UNIT II
Communication: Oral & Written
Oral communication Meaning, Advantages/Disadvantages
Oral communication is that the process of expressing information and concepts by word of mouth. Study the kinds and benefits of speech and find ways to enhance your speech skills.
Definition and sort
Good communication skills are the ticket to success within the academic and business world. But have you ever been overwhelmed by fear and anxiety before getting to employment interview or speaking ahead of an audience? Knowing when to settle on speech and developing your speaking skills can assist you at every stage of your career.
Oral communication is that the process of verbally communicating information or ideas from one individual or group to a different. Speech is either formal or informal. Here are some samples of informal verbal communication:
As technology advances, new sorts of speech still be developed. Videophone and video conferencing combine audio and video to permit remote workers to ascertain and ask one another. Other modern oral communications include podcasts (audio clips accessible over the Internet) and voice Internet Protocol (VoIP), which allows callers to speak over the web and avoid telephone charges. Skype is an example of VoIP.
It may take the subsequent forms:
(i) Reports,
(ii) Circulars;
(iii) Magazines;
(iv) Manuals;
(v) Memoranda;
(vi) Newspapers;
(vii) Pictures, diagrams, graphs, etc.;
(viii) Agreements;
(ix) Rule and Procedure books;
(x) Orders;
(xi) Instructions;
(xii) Notice Boards, etc.
Merits or Advantages of Oral Communication
(i) it's less costly or economical as compared to written communication.
(ii) it's quicker and saves in time.
(iii) it's simpler than written communication.
(iv) It establishes a personal touch and results in greater understanding.
(v) Misunderstanding or doubts are often removed then and there.
(vi) Immediate reaction, motivation or response of the receiver are often taken.
(vii) it's more flexible and therefore the messages are often changed to suit the requirements and response of the receiver.
(viii) It provides because the only means of conveying messages in times of emergencies.
Demerits and drawbacks of Oral Communication:
Oral communication has the subsequent limitations or draw backs:
(i) It's less reliable.
(ii) It's influenced by self-interest and attitude of the people.
(iii) Speech has the tendency of being distorted.
(iv) It provides no record for future reference.
(v) It's not suitable for lengthy message.
(vi) It doesn't provide sufficient time for thinking before conveying the message.
(vii) It's language problems, one may mean to convey something, but thanks to his way of speaking, it's going to convey something else.
(viii) It can't be used to communicate with people scattered over distant places.
Written communication Meaning, Advantages/Disadvantages
Written communication refers to the process of communicating a message through written symbols. In other words, the message exchanged between two or more people who use written language is called written communication.
Written communication is that the commonest and effective mode of business communication. In any organization, emails, notes, reports, documents, letters, diaries, job descriptions, employee manuals, etc. are a number of the foremost commonly used sorts of written language.
Such communication is used when the information sent is long and contains complex terms that cannot be explained verbally. The organization also keeps the document in writing so that it can be used as a reference and evidence for transactions at any time in the future. Therefore, it is imperative that all business organizations develop effective writing skills and in still them in all employees.
The validity of the written content depends on the correct selection of words, their organization into the correct sentence order, and the sentence cohesion. Written information is considered more legal and valid than spoken language. Also, people rely more on what is written than what is said orally. However, unlike verbal communication, feedback in written communication is not immediate, as it is not voluntary and takes time to become understandable.
Merits or Advantages of Written Communication:
(i) It ensures transmission of knowledge in uniform manner, i.e., everyone concerned has similar information.
(ii) It provides a permanent record of communication for future reference.
(iii) It's a perfect way of transmitting lengthy messages.
(iv) It ensures little risk of unauthorized alteration within the message.
(V) It's the sole means of exchanging information at distant places even beyond telephonic range.
(vi) It tends to be complete, clear, precise and proper.
(vii) It is often quoted as a legal evidence just in case of any disputes.
(viii) It's suited to convey message to an outsized number of persons at one and therefore the same time.
Demerits or Disadvantages of Written Communication:
(i) It's expensive.
(ii) It's time consuming.
(iii) It becomes difficult to keep up secrecy about a written communication.
(iv) It's rigid and doesn't provide any scope for creating alterations for inaccuracies which may have crept in.
(v) It's very formal and lacks personal touch.
(vi) It encourages red-tapism and involves numerous formalities.
(vii) It's going to be interpreted during a different manner by different people.
(viii) It often becomes lengthy, when messages are conveyed in writing. speech implies
Types: Formal channel of communication:
A formal channel of communication is that the means of communication normally controlled by people in positions of authority in an organisation. Hence, it's also been mentioned as an organization’s ‘main line of operational communication’.
All the reports, records and other forms that provide working information to varied parts of an organisation are included within the formal channel of communication. These channels of communication don't function automatically. a good business organisation will ensure that these are carefully planned and designed to its needs.
Advantages:
(i) Effective:
Formal channels are considered the simpler of channels of communication. With organizations constantly growing in size, formal channels help to bridge the gap within the communication process. it's a readily available means to succeed in through to each corner of an organisation, which might rather be difficult.
(ii) Prevent bogging:
In formal channels, the principles are well laid. for instance, a worker communicates with the supervisor, the supervisor with the manager, and so on. Thus, only necessary information gets filtered and sent to the top. It prevents the top-level management from getting caught up with the irrelevant nitty-gritty (the practical details) of data and leaves it free for bigger decisions and overall management.
(iii) Better monitoring:
An organisation can design formal channels to suit its specific needs. this will help monitor organizational activities. It can make sure that problems are solved without too much delay.
(iv) Good atmosphere:
Good formal channels of communication reflect professionalism. they assist consolidate the organisation. They also keep the managerial personnel in control.
Disadvantages:
(i) Deter free flow of information:
Formal channels deter a free flow of data. Formality demands that the knowledge flow take a specific route only. This inhibits the natural flow of information.
(ii) Time-consuming:
Formal channels of communication often cause delays. the knowledge may not directly reach the person for whom it's meant. it'll often need to take a circuitous formal route where the intervening links could also be meaningless. As a result, formal channels of communication can become time-consuming.
(iii) Affects decision-making:
Filtering and monitoring of data at lower levels may be a double- edged sword. While it's its advantages, it's going to also prevent vital information from reaching the top management. this might change the perspective while making decisions.
Informal Channel of Communication / Grapevine:
The informal channel of communication is commonly discouraged or looked down upon in an “organization, and isn't officially sanctioned. it's popularly mentioned as grapevine. this is often because it runs altogether directions regardless of the formal structure.
The origin of the term grapevine are often traced to the way the botanical vine grew over telegraph wires, making telegraphic messages go in unintended directions. In business life, grapevine owes its existence to man’s gossipy nature.
Humans tend to talk loosely or lightly with their associates wherever they'll be. Time to time they feel the need to get freed from the necessity to stay to logic or truth.
As people set about their work, they need casual conversation with their friends within the office. These conversations affect both personal and business matters. This leads to the generation of a rumour mill, which may be a grapevine.
Grapevine is assessed into four categories:
Grapevine satisfies the social needs of members, results in more relaxed human relations (partly through the release of fantasy), serves to fill the possible gaps within the formal communication and links even those people that do not fall within the official chain of command.
Other characteristics of grapevine are:
(i) It's more people-oriented then issue-oriented.
(ii) Might not be totally authentic and dependable.
(iii) Grapevine transmission flows altogether directions in an organisation.
(iv) Grapevine information travels in no time.
(v) Its responsibility can't be fixed.
Factors resulting in grapevine:
A rumour mill becomes active when the subsequent factors exist in an organisation:
(i) An absence of sense of direction, especially in times of crisis. The more the uncertainty, the greater the rumouring.
(ii) The formation of favoured groups of employees by the management. This breeds insecurity among other employees resulting in rumours.
(iii) an absence of self-confidence amongst employees results in the formation of groups. These groups often run rumour mills.
Advantages:
(i) Speed:
Speed is that the most remarkable characteristic of this channel of communication. it's possible to transmit information remarkably fast since there are no formal barriers and no stopping. A rumour, thus, may spread sort of a wildfire.
(ii) Feedback:
The feedback through this channel is far faster than a formal channel of communication. The channel is like the pulse of an organisation. The reaction to the selections, policies, directives and directions often reaches managers faster through this channel than through the formal one.
(iii) Parallel function:
The informal channel doesn't have official sanction, but is an inevitable parallel to the formal channel. It works as a supplementary channel of communication in an organisation. Good managers are known to use the informal channel to their benefit for transmitting information otherwise unfit for formal channels.
(iv) Support system:
A grapevine is an informal web developed by employees within an organisation. It brings them closer and provides them immense satisfaction.
Disadvantages:
(i) Less credible:
A grapevine is less credible than a proper channel of communication. It can't be taken seriously because it involves only the word of mouth. It is, therefore, likely to be contradicted.
(ii) Selective information:
Informal channels usually fail to hold the entire information. As a result, the receiver doesn't get the essence of the entire message. Mischief mongers or vested interests may use the channel for transmitting information.
(iii) Creates trouble:
A grapevine can foster trouble within an organisation as there's no control over the information sent, received, its portrayal and perceptions. Information gets distorted. Grapevines are often synonymous with the spreading of false or wild stories.
(iv) Leakage:
Information may get leaked at the incorrect time. The term ‘open secret’ in an organisation can often is attributed to such leaks.
Key takeaways:
Summarizing annual report of companies
The annual report is a comprehensive report detailing the activities of the company in the previous year. Its purpose is to provide users, such as shareholders and potential investors, with information about the company's operations and financial performance.
What is included in the annual report?
The annual report provides a great deal of information to readers who can get an overview of the company's overall performance the previous year. It is important to note that many annual reports are not traditional reports that contain a large amount of text. Many companies incorporate many graphics and images, which makes the document visually appealing.
The structure of annual reports is undoubtedly different for each company, but most annual reports typically include:
The following may be a brief description of every item.
1. Letter from the CEO
The letter from the CEO is addressed to shareholders and provides an overview of the company's performance over the previous year. CEOs usually spend a lot of time writing letters to emphasize the company's performance. This is because its performance is related to the industry in which it operates. Since the letter is the primary reader of the report, it may refer to information that shareholders are interested in.
2. Performance highlights
Annual reports usually provide sections to highlight some of the company's key achievements, such as special initiatives, goals achieved, or awards received by the company or its employees. The main goal of this section is for shareholders to be happy with their investment in the company and to convince potential investors to do the same.
3. Financial statements
Financial statements are an important element of an annual report and provide users with quantitative data on certain aspects of their financial performance for the previous fiscal year.
Annual reports typically include financial statements like balance sheets, income statements, and income statements. In addition, it often contains graphs and charts to help break down financial information into readable information.
4. Future outlook
Annual reports typically include information about the company's future performance in order to provide shareholders with information about the company's future goals and objectives. Investors have a complete understanding of the company's current position in each industry and the company's plans for future growth. The report also includes information about your company's strategy and how you plan to implement it in the coming years.
5. Format
Hard copy annual reports are still commonplace, but electronic versions are becoming more and more popular and can be found on the websites of many companies. The electronic version will give more users access to the report in PDF or other formats.
Interactive online reports are becoming more and more popular. This allows users to virtually flip through reports and expand graphics.
Who uses the annual report?
Annual reports are often published and are aimed at a large external audience, including shareholders, potential investors, employees and customers. Some companies and non-profits look at other companies' annual reports to better understand the value of the latter and see if partnerships and other collaborations are feasible in the general community. Can also be an audience.
While these are primarily used to convey financial and performance-related information, the annual report is also used as an advertising tool to highlight some of the company's key initiatives or goals recently achieved.
1. Shareholders and potential investors
Shareholders and potential investors use their annual reports to better understand the company's current position to make investment decisions. The annual report helps potential investors decide whether to shop for shares. It also provides insights into the company's future plans and their goals and objectives.
2. Employee
Employees often use annual reports to understand some of the company's different key areas. Many employees are also shareholders of the company, due to stock option benefits and other schemes. This provides employees with an incentive to become a shareholder.
3. Customer
Corporate customers can use their annual reports to get an overview of the different companies and help them decide which company to build relationships with. Customers are interested in working with high quality suppliers of products and services, and the annual report allows companies to highlight their core values and objectives.
They also make good use of the financial information contained in their annual reports.
Writing minutes of meetings
What are the minutes?
Minutes are notes that are recorded during a meeting. They focus on the key issues being discussed, motions proposed or voted on, and activities to be undertaken. The minutes of a meeting are usually created by a designated member of the group. Their job is to provide an accurate record of what happened during the meeting.
Procedures related to recording minutes
There are five main steps to recording the minutes of a meeting. they are:
Advance planning
If the meeting is well planned in advance, it's much easier to take a few minutes. However, the chair and secretary or minutes keeper must work together to determine the agenda for the meeting in advance. For example, the person who records the minutes can work with the chair to create a document that acts as an agenda and provides a format for the meeting.
Meeting Agenda
If the chair and clerk are unable to meet and draft, it is the clerk's responsibility to obtain a copy of the agenda before the meeting begins. The meeting agenda serves as a guide on how to take notes and prepare the minutes. In addition, the agenda also contains other details that need to be included in the minutes. They include:
Expectations
When individuals are selected as minutes recorders, it is important for them to know what they are expected of. Therefore, individuals need to approach the chair of the committee and ask about their role in the meeting. For example, if the meeting contains a motion for a proposal, the designated member must ask if the name of the motion for the proposal and the secondment should be included.
What to include in the minutes?
Before recording the details, the designated minutes recorder should be familiar with the type of information that needs to be recorded. Although groups may record notes in a particular format, the minutes of a meeting typically contain the following details: Overall.
The process of writing minutes
E- correspondence.
E-communication concept
The need for the Internet is increasing. Whether you are an expert, student, non-expert, or expert, everyone has a broad eye on the Internet for everyday use. There are many things you can do on the Internet. Perhaps the use of the Internet has made many things much easier. Today, even the creation of formal emails is accessible, and many companies don't even need to train their employees in this regard.
Banking online, finding an overseas educational institution, and sending corporate emails has never been easier. From basic to complex tasks, everything can be done on the Internet today.
All of us look for answers in the sea of knowledge known as the World Wide Web (www). The World Wide Web provides a system that is reciprocally linked to many documents and can be accessed from the Internet.
You can use your web browser to navigate through various hyperlinks to search for images, text, videos, and many other multimedia. Many people misunderstand that the Internet and the World Wide Web are the same thing.
But these things are actually very different from each other. They are related to each other, but not similar. This brings us e-communication.
What is E-communication?
When one company sends an email to another and a response to that email is given, communication between the companies is formed. Such communication, when done via online means of e-mail, is called e-communication.
When one company sends an email to another and a response to that email is given, communication between the companies is formed. Such communication, when done via online means of e-mail, is called e-communication.
Therefore, electronic communications are usually election or email communications. The use of communication here is done via electronic means. Information between the parties is exchanged via email address.
Therefore, it is feasible for both parties to provide the correct email address. This is how both receive information.
Compose a formal email
Email composition is considered a very important part of any organization. It is generally considered the only form of written communication. Therefore, it is very important.
Also, emails often contain company personal information, so the person sending the email should be careful.
Therefore, it is his duty not to share this information with others. Before we know more about composing formal emails, we need to understand the concepts and features of composing emails.
Email concept
Email, an abbreviation for email, is a very common method of formal communication in an organization. This process involves sending and receiving messages in the form of text, files, images, and so on.
There are also many options for sending automatic emails to more people using the mailing list and email merging options. There are many forms of oil used in tissues.
They range from book chapters to business presentations to detailed contracts. Graphic files and artwork can also be sent by email.
In today's era, many businesses revolve around email and the communication that takes place through it. The reason is the advantage that email has over other forms of communication. The main thing is 24-hour availability.
Over the last decade, email has become the most important form of business communication, and therefore many small businesses are beginning to adopt it.
As a result, many consultants advise companies to compose emails for ease of use.
Another factor related to email is security and security. Now you can easily and securely transfer texts, images, and videos by email.
Email features:
Cost-effectiveness: Email is very cost-effective and provides communication in a faster way than other modes of communication. With the help of your smartphone, you can easily send emails anytime, anywhere.
Package: Messenger and Outlook allow you to compose emails in different formats. This can help you send it to anyone right away. You can also use the address box to allow the sender to send the email without any problems. You can use email to resize fonts, highlight important points, save images, and more.
Spam: Junk e-mail and junk e-mail can be sent to the junk e-mail folder without any effort. These emails may be advertisements, promotions, jobs, etc. that you are not interested in.
Signature: You can customize your signature based on your email requirements. Whenever you reply to someone or send an email to someone, this signature will automatically appear at the bottom of the email. Therefore, you don't have to write the details over and over again.
Attachment: This feature allows you to share documents, presentations, photos, videos, etc. with your email. Attachment size is limited.
Key takeaways:
Soft Skills – Definition, List, & Examples
Hiring managers usually explore for two sorts of skills in the prospective candidates – hard skills and soft skills. Hard skills are job-specific skills which are attained by attending school or training programs or through experiential learning on the job. But if you’re trying to find what other important skills hiring managers search for while screening resumes, read on as we explain soft skills and their importance.
Soft Skills
Soft skills are interpersonal skills which are used to describe your approach to life, work, and relationships with people. Unlike hard skills, these aren't professional job-specific skills like accountancy, graphics designing, etc. Soft skills are your unique point which provides you a competitive edge over others within the workplace and in life.
Other names given to soft skills are people skills, interpersonal skills, and social skills.
Examples of Soft Skills
Soft skills comprise of personal attributes, communication skills and talents, and personality traits which differentiate people with similar hard-skill-set from one another.
Some samples of soft skills are:
Meaning and Definition
Soft Skills are often defined as “personal attributes that enable someone to interact effectively and harmoniously with other people”. This skill is indeed, one among those rare intangible abilities which will make a difference between success or failure. during this article, we'll discuss the significance of soft skills and how it helps you to succeed.
We are well aware that, one must sharpen technical skills to urge employment. While professional and technical skills might get you a job and open the opportunities, Soft skills will provide the needed icing on the cake if you actually wish to achieve this competitive world. Your work ethic, your attitude, your emotional intelligence, your communication skills and other personal attributes are a number of the soft skills which are crucial for your career success.
When you are equipped with soft skills, your chances to excel as a leader are high. Motivating, problem-solving, delegating and team building would be a cake walk in the corporate world. One should know, the way to get alongside people and being positive is crucial for attaining success.
Soft Skills Importance
Most interactions with people require some level of soft skills. At a corporation you might be negotiating to win a new contract, presenting your new idea to colleagues, networking for a new job, and so on. We use soft skills every day at work and developing these soft skills will assist you win more business and accelerate your career progression.
On the opposite hand, a lack of soft skills can limit your potential, or maybe be the downfall of your business. By developing strong leadership, delegation, teamwork, and communication abilities, you'll run projects more smoothly, deliver results that please everyone, and even positively influence your personal life by improving how you interact with others.
Outside of the office, soft skills like communication are used to build friendship groups and meet potential partners. You might be negotiating the worth of your new house renovation, or mentoring your neighbour’s children on the weekend. Soft skills are useful both in our professional and private lives.
The importance of soft skills
1. Career progression and promotion
iCIMS Hiring Insights (2017) found that "Ninety-four percent of recruiting professionals believe an employee with stronger soft skills features a better chance of being promoted to a leadership position than an employee with more years of experience but weaker soft skills."
It's become vital to develop these skills if you would like to progress in your career as they're going to set you aside from others at the interview and on the work.
2. The modern workplace is interpersonal
Skills like active listening, collaboration, presenting ideas and communicating with colleagues are all highly valued within the modern workplace. Strong soft skills ensure a productive, collaborative and healthy work environment, all crucial attributes for organisations in an increasingly competitive world.
3. Customers and clients demand soft skills
Consumers these days have a large number of choices of where to shop for from, bought about by the internet and smartphones. For these consumers, convenience and low prices are easy to return by, so customer service is commonly what influences the choice to use a specific business.
The ability to speak at a person's level with customers is therefore an important think about an organisation’s success.
4. The longer-term workplace will believe soft skills
Automation and artificial intelligence will lead to a greater proportion of jobs relying on soft skills. Advances in technology have caused tasks that need hard skills to say no, making soft skills a key differentiator within the workplace. A study by Deloitte Access Economics predicts that “Soft skill-intensive occupations will account for two-thirds of all jobs by 2030”.
As the cost of robots decreases and therefore the performance of AI improves, jobs like manufacturing line workers will become automated. Traditional skills like teamwork, communication and important thinking are going to be more important than ever.
5. Soft skills are hard to automate
Following on from the previous point, soft skills like emotional intelligence are hard to automate and unlikely to become automated anytime soon. this suggests they're expected to become more desirable within the near future.
However soft skills are often difficult to show and track improvements on. Companies like Virtual Speech are tackling this by using VR as a way to enhance soft skills.
6. Soft skills are in high demand by recruiters
Soft skills are in high demand in the workforce. consistent with the 2017 paper by a Harvard student on the importance of social skills in the labour market, jobs requiring high levels of social interaction grew by nearly 12 percent as a share of the U.S. labour force. Most in-demand soft skills
In the paper’s conclusion, it reasons that because computers are very poor at simulating human interaction, social skills are still important. Therefore, individuals should still look to enhance their social and soft skills through activities like volunteering, leading a team or maybe by performing on an open-source project with people.
The importance of sentimental skills to businesses
Soft skills are needed across all industries, as an example, strong communication skills are needed whether you're working as a nurse, a hairdresser, a mechanic etc. Developing each soft skill comes with its own advantages, for instance, improving communication will help your employees interact more effectively and improvements in time-management can increase productivity.
There also are general benefits of employees developing their soft skills:
Grooming Manners and Etiquettes:
Business dress code is commonly a matter of common-sense prevailing while deciding what to wear to the work place. However, cases of dressing disasters still occur, especially during the summers once you might find a colleague dressed up to work with a "day at the beach" hangover.
The reason these eyebrow-raising errors in dress codes occur is that a lot of companies, especially start-ups and small to medium-scale businesses, have relaxed norms to almost no norms on dress code. Even if there are dress code rules, at times, they're vague and ambiguous. In such situations, it's always advisable to err on a part of “too formal” attire, as against arriving dressed up informally enough to boost a few eyebrows.
A few common errors people make in business dressing are −
In addition to the ideas discussed here, there are some areas that require to be taken care of before you finally enter the premises and knock on that door. let us discuss these −
Final Tips for Grooming-
Effective Speaking
Speaking effectively is defined as speaking in such a way that your message is clearly heard and, if possible, acted upon. There are two main elements to speaking effectively: what you say, and the way you say it.
What you say means your choice of words. The words you may use when chatting to a friend are likely to be quite different from those utilized in a proper presentation or interview.
Similarly, the way that you speak also will vary in several situations. However, there also are likely to be some common factors: for instance, whether you naturally talk quietly or loudly, and how you use body language.
This page discusses aspects of effective speaking. It also suggests ways in which you can become a more effective speaker.
Aspects of Effective Speaking
Whether you're talking to a major conference about a new scientific discovery, your children about their behaviour or your boss a few pay rises, you need to be able to speak effectively. This suggests considering every possible tool and aspect to make sure that nothing distracts or detracts from your message.
Aspects of Effective Speaking
If unsure about your meaning, your audience will come to the words that you used and double-check what you might have meant. it's therefore important to decide on carefully, especially when you are saying something important. Things to consider include:
Your audience
The words you select will be different if you are talking to 200 people at a conference, a trusted colleague, your boss, or your children. you need to believe your audience’s overall level of understanding of the subject, and also the sort of language that you use.
Shorter sentences are easier to process and understand
Using shorter sentences also creates urgency.
Simpler words also are easier to understand. If you cannot explain something in simple terms, you've got probably not understood it yourself. this is often particularly important if your audience are not all native speakers of the language.
Accents
They may also, however, in some situations, create potential barriers to communication. for instance, if you've got a really strong accent, people from another area or country may find it harder to understand what you're saying. you'll therefore need to slow down your speech to ensure that they need time to process what you're saying.
It is worth remembering, however, that words are only a part of your overall communication and message. The tone of voice and your body language also send strong messages.
You’re Voice
Your voice can reveal as much about your personal history as your appearance. The sound of a voice and the content of speech can provide clues to an individual's emotional state.
For instance, if self-esteem is low, it's going to be reflected by hesitancy within the voice. A shy person may speak quietly, but someone who is confident in themselves will be more likely to own command of their voice and clarity of speech.
It is worth taking time to boost your command over your voice, especially if you find it hard to talk publicly. It can even help to boost your confidence!
It is important to urge used to the sound of your own voice. most people are more relaxed in a private situation, particularly at home, where there are no pressures to conform to any other social rules and expectations. this is often not the case in public situations when there are all kinds of influences exerted upon the way people speak.
You might also note any aspects of your speech which reduce the overall effectiveness of your message. This might include a tendency to mention ‘um’ or ‘er’ a lot, to slur one or more letters together, or stammer slightly
Often people don’t just like the sound of their own recorded voice - within the same way that some people do not like photographs of themselves - they can feel embarrassed.
Most of us aren't used to hearing our own voices and these feelings are totally normal. Get past the initial, ‘Do i really sound like that?’ stage and develop a far better understanding of your voice.
The more you get used to the sound of your voice functioning during a slightly more formal way, the better it's when doing it 'for real'. In conversational mode, individuals tend to talk in short phrases, a couple of at a time. Speaking or reading aloud helps you to become wont to the more fluent sound of your voice.
Slow down: it's a natural reaction to want to get it over as fast as possible and this often causes people to stumble over their words. Speeding up also occurs once you are nervous and usually makes you more difficult to understand.
Keep your head up: Try to not tuck your chin into the book as your voice is then addressing the ground. Hold your book higher and project your voice.
Pause occasionally: Let the end of a sentence or the end of a paragraph offer you a chance of a small, two or three second rest. Pauses are often useful for emphasis.
Vocal Production
The following three core elements of vocal production got to be understood for anyone wishing to become an effective speaker:
Volume
This is not a question of treating the voice just like the volume control on the TV remote. Some people have naturally soft voices and physically cannot bellow. Additionally, if the voice is raised an excessive amount of , tonal quality is lost. rather than raising the voice, it should be 'projected out'. Support the voice with many breath - the further you would like to project the voice out, the more breath you need. It also must come from the diaphragm, not the throat.
When talking to a group or meeting, it's important not to aim your talk to the front row or simply to the people nearest you. Instead, you would like to consciously project what you've got to say to those furthest away. By developing a strong voice, as opposed to a loud voice, you'll be seen as someone positive.
Clarity
Some people tend to talk through clenched teeth and with little movement of their lips. it's this inability to open mouths and failure to form speech sounds with precision that's the root explanation for inaudibility. The sound is locked into the mouth and not let loose.
To have good articulation it's important to unclench the jaw, open the mouth and provides full benefit to every sound you make, paying particular attention to the ends of words. this may also help your audience as a particular amount of lip-reading will be possible.
Variety
To make speech effective and interesting, certain techniques are often applied. However, it's important to not sound false or as if you're giving a performance. Words convey meaning, but the way that they're said reflects feelings and emotions. Vocal variety can be achieved by variations in:
Pace: this is the speed at which you talk. If speech is just too fast, then listeners won't have time to assimilate what's being said. it's also an honest idea to vary the pace - quickening up then |every now and then"> sometimes and then slowing down – because this may help to maintain interest.
