Loosely Coupled Multiprocessor System:
It is a type of multiprocessing system in which, There is distributed memory instead of shared memory. In loosely coupled multiprocessor system, data rate is low rather than tightly coupled multiprocessor system. In loosely coupled multiprocessor system, modules are connected through MTS (Message transfer system) network.
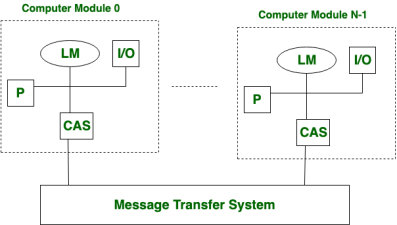
Fig 1- message transfer system
Tightly Coupled Multiprocessor System:
It is a type of multiprocessing system in which, There is shared memory. In tightly coupled multiprocessor system, data rate is high rather than loosely coupled multiprocessor system. In tightly coupled multiprocessor system, modules are connected through PMIN, IOPIN and ISIN networks.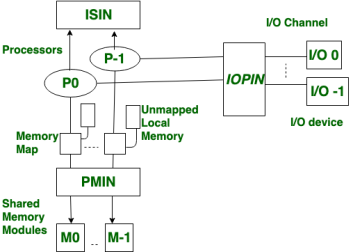
Fig 2 - modules are connected through PMIN, IOPIN and ISIN networks
Let’s study the difference between loosely coupled and tightly coupled multiprocessor system:
S.NO | Loosely Coupled | Tightly Coupled |
1. | There is distributed memory in loosely coupled multiprocessor system. | There is shared memory, in tightly coupled multiprocessor system. |
2. | Loosely Coupled Multiprocessor System has low data rate. | Tightly coupled multiprocessor system has high data rate. |
3. | The cost of loosely coupled multiprocessor system is less. | Tightly coupled multiprocessor system is more costly. |
4. | In loosely coupled multiprocessor system, modules are connected through Message transfer system network. | While there is PMIN, IOPIN and ISIN networks. |
5. | In loosely coupled multiprocessor, Memory conflicts don’t take place. | While tightly coupled multiprocessor system have memory conflicts. |
6. | Loosely Coupled Multiprocessor system has low degree of interaction between tasks. | Tightly Coupled multiprocessor system has high degree of interaction between tasks. |
7. | In loosely coupled multiprocessor, there is direct connection between processor and I/O devices. | While in tightly coupled multiprocessor, IOPIN helps connection between processor and I/O devices. |
8. | Applications of loosely coupled multiprocessor are in distributed computing systems. | Applications of tightly coupled multiprocessor are in parallel processing systems. |
Key Takeaway
Loosely Coupled Multiprocessor System:
It is a type of multiprocessing system in which, There is distributed memory instead of shared memory. In loosely coupled multiprocessor system, data rate is low rather than tightly coupled multiprocessor system. In loosely coupled multiprocessor system, modules are connected through MTS (Message transfer system) network.
Tightly Coupled Multiprocessor System:
It is a type of multiprocessing system in which, There is shared memory. In tightly coupled multiprocessor system, data rate is high rather than loosely coupled multiprocessor system. In tightly coupled multiprocessor system, modules are connected through PMIN, IOPIN and ISIN networks.
Clustered storage can overcome several key obstacles that storage professionals face today; capacity, storage I/O and expandability. There are two classifications of storage clusters, loosely coupled and tightly coupled and each have their place in the environment.Tightly coupled clusters tend to be focused on primary storage, although it is available in archive and it is even used in disk to ...
Clustered storage can overcome several key obstacles that storage professionals face today; capacity, storage I/O and expandability. There are two classifications of storage clusters, loosely coupled and tightly coupled and each have their place in the environment.
Tightly coupled clusters tend to be focused on primary storage, although it is available in archive and it is even used in disk to disk backup systems. In a tightly coupled cluster the data is divided up between nodes in the cluster at some level of granularity smaller than a file, typically a block or sub block level. Unlike a typical dual controller architecture where performance peaks at about half of drive capacity and then declines, a tightly coupled cluster should see improved performance as more drives and nodes are added to the environment.
The downside is that the components of the cluster are more strict, most always come from the supplier, don't allow for flexibility of mixing manufacturers or even tiers of systems from the supplier. While some will use proprietary components with special capabilities, many will use off the shelf Intel or Xyratex storage servers and then add their software plus some sort of interconnect, typically ethernet, but some will use advanced interconnects like Infiniband.
Loosely coupled clusters are essentially stand alone dual controller systems with a global name space that reduces the management of the environment. This has the advantage of greater flexibility in the members of the cluster and that the cluster can start with just one member. Unlike a tightly coupled cluster the data is not stored across nodes in the cluster, the entirety of the file must be on a single node. It can however be mirrored to other nodes for redundancy and some storage software will know to use the secondary copy as a backup automatically.
Loosely coupled clusters have the downside that maximum performance and capacity is limited to the performance of the node that houses the data. The performance does not scale up as nodes are added like a tightly coupled cluster does. As a result loosely coupled clusters tend to be applied where performance is important but inexpensive capacity is more important. Cloud storage being one of the more ideal candidates.
Both styles of clustered storage can address the problems of scale, I/O and expandability and many suppliers may be able to blur the differences between the two by either driving up dual controller performance or driving down storage costs. Review both technologies and understand which one makes the most sense for what your storage demands are.
Key Takeaway
Clustered storage can overcome several key obstacles that storage professionals face today; capacity, storage I/O and expandability. There are two classifications of storage clusters, loosely coupled and tightly coupled and each have their place in the environment. Tightly coupled clusters tend to be focused on primary storage, although it is available in archive and it is even used in disk to ...
Clustered storage can overcome several key obstacles that storage professionals face today; capacity, storage I/O and expandability. There are two classifications of storage clusters, loosely coupled and tightly coupled and each have their place in the environment.
Earlier computing features were good to solve simple problems, but they have no ability to sync up the current day technologies and advancements. Pricing scenarios, low performance, reliability and some of the other reasons couldn’t gain access to manage huge data and previous computing systems can’t clear today’s IT problems. In the scope of this, IT departments introduced an innovative approach in solving the limitations of a single system and that was “Cluster Computing”. The advantages of this technology allowed many organizations to implement this technology in their activities. And today the prominence of this made us discuss these concepts.
What is Cluster Computing?
Cluster computing refers that many of the computers connected on a network and they perform like a single entity. Each computer that is connected to the network is called a node. Cluster computing offers solutions to solve complicated problems by providing faster computational speed, and enhanced data integrity. The connected computers execute operations all together thus creating the impression like a single system (virtual machine). This process is termed as transparency of the system. Based on the principle of distributed systems, this networking technology performs its operations. And here, LAN is the connection unit. This process is defined as the transparency of the system. Cluster computing goes with the features of:
Clusters’ hardware configuration differs based on the selected networking technologies. Cluster is categorized as Open and Close clusters wherein Open Clusters all the nodes need IP’s and those are accessed only through the internet or web. This type of clustering causes enhanced security concerns. And in Closed Clustering, the nodes are concealed behind the gateway node and they offer increased protection.
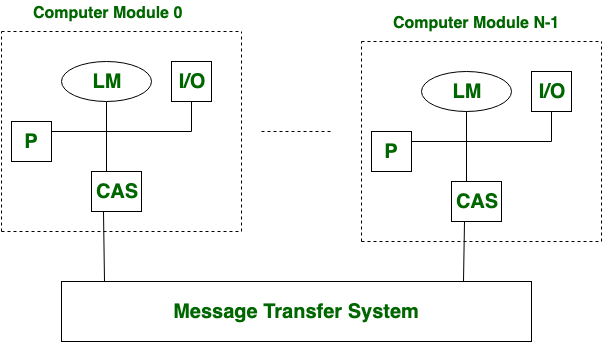
Fig 3 - Cluster computing operation
Types of Cluster Computing
As clusters are extensively utilized in correspondence to the complexity of the information, to manage content and the anticipated operating speed. Many of the applications that anticipate high availability without a reduction in downtime employ the scenarios of cluster computing. The types of cluster computing are:
Cluster Load Balancing
Load balancing clusters are employed in the situations of augmented network and internet utilization and these clusters perform as the fundamental factor. This type of clustering technique offers the benefits of increased network capacity and enhanced performance. Here the entire nodes stay as cohesive with all the instance where the entire node objects are completely attentive of the requests those are present in the network. All the nodes will not operate in a single process whereas they readdress the requests individually as they arrive depending on the scheduler algorithm. The other crucial element on the load balancing technique is scalability where this feature is accomplished when every server is totally employed.
Along with the servers in load balancing which have a similar capacity in client reaction, many of the concerns are created as many of the requests might be addressed by these servers those might be in confusion. So, load balancing creates balance for the users and servers. Even load balancing allocates incoming requests or traffic for its resources from the connected computers which operate similar programs and those develop as a cluster. When a node failure occurs, then the requests are again allocated across the available nodes. This approach is implemented in Linux web servers.
High Availability Clusters
These are also termed as failover clusters. Computers so often faces failure issues. So, High Availability comes in line with the augmenting dependency of computers as computers hold crucial responsibility in many of the organizations and applications. In this approach, redundant computer systems are utilized in the situation of any component malfunction. So, when there is a single point malfunction, the system seems to be completely reliable as the network has redundant cluster elements. Through the implementation of high availability clusters, systems can go with extended functionality and provides consistent computing services like complicated databases, business activities, customer services like e-websites and network file distribution.
High-Performance Clusters
This networking approach utilizes supercomputers to resolve complex computational problems. Along with the management of IO-dependent applications like web services, high-performance clusters are employed in computational models of climate and in-vehicle breakdowns. More tightly connected computer clusters are developed for work that might consider “supercomputing”.
High Availability + Load Balancing
This integrated solution provides extended performance showing no complicated breakdowns. The combined performance of two clustering techniques provides an ideal solution for the network applications and for ISPs too. Few of the features of this integrated technique are as follows:
• Enhanced levels of service quality for conventional network activities
• Offer an extensively scalable architecture context
• Transparent assimilation for stand-alone functionalities and non-clustered collectively in a single virtual system
Cluster Computing Architecture
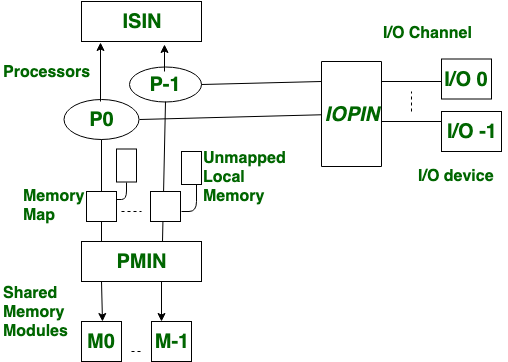
Fig 4 - Cluster computing architecture
Advantages of Cluster Computing
There are numerous advantages of implementing cluster computing in the applications. Few of them to be discussed are as follows:
Cost efficacy – Even mainframe computers seems to be extremely stable, cluster computing is more in implementation because of their cost-effectiveness and economical. Also, these systems provide enhanced performance than that of mainframe computer networks.
Processing speed – The cluster computing systems offer the same processing speed as that of mainframe computers and the speed is also equal to supercomputers.
Extended resource availability – Computers come across frequent breakdowns, so to eliminate this failure, cluster computers are available with high availability. So, when one node gets failed, the other nodes will be active and will function as a proxy for the failed node. This makes sure for enhanced availability.
Expandability – The next crucial advantage of this cluster computing is its enhanced scalability and expandability. As they instantiate the prospect to combine multiple additional resources or the networks to the prevailing computer system.
Flexibility – Cluster computing can be upgraded to the superior specification or extended through the addition of additional nodes (computer systems).
Applications
There exist numerous applications of cluster computing, Few of those are:
Differences between Cluster and Grid Computing
As we have already discussed the concepts of cluster computing, now we shall have a glimpse of what grid computing is?
Grid computing can be stated as the network of either heterogeneous or homogeneous computer systems all functioning together over far distances to achieve a task that would rather be complicated for a single computer to achieve.
Even cluster and grid computing seem to be almost similar, there exists a lot of differences between two either in the performance, operation, and construction. Let’s be clear on the differences between these computing technologies.
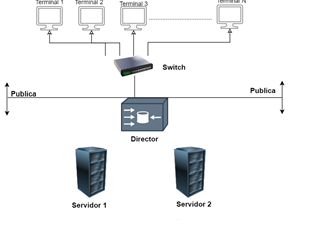
Fig 5 - Grid computing architecture
The differences between cluster computing & grid computing include the following.
Cluster Computing | Grid Computing |
Connected computers have to be heterogeneous which means that they should have a similar kind of OS and hardware. | Connected computers can have dissimilar OS and hardware. They can be either heterogeneous or homogeneous. |
All the nodes in this are committed to performing a similar operation and no other operation is allowed to be done | The nodes here allot their unused processing resources for the grid computing network. |
Every node is so close to the next one | The nodes can be placed at a far distance from each other |
All the nodes in the network are connected through the high-speed LAN connection. | All the nodes in the network are connected either through low-speed buses or via the internet. |
They are connected in the format of centralized network topology | The nodes are connected in the format of either distributed or de-centralized network topology |
Here, scheduling is managed by the central server | It can also have a server, but each computer performs in its own method |
The entire system is with a centralized resource administrator | Each of the computers handles its resources in an independent way |
The entire system works as one | Each computer is autonomous, and anyone can choose for this at anytime |
These are tightly connected systems | These are loosely connected systems |
It follows single system functionality | It follows diversity and dynamism |
The Need for Cluster Computing
Everyone might have faced the situation of low-speed services and content criticality. Cluster computing resolves the need for content criticality and process services in a quicker approach. As Internet Service Providers look for enhanced availability in a scalable approach, cluster computing will provide this. And even, this technology is the heavy need for the film industry as they require this for rendering extended quality of graphics and cartoons. Implementation of the cluster through the Beowulf method also resolves the requirement of statistics, fluid dynamics, genetic analysis, astrophysics, economics, neural networks, engineering, and finance. Many of the organizations and IT giants are implementing this technology to augment their scalability, processing speed, availability and resource management at the economic prices.
Key Takeaway:
Earlier computing features were good to solve simple problems, but they have no ability to sync up the current day technologies and advancements. Pricing scenarios, low performance, reliability and some of the other reasons couldn’t gain access to manage huge data and previous computing systems can’t clear today’s IT problems. In the scope of this, IT departments introduced an innovative approach in solving the limitations of a single system and that was “Cluster Computing”. The advantages of this technology allowed many organizations to implement this technology in their activities. And today the prominence of this made us discuss these concepts.
Text Books:
Reference Books: