UNIT-3
AC Circuits
Average Value:
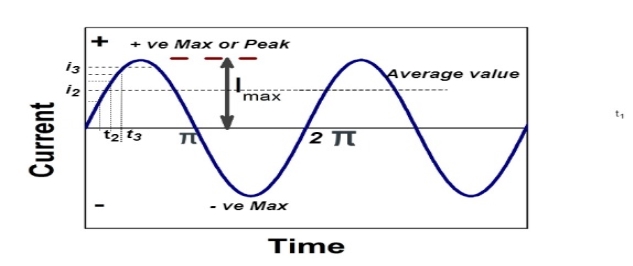
The arithmetic mean of all the value over complete one cycle is called as average value
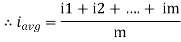
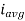 =
= 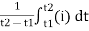
For the derivation we are considering only hall cycle.
Thus 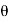 varies from 0 to ᴫ
varies from 0 to ᴫ
i = Im Sin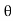
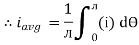
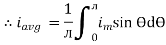
Solving
We get
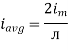
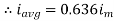
Similarly, Vavg=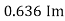
The average value of sinusoid ally varying alternating current is 0.636 times maximum value of alternating current.
RMS value: Root mean square value
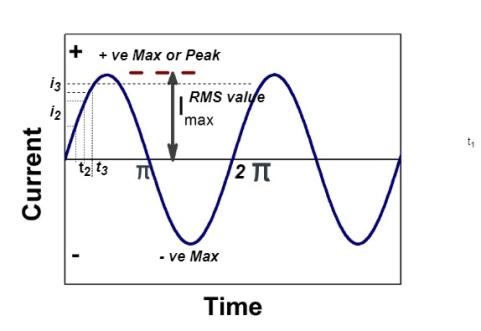
The RMS value of AC current is equal to the steady state DC current that required to produce the same amount of heat produced by ac current provided that resistance and time for which these currents flows are identical.
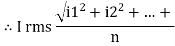
I rms = 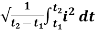
Direction for RMS value:
Instantaneous current equation is given by
i = Im Sin 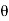
But 
I rms = 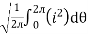
= 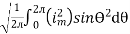
=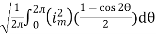
=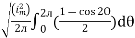
Solving
=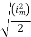
=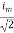
Similar we can derive
V rms= 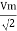 or 0.707 Vm
or 0.707 Vm
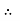 the RMS value of sinusoidally alternating current is 0.707 times the maximum value of alternating current.
the RMS value of sinusoidally alternating current is 0.707 times the maximum value of alternating current.
Form Factor:
Form Factor = 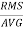
For sine wave form factor = 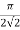
For an AC current waveform crest factor = Peak value of current/ rms value of current
For sine wave the crest factor = 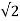
Reactance
- Inductive Reactance (XL)
It is opposition to the flow of an AC current offered by inductor.
XL = ω L But ω = 2 ᴫ F
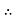 XL = 2 ᴫ F L
XL = 2 ᴫ F L
It is measured in ohm
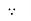 XL∝FInductor blocks AC supply and passes dc supply zero
XL∝FInductor blocks AC supply and passes dc supply zero
2. Capacitive Reactance (Xc)
It is opposition to the flow of ac current offered by capacitor
Xc = 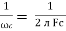
Measured in ohm
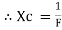 Capacitor offers infinite opposition to dc supply
Capacitor offers infinite opposition to dc supply 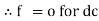
Impedance (Z)
The ac circuit is to always pure R pure L and pure C it well attains the combination of these elements. “The combination of R1 XL and XC is defined and called as impedance represented as
Z = R +i X
Ø = 0
 only magnitude
only magnitude
R = Resistance, i = denoted complex variable, X =Reactance XL or Xc
Polar Form
Z = 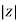 L I
L I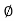
Where 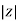 =
=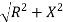
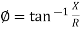 Measured in ohm
Measured in ohm
Admittance:
The reciprocal of impedance is admittance. Its unit is mho (siemens)
Y=  =
= 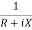
V=IZ
I=VY
Y= 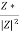 =
= 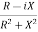
Y= G+iB
G= 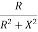
B= 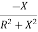
Real Power: [P]
It is nothing but the actual power being used in a circuit.
P=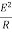 = I2R Watts
= I2R Watts
Reactive Power: [Q]
It is the function of reactance in the circuit X. Mainly reactive loads are inductor and capacitors. These elements dissipate zero power. These element shows that they dissipate power. This is called as reactive power.
Q=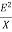 = I2X VAR (volt-Ampere-Reactive)
= I2X VAR (volt-Ampere-Reactive)
Apparent Power: [S]
It is the product of a circuit voltage and current without reference to phase angle. It is the combination of both reactive and real power.
S=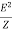 = I2Z VA (volt-Ampere)
= I2Z VA (volt-Ampere)
Power Triangle:
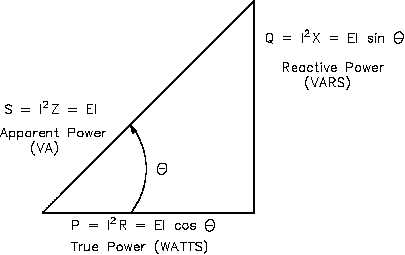
Cosφ= 
Sinφ = 
Tanφ= 
Definition: it is defined as the phenomenon which takes place in the series or parallel R-L-C circuit which leads to unity power factor
Voltage and current in R – L - C ckt. Are in phase with each other
Resonance is used in many communicate circuit such as radio receiver.
Resonance in series RLC series resonance in parallel RLC anti resonance / parallel resonance.
- Condition for resonance XL = XC
- Resonant frequency (Fr): for given values of R-L-C the inductive reactance XL become exactly equal to the capacitive reactance Xc only at one particular frequency. This frequency is called as resonant frequency and denoted by (fr)
- Expression for resonant frequency(fr): we know thet XL = 2ƛ FL - Inductive reactance
Xc = 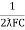 - capacitive reactance
- capacitive reactance
At a particular frequency ȴ = fr, the Inductive and capacitive reactance are exactly equal
 XL = XC ……at ȴ = fr
XL = XC ……at ȴ = fr
Ie 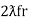 L =
L = 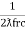
 fr2 =
fr2 = 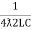
 fr =
fr = 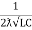 H2
H2
And 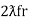 = wr =
= wr = 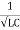 rad/sec
rad/sec
Quality factor / Q factor
The quality of resonance circuit is measured in terms of efficiency of L and C to stare energy and the efficiency of L and C to store energy as measured in terms of a factor called quality factor or Q factor it is expressed as
Q = 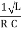 and Q =
and Q = 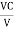
The sharpness of tuning of R-L-C series circuit or its selectivity is measured by value of Q. As the value of Q increases, sharpness of the curve also increases and the selectivity increases.
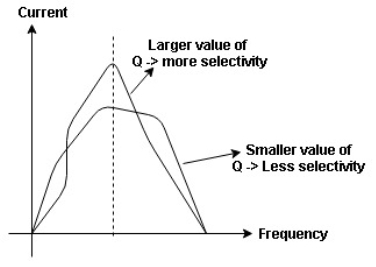
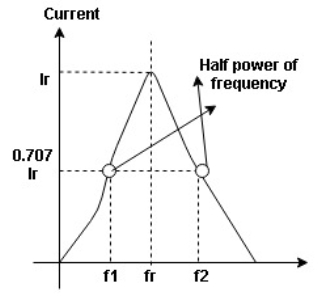
Bandwidth (BW) = f2 = b1
 and
and  are the frequency at which the power delivered to the resistor is reduced to 50% of the power delivered to it at resonance
are the frequency at which the power delivered to the resistor is reduced to 50% of the power delivered to it at resonance  these frequency are called as half power frequency
these frequency are called as half power frequency
Bw = fr/Q
Resonance in Parallel circuit:
When a coil is in parallel with a capacitor, as shown below. The circuit is said to be in resonance.
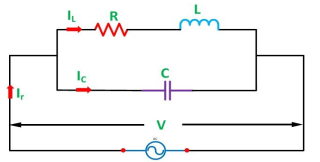
The resonant frequency for above circuit is fr = 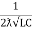 Hz
Hz
The current at resonance is I=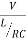
The value L/RC is known as dynamic impedance.
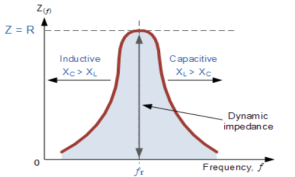
The current at resonance is minimum. The circuits admittance must be at its minimum and one of the characteristics of a parallel resonance circuit is that admittance is very low limiting the circuits current. Unlike the series resonance circuit, the resistor in a parallel resonance circuit has a damping effect on the circuit bandwidth making the circuit less selective.
Also, since the circuit current is constant for any value of impedance, Z, the voltage across a parallel resonance circuit will have the same shape as the total impedance and for a parallel circuit the voltage waveform is generally taken from across the capacitor.
Bandwidth and selectivity:
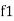 and
and 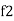 are the frequency at which the power delivered to the resistor is reduced to 50% of the power delivered to it at resonance
are the frequency at which the power delivered to the resistor is reduced to 50% of the power delivered to it at resonance  these frequency are called as half power frequency
these frequency are called as half power frequency
Bw = fr/Q
Q = 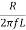 =
= 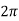 fCR = R
fCR = R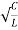
Resonant Frequency:
The resonant frequency for parallel resonant circuit is given as
fR= 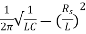
Where L= inductance of the coil
C = is the capacitance
Rs = Resistive value of coil.
Que) A coil takes a current of 6A when connected to 24V dc supply. To obtain the same current with 50HZ ac, the voltage required was 30V. Calculate inductance and p.f of coil?
Sol: The coil will offer only resistance to dc voltage and impedance to ac voltage
R =24/6 = 4ohm
Z= 30/6 = 5ohm
XL = 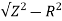
= 3ohm
Cosφ =  = 4/5 = 0.8 lagging
= 4/5 = 0.8 lagging
Que) The potential difference measured across a coil is 4.5V, when it carries a dc current of 8A. The same coil when carries ac current of 8A at 25Hz, the potential difference is 24V. Find current and power when supplied by 50V,50Hz supply?
Sol: R=V/I= 4.5/8 = 0.56ohm
At 25Hz, Z= V/I=24/8 =3ohms
XL = 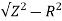
= 2.93ohm
XL = 2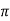 fL = 2
fL = 2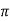 x 25x L = 2.93
x 25x L = 2.93
L=0.0187ohm
At 50Hz
XL = 2x3 =6ohm
Z = 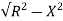 = 5.97ohm
= 5.97ohm
I= 50/5.97 = 8.37A
Power = I2R = 39.28W
Que) A coil having inductance of 50mH an resistance 10ohmis connected in series with a 25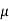 F capacitor across a 200V ac supply. Calculate resonant frequency and current flowing at resonance?
F capacitor across a 200V ac supply. Calculate resonant frequency and current flowing at resonance?
Sol: f0=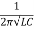 = 142.3Hz
= 142.3Hz
I0 = V/R = 200/10 = 20A
Que) A 15mH inductor is in series with a parallel combination of 80ohm resistor and 20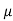 F capacitor. If the angular frequency of the applied voltage is 1000rad/s find admittance?
F capacitor. If the angular frequency of the applied voltage is 1000rad/s find admittance?
Sol: XL = 2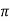 fL = 1000x15x10-3 = 15ohm
fL = 1000x15x10-3 = 15ohm
XL = 1/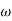 C = 50ohm
C = 50ohm
Impedance of parallel combination Z = 80||-j50 = 22.5-j36
Total impedance = j15+22.5-j36 = 22.5-j21
Admittance Y= 1/Z = 0.023-j0.022 siemens
Que) A circuit connected to a 100V, 50 Hz supply takes 0.8A at a p.f of 0.3 lagging. Calculate the resistance and inductance of the circuit when connected in series and parallel?
Sol: For series Z =100/0.8 = 125ohm
Cosφ = 
R = 0.3 x 125 = 37.5ohm
XL = 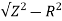 = 119.2ohm
= 119.2ohm
XL = 2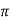 fL = 2
fL = 2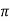 x 50x L
x 50x L
119.2 = 2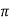 x 50x L
x 50x L
L= 0.38H
For parallel:
Active component of current = 0.8 cosφ = 0.3x0.3 = 0.24A
R = 100/0.24 =416.7ohm
Quadrature component of current = 0.8 sinφ = 0.763
XL= 100/0.763 = 131.06ohm
L= 100/0.763x2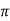 x50 = 0.417H
x50 = 0.417H