Unit 1
Basic of Environmental Studies
Definition
Environment as a word covers the sum of extrinsic forces, factors and suitable conditions, which are essential for the origination and survival of all life forms. ‘Environment’ is composed of every external factor that has influenced all living organisms since birth.
Environment is the aggregate of physical, chemical, biological and social components on Earth which are capable of causing direct or indirect effects on the survival of living and non-living things and their interactions.
|
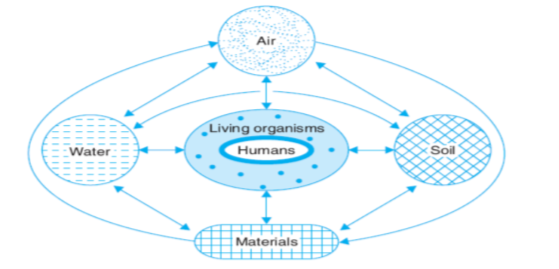
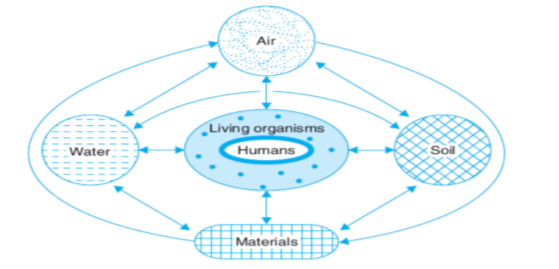
Interaction of Air, Water, Land (Soil), Resources (Materials) with Living Organisms constitutes Environment.
Study of environment & its components is a multidisciplinary field as it consists of Science, Arts, Commerce, Mathematics and other specialized fields such as Geography, Topography, Anthropology, etc.
Environmental studies provide us a platform for the thorough study of living organism and its surroundings.
|
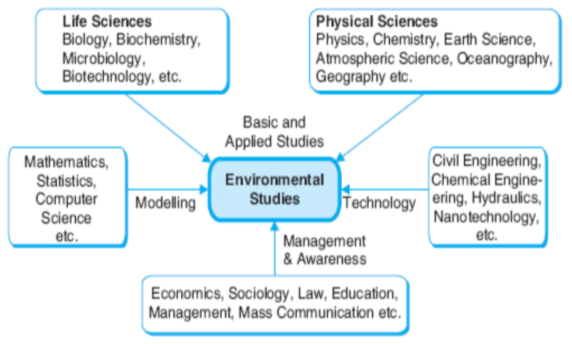
Depiction of Multidisciplinary Nature of Environmental Studies & its Components
- Environmental Studies as Applied Life Science: Life sciences including botany, zoology, microbiology, genetics, biochemistry, biotechnology, etc. help us in understanding the biotic components of environment and their interactions with each other and with abiotic components.
- Environmental Studies as Basic Physical Sciences: Core branches of physical sciences such as Chemistry, Physics, Geography, etc. give us an overview of chemical & physical structure of biotic components. Flow of energy transfer from one form to another also comes under this domain.
- Environmental Studies as Modeling Tool: It includes Mathematical Interpretations, Statistical Data Analysis, Computer Aided Analysis of Environment & its components.
- Environmental Studies as Technology: Branches of Civil Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Environmental Engineering, etc. have to deal with sustainable technological development without harming the environment in the form of Pollution Control, Waste Treatment and Reduction in overexploitation of natural resources.
- Environmental Studies as Management & Awareness: It covers all the rules regulations, laws and acts made in order to protect the environment and to create equilibrium between all life forms to sustain life and growth on earth.
The science of Environment studies is a multidisciplinary science because it depends on various disciplines like chemistry, physics, medical science, etc. It is the science of physical phenomena in the environment. It is inherently a multidisciplinary field that draws upon not only its core scientific areas, but also applies knowledge from other non-scientific studies such as economic, law and social science.
1. Physics:
- To understand the flux of material and energy interaction.
- To construct mathematical models of environment.
2. Chemistry:
- To understand the molecular interactions in the system.
3. Biology:
- To describe the effects within the plant and animal kingdom and their diversity.
4. Atmospheric Science:
- To examine the phenomenology of the Earth's gaseous outer layer with emphasis upon interrelation to other systems.
- It comprises meteorological studies, greenhouse gas phenomena, airborne contaminants, sound propagation phenomena related to noise pollution, and even light pollution.
5. Ecology:
- To analyse the dynamics among an interrelated set of populations, or a population and some aspects of its environment.
- These studies could endangered species, predator interactions, effects upon populations by environmental contaminants, or impact analysis of proposed land development upon species viability.
6. Environmental Chemistry:
- To study the chemical alterations in the environment.
- Principal areas of study include soil contamination and water pollution.
- The topics of analysis involve chemical degradation in the environment, multi-phase transport of chemicals and chemical effects upon biota.
7. Geo-science:
- It includes environmental geology, environmental soil science, volcanic phenomena and evolution of the earth's crust.
- In some classification systems, it can also embrace hydrology including oceanography.
8. Mathematics and Computer Science:
- It will help in environmental modeling and analysis of environment related data.
9. Economics:
- It deals with economical aspects of various components of environment.
10. Law:
- It helps in framing of environment related laws, Acts, rules and their monitoring.
11. Social Science:
- It helps in dealing with population and health related issues.
Scope and importance
Like its multidisciplinary nature, scope of Environmental Studies is also wide as follows:
1. The study makes mindfulness among the individuals to think about different sustainable and non-renewable assets of the surroundings.
2. It gives the information about natural frameworks and circumstances related to human survival.
3. It gives fundamental idea about biodiversity and risks related to it.
4. The examination empowers one to create a cause & effect relationship of consequences caused by human activities of our natural surroundings.
5. It empowers one to choose most suitable alternative from available pool in order to reduce overuse of natural resources.
6. The awareness of Environmental Studies empowers ecologically educated residents by letting them know about the natural demonstrations, rights, rules, regulations, enactments, amendments in the existing environmental acts and so on to settle on proper decisions and choices for the insurance and improvement of the earth and its inhabitants.
7. The study reveals the social issues like over population, health, cleanliness and sanitation. It gives remedial measures to these issues in the most suitable manner.
8. The investigation attempts to recognize and create the eco-friendly skills and non-conventional technologies that would not create any hindrance in the pathway of development without putting an extra burden on environment.
9. It shows us the requirement for supportable usage of resources as these assets are acquired from our predecessors. Hence it is our responsibility to pass these on to our forthcoming generations without decaying their overall quality.
10. The scope of Environmental Studies is incomplete without its impact on employment opportunities in the form of Environmental-Journalism, Research & Development, Environmental Management, etc.
Importance:
1) Environmental studies help us to maintain ecological balance and equilibrium in the environment by providing a basic platform for interaction of environmental system and inter-related processes.
2) It gives information regarding the changes that takes place due to various factors and helps in gathering skills to analyses various environmental processes and the effect of human activities on them.
3) Environmental studies help to achieve sustainable development in order to achieve a state of optimum utilization of resources without affecting the needs of future generations. It ultimately makes us understand the relationship between development and the environment.
4) This field helps to educate people regarding their responsibilities and lawful duties towards the protection of environment.
5) Environmental study helps us to analyses the impact of human activities on various processes occurring in water, air and land which leads to contamination and results in environmental pollution
6) It also deals with the most important issues like safe and clean potable water, health-hygiene and cleanliness of surroundings
7) The discipline provides knowledge of the environment and various environmental issues. It examines the scientific base for environmental, cultural and social concerns about our present energy needs, global climate changes, toxic emission and waste disposal.
8) Development and optimum utilization of energy resources is an important aspect of environmental studies.
9) Environmental acts, rules, regulations, law, amendments and fields like business administration, environmental engineering is emerging as new career opportunities under its domain.
10) To analyze the complex nature of vast bio-diversity on our planet, we need scientific approach of Environmental - Studies.
Key Takeaways:
- Environment is the aggregate of physical, chemical, biological and social components on Earth which are capable of causing direct or indirect effects on the survival of living and non-living things and their interactions.
- The science of Environment studies is a multidisciplinary science because it depends on various disciplines like chemistry, physics, medical science, etc. It is the science of physical phenomena in the environment.
- Environmental studies help us to maintain ecological balance and equilibrium in the environment by providing a basic platform for interaction of environmental system and inter-related processes.
There are three major components of environment. These are as follows:
- Physical component.
- Biological component.
- Social component.
Physical component of environment:
- Physical component of environment includes air, water, soil, light, temperature, climate, etc.
- The physical components are also termed as abiotic components of the environment.
- These environmental components account for determination of living conditions for the human population.
- Physical component of the environment is again classified into three parts as follows:
- Atmosphere (gas)
- Hydrosphere (liquid)
- Lithosphere (solid)
Structure of atmosphere:
- The atmosphere is broadly classified into four major zones.
- These zones are named as Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere and Thermosphere.
- These three parts portrays the three important states of matter forming the environment.
- This physical component of environment includes abiotic components like air, water and soil.
- All these abiotic components affect much more to all living organisms along with human.
- Water and temperature are the most significant abiotic components affecting living beings as water is important for survival of livings.
- Water plays a vital role to keep optimum temperature of the body and perform metabolic activities.
- All living things perform in a particular range of temperature.
- Growth of living beings will be affected when temperature will not fall in that range.
- Air is one of the major physical components, which is needed for respiration.
- All living beings along with plants and animals need oxygen for their survival.
- In metabolic process, oxygen is inhaled into the body and exhaled in form of CO2.
- On contrast to it, the plants consume CO2 for food preparation during photosynthesis and releases oxygen to the emvironment.
- Soil is another important component for all living beings to build their habitat.
- It is the soil where plant grows and human builds houses to live in.
- Soil serves to retain ground water which is obtainable for drinking and other farming activities.
Biological component of environment:
- The biological component of environment is also termed as biotic component.
- This biological component includes all living things like plants, animals and small micro-organisms like bacteria, algae and fungi.
- Biological component interrelates with the abiotic component of the environment. Interaction of these two components forms various ecosystems like forest ecosystem, pond ecosystem, marine ecosystem, desert ecosystem, etc.
- Biosphere is independent and large ecosystem.
- All ecosystems has three different types of living organisms; i.e. producers, consumers and decomposers.
- Producer includes mainly green plants and other photosynthetic bacteria which synthesizes various organic substances such as carbohydrates, proteins, etc., with the aid of water, soil and light energy.
- Consumers rely on green plants for their nutrition as these green plants produces organic food materials.
- Decomposers are responsible to decompose dead plants and animals and yields various important minerals for the running of the natural cycles.
Social component of environment:
- The third component of environment is social component.
- This component is mainly consists of various groups of population of different living beings like birds, animals, etc.
- Human is the most independent and intelligent living organism.
- Like all other living creatures on earth, man constructs house, prepares food and delivers waste materials to the environment.
- It has been said about human by Greek philosopher, Aristotle that human is a social animal.
- He prepared various laws, policies for the proper functioning of the society.
- These three components of the environment give rise to four important zones like Atmosphere, Hydrosphere, Lithosphere and Biosphere.
- There is continual interaction among these four zones.
- These interactions include the transport of various elements, compounds and different forms of energy.
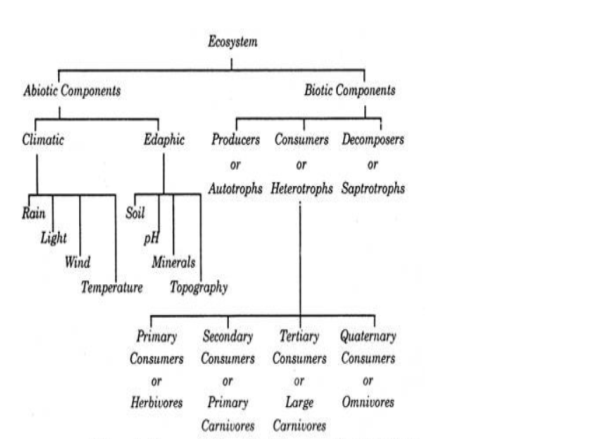
Ecosystem has 2 major components:
1) Biotic (Living)
2) Abiotic (Non- Living)
These 02 components when interacts with each other in a system, then give rise to an ecosystem.
Biotic Components are of 3 further types:
1) Producers
2) Consumers
3) Decomposers
Producers, consumers and decomposers
1) Producers: They prepare their own food and initiate the cycle.
Example: Plants prepare their own food with the help of photosynthesis.
2) Consumers: These are primary (who feeds on producers) & secondary (who feed on both producers and primary consumers)
Example: Herbivores & Carnivores
3) Decomposers: Feeds on dead of lifeless residues of producers and consumers.
Example: Bacteria, Fungi, etc.
Abiotic Components are of 2 sorts:
1) Climatic Factors (Rain, Lightning, Humidity, Wind, Temperature, etc.)
2) Edaphic Factors (Soil based factors such as pH, minerals, etc.)
|
Classification of Ecosystem and its components
Functions:
Basic function of ecosystem is merely an exchange of energy and nutrients in the food chain which impacts the survival of existence of all life forms. This exchange is responsible for the setting up of equilibrium between biotic and abiotic components.
Key Takeaways:
- There are three major components of environment. These are as follows: Physical component, Biological component and Social component.
- Ecosystem has two major components Biotic and Non-Biotic.
References:
- Textbook Of Environmental Science By Deeksha Dave And E.Sai Baba Reddy, Cengage Publications.
- Text Book Of Environmental Sciences And Technology By M.Anji Reddy, Bs Publication.
- Comprehensive Environmental Studies By J.P.Sharma, Laxmi Publications.
- Environmental Sciences And Engineering – J. Glynn Henry And Gary W. Heinke – Prentice Hall Of India Private Limited.
- A Text Book Of Environmental Studies By G.R.Chatwal, Himalaya Publishing House