UNIT I
Communication
Business Communication — Definitions and Meanings:
The word "communication" comes from the Latin word "communis", which suggests something common. Therefore, communication means sharing common ideas. The meaning of a communication dictionary is to convey and exchange information and share ideas.
It is the process by which two or more people communicate or exchange ideas and concepts between themselves. Consistent with W.H. Newman and C.F. Summer, "Communication is the exchange of facts, ideas, opinions, or feelings between two or more people."
Communication is the process of sending information and understanding from one person to another, or from one unit to another, with the goal of getting a given response from the recipient. Through this process, two or more people exchange ideas and understandings and have a specific effect on the behaviour of others.
This is a two-way channel for sending ideas, feelings, plans, commands, instructions, reports, and suggestions that affect an organization's attitude toward purpose. The communicator's goal is to convey undistorted meaning and ideas. The success of a leader, and therefore a company, depends on the appropriateness of communication.
It is the manager's responsibility to communicate and maintain channels where he can communicate his thoughts and policies to his subordinates and receive explanations of his reactions and problems.
Louis A. Allen defines communication in the following ways:
"Communication is the sum of all the items that one person does when he wants to form an understanding in another's mind. It is a bridge of meaning. It is the scientific and continuation of communicating, listening and understanding. Process is included. "
This definition includes two aspects of communication.
First, there are facts, feelings, ideas, etc. that are communicated. This means that you need a recipient to communicate.
Second, the definition emphasizes the comprehension element within the communication process. Understanding can only be shared by someone who understands the destination of the message in the same way that the sender of the message wants him to know.
Therefore, communication involves sending a message, or sending and physically receiving a message. Correct interpretation and understanding of the message is important from the perspective of organizational efficiency. Effective communication itself can be its accurate transmission and reception and its correct understanding.
In their book "Business Communication Today", C. L. Bovee, J. V. Thill, B. E. Schatzman writes: However, communication is only effective if the message is known, and it is effective when it stimulates behavior or encourages the recipient to think in new ways. "
Communication between people to convey personal information, messages, or thoughts is personal communication. However, the exchange of business data, facts, and concepts is sometimes referred to as "business communication." Business communication is communication about commercial activities that propose to provide goods and services to consumers for the purpose of profit.
This is the process by which information, facts, ideas, orders, advice, decisions, etc. are communicated, transmitted, or exchanged between or between people involved in the business. Therefore, communication about trade, law, finance, management, management, etc. of a for-profit company is sometimes called "business communication".
The success of a for-profit company depends heavily on good communication. Effective communication removes obstacles to achieving the goals of a for-profit company. Ineffective communication and communication failures can result in loss of cash, time, energy, opportunities and even business credibility.
In this era of globalization, all for-profit companies, large and small, need proper communication for their existence. Business success depends heavily on communication success.
In an era of speed, complexity and competition, it is very important to send product data to the end consumer. It is impossible for them to contact and purchase a product unless they understand the company's product. Communication plays an important role in this area.
Main Features:
Three characteristics of business communication:
Business communication has certain features or characteristics that make it different from other communications.
Communication that becomes business communication must meet the following conditions.
1. Practical
2. In fact,
3. Clear and concise
4. Target oriented,
5. It is persuasive.
1. Practical:
Effective business communication deals with the wise side of information that explains why, how, when, and therefore similar queries. It avoids unrealistic, imaginary, unnecessary things. Important or repetitive information to avoid wasting time. Give the recipient important information.
2. Fact:
In general, business messages contain facts and numbers instead of the overall idea. Important dates, places, times, etc. should be clearly mentioned during business communication.
3. Clear and concise:
The language used in business communication must be simple, clear, concise, and clear. Charts, photos, diagrams, etc. may be used to summarize or clarify information.
4. Target oriented:
Business communication requires a chosen purpose and needs to be properly planned so that goals are often achieved.
5. Persuasiveness:
Business communication often plays a compelling role. It persuades employees to perform their duties and customers to purchase products or services. The above essential features are related to communication messages or information.
Classification of Communication:
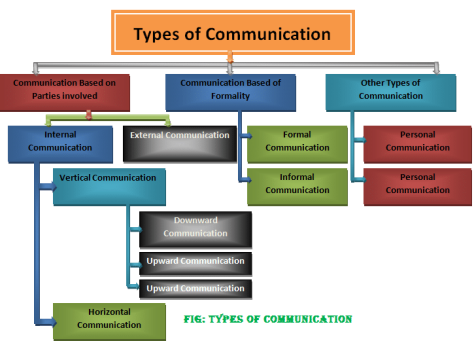
Some of the types of communication are:
1. According to the business area.
2. According to the relationship.
3. Depends on the direction.
4. According to the means.
1. Operation area:
(i) Internal communication:
“Internal communication” can be the process of communication within an organization between superiors and subordinates, colleagues, or between two or more groups. It is formal or informal, oral or written. It flows upwards, downwards, or horizontally, depending on your requirements.
Oral means of communication include face-to-face discussions, verbal instructions, messages, telephone calls, intercoms, conferences, conferences or seminars, and speeches. Written methods include notifications, circulations, notes, reports, charts or graphs, and bulletin boards, Email, fax, etc.
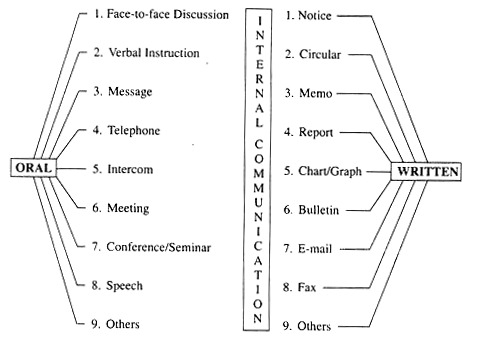
Methods of Internal Communication
(ii) External communication:
Business organizations need to communicate with external agencies such as customers, suppliers, investors, other establishments, banks, insurance companies and government agencies. Such communications are sometimes referred to as "external communications" because their business domain is with people. Outside the organization.
International business organizations have come to communicate with foreign individuals, government agencies / organizations, and more. Oral external communications are formed through face-to-face discussions, meetings, conferences, seminars, telephone calls, speeches, and more. Written processes include notifications, letters, telegrams, reports, emails, advertisements, faxes, handouts and more.
2. According to the relationship:
(I) Formal communication:
"Formal communication" is the transfer of knowledge or direction in a formal organizational structure. Formal communication maintains the relationship between superiors and subordinates. When a manager tells a deputy manager to perform some tasks, it is an instance of formal communication. Formal communication directs workers to have a clear understanding of what the manager is trying to do, and is usually codified and expressed in writing in manuals, handbooks, newsletters, annual reports, and so on.
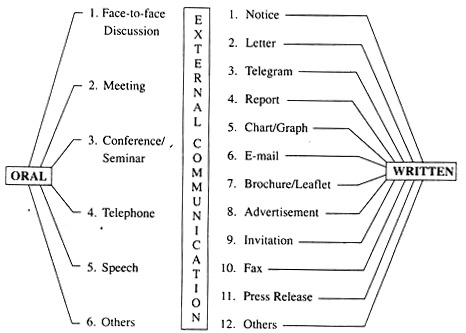
Methods of External Communication
(ii) Informal communication:
"Informal communication" is communication between members of a gaggle or a group, not premised on formal relationships within an organizational structure, but informal relationships between people of equal or different levels. It is premised on understanding. It is referred to as the "grape vine", which represents an informal means of disseminating information and gossip. It does not follow structural routes or processes. It moves in any direction. It's direct, voluntary, flexible, unplanned, and fast-moving.
3. According to the direction:
(I) Vertical communication:
The flow of upward and downward communication constitutes "vertical communication". In such communications, messages and information are sent from higher-level agencies to their subordinates and vice versa.
(A) Downward communication:
Downward communication refers to the flow of data or understanding from high-ranking people to low-level people. I. In an organization, lower-level people have a high degree of fear and respect for such communication, and as a result, that communication is highly acceptable.
Downward communication
(B) Upward communication:
Communication is claimed to be positive when moving from a subordinate to a boss. Reports and suggestions, opinions and attitudes, complaints and complaints fall into this category. "Upward communication" is less common because it is less preferred by top managers due to its cumbersome and complex nature.
Upward communication
(ii) Horizontal communication:
"Horizontal or sideways communication" is between two subordinates or head at the same level and under the same boss. This is especially important in large or decentralized organizations. Staff can help communicate information between positions and units at comparable levels.
Horizontal communication
(iii) Diagonal communication:
Communication between executives or employees in different departments is called "diagonal communication." There is no clear direction. Upward, downward, and horizontal communication takes place. Both verbal and written means of communication are used. It's mostly informal. There is a good relationship between subordinates and bosses. It's very helpful in solving problems and avoiding conflicts, but it's likely to spread rumours.
Diagonal communication
4. By means:
(i) Oral communication:
"Verbal or verbal communication" means the transmission of spoken commands, messages, or suggestions. It is done face-to-face or through a speaking instrument such as a telephone.
Oral communication may occur directly between one person and another or in a group, or indirectly through a meeting or conference. No matter which tool you use, it saves you a lot of time and allows for personal contact. It fosters a friendly and supportive spirit, ensures quick understanding and proper explanation, encourages questions and answers, and stimulates interest.
The speaker is also in a position to understand the reaction of the listener. Again, it's perfect for confidential urgent discussions. However, it is not suitable if the space between the speakers and the listener is too long. It is also inappropriate if the message to be communicated is long and reaches many people at the same time. Also, there is a lack of recorded evidence and future references, and listeners do not have much time to think, act, and react.

Oral communication
(ii) Written communication:
"Written Communication" means sending a message, order, or instruction in writing via a letter, circulation, manual, report, telegram, office memo, bulletin board, etc. This is a good way to communicate and is suitable for long-distance communication and repetition. Standing order. It may create a record of evidence and future references and send it to multiple people at once.
It gives the recipient enough time to think, act, and react. Written communication to be effective must be clear, concise and complete. In addition, it is time consuming, costly, unable to maintain confidentiality, difficult to explain all issues, lacking the opportunity to clarify, inflexible and ineffective in emergencies.

Written communication
(iii) Gesture communication:
Communication is often done through body movements, facial expressions, smiles, voice modulation, signs, handshakes, rubbing hands, eye-to-eye contact, and a type of walking. Communication is called a "gesture" because it is formed by body gestures. communication. '
The methods of communication are different, but it should be remembered that not everyone is used exclusively. Therefore, various methods can be combined and used according to the purpose of communication.

Gesture communication
Barriers to Communication:
There are multiple barriers to the communication process. Intended communiqués are often disturbed and distorted, resulting in confusion and communication failure. Effective communication barriers can be of many types, linguistic, psychological, emotional, physical, and cultural. All these types are described in detail below.
Barriers are one of the most restrictive barriers to effective communication. Language is the most commonly used communication tool. The fact that all major regions have their own language is one of the barriers to effective communication. Even if the dialect is thick, communication may not be successful.
According to some estimates, the dialects of the two regions change within a few kilometers. Even within the same workplace, different employees have different language skills. As a result, communication channels across the organization suffer from this.
Therefore, with this barrier in mind, different considerations must be given to different employees. Many of them are very fluent in certain languages and others will be accustomed to these languages.
2. Psychological barriers:
There are a variety of mental and psychological problems that impede effective communication. Some people suffer from stage phobias, speech disorders, phobias, depression, and more. All of these conditions can be very difficult to manage and can limit the ease of communication.
3. Emotional barriers:
An individual's emotional IQ determines the ease and comfort of communication. Individuals who are emotionally mature are ready to communicate effectively. On the contrary, those who inherit emotions face certain difficulties.
The perfect combination of emotions and facts is important for effective communication. Emotions such as anger, frustration, and humor can obscure an individual's decision-making ability and limit the effectiveness of communication.
4. Physical barriers to communication:
They are the most obvious barriers to effective communication. These barriers can be removed almost easily, at least in principle. These include barriers such as noise, door closures, equipment failures used in communications, and cabin closures. In large offices, the combination of physical separation between different employees and failed equipment can create serious barriers to effective communication.
5. Cultural barriers to communication:
As the world becomes more and more globalized, every large office can have people from several parts of the world. Different cultures have special implications for some of the basic values of society. Clothing, religion or lack of them, food, drinks, pets, and therefore general behavior, change dramatically from one culture to another.
Therefore, these different cultures need to be taken into account when communicating. This is what we call culturally appropriate. Many multinationals offer special courses at the orientation stage to help people understand other cultures and learn how to be polite and tolerant of other cultures.
6. Organizational structural barriers:
As we have seen, there are many ways to communicate at the organizational level. Each of these methods has its own problems and constraints, which are barriers to effective communication. Most of these barriers result from incorrect information and lack of proper transparency available to employees.
7. Attitude barrier:
Certain people want to be left alone. They are introverted or simply less sociable people. Others want to be sociable and sometimes cling to extra! Both of these cases can be barriers to communication. Some people have attitude problems such as huge ego and unfriendly behavior.
These employees can cause serious tension within the communication channels in which they exist. Certain personality traits such as shyness, anger, and social anxiety can also be eliminated through courses and proper training. However, issues such as egocentric behavior and selfishness may not be fixed.
8. Perceptual barrier:
Different people have different perceptions of similar things. This is often a fact that must be taken into account in the process of communication. Knowledge of the audience's perceptual level is essential for effective communication. All messages or communiqués should be simple and clear. There should be no room for a diverse set of interpretations.
9. Physiological barrier:
Certain disorders, illnesses, or other restrictions can also impede effective communication between different channels of an organization. High-pitched voice, dyslexia, etc. are some samples of physiological barriers to effective communication. However, these are not important as they are easily corrected and removed.
10. Technical barriers and social religions barrier:
Other barriers include technical barriers. Technology is evolving rapidly, and as a result, it is difficult to keep up with the latest developments. Therefore, technological advances can be a barrier. In addition to this, the cost of technology is usually very high.
Key takeaways:
Typing and Duplicating-
Input and duplication:
Communications drafted or dictated by executives (letters, circulations, reports, etc.) are sent to typing personnel before they are ready for typing or duplication. Typing or duplication can be done by department or centralized in a pool.
Generally, you need to enter at least two copies of each document. A typical standard typewriter can use carbon paper to make up to 10 easy-to-read copies. Electric typewriters can make up to 30 readable copies on carbon paper. If you need many copies of the same document, a duplicator is used. The duplicator can make up to 200 suitable copies from the same original or master. For even more copies, some form of printing press may be used to increase economics.
There are two ways to organize your typing work in a large organization.
(A) Decentralized or departmental input. (B) Central pool for input. Let's elaborate on them.
a) Department typing: Typing work for each department within a department is performed by a unique set of typists which is called Departmental typing.This arrangement has the following advantages and disadvantages:
Advantage:
1) Typists are familiar with the nature of departmental work, so they can work efficiently.
2) Typists can easily query and correct draft discrepancies and errors, saving time.
3) You can give priority to entering emergency letters as needed. Therefore, the delay is eliminated.
4) Department typists foster loyalty to improve morale and efficiency.
Cons: Disadvantages:
1) The workload is unevenly distributed in the office. Typists in some departments can be overloaded with work, while typists in some other departments may not have enough work.
2) Department typing is uneconomical because it requires more typists to be appointed than justified by the total workload of the office.
3) The noise generated by typing interferes with the work of other staff in the department.
b) Centralized typing pool: In this arrangement, all typists in the office are gathered in a "pool" and housed in a separate department or space. Input work for all departments is sent to the pool. A qualified supervisor or senior typist is responsible for assigning and verifying the work of the pool typist. Once entered, the entered document will be returned to the relevant department for signature.
Advantage. : centralized pool placement has the following advantages:
1) Distribute the workload evenly and evenly among the typists.
2) It brings an overall economy of office costs.
3) Guarantee better supervision by qualified supervisors.
4) The pool typists are housed in a separate room, so noise does not interfere with the work of the department.
Disadvantages: Pool placement also has the following disadvantages:
1) "l001 typists have nothing to do with department staff or work." "As a result, they lose their personal interest in work and can affect morale and efficiency.
2) If the work is of a too technical or professional nature, pool typists may face difficulties in dealing with the work. Work is often delayed because typists need to contact the department to correct draft errors and discrepancies.
Mechanical assistance for transfer work
Transcription of communications, or typing and replication, is done with the help of various types of machinery. Improved types of typewriters and duplicators have been developed to speed up transfer operations at low cost. Some of the more important devices are described below.
Typewriter:
A typewriter is the most commonly used machine for entering all types of correspondence. There are four main types of typewriters used. i) Portable typewriter
ii) Standard manual typewriter iii) Standard electric typewriter iv) Automatic typewriter.
i) A portable typewriter is a small, lightweight and compact machine. They incorporate the main features of a standard typewriter, except for facility fatigue. These are commonly used by executives to enter personal or confidential characters.
External communication
ii) The Standard manual typewriter is a larger size with different length carriages for doing different types of work. Keyboards typically have 45 keys that give 90 letters, both alphabetic and numeric. There is an aggregation function required to enter invoices, statistics, etc. As the name implies, the input is done manually. This machine can make up to 10 original copies using carbon paper. A variation of a regular standard typewriter is a variable typewriter. You can type in different styles and sizes
Typeface. Instead of the type carried by a fixed rod, this machine
Interchangeable circular blocks (known as "golf balls") in different sizes and styles. These machines are used to enter sales.
An electric typewriter is a standard machine that runs on electricity. Enter manually to activate the key. The keys are fast and evenly produce the perfect impression. Carriage movement and margin settings are controlled automatically. With carbon paper, you can make up to 30 original copies. It has the advantage of high-speed typing that minimizes typist fatigue.
Automatic typewriters can automatically fill in documents from punched or recorded issues. Same principle is applied as a player piano. The master is prepared by punching the coded text of the characters into a stencil recorded on paper tape or magnetic tape or disc. When you put the master on the machine and turn it on, the characters are automatically entered on the paper at high speed. Entering fast can save labor and costs.
Duplicator-
Duplicate is an alternative to printing. This has the advantage of making multiple copies of the text quickly and economically.
Various types of replication processes and .machines are commonly used in modem offices. The two main types of replication process are:
i) Stencil duplication. Other types of copying processes and machines used include multigraphs, typographic duplicators, and offset lithography. The spirit replication and stencil replication process are described below.
ii) Spiritual duplication: This process is also known as the Hectographed process. This is a cheap and fast process that can be used by staff with little training. In this process, the master is prepared by typing or writing on a sheet of glossy paper lined with Hectographed carbon. This reverses the impression of the text on the back of the paper. When the master comes in pressure with a spirit-moistened replica par, the impression of carbon is
The master melts and leaves a mark on the paper. You can get 300-450 copies from one master.
Hectographed duplicators are usually rotary, but flatbeds are also possible. On rotary machines, secure the master to the drum or cylinder so that the carbon impression is on the outside. As the drum spins, the paper is automatically fed, giving it a lively, moist and impressed copy paper. The machine can be operated manually or electrically. You can make 60 to 150 copies per minute. In the flatbed process, the original text is written on paper with Hectographed ink or entered with Hectographed ribbon or carbon. The paper is then pressed against a flat gelatin surface that impresses and becomes the master. Press a sheet of mentally moistened copy paper against the gelatin beo get a copy.
iii) Stencil replication: In this process, the master is cut on the stencil by hand using a typewriter (with the ribbon removed) or a steel pen. The stencil is made of a fibrous material coated with plastic. The stencil is placed on the machine's inked drum. When the drum rotates, copy paper is sent to and from the drum. I get the impression of the pressure roller. One master stencil is suitable for making 500 to thousands of copies. You can also save it for future use. The stencil duplicator or mimeograph can be operated manually or electrically. Equipped with a self-inking device, the paper is fed automatically. Can produce 60-200 good copies per minute, depending on the type of machine.
Key takeaways:
Introduction to The Essentials of Business Communication
The business world is filled with opportunities for lack of communication to spoil great ideas and other great situations. As a result, it's imperative that companies establish effective communication policies which employees carefully review and apply them. In some cases, effective business communication is in line with basic etiquette. In other words, treat others fairly and interact with them politely. In other cases, business communication has created a singular communication niche that takes under consideration the ever-changing expectations of the fashionable world.
Interact professionally
Professionalism guarantees that you simply are going to be left behind or revoked once you shouldn't be told or revoked. within the business world, this will mean the difference between a multi-million dollar contract and a company's failure. additionally , professionalism is usually categorized into the etiquette category and therefore the "golden rule" of treating you wish somebody else treats you. Professionalism brings carefully crafted reports, accurate presentations of data , and always keeps in mind that the corporate exists not just for itself except for its customers.
Avoid being invisible
With the arrival of the web age, the invisible face of computers is becoming an increasingly problematic issue for businesses. On the one hand, computer-based communication is straightforward and convenient. On the opposite hand, it can make a corporation feel elusive to its customers and make them desire they're communicating with machines instead of people. As a result, effective business communication requires companies to show to themselves, allow customers to interact with people rather than voice recordings, and supply a private touch when addressing customer concerns. there is.
Develop confidence, not arrogance
Confidence is of fantastic quality, but self-confidence are often confused with arrogance, leading to poor communication and lost opportunities. Customers and colleagues got to confirm that their employees are confident in their abilities and therefore the knowledge to convey important information. Acting confidently is a component of professionalism and etiquette. But when you're confident, it loses its appeal and focuses on your employees, not your customers and colleagues.
Creation of friendliness
The variety of social networking sites available provide businesses with the means to make familiarity and redefine their image for an ever-evolving audience. Even the most important companies can cash in of business communication opportunities to remind their customers that they're made from people, and that they can comfortably interact with them once they need them. With a spread of Internet options available, businesses offers online forums for discussions with customers, Facebook accounts that allow customers to be "friends", and instant messaging that permits customers to answer questions quickly.
Citing references, and using bibliographical and research tools.
Why use a citation tool?
Bibliography and References -What's the difference?
When writing a tutorial treatise, you would like to incorporate an inventory of the sources you wont to write the treatise. There are two main ways to list sources employing a reference list or bibliography.
References include sources that are directly cited within the treatise. for every source, there's a minimum of one text citation within the body of the treatise. APA citations, AMA citations, and MLA citations are used as reference lists in Citation styles
Bibliography, on the opposite hand, contains all the sources utilized in the treatise, whether directly cited or not. The bibliography should include all the fabric referenced when writing the treatise. Two citation styles that use bibliography are Chicago citations and Oxford citations are .
Both the bibliography and bibliography appear at the top of the work being written and are usually organized alphabetically. The treatise can include both a reference list and a bibliography.
Key takeaways:
A project report may be a document that gives details of the general picture of the proposed business. The project report provides an outline of the project proposal to verify the outlook for the proposed plan / activity.
Project reports are documents associated with investment. It contains the info on which the project was evaluated and determined to be feasible. It consists of data on economic, technical, financial, administrative and production aspects. It allows entrepreneurs to understand the input and helps him get loans from banks and financial institutions.
The project report contains detailed information on required land and buildings, annual manufacturing capacity, manufacturing processes, machinery and equipment, prices and specifications, staple requirements, electricity and water requirements, talent needs, and project marketing costs. It is Project production, financial analysis and economic feasibility.
Index of the project report
The index of the project report are as follows.
1. General information:
The project report should provide information about the industry to which the project belongs. you would like to supply information about the industry's past experience, current situation, issues, and future prospects. If the proposed business may be a manufacturing department, you would like to supply information about the products which will be manufactured and why you select them. It must elaborate on the demand for products within the local, domestic and global markets. you would like to obviously identify your business options and clarify why you're starting your business.
2. Executive summary:
The project report should describe the aim of the business and the way it is often successful. an entire picture of the business regarding capital, operations, methods of functioning and execution of the business must be provided within the project report. It must mention the assumptions and risks commonly involved in business.
3. Organizational overview:
The project report should show the organizational structure and patterns proposed to the unit. you want to specify whether the ownership is predicated on a sole proprietorship, a partnership, or an organization. you would like to supply information about promoter biodata, like financial health. The name, address, age qualifications, and knowledge of the proposed business owner or promoter must be included within the project report.
4. Project description:
You should provide a quick description of the project and supply details about:
If your business is service-oriented, you would like to state the sort of service provided to your customers. you would like to explain intimately the way to serve your customers.
5. Marketing plan:
The project report should clearly state the expected aggregate demand for the merchandise. you would like to list the worth at which the merchandise are often sold on the market. We also got to mention the strategies adopted to win the market. After-sales service, if any, are going to be provided and must even be included within the project. you would like to elucidate the way to distribute the merchandise from the assembly unit to the market. The project report should include the following:
6. Capital structure and operating costs:
The project report should include the entire capital requirements for the project. The source of funding should be stated, also because the extent of the owner's funding and borrowing. capital requirements must be stated and therefore the source must even be stated within the project. Estimates of total project costs should be weakened into land, buildings and engineering , plants and machinery, other fixed assets, reserve and preoperative costs, and dealing capital. The venture's proposed financial structure must indicate the expected sources and conditions of equity and debt financing. Operating costs should even be elaborated during this section.
7. Management plan:
The project report should state that:
a. Business experience of business promoters,
b. Management details,
c. Obligations and responsibilities of Team member
d. The organization's current human needs,
e. the way to manage your business,
f. Recruitment and training planning,
g. Management programs and policies.
8. Financial Aspect:
The projected income statement and balance sheet must be presented in the project report to determine the profitability of the business. You need to view the estimated sales, production costs, gross profit, and net profit that you might get from the proposed unit. In addition to the above, forecast balance sheets, cash flow statements and cash flow statements should be prepared each year for a period of at least 3 to 5 years. The income statement and cash flow forecast should include a three-year summary, monthly details for the first year, and quarterly details for the second and third years. The break-even point and return on investment should be included in the project report. The use of accounting and inventory management systems is commonly covered in this section of the project report. The project report should state whether the business is economically and economically viable.
9. Technical Aspects:
The project report provides technical and technical aspects of the project. It covers information on the technologies, production processes, machine capabilities, pollution control plants, etc. selected for the project.
10. Implementation of the project:
All proposed business units need to create a timetable for the project. It must indicate the time that can be completed in the activities related to the establishment of the company. The implementation plan shows the expected schedule for project preparation and completion.
11. Social responsibility:
The proposed unit draws input from society. Therefore, contributions to society in the form of employment, income, exports and infrastructure. Business outcomes should be displayed in the project report.
What is a detailed project report? How is it different from the feasibility study report?
A feasibility study report is created to support your investment proposal. The feasibility of various aspects related to technology, commerce and finance will be investigated in detail by the experts and consultants brought into the feasibility study report. The Feasibility Study Report is called the Techno Economic Feasibility Study. This is the main report on the formulation of investment proposals. The detailed project report is the basic documentation for planning and implementing your project.
Writing Reports on Field Work/Visits To Industries, Business Concerns etc.
Students, especially those engaged in research in engineering, computing , and similar disciplines, are required to participate in so-called industrial visits. they're expected to go to the economic plant, confirm it's working and report on this event.
Unfortunately, they're rarely given coherent instructions on how it should be done. Here, i will be able to clarify now a touch .
First of all, it should be understood that, in theory , it's not expected to supply great insight into the interior workings of the plant visited. you ought to simply tell how it all went. In most cases, you'll tend instructions on the way to organize your report. this suggests that if you've got any questions on the format, you would like to contact the university. However, most reports contains a page , project name, name and standing , report destination name and standing , university name, factory name, and date and site of the visit.
Preface:
This section provides preliminary information about the event, including who proposed and hosted the event, the complete designation of the facilities visited, and therefore the names of the schools and faculties. Remember to say the names and titles of the people that played a crucial role in hosting and conducting the event, the school members who accompanied the scholars , and therefore the total number of participants, both students and school members.
Travel / work plan details:
Here we offer a timeline of visits and list all parts of the journey one by one. Where and when did you begin , when and where did you attend seminars and other events related to your visit, what industries and facilities you visited, when the event ended, and when did you return? No details needed. you merely provides a short report of your actions and movements.
Detailed explanation:
This section details the more important stages of your visit. If you attend a seminar, mention when and where it had been held, how long it had been held, who conducted the seminar, what you learned, and your general impression. If you visit a specific facility, list them and their location, and mention the staff you accompanied during the visit, the new information you bought within the process, and your impressions of the visit.
Travel details:
This part mainly contains technical and statistical information. it's the name of a school member who accompanies you and other students participating within the visit, where you stay and with the assistance of which everything is organized.
Student feedback:
Finally, students are alleged to provides a general opinion about the event as an entire . Whether it helped, whether the factory staff were kind and supportive, and whether or not they gained certain new knowledge and knowledge from the event. Please state who participated within the production of this report and complete it.
In general, there's nothing particularly difficult about creating an industry visit report. you do not need to believe anything. Please follow the university guidelines and list all the points to notice .
Business Negotiations:
Communication is the essence of business and management processes. Business communication refers to learning shared between people inside and outside a corporate organization that is conducted for the commercial benefit of the company. It can also be defined as the dissemination of information within the business by those people. Business communication is communication between two or more parties involved in a business. According to Brennan, "Business communication is the expression, channeling, reception and exchange of ideas in commerce and industry." In WH's opinion, "business-related ideas, news and exchanges of ideas between stakeholders are , Called business communication. ”There are many aspects that play an important role in this exchange of opinions and ideas, including negotiation. Therefore, this article describes bargaining skills in business communication.
Importance of negotiations in business communication:
Negotiation is a discussion between people who take into account the needs and interests of everyone so that no one gets lost. In business communication, it is very important to avoid conflicts and find the right alternatives for everything. Good negotiations contribute significantly to the success of your business and are very important for building better relationships. The purpose of the negotiations is to reach a mutually beneficial agreement. Negotiation is a give-and-take process, meaning giving a concession to the other party. This makes little sense to you, but it does mean a lot to the other person. Good negotiation means satisfying each party and willing to do business with each other in the future. Good negotiations are valued in today's highly competitive market. For those who do not have the bargaining skills of business communication, these skills can be developed through practice and various strategies.
Negotiation strategy is a skill that negotiators adopt to gain an advantage. Good negotiators strive to achieve successful results that are beneficial to both parties. People will want to work with you when you have the potential to negotiate. Learning how to negotiate and improving your skills is an important part of business communication. The ability to negotiate well is the key to personal and business success. Using effective business communication and interpersonal skills is an important strategy used by negotiators to get what they want. Another strategy for improving your business communication skills is to learn how to negotiate with your response. The way you learn to improve your business communication bargaining skills is to put it into practice. Take every opportunity to learn how to negotiate and become proficient. Negotiation is just a game and you have to keep playing and applying strategies until you learn to win each time.
Negotiation skills in business communication
Negotiation skills help businesses solve the differences that occur between different people in a business environment. All workers rely on communication skills to keep negotiations going smoothly, so certain skills need to be adopted for successful negotiations. Negotiation skills are a desirable asset for job seekers, as they are very important in the business and are one of the key skills evaluated when hiring employees. Effective negotiation requires a set of communication and interpersonal skills to achieve the desired results. Below are some of the skills you need to negotiate in business communication –
Interpersonal Skills – Interpersonal skills include the ability to manage relationships and interact well with others. People with interpersonal skills are effective in guiding change, have good communication skills, and can resolve conflicts through cooperation and negotiation.
Active Listening – Active listening is another bargaining skill in business communication. Rather than reacting impulsively in conflicting situations, active listeners actively listen to what everyone has to say, identify the root cause, and draw conclusions. ..
Emotional Control – Emotional control refers to the ability to control, redirect, and properly express destructive moods and emotions. Emotional control relies on the individual's ability to exercise restraint and control impulses during emotional expression. This is an important element of business communication.
Collaboration and Teamwork – The ability to perform collaboration and effective teamwork is an important bargaining skill in business communication. The ability to make participatory decisions and discussions by considering and adding value to the opinions and opinions of all involved is a great asset for effective negotiations.
Empathy – Empathy, or the ability to share the feelings and experiences of others as if they were yours, is another bargain.skill. It is the ability to understand and respond to the emotional state of others. Empathetic people are self-disciplined, competitive, and proactive. They are witty and determined.
Patience – Patience is another very important bargaining skill in business communication. A person with patience can react rather than react and is not impulsive in decision making. Communication is effective when both individuals and groups can communicate patiently and have peaceful conversations.
Confidence – Confidence in your beliefs and opinions is important in business communication negotiations. During negotiations, individuals need to express their opinions with complete confidence and assertiveness and reach agreements or conclusions that are beneficial to everyone.
Attracting deals requires skills, knowledge and awareness. To negotiate effectively is to accept the situation you are facing. When it comes to negotiations, most of us aren't very good at estimating our abilities. If you are a good negotiator, you can increase your business and make it a successful endeavor. Negotiation skills in business communication are important because they are some of the key skills evaluated today before hiring employees. Some already have such skills, while others can continue to practice to develop these skills for effective communication and performance.
Key takeaways:
References: