UNIT 3
Project Scope, Time and Cost management
Requirements can be categorized into different types, such as business requirements, solution requirements, stakeholder requirements, migration requirements, and quality requirements. Requirements are considered the basis of a WBS (Work Breakdown), and project managers working on a particular project have nothing to do, which makes it difficult without requirements documentation.
Requirement collection: Definition
Compile requirements are the process of deciding to meet the objectives of a project management task, in addition to documenting and managing the needs and requirements of stakeholders.
The requirements collection document contains details of the objectives needed to meet stakeholder requirements and ensure project satisfaction. Collection requirements act as a framework that provides a baseline for project budgets, schedules, quality specifications, risks, and resource planning.
Project Management-Requirement Collection Process
The requirements collection process, which is an important aspect of a project, helps define project scope during scope management. It is the project manager's responsibility to ensure that all requirements are obtained using a set of tools and techniques for collecting requirements from the project. It is imperative that project managers be very agile in collecting requirements and also need to use appropriate requirements collection tools throughout the project life cycle. The project manager is responsible for the success of the project so as not to overlook the requirements of the project results.
This article also details requirements collection techniques.
Project Requirements: Project requirements are the expectations of project stakeholders regarding the outcome.
Gathering requirements processes-the basis of project scope
Step 1: Identify the needs of "stakeholders".
Step 2: Document your needs and requirements.
Step 3: Address them throughout the project to achieve the project objectives. ""
Most of these projects met schedule and budget standards, but did not meet stakeholder requirements. Competition for this product was observed at the final delivery of the project or at the end of the project. This process negatively impacts the success of the project.
Gather requirements: tools and techniques
Expert judgment
The following are topics that individuals or groups should have specialized knowledge and experience.
Data collection
The following data collection techniques can be used in the requirements collection process:
Brainstorming
A group thinking activity where several people from different teams get together to list the requirements of the project. Also, during a brainstorming session, new ideas are generated from existing plans to help identify new requirements.
Interview
Interviews are the first requirement collection method. It can be done officially or informally. A key feature of this process is the area of expertise that helps project managers identify and define the characteristics and capabilities of participants, sponsors, stakeholders, other experienced project executives, and project deliverables. It is useful for interviewing. The desired product.
Focus group
Focus groups are techniques used to elicit the requirements of a particular stakeholder. For example, a project manager can first arrange a meeting with the company's CEO to learn about the requirements, and then arrange another meeting with the functional manager to understand the requirements.
Questionnaires and surveys
This technique is best if you have a large number of stakeholders involved in your project. For example, if your project has 200 stakeholders associated with it, it can take a lot of time to gather information from each individual and evaluate your requirements. As a result, project managers are required to create a survey, conduct a survey, and collect a requirements list.
Benchmark
Benchmarks compare real or planned practices (procedures and operations) with those of comparable organizations (internal or external) to identify best practices, generate ideas for improving scope, and in fact. A process used to provide a framework for measuring the performance of.
Data analysis
Data analysis deals primarily with processes related to document analysis. The main purpose of document analysis is to review and evaluate all relevant document information. This process is used to retrieve requirements by carefully analysing existing documents and identifying details related to the requirements.
Various documents are analysed to get the information needed for the requirements process. They are:
Decision making
|
Figure 1
The decision-making techniques that can assist in the requirements collection process are:
Voting
Voting is a collective decision-making method, an evaluation process with a variety of options with defined results. The following is an example of a voting method.
Unanimity: Unanimity is a decision achieved when everyone agrees on a single course of action. One of the effective ways to reach an agreement is the Delphi method. In this approach, a group of selected experts and stakeholders answer the questionnaire and provide feedback on questions that cover all areas of the project. These responses resent decision makers until consensus is reached among stakeholders.
Majority: Suggestions and ideas gathered from experts are selected based on the majority of people who support the process. This allows project managers to select and implement the best ideas to meet their requirements.
Plural: Even if there is no room for a majority-based decision, the decision is finalized based on the opinions of the most important groups within the organization.
Autonomous decision making
As the title suggests, decisions are made by a single individual with the ultimate authority of the organization.
Multiple-criteria decision analysis
A technique that uses a decision matrix to provide a systematic and analytical approach for determining criteria such as risk level, uncertainty, and assessment, and to evaluate and rank many ideas.
Data representation
The following data representation techniques can be used in the process of collecting requirements:
Affinity diagram
A method in which all collected or collected ideas are separated accordingly based on their similarities.
Idea / Mind Mapping
Ideas generated through brainstorming sessions are integrated into a single map to eliminate traditional concepts and understand disagreements that help create new plans.
Interpersonal skills and team skills
The interpersonal and team skill techniques you can use in the process of collecting requirements are:
Nominal group technique
A technique that uses skills to prioritize existing ideas rather than developing new ones. In this process, plans are ranked based on their value. This allows the team to focus on key concepts for generating project requirements.
Observation
Observations, also known as "job shadowing," are the process by which an observer sees a business expert performing his or her job. The main process is to closely observe the activities taking place in different areas to identify the actual requirements of consumers, stakeholders, sponsors, etc.
Facilitation
Facilitation is a session-focused approach that brings together key stakeholders to define product requirements. In general, each group of project stakeholders looks at the project from a unique perspective and states its requirements. Workshops are seen as the primary method for quickly defining requirements between features and adjusting for stakeholder differences.
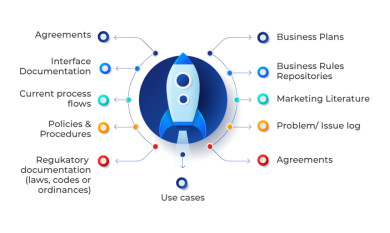
Context diagram
To get the actual knowledge to understand the scope, the context diagram provides an example of the scope model. This allows project managers to visualize how business systems (processes, equipment, and computer systems) work. This process is used to find out how the business system interacts with other users.
|
Figure 2
Prototype
A technique that involves the process of creating a model of the actual product to be realized. The team builds this model of the product and passes it on to stakeholders to collect feedback. Because the model is a concrete product, stakeholders should thoroughly check the model and change if any changes are found, rather than just sharing and discussing abstract expressions and ideas. Can be requested.
Collection of requirements process inputs
Project plan
To create the detailed requirements of the project, the project manager uses high-level descriptions derived from the project charter to determine the scope of the product.
Project management plan
The project management plan contains the following components:
Scope management plan
As the scope management plan determines the essential and valuable aspects of the project, it provides clarity for the project team to determine the types of requirements it collects for the project.
Requirements management plan
The project manager's primary priority is to define and document the needs of stakeholders. Requirements management plans play an important role in providing methods / processes that can be used throughout the requirements collection process to help project managers achieve these needs.
Stakeholder management plan
Stakeholders are understood to be an integral part of the project. Stakeholder management plans are used by project managers to understand the communication requirements of stakeholders and the level of involvement to evaluate and adapt to meet their level of participation in achieving requirement activities.
Project document
The inputs you can consider in the project document are:
Assumption log
The Assumption Log process identifies assumptions about products, projects, stakeholders, the environment, and other important factors that can affect the outcome of a particular project.
Lessons learned registration
The lessons learned process is used to provide information on effective requirements-gathering techniques, especially using adaptive and iterative product development methodologies.
Stakeholder registration
Identifying the key stakeholders of a project is an important task because it provides information about the requirements of the project. This identification process is simplified by using stakeholder registration. Registers help you understand the key needs and key expectations of stakeholders associated with your project.
Business documents
Business cases influence the way business documents work under the requirements collection process. You can use this particular technique to describe the necessary, desirable, and optional criteria needed to meet your business needs.
Agreement
Contracting techniques are used to collect information about a project and the product requirements needed to complete a particular project.
Corporate environmental factors
The corporate environmental factors that can affect the collection requirements process are: – Organizational culture, infrastructure, HR management, and marketplace status.
Organizational process assets
A repository of lessons, including project policies, procedures, historical information, and information from previous project successes, is an organizational process asset that influences the collection requirements process.
- Requirement collection-output
- Requirements documentation
A method of explaining how individual requirements meet the business needs of a project. Requirements start at a high level and can gradually become more detailed as more information about the requirements becomes available.
The requirements need to be clear, traceable, complete, consistent, and accepted by key stakeholders, even before they are listed in the project plan. Requirements documents can take many forms.
This can be a simple document listing all the requirements categorized by stakeholders and priorities, to a more complex form with detailed summaries, descriptions, and attachments.
The requirements document components include:
- Business requirements
- Business and project objectives for traceability
- Business rules of the executing organization
- Guidance on organizational principles.
- Stakeholder requirements
- Make a note of the potential impact of stakeholder requirements on other organizational areas
- Be aware of how stakeholder requirements can affect entities inside and outside the executing organization
- Stakeholder communication and reporting requirements.
- Solution requirements
- Providing solutions for functional and non-functional requirements
- Providing solutions that meet technical and standard compliance requirements
- A solution that provides support and training requirements
Project requirements
- Requirements based on levels of service, performance, safety, compliance, etc.
- Requirements that are approved and meet acceptance criteria.
- Migration requirements
- Requirements prerequisites, dependencies, and constraints
- Requirements Traceability Matrix
The Requirements Traceability Matrix is a document that links requirements throughout the validation process. The purpose of the Requirements Traceability Matrix is to ensure that all the requirements defined for a system add business value by linking the system to business and project objectives.
This is a process that provides a way to track requirements throughout the project life cycle, ensuring that requirements approved in the requirements document are delivered at the end of the project. Finally, it provides a structure for managing changes to the product scope.
Different types of tracing processes performed at the requirements traceability matrix stage:
Business needs
Project managers need to track all the business needs they need to achieve.
Purpose of the project
It is imperative that project managers track project objectives to ensure that they are achieved in a timely manner.
Project scope / WBS deliverables
The project manager should always keep track of the project scope. Deliverables may not be achieved if the scope of the project deviates.
Product design
To achieve project implementation efficiently, project managers need to track product design paths that have been completed and approved by all key stakeholders involved in the project.
Product development
At every stage of the project life cycle, track development to ensure that the project achieves its intended scope.
Test strategy and test scenario
You need to develop appropriate steps to test your product after it has been run. The project manager also needs to run test scenarios that require the product to be tested correctly in order to create the required artifacts.
High level requirements for more detailed requirements
The project manager cannot consider all requirements to have the same scope. There will be a high level of requirement to gain more scope. Therefore, to meet these requirements, project managers need to assign more requirements to such components.
The role of the project manager in collecting requirements
As a project manager, make sure you are familiar with the following requirements management process:
The plan describes how each phase of the requirements collection process takes place. The best recommendation for project managers is to create and share a planning document to minimize confusion and ensure that all stakeholders are on the same page.
Identification in this process begins with identifying all stakeholders and understanding the needs of the organization. Project managers need to leverage their skills and decisions to determine the most appropriate way to obtain this information, such as one-on-one interviews, focus groups, surveys, and “use cases”.
Documenting – If business requirements and their approvals are not documented in sufficient detail, project managers should rely on recollections and project insights. This can be dangerous. It is imperative to document all requirements and apply a unique ID number to each requirement for easy reference and tracking throughout the process. Demonstrating different "use cases" using process flowcharts or diagrams can be very helpful in reviewing a process and planning how users will interact with the new process. It also helps to show the "advantages" of the new process / system.
Analysis – Stakeholders may have unrealistic expectations for the new system. Due to budget and other constraints on every project, careful analysis should be performed to determine the costs, relevance, dependencies, and resources required to achieve each requirement.
Prioritization – The data generated from the analysis phase helps you prioritize your requirements. Project managers should always ensure that requirement prioritization and linked approvals are documented. One step that is often overlooked during this phase is communicating with stakeholders and setting expectations. Therefore, prioritize the requirements that need to be implemented in your project.
Management – Some requirements may need to be modified if the requirements have been identified and appear to have been approved. How does the project manager handle or control change requirements when there are budget or time constraints?
Approval – The role of the project manager is to know who has the final say on all project requirements and to document all approvals in writing. Experienced project managers can overcome the obstacles associated with requirements collection and act as a link between end users and teams developing new systems, products, or databases.
What is involved in collecting project requirements?
Gathering requirements involves defining and documenting product features that are initiated and delivered during the project process used to create the product. The project team also produces a requirements document and a requirements traceability matrix as output for the requirements collection process. Gathering project requirements also includes stakeholder interviews, surveys, and surveys.
For IT-related projects, it's useful to divide requirements development into categories called draws, analytics, specifications, and validation. Requirements are often unclear early in the project, so it is essential to use an iterative approach to define requirements.
Why is it often difficult to collect requirements?
Gathering requirements is easier than it looks. However, most project failures can be traced back to defective requirements. The project involves collecting requirements, but there are several reasons why collecting requirements is difficult.
- Underestimation of work
- Unknown requirement
- Depends on the user
- Analytical paralysis
- Inadequate requirements
Summary
Gathering requirements is an essential process because if requirements from stakeholders are not properly collected, the scope of the project may be incorrect. For successful scope management, the project manager must select and implement the appropriate method for collecting requirements. All details are considered important in determining and finalizing the main requirements. Therefore, you can use all the features / components mentioned in the article to collect the requirements to meet the purpose of your project.
Key takeaways
- Compile requirements are the process of deciding to meet the objectives of a project management task, in addition to documenting and managing the needs and requirements of stakeholders.
- The requirements collection process, which is an important aspect of a project, helps define project scope during scope management.
- Project Requirements: Project requirements are the expectations of project stakeholders regarding the outcome.
- A process used to provide a framework for measuring the performance of.
- A technique that involves the process of creating a model of the actual product to be realized.
- Identification in this process begins with identifying all stakeholders and understanding the needs of the organization.
- Gathering requirements involves defining and documenting product features that are initiated and delivered during the project process used to create the product.
- Gathering requirements is an essential process because if requirements from stakeholders are not properly collected, the scope of the project may be incorrect.
A series of processes that ensure that the scope of a project is accurately defined and mapped is known as process management. Scope management techniques allow project managers and supervisors to allocate the appropriate amount of work needed to successfully complete a project. This is primarily concerned with controlling whether it is part of the scope of the project.
What is a project scope?
A scope is a detailed set of project artifacts or features. These deliverables are derived from the requirements of the project.
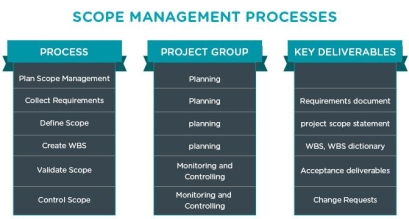
The three processes of project scope management are:
Plan
The planning process is when you try to capture and define the work that needs to be done.
Control
The control and monitoring process focuses on tracking, scope creep, tracking, and documenting disapproval / approval of project changes.
Closed
In the final process, closing involves auditing the project deliverables and evaluating the results against the original plan.
Project scope statement
The scope of a project is to clearly identify the work required to successfully complete or deliver a project. One of the project manager's responsibilities is to ensure that only the required work (scope) is performed and that each deliverable can be completed within the allotted time and budget.
Documenting the scope of a project describes the boundaries of the project, establishes responsibilities for each member of the team, and sets the steps for how to validate and approve completed work. This document is sometimes referred to as a scope statement, work description, or reference condition.
Steps involved in project scope management
The project manager must define the scope of the project no matter which method is selected. This is an example of a systematic process for capturing, defining, and monitoring scopes.
Define project needs
Defining project needs is the first step in establishing a project timeline, allocating project resources, and setting project goals. Only in these defined steps can you understand what you need to do. That is, you need to define the scope of your project. Once that's done, you can assign tasks to team members and give them instructions to carry out the project at a specified time and budget.
Understand the purpose of the project
To define the scope of a project, it is important to first establish the purpose of the project. This may include creating new products, creating new services within your organization, or developing new software. There are several purposes that can be central to the project. The project manager ensures that the team delivers results according to the specified functionality.
Define project scope
The resources and work used to create a product or service basically define the scope of the project. Scopes generally outline the goals that will be achieved to achieve satisfactory results.
Steps to define the scope of the project
- Purpose of the project
- Target
- Subphase
- task
- resource
- budget
- Schedule
To define the scope of your project, specify the above parameters.
Once these parameters are established, the project limits need to be clarified and aspects not included in the project should be identified. By doing this, the scope of the project will clarify to stakeholders, senior management, and team members what is and is not included in the final product or service.
In addition, the scope of the project requires specific goals for the organization implementing the project.
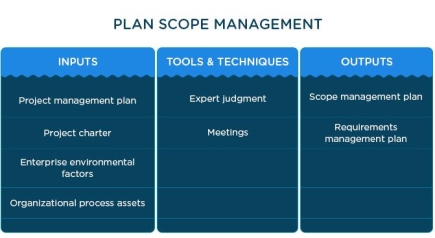
Plan scope management
This process creates a scope management plan. Scope management plans describe project scope and document how to further define, validate, and control project scope.
It also contains information on how to prevent or handle scope creep, handle change requests, escalate paths for mismatched scope elements between stakeholders, the process of creating scope statements, WBS, and how to accept artifacts.
Requirements can be classified into various types such as business requirements, solution requirements, stakeholder requirements, transition requirements, quality requirements, etc. requirements. Requirements are considered the basis of the WBS (work breakdown structure) and for project managers working on a particular project would be difficult without a requirements document because they will have nothing to work on.
|
Figure 3
Collect requirements: Definition
The Compile Requirement is a process that determines, in addition to documenting and managing the needs and requirements of the stakeholders, to meet the objectives of the project management task. The documentation that takes place within the wants gathering process is taken into account important because it provides the idea for outlining and managing the scope of the project.
The collection requirement acts as a framework that provides a baseline for the project's budget, schedule, and quality specifications, risk, and resource plan.
|
Figure 4
Project Management - Requirements Collection Process
An essential aspect of the project, the requirements gathering process helps define the project scope during scope management. With a set of tools and techniques to collect requirements from projects, it is the responsibility of a project manager to ensure that all requirements are captured. As a project manager, it is essential to be very nimble in gathering requirements and you also need to use the right requirements gathering tools throughout the project life cycle. Making sure to not miss any requirements of the project result, a project manager is liable for the success of the project.
Also, in this article, he will understand requirements gathering techniques in detail.
|
Figure 5
Project requirement: The requirements of a project are the expectations of the project stakeholders about its results. According to PMI, "Gathering requirements is that the method of determining, documenting and managing the wants and requirements of interested parties to satisfy the objectives of the project."
Gathering Requirements Process - The Basis for Project Scoping
Step 1: Identify "Stakeholder" Needs.
Step 2: Document the needs and requirements.
Step 3: Manage them throughout the project to satisfy project goals. "
According to PMI, around 70% of project failure is attributed to requirements gathering. While most of these projects met schedule and budget criteria, they did not meet stakeholder requirements. This Product conflict was observed during the ultimate delivery of the project or the closing phase of the project. This process has a negative impact on the success of the project!
Collect requirements: tools and techniques
Expert judgment
The following are the topics in which individuals or groups should have specialized knowledge and experience:
Data collection
The data collection techniques that can be used for the requirements collection process are:
Brainstorming
A groupthink activity, where several people from various teams meet to list the requirements of a project. And during the brainstorming session, new ideas are generated from existing plans, helping to identify new requirements.
Interviews
The interview is the first requirement gathering technique. It can be done both formally and informally. The critical feature of this process is that it helps the project manager interview participants, sponsors, stakeholders, and other experienced project executives, and subject matter experts who can help identify and define the characteristics and functions of the deliverables of the project. desired product.
Focus groups
The focus groups compile pre-qualified stakeholders and material experts to seek out their expectations and attitudes a couple of proposed project. Focus Group is a technique used to elicit a specific set of stakeholder requirements. For example, the project manager may first arrange a meeting with the CEOs of a company to learn about their requirements and then arrange a separate meeting with the functional managers to understand their requirements.
Collect requirements
This process involves documenting the needs of stakeholders with the stated intention to achieve project objectives. In this process, managers use several techniques and tools to collect project requirements from stakeholders. The process tries to leave nothing behind, resulting in a detailed list of project requirements. If this process is carried out thoroughly and correctly, it can greatly reduce the possibility of unpleasant surprises as the project comes to an end.
The table below presents the inputs, tools and techniques and outputs of the requirements collection process.
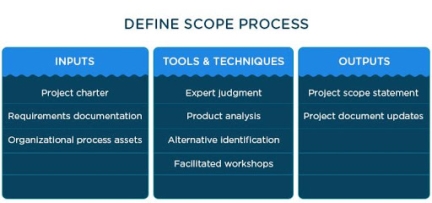
Define the scope
|
Figure 6
This process involves the preparation of a detailed description of the project and its main deliverables. The scope clearly indicates what the project is supposed to achieve and what it cannot accomplish. Supporting documents are reviewed to ensure that the project will deliver work in accordance with the stated objectives. The resulting scope articulates the needs of stakeholders and communicates the performance expectations of the project.
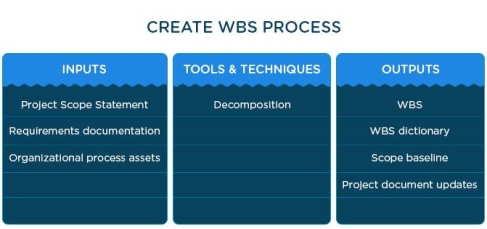
Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is an important part of the scope management process, and the PMI® emphasizes this aspect - many project managers often skip this step, leading to inaccurate planning.The WBS gives the project manager and team the ability to break down a high-level scope statement into smaller, manageable units of work, known as work packages. The resulting WBS should provide an entire list of all work packages required to finish the project
The table below presents the inputs, tools and techniques and results of the process of creating a work breakdown structure.
|
Figure 7
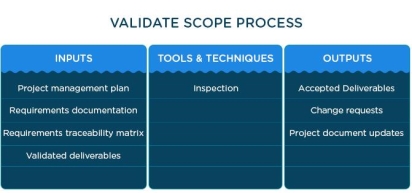
Validate the scope
The main focus of the scope validation process is customer acceptance. This is when the project client formally accepts all of the project deliverables. This process occurs at the top of every phase. During the process, the client gives his opinion on the work carried out.
The table below shows the inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs of the scope validation process.
|
Figure 8
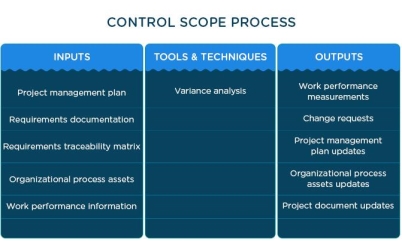
Scope of control
Control Scope is the last group of processes in project scope management. The process of controlling scope is to monitor the status of the project and manage changes to the scope.
The table below shows the inputs, tools, and techniques, and outputs of the oscilloscope control process.
This process involves evaluating additional client requirements or proactively ignoring the scope of the project.
|
Figure 8
Project Scope Management
There are some common issues with running Project Scope Management that can lead to issues once the project has started. We recommend that you consult all of the Scope Management documentation with an eye on:
Ambiguity
Ambiguity of scope often leads to unnecessary work and confusion. To avoid this, the scope must be clearly defined and precise.
Incomplete definition
Incomplete perimeters lead to planning slips, which leads to cost overruns. To avoid this, the scope must be complete and precise.
Transience
Transient spans lead to perimeter drift, the main cause of delivery delays and “endless” projects. To avoid this, the scope document must be finalized and remain unchanged for the duration of the project.
Non-collaborative scope
Scope that is not collaboratively prepared leads to misinterpretations of requirements and designs.
Why do project managers need scope management?
Effective management of the project scope requires clear communication, to ensure that stakeholders and team members understand the scope of the project while also agreeing on how the project objectives will be achieved.
Scope management helps avoid the challenges a project might face with an inflated scope and an indiscernible list of requirements.
Key takeaways
- A series of processes that ensure that the scope of a project is accurately defined and mapped is known as process management.
- The scope of a project is to clearly identify the work required to successfully complete or deliver a project completed within the allotted time and budget.
- Defining project needs is the first step in establishing a project timeline, allocating project resources, and setting project goals.
- To define the scope of a project, it is important to first establish the purpose of the project.
- The resources and work used to create a product or service basically define the scope of the project.
- An essential aspect of the project, the requirements gathering process helps define the project scope during scope management.
- The requirements of a project are the expectations of the project stakeholders about its results.
- Effective management of the project scope requires clear communication, to ensure that stakeholders and team members understand the scope of the project while also agreeing on how the project objectives will be achieved.
- Control Scope is the last group of processes in project scope management.
- The main focus of the scope validation process is customer acceptance.
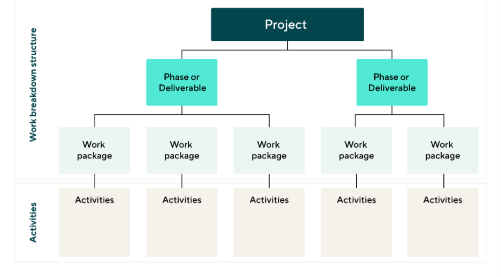
Define Work Breakdown View
The goal of WBS is to form large projects that are easier to manage. Work Breakdown Structure is a hierarchical tree structure that describes a project and divides it into smaller, more manageable parts. Wrike allows you to create WBS by creating folders and subfolders. In addition, individual tasks can be subdivided into subtasks.
How to create an exploded view
Project managers need to ensure that all important inputs and deliverables are seamlessly collected and prioritized. You can use Gantt charts, flowcharts, spreadsheets, or lists to give a hierarchical overview of the importance and connectivity between the tasks required to complete your project.
After describing the artifacts and tasks in order of completion, you can assign each task to a member of the project team. Keep team members out of the weight of your project by using your knowledge of skills, strengths, and availability to distribute tasks and responsibilities across the team.
Features of work exploded view
The PMI definition adds that the WBS structure needs to be built so that each new level in the hierarchy contains all the work needed to perform the parent task. That is, each parent task item must contain multiple child tasks for the parent task item to be considered complete.
Example of work exploded view
Exploded views for each project may vary. You don't have to follow one method to create a good WBS.
Project managers may need to experiment to determine the best WBS for themselves and their team. The purpose is to show the hierarchy and scope of the project and to make progress clear to everyone involved in the project (whether team members or external stakeholders).
Here are some examples of working exploded views. You can use any of these elements to write a WBS.
Work exploded view worksheet. You can effectively configure the WBS in your spreadsheet to focus on different phases, tasks, or deliverables of columns and rows.
Organization chart of work exploded view. You can configure WBS in a general workflow. Most of the WBS examples and templates you can find are flowcharts.
A list of work exploded views. The WBS can be configured as a simple list of tasks or artifacts and subtasks. This is the easiest approach to creating a WBS.
Work exploded view Gantt chart. WBS can be configured as a Gantt chart that represents both a spreadsheet and a timeline. WBS structured Gantt charts allow you to link task dependencies to view project milestones.
|
Figure 9
Example of work exploded view
Here is an example of a peace breakdown structure
What is the difference between WBS and Peace Breakdown Schedule?
Various detailed project documents support WBS. Among them, risk management plan, quality plan, supply plan, communication plan
Validating Scope
How do you validate the scope of your project?
The central function of the project management process is to achieve the project deliverables. The deliverables of these projects need to be formally accepted by stakeholders. To ensure that the process runs smoothly, a scope validation process is implemented to validate and guarantee the quality of the artifacts.
Validation scope definition
Scope validation is the process of formalizing the approval of the finished project deliverables. The process by which stakeholders have received the agreed and formalized approval. This is primarily related to product recognition by verifying each deliverable. This particular process is required to create various documents such as project document updates, work performance information, approved deliverables, and change requests.
The scope validation process is primarily focused on deliverables, so the validated deliverables are obtained from the Control Quality team. Deliverables are reviewed with the customer to ensure they are satisfactorily completed before they are officially received. The various outputs of the project management knowledge domain are treated as baselines for the final acceptance of artifacts such as scope baselines and work performance data.
Features related to the scope validation process:
Scope validation-input
- Project management plan
The project management plan contains a scope management plan that helps you specify how to obtain formal approval of the completed project artifacts. The components of the project management plan are described below.
Scope management plan
The scope management plan determines how to obtain formal approval of the completed project artifacts.
Requirements management plan
A requirements management plan for the process that describes how to verify project requirements.
Scope baseline
The scope baseline is compared to the actual results of the project at completion to determine if changes, corrections, or precautions need to be implemented in the project.
2. Project document
The project documentation that can be considered as input to the scope validation process is:
Lessons learned registration
Lessons learned in the current or previous project can be applied or implemented in later phases or stages of the project to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of validating the project deliverables.
Quality report
The quality report contains information on all quality issues related to the project and recommendations for improvements previously escalated by the project team. The quality report also includes details of the findings provided by the quality control process. This information is reviewed and checked before the product is accepted.
Requirements documentation
The requirements documentation process lists all projects, products, and other types of requirements for projects and products, along with their acceptance criteria. With these important aspects in mind, project managers need to provide stakeholders with the desired objectives. Well-documented requirements make it easy to detect deviations from the agreed range for a project or product.
Requirements Traceability Matrix
The Requirements Traceability Matrix links requirements to their origin and tracks them throughout the project life cycle. It also compares project performance to project management plans, links requirements to all goals, and adds business value to deliverables.
3. Verified artifacts
A validated deliverable is the process by which the deliverable is completed and internally checked for accuracy and quality through a quality control process.
Work performance data
Work performance data includes the degree of compliance with the requirements, the number and severity of nonconformities.
Scope Verification-Tools and Techniques
Inspection
Inspection is the process of inspecting work products to determine if they comply with documented standards. The results of the test usually include measurements and can be performed at any level. Inspections are also known as reviews, product reviews, audits, and walkthroughs.
Group decision-making method
Group decision-making methods evaluate alternatives to group settings and reach consensus that leads to final decisions. This will help you reach your goals.
Scope validation-output
Accepted deliverables
Approved deliverables are deliverables that meet the approval criteria of the project management plan and have been approved by the appropriate stakeholders. Obtaining approval is a key outcome of this process and is typically performed by project managers, customers, sponsors, and feature or operations managers.
Change request
All final deliverables are fully accepted by stakeholders and such unaccepted deliverables are guaranteed to be documented with reasons for disapproval. In such cases, the deliverable needs to be changed, when the process of requesting change is enabled to repair the defect. After the change requests are executed, they are confirmed through the execution of the-integrated change process method.
Work performance information
Information about which artifacts have been started, their progress, which artifacts have been completed, or which artifacts have been accepted. The work performance information process takes place at every specific stage of the project life cycle.
Update project documentation
A document that defines a product, or a document that reports the status of a product upon completion. Validated project documents may require approval from the customer or sponsor in the form of a signature or sign-off.
Lessons learned registration
The lessons learned will be updated in a timely manner with information on the challenges faced by the project team, how to avoid them, and approaches that worked well to validate the deliverables.
Requirements documentation
The requirements document is updated with the actual results of the validation activity. In certain situations, the actual results obtained may exceed the requirements of the project.
Requirements Traceability Matrix
All results obtained through the validation process are updated within the requirements traceability matrix. It also contains information about the various methods used and the actual results of the process.
The scope validation process plays an important role because it focuses primarily on validating the deliverables that are delivered to stakeholders. Its main function is to achieve the criteria and deliverables mentioned by stakeholders in the project management plan. If you do not implement the scope validation process, the artifacts will not be accepted and you will have to go through the change request process.
Controlling Scope
Control scope is probably one of the most important processes in maintaining a scope baseline, changing the scope baseline as needed. Project managers primarily try to avoid scope creep. This is a process that extends in an uncontrolled way.
Definition of control scope in the project
Control Scope is the process of monitoring the status of projects and product scopes and managing changes to scope baselines. Control scope is the process that allows you to maintain scope baselines throughout the project life cycle.
The key components used to develop a control scope process are:
Control range-input
Project management plan
The process of controlling scope involves many goals to be achieved. The following criteria in your project management plan help you manage your scope.
Scope management plan
The process of monitoring and controlling project scope is a major advantage of scope management planning.
Requirements management plan
A process that is part of a project management plan. Learn how to analyze, document, and manage project requirements.
Change management plan
As the title suggests, the change management process focuses primarily on changes that occur during the life cycle of a project.
Configuration management plan
The process used to identify the components that require formal change management and implement the change management process to monitor the required changes.
Scope baseline
Scope baseline is an approved project scope and is used to determine and prevent scope creep during scope change management. The scope baseline consists primarily of project scope statements, work breakdowns, and WBS dictionaries. Only by implementing this scope baseline can you orient your project in the right direction.
Performance measurement baseline
Processes that use earned value analysis use performance measurement baselines to compare actual results to determine if changes, corrective actions, or precautions are needed.
Project document
Here is a list of project documents that can be considered input to this process –
Lessons learned registration
To improve project scope control, lessons learned early in the project are applied or implemented in the project accordingly.
Requirements documentation
Project requirements are always tracked, tested, measured, complete, consistent and require significant stakeholder acceptance. To ensure this, the requirements should be well documented so that the project manager can easily detect project deviations.
Requirements Traceability Matrix
A tool that helps you detect and identify the impact of changes that impact your project and deviate from the baseline and deliverables of the predicted scope.
Work performance data
Work performance data is a way to document the number of change requests received, the number of approved changes, and the number of artifacts in a completed project.
Organizational process assets
Organizational process assets contain specific policies and procedures set by the executing organization for scope management. It also describes aspects such as formal and informal scope that exist in the enterprise, and how to monitor and report.
Control scope tools and techniques
Data analysis
Data analysis techniques which will be utilized in the control scope process include:
Analysis of variance
Variance analysis is a method used to determine the extent and cause of variance between the baseline of a project and the actual performance that occurs during the execution phase. The project manager can analyze the performance of the project only if a comparison is made.
Trend analysis
Control range-output
Work performance information
Work performance information contains information about the actual performance of the project scope when compared to the scope baseline. All the causes of scope differences and the consequences of the changes are documented in the work performance information. The entire process provides the basis for project scope decisions.
Change request
Requests to change scope baselines or other aspects of the project management plan typically occur when an analysis is performed on scope performance. A change request consists of a precautionary or corrective action, a defect repair, or an extension request
Update project management plan
From time to time, you need to update your project management plan. The main area of update is –
Scope management plan
The scope management plan is updated to reflect the changes that occur in the project to show how scopes are managed.
Scope baseline update
Whenever an approved change request affects the project scope, the scope statements, WBS, and WBS dictionary are modified to suit the changes and executed accordingly.
Schedule baseline
Changes to the schedule baseline are included depending on the approved changes in scope, resources, or schedule estimates. In certain situations, a revised scheduled baseline is needed to provide a viable basis for performance measurement.
Cost baseline
The purpose of the cost baseline is the same as that of the schedule baseline. All changes that occur will be incorporated according to the approved changes in scope, resources, or cost estimates. In certain situations, a revised cost baseline is needed to provide a viable basis for performance measurement.
Performance measurement baseline
All changes related to the performance measurement baseline are incorporated according to the approved changes in scope, schedule performance, or cost estimates. In some cases, change requests are made to revise the performance measurement baseline to provide a realistic basis for performance measurement.
Update project documentation
Documents that may need to be updated include requirements documents and requirements traceability matrices. The requirements document describes how the project requirements meet your business needs. The matrix helps you link your requirements to your needs and track their development throughout the project life cycle. Making sure that both documents are up-to-date can help you manage and control changes to your project's scope.
Lessons learned registration
A record of lessons learned can be updated in an efficient and effective way to control scope, such as the cause of differences and the corrective actions chosen to complete the project.
Requirements documentation
Requirements documentation is primarily used to update with added or modified requirements.
Requirements Traceability Matrix
The main purpose of the Requirements Traceability Matrix is to update to reflect the updates in the requirements document.
The importance of scope of control is to document changes and notify stakeholders. Other management plans, such as scope management plans, are also affected by project management activities and provide feedback on how project managers implement approved changes. As a result, this also has a significant impact on the entire project life cycle. This process also requires updating the project documentation, requirements documentation, and traceability matrix.
Key takeaways
- Work Breakdown View (WBS) in Project Management is a way to perform complex projects in several stages. This is a way of dividing and governing large plans, so things can be done faster and more efficiently.
- It is imperative to discuss the scope of the project with all stakeholders and key team members involved before creating an exploded view.
- Each WBS level represents a new and more detailed definition of the work required to complete the project.
- Project managers may need to experiment to determine the best WBS for themselves and their team
- When created in detail, an exploded view is a roadmap that guides a team, whether simple or complex, as it completes the project.
- The central function of the project management process is to achieve the project deliverables.
- The deliverables of these projects need to be formally accepted by stakeholders.
- Scope validation is the process of formalizing the approval of the finished project deliverables.
- The requirements documentation process lists all projects, products, and other types of requirements for projects and products, along with their acceptance criteria.
- Control scope is probably one of the most important processes in maintaining a scope baseline, changing the scope baseline as needed.
- The importance of scope of control is to document changes and notify stakeholders.
- Documents that may need to be updated include requirements documents and requirements traceability matrices.
- Requests to change scope baselines or other aspects of the project management plan typically occur when an analysis is performed on scope performance.
- Trend analysis may be a method want to examine the performance of a project from time to time to ascertain if the performance of the project is deteriorating or improving.
- Organizational process assets contain specific policies and procedures set by the executing organization for scope management.
Planning Schedule Management
How to plan project schedule management?
Chaos is what happens when there is no proper project schedule management. What if you don't know which resource to use? When do resources need to be implemented in a project? Time span to complete project? Project schedule management ensures that equipment does not fail during the project cycle.
In short, planning project scheduling is the most useful tool for project managers to get an overview of the tasks that are part of their project.
Definition of schedule management
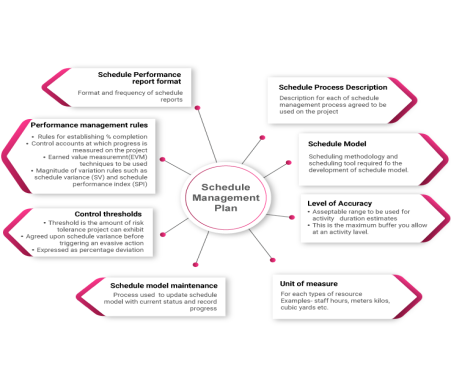
The strategic advantage of the schedule management process is that it monitors and manages the schedule for the entire project.
The scheduling procedure begins with a project that is expected to be delivered according to stakeholder requirements. Scheduling involves technical work that creates changes that generate productivity and handle aspects such as risk management and stakeholder management.
Differences between schedule management planning and schedule development:
Schedule management planning incorporates schedule design and planning. Scheduling plans help end clients recognize an overview of their reports, from work breakdown structure (WBS) distinctions to calendar and activity code descriptions. Scheduling allows organizations to choose base-up or top-down methods primarily to address schedule improvements, from deciding on recurring updates to building levels of detail.
Scheduling is a standard scheduling concept consisting of a large number of well-known treatises and books in business. Scheduling is structured and well-provided because you anticipate that you have a valuable schedule management plan.
Purpose and importance of schedule management planning:
A well-planned schedule is a guide for all projects. The basic motive is the same schedule as the execution procedure. Therefore, it incorporates the need to ensure time-related costs, budget control, billing avoidance and documentation, and more. The motivation for a project schedule is structured and focused on the progress of the schedule management plan.
It guarantees the organization by strengthening the project by guiding thoroughly Therefore, a good plan is guaranteed and the project can be monitored according to the schedule management plan.
Practical schedule management in your project helps your organization to:
Creating a project schedule is an important activity that includes identifying tasks, ordering those projects, and setting goals for those activities along with a project schedule management plan. Competencies need to be procured with a wealth of experience, just as project management scheduling expertise seems to be relevant.
Schedule management planning is the most important project management planning idea. Helps plan the schedule and guides the improvement of the project. Planning is an organized and documented system aimed at accelerating the schedule development process and including all the data needed to ensure that the final product is suitable for all the needs of the organization.
Defining Activities, Sequencing and Estimating Activity Resources & Duration
Defining sequence activity in a project
The project manager is responsible for the full development of the project. The process runs smoothly by incorporating project planning and coordination of objectives. Therefore, the reason a project fails is when the project manager can create a work analysis structure but cannot execute it. As a project manager, you should consider planning your project, including all project management skills, knowledge, and tools and techniques.
This article describes the project sequence activity and its process, importance, and therefore the got to determine the project activity sequence.
Definition of sequence activity
Sequence activity, a strategy that distinguishes and authenticates affiliates within a project activity, provides a consistent work plan to maximize the constraints of the project. Throughout the project, the execution process is planned to improve performance.
Sequence activities are designed to be divided into project management process groups and knowledge areas. By using the results of the steps, in project schedule development, you define sequence activities, estimate activity resources, combine with scheduling tools to estimate activity duration, and create a schedule model.
How to order the activities of a project?
Sequences can be performed using project management software or using manual or mechanized procedures. The sequence activity process focuses on converting project activity from an inventory to a diagram and acting because the initiative in publishing a schedule baseline.
The chart below shows a data flow diagram of sequence activity on how all activities except the first and last connect to at least one predecessor activity and at least one successor activity with the proper logical affiliation.
Sequence activity process in project management
Sequence activity is that the process of identifying and documenting the relationships between project activities. Therefore, the basic reason for the sequence activity process is to end the project scope and complete the activity interrelationships to achieve the purpose of the task.
A realistic project schedule should be appropriate by creating a logical relationship. It may be essential to utilize lead times or lag times between exercises to support wise and reachable business planning. Sequences can be run using software built for project management, manual or computerized procedures. The Sequence Activity process focuses on changing the project activity from a list to a diagram and performing it as the first step in distributing the schedule baseline.
Example network diagram of sequence activity process
|
Figure 10
The main result of this process is a network diagram
If the activity period is added, the network diagram shows the critical path
This figure shows a sample network diagram as a result of the sequence activity process.
As you can see, after the project started
Activity # 1 must start first.
When activity # 1 ends, activity # 2 and activity # 3 start.
Activity # 4 can only be started after activity # 2 is finished.
And the last activity, activity # 6, can only be started when activity # 4 and activity # 5 are completed.
After the completion of activity # 6, the project will end.
Note that this is a simple sample network diagram to show what the network diagram looks like. In a real project, the process of network diagram and sequence activity is much more complicated than this because of the large number of project activities.
Tools used in the project management sequence process
In the process of ordering activities in project management, the project manager identifies and records the relationships between different project activities so that you can define the best logical sequence that can produce the highest efficiency. Ultimately, the project manager can develop the project management sequence process.
There are three tools and techniques utilized in the project management sequence process.
- Priority projection (PDM)
- Dependency determination
- Reeds and rugs
Why is it important to determine the activity sequence of a project?
If you don't fully understand what you should do, you can't plan. It may also interfere with or obsolete activities in the future. You may also find yourself running out of time and money after performing a short activity first.
You can't decide how difficult a project is to do without ordering the activities. Some different diagrams are the same as the project network diagram. For example, transport modelling tries to find the shortest path between two points. In these figures, you only have to follow one path. In the project network diagram, all activities must be completed to complete the project.
Priority projection in sequence activities
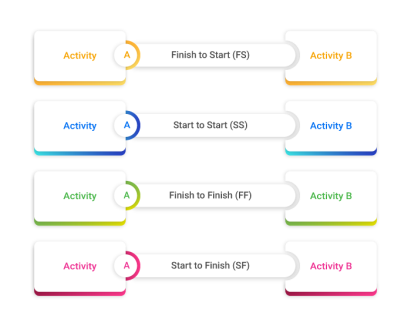
The Precedence Diagramming Method is a method used to develop a scheduling model in which activity is represented by a node that is connected by a projectile to one or more of its successors.
The Precedence Diagramming Method incorporates four types of dependencies or
|
Figure 11
logica l predecessor and successor relationships:
End to Start: Subsequent activities cannot be started until the predecessor activity is complete.
End to End: Subsequent activities cannot be completed until the previous activity is complete.
Start from Start: Subsequent activities cannot start unless the predecessor activity has started.
From start to end: Subsequent activities cannot end until the predecessor activity has started.
Once you have derived the connections between the activities of your project, you will receive a sequence that specifies their affiliations and sets up the linked activities. This setting is known as the project network diagram.
Need to determine the activity sequence of a project
You can't determine the most difficult way your project can do without ordering the activities. Many diagrams resemble a network diagram of a project, so try to track the most accessible route between the two points. Only one point needs to be taken from the illustration. In the project network diagram, all activities of the project must be completed.
Sequence activity leads and lags
Leads and lags are one of the essential tools for ordering project activities.
Subsequent activities can be started early. This is related to the support for the Finish-to-Start type, which is the most basic connection between activities. Leads allow you to start working on your successor right away.
The lag associated with the start-to-start type of dependency between exercises performs subsequent actions and defer its start. For example, if you choose to delay the procurement of building materials for only three days after the design of your plan begins. It looks like it starts with 3 days of slack time.
Finally, when you finish ordering the project activities, you'll see that some changes have been made to the inputs used, the activity list and activity attributes. You have the opportunity to identify a particular risk. Therefore, the project manager updates the project documentation and other output.
Key takeaways
- Chaos is what happens when there is no proper project schedule management. What if you don't know which resource to use?
- Schedule management planning incorporates schedule design and planning.
- Scheduling plans help end clients recognize an overview of their reports, from work breakdown structure (WBS) distinctions to calendar and activity code descriptions.
- In all organizations, projects are an essential way to build value. In today's business context, all organizations need to be able to meet and schedule the right budgets, resource shortages, and the latest technology trends.
- Schedule management planning is the most important project management planning idea.
- Sequence activity, a strategy that distinguishes and authenticates affiliates within a project activity, provides a consistent work plan to maximize the constraints of the project.
- If the activity period is added, the network diagram shows the critical path
- An important result of the sequence activity process is the network diagram. The project network diagram represents the activity in the activity ID box and shows the interrelationship between the activity and the vault.
- The Precedence Diagramming Method incorporates four types of dependencies or logical predecessor and successor relationships.
- The lag associated with the start-to-start type of dependency between exercises performs subsequent actions and defer its start.
Project schedule management: the way to plan, develop, maintain and control?
In any organization, projects are an important method to get value. Running a corporation with a scarcity of ideas and without proper planned schedules for projects would cause failure. regardless of what the dimensions or scope of your project is, the project schedule articulates when each activity should be done, what's already done, and therefore the sequence during which things should be finished.
In today's business environment, every organization must have the power to manage and schedule with tight budgets, resource constraints, and therefore the latest technology patterns.
This article looks at how project managers should implement certain factors in planning, developing, maintaining, and controlling the project schedule.
What is schedule management?
Schedule management may be a procedure that needs the establishment of policies and documentation to take care of , develop, manage, and control time and resource schedules for project completion. The strategic advantage of the schedule management process is that you simply will monitor and manage the schedule throughout the project.
The scheduling procedure begins with the projects that are expected to be delivered consistent with the wants of the stakeholders. Schedule Management includes technical work that generates productivity and brings changes that handle aspects like risk management and stakeholder management.
|
Figure 12
Schedule management
Project Scheduling in Project Management - Explained!
The project schedule may be a technique that teaches what work must be done, what resource within the organization will do the work, and therefore the time periods during which that employment must be done. The project schedule should reflect most of the work associated with delivering the task on time. Without an entire schedule, the project manager won't be ready to communicate regarding the value and resources that are important to delivering the project.
Some programs allow project managers to trace project-related schedules, resources, budgets, and assets in real time. The project schedule are often updated and viewed by colleagues associated with the task, keeping everyone informed on the general status of the project.
Project schedule planning in project management!
The construction policies procedure, methodology, and project documentation provide guidance and guidance on how the task schedule are going to be monitored throughout the project. The intent of a project schedule is organized and focused supported the progress of the Schedule Management Plan.
Project plans should consider the subsequent aspects,
Project schedule planning is an important activity that comes with identifying project activities, sequencing them, and defining objectives for those activities alongside the project schedule management plan. As relevant as project management scheduling ability is in every way, proficiency must be obtained with significant experience.
|
Figure 13
Develop the project schedule in project management!
- Developing the project schedule refers to planning the timing and sequence of project activities.
- The project schedule shows:
- Time estimates (duration) for all project tasks
- Task start and end dates
- Names of staff resources assigned to finish tasks
- Task sequence
A noteworthy segment of a project's schedule may be a work breakdown structure (WBS). The project schedule is meant to reflect the work breakdown structure.
Project scheduling is that the key to making sure the first project plan, and therefore the outcome of the project is a minimum of close enough for the project to be a hit. Developing project schedules helps the project team to stay necessary activities on target. The PMBOK Program Management knowledge area explains the critical processes within the development of a project program.
5 steps to assist develop a project schedule
Project management has always been fascinating for a way thing work and the way to form things work better. Therefore, a project schedule goes through the design phase of any project. The means expected to schedule a project are listed below:
Define activity allows project managers to use the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) and a deliverables diagram to determine and begin assignments that are essential to end on time. This ensures that they're conscious of the activities that require to be included within the plan.
The sequence of activities helps determine the connection between project activities. Ordering the tasks and identifying the dependencies (Finish to start out, Finish to end, Start to start out, Start to finish) is that the next step.
Make estimates. The project team has defined activities and tasks in a breakdown structure; the next stage is to choose the use of time to complete the project. To calculate the schedule, having an estimate of what to do, how to do it, and the essential part of the equation is how far a project should take to finish.
Determine the dependencies. Projects are not always simple. On a regular basis, a project cannot be started until the one in progress has finished. This is called task dependencies. As project supervisors, you can also follow a methodology by following your schedule to accommodate these related projects.
The last step is to allocate resources to finalize your planned program. Choose which resources to complete assigned tasks on time. As a project management team, you must have adequate resources and your time must be considered in planning assignments.
When you've intended to formulate a project schedule, get your manager's feedback and implement the essential changes that need to be completed. You will need to estimate the project plan before proceeding to execute the plan. Once the project is in progress, it will help you compare the planned dates with the actual ones. Keep in mind the homework goals that will help you set a schedule once you complete the process.
Maintain the project schedule in project management!
In the midst of essential project management skills, booking can influence, decisively or unfavourably, most territories within a task. Inadequate project schedules can create a roadblock to managing your project schedule, thereby creating a disruption for people and production equipment that leads to project failures.
Here are some techniques that can help you keep your project on schedule:
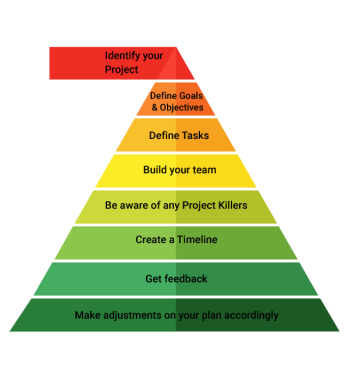
Project planning: A successful project is all about planning. A well-designed project plan will save you time, cash, and considerable brain pain once the business ships. To get started, creating a project plan should focus on the following components:
|
Figure 14
Once the project plan is ready, present it to all board members to use as a roadmap during the project.
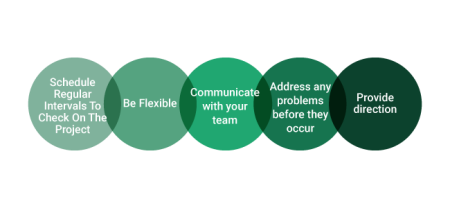
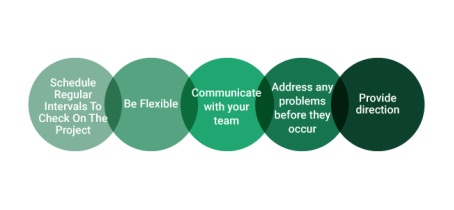
Keep the project on track: A clear and well-defined project plan can help guide the project team through the project. A constant review, revision and monitoring of the project is also necessary from the beginning to the end of the project.
|
Figure 15
Use project management software - Regardless of how detailed the project plan is and how prepared it is, project managers face many challenges. Fortunately, technology has made monitoring everything from online life records to customer connections more powerful and advantageous. Project managers also prefer to have access to software that has simplified their lives.
|
Figure 16
Time Management - For every project management team, it is always an advantage to be trained to effectively manage time in the workplace. While there are a variety of methods a project management team could use to deal with the opportunity, here are some of the best techniques to follow:
- Delegated Tasks
- Prioritize your tasks
- Organize more effective meetings
- Learn to say no. '
- Write tomorrow's homework today
Celebrate Success - Once the project is complete with the right strategies in place, the best opportunity for the project management team is to celebrate. A popular method of observing is dining out as a team or having some celebratory drinks. Rewarding the team with a certification or thanking the team in person is also a good sign.
Control of the project schedule” in Project Management
This procedure helps lessen the threat of a late delivery when handled well. In addition to monitoring status, the schedule control process updates projects and manages the change in schedule so that project managers
Control the project schedule: techniques
- When using Earned Value Management (EVM), the schedule variance and schedule performance index are used to assess the extent of schedule changes.
- In controlling the schedule, it is essential to decide whether the schedule variance needs corrective action. For example, if a project is interrupted it has a negative impact on the scheduling plan and therefore requires immediate action.
- Use the critical string programming method; you are allowed to compare the amount of defense needed and the remaining security to regulate the status of the program.
- Schedule performance measurements are used to assess the amount of variance from the original schedule baseline. The added float variance is also a vital module for evaluating project time performance.
- The essential aspects of controlling the project schedule include deciding the reason and the level of change from the schedule baseline and choosing whether corrective or preventive action is required.
Conclusion
By not using the correct procedure for the project schedule, things can go wrong with any project. And this is the time when you think of something to simplify and track the progress of your project as needed.
Key takeaways
- In any organization, projects are an important method to get value. Running a corporation with a scarcity of ideas and without proper planned schedules for projects would cause failure
- Schedule management may be a procedure that needs the establishment of policies and documentation to take care of develop, manage, and control time and resource schedules for project completion
- The scheduling procedure begins with the projects that are expected to be delivered consistent with the wants of the stakeholders.
- The project schedule may be a technique that teaches what work must be done, what resource within the organization will do the work, and therefore the time periods during which that employment must be done.
- Some programs allow project managers to trace project-related schedules, resources, budgets, and assets in real time.
- The construction policies procedure, methodology, and project documentation provide guidance and guidance on how the task schedule are going to be monitored throughout the project.
- Project scheduling is that the key to making sure the first project plan, and therefore the outcome of the project is a minimum of close enough for the project to be a hit.
- The sequence of activities helps determine the relationship between project activities. Ordering the tasks and identifying the dependencies (Finish to start, Finish to finish, start to start, start to finish) is the next step.
- Control a schedule in a project Management means the approach to monitor the status of the project and consequently update and manage project changes to the scheduled baseline to achieve the goal.
- When you've intended to formulate a project schedule, get your manager's feedback and implement the essential changes that need to be completed.
- You will need to estimate the project plan before proceeding to execute the plan. Once the project is in progress, it will help you compare the planned dates with the actual ones
- Project scheduling is that the key to making sure the first project plan, and therefore the outcome of the project is a minimum of close enough for the project to be a hit.
- When you've intended to formulate a project schedule, get your manager's feedback and implement the essential changes that need to be completed.
Project Cost Management Overview
Projects cost money. In most cases, a project will operate with a cost constraint. "
Project cost management considers four cost categories, namely direct costs, indirect costs, variable costs, and fixed costs.
Importance of project cost management
- There is no doubt that managing project costs is vital to the success of a project. One reason is that cost management provides a framework with which you can estimate, control, and manage costs. Additionally, the cost baseline for a project provides a means of monitoring project performance.
- It is possible to determine when a project is on or off course and allows to mitigate cost overruns. Finally, project cost management promotes transparency in the allocation and disbursement of funds. In this case, the projects will deliver value to clients and fulfil obligations to suppliers and stakeholders.
- Cost management includes implementing an effective strategy, as well as providing the resources and process discipline to enable and ensure the highest possible level of quality, reliability and productivity at the lowest total cost. It is not about cost in the sense of reducing costs. It is as strategic as it is operational.
Adopted and passionately implemented, the following seven principles provide both a solid business model and the essence of a cost management spirit. Together they provide a roadmap for business success.
Provide clear and consistent performance goals
The first step in any company is to ensure clear and aligned expectations. This is especially true in cost management, where many managers only have experience cutting costs, such as downsizing, streamlining products and facilities, and reducing capital budgets. While these actions are sometimes necessary, effective cost management relies on a day-to-day process discipline that continually addresses the root cause of overstaffing, unprofitable and over-expanded product lines, and systems justification and implementation. marginally effective control systems.
For example, in an industry where low cost is the primary driver of business success, there are four fundamental or cost drivers: production scheduling, maintenance effectiveness, product offerings, and technical knowledge. Each can be a profitability tool or a low-cost root cause. Understanding this distinction is the first step to effective cost management.
The second element, aligned expectations, is equally important. Even with clear revenue expectations, a well-intentioned and aggressive sales and marketing organization can offset its top-of-the-line successes by adding products, packaging options, and channels to market that, in fact, add much more cost than the projected benefit of the increase. about the sales. .
Similarly, there are potential cost trade-offs between traditional procurement cost-saving processes and the manufacturing need for process stability and variance reduction. This is especially true in pharmaceutical, alternative medicine, dietary supplement, and food processing companies, where product integrity and consistency are the keys to business success. For effective cost management, performance expectations and objectives must be aligned so as not to offset achievements in one area by increasing costs in another.
Provide knowledge, tools to succeed
The meanings of the words knowledge and tools depend on one's beliefs about the basic motivations behind human behaviour. If the executive leadership of an organization believes that most employees come to work with the will and desire to do the best they can, the job of motivating and performing employees is very straightforward. The level of knowledge and ability of each individual becomes the essential component of the ability of employees to perform well.
For example, if an organization wants to optimize compensation
This same principle applies within the ranks of management. To enable and ensure effective cost control, managers must understand the specific cost drivers of their business. They need to know the difference between efficiency and structural cost. They need to have a technical understanding of the production and sales process, as well as have a detailed understanding of the systems that drive the daily activities of the business.
The deeper the executive understanding of your organizations' cost drivers, the greater the opportunity for effective cost management versus cost reduction.
Understand the real costs
Standard cost is the building block in the vast majority of business decision-making, from budgeting, price and variance reporting, to formulating performance-based incentive plans and strategies. Standard cost data drives new product pricing, advertising, marketing, and capital investment decisions. The importance of having accurate standard cost data cannot be underestimated.
It is well known and accepted that when using standard cost average applied overhead systems, the costs of high-volume products are overstated and the costs of low-volume products are underestimated. What is less recognized, or at least recognized, is that the costs of low-volume products in such systems are often charged less than five to ten times. Understanding and accepting the need for accurate product costing has always been a challenging management task.
It is extremely difficult to accept that the background data used for many years in decision making can be the root cause of many business deficiencies. This is especially true in calculating product costs and prices and in justifying and introducing new products.
Study after study, average applied overhead analysis targeting the lowest 50 percent (by volume) of all products offered represents less than 5 percent of sales volume and productive workforce, therefore, they are allocating less than 5 percent of all overhead, but accounts for 20 to 30 percent of all non-material cost. In other words, more than 50 percent of products are sold at a loss. Until this cost distortion is recognized and corrected, major management decision systems, including the formulation of long-term strategies, remain extremely difficult to validate. Accepting such a reality has been nearly impossible for many of our best executives.
Excellence - the only acceptable performance goal
Today, customers do not expect or accept malfunctions; they expect excellence in performance.
One of the most important keys to effective cost management is setting the bar for excellence: minimum quality of 1.33 Cpk; safety without injury; zero delays in delivery; product cost reduction year after year; and predictable and regular technical improvement.
Reduce organizational complexity
The luxuries of yesterday are the burdens of today. Today, the term high value can be used to describe only the most basic essential activities. In many industries, most organizations can only afford the highest contributing activities.
Organizations with the most effective cost management are consistently and boldly applying the relevance and value test to every day-to-day activity.
They question everything. What does this activity do to make and maintain sales or improve margins? What additional costs will this activity add? What does this investment do to improve quality or provide greater production flexibility? Products, customers, etc., that do not meet these standards should be recalled.
For example, if a classy maintenance management system is down, it's often better to shut it down and return to basics than to feature the continued cost of repairing and maintaining a low-value system.
Looking back at standard cost, if 50 percent of the product variety represents less than 5 percent of total sales, but creates 20 to 30 percent of the non-material variable cost, then product by product, they too must. pass the contribution test. value.
Commit to broad, knowledge-driven participation
There are two very important reasons to focus on knowledge and participation. The first is the simple truth that people who do not participate do not compromise easily. It is earned with knowledge and respect. These two elements of success, leadership and commitment, are central keys to profitable excellence.
As we review the seven principles of effective cost management, it becomes clear that excellence in each of them depends on what business strategist W. Edwards Deming called insight. The central factor of employee participation or empowerment has always been the perceived quality of the decisions made and the problems solved.
Standard cost, reduced complexity, and maintaining a credible and valuable performance system are driven by the common denominator of knowledge-driven engagement. Only employees with the knowledge and opportunity to make successful decisions can pave the way for future business success.
Management decisions have an impact on organizational costs
That is, costs are integrated into an organization through management systems and management decisions.
Therefore, the second part of this reality lies in management's ability to embrace change, challenge its own past decisions, and aggressively embrace the power and potential of its employees. It is based on the ability to accept the fact that most of the organizational costs have been created and supported by the decision making of previous leadership.
Ultimately, effective, process-based cost management is based on company culture. It is a lifestyle.
Key takeaways
- Projects cost money. In most cases, a project will operate with a cost constraint. "
- Project cost management considers four cost categories, namely direct costs, indirect costs, variable costs, and fixed costs.
- There is no doubt that managing project costs is vital to the success of a project.
- One reason is that cost management provides a framework with which you can estimate, control, and manage costs.
- Additionally, the cost baseline for a project provides a means of monitoring project performance
- Standard cost is the building block in the vast majority of business decision-making, from budgeting, price and variance reporting, to formulating performance-based incentive plans and strategies
- Technical knowledge, well-understood and aligned performance systems and absolute data integrity add to a culture of performance, a spirit of cost management behaviour.
- The luxuries of yesterday are the burdens of today. Today, the term high value can be used to describe only the most basic essential activities.
- There are two very important reasons to focus on knowledge and participation.
- Decisions about the number of products, the customers they serve, and the way the business is run drive costs. It's what we do versus how well we do that determines the vast majority of an organization's costs.
Means of financing, types of financing, sources of finance
Finance is defined as the management of money and includes activities such as investing, borrowing, lending, budgeting, saving and forecasting. The easiest way to define finance is by providing examples of the activities it includes. There are many different career paths and jobs that perform a wide range of finance activities. Below is a list of the most common examples: -
i) Investing personal money in stocks, bonds or guaranteed investment certificates (GICS).
ii) Borrowing money from institutional investors by issuing bonds on behalf of a public company.
iii) Lending money to people by providing them a mortgage to buy a house with
iv) Using Excel spreadsheets to build a budget and financial model for a corporation.
v) Saving personal money in a high interest savings account.
In other words, financing is borrowing money with a promise to repay that money and some additional fee, or interest over a period of time.
Project financing is a loan structure that depends on the project's cash flow for repayment, with the project’s assets, rights and interests. It is the long-term financing of infrastructure and industrial projects based upon the projected cash flows of the project rather than the balance sheets of its sponsors.
There are mainly two types of finance: -
i) Debt Finance: - Generally the cash which one acquire to maintain or run one's business is known as debt finance. Debt finance does not provide ownership control to the money lender, the borrower must repay the principal amount along with the agreed interest rate. The interest rate is calculated based on the loan amount, duration, the purpose for borrowing the specific type of finance and inflation rate
Debt finance can be classified into three types: -
1) Short-term Debt Finance: - Loans generally needed for a period of more than one hundred and eighty days is called short-term debt finance. These loans are borrowed for covering the shortage of finance and temporary or occasional requirements. Short term finance is required for daily business activities such as paying wages to staffs or getting raw materials.
2) Medium-term Debt Finance: - Loans generally required for a period of more than one hundred and eighty to three hundred and six five days is called medium-term debt finance. The business generally depends on the way of using the funds and it repays the loan from the sources of the cash-flow of the businesses.
3) Long-term Debt Finance: - Loans generally required for a period of more than three hundred and sixty-five days is called long-term debt finance. This type of finance is mostly needed for buying plant, land, restructuring offices or buildings etc for a business. Long term finance has a better interest rate than short-term finance.
ii) Equity Finance: - Equity finance means raising capital for businesses by issues or offering shares of the company. Renowned companies use this finance to raise additional capital for the expansion of their business. Basically, each share is an owner's unit for that specific company.
The other types of finance are: -
i)Public Finance: - Public finance deals with the study of the state's expenditure and income. It includes only the government's finances. It can be classified into three types: -
A) Public expenditure, which means the expenses incurred by the government for its maintenance and for the welfare and preservation of the economy, society and the nation,
B) Public revenues, which include all the receipts and income irrespective their nature and source which the government acquires during the given period,
C) Public debt, which means the loans raised which is a source of public finance.
ii) Personal Finance: - Personal finance includes the ways which families or individuals get, budget, spend and save monetary resources over a period, considering different future life events and financial risk.
iii) Corporate Finance: - Corporate finance includes financial activities pertaining to running a corporation. It is a department or division which oversees the finance functions of a company.
iv) Private Finance: - Private finance denotes an alternative method of corporate finance helping a company raise fund to avoid monetary problems with a limited time frame.
Businesses can raise capital through various sources of funds which are classified into three categories.
1) Based on period - The period basis is further divided into three sub-division.
i) Long term source of finance - This long-term fund is used for more than five years. The fund is arranged through preference and equity shares and debentures etc and is accumulated from the capital market.
ii) Medium term source of finance - These are short term funds that last more than one year but less than five years. The source includes borrowings from a public deposit, commercial banks, commercial paper etc.
iii) Short term source of finance: - These are funds just required for a year. Working capital loans from commercial bank and trade credit etc are a few examples of these sources.
2) Based on Ownership - These sources of finance are divided into two categories.
i) Owner's funds - This fund is financed by the company owners, also known as owner's capital. The capital is raised by issuing preference shares, retained earnings etc. These are for long term capital funds which form a base for owners to obtain their right to control the firm's management and operations.
ii)Borrowed funds: - These are the funds accumulated with the help of borrowings or loans for a particular period of time. This source of fund is the most common and popular amongst the businesses.
3) Based on Generation: - This source of income is categorized into two divisions.
i) Internal sources: -The owners generated the funds within the organization. Example includes selling off assets etc.
ii) External sources: - The fund is arranged from outside the business. For example, issuance of equity shares to public, debentures etc.
The sources of business finance are retained earnings, equity, term loans, debt, letter of credit, debentures, euro issue, working capital loans and venture funding etc.
Government assistance towards project management for start-ups, cost control (operating cycle, budgets& allocations)
Different fields of start-ups like fintech, ed tech, pharma, e-commerce, supply chain, and even consumer marketing is gaining momentum due to increased funding and supportive policies. This initiative not only supports great minds but allows competition and equal representation in the business world.
India has launched many initiatives to boost the entrepreneurship network of India.
1) Start-up India: - Launched on 16th January 2016 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, it falls under the Department of industrial policy and promotion. The idea has been to give support to entrepreneurs by the ease of compliance and relaxed norms along with a credit guarantee fund launch for start-ups.
2)Aspire: - India always aims to improve the rural region by launching plans to support the poor. ASPIRE is one such plan which falls under the MSME, which targets the enthusiasm for innovation and development, mainly in the Agro-industry.
3)MUDRA Bank: - The Micro Units Developments Refinance Agency (MUDRA) Bank is a credit facility launched to support rural start-ups. Many small-scale foods and beverage start-ups have succeeded due to support from the MUDRA scheme.
4) Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship: - This Ministry and its wise allocation of resources show India's dedication to promote entrepreneurship. A ministry made to take care of and cater to the start-up world, continuously plans skill development sessions, tutorials, events and seminars while also looking after gap funding.
5)Atal Innovation Mission: - Setup by Niti Aayog, the ideology of this Mission is to create cooperation between state, central, and local innovation schemes and execute entrepreneurship spirit right from schools to corporates.
6) E-biz Portal: - Launched in 2013, e-Biz is a one-of-a-kind portal that allows Government to Business interactions (G2B). With 24*7 online functioning, it acts as on single forum for all transactions, clearances and activities from both parties.
7) DIDF: - The Dairy Processing and infrastructure Development Fund of DIDF is a fund structure under NABARD where milk producing companies, milk unions will find support.
8)SIP-EIT: - The support for international patent protection in electronics & information technology focuses on helping technology start-ups which are the recent trending category of business.
9)Multiplier Grants Scheme: - Launched under the department of electronics and information technology, MGS focuses on increasing Research and Development to develop key products and packaging structures.
10) Credit Guarantee Scheme for Start-ups: - Commonly known as CGSS, this scheme also concentrates on providing financial stability to micro and small industries. It gives loans with zero collateral, with additional help in the form of subsidized interest rates. The scheme has been known to target manufacturing units, while also managing a corpus of Rs. 100 lakhs.
Cost Control (Operating Cycle, Budgets & Allocations)
Business firms aim at producing the product at the minimum cost. It is necessary in order to achieve the goal of profit maximization. The success of financial management is judged by the action of the business executives in controlling the cost. This has led to the emergence of cost accounting systems. Cost control by management means a search for better and more economical ways of completing each operation. Cost control is simply the prevention of waste within the existing environment. This environment is made up of agreed operating methods for which standards have been developed.
These standards may be expressed in a variety of ways, from broad budget levels to detailed standard costs. Cost control is the procedure whereby actual results are compared against the standard so that waste can be measured and appropriate action taken to correct the activity.
The operating cycle is simply the amount of cash flow that a company needs to maintain and grow the company. It is the cash flow needed to move the product. When a company has a short operating cycle than the company requires less cash to maintain the operation of the company so the company can sell at small margins. If the company has a long operating cycle the company will end up costing more even at a moderate level. Kerzner, H., 2009, a manager wants to keep the operating cycle short to cut down on the cost required to run the business. It is the process that distributes the cash of the company, turn the cash into product, get the product out to the consumer, and returning the cash to the company and stockholders.
Budgeting takes the assumptive cost of the project, set a budget, and compare the projected cost to the actual cost of the project. This is comparing the actual money being spent on the project in comparison to the budget that was projected for the operating life cycle. A big way to keep close attention to the budget is through the s-curve.
Cost allocation is a process of providing relief to shared service organization's cost centers that provide a product or service. In turn, the associated expense is assigned to internal client's cost centers that consume the products and services. For example: - the CIO may provide all IT services within the company and assign the costs back to the business units that consume each offering.
An effective cost allocation methodology makes an organization to identify what services are being provided and what they cost, to allocate costs to business units and to manage cost recovery.
Key takeaways
- Finance is defined as the management of money and includes activities such as investing, borrowing, lending, budgeting, saving and forecasting.
- Project financing is a loan structure that depends on the project's cash flow for repayment, with the project’s assets, rights and interests.
- With the latest improvement in India's ease of business ranking, there has been a higher push by the government to also create a nurture a start-up ecosystem in the economy.
- Business firms aim at producing the product at the minimum cost. It is necessary in order to achieve the goal of profit maximization.
- The success of financial management is judged by the action of the business executives in controlling the cost.
- The operating cycle is simply the amount of cash flow that a company needs to maintain and grow the company.
References
- https://www.greycampus.com/blog/project-management/project-management-how-to-collect-requirements-for-your-project-effectively
- https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/a-guide-to/9781935589679/sub5.2.xhtml#:~:text=Collect%20Requirements%20is%20the%20process,project%20scope%20including%20product%20scope.
- https://totally.tech/quick-guides/how-to-define-the-scope-of-a-project/
- https://blog.masterofproject.com/validate-scope-process/
- https://www.aiche.org/academy/courses/ch137/three-keys-managing-project-successfully?gclid=Cj0KCQiAvbiBBhD-ARIsAGM48byuxq5Nf5Tj_uQJuZigYJVYjlcktDzIUPNvWQr6S4-uJ8Do1cohtV4aAmrMEALw_wcB
- https://www.greycampus.com/opencampus/project-management-professional/schedule-management-plan
- https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/a-guide-to/9781935589679/sub6.1.xhtml#:~:text=Plan%20Schedule%20Management%20is%20the,and%20controlling%20the%20project%20schedule.
- https://blog.masterofproject.com/estimate-activity-durations-process/
- https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newPPM_71.htm