Volume: By raising or lowering volume occasionally, you'll create emphasis. If you drop your voice to almost a whisper (as long because it is projected) for a sentence or two, it'll make your audience suddenly alert. take care to not overuse this technique, though, or it'll lose its impact.
Pitch - Inflection - Emphasis: When speaking in public, try to convey the information with as much vocal energy and enthusiasm as possible. This doesn't mean your voice has got to swoop and dive everywhere the place in an uncontrolled manner. try to make the talk interesting. Remember that once you are nervous or excited, your vocal cords tense and shorten, causing the voice to get higher. Emphasise certain words and phrases within the ask convey their importance and help to add variety.
Pause: Pauses are powerful. they will be used for effect to highlight the preceding statement or to achieve attention before a crucial message. Pauses mean silence for a couple of seconds. Listeners interpret meaning during pauses so have the courage to remain silent for up to 5 seconds – dramatic pauses like this convey authority and confidence.
Body Language
However, your body language is additionally important. This includes how you stand, your facial expressions, the way you use your hands to emphasize your speech, and even whether and with whom you create eye contact.
There is more about the way to use body language to speak effectively in our page on body language. This includes considering how distant you're from your audience, and thus whether you need to exaggerate your gestures to form them clearer.
The importance of congruence
Perhaps the foremost important aspect of effective communication is congruence.
For communication to be effective, your non-verbal communication must reinforce your words: the 2 must say the same thing. Non-verbal communication is far harder to disguise than verbal—if you see that someone’s body language is giving a special message from their words, it pays to listen to the non-verbal communication first because it is more likely to reflect their real views.
You may therefore get to put some thought into how you want to use body language and other non-verbal cues. this is often particularly important if you're trying to urge across a difficult or unwelcome message.
Interview Skills -
1. Do your background research.
This may not seem like an actual interview skill, but it is. If you walk into an interview saying, "Now, what do you do again?" and "Do you guys have funding yet?" you're doomed before you start. no matter how sparkly your personality is, you have to do the background research.
2. Be polite to everyone.
You may have heard stories of individuals who were rude to the receptionist, cut someone off in the parking lot, or yelled at the barista at the cafe round the corner then didn't get the job. These things happen, and they can ruin your chances. i will be able to never, ever, not during a million years hire the one that is rude to the receptionist or barista. Many recruiters and hiring managers feel the same.
3. Watch your body language.
Some of them are especially important in an interview. For instance:
4. Watch your real language.
If you have a potty mouth, reserve it for your friends, and not for the interview. If the interviewer is letting the f-bombs fly, you'll feel more comfortable doing the same, but otherwise, use words that express your actual feelings and concepts.
5. Review your own resume.
You know what you probably did, right? Are you sure? I once got caught off guard in an interview when the hiring manager asked me a selected question about an accomplishment on my resume. I had to stumble for a moment before my brain latched on to what she was talking about. Don't make that mistake. Refresh your memory, especially old jobs.
6. Prepare for standard questions.
Lots of interviewers are getting to ask you to "tell me a few times when ..." followed by something appropriate for your field and this particular job. you ought to have great answers prepared for this. Brainstorm a list of possible questions and work on your answers.
7. Prepare your wardrobe.
Yes, people judge you by what you're wearing. Most interviewers aren't going to care the brand of your jacket, or if the heel of your shoe is scuffed, but you ought to be dressed appropriately. Generally, for many professional jobs that means a suit, or one step lower. If you're concerned, attend their parking lot before the interview and watch people begin. If their style is business casual, you ought to wear a suit. If they're wearing jean and flip flops, you're probably fine in business casual, but better to be overdressed than underdressed, in most industries.
8. Prepare your questions.
Don't ask questions that could be answered by watching the company website. Do ask questions on the challenges of the position, what success seems like, and the way this position fits in with the organization's goals. Remember, you want to look like you're really interested in succeeding during this position, and you need this information to try to so.
9. Don't badmouth your former employer.
You're most likely getting to be asked why you're looking to leave your current job (or why you left your last job if you're unemployed). Don't lie, but don't be super negative either. "My boss may be a huge jerk. She is nit-picky, plays favourites, and smells like tuna" this stuff may all be true, but you don't come out looking good. find out how to explain why you're leaving, why you bought fired, what you learned from it, and the way this all means this new job may be a great fit.
10. Don’t forget the thank you card.
It doesn't need to be a card anymore; an email will do exactly fine. you'll get hired without one, but it is a nice gesture to send a fast follow up email to the hiring manager and recruiter. It keeps you in their minds and shows your politeness, which brings this full circle. You start by being nice to everyone, and you finish the interview by being nice to everyone, and you increase your chances.
Listening Skills
_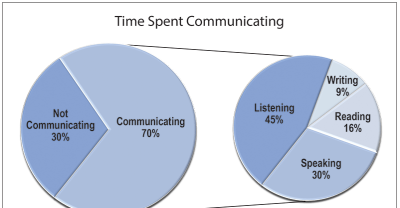 _____________________
_____________________
The Purpose of Listening
There is no doubt that effective listening is a particularly important life skill. Why is listening so important?
1. To specifically specialise in the messages being communicated, avoiding distractions and preconceptions.
2. To realize a full and accurate understanding into the speakers point of view and concepts.
3. To critically assess what's being said. (see our page on critical thinking for more).
4. To look at the non-verbal signals accompanying what's being said to enhance understanding.
5. To point out interest, concern and concentration.
6. To encourage the speaker to speak fully, openly and honestly.
7. To develop an selflessness approach, putting the speaker first.
8. To reach a shared and agreed understanding and acceptance of each side views.
Barriers to Effective Listening
For example, one common problem is that rather than listening closely to what someone is saying, we frequently get distracted after a sentence or two and instead start to think about what we are going to say in reply or think about unrelated things. this suggests that we do not fully hear the rest of the speaker’s message.
This problem is attributed, in part, to the difference between average speech rate and average processing rate. Average speech rates are between 125 and 175 words a minute whereas we will process on the average between 400 and 800 words a minute. it's a common habit for the listener to use the spare time while taking note of daydream or believe other things, instead of focusing on what the speaker is saying.
Of course, the clarity of what the speaker is saying also can affect how well we listen. Generally we discover it easier to focus if the speaker is fluent in their speech, has a familiar accent, and speaks at an appropriate loudness for things . it's more difficult, for instance, to focus on somebody who is speaking very fast and very quietly, especially if they're conveying complex information.
We can also get distracted by the speaker’s personal appearance or by what somebody else is saying, which sounds more interesting.
These issues not only affect you, but you're likely to show your lack of attention in your body language.
Generally, we discover it much harder to regulate our body language, and you're likely to point out your distraction and/or lack of interest by lack of eye contact, or posture. The speaker will detect the matter, and probably stop talking at the best. At worse, they'll be very offended or upset.
Principles of Effective Listening-
1. Stop Talking
Don't talk, listen.
When somebody else is talking hear what they're saying, don't interrupt, hash out them or finish their sentences for them. Stop, just listen.
When the opposite person has finished telling you may need to clarify to confirm you have received their message accurately.
2. Prepare yourself to listen
Relax.
Focus on the speaker. Put other things out of mind. The human mind is definitely distracted by other thoughts – what’s for lunch, what time do i want to leave to catch my train, is it getting to rain – attempt to put other thoughts out of mind and consider the messages that are being communicated.
3. Put the Speaker at ease
Help the speaker to feel free to talk.
Remember their needs and concerns. Nod or use other gestures or words to encourage them to continue.
Maintain eye contact but don’t stare – show you're listening and understanding what's being said.
4. Remove Distractions
Focus on what's being said.
Don’t doodle, shuffle papers, look out the window, pick your fingernails or similar. Avoid unnecessary interruptions. These behaviours disrupt the listening process and send messages to the speaker that you simply are bored or distracted.
5. Empathise
Try to understand the opposite person’s point of view.
Look at issues from their perspective. let go of preconceived ideas. By having an open mind, we will more fully empathise with the speaker. If the speaker says something that you simply disagree with then wait and construct an argument to counter what's said but keep an open mind to the views and opinions of others.
6. Be patient
A pause, even an extended pause, doesn't necessarily mean that the speaker has finished.
Be patient and let the speaker continue in their own time, sometimes it takes time to formulate what to say and how to say it. Never interrupt or finish a sentence for somebody.
7. Avoid Personal Prejudice
Try to be impartial.
Don't become irritated and do not let the person’s habits or mannerisms distract you from what the speaker is basically saying.
Everybody features a different way of speaking - some people are for instance more nervous or shy than others, some have regional accents or make excessive arm movements, some people wish to pace whilst talking - others like to sit still.
8. Listen to the Tone
Volume and tone both boost what someone is saying.
A good speaker will use both volume and tone to their advantage to stay an audience attentive; everybody will use pitch, tone and volume of voice in certain situations – let these assist you to understand the emphasis of what's being said.
9. Listen for Ideas – Not Just Words
You need to urge the entire picture, not just isolated bits and pieces.
Maybe one among the foremost difficult aspects of listening is that the ability to link together pieces of data to reveal the ideas of others. With proper concentration, letting go of distractions, and focus this becomes easier.
10. Wait and watch for Non-Verbal Communication
Gestures, facial expressions, and eye-movements can all be important.
We don’t just listen with our ears but also with our eyes – watch and pick up the extra information being transmitted via non-verbal communication.
Group Discussion
Purpose of a group discussion is larger than simply judging your knowledge. The underlying reason why a GD is conducted is to assess you as a team member. you're alleged to possess a collection of group discussion skills to ace during this round.
Please undergo some crucial group discussion skills below to craft your very own GD strategy accordingly.
Reasoning
Try to find the GD topic category that you are comfortable with. Also, follow the news regularly to remain updated about Current Affairs. If you're good at debating, factual or social topics are your forte. Bookworms (or avid readers) may have an edge over the rest in abstract and situation-based topics.
Speaking
If the given topic is familiar, you must start the GD. Collect your ideas systematically (preferably in points) and start speaking. If not, attempt to jump in as a second or 3rd speaker. so as to talk confidently during a GD, commit yourself completely to English at least a week before the round.
You have to consciously train yourself to communicate in English sort of a pro. Build a good command over the language that you are going to be discussing in. So, listen to English songs, watch English movies and sitcoms, follow English news and read a newspaper daily for 15 days at least, before your GD.
Time Management
In the time given before the beginning of GD, define the topic, write 2-3 pros and cons and provides a 3 point structure to the discussion. The structure has relevancy typically for current affairs and social/factual topics. So frame just 3-4 points for a turn and try to end those points in time.
Presentation
If you are ready to start then use a line or two to define the subject and spell out the structure.
Paraphrasing/summarizing
If you manage to go second or third then paraphrase the explanation of the topic, propose a structure if missed by the first speaker and provides a couple of some pros and cons.
Creativity
People speaking afterward should either attempt to repose on the points given by others or attempt to bring in a replacement dimension to the discussion. during a socially inclined topic, pitch every angle of the argument and take a middle path. Bring out different views and excerpts from the speeches/articles for a subject of current affairs. And for situation-based topics, attempt to have a couple of guidelines and follow them to hold forward the discussion
Listening
Once you're through with your point, listen passionately to what others are speaking. Nod if you agree. Keep watching others and understand their facial expression.
Proactive
If there are N people during a GD then you should be the N-th turn for raising your points. If you're speaking at N-1 or N-2 then you're dominating the GD which is really a good sign, So in a group of 8 people, attempt to snatch the 6th-7th turn.
Public speaking
Once you get your chance to talk, speak slowly and with authority. Focus more on ensuring that your points are understood by people instead of becoming self-conscious or self-analyzing your speaking skills or relevance of points.
Social engagement
Don’t be self-conscious and keep thinking or rehearsing your points. Use this point to know the points given by others. Use somebody’s point by rephrasing it and posting it to someone who has not engaged within the discussion so far.
Memory and recalling
Bringing an international perspective with statistics or an anecdote creates a good impression.
Writing
Write down just 4-5 words because you don’t want to risk a blank thought at your turn. it's an opportunity and it's happened to me variety of times when I thought of my argument but was completely blank when my turn came.
Analytics
The interviewer tests you on several parameters (especially your ability to see , articulate and conceptualize), not just on your points. So make sure you're covering all the parameters. Give your ideas a structure, listen, bring the group back if they digress, give the topic a replacement dimension, build-up on someone else’s point, give credits to a fellow participant, etc.
Leadership skills and initiative-taking ability
Taking initiative is indicative of your ability to impart direction to the group and define the key issue(s) along which the discussion has to progress. The three "Cs" which rank you high on this parameter are clarity (the details to be discussed), content (the vertical depth in each point) and confidence. The "Key Word Approach", wherein you begin with defining the dominant words within the topic then develop subsequent constructs, can assist you to initiate effectively. this may also demonstrate your leadership skills.
For example, during a topic like "Should Republic Day celebrations be redefined?", the key words are "Republic" and "redefined". Thus, a good strategy is often giving a backdrop against which this day is celebrated, then graduating to the way it's celebrated and finally talking about ways and means of redefining (if at all). If demonstrated properly, this skill gets you within the visible limelight and reflects your ability to break the ice and evoke a discussion! However, if mishandled (e.g., you'll begin on a high note then abruptly recede into an eerie silence), it puts you in an embarrassing position!
Knowledge
Knowledge reflects your ability to possess an opinion on issues and concerns of contemporary relevance and hence your ability to attach with different aspects of the environment (economic, political, business, social, etc.). It assumes, even more, relevance for a fact-intensive topic like "Indian Economy within the post WTO regime". Here, knowledge becomes a pointy differentiator and helps you to leverage a robust competitive advantage. Unless you've got the requisite knowledge of the given topic, your discussion runs the danger of being shallow and superficial. Being well versed in current affairs and problems with concurrent importance can assist you to do well along this parameter.
Group Dynamics:
This basically demonstrates the skill to strike a balance between individual excellence and group performance. an individual scoring high on this parameter are going to be more probable to work in groups and hence contribute effectively to organizations. It also reflects your team skills, listening skills and willingness to simply accept diverse viewpoints.
Logical Ability/Analytical Skills
This indicates your ability to effectively flowchart your thought process and analyze the subject in a comprehensive manner. It reflects your ability to construct logical arguments and structure the discussion during a streamlined manner, avoiding random forays.
Lateral Thinking:
This reflects your ability to think off the feet and contribute on a creative and unorthodox tangent. it's even more relevant for an abstract topic, where the scope to view the subject from an avant-garde angle is proportionately more (e.g., during a topic like "red and blue", somebody who translates this into a coke (red) and Pepsi (blue) warfare or discuss the marketing strategies of kingfisher (red) and jet (blue) or harp on the gender differences as mentioned in John Gray's "Men are from Mars (red) and women are from Venus (blue)", will certainly stand apart.)
Communication Skills:
This evaluates the candidate's ability to attach with the group and is measured from a dual perspective - verbal and non-verbal. While verbal communication scores the student on parameters like fluency, articulation and modulation, the non-verbal quotient defines his/her adequacy vis-&-vis visual communication, gesticulation, eye contact and posture.
Oral Presentation Skills
There is a myth that great speakers are born, not made. this is often based on the misconception that somehow certain individuals have the innate ability to stand ahead of an audience with no anxiety and provides a moving, dynamic speech. the reality is, however, that great speakers generally spend years developing and practicing their art of communication. All great speakers had to learn the fundamentals of organization, preparation, delivery and dealing with anxiety. so as to do anything well, it takes constant practice and a mastery of the fundamentals. Speaking is not any different.
One of the foremost important techniques you'll apply to become a more confident and effective speaker is to scale back anxiety. If implemented, the subsequent tips could help reduce your anxiety before your next presentation:
Planning your presentation is another component to becoming an efficient speaker and presenter. There are essentially two steps that should be followed before delivering a presentation: 1) develop your objectives and 2) analyze your audience. In preparation, one must identify the values, needs and constraints of the attendees and the level of data of the audience. for instance, do not use slang, jargon, acronyms, or technical terms without explanation. It should even be determined beforehand “what will work” and “what won’t work”. In other words, what will gain you the foremost favourable reaction. in order to establish these items in advance, you ought to put yourself within the shoes of the people that will be listening to your presentation.
The next phase towards improving your effective public speaking skills is organizing your thoughts. There is variety of steps to the present process:
Step #1 Brainstorm main ideas. Use index cards or post it notes and only use one idea per card.
Step #2 State the sub points. Ideally there should be between 2-5 sub points in your presentation. Be specific using explanations, data and evidence to back up your points.
Step #3 State the benefits. Specifically state the advantages before and at the end of the body of your presentation.
Step #4 Develop hand-outs. Hand-outs should reinforce details, summarize action items and include supporting data.
Step #5 Develop visual aids (PowerPoint slides, charts and graphs). Visual aids should be wont to focus the eye of your audience, reinforce the verbal message and to stimulate interest. Confine mind that effective presentations are people-centred, not media-cantered. Too many presentations believe the media to hold the message. While the media can certainly help, it’s your interaction and rapport with the audience that creates the difference between an efficient or ineffective presentation.
Step #6 Main idea preview/review sentence (i.e. tell them what you’re getting to tell them, tell them, then tell them what you told them).
Step #7 Develop the introduction. Get the audience to focus their attention on you, provide background information and introduce yourself – who you're and why you’re qualified.
Step #8 Develop the conclusion. Your conclusion should be persuasive sort of a “call to action”. Spell out what specifically they have to do, when and the way .
The delivery of your presentation is another key to a successful presentation. an efficient presentation should be delivered within the following sequence:
In order to return across to your audience as confident and persuasive, you should consider the way you physically deliver your points to your audience. the subsequent are some helpful tips to assist you achieve A level of confidence in delivering your presentation:
Level of confidence in delivering your presentation:
Key takeaways:
Correspondence: Handling Correspondence
The most convenient thanks to reach people is to send a message by text or letter. These are some sorts of communications utilized in business. this is often called business communication. Get wont to business communication.
Suppose you're given a course project at a university. There are 6 people in each group. for instance, you and your other five friends plan to attend the subject. How does one contact them? Is it always possible to satisfy them? Is it always possible to speak to them?
Suppose you would like to ask a professor something. for instance, he isn't in town at that point. How does one answer the question? does one want to attend for him to return back? number! you'll contact them by sending them a text message or writing an email.
Business communication
Just as we express our opinions, opinions, thoughts and concepts by writing them. Business people also feel the necessity to precise themselves. it's not always possible for them to recollect all the small print of their business.
They use the only way of expression: written language. written language within the business world is business communication.
Meaning of Business Correspondence
All communication within the sort of letters is communication. Business people express themselves through business communications. you'll also ask questions and uncertainties through business communications.
Businessmen write and receive letters in their daily lives. Communication between or within two organizations falls into this category. Supplier letters, complaint letters, inquiry letters, and job seekers are just a couple of examples.
Importance of business communication
Business communications help some organizations achieve their goals. Through it you'll achieve your goals.
1. Maintain a correct relationship:
Not all companies or organizations are always ready to reach a selected person. This costs any business. Here, business communications are often a rescue for any business.
This helps maintain a correct relationship between the parties. Business response strengthens your business. it's also useful for internal communication. This makes communication within the organization clearer and more accurate.
2. Evidence:
Written communication is evidence. Business communications help business people keep a record of all the facts. These written records function evidence.
3. Creating and maintaining goodwill:
This helps create and maintain goodwill between the enterprise and its customers. Inquiries, complaints, suggestions and feedback letters can help your company grow and maintain its credibility.
4. Cheap and convenient:
Cheap and convenient business communication.
5. Formal communication:
Business communication acts as formal communication between the 2 . it's going to be a seller and a buyer. It is often between an employee and an employer. The language used is formal and logical.
It helps to disambiguate and doubt the people involved within the business. Formal communication in business is protected and accepted.
6. Contribute to business expansion:
Business communications help businesses achieve their set goals. It also ensures business expansion. you'll grow your business by not dalliance and making good use of human resources.
Information about some resources, products, and markets is straightforward to make. you'll also spread the news of business expansion with it.
Types of business communication
There are many sorts of correspondence. Get wont to a number of them.
1. Internal communication-
This refers to the correspondence between individuals, departments, or branches of an equivalent organization.
2. External communication-
This refers to the correspondence between two individuals. These aren't from an equivalent organization. All communications outside the organization are external communications. Customers and suppliers, banks, educational institutions, and government agencies fall under this category.
3. Daily communication-
Refers to daily etiquette. The communications made for inquiries, orders, replies, acknowledgments, in-vitations, and booking letters are routine communications.
4. Sales support-
Refers to communications associated with sales. Sales letters, sales reports, invoices, and order confirmations are on sale. Invoices and financial statements are examples.
5. Personalized communication-
It refers to a response supported emotional factors. Request letters, recommendations, and Congratulations. Referrals, permits, and denials of conditions are some examples.
6. Circulation-
This refers to the communication of commonalities to several people and businesses. Notifications, bid announcements, address changes, and new branch openings fall under this category. Introducing new products is one example.
Drafting Correspondence
Understand the drafting of communications
Effective communication guarantees efficient and economical communication services. Drafting communications improves the goodwill of the organization. The responsibility for drafting communications is based on the nature of the communications and the type of organization. In general, routine communications are created by lower-level clerk. Important and confidential communications are drafted by the organization's executives.
Larger organizations also have more traffic.
The required messages or information are collected from various sources.
Stages related to drafting:
1. The required messages or information are collected from various sources.
2. The style of the letter depends on the nature of the communication.
3. A rough copy is made in the early stages.
4. The rough copy will be forwarded to the appropriate person for any necessary additions, deletions, or corrections.
5. Once again, the employee who created the rough copy reads the rough copy.
6. Rough copies may be handed over to a typist or computer programmer for production.
7. Again, the copy made will be read by the person who drafted the copy. If there are any corrections, you can make the corrections.
8. The copy made will be arranged for signature from the responsible person involved.
9. The signed copy is also verified by the employee working with the communication.
10. Now you are ready to send the letter.
Principles of drafting communications
Littlefield and Rachel set the principles for drafting communications. They are shown below.
1. Determining purpose: Generally, there is a main purpose of communicating some information and a secondary purpose of communicating usefulness and goodwill.
2. Message planning: Before you start communicating, you need to collect ideas from the entire office and arrange them in a logical order.
3. Use of language: You should choose a conversational language for the purpose of clear direction and simplicity.
4. Compact and clean: The message should lead to the completion of the job. All questions should be answered in communication.
5. Brief explanation: All points should be briefly explained.
6. Courtesy: All communication must be polite, compassionate, friendly and helpful.
7. Read the proofreading carefully: Good documentation can be spoiled by grammar and typos. Mistypes can be related to spelling names, improper placement of words and letters, incorrect numbers, and sentence order. Also, you may not be able to enclose what you need. Therefore, careful calibration is required for a complete and valuable response.
How to draft communication
Careful drafting of office communications is required to maintain the efficiency of office functions. The goodwill of an organization is increased through qualitative communication. The responsibility for creating a communication is based on the type of communication. In general, routine communications are drafted by clerks, modified by supervisors, and approved by executives. However, the following communication methods are used to create the communication:
Here is a brief description of how to draft a communication:
1. Draft letter
Oralizing letters is an important and generally accepted method for generating communications. The following dictation methods can be adopted.
1. Oral to a journalist
This is a popular and widely accepted format for dictating letters. Executives dictate the content of the letter to the shorthand typist. The quick reporter can then convert the dictation into a specific business letter. Therefore, drafted letters can be quickly reviewed and signed by executives.
The main advantage of this method is that there is no time loss and the accuracy of the characters is high. The reason is that there is face-to-face contact between executives and journalists. The main drawback of this method is that both executives and journalists need to be present when dictating.
2. Dictation to the dictation machine
Executives dictate a letter containing destination details with a reference number to a machine called a Dictaphone. The message is recorded on the machine using tape or disc. The typist can then transcribe and type the characters. Executives can dictate letters at their own convenience, and typists also type letters at their own convenience. Both executives and typists cannot physically exist at the same time. Therefore, this method is almost economical and convenient.
3. Drafting communication
The secret letter was personally written by an executive. From time to time, executives can give a rough overview of the letter. The journalist then prepares the letter in its entirety, and the typist types the latter letter.
2. Form letter
Some letters are sent by organizations that have stereotyped answers and texts. The same type of information may be provided to many people every day. Therefore, the organization can follow the printed form or card instead of writing a letter individually each time. These are known as form letters.
According to J.C. Denyer, a form letter is a standardized letter that businesses use to answer all communications of a similar repetitive nature and is used to provide the same information for many communications.
The body of the letter is already printed on these forms and you only need to include your name, date and recipient details when sending the letter. This type of task is assigned to a designated clerk. Form letters can be useful for confirmations, debt collections, price inquiries, delivery date requests, reminder letters, and more.
Benefits of form letters:
There are several benefits to using a form letter. A brief description of them is given below.
1. Save time by avoiding writing individual letters to everyone.
2. Form letters are easy for juniors to handle. This saves costs for supervisors and senior clerical staff.
3. Incoming letters that require regular replies can be easily answered using the form letter.
4. The handling of communications is uniform and there are no personal differences.
Disadvantages of form letters
The main drawbacks of form letters are:
1. The form letter has no personal touch. Therefore, we may neglect our customers' feelings.
2. The form letter will be created in the specified format and style. Therefore, it is unlikely to affect the recipient.
3. All customers are treated equally in business. Sometimes it is necessary to discriminate between customers.
4. Form letters cannot be used to meet the needs of individual customers.
3. Use standard paragraphs
Many subjects are dealt with from time to time. Similarly, in other words, the same type of treatment may be given to several subjects, for which standard paragraphs may be devised and used. Proper care should be devoted to feeling a personal touch through standard paragraphs. Idioms and phrases used at the minimum level. The dictator should create an impression of how to dispose of all letters carefully and devotedly through standard paragraphs.
Benefits of standard paragraphs
Using well-developed standard paragraphs has the following advantages:
1. You can save time and effort by writing letters repeatedly
2. Ordinary employees can do a better job.
3. The speed of work leads to higher output.
4. Use carefully selected words, sentences and paragraphs for better results
5. This job may be interesting to the correspondent, as the entire letter is not standardized.
6. Standardized paragraphs avoid inappropriate, flawed, or inappropriate languages.
7. The work of checking the carbon copy is reduced, which leads to efficiency.
8. There is a need for less supervision and there is a minimum supervision cost.
9. There is no personal prejudice and all customers are treated equally and equally.
10. New correspondents can be easily trained by dictation
Disadvantages of standard paragraphs
The drawbacks of standard paragraphs are listed below.
1. Standard paragraphs can be used indiscriminately. In this way, personal touch can be lost.
2. Inappropriate and incorrect standard paragraphs can make a bad impression on customers and affect the goodwill of the organization.
Standard paragraph suggestions
The following steps may be taken to enhance the usefulness of standard paragraphs and the reputation of the organization.
1. Each paragraph should be carefully created by someone who has a good knowledge of the work.
2. Standard paragraphs should be tested and revised regularly to match the changing circumference.
3. Each paragraph dealt with only one issue.
4. If the need arises, non-standard verbal dictation can be used.
5. These paragraphs should form part of the office correspondence manual.
4. Outline letter
The executives of the organization do not have time to draft the letter. Sometimes you don't have time to dictate a letter. Therefore, busy business owners only need to write down the outlines and points covered in letters and circulations. The actual drafting of the letter is done by a secretary or correspondent.
5. Self-drafting of communications
Drafting a written letter is one way to do this. This is usually done by the executives of the organization. This method is performed every time a critical, complex, or confidential communication draft is created.
Key takeaways:
References: