Unit 4
Quality Management
When people use the word "Quality", it is generally synonymous with "good". Many brands promote their products as "high quality" or "superior quality" in this way without actually defining what the characteristics of "Quality" are, and we are more likely to see it in marketing material than in a comprehensive business policy or process documents.
What is quality?
Satisfy a set of inherent characteristics defined explicitly or implicitly.
Provide products or service features that customers need. These characteristics lead to customer satisfaction and exceeding customer expectations, which, in turn, generates higher income for the producer. Ensuring quality by adding features that customers want while ensuring consistency and reliability with each iteration comes at a cost, but the cost of not embracing quality is much higher, including loss of market share, lost opportunities, damage to the brand and recalls thanks to design and manufacturing flaws.
Design features free of deficiencies and errors. Products or services that are deficient and do not perform as they should require review or, if brought to market, cause costly recalls and customer dissatisfaction, all of which cost the organization money, time and brand integrity. Defects found in later stages of product development are much more expensive than if they had been detected earlier.
Ensuring continuous improvement (CI) to address root causes of defects that are inherent in processes, tools, and designs and that have significant impact. By addressing root causes through CI rather than symptoms, organizations can reduce the cost of quality, increase efficiency, maintain a culture of quality, minimize rework activities in shop and back office, reduce waste and ultimately have fewer recall events. Revenue and overall market share increase as a result of improved product quality, higher levels of customer satisfaction, and increased market share. According to the Centre for Business and Economic Research, every $ 1 invested in Quality produces $ 16 in cost reduction and a $ 3 increase in profits.
Some examples of requirements include:
- Customer specifications like reliability, availability, accuracy, and delivery dates.
- Value of goods and services purchased, such as ROI and productivity gains.
- Various ISO standards related to quality, including ISO 9001, IATF 16949 and ISO 13485.
- Legal requirements like the Food Safety Modernization Act, the FDA code of federal regulations, the Canadian Standards Association, Underwriters Laboratories, EU directives, and therefore the Occupational Safety and Health Act.
- Various industry requirements.
State the importance of quality management for an organization?
Quality is one of the most important principles of management. Maintaining the spheres of quality in each and every facet of the business helps the company attract loyal customers, maintain regular cash flows and beat the competition in the market.
Understanding and following the importance of quality management is not only the responsibility of the top management of the company, but also of each and every one of the employees.
Importance of quality management
1) Consistent quality and manufacture of products.
It is highly imperative for companies to plan, design, execute and manufacture product offerings for the target market, recognizing the importance of quality management and maintaining the parameters of total quality management in every facet.
Helps maintain quality domains consistently and continuously. In addition, the firm may conduct market research and studies on a regular basis with the aim of offering products that are a testament to the quality and its principles.
2) ensures long-lasting efficiency
When we talk about the efficiency factor while we talk about the importance of Quality Management, it is not only limited to the labor efficiency of the personnel that is dedicated to the manufacture of the products, but also to each and every one of the employees of the company and even types of machinery.
When all employees in the company, from engineers to sales managers, understand and follow the importance of quality management, their efficiency improves as they know that the product they are making and selling is the best in class.
The confidence and agility that is acquired by understanding the general process, increase your efficiency in multiples. And all of this has a cascading effect on sales and overall company profits.
3) Higher levels of productivity
When the company realizes and follows the importance of quality management in each of its business operations, there is an increase in employee productivity.
They know and understand that they are working on something unique and of high quality, in addition to that due to the high-quality parameters, obstacles and bottlenecks are solved automatically, thus increasing their productivity levels.
4) Attract a group of loyal customers
It is the rule of the thumb of all commercial and industrial domains that the company can successfully survive and thrive in an always competitive market
Today, the customer is presented with many options and alternatives on a silver platter and is much more conscious of quality standards with the help of social media and digital marketing. Therefore, it is very important that companies follow the importance of quality management to attract and retain loyal customer group and ring their cash registers.
5) beat the competition in the market
To successfully survive and prosper in the market that is always high on competition from new and existing brands, it is vital that companies understand the importance of quality management and make it an integral part of their goals and work. culture.
There are many brands on the market that have to close their stores and business operations in a short period of time, as they cannot meet quality standards. As mentioned above, the customer today is much more aware and agile, plus there are many other brands on the market waiting for them to leave.
Therefore, TQM is one of the sure ways and means to beat the competition and forge a distinctive identity for your brand in the market.
6) Improved brand equity
Continuing with the point mentioned above, each brand needs a higher market share and improved brand equity. And it's the aspect of shrewdly following and understanding the importance of quality management that helps the company make its brand equity and value skyrocket among other prominent players in the market.
7) Customer satisfaction:
Customer satisfaction and monitoring the importance of quality management go hand in hand.
Most of today's customers want to opt for high-quality products and don't mind paying extra money for them. And if there is some kind of fault in the quality of the products, the customer notices it at the same moment and perceives the brand in a negative way.
With the power of social media and various industry-specific forums in the digital space, no customer needs time to broadcast.
8. Reduced risk
Another aspect that helps the corporate to enhance and maintain the worth of its brand within the market is risk reduction. And risks only occur in business operations when the corporate doesn't adhere to quality benchmarks.
Risks occur primarily during the manufacturing process of products and in handling customers during before and after sales procedures. Therefore, it's vitally important for companies to know the importance of quality management, especially in these two aspects of the business.
9) Less human error
When the firm follows the Importance of Quality Management, it also follows a group of guidelines and principles that are framed for every of the business operations. And from top management to company management trainees, everyone should imitate.
This leads to fewer human errors that improve productivity and work efficiency levels. Also, with less human error there's little or no chance of risk.
10) Increase in income and profits
In today's dynamic market, where competition is usually high, it's very difficult for the corporate to get the specified revenue and benefits to satisfy its long- and short-term goals. And following the importance of quality management is one among the sure ways to realize all business purposes and goals.
It guarantees a high level of customer satisfaction, high brand equity, increased market share, loyal customers and a competitive advantage. But repeatedly, firms fail to know this easy and one among the foremost crucial fundamentals, causing them to incur losses.
Conclusion
Rather than the discussion points mentioned above, it can alright be concluded that it's highly imperative for companies in today's dynamic market to know and follow the importance of quality management.
The firm has got to integrate quality principles into each of its business aspects to realize a competitive advantage and keep clients happy and satisfied. additionally, it also attracts new customers and a gaggle of loyal employees who are willing to partner with the corporate.
Planning Quality Management
The Quality Management Plan is a project management process that identifies the quality of the project requirements and standards, as well as the deliverable. He is also responsible for documenting how established standards and quality requirements are being met.
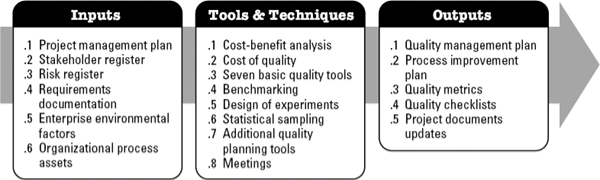
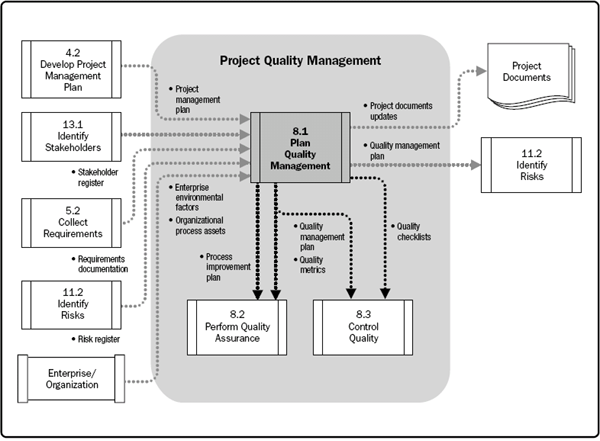
The advantage of this process is that it guides and directs how quality should be managed and validated throughout the project implementation. To create the Quality Management Plan, inputs such as the project management plan, the risk register, the requirements documentation, the stakeholder register, the assets of the organizational process and the environmental factors of the company are necessary. This project management process is important to make the standard management plan, quality metrics, and checklist. It can also lead to project document updates.
It is essential to note that quality planning must be done with other planning processes. For example, changes to deliverables may require cost and schedule adjustments, as well as risk analysis to show how the entire plan impacts. Quality planning is critical in project management and plan quality management ensures that everything is in place before the project is implemented.
Planning Communications Management Planning Communications Management is a project management process that participates in developing the necessary approach to:
- Quality control internal control involves activities that are wont to assess whether the merchandise or service meets the standard requirements that are specified for the
- Quality control measures the quality of a product, service or process should always be checked in project management. This is why
- Quality management plan the concept of quality management plan as it relates to the field of project management refers specifically to the input / output.
|
Figure 1
Plan Quality Management Inputs, Tools and Techniques and Outputs
|
Figure 2: Plan Quality Management Data Flow Diagram
Key takeaways
- When people use the word "Quality", it is generally synonymous with "good".
- Satisfy a set of inherent characteristics defined explicitly or implicitly.
- Provide products or service features that customers need. These characteristics lead to customer satisfaction and exceeding customer expectations, which, in turn, generates higher income for the producer.
- Ensuring continuous improvement (CI) to address root causes of defects that are inherent in processes, tools, and designs and that have significant impact.
- Quality is one of the most important principles of management.
- Maintaining the spheres of quality in each and every facet of the business helps the company attract loyal customers, maintain regular cash flows and beat the competition in the market.
- It is essential to note that quality planning must be done with other planning processes.
- The Quality Management Plan is a project management process that identifies the quality of the project requirements and standards, as well as the deliverable.
One of the foremost common mistakes most examinees make is to confuse between the 2 processes in Project Quality Management, that is, Perform Quality Assurance with Perform internal control. However, it's quite natural for us to form this error because the difference between the 2 processes is subtle. Unless an individual works during this field, it'll be difficult for them to know how these two processes work and what are the elemental differences between the 2 . The PMP certification exam has quite few questions supported these two processes and having an honest understanding of those processes could help us get the right answers to those questions.
Basics of quality management
Before taking a glance at these two processes, let's first understand some quality management concepts which will allow us to raised understand these two processes. they're "Prevention over inspection" and "DIRFT - catch on right the primary time." At the guts of those two concepts is that the concept everything we deliver must be delivered without errors from the beginning of the project. it's quite expensive to correct a bug later within the project. Now, how is it possible to make sure that our deliverables are error-free? the solution is simple: we've to place in situ the proper processes which will help us produce an error-free deliverable whenever a deliverable is produced. However, there'll always be some deviation from even the simplest processes. that's why we even have to implement some controls which will measure results in order that we will make the required adjustments.
Therefore, quality assurance is about processes that are wont to prevent any defects and internal control are the measures we've to detect and repair any remaining defects.
Let's now take a glance at each of those processes individually to raised understand them.
Perform quality assurance
Execution quality assurance is an execution process and is primarily concerned with overall process improvements to make sure that each time a product is produced, it's error-free. If the standard of processes and activities is improved, then the standard of the merchandise should also improve alongside an overall reduction in cost. Quality assurance starts very early and continues throughout the project life cycle. Since this process uses a number of the results of the plan's quality process, it's not done until after the standard plan is formed.
The quality audit may be a key tool utilized in this process. Quality audits allow us to review the project to assess which activities happening within the project got to be improved and which of them meet quality standards. Quality audits have a dual objective to enhance product acceptance and improve the general cost of quality.
The quality assurance department conducts these audits periodically as a part of the execution process by watching internal control measurements to ascertain if there's any indication that standards, policies, plans and procedures aren't being followed or that procedures aren't being followed. producing the expected results. quality results. This department also issues change requests, including notifications of areas that require preventive action, corrective action, and defect repair. additionally, to the present, the standard assurance department looks for project best practices or process improvements which will be used throughout the organization.
Perform internal control
Implementation internal control may be a monitoring and control process and analyses specific results to work out if they conform to quality standards. This process involves both the project and therefore the product deliverables and is administered throughout the project life cycle.
This process typically uses statistical sampling instead of analysing each and each result. There are many sampling techniques that are utilized in various industries and therefore the practice is usually very complex and tailored to every industry. the standard control process uses the inspection tool to make sure that the work results are what they're alleged to be. This process ensures that everything that's produced meets quality standards.
This process is completed beginning with the assembly of the primary deliverable and continues until all deliverables are accepted.
The quality control department measures project performance from the beginning of planning to the end of the project against standards, policies, plans and procedures. As a result of these measurements, the department also issues change requests, including notification of areas that need preventive action, corrective action, or defect repair.
Let's take a look at an example to better understand the two processes.
Example
Suppose we are manufacturing laptops. In Quality Control, we must implement all processes to ensure that each laptop is manufactured without defects. This would include the types of manufacturing equipment used, the training of people and the documentation of all production processes. Quality control comes into play after the fact testing the finished product. For example, we can do a sample test to see if a randomly selected laptop from our production line passes or fails to meet quality standards.
Key takeaways
- One of the foremost common mistakes most examinees make is to confuse between the 2 processes in Project Quality Management, that is, Perform Quality Assurance with Perform internal control.
- Before taking a glance at these two processes, let's first understand some quality management concepts which will allow us to raised understand these two processes.
- They're "Prevention over inspection" and "DIRFT - catch on right the primary time."
- Execution quality assurance is an execution process and is primarily concerned with overall process improvements to make sure that each time a product is produced, it's error-free.
- Implementation internal control may be a monitoring and control process and analyzes specific results to work out if they conform to quality standards.
- The quality control department measures project performance from the beginning of planning to the end of the project against standards, policies, plans and procedures.
The old seven "." the primary seven "." the essential seven ".
Quality professionals have many names for these seven basic quality tools, first highlighted by Kaoru Ishikawa, professor of engineering at the University of Tokyo and father of "quality circles." He begins his quality journey by mastering these tools, and he will have a reputation for them too: indispensable.
Cause and Effect Diagram (also called Ishikawa or Fishbone Diagrams): Identify many possible causes of an impact or problem and classify ideas into useful categories.
Check sheet: structured and ready form for collecting and analysing data; a generic tool which will be adapted for a good sort of purposes.
Control chart - A chart wont to study how a process changes over time. Comparison of current data with historical control limits results in conclusions about whether process variation is consistent (under control) or unpredictable (out of control, suffering from special causes of variation).
Histogram - the foremost commonly used graph to point out frequency distributions or the frequency with which each different value occurs during a data set.
Pareto chart: a bar graph showing which factors are most vital.
Scatterplot: Plots pairs of numerical data, one variable on each axis, to seek out a relationship.
Stratification: a way that separates collected data from a spread of sources in order that patterns are often seen (some lists replace stratification with a flowchart or execution diagram).
Do you want more quality tools?
- Q Tools TM Package
- Plan-Do-Study-Act
- Fishbone diagram
- Run table
- Pareto chart
- Flowchart
- Dispersion diagram
- Check sheet
Seven basic quality tools
These assist you start with the seven basic quality tools.
- Cause and effect diagram
- Check sheet
- Control table
- Histogram
- Pareto chart
- Dispersion diagram
- Stratification
Key takeaways
- Quality professionals have many names for these seven basic quality tools, first highlighted by Kaoru Ishikawa, professor of engineering at the University of Tokyo and father of "quality circles."
- He begins his quality journey by mastering these tools, and he will have a reputation for them too: indispensable.
The new management planning tools are defined as the methods to achieve the expected results that have not been used before.
In 1976, the Union of Japanese Scientists and Engineers (JUSE) saw a requirement for tools to market innovation, communicate information, and successfully plan large projects. A team researched and developed these seven new control tools, often called the seven management and planning tools, or simply the seven management tools:
Affinity diagram: organize a large number of ideas in their natural relationships.
Interrelation Diagram: Shows cause and effect relationships and helps analyze the natural links between different aspects of a posh situation.
Tree Diagram: Breaks down broad categories into ever finer levels of detail, helping to man ever step-by-step thinking from general to specific.
Matrix Diagram - Shows the connection between two, three, or four groups of data and may provide information about the connection, like its strength, the roles played by various individuals, or measures.
Array Data Analysis - A complex mathematical technique for analysing arrays, often replaced by a similar prioritization matrix. A prioritization matrix is an L-shaped matrix that uses pairwise comparisons of a list of options with a set of criteria to choose the best options.
Arrow Diagram - Shows the required order of tasks in a project or process, the best schedule for the entire project, and potential planning and resource problems and their solutions.
Process Decision Program Chart - Systematically identify what could go wrong in a developing plan.
Improving IT Project Quality
Quality matters! Quality separates the professional from the hobbyist and it takes commitment, focus, and sometimes courage, to take care of consistent project quality and deliver it on budget.
When you're delivering a multi-million-pound IT project, poor project quality can have profound effects, leading to rework, scheduling delays, higher costs, frustration, morale issues, and lack of customer satisfaction. So how are you ready to confirm that you simply maintain consistent project quality from start to finish?
1. Define quality
Quality is ambiguous, it can mean many things. for instance, the Project Management Body of knowledge (PMBOK) defines quality as "conformance with requirements and fitness for use", ISO 9000 defines quality as "the degree to which a group of inherent characteristics meet the wants ”.
Regardless of the sort or size of project you're managing, take the time to define the standard criteria for your current work in order that your team members understand what it's and the way to realize and improve it.
2. Commitment to quality
A company's commitment to quality must come from the highest and be repeatedly reinforced. Unless a corporation regards quality as its only non-negotiable goal, workers will inevitably feel the necessity to compromise and quality will slip.
As a manager or project leader, decide to quality, share the commitment alongside your staff, and believe how you'll handle any conflict between your stated goal and a beautiful shortcut that saves costs and compromises quality.
3. Meet the project requirements!
Once you've got defined the standard criteria and project requirements, stick with them! Balance continual project improvements with gold plate requirements. Adding features that the customer didn't request increases the likelihood of delays and increases the value. Project managers drive project quality and enhancements, but watch out for extras that are out of reach.
4. Manage quality
Work together with your project team to define a practical approach to managing quality, including applicable standards and quality processes. These are driven by its quality standards and processes contained within the project plan.
5. perform quality assurance
Execute your quality management plan using the standards and processes defined within the project plan. Perform a top-quality audit to assess how well the team is following the plan and meeting your client's expectations.
6. Check the standard
Make sure the deliverables are correct and freed from defects and specialise in quality from the start to the top of the project. Perform inspections to spot defects. start as soon as possible; Identifying and correcting defects near the purpose of origin saves time and money.
7. specialise in requirements
. Clear, well-defined requirements cause less rework and scheduling delays. specialise in improving the wants process - get them, analyze them, document them and validate them.
8. Follow the project processes
Follow the processes and tasks contained in your project plan. If you identify a more efficient thanks to do something, add it to the decide to continually improve processes.
9. Lessons learned
Document the teachings learned after the project phases and at the top of the project to assess your processes and "incorporate" all improvements at the project plan and translate them into future projects. this is often a part of your knowledge management strategy; you create a knowledge bank and use the teachings learned from the last project for brand spanking new and existing projects.
10. Project summary
The project brief is quite an off-the-cuff conversation about what worked and what didn't, but delves into why things happened (or didn't happen). a quick can sometimes be even as painful because the project itself, especially when your project has failed, and you would like to research where things went rather than rushing headlong to your next project, take the time for a comprehensive report with both your team and your client, in order that over time, you continually improve the standard consistency of your projects and deliver more of them. successfully.
Ways to take care of consistent project quality
- Define quality
- Commit to quality
- Meet project requirements
- Manage quality
- Perform quality assurance
- Control the standard
- Focus on requirements
- Follow the project processes
- Document the teachings learned
Key takeaways
- The new management planning tools are defined as the methods to achieve the expected results that have not been used before.
- A team researched and developed these seven new control tools, often called the seven management and planning tools, or simply the seven management tools
- Quality matters! Quality separates the professional from the hobbyist and it takes commitment, focus, and sometimes courage, to take care of consistent project quality and deliver it on budget.
References
- https://www.managementstudyguide.com/importance-of-quality-management.htm
- https://www.projectmanager.com/blog/project-quality-management-quick-guide
- https://www.projectengineer.net/knowledge-areas/project-quality/plan-quality-management/
- https://www.qualitymag.com/articles/95237-what-is-quality-management-and-why-does-it-matter
- https://www.altexsoft.com/whitepapers/quality-assurance-quality-control-and-testing-the-basics-of-software-quality-management/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/quality-assurance-program
- https://www.toolsqa.com/software-testing/istqb/quality-assurance-and-quality-control/
- https://plasticpipe.org/pdf/chapter-8_quality_control_quality_assurance.pdf
- https://www.brighthubpm.com/certification/72854-a-roundup-of-quality-control-tools-and-techniques/
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/315656326_Seven_Basic_Tools_of_Quality_Control_The_Appropriate_Techniques_for_Solving_Quality_Problems_in_the_Organizations