UNIT - 3
HARDENED CONCRETE
WATER CEMENT RATIO
- The water–cement ratio is the ratio of the load of water to the load of cement utilized in a concrete blend.
- A decrease ratio ends in better electricity and durability, however might also additionally make the combination hard to paintings with and form. Workability may be resolved with using plasticizers or super-plasticizers.
- Often, the ratio refers back to the ratio of water to cement substances, w/cm.
- Cement substances encompass cement and supplementary cement substances which include fly ash, floor granulated blast-furnace slag, silica fume, rice husk ash and herbal pozzolans.
- Supplementary cement substances are delivered to reinforce concrete.
- However, a combination with a ratio of 0.35 might not blend very well, and might not glide nicely sufficient to be positioned.
- More water is consequently used than is technically important to react with cement. Water–cement ratios of 0.45 to 0.60 are greater usually used.
- For better-electricity concrete, decrease ratios are used, in conjunction with a plasticizer to boom flow ability.
Key take ways
A decrease ratio ends in better electricity and durability, however might also additionally make the combination hard to paintings with and form. Workability may be resolved with using plasticizers or super-plasticizers.
The average volume of hydrated cement in the combined volume of capillary pores and hydrated cement paste is known as the gel / space ratio. Indicated by r. Strength (1958) found that the dense strength of the concrete was 34000 r3 psi(234 r3 M Pa) and fortunately it did not find the influence of the concrete mix and its age in the energy forecast. To find out the meaning and significance of the gel / space ratio it is necessary to discuss the hydration product volume.
Volume of hydration product
- The perfect seating space for hydration products is a summary of the total volume of new cement and water mixing volume. In this case, if a small amount of water is lost through the reduction of cement and due to bleeding is ignored, the water consumed by chemical reactions with C2S and C3S is found to be 21 and 24 percent (most likely) the size of the two appropriate silicates.
- If the final reaction of hydrate C4AF is
C4AF + 2 C A(OH)2 + 10H = C3AH6 + C3FH6
- The relevant figures for C3AF and C3A are 37 and 40 percent. Equation (1) also varies almost exclusively due to our limited knowledge of stoichiometry for hydration products and no quantity of chemically mixed water will be found.
- Non-convertible water cut under certain conditions is considered to be 23% in the case of waterless cement (measured in quantity); in the case of type II, a moderate sulphate cement, this value is about 18%. The gravitational force of hydration products is that the resulting volume is greater than the total volume of waterless cement.
- The estimated amount of gravity of the hydration product in a complete structure, including the pores found in the most potential structure, is 2.16.
- Here we provide an indication of the calculation of the volume change during hydration.
Key take ways
The average volume of hydrated cement in the combined volume of capillary pores and hydrated cement paste is known as the gel / space ratio. Indicated by r.
Concrete enhances strength with continuous hydration. The rate of energy gain is rapid and the rate decreases with age. It is customary to take 28 days of energy as a full concrete strength. But in reality, concrete lasts more than 28 days.
Percentage of concrete strength in various ages
The strength of concrete increases with age .The table shows the strength of the concrete age differently compared to the strength in 28 days.
Age | Strength percentage |
1 days | 16 % |
3 days | 40 % |
7 days | 65 % |
14 days | 90 % |
28 days | 99 % |
Key take ways
Concrete enhances strength with continuous hydration. The rate of energy gain is rapid and the rate decreases with age. It is customary to take 28 days of energy as a full concrete strength. But in reality, concrete lasts more than 28 days.
Maturity
The maturity of the concrete indicates how far the treatment has progressed. Growing the relationship between concrete temperature, time and energy gain. It is represented by a reference value that can be measured in real time in the field.
How to Mature
- The ripening method, often referred to as maturation, is a method of testing the strength of new local concrete by associating time measurements with temperature and actual energy values.
- To speed up schedules, increase safety, and improve construction methods, construction teams want to know the strength of their concrete in the workplace in real time. Since maturity is related to concrete strength, maturity method is a way of achieving this without relying solely on the standard specimens of testing and laboratory testing.
- Growth is calculated following the changes in the temperature of the new concrete over time. Since each concrete compound has its own solid-maturing properties, we can use maturation to measure the strength of that compound at any time after laying.
- Once we know the ripeness of a particular concrete, we can use special relationships of concrete with the strength of the maturity to make a reliable measure of its strength.
Basic Steps
- Monitor internal temperatures during healing
- Use the internal temperature history tracked to calculate maturity
- Use maturity relationships to measure strength
Key take ways
The maturity of the concrete indicates how far the treatment has progressed. Growing the relationship between concrete temperature, time and energy gain. It is represented by a reference value that can be measured in real time in the field.
- Previously it was thought that the use of a larger compact size led to higher power This was because the larger compound the lower surface area was completely above the surface, therefore, the lower the water requirement for a given performance. Therefore, a low water / cement scale can be used which will lead to higher concrete strength.
- However, over time it was found that the use of the combined size did not affect the maximum power as expected from theoretical reasoning for the following reasons.
- The large size of the large size provides a low level of development of gel bonds facing a low concrete strength.
- Second the size of the wide scale creates a difference in concrete that will prevent the same distribution of load when pressed.
- When using a large size aggregate, due to internal bleeding, the switching area will be very weak due to the development of small cracks leading to a reduction in the compression force.
- Typically, high-strength concrete or rich concrete is adversely affected by the use of large size sizes. However, in composite bodies or weak concrete the influence of the size of the whole collection is reduced.
- It is interesting to note that in green mix the larger compounds give the highest energy while in the rich mix the smaller combinations bring the higher energy. The diagram below shows the influence of the large size of the compound with the compressive strength of the concrete.
Key take ways
The large size of the large size provides a low level of development of gel bonds facing a low concrete strength.
Second the size of the wide scale creates a difference in concrete that will prevent the same distribution of load when pressed.
COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH
- The compression takes a look at indicates the exceptional feasible electricity concrete can gain in best conditions.
- The compression takes a look at measures concrete electricity with inside the hardened state.
- Field concrete samples are organized, cured and examined consistent with ASTM preferred procedures.
- Specimens are organized from concrete taken from exclusive creation sites.
- Following methods and calculations are used for measuring compressive electricity of cylindrical concrete specimens.
Test Procedure
- Placing the Specimen — The plain (decrease) bearing block is located, with its hardened face up, at the desk of the trying out device without delay beneath the spherically seated (top) bearing block. The bearing faces of the top and decrease bearing blocks are wiped clean and the take a look at specimen is located at the decrease bearing block.
- Zero Verification and Block Seating— previous to trying out the specimen, it's far demonstrated that the weight indicator is ready to zero. If the indicator isn't always well set to zero, it's far adjusted.
- Rate of Loading— the weight is implemented constantly and without shock.
- Standards specify that for trying out machines of the screw type, the shifting head shall tour at a charge of about zero.05in. (1mm)/min while the device is jogging idle. While for hydraulically operated machines, the weight will be implemented at a charge of motion (platen to crosshead measurement) similar to a loading charge at the specimen in the variety of 20 to 50 psi/sec (0.15 to 0.35 M Pa/sec).
- During the software of the primary 1/2 of of the expected loading phase, a better charge of loading is allowed.
- No adjustment is made with inside the charge of motion of the platen at any time at the same time as a specimen is yielding swiftly right away earlier than failure.
- Load is implemented till the specimen fails, and the most load carried via way of means of the specimen all through the take a look at is recorded. The form of failure and the arrival of the concrete also are noted.
|
Fig1
Compression Testing Machine
Calculations:
Concrete Cylinder Loading Samples Compressive energy of the specimen is calculated through dividing the most load carried through the specimen all through the check with the common cross-sectional area.
Determine and specific the end result to the closest 10 psi (0.1 M Pa).
Key take ways
The electricity of air-dried cores is on common 14 percentages large than the electricity of soaked cores.
- Concrete cylinders and cube specimens for pressure testing are compared with previous research studies, including test procedures, factors affecting the cylinder / cube power rating, and conversion materials and measurements.
- The main difference between cylinder and cube test procedures is installation.
- The cylinder limits are usually not a plane or similar enough to fit well with the platens of pressure gauges, so they must be fitted with sulfur, neoprene, or other suitable material for proper distribution of the applied load.
- The tubes, however, are not binding but are attached to solid molds with aerial and parallel sides.
- During testing, they are examined on both sides so that the machine is properly aligned with the cube areas.
- Factors affecting the cylinder / cube power ratio are
1) The distribution, healing and testing process;
2) Specimen geometry;
3) Energy level;
4) Loading direction and machine features; and
5) Aggregated estimates.
- Previous attempts to determine the relationship of art transformations and mutations have shown that it is difficult (if not possible) to predict the relationship between cylinder and cube power.
- Previous studies have also shown that the cylinder / cube power ratio is between 0.65 and 0.90, although the ratios outside the range are also detected.
- Based on this previous research study, replacement of cylinder tests with chemical tests is not recommended.
Key take ways
The main difference between cylinder and cube test procedures is installation.
The cylinder limits are usually not a plane or similar enough to fit well with the platenes of pressure gauges, so they must be fitted with sulfur, neoprene, or other suitable material for proper distribution of the applied load.
Objective:
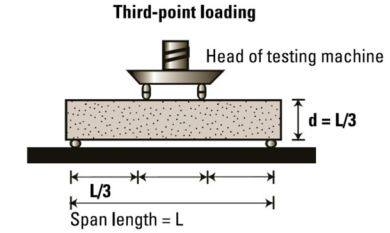
- To decide the Flexural Strength of Concrete, which comes into play whilst a avenue slab with insufficient sub-grade guide is subjected to wheel masses and / or there are extent modifications because of temperature / shrinking.
Equipment & Apparatus:
- Beam mildew of length 15 x 15x 70 cm (whilst length of mixture is much less than 38 mm) or of length 10 x 10 x 50 cm (whilst length of mixture is much less than 19 mm)
- Tamping bar (forty cm long, weighing 2 kg and tamping phase having length of 25 mm x 25 mm)
- Flexural take a look at gadget– The mattress of the checking out gadget will be furnished with metal rollers, 38 mm in diameter, on which the specimen is to be supported, and those rollers will be so hooked up that the space from center to center is 60 cm for 15.0 cm specimens or forty cm for 10.0 cm specimens.
- The load will be implemented via comparable rollers hooked up on the 1/3 factors of the assisting span that is, spaced at 20 or 13.3 cm center to center.
- The load will be divided similarly among the 2 loading rollers, and all rollers will be hooked up in this sort of way that the burden is implemented axially and without subjecting the specimen to any torsion stresses or restraints.
|
Fig no 2
Flexural testing machine
Procedure:
- Prepare the check specimen via way of means of filling the concrete into the mold in three layers of about identical thickness.
- Tamp every layer 35 instances the use of the tamping bar as distinct above.
- Tamping have to be disbursed uniformly over the whole cross section of the beam mildew and in the course of the intensity of every layer.
- Clean the bearing surfaces of the assisting and loading rollers, and get rid of any free sand or different cloth from the surfaces of the specimen in which they may be to make touch with the rollers.
- Circular rollers synthetic out of metallic having pass phase with diameter 38 mm may be used for presenting assist and loading factors to the specimens.
- The duration of the rollers will be at the least 10 mm greater than the width of the check specimen.
- A general of 4 rollers will be used, 3 out of which will be able to rotating alongside their very own axes.
- The distance among the outer rollers (i.e. span) will be 3d and the gap among the internal rollers will be d.
- The internal rollers will be similarly spaced among the outer rollers, such that the whole gadget is systematic.
- The specimen saved in water will be examined right away on elimination from water; while they may be nevertheless wet.
- The check specimen will be positioned with inside the device efficiently targeted with the longitudinal axis of the specimen at proper angles to the rollers.
- For mould specimens, the mold filling route will be ordinary to the route of loading.
- The load will be implemented at a price of loading of 400 kg/min for the 15.0 cm specimens and at a price of 180 kg/min for the 10.0 cm specimens.
Calculation:
- The Flexural Strength or modulus of rupture (fb) is given via way of means of
- F b = pl/bd2 (while a > 20.0cm for 15.0cm specimen or > 13.0cm for 10cm specimen)
O r
- F b = 3pa/bd2 (while a < 20> 17.zero for 15.0cm specimen or < 13> 11.0cm for 10.0cm specimen.)
Where,
a = the gap among the road of fracture and the closer assist, measured at the middle line of the tensile aspect of the specimen
b = width of specimen (cm)
d = failure factor intensity (cm)
l = supported duration (cm)
p = max. Load (kg)
Safety & Precautions:
- Use hand gloves while, protection footwear on the time of check.
- After check transfer off the device.
- Keep all of the uncovered metallic elements greased.
- Keep the manual rods firmly constant to the bottom & pinnacle plate.
- Equipment have to be wiped clean very well earlier than trying out & after trying out.
Key take ways
Beam mildew of length 15 x 15x 70 cm (whilst length of mixture is much less than 38 mm) or of length 10 x 10 x 50 cm (whilst length of mixture is much less than 19 mm)
- The pressure of the concrete is eight times greater than its strength.
- This refers to the established relationship between the compressive strength and the strength of the concrete. In fact, there is a close relationship but not a direct relationship.
- The degree of stiffness and pressure is low at high pressures.
- Experimental results also showed that concrete in stress and stress (both direct and indirect tension) is highly correlated but the relationship does not have a direct equation.
- The degree of strength and durability depends on the strength of the concrete.
- Thus, the increase in tensile strength, increases the tensile strength, but the rate of increase in tensile strength decreases steadily.
- The strength of concrete is more sensitive to improper treatment than to compressive strength.
This is possible for two reasons:
(a) The formation of a low-grade gel due to improper treatment.
(b) The formation of multiple shrinking cracks due to improper treatment. The use of pozzolanic materials showed an increase in strength.
- The Central Road Research Institute Delhi has conducted extensive research to build a relationship between the strength and durability of concrete in the construction of concrete roads.
- Based on the research experimental data, CRRI suggested the following relationship between flexural strength and concrete compression strength:
y = 11 x - 3.4
- where is the compressive strength of MPa concrete and x and its flexibility? This relationship depends on the size of the coarse aggregate. Energy is available to vary in type and quantity of composite.
Relationships are renewed below:
(a) With a crushed stone of 20 mm y = 15.3 x - 9.0
(b) 20 mm Natural Graval y = 14.3 x - 10.4
(c) For 40 mm Crushed Stones y = 9.9 x -5.5
(d) 40 mm Natural Graval y = 9.8 x - 2.5
Key take ways
The pressure of the concrete is eight times greater than its strength.
This refers to the established relationship between the compressive strength and the strength of the concrete. In fact, there is a close relationship but not a direct relationship.
Elastic Limit:
- When an external force is activated in the body, the body usually receives a certain difference. If the external force is removed and the body returns to its original shape and size, the body is known as body and elasticity.
- This property, when certain things come back to them the first position after the removal of external forces, is called stiffness.
- The body will regain its original shape and size only when the distortion is caused by external force, within a certain limit.
- So there is a limited amount of coercion to the inside that is, the twist disappears completely from the removal of energy.
- The amount of stress corresponding to this fixed measure is known as the expansion limit of the story.
Hooke's Law:
It states that when the load is loaded within the stretch limit, the pressure is equal to the weight produced by pressure. This means that the rate of pressure of the same type remains constant within the stretch limit.
Stress / strain = constant
This constant is always known as elastic contact
Types of Elastic Constants:
There are three elastic constants;
- Normal stress / normal strain = Young's modulus or Modulus of elasticity (E)
- Shear stress / Shear strain = Shear modulus or Modulus of Rigidity (G)
- Direct stress / Volumetric strain = Bulk modulus (K)
Young's Modulus or Modulus Strength (E):
It is defined as a measure of normal pressure (σ) in longitudinal stiffness (e).
E = (σn) / (e)
Modulus of Rigidity or Shear Modulus (G or C):
It is the ratio between shear pressure (τ) and shear strain (es). Indicated by G or C.
G = τ / es
Bulk Modulus or Volume Modulus for Elasticity (K):
It can be defined as the rate of normal pressure (on each surface of a solid cube) to the type of volume. Described by K. Bulk modulus is a measure of the resistance of an object to change the volume without a change of shape or form.
K = Direct stress / Volumetric strain
= σ / ev
Relationship between E, K and Poisson's Ratio (µ or 1 / m):
Think of a cubic object under volumetric pressure - which works simultaneously next to the alignments x, y and z.
Problems that arise with these three indicators can be worked out by downloading the effect of each stress.
Strain in x-direction,
e x = strain in x-direction due to sigma x - strain in x-direction due to sigma y strain in x-direction due to σ Z
= σ x / E – σ y / m E – σ z / m E ------------------ (1)
But σ X = σ Y = σ Z = σ
So σ X = σ / E - σ / m E - σ / m E
σ X = σ / E (1-2 / m)
Similarly σ Y = σ / E (1-2 / m) and = Z = σ / E (1-2 / m)
Now the Volumetric type
e V = e X + e Y + e Z = 3σ / E (1–2 / m) ---------- (2)
From the modulus plural K = σ / e V
K = σ / {3σ / E (1–2 / m)}
For simplicity E = 3K (1-2 / m) or E = 3K (1-2µ)
Relationship between E, G and Poisson's Ratio (1 / m or µ):
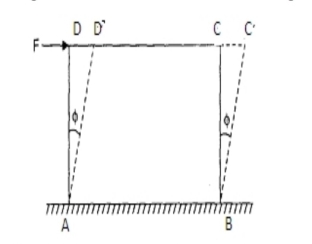
The cubic element ABCD is positioned on the lower surface and is exposed to the cutting force on the upper surface. The block meets the following results due to this shear load:
|
Fig no 3
Block where load apply
1. The shear pressure is caused on the DC and AB surface
2. Reducing shear stress of the same size is set on the faces of AD and BC.
3. The block distorts the new ABC'D 'configuration.
4. Separated AC expands (contrast) and diagonal BD decreases (congestion).
Longitudinal type 'e' in diagonal AC = (AC '- AC) / AC = (AC ’- AE) / AC = EC ’/ AC ----------- (1) When CE is specified from C to AC '. Since CC’s are very small, consider Angle ACB = angle ACB = 450 So EC '= CC'cos450 = CC' / √2 Long-term type ‘e’ = CC ’/ AC√2 = CC ’/ √2.BC.√2 = tan Φ / 2 = Φ / 2 = e S / 2 ------------------ (2) Where, Φ = CC ’/ BC represents the shear type (e S) For shear pressure τ and modulus of rigidity G, shear type (e S) = τ / G ------------ (3) Setting shear type (e S) = 2. Longitudinal type Longitudinal stiffness of diagonal AC = τ / 2 ----------- (4) Strain in a disconnected AC is also provided by = Strain due to the tensile stress in the AC - strain due to the compressive stress in the BD = τ / E - (–τ / m E) = τ / E (1 + 1 / m) ------------- (5) From equals (4) and (5), we obtain τ / 2G = τ / E (1 + 1 / m) or E = 2G (1 + 1 / m) or E = 2G (1 + µ) ------------- (6) Relationships between E, G and K: With reference to the (1) and (6) relationships obtained above, E = 2G (1 + µ) = 3K (1- 2 µ) Subtracting 1 / m from these two E expressions, we have E = 9KG / (G + 3K) Finally; E = 2G (1 + µ) = 3K (1 - 2 µ) or E = 9KG / (G + 3K) |
Key take ways
Normal stress / normal strain = Young's modulus or Modulus of elasticity (E)
Shear stress / Shear strain = Shear modulus or Modulus of Rigidity (G)
Direct stress / Volumetric strain = Bulk modulus (K)
The following factors affect the modulus value of the elasticity:
1. The Power of Concrete:
- It is one of the most important factors affecting the dynamic modulus. Higher power provides a higher value for the durability module.
2. The Moisture Status of Concrete:
- The modulus density of the wet sample modulus is found to be higher from 3 to 4 G Pa (3.2 to 4.3 x 104 kg / cm2) than the dry specimen i.e., the density of the wet concrete modulus is 16.3% up to 7.5 according to its power pressure. A high value of 16.3% is considered for the low power i.e., 21 M Pa and 7.5% increase by 70 MPA strength, While the strength of wet concrete is found under dry concrete. The type of wet concrete is found under dry concrete, which is why the modulus of elasticity is higher in wet concrete than in dry concrete.
3. Aggregate Features:
- The aggregate modulus and its volumetric value affect the concrete solidity modulus as follows:
(a) Lifting the aggregate modulus, raises the concrete reinforcement modulus. The aggregate modulus is higher than the cement attachment modulus.
(b) The larger the volume of the mix, the higher the durability of the concrete. However, the strength of concrete is not significantly affected by these structures.
4. Age Result:
- The concrete strength module increases much faster with age than concrete strength. Thus the relationship between a concrete strength module and its strength depends on age.
5. Assemble the Part:
- It has been observed that rich mixes have higher modes of concrete strength i.e., it raises the amount of cement; the higher the modulus the stronger. The modulus strength of the concrete mixing strength ratio 1: 1.67: 2 is found to be 31.9 G Pa while a mixture of 1: 2.5: 3 is 25 G Pa of the same age as the wet conditions.
- The composite module of composite concrete of light weight usually varies from 40 to 80% of the standard concrete module of the same strength of the same strength actually being the same as cement paste.
6. Stress Status-Curve Curve:
- The shape of the pressure curve affects the fixed static of the concrete strength of the E c, but not the strong Ed modulus which is why the ratio of Ec and Ed can be adjusted. The relationship between the modulus of strength and strength is not significantly affected by temperatures up to 230 ° C as both structures differ in temperature in the same way. Steam cured concrete has a slightly lower modulus than water-treated cement of the same strength.
Key take ways
Factors affecting modulus of elasticity
1. The Power of Concrete:
2. The Moisture Status of Concrete:
3. Aggregate Features:
4. Age Result:
5. Assemble the Part:
6. Stress Status-Curve Curve:
Creep
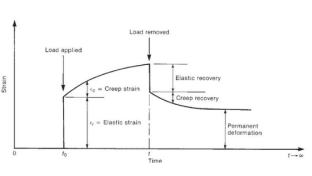
Creep is a gradual increase in the weight of a building member who has been experiencing a load for some time. When the concrete is loaded under pressure, the type of stretching increases. If this load rests on the joint, the type of movement that is made and the time.
|
Fig no 4
Creep Strains due to Loading at time, t0 and unloading at time t
Values from the input type are used in deflection calculations. According to BS8110: Part 2 section 7.3, the concrete type, cc can be predicted from:
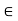 cc=( Stress / Et )×
cc=( Stress / Et )× 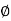
Where:
E t: is a modulus of concrete reinforcement with age loading t
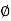 is the creep coefficient that can be taken from Figure 7.1 of BS8110: Part 2
is the creep coefficient that can be taken from Figure 7.1 of BS8110: Part 2
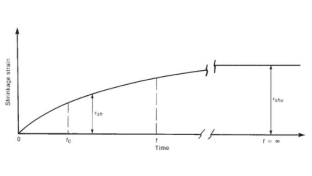
Shrinkage
Shrinkage is a reduction in concrete when drying and hardening due to evaporation of moisture content. The amount of reduction increases over time. The composite content contained in concrete are the most important factors contributing to the reduction. This is because the greater the concentration, the lower the shrinkage and the higher the composite content, the lower the water content of the cement and the performance will be. Decreased humidity also increases the risk of dehydration.
|
Fig no 5
Shrinkage Diagram of an Unloaded Specimen
On the other hand, Shrinkage is discussed in BS8110: Part 2, section 7.4. Values obtained from shrinkage pressure are used in the calculation of deflection. Limitations of the reduction of the reinforced concrete section can be found in:
Є s h/ (1+ K ᵨ)
Where:
- Є s h reduction of clear concrete
- ᵨ is a metal compound related to that of concrete
- K is coefficient, is considered to be 25 for internal exposure and as 15 for external exposure
Factors affecting creep and shrinkage
Factors affecting creep
Creep has been found to be affected by the following:
1. Cement paste
- It should be noted that it is actually a concrete cement that penetrates the bottom. The role of concrete assembly is self-assembly. Normal normal weight measurements are not obliged to enter under the existing pressure of the concrete. Movement is therefore a function of the dynamic content of the cement paste, but the relationship is inconsistent.
2. Aggregate content:
- It can be noted that in most standard mixes the variability of the combined content is small, but with an increase in the volumetric content of the composite from 65% to 75% it can be reduced by 10%. The placement, size and shape of the joint have been shown to affect mobility. It is believed that their greatest influence lies in the combined concrete content provided in all cases.
- In fact, there are certain composite structures that influence the movement of concrete.
They are as follows:
(a) Modulus of Elasticity of Aggregate:
This is a very important factor, influencing the movement of concrete. The higher the modulus elasticity of aggregate, the greater the resistance provided by the aggregate to the strong slope of the cement adhesion i.e. less creep.
(b) Quality of aggregate:
The joints influence the penetration of the concrete with the effect of preventing the size of the stretch. The vibration of the attachment under the load is prevented by non-moving assembly. The durability of the composite, the additional blocking effect that causes the size of the creepy substance. After about 25 years, the sandstone shows very low penetration while the limestone shows very low penetration.
(c) Quantity of integration:
Eagerness was also found to contribute to the emergence of concrete, but it is not an independent factor influencing the movement of concrete. Aggregate porosity plays an important role in the moisture transfer to concrete, which is associated with the movement of concrete, as moisture transfer creates conditions for the development of suspension. Increase the porosity, Reduce the modulus of elasticity, so it is much higher.
3. Effect of mineral composition of aggregate:
- Although it is not possible to make a general statement about the size of concrete made from different types of composites, it has been observed that after 20 years of storage in a 50% moist environment, sand aggregate sandstone has shown to go more than twice as much as made of lemon stone.
- A significant difference between the creeping types of concrete made by different aggregates has been found by RUSCH et al. He noted that after 18 months under load with an average humidity of 65% the maximum rise was five times the lowest rise. Growth collections include basalt, quartz, gravel, marble, granite and sandstone.
- The proportions, textures and overall size of the combination were found to affect mobility. The greater the size of the composite uniform from fine to composite, the less concrete the concrete will be. This is especially true for groundwater / cement mortar concrete.
4. Effect of Combined Weight Light:
- Recent research has shown that the weight of the compound has no effect on creeping things. The high reduction of concrete made with low-weight composites is due to the low-strength module of the combined light intensity.
- As a general rule, it can be said that the increase in the quality of the structure in the ratio of the weight of the concrete is almost the same as that of concrete made of standard composite. The flexible reduction of concrete for small-scale composites is usually greater than for conventional concrete. The rate of skipping to elastic flexibility is therefore small in low weight concrete.
5. Effect of stress:
- In a direct pressure test in concrete a direct correlation of equilibrium between the input and the applied load has been found, but the upper limit is uncertain. In terms of the severity of the pressure, the upper limit is raised between 0.3 to 0.6.
- In the concrete sample pressure test, a small crack occurs between the stress / strength values of 0.4 to 0.6. So when the split ends, the behavior will change. It can therefore be concluded that within the scope of operational pressures, the balance between movement and pressure is positive.
- In addition to the equilibrium limit, the increase increases with increasing stress at an increasing rate and above a certain degree of stress / strength, mobility produces time failure. This stress / strength ratio exists in the region of 0.8 to 0.9 temporal static forces.
6. The Power Effect of Concrete on Creep:
- It has been observed that the strength of concrete plays a major role in the increase in width. Creep was obtained in proportion to the strength of the concrete during the installation of the load.
- Linear activity between movement and stress / energy in a relative humidity
7. Part Mixing Effect:
- In many parts of the same usability, the difference in cement is very small. For example, consider a standard composite concrete with a rating / cement value such as 9, 6 and 4.5 and a w / c corresponding to 0.75, 0.55 and 0.4, by weight the cement paste content can be 24, 27 and 29% respectively. The difference in cement paste is not significant. So the movement of these concerts should also not be too different, but in reality this is not true as the w / c ratio has a significant impact on mobility.
- We know that the w / c ratio is a key factor influencing porosity and strength. So lower the water / cement ratio, and increase the power. With the constant adhesion of cement paste, the decrease in water / cement ratio results in a decrease in the absorption or increase in the water / cement level, an increase in penetration. So with a wide range of mixtures, the mobility is in proportion to the strength of the concrete in the load-bearing years.
Effect of age at the time of loading:
- It has been observed that with some types of concrete, the movement decreases as the age at the time of installation increases as the strength increases with age
Cement Type Effect:
- The effect of the type of cement on the creep is not straightforward, but the type of cement affects the strength of the concrete, which is why the texture is affected. On the basis of the equilibrium of the stress / energy ratio many chemicals in Portland have logically led to similar outbreaks.
Effect of fineness of cement:
- The end of the cement affects the growth of energy at a young age and therefore affects mobility. It was noted that cement in a good nest was great at first, but after 1000 days it became smaller due to gaining greater strength.
Effect of relative humidity of ambient air
- Considered that in a given concrete, it reduces the humidity associated with the surrounding air, increasing movement. The relative humidity effect of 10,070 and 50% humidity in deformation
Effect of size of Specimen
- Creep has been found to decrease with the size of the template. The size effect is expressed in terms of the volume / face measurement of the concrete member
Effect of temperature of concrete:
- In the past the importance of the thermal impact on the rise has taken on greater importance due to the use of concrete in nuclear pressure vessels and in other structures such as bridges, multi-line buildings etc. The time at which the temperature of the concrete rises compared to the time of installation of the load, affects the thermal conductivity. If the full concrete has been burned and loaded at the same time, the infiltration is found to be greater than when the concrete was burned during the curing process.
- The flow of cured cement to high temperatures is low because the strength of concrete is higher when treated at higher temperatures than when treated at normal temperatures before heating and loading.
- It is detected if closed concrete is blocked by high temperatures at the same time or just before installation, a rapid increase in movement occurs as the temperature rises to about 50 ° C, then a decrease occurs in creep at a temperature of about 120 ° C and then rises again to at least 400 ° C. The initial increase in penetration is due to the rapid expulsion of easily drained water. When all of that water has been removed, the movement is greatly reduced and is equal to the previous dry concrete. entering the temperature range is seen as part of the jump to 20 ° C. At temperatures below 20 ° C (68 ° F) the rise decreases until the formation of ice causes an increase in temperature, but below freezing it also decreases.
Effect of Admixtures and Plasticizers:
- Admixtures and plasticizers found increase concrete, but not in all cases, so before using their effect should be tested.
Factors affecting shrinkage
Factors Affecting Decrease in Concrete:
The degree of initial reduction of concrete and cement depends on a number of factors namely:
01. Cement Content:
As a general rule, an increase in the richness of the concrete mix leads to a decrease in dryness.
02. Water Content:
In short, it can be said that the more water used in that concrete mix, the greater the reduction. So wet mixing has a lot less reduction than dry mixing like any other.
03. Integration:
By using the maximum possible size of the concrete collection and ensuring good installation, the water demand for the required performance is reduced and the concrete obtained thus has a small decrease due to the reduction of hard concrete.
04. Healing:
Treatment also plays an important role in reducing weight loss. If treatment is to be started as soon as the first set occurs and is continued for at least 7-10 days the decrease is relatively small.
05. Excess Payment of Aggregates:
The presence of excess fines such as silk, clay and dust in joints has a significant impact on the level of concrete decay. The presence of fines increases a certain area of scale and consequently the need for water.
06. Chemical Composition:
The chemical composition of cement and cement also contributes to the reduction. Fast hard cement has a much lower cost than Ordinary Portland Cement.
07. Heat:
An important factor influencing the water demand for concrete is therefore its reduction in the temperature of the new concrete. Barks made in mild winters have a lower tendency to crack than shows in hot summer months.
08. Humidity:
The size of the shrinkage also depends on the relative humidity of the dry air. Therefore, the decline is very small in coastal areas where the relative humidity remains high throughout the year. Low moisture content can also cause plastic degradation in concrete.
In the RCC, 1/3 (33%) of concrete decomposition occurs within the first 10 days, ½ (50%) within one month and ½ (50%) within one year. Therefore, shrinkage cracking in concrete continues to occur and expands up to a year.
Key take ways
Creep is a gradual increase in the weight of a building member who has been experiencing a load for some time. When the concrete is loaded under pressure, the type of stretching increases. If this load rests on the joint, the type of movement that is made and the time.
Shrinkage is a reduction in concrete when drying and hardening due to evaporation of moisture content. The amount of reduction increases over time. The composite content contained in concrete are the most important factors contributing to the reduction.
- Non Destructive trying out is a trying out and evaluation method utilized by enterprise to assess the homes of a cloth, component, shape or gadget for feature variations or welding defects and discontinuities without inflicting harm to the authentic part.
- NDT additionally referred to as non-negative examination (NDE), non-negative inspection (NDI) and non-negative evaluation (NDE).
- There are some of awesome advantages, the maximum apparent of that's that the portions being examined are left undamaged via way of means of the manner, making an allowance for an object to be repaired instead of changed have to any troubles be found.
- It is likewise a completely secure trying out technique for operators, with maximum strategies being innocent to humans, despite the fact that a few forms of check - which include radiographic trying out - nevertheless want to be performed below strict situations.
- This trying out method also can assist save you damage or fatalities via way of means of making sure structures, additives and equipment is secure.
- Non-negative trying out is likewise a completely correct manner of inspection because the exams are repeatable and some of exams may be used collectively to correlate outcomes.
- These trying out techniques also are economical. Unlike negative trying out, NDT is price powerful as it may save you the want to update an object earlier than malfunction happens without destroying the piece itself.
- This trying out method additionally gives operators peace of mind, understanding that system is functioning because it have to, stopping destiny injuries and figuring out any measures that may be taken for lifestyles extension.
- It is likewise beneficial for trying out of welds and verification of welding approaches to make sure that a welding manner has been finished to the best specification with inside the bounds of excellent manipulate, as an example to make certain that the bottom metallic has reached the best temperature, cooled on the particular price and that well matched substances had been used to save you welding defects.
Key take ways
There are some of awesome advantages, the maximum apparent of that's that the portions being examined are left undamaged via way of means of the manner, making an allowance for an object to be repaired instead of changed have to any troubles be found.
Objective:
- The rebound hammer technique might be used for:
- assessing the possibly compressive electricity of concrete with the assist of appropriate correlations among rebound index and compressive electricity,
- assessing the uniformity of concrete,
- assessing the excellent of the concrete in relation to traditional requirements, and
- Assessing the excellent of 1 detail of concrete when it comes to another.
Principle:
- When the plunger of rebound hammer is pressed in opposition to the floor of the concrete, the spring controlled mass rebounds and the volume of such rebound relies upon up on the floor hardness of concrete.
- The floor hardness and consequently the rebound is taken to be associated with the compressive strength of the concrete.
- The rebound is examining off alongside a graduated scale and is unique as their sure variety or rebound index.
Procedure:
- For trying out, smooth, easy and dry floor is to be selected. If loosely adhering scale is present, this have to be rubbed of with a grinding wheel or stone. Rough surfaces due to incomplete compaction, lack of grout, spalled or tooled surfaces do now no longer deliver dependable outcomes and have to be avoided.
- The factor of effect is to be at the least 20 mm far from any facet or form discontinuity.
- For taking a measurement, the rebound hammer is to be held at proper angles to the floor of the concrete member. The check can as a result be performed horizontally on vertical surfaces or vertically upwards or downwards on horizontal surfaces. If the state of affairs demands, the rebound hammer may be held at intermediate angles additionally, however in every case, the rebound variety may be unique for the equal concrete.
- Rebound hammer check is performed round all of the factors of remark on all on hand faces of the structural detail. Concrete surfaces are very well wiped clean earlier than taking any measurement.
- Around every factor of remark, six readings of rebound indices are taken and common of those readings after deleting outliers as consistent with IS: 8900-1978 turns into the rebound index for the factor of remark.
|
Fig no 6
Showing Rebound Hammer
Interpretation of Result:
- The rebound hammer technique offers a handy and speedy indication of the compressive energy of concrete via organism appropriate correlation among the rebound index and the compressive energy of concrete. The process of acquiring such correlation is given in 4.2.
- It is likewise mentioned that rebound indices are indicative of compressive energy of concrete to a constrained intensity from the floor. If the concrete in a selected member has inner micro cracking, flaws or heterogeneity throughout the cross-section, rebound hammer indices will now no longer imply the equal.
- As such, the estimation of energy of concrete with the aid of using rebound hammer technique can't be held to be very correct and in all likelihood accuracy of prediction of concrete energy in a shape is ±25 percent.
- If the connection among rebound index and compressive energy may be checked with the aid of using assessments on center samples acquired from the shape or well-known specimens made with the equal concrete substances and blend proportion, then the accuracy of consequences and self-belief thereon are substantially increased.
Key take ways
The rebound is examining off alongside a graduated scale and is unique as there sure variety or rebound index.
- This take a look at is accomplished to evaluate the nice of concrete with the aid of using ultrasonic pulse pace technique as according to IS: 13311 (Part 1) – 1992. The underlying precept of this take a look at is –
- The technique includes measuring the time of journey of an ultrasonic pulse passing via the concrete being tested. Comparatively better pace is acquired whilst concrete nice is ideal in phrases of density, uniformity, homogeneity etc.
- Procedure to decide energy of hardened concrete with the aid of using Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity:
- Preparing for use: Before switching at the ‘V’ meter, the transducers ought to be linked to the sockets marked “TRAN” And” REC”.
- The ‘V’ meter can be operated with either:
a) The inner battery,
b) An outside battery or
c) The A.C line.
- Set reference: A reference bar is supplied to test the tool zero. The pulse time for the bar is engraved on it. Apply a smear of grease to the transducer faces earlier than putting it on the other ends of the bar. Adjust the ‘SET REF’ manage till the reference bar transit time is acquired at the tool read-out.
- Range selection: For most accuracy, it's miles endorsed that the 0.1 microsecond variety be decided on for route duration up to 400mm.
- Pulse pace: Having decided the maximum appropriate take a look at factors at the fabric to be tested, make cautious dimension of the route duration ‘L’. Apply couplant to the surfaces of the transducers and press it tough onto the floor of the fabric. Do now no longer flow the transducers whilst a analyzing is being taken, as this could generate noise indicators and mistakes in measurements. Continue keeping the transducers onto the floor of the fabric till a steady analyzing seems at the show, that's the time in microsecond for the ultrasonic pulse to journey the distance ‘L’. The imply price of the show readings ought to be taken whilst the gadgets digit hunts among values.
Pulse pace=(Path duration/Travel time)
- Separation of transducer leads: It is really helpful to save you the 2 transducer leads from getting into near touch with every different whilst the transit time measurements are being taken. If this isn't always accomplished, the receiver lead would possibly pick-up undesirable indicators from the transmitter lead and this will bring about a wrong show of the transit time.
Interpretation of Results:
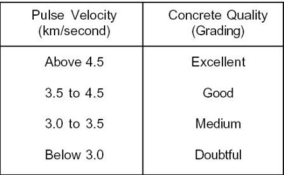
- The nice of concrete in phrases of uniformity, occurrence or absence of inner flaws, cracks and segregation, etc., Indicative of the extent of expertise employed, can as a consequence be assessed the use of the recommendations given below, that have been advanced for characterizing the nice of concrete in systems in phrases of the ultrasonic pulse pace.
|
Fig no 7
Table of pulse velocity
Key take ways
Set reference: A reference bar is supplied to test the tool zero. The pulse time for the bar is engraved on it. Apply a smear of grease to the transducer faces earlier than putting it on the other ends of the bar. Adjust the ‘SET REF’ manage till the reference bar transit time is acquired at the tool read-out.
References
- A.M Neville J.J.Brooks Concrete technology
- A.M Neville Concrete technology
- IS 10262 - 2009, Recommend guidelines for Concrete
- IS 456 - 2000, Indian Standard plain and reinforcement Concrete.