- IBM 7094
- CDC 1604
- CDC 3600
- UNIVAC 1108
… many more
- Advantages:
- Due to the presence of transistors instead of vacuum tubes, the size of electron component decreased. This resulted in reducing the size of a computer as compared to first generation computers.
- Less energy and not produce as much heat as the first genration.
- Assembly language and punch cards were used for input.
- Low cost than first generation computers.
- Better speed, calculate data in microseconds.
- Better portability as compared to first generation
- Disadvantages:
- A cooling system was required.
- Constant maintenance was required.
- Only used for specific purposes.
3. THIRD GENERATION
- Introduction:
- 1965-1971 is the period of third generation computer.
- These computers were based on Integrated circuits.
- IC was invented by Robert Noyce and Jack Kilby In 1958-1959.
- IC was a single component containing number of transistors.
- Few Examples are:
- PDP-8
- PDP-11
- ICL 2900
- IBM 360
- IBM 370
… and many more
- Advantages:
- These computers were cheaper as compared to second-generation computers.
- They were fast and reliable.
- Use of IC in the computer provides the small size of the computer.
- IC not only reduce the size of the computer but it also improves the performance of the computer as compared to previous computers.
- This generation of computers has big storage capacity.
- Instead of punch cards, mouse and keyboard are used for input.
- They used an operating system for better resource management and used the concept of time-sharing and multiple programming.
- These computers reduce the computational time from microseconds to nanoseconds.
- Disadvantages:
- IC chips are difficult to maintain.
- The highly sophisticated technology required for the manufacturing of IC chips.
- Air conditioning is required.
4. FOURTH GENERATION
- Introduction:
- 1971-1980 is the period of fourth generation computer.
- This technology is based on Microprocessor.
- A microprocessor is used in a computer for any logical and arithmetic function to be performed in any program.
- Graphics User Interface (GUI) technology was exploited to offer more comfort to users.
- Few Examples are:
- IBM 4341
- DEC 10
- STAR 1000
- PUP 11
… and many more
- Advantages:
- Fastest in computation and size get reduced as compared to the previous generation of computer.
- Heat generated is negligible.
- Small in size as compared to previous generation computers.
- Less maintenance is required.
- All types of high-level language can be used in this type of computers.
- Disadvantages:
- The Microprocessor design and fabrication are very complex.
- Air conditioning is required in many cases due to the presence of ICs.
- Advance technology is required to make the ICs.
5. FIFTH GENERATION
- Introduction:
- The period of the fifth generation in 1980-onwards.
- This generation is based on artificial intelligence.
- The aim of the fifth generation is to make a device which could respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.
- This generation is based on ULSI(Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology resulting in the production of microprocessor chips having ten million electronic component.
- Few Examples are:
- Desktop
- Laptop
- NoteBook
- UltraBook
- Chromebook
… and many more
- Advantages:
- It is more reliable and works faster.
- It is available in different sizes and unique features.
- It provides computers with more user-friendly interfaces with multimedia features.
- Disadvantages:
- They need very low-level languages.
- They may make the human brains dull and doomed.
Classification of Computers
Computer scan is broadly classified by their speed and computing power.
Sr.No. | Type | Specifications |
1 | PC (Personal Computer) or Micro-Computers | It is a single user computer system having a moderately powerful microprocessor. It is termed as a computer that is equipped microprocessor as its CPU. |
2 | Workstation | It is also a single user computer system, similar to the personal computer, however, has a more powerful microprocessor. |
3 | Mini-Computer | It is a multi-user computer system, capable of supporting hundreds of users simultaneously. |
4 | Main Frame | It is a multi-user computer system, capable of supporting hundreds of users simultaneously. Software technology is different from minicomputer. |
5 | Super-Computer | It is an extremely fast computer, which can execute hundreds of millions of instructions per second. |
PC (Personal Computer)
 A PC can be defined as a small, relatively inexpensive computer designed for an individual user. PCs are based on the microprocessor technology that enables manufacturers to put an entire CPU on one chip. Businesses use personal computers for word processing, accounting, desktop publishing, and for running spreadsheet and database management applications. At home, the most popular use for personal computers is playing games and surfing the Internet.
A PC can be defined as a small, relatively inexpensive computer designed for an individual user. PCs are based on the microprocessor technology that enables manufacturers to put an entire CPU on one chip. Businesses use personal computers for word processing, accounting, desktop publishing, and for running spreadsheet and database management applications. At home, the most popular use for personal computers is playing games and surfing the Internet.
Although personal computers are designed as single-user systems, these systems are normally linked together to form a network. In terms of power, nowadays high-end models of the Macintosh and PC offer the same computing power and graphics capability as low-end workstations by Sun Microsystems, Hewlett-Packard, and Dell.
Workstation

The workstation is a computer used for engineering applications (CAD/CAM), desktop publishing, software development, and other such types of applications which require a moderate amount of computing power and relatively high-quality graphics capabilities.
Workstations generally come with a large, high-resolution graphics screen, a large amount of RAM, inbuilt network support, and a graphical user interface. Most workstations also have mass storage device such as a disk drive, but a special type of workstation, called diskless workstations, comes without a disk drive.
Common operating systems for workstations are UNIX and Windows NT. Like PC, workstations are also single-user computers like PC but are typically linked together to form a local area network, although they can also be used as stand-alone systems.
Minicomputer
It is a midsize multi-processing system capable of supporting up to 250 users simultaneously.

Mainframe
The mainframe is very large in size and is an expensive computer capable of supporting hundreds or even thousands of users simultaneously. Mainframe executes many programs concurrently and supports much simultaneous execution of programs.

Supercomputer
Supercomputers are one of the fastest computers currently available. Supercomputers are very expensive and are employed for specialized applications that require an immense amount of mathematical calculations (number-crunching).

For example, weather forecasting, scientific simulations, (animated)graphics, fluid dynamic calculations, nuclear energy research, electronic design, and analysis of geological data (e.g. In petrochemical prospecting).
Computer - CPU (Central Processing Unit)
Central Processing Unit (CPU) consists of the following features −
- CPU is considered as the brain of the computer.
- CPU performs all types of data processing operations.
- It stores data, intermediate results, and instructions (program).
- It controls the operation of all parts of the computer.

CPU itself has following three components.
- Memory or Storage Unit
- Control Unit
- ALU(Arithmetic Logic Unit)
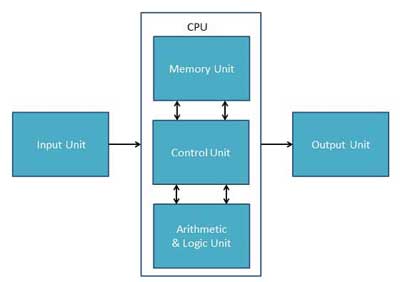
Memory or Storage Unit
This unit can store instructions, data, and intermediate results. This unit supplies information to other units of the computer when needed. It is also known as internal storage unit or the main memory or the primary storage or Random Access Memory (RAM).
Its size affects speed, power, and capability. Primary memory and secondary memory are two types of memories in the computer. Functions of the memory unit are −
- It stores all the data and the instructions required for processing.
- It stores intermediate results of processing.
- It stores the final results of processing before these results are released to an output device.
- All inputs and outputs are transmitted through the main memory.
Control Unit
This unit controls the operations of all parts of the computer but does not carry out any actual data processing operations.
Functions of this unit are −
- It is responsible for controlling the transfer of data and instructions among other units of a computer.
- It manages and coordinates all the units of the computer.
- It obtains the instructions from the memory, interprets them, and directs the operation of the computer.
- It communicates with Input/Output devices for transfer of data or results from storage.
- It does not process or store data.
ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
This unit consists of two subsections namely,
- Arithmetic Section
- Logic Section
Arithmetic Section
Function of arithmetic section is to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. All complex operations are done by making repetitive use of the above operations.
Logic Section
Function of logic section is to perform logic operations such as comparing, selecting, matching, and merging of data.
Input Unit
Following are some of the important input devices which are used in a computer −
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Joy Stick
- Light pen
- Track Ball
- Scanner
- Graphic Tablet
- Microphone
- Magnetic Ink Card Reader(MICR)
- Optical Character Reader(OCR)
- Bar Code Reader
- Optical Mark Reader(OMR)
Keyboard
Keyboard is the most common and very popular input device which helps to input data to the computer. The layout of the keyboard is like that of traditional typewriter, although there are some additional keys provided for performing additional functions.

Keyboards are of two sizes 84 keys or 101/102 keys, but now keyboards with 104 keys or 108 keys are also available for Windows and Internet.
The keys on the keyboard are as follows −
S.No | Keys & Description |
1 | Typing Keys These keys include the letter keys (A-Z) and digit keys (09) which generally give the same layout as that of typewriters. |
2 | Numeric Keypad It is used to enter the numeric data or cursor movement. Generally, it consists of a set of 17 keys that are laid out in the same configuration used by most adding machines and calculators. |
3 | Function Keys The twelve function keys are present on the keyboard which are arranged in a row at the top of the keyboard. Each function key has a unique meaning and is used for some specific purpose. |
4 | Control keys These keys provide cursor and screen control. It includes four directional arrow keys. Control keys also include Home, End, Insert, Delete, Page Up, Page Down, Control(Ctrl), Alternate(Alt), Escape(Esc). |
5 | Special Purpose Keys Keyboard also contains some special purpose keys such as Enter, Shift, Caps Lock, Num Lock, Space bar, Tab, and Print Screen. |
Mouse
Mouse is the most popular pointing device. It is a very famous cursor-control device having a small palm size box with a round ball at its base, which senses the movement of the mouse and sends corresponding signals to the CPU when the mouse buttons are pressed.
Generally, it has two buttons called the left and the right button and a wheel is present between the buttons. A mouse can be used to control the position of the cursor on the screen, but it cannot be used to enter text into the computer.

Advantages
- Easy to use
- Not very expensive
- Moves the cursor faster than the arrow keys of the keyboard.
Joystick
Joystick is also a pointing device, which is used to move the cursor position on a monitor screen. It is a stick having a spherical ball at its both lower and upper ends. The lower spherical ball moves in a socket. The joystick can be moved in all four directions.

The function of the joystick is similar to that of a mouse. It is mainly used in Computer Aided Designing (CAD) and playing computer games.
Light Pen
Light pen is a pointing device similar to a pen. It is used to select a displayed menu item or draw pictures on the monitor screen. It consists of a photocell and an optical system placed in a small tube.

When the tip of a light pen is moved over the monitor screen and the pen button is pressed, its photocell sensing element detects the screen location and sends the corresponding signal to the CPU.
Track Ball
Track ball is an input device that is mostly used in notebook or laptop computer, instead of a mouse. This is a ball which is half inserted and by moving fingers on the ball, the pointer can be moved.

Since the whole device is not moved, a track ball requires less space than a mouse. A track ball comes in various shapes like a ball, a button, or a square.
Scanner
Scanner is an input device, which works more like a photocopy machine. It is used when some information is available on paper and it is to be transferred to the hard disk of the computer for further manipulation.

Scanner captures images from the source which are then converted into a digital form that can be stored on the disk. These images can be edited before they are printed.
Digitizer
Digitizer is an input device which converts analog information into digital form. Digitizer can convert a signal from the television or camera into a series of numbers that could be stored in a computer. They can be used by the computer to create a picture of whatever the camera had been pointed at.

Digitizer is also known as Tablet or Graphics Tablet as it converts graphics and pictorial data into binary inputs. A graphic tablet as digitizer is used for fine works of drawing and image manipulation applications.
Microphone
Microphone is an input device to input sound that is then stored in a digital form.

The microphone is used for various applications such as adding sound to a multimedia presentation or for mixing music.
Magnetic Ink Card Reader (MICR)
MICR input device is generally used in banks as there are large number of cheques to be processed every day. The bank's code number and cheque number are printed on the cheques with a special type of ink that contains particles of magnetic material that are machine readable.

This reading process is called Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR). The main advantages of MICR is that it is fast and less error prone.
Optical Character Reader (OCR)
OCR is an input device used to read a printed text.

OCR scans the text optically, character by character, converts them into a machine readable code, and stores the text on the system memory.
Bar Code Readers
Bar Code Reader is a device used for reading bar coded data (data in the form of light and dark lines). Bar coded data is generally used in labelling goods, numbering the books, etc. It may be a handheld scanner or may be embedded in a stationary scanner.

Bar Code Reader scans a bar code image, converts it into an alphanumeric value, which is then fed to the computer that the bar code reader is connected to.
Optical Mark Reader (OMR)
OMR is a special type of optical scanner used to recognize the type of mark made by pen or pencil. It is used where one out of a few alternatives is to be selected and marked.

It is specially used for checking the answer sheets of examinations having multiple choice questions.
Output Unit
Following are some of the important output devices used in a computer.
- Monitors
- Graphic Plotter
- Printer
Monitors
Monitors, commonly called as Visual Display Unit (VDU), are the main output device of a computer. It forms images from tiny dots, called pixels that are arranged in a rectangular form. The sharpness of the image depends upon the number of pixels.
There are two kinds of viewing screen used for monitors.
- Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT)
- Flat-Panel Display
Cathode-Ray Tube (CRT) Monitor
The CRT display is made up of small picture elements called pixels. The smaller the pixels, the better the image clarity or resolution. It takes more than one illuminated pixel to form a whole character, such as the letter ‘e’ in the word help.

A finite number of characters can be displayed on a screen at once. The screen can be divided into a series of character boxes - fixed location on the screen where a standard character can be placed. Most screens are capable of displaying 80 characters of data horizontally and 25 lines vertically.
There are some disadvantages of CRT −
- Large in Size
- High power consumption
Flat-Panel Display Monitor
The flat-panel display refers to a class of video devices that have reduced volume, weight and power requirement in comparison to the CRT. You can hang them on walls or wear them on your wrists. Current uses of flat-panel displays include calculators, video games, monitors, laptop computer, and graphics display.

The flat-panel display is divided into two categories −
- Emissive Displays − Emissive displays are devices that convert electrical energy into light. For example, plasma panel and LED (Light-Emitting Diodes).
- Non-Emissive Displays − Non-emissive displays use optical effects to convert sunlight or light from some other source into graphics patterns. For example, LCD (Liquid-Crystal Device).
Printers
Printer is an output device, which is used to print information on paper.
There are two types of printers −
- Impact Printers
- Non-Impact Printers
Impact Printers
Impact printers print the characters by striking them on the ribbon, which is then pressed on the paper.
Characteristics of Impact Printers are the following −
- Very low consumable costs
- Very noisy
- Useful for bulk printing due to low cost
- There is physical contact with the paper to produce an image
These printers are of two types −
- Character printers
- Line printers
Character Printers
Character printers are the printers which print one character at a time.
These are further divided into two types:
- Dot Matrix Printer(DMP)
- Daisy Wheel
Dot Matrix Printer
In the market, one of the most popular printers is Dot Matrix Printer. These printers are popular because of their ease of printing and economical price. Each character printed is in the form of pattern of dots and head consists of a Matrix of Pins of size (5*7, 7*9, 9*7 or 9*9) which come out to form a character which is why it is called Dot Matrix Printer.

Advantages
- Inexpensive
- Widely Used
- Other language characters can be printed
Disadvantages
- Slow Speed
- Poor Quality
Daisy Wheel
Head is lying on a wheel and pins corresponding to characters are like petals of Daisy (flower) which is why it is called Daisy Wheel Printer. These printers are generally used for word-processing in offices that require a few letters to be sent here and there with very nice quality.

Advantages
- More reliable than DMP
- Better quality
- Fonts of character can be easily changed
Disadvantages
- Slower than DMP
- Noisy
- More expensive than DMP
Line Printers
Line printers are the printers which print one line at a time.

These are of two types −
- Drum Printer
- Chain Printer
Drum Printer
This printer is like a drum in shape hence it is called drum printer. The surface of the drum is divided into a number of tracks. Total tracks are equal to the size of the paper, i.e. for a paper width of 132 characters, drum will have 132 tracks. A character set is embossed on the track. Different character sets available in the market are 48 character set, 64 and 96 characters set. One rotation of drum prints one line. Drum printers are fast in speed and can print 300 to 2000 lines per minute.
Advantages
- Very high speed
Disadvantages
- Very expensive
- Characters fonts cannot be changed
Chain Printer
In this printer, a chain of character sets is used, hence it is called Chain Printer. A standard character set may have 48, 64, or 96 characters.
Advantages
- Character fonts can easily be changed.
- Different languages can be used with the same printer.
Disadvantages
- Noisy
Non-impact Printers
Non-impact printers print the characters without using the ribbon. These printers print a complete page at a time, thus they are also called as Page Printers.
These printers are of two types −
- Laser Printers
- Inkjet Printers
Characteristics of Non-impact Printers
- Faster than impact printers
- They are not noisy
- High quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Laser Printers
These are non-impact page printers. They use laser lights to produce the dots needed to form the characters to be printed on a page.

Advantages
- Very high speed
- Very high quality output
- Good graphics quality
- Supports many fonts and different character size
Disadvantages
- Expensive
- Cannot be used to produce multiple copies of a document in a single printing
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers are non-impact character printers based on a relatively new technology. They print characters by spraying small drops of ink onto paper. Inkjet printers produce high quality output with presentable features.

They make less noise because no hammering is done and these have many styles of printing modes available. Color printing is also possible. Some models of Inkjet printers can produce multiple copies of printing also.
Advantages
- High quality printing
- More reliable
Disadvantages
- Expensive as the cost per page is high
- Slow as compared to laser printer
Storage Unit
A storage device is a piece of computer hardware used for saving, carrying and pulling out data. It can keep and retain information short-term or long-term. It can be a device inside or outside a computer or server. Other terms for storage device is storage medium or storage media.
A storage device is one of the basic elements of any computer device. It almost saves all data and applications in a computer except for hardware firmware. It comes in different shapes and sizes depending on the needs and functionalities.
Types of Storage Devices
There are two different types of storage devices:
| Primary Storage Device | Secondary Storage Device |
Size | Smaller | Larger |
Data Retention | Temporary | Permanent |
Location | Internal | Internal / External |
Examples | RAM, Cache Memory | Hard disk, Compact Disk Drive, USB storage device |
Examples of Storage Device
- Magnetic Storage Device – one of the most popular types of storage used.
- Floppy diskette – A normal 3 ½ inch disk can store 1.44 MB of data.
- Hard drive – An internal hard drive is the main storage device in a computer. An external hard drive is also known as removable hard drive. It is used to store portable data and backups.
- Magnetic strip – Magnetic tape drive stores video and audio using magnetic tape, like tape and video tape recorders.
- Super disk – A disk drive and diskette that can hold 120 MB and 240 MB of data.
- Cassette tape – A magnetic storage device used for audio recording and playback.
- Zip diskette – Like a floppy diskette but more advanced.
- Optical Storage Device – uses lasers and lights as its mode of saving and retrieving data.
- Blu-ray disc – A digital optical storage device which was intended to replace the DVD format.
- CD-ROM disc – An optical storage device that is read-only or cannot be modified nor deleted.
- CD-R and CD-RW disc – CD-R is a recordable disc that can be written to once, while CD-RW is a rewritable disc that can be written to multiple times.
- DVD-R, DVD+R, DVD-RW and DVD+RW disc – DVD-R and DVD+R are recordable discs that can be written to once, while DVD-RW and DVD+RW are rewritable discs that can be written to multiple times. The difference between the + and – is in the formatting and compatibility.
- Flash Memory Device – is now replacing magnetic storage device as it is economical, more functional and dependable.
- Memory card – An electronic flash memory device used to store digital information and commonly used in mobile electronic devices.
- Memory stick – A memory card that is removable.
- SSD – Solid State Drive – A flash memory device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to save data steadily.
- USB flash drive, jump drive or thumb drive – A small, portable storage device connected through the USB port.
- Online and Cloud – is now becoming widespread as people access data from different devices.
- Cloud storage – Data is managed remotely and made available over a network. Basic features are free to use but upgraded version is paid monthly as a per consumption rate.
- Network media – Audio, Video, Images or Text that are used on a computer network. A community of people create and use the content shared over the internet.
- Paper Storage – method used by early computers for saving information.
- OMR – stands for Optical Mark Recognition – A process of capturing marked data of human from forms like surveys and tests. It is used to read questionnaires with multiple choices that are shaded.
- Punch card – A piece of hard paper used to contain digital information coming from the perforated holes. The presence or absence of holes in predetermined positions define the data.
Computer - Applications
The application of computers in various fields.
Business

A computer has high speed of calculation, diligence, accuracy, reliability, or versatility which has made it an integrated part in all business organizations.
Computer is used in business organizations for −
- Payroll calculations
- Budgeting
- Sales analysis
- Financial forecasting
- Managing employee database
- Maintenance of stocks, etc.
Banking

Today, banking is almost totally dependent on computers.
Banks provide the following facilities −
- Online accounting facility, which includes checking current balance, making deposits and overdrafts, checking interest charges, shares, and trustee records.
- ATM machines which are completely automated are making it even easier for customers to deal with banks.
Insurance

Insurance companies are keeping all records up-to-date with the help of computers. Insurance companies, finance houses, and stock broking firms are widely using computers for their concerns.
Insurance companies are maintaining a database of all clients with information showing −
- Procedure to continue with policies
- Starting date of the policies
- Next due installment of a policy
- Maturity date
- Interests due
- Survival benefits
- Bonus
Education

The computer helps in providing a lot of facilities in the education system.
- The computer provides a tool in the education system known as CBE (Computer Based Education).
- CBE involves control, delivery, and evaluation of learning.
- Computer education is rapidly increasing the graph of number of computer students.
- There are a number of methods in which educational institutions can use a computer to educate the students.
- It is used to prepare a database about performance of a student and analysis is carried out on this basis.
Marketing
In marketing, uses of the computer are following −

- Advertising − With computers, advertising professionals create art and graphics, write and revise copy, and print and disseminate ads with the goal of selling more products.
- Home Shopping − Home shopping has been made possible through the use of computerized catalogues that provide access to product information and permit direct entry of orders to be filled by the customers.
Healthcare
Computers have become an important part in hospitals, labs, and dispensaries. They are being used in hospitals to keep the record of patients and medicines. It is also used in scanning and diagnosing different diseases. ECG, EEG, ultrasounds and CT scans, etc. are also done by computerized machines.
Following are some major fields of health care in which computers are used.

- Diagnostic System − Computers are used to collect data and identify the cause of illness.
- Lab-diagnostic System − All tests can be done and the reports are prepared by computer.
- Patient Monitoring System − These are used to check the patient's signs for abnormality such as in Cardiac Arrest, ECG, etc.
- Pharma Information System − Computer is used to check drug labels, expiry dates, harmful side effects, etc.
- Surgery − Nowadays, computers are also used in performing surgery.
Engineering Design
Computers are widely used for Engineering purpose.
One of the major areas is CAD (Computer Aided Design) that provides creation and modification of images. Some of the fields are −

- Structural Engineering − Requires stress and strain analysis for design of ships, buildings, budgets, airplanes, etc.
- Industrial Engineering − Computers deal with design, implementation, and improvement of integrated systems of people, materials, and equipment.
- Architectural Engineering − Computers help in planning towns, designing buildings, determining a range of buildings on a site using both 2D and 3D drawings.
Military

Computers are largely used in defence. Modern tanks, missiles, weapons, etc. Military also employs computerized control systems. Some military areas where a computer has been used are −
- Missile Control
- Military Communication
- Military Operation and Planning
- Smart Weapons
Communication
Communication is a way to convey a message, an idea, a picture, or speech that is received and understood clearly and correctly by the person for whom it is meant. Some main areas in this category are −

- Chatting
- Usenet
- FTP
- Telnet
- Video-conferencing
Government
Computers play an important role in government services. Some major fields in this category are −

- Budgets
- Sales tax department
- Income tax department
- Computation of male/female ratio
- Computerization of voters lists
- Computerization of PAN card
- Weather forecasting