UNIT II
Planning and Strategic Planning
|
Just as management is a never-ending activity, so is planning. In fact, business planning is one of the main functions of management. It sets the stage for all subsequent management functions like organizing, leading, etc. Let's understand the concept of planning.
We already know what planning is, it is deciding in advance what to do. It is the basis for all future plans of the organization. Planning bridges the gap between where the organization currently is and where it wants to be.
So, in essence, business planning comprises setting goals for the organization and developing an idea of action to realize these goals. Once goals are set, managers and workers can have a clear vision of what to work towards.
Managers are a very important part of the business planning function. Planning requires innovation, creativity, and multitasking on the part of managers. And planning is a function that managers at all levels must perform, that is, upper, middle and lower management.
Planning is one among the foremost important and essential functions of management. It is an activity that managers at all levels must carry out. So, depending on the level of management, the type of plan will be different. Let's look at the different types of management plans.
Plan types
Planning is a ubiquitous management function; it has an extensive scope. So, all managers at all levels participate in planning. However, the plans made by the higher-level manager will be different from those made by the lower managers.
Plans also differ in what they seek to achieve and the methods that will be used to achieve them. So, let's look at the types of plans managers are faced with.
Goals
This is the first step in planning the organization's action plan. Goals are the foundation of any business and the desired goal / outcome that the business plans to achieve, thus they are the end point of all planning activity.
For example, one of the goals of an organization might be to increase sales by 20%. The manager will then plan all the activities of the organization with this ultimate goal in mind. When framing your organization's goals, a few points should be kept in mind.
- Goals should be framed for a single activity in mind.
- They must be results oriented. The objective must not frame any action
- The objectives must not be vague, they must be quantitative and measurable.
- They should not be unrealistic. The objectives must be achievable.
Strategy
Obviously, this is the next type of plan, the next step that follows the objectives. A strategy is a complete and comprehensive plan to achieve these objectives. A strategy may be a plan that has three specific dimensions
Set long-term goals
Select a specific course of action
Allocate the necessary resources for the plan.
The training strategy is generally reserved for the top level of management. In fact, it defines all future decisions and the long-term scope and general direction of the company.
Politics
Policies are generic statements, which are basically a guide to channel energies towards a specific strategy. It is the general way for an organization to understand, interpret and implement strategies. Like for example, most companies have a return policy or a hiring policy or a pricing policy, etc.
Policies are set at all levels of management, from primary policies at the highest level to secondary policies. Managers must formulate policies to assist employees navigate a situation with predetermined decisions. They also help employees make decisions in unexpected situations.
Procedure
Procedures are the following types of plans. They are a step-by-step guide to the routine to perform the activities. All employees must follow these staggered sequences so that activities can be carried out in an organized manner.
The procedures are described in chronological order. So, when employees follow the instructions in order and completely, the success of the activity is practically guaranteed.
Take, for example, the procedure for admitting a student to a university. The procedure begins with the completion of an application form. It will be followed by a collection of documents and the classification of applications accordingly.
Rules
Rules are very specific statements that define an action or a non-action. Also, the rules do not allow any flexibility, they are final. All employees of the organization must follow and enforce the rules. Not following the rules can have serious consequences.
The rules create an environment of discipline in the organization. They guide the actions and behaviour of all employees in the organization. The "no smoking" rule is an example.
Program
Programs are a detailed statement that describes policies, rules, objectives, procedures, etc. of a company. These programs are important in the implementation of all kinds of plans. They create a link between the objectives, procedures and rules of the company.
Primary programs are conducted at the top level of management. To support the primary program, all managers will undertake other programs at the middle and lower levels of management.
Methods
The methods prescribe the ways in which the specific tasks of a procedure must be performed. Additionally, the methods are very specific and detailed instructions on how employees should perform each task in the planned procedure. So, managers form methods to formalize routine jobs.
Methods are very important types of plans for an organization. They help in the following ways
- Give clear instructions to employees, eliminate any confusion
- Ensures uniformity in employee actions
- Standardize routine jobs
- It acts as a general guide for employees and managers.
Budget
A budget is a statement of the expected results that managers expect from the company. Budgets are also a significant statement, so they are expressed in mathematical terms. A budget quantifies the prognosis or future of the organization.
There are several means to prepare budgets that managers make. There is the obvious financial budget, which forecasts the profit of the company. Then there are the operating budgets generally prepared by lower-level managers. Cash budgets control the cash inflows and outflows of the business.
Importance of business planning
Planning is an important function of management; it tells the manager where the organization should go. It also helps the organization reduce uncertainty. Let's take a look at some important planning functions.
1] Planning provides a sense of direction
Planning means drawing up a predetermined plan of action for the organization. Actually, it establishes in advance what and how the work should be done. This helps provide workers and managers with a sense of direction, a guide in some way. Without planning, your actions would be uncoordinated and disorganized.
2] Planning reduces uncertainty
Planning not only sets goals, but also anticipates any future changes in the industry or organization. So, it allows managers to prepare for these changes and allows them to deal with uncertainties. Planning takes into account past events and trends and prepares managers for any uncertain events.
3] Planning reduces waste
The detailed plans made take into account the needs of all departments. This ensures that all departments are in tune with the plan and that all their activities are coordinated. There is clarity in thought that leads to clarity in action. All work is done without interruptions or loss of time or resources,
4] Planning invokes innovation
Planning actually involves a lot of innovation on the part of managers. Being the first management function is a very difficult activity. It encourages the manager to broaden his horizons and forces him to think differently. That is why managers must be creative, insightful and innovative.
5] Make decisions = Facilitate
In business planning, the objectives of the organization have been set, an action plan has been developed and predictions have even been made for future events. This makes it easy for all managers at all levels to make decisions with some ease. The decision-making process also becomes faster.
6] Sets standards
Once business planning is done, managers have now established goals and standards. This provides the manager's standards against which he can measure actual performance. This will help the organization to measure whether the objectives have been met or not. Therefore, planning is a prerequisite for control.
Planning limitations
While business planning is mandatory and a need for every organization, it has some restrictions. Let's take a look at some of it:
1] Stiffness
Once the planning function is completed and the action plan is established, the manager tends to just follow the plan. The manager may not be in a position to change the plan depending on the circumstances. Or the manager may not be willing to change the plan. This type of rigidity is not ideal for an organization.
2] Not ideal in dynamic conditions micas
In an economic environment, something is rarely stagnant or static. Economic, political, environmental and legal conditions continue to change. In such a dynamic environment, it becomes difficult to predict future changes. And if a manager cannot forecast accurately, the plan can fail.
3] Planning can also reduce creativity.
While making a plan requires creativity, managers blindly follow the plan. They don't change the plan according to the dynamic nature of the business. Sometimes they don't even make the right suggestions to top management. Work becomes routine.
4] Planning is expensive
Planning is an expensive process. Because it is an intellectual and creative process, it is necessary to hire specialized professionals for the job. Also, it involves a lot of research and data collection and number processing. At times, the cost of the planning process can outweigh its benefits.
5] Not completely accurate
When planning, we have to predict the upcoming and forecast certain future events in the organization and the industry. So, of course, there cannot be one hundred percent certainty in such cases. So, it can be said that business planning lacks precision.

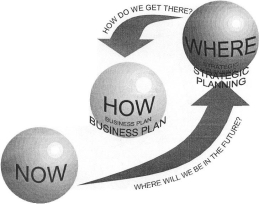
Everything you would like to understand about strategic planning. Strategic planning means planning strategies and implementing them to realize the objectives of the organization.
Start by asking yourself simple questions like: What are we doing? Should we keep doing it or change our line or the way we work? what's the impact of social, political, technological and other factors on our operations? Are we prepared to simply accept these changes, etc.?
Strategic planning helps to understand what we are and where we would like to travel in order that environmental threats and opportunities are often taken advantage of, given the strengths and weaknesses of the organization.
Strategic planning may be a systematic and formally documented process for deciding what few key decisions a corporation, viewed as a company whole, must make correctly so as to prosper within the years to return.
Strategic planning - Meaning
Strategic planning means planning strategies and implementing them to realize the objectives of the organization. Start by asking yourself simple questions like: What are we doing? Should we keep doing it or change our line or the way we work? what's the impact of social, political, technological and other factors on our operations? Are we able to accept these changes, etc.?
Strategic planning helps to understand what we are and where we would like to travel in order that environmental threats and opportunities are often taken advantage of, given the strengths and weaknesses of the organization.
Strategic planning is that the formalization of designing during which plans are remodelled long periods of your time for the effective and efficient achievement of the organization's objectives. Strategic planning is predicated on an in depth environmental scan. it's a projection of environmental threats and opportunities and an attempt to mix them with the strengths and weaknesses of the organization.
While long-term planning might not be fully equipped to soak up environmental impacts, strategic planning is completed to know, anticipate, and absorb environmental vagaries. Strategic planning is an ongoing process. Whenever business organizations want to realize a better rate of growth or change their operations, they need a far better management data system, they coordinate the activities of various departments, they eliminate complacency of organizations; they create strategic plans.
Planning are some things we do before taking action; that’s, it's an anticipated decision-making. it's a process of deciding what to try to and the way to try to it before action is required.
The strategic plan of the corporate is that the start line for planning. It is a guide for the event of solid sub-plans to realize organizational objectives. The goal of strategic planning is to assist a corporation select and organize its businesses during a way that keeps it healthy despite unexpected changes within the environment. it's intended to shape or reshape the company's businesses and products to supply targeted growth and profit.
An interesting question which will come to mind is how conventional long-term planning gave thanks to strategic planning. Before the primary 1970s, managers who made long-term plans generally assumed that plans for the long run were simply extensions of what the organization had exhausted the past.
However, environmental shocks during the 1970s and 1980s, like energy crises, deregulation of the many industries, accelerating technological change, and increasing global competition undermined this approach to long-term planning.
These changes within the "rules of the game" forced managers to develop a scientific approach to analysing the environment, assessing the strengths and weaknesses of their organization, and identifying opportunities where the organization could have a competitive advantage. As a result, the worth d was recognized
Strategic planning concept:
Planning is related to the future. A planning process implies different degrees of future.
Some parts of the organization require planning for many years into the future, while others require planning only for a short period.
For example, capital spending is related to a long-term period, while a year's budget is short-term in nature. The first is called strategic planning or long-term planning.
"Strategic planning" can be defined as the process of determining the organization's objectives and the resources that will be used to achieve these objectives, as well as the policies that guide the investment use, and arrangement of these resources.
Examples of strategic planning in an organization are: business diversification into new lines, planned growth rate in sales, type of products to be offered, etc. Strategic planning encompasses all functional areas of the business and is affected within the existing and long-term. framework of economic, technological, social and political factors.
It also involves the analysis of various environmental factors, particularly with regard to how an organization relates to its environment. Generally, for most organizations, the strategic planning period varies between three and five years.
Strategic planning process:
The strategic planning process consists of the subsequent steps:
1. Determination of mission and objectives:
Strategic planning begins with determining the mission of the organization. The main objectives for which the organization has been created must be clearly defined. Strategic planning deals with the long-term relationship of an organization with its external environment. Then, the business mission must be set in terms of the social impact of the organization.
2. Environmental analysis:
To identify opportunities and threats, the external environment of the organization is analyzed. A list of important factors that can affect the activities of the organization is prepared.
3. Self-assessment:
In the next step, the strengths and weaknesses of the organization are analyzed. This analysis will allow the company to capitalize on its strengths and minimize its weaknesses. The company can use external opportunities by focusing on its internal capacity. By combining its strengths with environmental opportunities, a company can face competition and achieve growth.
4. Strategic decision making:
Then strategic alternatives are generated and evaluated. After that, a strategic decision is made to reduce the performance gap. The organization must select the alternative that best suits its capabilities. For example, to grow, a company may enter new markets or develop new products or sell more in current markets.
The choice of strategy depends on the external environment, the perception of management, the attitude of management towards risk, past strategies and the power and efficiency of management.
5. Implementation and control of the strategy:
Once the strategy is decided, it must be translated into tactical operational plans. Programs and budgets are developed for each function. Control must be developed to evaluate performance as the strategy is implemented.
Whenever actual results are below expectations, the strategy should be reviewed or re-evaluated. It must be modified and adapted to changes within the external environment.
Importance of strategic planning:
Strategic planning offers the subsequent benefits:
1. Economic benefits:
Companies that make strategic plans have good sales, low costs, high EPS (earnings per share) and high profits. Companies have economic benefits if they create strategic plans. Companies like Reliance, Infosys, Tata, Wipro, Deloitte, etc. they're the giants that report good financial results as a results of sound strategic planning.
2. Guide to organizational activities:
Strategic planning guides members toward organizational goals. Unify organizational activities and efforts toward long-term goals. Guide members to become who they need to become and to try to what they need to try to. It focuses on specific goals that make it clear to members during which direction to maneuver. Making a profit is a smaller amount significant than getting a rate of growth of 10% per annum.
Paying high dividends is a smaller amount significant than paying dividends at a 40% rate. Meeting the requirements of society is a smaller amount meaningful than providing free education to schoolchildren during a specific community. Resource allocation and attempts to realize objectives are facilitated by clear specifications in strategic planning. It makes the objectives operational and provides the proper direction to the activities of the organization.
3. Competitive advantage:
In the world of globalization, companies that have a competitive advantage (ability to deal with competitive forces) have better financial and sales results. this is often possible if you foresee the longer term. the longer term is often predicted through strategic planning. It enables managers to anticipate problems before they arise and resolve them before they worsen.
4. Minimize risk:
Strategic planning provides knowledge to evaluate risk and frame strategies to attenuate risk and invest in safe business opportunities. the probabilities of creating mistakes and selecting the incorrect goals and methods are therefore reduced.
Risk is inherent altogether businesses and it's almost certain that not anticipating risk through strategic planning will cause business failure, unless proven otherwise accidentally. Business companies operating during a dynamic, changing, and risky environment cannot deal with a scarcity of strategy, the incorrect strategy development, or ineffective strategy implementation.
5. Beneficial for companies with an extended gestation gap:
The time span between investment decisions and therefore the generation of income from those investments is named the gestation. During this era, changes in technological or political forces can affect the implementation of selections and plans can therefore fail. Strategic planning discounts the longer term and allows managers to face threats and opportunities. Big amount of money is required in projects followed by expected financial returns.
6. Promotes motivation and innovation:
Strategic planning involves managers at the very best levels. Not only are they committed to goals and methods, but they also come up with new ideas for strategy implementation. This promotes motivation and innovation. It also provides motivation to lower-level people once they know that their efforts are contributing to the organization's goals.
The satisfied workforce is that the strength of the organization. Save huge costs in reducing absenteeism, job turnover, role conflicts, etc. It promotes discipline within the organization and improves the effectiveness of human resources and also organizational effectiveness.
7. Optimal use of resources:
Strategic planning makes better use of resources to realize maximum performance. Resources are scarce and strategic planning helps to use them where they're needed most.
If your grand strategy is correct, any number of tactical mistakes are often made, and yet the corporate succeeds.
Limitations of strategic planning:
- Lack of knowledge:
Strategic planning requires tons of data, training and knowledge. Managers must have high conceptual skills and skills to form strategic plans. If they are doing not have the knowledge and skill to organize strategic plans, the specified results won't be achieved. it'll also end in huge financial losses for the organization. This limitation is often overcome by training managers to form strategic plans.
2. Interdependence of units:
If business units at different levels (corporate level, business level, and functional level) aren't coordinated, it can create problems for the effective implementation of strategic plans.
3. Managerial perception:
To avoid developing risky goals and methods that they will not be ready to achieve, managers can land on sub-optimal goals and plans. Sometimes short-term commitments also defer long-term strategy development.
4. Financial considerations:
Strategic planning requires an excellent deal of your time, money, and energy. Managers are often constrained by these considerations when making effective strategic plans. These limitations are generally conceptual and may be overcome through rational, systematic and scientific planning. Researchers have shown that companies that make strategic plans outperform people who don't.
5. Exchange problems:
The factor acts more as a limiting think about light of changes in future conditions. during a complex and rapidly changing environment, the succession of latest problems is usually magnified by implications that make planning difficult. the matter of change is more complex in long-term planning.
Current conditions tend to weigh heavily on planning and, by overshadowing future needs, can sometimes cause errors in judgment. Factors like changing technology, consumer tastes and needs, business conditions, and lots of others change rapidly and sometimes in unpredictable ways. Under such conditions, the design activities administered in one period might not be relevant for an additional period because the conditions in two periods are quite different.
6. Failure of people:
There are many reasons why people fail to plan, both at the formulation and implementation levels. a number of the foremost important failures are the shortage of commitment to planning, the shortage of development, solid strategies, the shortage of clear and meaningful objectives, the tendency to overlook the premises of designing , the lack to ascertain the scope of the plan, inability to ascertain planning as a rational approach, over-reliance on past experience, failure to use limiting factor principles, lack of support from top management, lack of delegation of authority, lack of control techniques adequate and resistance to vary .
These factors are liable for improper planning or incorrect planning within the organizations in question.
- Time and cost:
When browsing the strategic planning process, managers must also consider both time and price factors. the varied steps of designing can go as far as possible because there's no limit to precision in planning tools. But planning is suffering from time and price factors.
Time may be a limiting factor for all managers within the organization and if they're busy preparing elaborate reports and directions beyond a particular level, they're risking their effectiveness. Excessive time spent securing information and trying to suit it into a compact plan is dysfunctional within the organization.
2. Stiffness:
Often people feel that planning provides rigidity in management action. many sorts of internal inflexibilities are often the results of planning itself. Planning stifles initiative from employees and forces managers to adopt a rigid or straitjacket mode of performing their work. In fact, rigidity can make management work harder than necessary. this will end in lag in job performance, lack of initiative, and failure to adapt to the changing environment.
Many people feel that planning has limited value because the simplest results are often obtained by confusing the kinds of operations during which each situation is addressed when and if it seems relevant to the immediate problem. Although this planning rigidity factor may be a limiting factor, but without planning, it's really difficult to work particularly in large organizations.
Planning also involves costs on a part of the organization. the varied factors discussed above contribute to the restrictions of strategic planning, either by making planning ineffective or by making planned work less.

|
Reliance Jio SWOT Analysis
Reliance Jio Info COMM Limited or Jio as it is popularly known as a mobile network service based on LTE technology owned by Reliance Industries. The Navi Mumbai-based company offers 4G wireless network services and has the merit of being the only VoLTE operator in India today. The network covers the entire of India and is that the largest internet service provider within the country. Reliance Jio first launched its services in 2015 and began trading in September 2016. The company currently has a gross revenue of 108.9 million in the 2016-17 year.
Strengths in Reliance Jio's SWOT Analysis:
Strengths are defined as what each company does best in its range of operations, which can give you an edge over your competitors. The following are Reliance Jio's strengths:
- Strongest Customer Acquisition Strategy - Reliance Jio probably has the simplest customer acquisition strategy so far. The brand offered its services free of charge for 3-6 months to all its users. This resulted in millions of users using Reliance Jio and resulted in one of the best customer acquisition strategies in the history of telecommunications.
- Strong customer base: Jio boasts a whopping 100 million subscribers in the first 170 days of its launch, a record that no other provider has been able to record. This has also made Reliance Jio the largest Internet Service Provider in India.
- Technology: Jio currently uses the newest 4G LTE technology, which is one among the world's best technologies for the longer term. This supports Voice over LTE, which makes it scalable and compatible with 5G and 6G technologies that they are expected to be the future of wireless communication.
- Strong backing from parent company Reliance Industries: Reliance Industries may be a credible brand that echoes Indian sentiments and has great trust among customers. Jio's association with Reliance acts as a central strength.
- Brand Management - The rationale for Reliance Jio's huge customer base is that the brand management strategies it's adopted. The right promotion backed by lucrative offerings and credible brand ambassadors like Sharukh Khan and Amitabh Bachchan have helped create customer connectivity.
- Fast and extensive network: Reliance Jio has a presence in all 22 Indian telecommunication circles and is known for being a robust and fast network with no connectivity problems.
- Multiple offers with one name: Reliance Jio offer a variety of services such as movies, games, shopping, chat and messaging, etc., giving the customer many options to choose from.
WEAKNESSES IN THE Reliance SWOT ANALYSIS
Weaknesses are wont to ask areas where the business or brand needs improvement. Some of Reliance Jio's key weaknesses are:
- Late market entry: Reliance Jio has made a late market foray that had already established players like Airtel and Vodafone who had taken a place in the customer's mind.
- Activation issues: Reliance Jio faced numerous gestation issues because it was unable to contain the large volumes of consumers it had acquired. In such a case, there were delays in the activation of the SIM card during the period following its launch.
- Price controversies - Reliance Jio was criticized for having lowered its prices beyond the ethical to penetrate the market and this led to accusations such as corruption and money laundering against it.
- Too many gifts: Reliance Jio currently offers many services for free and this was one of the reasons for the increased share of sales. However, the business may not be able to pay for all of them in the long run, which can negatively affect the business.
- Poor data connection - Data connection is often poor from Reliance Jio and the range is lower, causing slower upload speeds in select regions.
Opportunities for Reliance Jio SWOT Analysis: Opportunities for Reliance Jio SWOT Analysis:
Opportunities refer to those avenues in the environment surrounding the business that you can capitalize on to increase your returns. Some of the opportunities include:
- Future-driven technology: Reliance Jio uses the VoLTE 4G network that is scalable to adapt.
- 5g and 6G technologies. This offers numerous avenues for Jio or future bandwidth expansion.
- Applications: Reliance Jio has VoLTE which has great reach in terms of bandwidth. Therefore, they can offer applications to customers that are paid or even free initially and pay for use later.
- Competitive costing plan Reliance Jio pleasures itself on being a low-cost Internet service provider and mobile operator. This can be used as a positioning to target more markets and increase your market share, as most of your competitors cannot afford your prices.
- Expansion to other countries: Currently, Reliance Jio is only operational in India. However, there is plenty of room for expansion to foreign countries, at least in neighbouring regions.
Threats in Reliance Jio's SWOT Analysis:
Threats are those factors in the environment that can be detrimental to the growth of the company. Some of the threats include:
- Customer Loss Risk: Customers prefer Jio primarily because of the low prices they offer. At a stage where the company increases its price, there may be a loss of customers.
- Elimination of free services: Jio is currently associated with a large number of gifts. Once they are removed, there may be a drop in sales for the business.
- Criticism and negative image: Reliance Jio have been involved in many controversies from the moment it was started. These have resulted during a negative brand image for the corporate.
- Poor Code of Ethics: Many of the strategies adopted by Reliance Jio, such as low prices, free bandwidth, and go-to-market strategies, have been shown to be unethical and this may affect the goodwill of the company. long-term.
What is SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) may be a framework won’t to assess the competitive position of a corporation and to develop strategic planning. The SWOT analysis assesses internal and external factors, also as current and future potential.
It is meant to provide a practical, fact-based, and data-driven check out the strengths and weaknesses of a corporation, its initiatives, or an industry. The organization must maintain accurate analysis by avoiding preconceived beliefs or gray areas and instead that specialize in real world contexts. Companies should use it as a guide and not necessarily as a recipe.
Understanding SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a technique for evaluating the performance, competition, risk, and potential of a business, as well as part of a business, such as a product line or division, industry, or other entity.
Using internal and external data, a SWOT analysis can tell a corporation where it must improve internally, also as help develop strategic plans.
Using internal and external data, the technique can guide companies toward strategies that are more likely to achieve success, and faraway from those during which they need been or are likely to be less successful.
SWOT matrix.
Analysts present a SWOT analysis as a square with each of the four areas that make up a quadrant. This visual layout provides a quick overview of the company's position. Although all the points of a particular title may not be of equal importance, they should all represent key ideas about the balance of opportunities and threats, advantages and disadvantages, etc.
SWOT analysis was used for the first time to analyze companies.
SWOT analysis example
In 2015, a SWOT analysis of The Coca-Cola Company's Value Line highlighted strengths such as its world-famous brand, extensive distribution network, and opportunities in emerging markets. However, it is also seen that lack and warning like foreign currency change growing public interest in "healthy" beverages, and competition from suppliers of healthy beverages.
Their SWOT analysis led Value Line to ask some tough questions about Coca-Cola's strategy, but also to point out that the company "will likely continue to be a premier beverage provider" that increased safe lender "a reliable source of knowledge. income and a little capital gains exposure. "
- Strengths describe how an organization excels and what distinguishes it from the competition: a strong brand, or A loyal customer base, a strong balance sheet, unique technology, etc. For example, a hedge fund may have developed its own business strategy that delivers outperforming results. Then you must decide how to use those results to attract new investors.
- Weaknesses prevent an organization from functioning at its optimum level. These are areas in which the company needs to improve to remain competitive: a weak brand, an above-average turnover, high levels of debt, an inadequate supply
- Opportunities ask favourable external factors that would give a corporation a competitive advantage. for instance, if a rustic reduces tariffs, an automaker can export its cars to a replacement market, increasing sales and market share.
- Threats ask factors that have the potential to harm a corporation. for instance, a drought may be a threat to a wheat producing company, because it can destroy or reduce crop yields. Other common threats include things like rising material costs, increased competition, labor shortages, etc.
Advantages of SWOT analysis
A SWOT analysis may be a good way to guide business strategy meetings. it's powerful to possess everyone within the room to debate the core strengths and weaknesses of the corporate then advance from there to define the opportunities and threats, and eventually to brainstorm. Often times, the SWOT analysis you imagine before the session changes to reflect factors that you simply weren't conscious of and would never have captured if it weren't for the group's opinion.
A company can use a SWOT for general business strategy sessions or for a selected segment, like marketing, production, or sales. This way, you'll see how the general strategy developed from the SWOT analysis will trickle right down to subsequent segments before you plan to it. you'll also add reverse with a segment specific SWOT analysis that feeds into a general SWOT analysis.
Internal and external factors
The four elements above are common to all or any SWOT analyzes. However, many firms further categorise these elements into two distinct subgroups: internal and external.
Generally, strengths and weaknesses are considered internal factors, as they're the results of organizational decisions under the control of your company or team.
|
Similarly, emerging competitors would be classified as a threat during a SWOT analysis, but since there's little or no you'll do about it, this makes it an external factor. this is often the rationale why you'll have seen SWOT analyzes called internal-external analyzes or IE matrices.
Importance:
SWOT analysis not only deals with making just four lists, it's far more than that.
The following points highlight its importance:
1. The SWOT analysis reveals whether the corporate is healthy or sick.
2. a corporation involves know both internal and external factors that affect its success or failure.
3. Helps in forming a technique to organize for potential threats from competitors.
4. SWOT analysis assesses the business environment intimately to form strategic decisions for the longer-term course of action.
In India, the importance of SWOT analysis has increased even more since 1991, that is, after the adoption of the LPQ (Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization) policy.
Now there's double competition for our own business concerns.
Internally, competition has increased thanks to liberalization and privatization. Telecommunications, insurance, banks, and lots of other sectors have now opened to the private sector. thanks to globalization, many multinational companies have come to India and that they are giving stiff competition to Indian companies. only one concern that creates your SWOT analysis survive. Globalization is a chance because our entrepreneurs can now go abroad and sell their products. it's a threat because our internal market is often captured by multinationals if we don't produce quality products.
Concepts of SWOT/TOWS/WOTS-UP
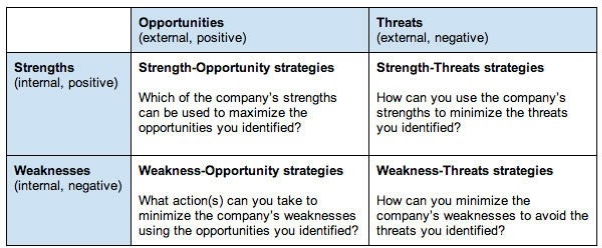
A TOWS analysis could also be a variant of a SWOT analysis and is an acronym for Threats, Opportunities, Weaknesses, and Strengths.
TOWS analysis is same as Swot which is engaged with the identification of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of an organization; however, often a key criticism of a SWOT analysis is that it does not show the relationships between the different factors and categories. For example, a particular threat can make a weakness much more significant. Whereas a TOWS analysis will seek to match internal factors with external factors to assist identify the relevant strategic options that a corporation could pursue. It can help an organization see how it can take advantage of opportunities, reduce threats, overcome weaknesses, and rest on strengths.
A TOWS may be a commonly used strategic planning tool and may add real value to a corporation, helping to require strategic planning one step further. Below is an example TOWS matrix.
Let's dive a little deeper into this.
A TOWS analysis allows a corporation to match its internal strengths and external opportunities (SO) to develop "maxi-maxi" strategies, those with the best potential for fulfilment. For example, strengths like high brand recognition or customer loyalty could be combined with the opportunity to launch a new product or service.
For example, such strategies could include developing strategic alliances or a more drastic strategy might be to withdraw from a selected market altogether.
In between, mini-maxi (WO) and maxi-mini (ST) strategies are designed to strengthen weaknesses, seize opportunities, and minimize threats using strengths. An example of a mini-maxi (WO) strategy is that a corporation may have identified a chance to outsource some aspects of its business operations, overcoming the weakness of the lack of specific skills within the organization.
It is important to remember that a TOWS analysis won't pinpoint which specific strategy to adopt, but it'll focus attention on the areas where action is required and provides some indication of the nature of that action.

Indian business environment: Concept, Components and Importance
|
Concept of business environment
You can start a business, but you need financial resources, such as finance, that you have to rely on financial institutions to succeed. Acceptance of social norms that must depend on society. Appropriate market conditions that must depend on the market. Sale of products / services that must be customer dependent. Labor that must depend on society.
Then there are natural resources and raw materials, which must depend on nature. Also, government legal support that must depend on the government. There are many factors and aspects that affect the business environment. These factors are many different components of a single concept called the business environment.
These business-dependent factors aren't stopped, they're very dynamic and constantly changing. For example, the trend, the Fidget Spinner trend, has provided the greatest impetus for the silicone mold industry to date.
The changing needs of customers and new innovations in the market are part of the business environment. The challenge for companies in this tech era is not to enter the market, but to survive in the market. Surviving the market means adapting to change as soon as possible. Adapting to change means being aware of the business environment.
Meaning of business environment
The power to compose a business environment is its suppliers, competitors, consumer groups, media, governments, customers, economic conditions, market conditions, investors, technologies, trends, and several other institutions operating outside the business. Makes up the business environment. These forces affect your business, even when it's outside the boundaries of your business.
For example, government tax changes can reduce customer purchases. Here, businesses need to reestablish prices to survive change. The business was not involved in initiating the change, but had to adapt to the change in order to survive or take advantage of profitable opportunities. Now let's talk about the importance of the business environment.
Importance of business environment
From the above, it can be said that the business environment is the most important aspect of any business. Recognizing ongoing changes not only helps businesses adapt to these changes, but also helps them use them as opportunities.
The business environment poses threats and opportunities for any business. A good business manager not only identifies and evaluates the environment, but also responds to these external forces. Considering the following facts, you can understand the importance of the business environment.
1. You can identify business opportunities
Not all changes are negative. If you understand and evaluate them, they can be the reason for your business's success. It is very necessary to identify change and use it as a tool to solve business and population problems.
For example, Phanindra Sama was plagued by ticket reservations in India. He used to travel long distances to travel agencies to book tickets, but even after traveling this distance, he wasn't sure if his seat was confirmed. He saw the opportunity to establish an app in the face of problems and co-founded an online ticket booking app called "redBus".
2. Helps to utilize useful resources
Careful scanning of your business environment can help you leverage the useful resources your business needs. This helps businesses track these resources and convert them into goods and services.
3. Dealing with change
Businesses need to be aware of the ongoing changes in their business environment, including changing customer requirements, new trends, new government policies, and technological changes. If your business is aware of these regular changes, you can provide a response to address those changes.
For example, when the Android OS market blossomed and customers began to prefer Android devices with simple interfaces and apps, Nokia couldn't keep up with the changes by not implementing Android OS on Nokia devices. They did not adapt and lost tremendous market price .
4. Planning support
Solve the problem or take the opportunity. After analyzing the changes presented, the business can incorporate plans to counter the changes for a safe future.
5. Helps improve performance
Companies that scan the environment thoroughly not only address the changes presented, but also thrive with them. Adapting to external forces helps businesses improve performance and survive in the market.
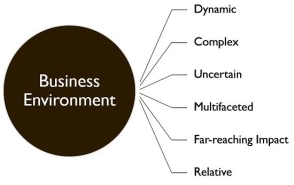
Characteristics of business environment:
|
(A) Overall external force
The business environment includes everything outside the organization.
When all these forces are applied, a business environment is formed.
Example: When Pepsi and Coca-Cola got permission to start a business in India, it was an opportunity for them and a threat to local manufacturers such as Goldspot and Camp Cola.
(B) Certain general forces
A specific force is a force that directly influences the operating activities of a company.
Examples: suppliers, customers, investors, competitors, finance personnel, etc.
General power is the power that indirectly influences the functioning of a company.
Examples: economic, social, political, legal and technical conditions.
(C) Mutual relationship
The various forces of the business environment are interrelated.
One component of the business environment affects the functionality of the other.
Example: Increased people's life expectancy and health consciousness are driving the demand for diet coke, olive oil and many other health products.
(D) Dynamic nature
The business environment is dynamic in nature and continues to change in the following ways:
(A) Technical improvement,
(B) Changes in consumer preferences,
(C) Entering new competition into the market.
Example: Many established companies in the FMCG (Fast-moving Consumer Goods) sector are focusing on producing products using natural ingredients in their "Patanjali Products" entry.
(E) Uncertainty
Due to future uncertainties, changes in the business environment cannot be accurately predicted.
It is very difficult to predict changes in the economic and social environment.
Example: The entry of many new companies has caused the price of Android smartphones to drop significantly.
(F) Complexity
All the forces of a business environment are interrelated and dynamic and difficult to understand.
The complex nature of the business environment can be understood with partial research.
Example: Raising the Goods and Services Tax to 15% increases government revenue (economic), improves people's social existence (social), reduces rich personal disposable income, and thereby inflation Helps to control.
(G) Theory of relativity
The business environment varies by location, region, and country.
Example: In China, as electricity consumption increases, electricity to the industry is provided at a lower price, which leads to mass production, but in India, high electricity consumption results in expensive electricity and production decreases. To do. The production cost will be high.
Planning purely means what to do in the future. When the business environment presents problems and opportunities, it is up to the business to decide what plans need to be devised to address the future.
Components of Business Environment
|
Andrews also correctly defines the company's environment as a pattern of all external influences that affect the life and development of the company. Keith Davis also states that the business environment is a collection of all the conditions, events and impacts that surround and influence it.
The business environment is constantly changing and uncertain. For this reason, the business environment is said to be the sum of all factors outside the control of the company's management. These factors are constantly changing and involve both opportunities and risks, or uncertainties. Undermine the future of business.
Some of the components of the business environment are: ---
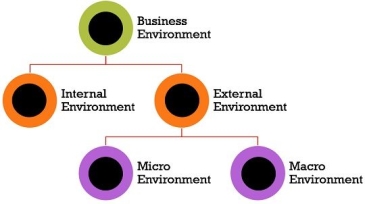
A. Internal environment – 1. Financial ability 2. Marketing ability 3. Operational ability 4. Human resources ability 5. General management ability
B. External environment – 1. Micro environment 2. Macro environment.
In addition, you will learn about other components of the business environment:
1. Economic environment 2. Technical environment 3. Social environment 4. Demographic environment 5. Political and legal environment 6. Global environment.
Business environment components: internal and external environment
Business Environment Components – Two Key Components: Internal and External
Component # 1. Internal environment:
This refers to all factors within an organization that affect the functioning of the organization. These factors are generally considered controllable. That is, the organization can change or change such factors.
Some of the important internal factors are:
I. Financial capacity:
Financial capacity factors relate to all relevant aspects related to the availability of funds, usage, management, and the capacity of an organization and its ability to implement its strategy.
Some of the key factors that affect an organization's financial strength are:
(A) Related to funding sources such as capital structure, capital raising, financing patterns, working capital availability, borrowing, capital and credit availability, reserves and surpluses, relationships with banks and financial institutions Factor.
(B) Factors related to the use of funds such as capital investment, acquisition of fixed assets, current assets, loans, distribution of dividends and relationships with shareholders.
(C) Factors related to cash management such as financial accounting and budgeting, business management systems, financial position, cash, inflation, credit, returns and risk management, cost reduction and management, tax planning and management.
II. Marketing ability:
Marketing capability factors relate to the ability to price, promote, distribute, and implement organizational strategies for a product or service and all relevant aspects related to that capability.
Some of these key factors that influence this marketing ability of an organization are:
(A) Product-related factors such as variety, differentiation, mixed quality, and positioning package.
(B) Price-related factors such as pricing objectives, policies, changes and protection benefits.
(C) Promotion-related elements such as sales promotion tools, sales promotion, advertising, and public relations.
(D) Integrated and systematic elements such as marketing mix, distribution system, market position, corporate image, marketing organization, marketing system, marketing management, information system.
III. Operational capacity:
Operational capacity factors relate to all relevant aspects related to the production of a product or service, the use of critical resources, and the ability of an organization to implement its capabilities and strategies.
Some of these key factors that influence this marketing ability of an organization are:
(A) Product-related factors such as variety, differentiation, mixed quality, and positioning package.
(B) Price-related factors such as pricing objectives, policies, changes and protection benefits.
c) Promotional elements such as promotional tools, promotions, advertising and public relations.
(D) Integrated and systematic elements such as marketing mix, distribution system, market position, corporate image, marketing organization, marketing system, marketing management, information system.
IV. Personnel ability:
The HR capacity factor is related to the existence and use of human resources and skills, and all relevant aspects related to the ability and ability to implement an organization's strategy.
Some of the key factors that affect an organization's human capabilities are:
(A) Factors related to the HR system, such as systems for selection, development, compensation, communication and evaluation of personnel plans, the location of HR departments within the organization, procedures and standards.
(B) Factors related to organizational and employee characteristics, such as corporate image, quality of managers, staff and workers, awareness of the employer's organizational image, availability of employee development opportunities, and working conditions.
(C) Factors related to labor relations such as trade unions – management relations, collective bargaining, safety, welfare and safety, employee satisfaction and morale, etc.
General management functions:
V. General management functions relate to the integration, coordination, and direction of functional functions towards a common goal and all relevant aspects related to the ability of an organization to implement its strategy.
Some of the key factors that affect an organization's general management capabilities are:
(A) General such as strategic management system, mission-related process, purpose and purpose setting, strategy formulation and implementation mechanism, strategic evaluation system, management information system, corporate planning system, top manager compensation and incentive system, etc. Elements related to the management system, etc.
(B) Factors related to general managers such as orientation and risk — trends, values, norms, personal goals, abilities, work abilities, achievements, balance of functional experience, etc.
Component # 2. External environment:
The external environment consists of all the factors that provide an opportunity or pose a threat to an organization. In a broad sense, the external environment includes various factors such as the international economy, the domestic economy, and the regional economy. Social change, demographic variables, political systems, technology, business attitudes, energy sources, raw materials, other resources, and many other macro-level factors make up the external environment.
Such a wide range of environmental awareness can be called a general environment. All organizations are somehow interested in the general environment, but their immediate concerns are limited to some of the common environments that may be referred to as relevant environments. , Organizations can focus their attention. About those factors that are closely related to their mission, purpose, purpose and strategy.
I. Micro environment: Micro external factors have a significant impact on a company's business operations. However, not all microfactors have the same impact on all companies in the industry. For example, suppliers, a key component of the micro-level environment, are often willing to offer materials to large companies at relatively low prices. They do not have the same attitude towards small businesses relatively.
Here are some important micro elements of the business environment.
a) Customers:
The main task of any business is to attract and retain customers. This is to ensure unique long-term profitability and market presence. Therefore, it is necessary to closely monitor the needs and desires of customers to ensure their joy. This will increase the number of loyal customers in the company.
Customer preferences and changes in preferences need to be predicted in advance, not just observed when they occur. The company also needs to make the necessary modifications to the product / service profile. Customers are the backbone of the company and that's exactly why the company exists.
b) Product:
Product elements such as demand, image, function, utility, function, design, life cycle, price, promotion, distribution, differentiation, and availability of alternatives to products and services also form a close part of the business environment. I will. Product / service functionality is the key to attracting / retaining customers.
c) Marketing broker:
This includes all people who promote the distribution of goods from production bases to various consumption bases. These are the intermediaries that form part of the distribution channel and those who help deliver the product / service to the ultimate consumer. The number can be small or large, depending on the length of the distribution chain and the type of distribution system your company employs. If this chain is hassle-free and works without many hurdles, it ultimately helps the organization.
d) Competitors:
The world has become a global market. There is fierce competition in every field. There are other entities that manufacture similar products and compete with the company for market share and sales. These need to be managed properly and market intelligence is needed to find future plans. These can play a major role in building or damaging the property of any company.
e) Supplier:
A key element in the microenvironment is the supplier, the supplier that supplies the company with raw materials, components, and machinery. Supplier must be reliable, act as a business partner, and work together to meet the ultimate consumer expectations. If the supplier is reliable, there is no need to hold large inventories that increase the risk of obsolescence or damage and block the company's working capital.
II. Macro environment:
A macro environment is a larger, uncontrollable environment composed of social forces that affect all other environments. They offer tremendous opportunities for any business and present threats that can be of great harm to the business. This environment is very important for understanding and studying for strategic planning and decision-making purposes.
It has a wider dimension than the micro environment. It consists of individuals, groups, institutions, events, conditions, and forces that the organization frequently contacts in the course of its functioning. The macro environment is, in fact, a real environmental factor that has the greatest impact on the growth and structure of any business.
It consists of the following components:
a) Sociocultural environment:
It consists of the society and culture of the place where the organization operates. This is a common entity and affects almost every enterprise in a similar way. Some of the key factors and impacts of working in the social environment are all factors that influence people's buying and consuming habits, their language, beliefs and values, habits and traditions, tastes and preferences, education and business.
These factors are:
- Demographic characteristics such as population, density and distribution.
- Social concerns such as the role of business in society.
- Social attitudes and values such as social expectations from business.
- Family structure
- Education level
- Awareness and work ethic
- Beliefs and values
- Local festival
b) Political environment:
The political environment consists of factors related to the management of public relations and the impact of the organization on its business. The political environment is closely related to the economic system and economic policy. For example, communist countries have a centrally planned economic system. Apart from the laws governing investment and related matters, most countries have many laws that regulate the conduct of their businesses. These laws cover matters such as product standards, packaging and promotions.
India is a democratic country with a stable political system, and the government plays an active role as a planner, promoter and regulator of economic activities. Therefore, businessmen are aware of the political environment facing the organization. Most business-related government decisions are based on political considerations in line with the political philosophy followed by the central and state-level ruling parties.
Some aspects of the political environment are:
I. General state of political development
II. Degree of politicization of business and economic issues
III. Political moral level
IV. Situation of law and order
V. Political stability
VI. Ruling party political ideology and practices
c) Economic environment:
The economic environment consists of macro-level patterns related to the areas of wealth production and distribution that affect an organization's business.
Some of the key factors and implications that work in the economic environment are:
I. An economic stage that exists at a particular time in a country.
II. Adopted economic structures such as capitalism, socialism and mixed economy.
III. Economic plan such as 5-year plan and annual budget.
IV. Economic policies such as industry, finance and fiscal policy.
V. Economic indicators such as national income, income distribution, GNP growth and growth rate, per capita income, disposable personal income, savings rate, investment, import / export value, balance of payments.
VI. Infrastructure factors such as financial institutions, banks, transportation, telecommunications equipment, and energy sources.
Below are some examples that emphasize the role of the economic environment.
1) Economic liberalization since the last 20 years has had various impacts on Indian industry. While most companies have the advantage of being able to freely change the composition and capacity of their products, they have also had some negative impacts in the areas of capacity overcapacity and intensifying competition.
With the partial deregulation of cement in 1982, production capacity and the resulting supply increased rapidly, and market conditions changed from severe shortage to a comfortable surplus. The liberalization of imports led to intensified competition in the capital goods industry, reducing profits and, as a result, many companies were unable to sustain their businesses.
2) India's public savings have traditionally been invested in fixed assets and precious metals. Shares of savings invested in the government have been carried through post offices and banks. But lately, investors are increasingly looking at other means such as stock markets and company deposits.
Recent changes in economic and fiscal policy have made many important developments. Entry into equity trading by leasing and finance companies, bonds, mutual funds, venture capital businesses, new financial products, banks and financial institutions is part of the development that provides resources for capital markets and project finance.
d) Regulatory environment:
The regulatory environment consists of factors related to the planning, promotion and regulation of government economic activities that affect an organization's business.
Some of the key factors and implications of operating in a regulated environment are:
I. Constitutional framework, principles of directive, basic rights, and distribution of legislative rights between the central and state governments.
II. Policies related to license monopoly, foreign investment and industrial finance.
III. Policies related to distribution and pricing and their management.
IV. Policies related to imports and exports.
V. Public sector, small industry, disease industry, rear area development, pollution control, and other policies related to customer protection.
Business and industry operate in a regulated environment. The relationship between the industry and the regulatory environment exists as a two-way process. The government has established policies, procedures, and rules for the industry to function.
There are many administrative controls over the business that are exercised through regulatory mechanisms.
Some of the important areas of management are:
1) Industrial policy and licenses;
2) Monopoly and restrictive trade practices.
3) Laws related to the operation of the company.
4) Import / export control and foreign exchange control.
5) Management of foreign investment and cooperation.
6) Management by consumer protection. And
7) Management of environmental pollution
e) Technical environment:
The technical environment consists of applied knowledge and elements related to the materials and machines used to produce goods and services that affect an organization's business. For many companies, technology is the most dynamic of all environmental factors. Individual companies are interested in their products and process technologies. This environment is made up of factors that accompany all sorts of technological advances or their lack.
Some of the specific factors that can be explained are:
I. Technology sources such as corporate sources, external sources, foreign sources.
II. Technology development, stage of change in development, rate of change in technology, research and development.
III. The impact of technology on the environment of humans, human mechanical systems, and technology.
IV. Communication and infrastructure technology and management technology.
V. Technical obsolescence.
In the Indian context, we can see that the state of technological development varies between different sectors of the industry. It is generally believed that the technical aspects of competition depend on customer needs and government policies.
f) Demographic environment:
This environment deals with the composition and characteristics of the place's population. All relevant descriptions of the location's population with respect to its demographic profile have a dramatic impact on business decisions. It is beneficial for any company to consider these aspects in detail before planning a strategy.
It includes elements such as:
- Average number of family members
- Population size
- Education level
- Economic stratification of population
- Job profile and income level
- Gender composition of the population
- Average life
- Religion, caste, customs and traditions
- Spatial mobility of population
Business Environment Components – Economic, Technical, Social, Demographic and Minority
The general environment of an organization is made up of key factors such as economic, technical, social, demographic, political, legal, and global power. These have positive, neutral and negative impacts on your business. Professor Alex Miller and Professor Gregory Dess describe this well under the title "Strategic Management."
Component # 1. Economic environment:
It is macroeconomic indicators that strategists study to influence their decisions. These indicators shape the health and well-being of the economy. These are determinants of a company's ability to make a profit and generate wealth. More important is the maximization of wealth, as it means maximizing profits and returning them to investments that generate more income.
The components of the economic environment are:
I. General economic situation:
The general economic situation that prevails in the economy is a determinant of economic prosperity and community well-being. These economic conditions are variables in which the amount of national income, per capita income, economic resources, income and wealth distribution, and economic development determine people's economic prosperity.
Revenue and its distribution determine the business outlook and therefore the business strategy. In an economy where it is low and per capita is relatively low, demand will decline. This pessimistic situation does not attract business people who invest in and execute manufacturing and marketing activities.
On the other hand, in an economy where the income of the economy is increasing, it leads to more and more investment and entry into industrial and marketing activities. In India, the backbone of the Indian economy, the Middle, is ready to increase income and invest in business.
Even NRI considers it beneficial to invest surplus income in this way, helping the Indian economy to become stronger and thus benefit from profits.
II. Economic system:
The economy is an arrangement that encourages the use of free resources to generate and distribute income, based on some accepted economic philosophies. Economy around the world is widely linked to Kabbalism, socialism, and communism as a hybrid economy called a pure variety or mixed economy.
India is the best example of a mixed economy, with the benefits of capitalism and socialism in one focus, eliminating the disadvantages of pure socialism or capitalism.
Capitalism gives maximum economic freedom in the management of economic activity, socialism talks about maximum domination by the state, mixed economy is freedom and the role of the state in which both the public and private sectors support each other. I have.
The collapse of the mighty nation formed in the early 20th century had to kick a bucket for a period of 100 years. Today, the Soviet Union is divided into small nations that were one of the greatest forces in the world linked to socialist ideology.
III. Economic policy:
It is the appropriate and timely economic policies adopted and implemented by the government that determine the fate of the state and its citizens. Think about India before 1991 and now. The Indian economy is on the verge of collapse and foreign exchange reserves were enough to pull another eight days.
It was a change in personality as a political leader and the brain behind them, together they freed India from control and opened the Indian economy to the whole world.
Private and public sector businesses that worked under the umbrella of protection were set up and faced the challenge of changing competition. Which foreign companies couldn't replace them as Indian players became global players?
IV. Economic growth:
Economic growth or development is the rise and maintenance of per capita income for all individuals who are members of the economy. It is economic growth, which represents increased consumer spending and lower pressure in the industrial sector, that provides more opportunities and enables businesses to withstand the severity of the threat. Other methods also apply. Declining economic growth and lower consumer spending will increase pressure and reduce profitability.
V. Interest rate:
Interest rates affect the demand for goods and services in the economy when they are purchased through borrowing. If interest rates are low, the demand for the product may be durable or non-durable. This gives Philip to a growing industry.
The opposite is true if the rate is high. Today, R.B.I is emerging at lowest interest rates to increase demand for durable and non-durable consumer goods, which will bring the Indian economy out of pessimism and tomorrow's rut.
The cost of capital also depends on interest rates. When they are getting capital at the lowest rates, the companies will encourage all companies to have ambitious plans and strategies in the case of borrowed funds.
VI. Exchange rate:
Exchange rates represent currency conversions to other currencies. It may be hard or soft. In 1991, the Indian Rupee was devalued to make Indian products cheaper in the global market to boost Indian exports. This was a great opportunity for all Indian exporters to export more commodities and reserves and earn forex.
Today, foreign exchange reserves are at a record high of Rs 200 billion, at least costly to boost quality production. Indian exporters do so only if they regularly understand and implement three strategies for export cost, export quality, and export volume. Therefore, it is the exchange rate that determines the fate of a country.
Component # 2. Technical environment:
The rapid development of technology has a strong impact on all organizations, not just those operating in high-tech environments such as microprocessor manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and fiber optic technology. The combined impact of computers, digital technology, and telecommunications affects most private and public sector businesses.
As J. Shunpeter, as rightly called by everyone else, it is the "permanent gate of creative destruction." Technology change is a creative and destructive process in that it is responsible for building new things by destroying old ones. Therefore, the core of progress is destruction.
This means that destruction and construction are not contradictory and provide complementary opportunities and threats. In an era of rapidly changing technology, the secret to success is triangular strategy. That is, managers need to anticipate, innovate, and excel to be successful.
Companies that do not do so will be thrown away. When an American boxer took over Muhammad Ali, he said: Ali, you are the best, but I am the latest. We have to learn from Japanese. Before the war, "Made in Japan" was a sign that no one bought it because the product was the cheapest but the quality was the lowest.
However, today, Japanese products are completely quality conscious, "zero defects", "automobiles" or "zips", "made in Japan", so there is a great demand. It talks about their ability to predict, innovate and excel. The Japanese are the best copy cuts and can innovate and excel others. Today, of the 2000 Toyota cars, 700 land daily on the soil of America, the great power of the United States.
The strategic impact of technology changes was successfully brought about in the fall of 1982, in the article "The Emergence of Technology Portfolios" by Russian thinker Basis Petrov.
(I) It may change the relative competitive cost position within the business.
(II) Can create new markets and new business segments
(III) By reducing or eliminating segment barriers, previously independent businesses can be disrupted or consolidated.
New ideas, new products, new processes New methodologies are the result of technological change. That means that changing the order offers many opportunities for threats. That's why it pays off when strategists are constantly monitoring the technology kingdom and its impact on the company and its activities.
Component # 3. Social environment:
The social environment is the socio-cultural environment. The socio-cultural environment is made up of a system of values, and the attitudes, beliefs, desires, expectations, aspirations, customs and customs of society change accordingly, and there are many opportunities and threats to the business operated for society. This socio-cultural environment covers aspects of society and its components.
For a business house, it means:
(I) Expectations from the business community for society
(II) Social attitudes towards business and its management
(III) View on job achievement
(Iv) Perspectives on authority structure, responsibilities and organizational position
(V) Views on customs, traditions and customs
(VI) Class structure and labor movement
(VII) Level of education.
These socio-cultural environmental factors affect organizations in three ways:
(I) Organizational goal setting,
(II) Organizational processes and
(III) Products and services provided by the organization.
The changes that occur in society due to the changes in accepted values are right for the members of society. Therefore, what a particular age group wears, eats and entertains is determined by cultural values. Today, everyone is aware of a particular lifestyle based on social norms. The outlook on life is that life is short — enjoy it at any cost.
As a result, more and more people are thinking about traveling to faraway places. Another thing is to get rich with simple money and storms. This has led the community to rely on lottery tickets, horse racing, betting and more. This also led to antisocial activity.
Today, kidnapping and hijacking are very common for getting loot. These activities have created a demand for products and services that facilitate these activities. Countering these has also provided services and products that provide self-defense.
Women's whereabouts are no longer limited to the kitchen. They are more educated and occupy reserved positions for men because they have an equal share. This meant that they didn't have time to prepare meals to care for their children. In this way, fast food habits are revealed, the services of domestic servants are increasing, and more and more families are seeking washing machines and entertainment on small screens.
The younger generation has the freedom of video surfing, nightclub participation, expensive and high quality clothing, shoes, deodorants and toiletries. Mobile, mobike and car are the needs of these young people. Similarly, older people look younger and want to be younger, which helps maintain their hair color and health. Nowadays, people are becoming more health conscious.
With this special attention and caution, they seek mineral water, preventative medications, preventive health checks, and dietary changes. Therefore, high cholesterol is a major cause of coronary artery disease. That's why people are looking for double or table refined cooking oils that consume too little. They avoid lean meat and choose white meat, that is, chicken and fish such as beef, mutton and pork.
Recently, social awareness has been increasing. Social issues such as pollution, social responsibility of businesses, and worker safety and welfare are becoming more prominent. The social demands placed on the business community as a social responsibility are increasing. Did this affect what the business house produces? What kind of process do you adopt? How will the product be packed? And so on.
Fully effective consumerism is responsible (responsible for the enactment of MRTP and consumer protection laws. Consumerism has influenced standards of technology, product quality, marketing activities and after-sales service. This is all about the business community producing and selling products and services that are determined by socio-cultural values.
Component # 4. Demographic environment:
Demographic characteristics deal with populations such as family size, fertility rate, growth rate, age structure, family size, education level, language, caste, income level, earners and non-earners. The demand for goods and services depends on those demands, the demand is the potential or real market, and the market means the real and potential consumers.
There is a positive relationship between population growth and demand for goods and services. Lower fertility has a direct or indirect impact on products and services for infants.
If the population is made up of older people than young people, they are in high demand for preventative and therapeutic medical services, medicines, awakening sticks, hair color, etc. If you have a lot of young people, you will need everything from convenience goods, specialty goods, and shopping goods by consumer segment.
Dislikes, style movements, fashion, and their part-time or full-time income.
These changes in population offer many opportunities and pose challenging threats as well. The availability of skilled and cheap workforce, and the increasing demand for consumer goods and services, may allow multinationals to invest in new activities.
Consumers in different countries may prefer "Made in India" products, where Indian companies have a cost advantage. It attracts foreign investment, which leads to optimal use of national resources and increased imports and exports.
Population change cannot be underestimated in many ways that provide good opportunities to pose a threat on the same path. It is up to the business house to form strategies for success and implement them to embrace these opportunities by effectively handling threats.
Component # 5. Political and legal environment:
The political and legal environment is, of course, called the regulatory environment. National, state and local governments play a constructive role as citizen administrators. To protect and promote the interests of citizens, they rely on regulatory activities that can be undertaken through constitutional provisions, government policy and industrial law.
As for the constitutional provisions of India, the Constitution of India was passed by the Constituent Assembly in 1949. Constitutional provisions provide guidelines for central and state governments to control and regulate socio-economic policies.
The provisions of the Constitution are divided into "basic rights" and "directive principles." Basic rights are set out in Articles 15, 16, 19, 23, and 24. Article 15 prohibits discrimination against citizens on the grounds of religion, race, caste, gender, or place of birth. Article 16 describes equal opportunity for all citizens in public employment, savings and the provision of settlements by the state.
Article 19 states that all citizens have the right to practice any profession, profession, trade or business. Article 23 describes the right to human exploitation and transportation. Article 24 provides for the prohibition of child labor under the age of 14 in factories, mines or dangerous work. Directive principles are principles and laws that can be enforced by a court.
These serve as guidelines for these governments and businesses. The main ones are:
(I) Promotion of people's welfare.
(Ii) Minimize income inequality and eliminate inequality in status facilities and citizens' opportunities.
(Iii) Secure appropriate means of livelihood for citizens.
(Iv) Equal amount of money paid to both men and women for equal work
(V) Providing fair and human working conditions and relieving childbirth
(Vi) Ensuring wages and working conditions to provide an appropriate standard of living.
(Vii) Participation in worker management.
(Viii) Proper distribution of ownership and management of natural resources to prevent the concentration of a small number of wealth and instead serve the public interest of the community.
When it comes to government policy, these are based on industrial resolutions. Industrial resolutions embody government policy in power. Government policy is both positive and negative in the approach. Policy frameworks and implementations provide four roles: regulation, publicity, entrepreneurship, and planners.
The "regulatory role" consists of:
(I) Restrictions on private sector participation in areas such as defense, industry and nuclear power.
(II) Management of plant capacity and location.
(III) Set an upper limit on expenses, ……… Lower limits on wages and bonuses, and provisions for legal welfare measures.
(IV) Regulations on equity participation and foreign investment.
(V) Corporate tax, professional tax, taxes such as entertainment expenses,
(VI) Import / export rules, tariffs, tariffs, etc.
"Promotional roles" include:
(I) Development of infrastructure for industrial and commercial activities such as roads, industrial parks, telecommunications equipment, electricity.
(II) Support for subsidies, investment subsidies, tax incentives, tax exemption periods, subsidized water or electricity charges, etc.
(III) Provide financial and financial incentives.
The "entrepreneurial role" has something to do with:
(I) Participation in businesses and industries where private sector participation is inadequate, that is, power generation and distribution.
(II) Ownership and management of reserved industries such as defense production, nuclear power, oil and gas.
(III) Management of industry in the public sector.
The role of planning covers the following areas:
(I) 5-year plan
(II) Industry prioritization
(III) Foreign participation and bilateral agreements with other states or countries.
(IV) Greenfield area development plan
(V) Regional development plans and programs.
Focusing on "industrial law", many laws have been passed from time to time to regulate industry and commerce.
Activities, protection of employee interests.
The most important things that the business community should take into account are the Indian Contract Act of 1872, the Trade Union Act of 1926, the Employee (Industry) Permanent Order Act of 1946, the Industrial Dispute Act of 1947, and Exports of 1947. Immigration law, capital issues. 1947, 1948 Factory Law, 1948 Employee National Insurance Law, 1951 Industrial Development and Regulation Law, 1952 Employee Reserve Fund Law, 1955 Mandatory Commodity Law, 1956 Indian Enterprise Law, 1956 Securities Contract (Regulation) ) Law, Trade Marking Act 1958, Weight and Measurement Act 1958, Income Tax Act 1961, Borm Act 1965, Exclusive and Restricted Trade Practices Act 1969, Water (Contaminated and Contaminated) Control) Act, Household Electrical Appliances (1976 Quality Control Act, 1981 Air (Pollution Prevention and Control) Act, 1986 Consumer Protection Act, 1986 Environmental Protection Act, 1992 Indian Securities Trading Committee law.
There is a tax law that is revised every year. The same applies to price control regulations.
These laws and sets are very important to administrators. Because his policies and strategies can't hate local law.
Component # 6. Global environment:
The global or international environment is especially important in the face of strong globalization turmoil. Changes in the global environment create a range of opportunities and threats to a company's domestic and international share. Thus, the collapse of national communism in Eastern Europe has created enormous growth opportunities for American multinationals, Western European countries, and the emerging "Tiger of Asia."
The removal of trade barriers between community members of the European Community in 1992 provided them with free trade opportunities. The case of the Eurodollar as a new currency in 1999 poses many opportunities and threats to the various currencies of member countries.
In 1991, the Government of India announced a new Indian policy to meet the needs of liberalization and globalization of the Indian economy. This meant a thorough overhaul of the government's monetary and fiscal policies, under which artificial trade barriers were dismantled and the "license and management large" was rejected.
Bold policy initiatives were in the areas of industrial licensing, foreign investment, foreign technology agreements, changes in MRTP legislation, reform of the public sector, promotion of the small-scale sales industry, and reform of trade policy. The price of globalization has influenced global events.
Therefore, the oil crisis of the 1980s, the formation of the European Union and other economic groups, the dismantling of the Soviet Union, and the recession. This strengthens the retention of MNC and TNC. As a result, new strategic concepts such as international value chains, networking and relationship marketing cannot be revealed. Today's managers are global players, so we need to analyze the international environment from both focus and distance.
Industry environment:
An industry is a group of companies that manufacture or provide services for the same product. Therefore, the steel industry means all units engaged in the production of steel or steel products. Similarly, we can talk about the automobile industry. Here, it means in a specific context. For example, a four-wheeled vehicle.
However, it can include two-wheeled vehicles, three-wheeled vehicles, six-wheeled vehicles, and eight-wheeled vehicles. Even when we talk about it, it consists of Scotty, or mopeds, scooters and motorcycles. Convenience is the basis for calculating costs and prices.
That is, each unit in the industry is a competitor to the other units. The industry environment has components such as competitors, customers, suppliers, and alternatives. Each is a competing force. Perhaps the best model of competition in the industry environment was developed by Michael Porter, who is considered a leader in strategy.
This pentaforce model is widely accepted and explains how competitiveness works within the industry. The following is a model of competitiveness described in Harvard Business Review, March-April 79, "How Competitiveness Shapes Strategy."
Every strategist or manager needs to study the impact of this pentaforce, which is constantly working in the industry.

An overview
Decision making is that the act of selecting between the available alternatives. There are countless decisions that humans make on a day-to-day basis. In business enterprises, decisions are made at every step. it's also considered one among the important functions of management.
Decision making concept
Decision making is that the act of selecting between the available alternatives. There are countless decisions that humans make on a day-to-day basis. In business enterprises, decisions are made at every step. it's also considered one among the important functions of management. Management functions like planning, organizing, staffing, directing, coordinating and controlling are administered through decisions. deciding is feasible when there are two or more alternatives to unravel one problem or difficulty. If there's just one alternative, it's not about making decisions. Management without decision is believed to be a person without a backbone. Therefore, deciding may be a problem-solving approach by choosing a selected course of action among several alternatives.
Decision making is that the selection, supported some criteria, of two or more possible alternatives. "- George R. Terry
In conclusion, we will say that call making is that the process of selecting a selected course of action among several alternatives to unravel organizational problems or difficulties.
Goal / Objectives Achievement:
Decision-making is vital to realize organizational goals / objectives within the given time and budget. Find the simplest alternative, use resources appropriately, and satisfy employees within the workplace. As a result, the goals or objectives of the organization are often achieved supported the specified result.
Employee motivation:
Decision making is vital to motivate employees within a corporation. Provides a general operating framework and guidelines for the operational level of staff. It also provides different sorts of facilities and benefits on time. As a result, employees are motivated for his or her job or work consistent with the wants of the organization.
Appropriate use of resources:
An organization has various resources like man, money, method, material, machine, market and knowledge. of these resources are used correctly without leakage or waste with the assistance of the proper decision at the proper time. As a result, a corporation can operate at minimal cost.
Selection of the simplest alternative:
As we know, the matter has multiple solutions. deciding is vital to pick the simplest alternative among several alternatives analysing them one by one using various financial, statistical and accounting tools / techniques.
Management performance evaluation:
Decision-making isn't only important in selecting the simplest alternative, but also essential in evaluating a manager's performance. the standard / success of the manager depends largely on the number of correct decisions that he can bring the success of the organization. Therefore, deciding is vital in judging the performance of the highest level of management.
Essential element / component:
Decision making is an important element / component for organizational success because without making the proper decision at the proper time, nothing is often accomplished consistent with plan.
Generalized function:
Decision making may be a generalized function of managers whose objective is to realize organizational objectives. Decisions must be made altogether management functions, like planning, organization, motivation, direction, and control, and altogether functional areas like production, marketing, finance, personnel, and research and development. It indicates that call making extends to several areas of the organization.
Steps within the decision-making process
For the rationality, reliability, and applicability of selections, managers must follow a sequential set of steps. a choice is claimed to be rational if the acceptable means are chosen to realize the specified ends.
Develop an alternate course of action:
As we know, a drag has multiple solutions. Therefore, the choice maker must develop the varied possible alternatives for a far better decision. While developing the choice course of action, he / she will also use his / her own knowledge, skills, experiences and technical support from the professional planner and experts.
Identification of the problem:
The initial stage of the decision-making process is identifying the precise problem. the matter can occur thanks to the gap between thinking and doing the method. the rationale for the issues is often internal or external. Decision makers must identify the right issues before making any decisions. it's not employment or a simple task. Therefore, you'll use your own knowledge, skills, experience, and gather information from internal and external sources. Identifying the right problem is believed to be almost half the decision-making process.
Problem analysis:
After identifying the right problem, the choice maker must analyze the matter systematically and scientifically in terms of cost, time, legality, organizational resources, and therefore the short- and long-term impact of the matter. In analysing the matter, she will use various financial, accounting, and statistical tools or techniques.
Selection of the best alternative:
After analysing the various alternatives, the decision maker has to select the best alternative among the various alternatives considering both the short and long-term impact. For this purpose, he / she can use her knowledge, skills and experiences. She may also worry about other stakeholders to make a better decision.
Decision review:
The last step in the decision-making process is to get responses or feedback from other stakeholders in the organization. If the answer is positive, the decision-making process is completed successfully. If the answer is no, then you must go through the first step to make a new organizational decision.
Evaluation of the alternative course of action:
After developing several possible alternatives, the decision maker must evaluate all the alternatives one by one to make a better decision. In this step, she should try to find the answers to the following questions.
- Is the alternative feasible in terms of cost, time, legality and other organizational resources or not?
- Is the alternative satisfactory to solve the organizational problems or not?
- Do the characteristics of the alternatives correspond to the business objectives or not?
Essential elements of the group decision-making process
Results of the group decision-making process Having an effective group decision-making process can be an important source of productivity improvement for your organization. Some surveys show that almost 50% of participants consider unfocused projects and meetings to be the main source of lost time and productivity during the workday. Many of these meetings support the group's decision-making activities. Any improvement in the group's decision-making process increases the value generated from a decision and at the same time improves organizational productivity.
The first option: What level of participation is needed?
When starting to make a decision, an initial choice must be made regarding the level of collaborative decision-making that is needed. Additional factors that will influence this choice include the value of the decision, the complexity, the time available, the number of alternative solutions, and the level of understanding required for the needs / wants.
The Vroom-Yetton-Jago decision tree can also help you choose the level of participation with simple answers to eight questions.
Select process
With the level of participation determined, a group decision-making process should be used to manage the activities and discussions that will generate the outcome of the decision. The process must:
- Planning decision-making that includes defining the success factors or criteria for the decision;
- Identify and generate decision alternatives;
- Manage the implementation of the decision.
- Please see our decision-making process for more information and details.
- Facilitation of group activities and discussions for decision-making
When it comes to larger groups, an effective group decision-making process will address how group interactions will be managed and facilitated. This should be addressed in the initial planning to ensure that the benefits of the group's contribution and coordination can be realized at all appropriate steps in the decision-making process. Good facilitation can avoid the inappropriate exchange of relevant information and process losses that are characterized by the meeting surveys mentioned within the opening paragraph.
Group facilitation or coordination should aim to:
- Motivate people to work together
- Provide clarity of objectives
- Structure group discussions and provide explicit coordination where mechanisms are clearly and intentionally described to eliminate any misunderstandings in intent
- Provide information to establish common understanding (such as definition of key terms) and promote appropriate exchange
- Provide mechanisms for the storage, retrieval, exchange, summary and repetition of information.
- Establish the communication channels necessary to satisfy the complexity needs of the tasks.
- Offer methods to reconcile conflicting information and the meaning of shared information.
- Address social needs for rules of interaction (such as equal treatment) and facilitate non-conflicting personal goals
- Promote objectivity, equitable participation and consensus while meeting objectives.
- Intervene in crisis, maintain order and resolve emotional conflicts
- Optimize the integration of knowledge, opinions and preferences in the collective decision of the group.
- Make the decision and meet the performance objectives of the decision-making process to achieve the required decision quality
- An important approach to avoiding groupthink captures minority positions, helping to avoid decision-making biases and potentially leading to a different path to follow. Additionally, many problem decompositions approaches and project management methods have been integrated with individual decision-making techniques to address team decision-making.
Choosing the group decision-making method
When executing the process, it will be necessary to determine the method to be used You may consider setting a minimum stake for validity.
Consensus: the majority agrees and no one objects.
Unanimous - Everyone must agree.
There is an astonishing amount of research devoted to understanding these various methods, and the group decision-making process will be most efficient when specific methods are selected during decision planning using the participation level option described above.
Tools to support the group decision-making process
Software tools can provide significant process support by addressing many of the needs identified above. Group decision-making techniques are provided in many tools and often incorporate methods for combining individual responses into proven decision-making techniques, such as Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA).
For large groups, the complexity in managing communications and tasks can be eased with the project management tools currently used in the organization. Once the group decision-making process for the specific decision has been defined, look for a tool or tools that address the specific needs of:
- Determine the level of participation;
- Facilitate group communication;
- Sharing information;
- Combining group entry;
- Task management;
- Apply the agreed decision-making technique or techniques;
- Record of information on decisions and;
- Provide the necessary reports.
- High-value, complex, and uncertain decisions can also benefit from expert facilitation or training, particularly if there is the expectation of heightened emotions and conflict in motivation.
2.5 Concept and process of organising – An overview, Span of management
Meaning of organizing:
Organizing may be a "process of defining the essential relationships between people, tasks and activities in such how that each one the organization's resources are integrated and coordinated to realize its objectives efficiently and effectively". - Pearce and Robinson
Organizing is thus:
(i) A structure, and
(ii) A process.
As structure:
The organization is a set of relationships that defines the vertical and horizontal relationships between people who perform various tasks and duties. The organizational task is divided into units, the people in each unit (departments) are assigned specific tasks and their relationship is defined in a way that maximizes organizational well-being and individual goals. The relationship between people is both vertical and horizontal.
As vertical relationships, the authority-responsibility structure of people at different levels in the same department is defined and as horizontal relationships, the authority-responsibility structure of people who work in different departments at the same levels is defined.
The organizational structure specifies the division of labor and shows how the different functions or activities are linked; to a certain extent it also shows the level of specialization of work activities. It also indicates the hierarchy and authority structure of the organization, and shows its subordinate relationships. - Robert H. Miles
The organization as a structure is a network of relationships (authority-responsibility structure) among all those who are part of the organization, working at any level in any department. It defines the relationships between jobs at various levels and the people who work in those positions. Emphasize positions more than people.
As a process:
While the structure designs the system and its subsystems, the process defines the way this structure is designed. The structure is the static concept that establishes relationships between various components of the organization. You first design the component and then establish relationships between these components.
These relationships are generally permanent. They do not change often unless hampered by outer environmental forces. Process is the dynamic concept that redefines the structure whenever necessary. Defines the change in the system over time.
While the structure defines how the work of the organization will be divided into various positions, groups and departments, the process defines the sequence from which the structure is designed. Define relationships between people in such a way that organizational goals are achieved efficiently.
As a process, the organization consists of two processes:
1) Differentiation,
(2) Integration.
Differentiation means the division of labor into smaller units and its assignment to individuals according to their abilities and capacities. Integration refers to the coordination of different activities towards a common goal. Provides unity of action towards organizational activities.
It implies:
(i) Job identification,
(ii) Grouping of work into smaller groups,
(iii) Assign work to each individual at all levels in each department,
(iv) Define the authority and responsibility thereof, and
(v) Establish relationships between people so that they contribute to the objectives of the organization in an integrated manner.
The structure and process of the organization are not independent concepts. They are complementary to each other. Once the organizational process is defined, the organizational structure is the end result or the result of that process. The organization structure is the result of the organization process. The organization is, in fact, a structured and continuous process that defines how to achieve the defined goals.
Organization process:
The organizing process involves the following steps:
(i) Determination of objectives:
Every organization is established by some objective or goal. Various tasks are determined to achieve this goal. For example, if the organization is established to export goods, it determines the nature and type of goods to be exported, the sources from which the raw material will be obtained, the countries where the goods will be exported, it will coordinate with foreign buyers, etc. Organizing workload is the first step in the organizing process.
(ii) Division of Activities:
Since one person cannot manage all activities, the entire task is split into smaller units and assigned to members. Work is assigned according to the qualification and ability of each person.
The division of labor leads to specialization which has the following benefits:
(a) Higher production:
Adam Smith illustrated a study in which a person could fabricate
Carry 20 pins a day if she worked alone. The production of pins was divided into sub-activities where each person performed the following specialized tasks: Stretching the wire - straightening the wire - cutting the wire - grinding the point - polishing it - putting the head of the pin and so on. It was observed that compared to the 20 pins produced by one person in a day, the division of labor and their specialization allowed 10 people to produce 48,000 pins in one day. See the wonders of specialization!
(b) Efficiency:
Performing the same task over and over again increases the skill and efficiency of workers.
(c) Facilitates the training of less qualified workers:
Since the complex task is divided into smaller units, less skilled workers can be trained to carry out those activities.
(iii) Grouping of activities:
Once work is divided to people, those who have same activities are divided into branches. Various departments like sales, finance, accounting, etc. are filled with people who have different skills and experience, but perform similar activities. departmentalization is grouping of activities into departments and each department is controlled by a set of rules, procedures, and standards.
(iv) Define authority and responsibility:
Each department is headed by a person responsible for its efficient operation. The department heads are designated to carry out the activities of their respective departments. The competence of the department head is guaranteed to match the job requirements of the department.
Each boss has the authority to do the work of the departmental members of him. He divides work to be done and commands to members of his department. This creates a relationship structure where each individual knows his superiors and subordinates and their subordinate relationships.
(v) Coordination of activities:
When departments work toward their objectives, conflicts can develop between departments that can obstruct the achievement of organizational goals. For example, the finance department wants to reduce costs, but the marketing department needs additional funds to market its products; This conflict can be resolved by coordinating so that all departments share common resources optimally. Work can be coordinated by defining relationships between various departments and people working in different positions.
(vi) Review and reorganization:
There is a constant evaluation of the organizational process so that changes can be made in the structure as a result of changes in environmental factors. Constant evaluation and reorganization are an integral part of the organizing process.
Importance of the organization:
Organization is important for the following reasons:
(i) Facilitates administration:
Senior managers cannot perform all organizational tasks as they will be overloaded to focus on strategic matters. It is essential that a part of the workload is shared by middle and lower-level managers. Senior executives will be relieved of routine business management and will focus on effective administration.
The basic elements of organization (division of labor, grouping of activities, distribution of authority and coordination) facilitate better management by senior management.
(ii) Growth and diversification:
A well-organized institution adapts to change and responds to growth and diversification. You can multiply your operations.
(iii) Create synergies:
The division of labor provides the benefits of synergies, that is, the total task accomplished by a group of people is more than the sum total of their individual achievements. People coordinate their tasks in the same department and in different departments which is beneficial.
(iv) Establishes responsibility:
When each person knows his superiors and subordinates, the organization can function efficiently. Establishing limitations in the area of operations defines people's responsibility to their immediate boss, which guides the organization towards its broader objectives.
(v) Optimal use of technology:
It is the era of technological developments. Organizations that do not have a well-developed technology will not be able to compete in the market. Well-organized structures allow organizations to optimally use and upgrade their technology and remain competitive in dynamic market conditions.
(vi) Facilitates communication:
Communication is the essence of the organization. The efficiency of the organization depends on how well the members of the organization communicate with each other. A well-designed communication system (vertical and horizontal) is facilitated through the effective organizational efforts of senior executives.
(vii) Facilitates creativity:
Creativity means creating something new. Develop new ways of doing things. A strong organization enables top management to improve the ways of doing things by delegating routine matters to people in the scale chain. C
(viii) Improve interpersonal relationships:
An organizational structure ensures that the workload is divided into well-defined jobs and assigned to people according to their abilities and skills. Placing the right person in the right job ensures job satisfaction and increased employee morale. This improves interpersonal relationships between people who work in the organization.
ix) Facilitates Coordination:
Well-defined goals and plans can fail if the organization's activities are not coordinated in a unified direction. A well-designed organizational structure promotes order and system in your activities. Coordinate the work of people at different levels in different departments.
People work in predefined dimensions and harmonize individual objectives with the objectives of the organization, the internal organizational environment with the external environment, and financial resources with non-financial resources.
(x) Facilitates teamwork:
Although people are responsible for the specific tasks assigned to them, they work collectively as a team and optimize the use of scarce organizational resources to achieve organizational goals. The organization, therefore, facilitates teamwork. Rather than viewing the organization's goals from personal perspectives, they view them from group perspectives. Organizational goals satisfy individual goals.
(xi) Facilitates Control:
The organization provides strong direction to activities and ensures that people work according to plans. This facilitates control and promotes organizational goals. Goals are determined and periodic feedback ensures compliance of actual performance with target performance.
(xii) Increase in production:
A strong organization divides activities into several departments (production, marketing, etc.). These departments specialize in their tasks and increase organizational production. Specialization is an important contribution of the organization that promotes greater production.
(xiii) Optimal allocation of resources:
The organization promotes the optimal allocation of resources. Resources are assigned to different departments (production, marketing, personnel, etc.) in order of priority. People are assigned jobs for which they are best suited. All activities are assigned to everyone in the organization. There is no duplication of work. The organization, therefore, avoids overlapping activities to ensure that collectively people working in different departments carry out activities that contribute to the organization's goals.
Different types of Authority
Authority is that the right to execute or order. It also allows its owner to allocate the organization's resources to realize organizational goals.
Authority at work:
Barnard defines authority because the character of communication by which a private accepts an order as governing the actions the individual takes within the system.
Barnard maintains that authority is going to be accepted only under the subsequent conditions:
- The individual can understand the order being communicated.
- The individual believes that the order is according to the aim of the organization.
- The individual sees order as compatible together with his personal interests.
- The individual is mentally and physically capable of complying with the order.
- The fewer of those 4 conditions are present, the less likely authority are going to be accepted and obedience are going to be required.
Barnad offers some guidelines for what managers can do to extend the likelihood that their orders are going to be accepted and obeyed. He maintains that more and more orders from a long-term manager are going to be accepted if:
- The manager uses formal channels of communication and these are familiar to all or any members of the organization.
- Each member of the organization is assigned a proper channel through which orders are received.
- The line of communication between the manager and therefore the subordinate is as direct as possible.
- The entire chain of command is employed to issue orders.
- The manager possesses the acceptable communication skills.
- The manager uses formal lines of communication just for organizational business.
- A command is authenticated as coming from an administrator.
Types of authority:
There are often 3 main sorts of authority within an organization:
- Line authority
- Staff authority
- Functional authority
Each type exists only to permit people to hold out the various sorts of responsibilities that are entrusted to them.
The most fundamental authority within a corporation, reflects the prevailing relationships between superiors and subordinates. It consists of the right to make decisions and provides order on behaviour related to production, sales or finances of subordinates.
Line authority
In general, line authority refers to matters that directly involve production, sales, finance, etc. of the management system and, as a result, with the achievement of objectives.
People directly liable for these areas within the organization have delegated line authority to assist them perform their required activities.
Personnel authority:
Staff authority consists of the proper to advise or assist those in line authority, also as other staff personnel.
Personnel authority enables managers to enhance the effectiveness of force to perform required tasks.
Line and staff personnel must work closely together to stay the organization efficient and effective. to make sure that force and staff work together productively, management must make sure that both groups understand the organization's mission, have specific goals, and realize that they're partners in helping the organization achieve its goals. objectives.
Size is probably the foremost important think about determining whether or not a corporation will have staff. The larger the organization, the greater the need and skill to use staff.
Functional authority:
Functional authority consists of the right to supply orders within a segment of the organization during which this right doesn't normally exist.
This authority is usually assigned to individuals to supplement the road or personal authority they already possess.
The functional authority generally covers only specific task areas and is operational only for designated periods of some time. it's given to people that, so as to satisfy responsibilities in their own areas, must be ready to exercise some control over members of the organization in other areas.
Decentralization
Decentralization means decentralizing decision-making authority to the lowest levels of the marginal hierarchy. In other words, when the power to make decisions and formulate policies is not in a single person at the top, but is transmitted to different people at various levels, it is called decentralization. However, the decision to make at a lower level should be important, otherwise it will not be a case of decentralization.
Advantage of decentralization
i. Reduces the burden of the senior executive:
Decentralization frees the top executive from the border to perform various functions. This also reduces the time available to senior executives to focus on other important managerial functions. So, the only way to hear his burden is to decentralize his decision-making power to subordinates.
ii. Facilitates diversification:
Under decentralization, products, activities and markets, etc., are facilitated, a centralized company with the neutralization of authority at the top level will have difficulties in diversification after a certain level because decision-making is taken back by one man. The organization will become more and more complete with the addition of new products and the establishment of more units. So the decentralized system will be more suitable for expanding companies.
iii. Quick decisions:
In the decentralized system, decision-making powers are delegated to the actual execution level. Therefore, it is not necessary to refer to the top level for most of the work. Speeds up the decision-making process.
iv. Risk division:
The company is divided into several departments under decentralization management that can experiment with new ideas in one department without mistrusting the others. This will reduce your risk if things turn bad.
v. Effective control and supervision:
With the delegation of authority, the scope of control will be effective. Under decentralization, lower-level executives also have full authority to make important decisions. So, they will recommend rewards or punishments according to their performances. This will improve supervision and control.
Disadvantages of decentralization: -
Decentralization suffers from a number of drawbacks and some of them are discussed below: -
i. Lack of coordination: -
Under decentralization, each department, section, or unit enjoys substantial powers. They have the power to formulate their own policies and programs. This is why it is sometimes difficult to coordinate the activities of various departments.
ii. Difficult to control: -
Under decentralized conditions, different units operate independently, making it difficult to control their activities. Senior management will not be able to exercise effective control because; does not stay in touch with the daily activities of various departments.
iii. Expensive: -
The decentralization system involves large overhead costs. Each department in decentralization has to be self-sufficient for its activities such as production, marketing, accounting, personnel, etc. For this reason, the decentralized system is suitable for large-scale organizations.
iv. Qualified Manager Lake: -
Decentralization will only be successful if qualified or competent people are employed to manage various jobs in different departments. Sometimes competent people are not available as required. The system will fail if competent people are not available.
Delegation of authority
Have you ever wondered why one restaurant fares so much better than another even if they serve the same quality of food and provide a similar dining experience?
The answer lies in better customer service that often sets a restaurant apart from the rest. So, what is the core of that?
Restaurant staff known for their customer service are often able to serve each customer with the same attention. Often times, this is because the managers of these restaurants delegate responsibilities so that none of the customers feel left out.
Delegation helps divide the workload and encourages employees to be more productive because they are not overloaded. Let's see how delegation of authority makes teamwork more efficient.
Meaning of delegation of authority
To define delegation of authority, we must understand the meaning of the term. Delegation of authority is a process that allows one person to assign a task to others. As a manager or leader, you are expected to multitask and meet various deadlines. To make sure you achieve your goals on time, you delegate responsibility to your team members. In short, the meaning of delegation of authority is to entrust tasks to someone and share the overall responsibility.
Elements of delegation of authority
There are three core elements involved in the delegation of authority process.
1. Authority
In the context of business organizations, authority is the right and power of an individual to efficiently allocate resources, make decisions, and give instructions to achieve organizational goals. This authority must be well defined and must not be misused. There is a co-dependent relationship between authority and responsibility, so authority must always be accompanied by an equal amount of responsibility to complete tasks successfully. However, the ultimate responsibility always rests with the person with the highest authority.
2. Responsibility
Responsibility refers to the scope or duty of an individual to complete the task assigned to him. Someone entrusted with responsibility must take responsibility for her tasks. It is better not to make excuses or give explanations if tasks are not completed. Responsibility without the proper authority can lead to dissatisfaction and discontent. It is best not to give someone too much authority and too little responsibility. Ultimately, managers and leaders may be held accountable for overall performance, but the most important responsibilities are in the hands of the employees.
3. Accountability
What is a delegation of authority without accountability? It is a component that differentiates between the performance of an individual and the expectations that were established in advance. Unlike authority and responsibility, accountability cannot be delegated to others. Anyone who sets out to complete a task is responsible for the efforts and results of it. For example, if Madan is assigned a task with the appropriate authority and delegates the task to Mohan, the responsibility rests with Mohan, but Madan remains responsible for the task.
Characteristics of the delegation of authority
- There are a few key things that managers and leaders need to keep in mind when delegating authority.
- You should not give up your authority completely. In other words, you must define the scope of your authority.
- You must always comply with the provisions of the organization's policies, rules and regulations.
- Once delegated, the authority can be further expanded or withdrawn, depending on the situation.
- You cannot delegate an authority that you do not possess yourself.
- The delegation of authority can be written or oral and specific or general.
- Not all team members are capable of assuming responsibilities, so you must consider the individual capabilities of your employees.
Types of delegation of authority
There are several types of delegation of authority. Let's analyze each type through different examples of delegation of authority:
1. Full delegation
Often times, recurring and repetitive jobs in organizations are fully delegated. For such tasks, there is minimal interference from managers and leaders, and team members have the highest authority. Imagine that you are the director of Human Resources for your organization. He surveys employees every quarter and reuses a set of standard questions and follows a particular protocol for circulating the surveys. If new members join your team, you can turn in that task in full. You can communicate goals in advance, and your team can present the final results after they collect the information.
2. Half delegation to do wonders.
Let's take these two examples of delegation of authority and see how half delegation can work:
Imagine that the "marketing" and "sales" teams are working toward the same goal. You can choose to delegate all marketing-related tasks to the marketing team and all partners and vendors.
Goals related to hip to the sales team. They can collaborate and help each other, but would be responsible for their respective goals and deadlines. Ultimately, you can monitor your performance and make sure each team has met your expectations.
Suppose you want to hire new employees. Going through hundreds of job applications is not easy, so you can delegate the preliminary task of reviewing resumes and shortlisting them to your team members. You can then view the shortlisted resumes. You can set certain expectations for your team to select candidates with the necessary skills and experience.
3. Outdoor delegation
The outdoor delegation is more useful in case of collaborations with another organization. For example, if you work with an outside agency, you can send in your best negotiators to develop a collaborative strategy. Once you receive a brief on the new business strategy with the necessary details, you can make the final decision without spending hours on travel or negotiations.
4. Intervention
When you have limited time on your hands, intervention is the way to go. After delegating tasks, you can communicate with your team members from time to time. It's a good way to keep track of individual signs of progress. It is especially beneficial when you have to work with new employees who do not have many years of experience behind them. For example, you can use the intervention method when you want to launch a new initiative. Ask your team to come up with ideas and submit them for your approval. Intervention is a time-saving technique.
5. Creative delegation
Projects that require innovation must be delegated. When more people are involved, the chances of suggesting unique ideas are greater. One person's creativity can boost team creativity. For example, if you are organizing Diwali celebrations in your office, you can create a plan and delegate responsibilities for implementation or ask your team to present their ideas. Both ways are good examples of creative delegation.
Importance of delegation of authority
The delegation of authority process is to ensure a productive and well-functioning workplace. The process can benefit you, your employees, and the overall organization, if done correctly. These are some of the benefits that highlight the importance of delegation of authority.
1. Higher productivity
Delegation helps employees finish tasks faster because work is spread over a group of people and everyone is accountable for their respective goals.
2. Personal development
When you delegate tasks, your team members have the opportunity to showcase their skills and experience in a particular area. With proper guidance, they can also improve their knowledge and skills.
3. Continuity
If you are busy or absent from work, your team can help you complete some of your work and ensure continuity and productivity.
4. Motivation of employees
When you assign new responsibilities, you show that you trust your employees to take control. They are motivated and motivated to use their full potential.
5. Professional growth
The more you delegate tasks to different members of your team, the more they understand your business goals and objectives. This leads to potential promotion within the organization.
Conclusion
Delegation of authority can be difficult if it is not executed correctly. Harappa Education's Navigating Workplaces course will teach you how to manage conflict effectively and adopt different perspectives. The Culture Fit framework will guide you in your assessment of workplace culture. Also, the Thomas Kilmann model will teach you the five essential ways to deal with conflict. Master the ability to lead and influence others and let your team prosper under your guidance!
Formal organization:
When managers are completing the organizing process, as a result of the organizing process, an organizational structure is made to realize systematic work and efficient use of resources. this sort of structure is understood as a proper organizational structure.
The formal organizational structure clearly details the work to be performed by each individual, the authority, the responsibility assigned to every individual, the superior-subordinate relationship and therefore the designation of every individual within the organization. This structure is made intentionally by managers to realize the organizational goal.
Characteristics of the formal organization:
(1) The formal organizational structure is made intentionally through the organizing process.
(2) the aim of the formal organizational structure is that the achievement of the organizational goal.
(3) within the formal organizational structure, each individual is assigned a selected job.
(4) within the formal organization, each individual is assigned a hard and fast authority or decision-making power.
(5) The formal organizational structure leads to the creation of superior-subordinate relationships.
(6) The formal organizational structure creates a scalar communication chain within the organization.
Advantages of the formal organization:
1. Systematic work:
The formal structure of the organization leads to a smooth and systematic operation of a corporation.
2. Achievement of organizational objectives:
A formal organizational structure is established to realize organizational objectives.
3. No work overlap:
Distribution of work is in systematic manner and then divided among various departments and employees in formal structure. Therefore, there's no possibility of duplication or overlapping of jobs.
4. Coordination:
The formal organizational structure leads to the coordination of the activities of varied departments.
5. Creation of the chain of command:
It clearly underlines the work of top subordinate and their relationship, that is, who reports to whom.
6. More emphasis on work:
The formal organizational structure places more emphasis on work than interpersonal relationships.
Disadvantages of the formal organization:
1. Delay in action:
By following the scalar chain and chain of command, actions lag behind the formal structure.
2. Ignore the social needs of employees:
The formal organizational structure doesn't give importance to the psychological and social needs of the workers which may cause demotivation of the workers.
3. Emphasis on work only:
It lays emphasis to numbers only; ignores relationships of mankind, creativity, talents, etc.
Informal organization:
In the formal organizational structure, individuals are assigned various jobs. While working in those jobs, people interact with one another and develop some social and friendly groups within the organization. This network of social and friendly groups forms another structure within the organization called the informal organizational structure.
The informal organizational structure is made automatically and therefore the main objective of this structure is to get psychological satisfaction. The existence of a casual structure depends on the formal structure because people working in several jobs interact with each other to form a casual structure and jobs are created during a formal structure. So, if there's no formal structure, there'll be no job, there'll be no people working in jobs and there'll be no informal structure.
Characteristics of the informal organization:
(1) The informal organizational structure is made automatically with none intentional effort from managers.
(2) The informal organizational structure is made by employees to get psychological satisfaction.
(3) It doesn’t have permanent path of control or communication flow.
(4) The source of data can't be known under an off-the-cuff structure, since a person can communicate with a person within the organization.
(5) The existent of an off-the-cuff organizational structure relies on the formal organizational structure.
Advantages of informal organization:
1. Fast communication:
The informal structure doesn't follow a scalar chain, so there could also be a more rapid spread of communication.
2. Satisfies social needs:
It lays emphasis to the emotional and social needs of person working which motivate employees.
3. Correct comments:
Through the informal structure, top-level managers can get real feedback from employees on various policies and plans.
Strategic use of informal organization. Informal organization are often wont to gain benefits in formal organization as follows:
1. Knowledge of the informal group are often used to gain support from employees and improve their performance.
2. Through the vine, important information is often transmitted quickly.
3. By collaboration with informal groups, executive can artfully take merit of both formal and informal organizations.
Disadvantages of informal organization:
1. Spread rumours:
According to a survey, 70% of the knowledge disseminated through the informal organizational structure are rumours which will mislead employees.
2. Without systematic work:
The informal structure doesn't form a structure for the right functioning of a corporation.
3. It can bring negative results:
If the informal organization opposes the policies and management changes, then it becomes very difficult to implement them within the organization.
4. More emphasis on individual interest:
The informal structure gives more emphasis to the requirements of the individual person as compared to the organizational interest.
Organization principles:
The principles are the guidelines that promote managerial thinking and action. The principles help managers to perform the organizational function effectively.
These principles are as follows:
(i) Principle of unity of objectives:
All the activities of the organization are oriented towards the objectives of the organization. The objectives are framed for each level (upper, middle and lower) and each functional area. The objectives must be clearly understood by everyone. They must support each other at each level to achieve goals at higher levels.
(ii) Organizational efficiency:
Organizational goals must be achieved efficiently. It means an optimal (efficient) use of resources, that is, maximum performance must be achieved with minimum inputs. Resources must be distributed among activities in various functional areas that collectively result in maximum performance through optimal use.
(iii) Division of labor:
Division of labor means dividing the main task into smaller units. The main task is divided into subtasks. This makes each person focus on his part of the job and perform it efficiently, thus increasing total production. The work should be divided and assigned to the workers according to their skills. This leads to specialization and contributes to organizational production.
(iv) Authority - Responsibility:
Authority and responsibility must go hand in hand. Responsibility means obligation to perform the assigned task. To carry out this task, authority must be delegated to everyone. Rather, given the authority, the assigned tasks (responsibility) should be within the scope of the authority. Authority without responsibility will result in misuse of authority, and responsibility without authority will result in poor performance.
(v) Delegation:
The total workload is divided into parts. Subordinates are assigned a share and given authority to carry out that task efficiently. Senior managers delegate some of their duties to lower levels and focus on important organizational matters. This speeds up organizational tasks and enables the organization to grow in a dynamic and competitive business environment.
(vi) Scalar chain:
The scalar chain is the line of authority that runs from the upper to the lower levels. Authority flows from the top down in this chain and responsibilities flow from the bottom up. This chain promotes communication between people at different levels and facilitates decision-making. Each person in the chain knows his superior and subordinate.
(vii) Scope of control:
Scope of control means the number of subordinates that a superior can effectively supervise. The exact number of employees a manager can supervise cannot be determined. It depends on the competence of the managers, the nature of the work, the control system, the capacity of the subordinates, etc.
However, if the manager can supervise a smaller number of workers, there will be more levels in the organization structure and vice versa. Supervision of a few subordinates creates tall structures and supervision of a large number of workers creates flat structures.
(viii) Unity of command:
A subordinate must have a boss. People should take orders only from their immediate boss. This brings discipline and order in the organization. Taking orders from two or more bosses can create confusion and indiscipline.
(ix) Balance:
There must be a balance between the different organizing principles. A balance must be maintained between centralization and decentralization, narrow and broad control, etc.
(x) Flexibility:
The organization must be flexible. Changes in the structure must be made in accordance with changes in environmental factors.
(xi) Continuity:
The organization must adapt to environmental changes for its long-term survival, growth and expansion.
(xii) Exception:
Not all matters should be reported to senior managers. Only significant deviations in the hierarchy should be reported. Routine matters should be handled by middle and lower-level managers. Develop lower-level managers as they deal with simple, routine problems.
(xiii) Simplicity:
The structure of the organization should be simple, that everyone can understand. People can work efficiently in a simple structure as they are free from various jobs and authority / responsibility associated with those jobs.
(xiv) Department:
It means dividing activities into specialized groups (departments) where each department performs a specialized organizational task. All activities of a similar nature are grouped into a department headed by the departmental manager. Departments can be created based on geographic locations, customers, products, etc.
(xv) Decentralization:
It means delegation of authority to lower-level managers. It becomes answerable to the authority of subordinates and increases organizational efficiency.
(xvi) Management unit:
All activities of a similar nature are grouped into a single unit (production or marketing), headed by the departmental manager. Directs the efforts of departmental members towards one objective; the departmental objective.
(xvii) Cooperation:
All people and departments must cooperate and help the organization achieve its objectives. Cooperation leads to teamwork and focuses on a unified goal.


References:
1. Business Management by Neerli Vashisth
2. Principles of Management by L.M Prasad