Unit 1
8085
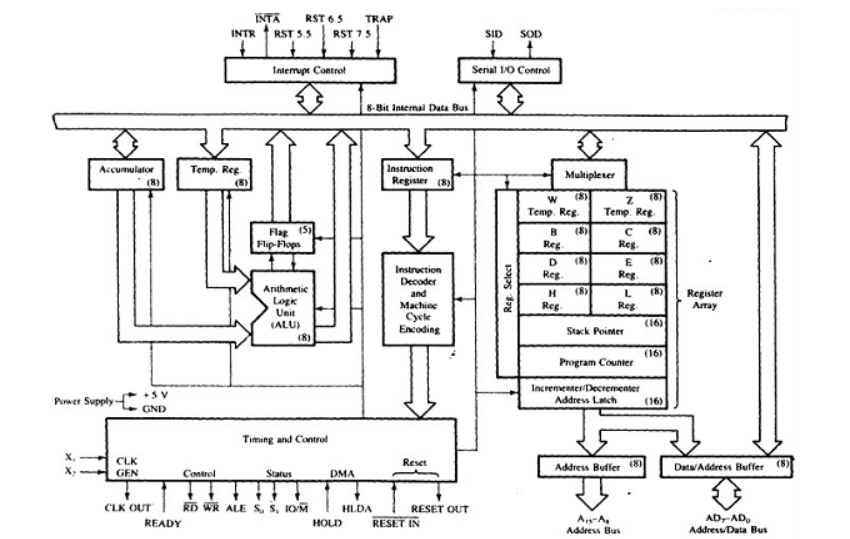
8085 consists of the following functional units −
Accumulator
The accumulator is an 8-bit register used to perform arithmetic, logical, I/O & LOAD/STORE operations. It is connected to internal data bus & ALU.
Arithmetic and logic unit
The arithmetic and logic unit performs arithmetic and logical operations like Addition, Subtraction, AND, OR, etc. on 8-bit data.
General purpose register
8085 consists of six general purpose registers in 8085 processor that is B, C, D, E, H & L. Each register holds 8-bit data. These registers work in pair to hold 16-bit data and their pairing combination is like B-C, D-E & H-L.
Program counter
It is a 16-bit register used to store the memory address location of the next instruction to be executed. Microprocessor increments the program whenever an instruction is being executed, so that the program counter points to the memory address of the next instruction that is going to be executed.
Stack pointer
It is 16-bit register which works like stack, which gets incremented/decremented by 2 during push & pop operations.
Temporary register
It is an 8-bit register, which holds the temporary data of arithmetic and logical operations.
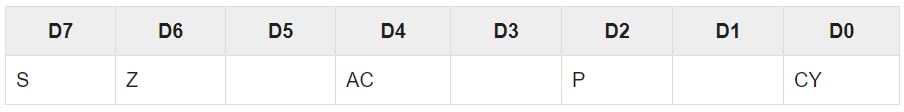
Flag register
It is an 8-bit register which holds 0 or 1 depending upon the result stored in the accumulator.
These are : −
Instruction register and decoder
It is an 8-bit register. When an instruction is fetched from memory then it is stored in the Instruction register. Instruction decoder decodes the information present in the Instruction register.
Timing and control unit
It provides timing and control signal to the microprocessor to perform operations. Following are the timing and control signals, which control external and internal circuits −
Interrupt control
It controls the interrupts during the process. When the microprocessor is executing the main program and whenever an interrupt occurs, the microprocessor shifts the control from the main program to process the incoming request. After the request is completed, the control returns to the main program.
There are 5 interrupt signals in 8085 microprocessors:
Serial Input/output control
It controls the serial data communication by using the two instructions: SID (Serial input data) and SOD (Serial output data).
Address buffer and address-data buffer
The content stored in the stack pointer and program counter is loaded into the address buffer and address-data buffer to communicate with the CPU.
The memory and I/O chips are connected to these buses, the CPU can exchange the desired data with the memory and I/O chips.
Address bus and data bus
Data bus carries the data to be stored. It is bidirectional whereas address bus carries the location to where it should be stored, and it is unidirectional. It is used to transfer the data & Address I/O devices.
The Classification of Instruction Set of 8085 is categorised into five different groups:
The data transfer instructions load the data into register:
Therefore, we can say that data transfer instructions copy data from source to destination. The source can be data or contents of register or contents of memory location whereas destination can be register or memory location. These instructions do not affect the flag register of the processor.
The arithmetic instructions perform addition, subtraction, increment and decrement operations.
Two registers cannot be added directly that is the contents of B and C registers cannot be added directly. To add two 16-bit numbers the 8085 provides DAD instruction. It adds the data within the register pair to the contents of the HL register pair and resulted sum is stored in the HL register pair.
Logical Operations:
The logical instructions perform logical, rotate, compare and complement operations.
Branching Operations:
These instructions allow the 8085 to change the sequence of the program, either unconditionally or under certain test conditions. These instructions include branch instructions, subroutine call and return instructions and restart instructions.
5.Stack, Input/Output and Machine Control Operations:
The input/output instruction allows the transfer of 8-bit data to input/output port. Machine instructions control the Machine operations such as interrupt, halt, or do nothing.
These instructions transfer data between registers or between memory and registers. The instruction is used to copy data from source to destination while copying the contents of source cannot be modified.
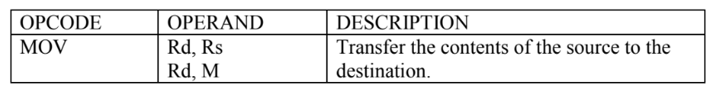
For example MOV B,C
MVI B,20H
LXI H, 4020H
LDA 6000H
Arithmetic Instructions
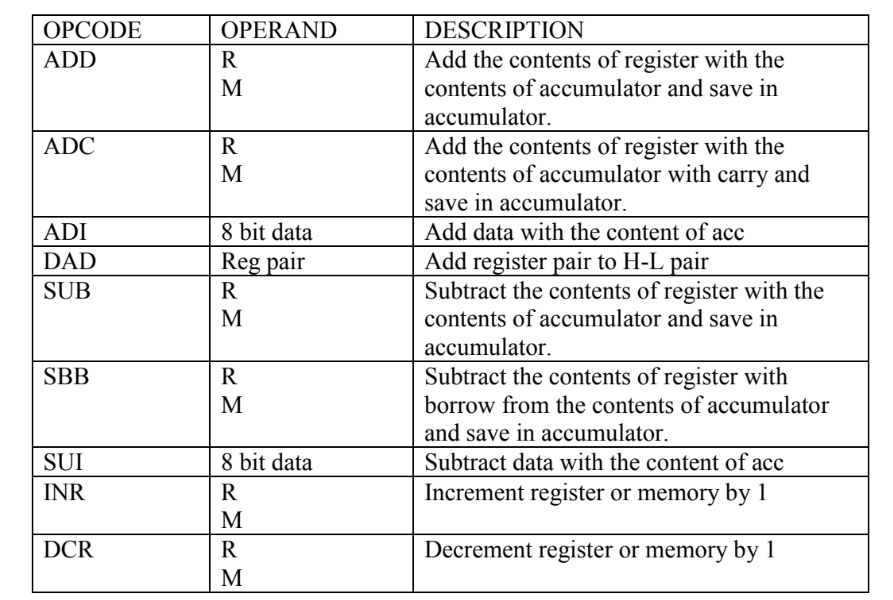
For example:
ADD C
ADC M
ADI 40H
DAD HL
SUB B
SUI 20H
INR C
Logical Instructions
The logical operations are:
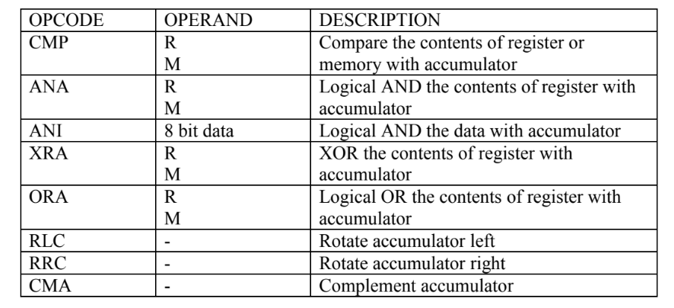
For example
CMP C
ANA B
ANI 40H
XRA M
ORA C
RLC
Branching Instructions
These instructions alter the normal sequential flow conditionally or unconditionally
OPCODE | OPERAND | DESCRIPTION |
JMP | 16-bit address | Jump unconditionally to the given location |
JC | 16-bit address | Jump if carry |
JNC | 16-bit address | Jump if no carry |
JZ | 16-bit address | Jump if zero |
JNZ | 16-bit address | Jump if no zero |
CALL | 16-bit address | Call unconditionaly |
RET | 16-bit address | Return unconditionally |
RST | 16-bit address | Restart (Software Interrupts) |
For example
JMP 2000H
RET
RST 6
Control Instructions
It controls the operation of microprocessor
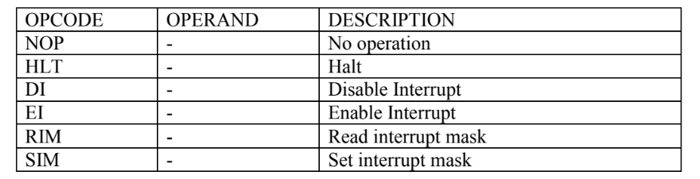
For example
NOP
EI
SIM
Initially it was N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor (NMOS) based microcontroller, but gradually versions were based on complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology. So, these microcontrollers were named as 80C51 where C it is based on CMOS technology.
It is an 8-bit microcontroller which means data bus is of 8-bits. Therefore, it can process 8-bits at a time. It is used in wide variety of embedded systems like robotics, remote controls, automotive industry, telecom applications, power tools etc.
8051 Microcontroller
System on a Chip :
It is also referred to as System on a Chip (SoC) microcontroller because it is a chip circuit/integrated circuit that holds many components of a computer together on a single chip which include CPU, memory, input output ports(I/O ports), timers and secondary storage.
Features –
Some of the features include:-
References
1. Microprocessor Architecture, Programming, and Applications with the 8085 Textbook by Ramesh S. Gaonkar
2. Microprocessor Book by A.P.Godse and D.A.Godse
3. Microprocessor And Microcontroller Book by A.P.Godse