UNIT IV
Office Automation
Office Automation: Machines and Equipment Used
Introduction:
As an IT manager, your job is much bigger than your title means. The company you work for, like all modern businesses, is run on technology. If the system goes down, the business will stop. Therefore, as all resident technology experts, you not only manage your team, but also implement, manage, and monitor systems that affect the productivity of your entire company.
This is a big role with a lot of pressure, but it's easy with tools that help automate tasks.
With the following 10 office automation tools, IT managers and their teams can keep their entire office running smoothly and increase the productivity of their entire company.
10 Best Office Automation Tools
Office automation tools are systems and software that automate the types of tasks that affect all employees of a company, not just a single team or department. Solve comprehensive productivity issues by creating automated workflows for repetitive tasks such as password resets, new employee on boarding, device management, and meeting room reservations.
The office automation tools listed below are the most acclaimed tools in IT kits. A list of workplace tools recommended and endorsed by IT professionals who use these tools in the workplace.
1. Password
1Password is a password manager that makes life easier for everyone in the office. Instead of saving your login details in your browser, or worse, on sticky notes that stick to your entire desk, people in your company store them in 1Password. Then, to access any password, you only need to remember one master password.
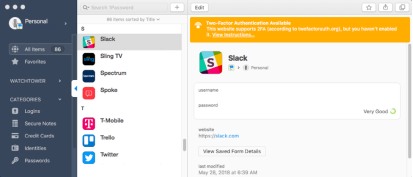
Even better, 1Password warns colleagues when passwords aren't very secure, tells them which sites offer two-factor authentication, and provides a tool that allows you to create random passwords with a click. , Helps keep the company safe. This makes managing personal passwords easier than ever and keeps your company data secure.
For IT teams, 1Password effectively eliminates password reset requests. You only need to remember the master password, so it's much less likely to be forgotten. But even so, 1Password's account recovery feature gives administrators the ability to reset their passwords.
Price: Starting at $ 3.99 per user per month for a team plan that includes unlimited vaults, admin controls, and 1GB storage for each user.
2. Better Cloud
According to a 2017 Better Cloud survey, companies use an average of 16 SaaS apps. All of these apps have a direct impact on IT, create security risks, and complicate users' on boarding, off boarding, and management. Better Cloud, a full-service SaaS application management tool, provides the solution.
Better Cloud provides IT teams with the tools they need to keep their company data secure and compliant. File storage used to identify publicly shared files Scan files in the app, automatically adjust file settings including social security numbers and credit card information, and monitor app usage Can identify potential internal security threats.
Better Cloud also simplifies user on boarding and off boarding with automated workflows. When you assign the right role to a new user, Better Cloud immediately gives that user access to the right app. Also, if someone leaves the company, we'll update it on Better Cloud to keep them from accessing the apps they use to run their business.
Price: Starting at $ 3 / month for Better Cloud One plans with customizable automated workflows, dashboard views for all users, and security audit logs.
3. Spokes
It's an innovative integrated ticketing system, a knowledge base that you'll actually learn while using it. If you have questions with your colleagues or need IT support, you do not need to submit a ticket. They just ask the spokes. The spokes either forward the request to the team's queue or provide an immediate and automatic response.
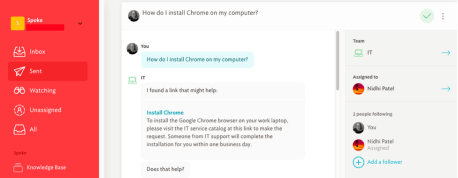
How? When your IT team responds to a question / request on Spoke, you have the option to add the answer to your knowledge base. Spoke then uses artificial intelligence to interpret queries and machine learning to determine which existing answer is best. As a result, teams spend less time responding to recurring requests, supporters spend less time waiting for help, and everyone spends more time on important and strategic tasks.
With Spoke, you can make requests in all the traditional ways, including email, SMS, and its web app. However, because it's built to work seamlessly with Slack through native integration, colleagues can issue tickets and receive answers and updates without leaving the Slack app.
Finally, Spoke is designed to be simple, so it's not just perfect for IT teams. This is useful for HR and office managers, who answer questions from colleagues and provide internal support.
Price: Starting at $ 1 / per user per month for a starter plan that includes one team.
4. Fleet Smith
Fleet smith is a device management tool designed for businesses using Apple devices. Instead of tracking all company devices in the complex. A spreadsheet, Fleet smith, captures all the data needed to track the status and status of all company-owned devices.
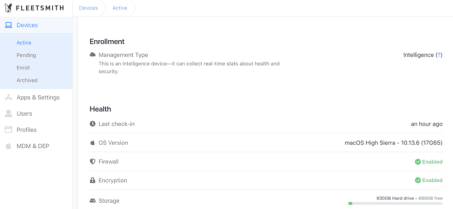
When a new employee gets a job at the company, we update the information on the device assigned by Fleet smith and assign the user to the team so that they can access the appropriate app. The user has access to all the apps needed to get started on the first day. Also, when you update an app that your company is using, Fleet smith will handle it automatically.
Tired of support tickets asking for help with connecting to Wi-Fi or printers? Fleet Smith has covered you. With Fleet smith, not only will new users automatically have access to the apps they need for their work, but they will also be able to sync their new devices to their printers and Wi-Fi. This allows you to work without issuing multiple support tickets, freeing your help desk and allowing you to focus on more strategic tasks.
Price: Free intelligence plans, including macOS intelligence, device assignment, and automatic device enrolment.
5. Envoy
If your company rarely welcomes visitors, it's probably not worth the money to pay a full-time receptionist to manage your front desk. Instead, IT managers can use tools such as Envoy to manage the front desk.
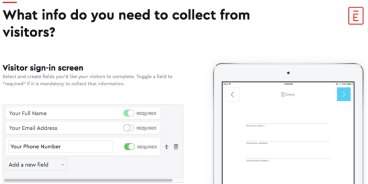
Envoy is an app that automates the visitor's sign-in process. It collects important details from visitors, reviews and signs contract documents such as NDAs, and automatically prints visitor badges. When the guest signs in and completes all necessary paperwork, Envoy sends an alert to the individual accepting the visitor to let them know that the guest has arrived.
Even if you already have a receptionist, Emboy makes their job easier. Reduce waiting time by letting guests sign in while the front desk is busy helping others. Also, if you receive a large number of deliveries, you can simply scan the barcode to alert the person who received the package. You will automatically receive a reminder until you receive the package.
Price: Free for basic plans including unlimited visitor sign-in and email host notifications. Starting at $ 99 per month for a standard plan that include printing badges and signing legal documents.
6. Duo
Tools such as Fleet smith, Jamf, and Oomnitza are great if your IT team is responsible for purchasing and distributing all your company's devices. However, not all companies fund the hardware of all employees. If you manage your company's IT that allows employees to use their personal devices for work, there are additional security threats that need to be prevented and explained.
Duo is designed for BYOD (Bring-Your-Own-Device) enterprises. You can provide access to company tools from non-company-issued devices without relying on a VPN. Instead, Duo monitors the reliability of devices connected to the network and limits or blocks access to users or devices that pose a security risk.
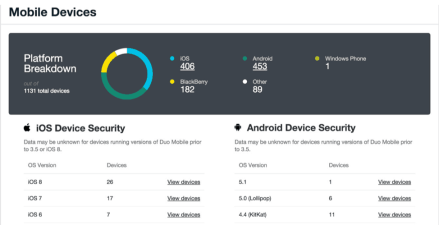
The user logs in using a two-factor authentication tool that proves that they are who they say they are. When you log in, Duo will evaluate your device's reliability. If the device is considered untrusted , both users and the IT team will be alerted to what updates or changes need to be made to get the device without risking the company's data. I will receive it.
Price: Free Duo Free plan, which includes two-factor authentication and protection for your on-premises apps. Starting at $ 3 per user for DuoMFA plans, including automated workflows, device security reports, SSO, and cloud app protection.
7. Kisi
Another way IT can save enterprise costs is to use technology to eliminate the need for security personnel. Use Kisi instead of having security guards at the front door of your office. Kisi is a cloud access control system that provides keyless entry technology for offices, server rooms, and other protected areas.
With Kisi, employees use their key cards or mobile devices to unlock office doors. If someone forgets their key cards at home, no one has to go get them. They can just use their phone to open the door.
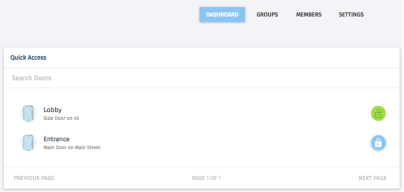
Kisi also makes it easy for employees to go onboard and off board. Drop new employees into the group so they have access to everywhere they need to go, or remove all employees who left the company from Kisi's dashboard. In addition, administrators can access reporting tools to see in and out activity and see who has accessed the safe area.
Price: Free for developer plans that include one door and access for up to 5 users. Starting at $ 150 per month for pay-as-you-go plans that include key card access and activity reports. Hardware and installation fees may also apply.
8. Dial pad
Desk phone costs and management can have a significant impact on your company's operating costs. And these days, it's a completely unnecessary expense. Tools like Dial pad allow companies to abandon their desk phones and replace them with modern systems that offer all the same functionality without expensive hardware.
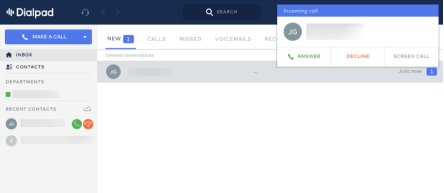
Dial pad provides each employee with an office phone number. When you receive a call to that number, simply answer it on your computer or mobile device. You don't need a desk phone. Even better, Dialpad supports all the traditional features of a desk phone, such as forwarding calls, holding callers, faxing documents, switching between calls, and receiving voice mail.
Dial pad also ships with Uber Conference, so you don't have to buy a separate system for both phone services and conferencing tools. Uber Conference supports voice and video conferencing, allowing users to join via email or text messages without a complex PIN.
Price: Starting at $ 15 per user per month for a standard plan that includes one office, up to three departments, and support for up to 100 users.
9. Security guard monitoring
You can wait for a support ticket from a panicked colleague whose computer has stopped working while preparing for an important client presentation. Or you can prevent these types of Nickels with tools such as Watchman Monitoring to help identify problems before they occur.
Watchman monitoring is a proactive support tool that monitors your company's devices and software and alerts you to issues that require your attention. Discover devices that need to be updated, hardware components that are throwing errors, when software subscriptions expire, and even server issues that can lead to significant data loss.
Your IT team will receive alerts about these types of issues and more. This allows the team to proactively modify them and increase the productivity of everyone in the office.
Price: From $ 75 / month for an in-house IT team introductory plan that includes problem detection, up to 25 computer records, and unlimited users.
10. Robin
Someone in your company needs to schedule a meeting. To connect your Mac to a projector, you need a projector, a certain number of seats, and hardware. Instead of paying a management assistant to find the perfect room, or one of the technicians to set up a room according to the needs of each conference organizer, a tool likes Robin.
Robin is a meeting room reservation app that allows everyone in the company to easily find existing meeting rooms with the necessary equipment and book those rooms without assistance. Employees search for a room in Robin's web app or calendar plug-in and book the room at the required date and time to prevent double bookings.
Robin also comes with analytics to help you determine which type of meeting room is the most in demand and the least utilized. This allows IT departments to provide company leadership with detailed reports on which rooms can be converted and which equipment is not needed.
Price: Starting at $ 20 per month for a basic plan that includes a schedule of 5 to 15 rooms, unlimited users, and a room display app for iOS and Android tablets.
Computers: Application and Advantages:
Computers have revolutionized the way businesses operate in their respective industries. Technology is so advanced that people who aren't using computers in their business are lagging behind. These non-computer businesses can be at great disadvantage to their competitors.
In particular, computers speed up the overall workflow of a business and reduce costs from every stage of performing a job / task in the business.
And every kind of business needs good computer applications.
Computer use in business
Computers can support different entities in different ways. Businesses have access to different types of software applications to meet different needs. These help companies manage files, documents, schedules, deadlines, and the overall workflow of all sections / departments.
Computers can also help your business by organizing all your information in a very accessible way. A typical business usually deals with large amounts of data (employees, products, orders, services, pricing, payroll databases, etc.).
Here are some common use cases for computers (from small businesses to large businesses):
Importance of computer applications in business
In this modern age, business cannot run smoothly without a computer and an internet connection. From restaurants to banks, from simple farms to plumbers, from lawyers to tax service providers every business in this world needs to use computer applications to improve their business ROI.
There are several areas where computers are usually useful for business –
1. Self-sufficiency
The application of computers has made businesses more self-sufficient in staff and businesses. This is to allow the computer to perform tasks that previously had to be outsourced. For example, companies can now use office software to prepare materials for employee training.
Desktop publishing software helps businesses create marketing materials. An online tax and accounting program allows businesses to prepare their own taxes. As a result, the company can carry out its dominant business.
This can be done while staying within the company, making the company more independent and less susceptible to errors. The error can be committed by an outside party. However, computers limit such opportunities.
2. Cost effective
Emerging technologies open up new tools and services. Services will be more affordable and companies will be able to save on staff salaries and office equipment.
By applying computers, people can work faster and more efficiently. It is possible for a company to hire fewer staff and save money. In addition, relatively inexpensive, networked computers allow businesses to store data more easily, saving on external file storage costs.
As a result, businesses no longer have to buy items such as copiers, fax machines, and typewriters that were used before the computer was no longer in use.
Correspondingly, you can launch potentially profitable businesses and spend less overhead. The email feature reduces shipping costs. Software applications reduce the need for large accounting departments. Computer applications enable efficient video conferencing, which in turn reduces the need for travel.
All the resources saved reach consumers more efficiently. The customer is then offered much more affordable products and services.
3. Speed
Computers help accelerate other business operations. This speed can be implemented in receiving consumer feedback, ordering raw materials, and inspecting products. As a result, using a computer is faster.
As a result, enterprises can operate much faster and produce better quality results.
4. Cheaper R & D
R & D, or R & D costs, is also significantly reduced by computer applications. Researchers can now conduct research using the Internet. Computer software applications help researchers develop and produce new products and services.
For example, instead of a company conducting or deciding on a direct focus group for a potential new product.
Companies can conduct extensive online research on what their target market is at a much lower cost.
In addition, new models of products can be manufactured online using virtual images and drawings, even if they are not hand-painted.
Created using software applications, these interactive models can make the product and its capabilities more feasible. This allows you to bring a product to life at a much lower cost than creating an actual physical model of a particular product.
5. Sale
Computers help increase the sales and profits of companies that use a company's website. Today, many companies use online media and operate 24 hours a day. This gives customers around the world the opportunity to purchase their products and services.
List of popular business software and computer applications.
Apps and software vary from company to company and are difficult to get on the list. Still, here's a list of all the popular applications that most businesses use:
Application Name | Use Cases |
Microsoft Excel or Google Sheet | Employee or Salary Sheet, Basic Calculation |
Microsoft Word or Google Doc | For Document Creation |
Microsoft PowerPoint or Numbers (Mac) | For Presentation Making |
QuickBooks | Accounting |
Wave | Invoicing |
Skype/Slack/Zoom | Team Collaboration & Online Meeting |
Asana/Trello/Base Camp/Ever note | Project Management & Meeting Notes taking |
Drop box or Google Drive | File & Document Storage |
PayPal, Square, Stripe | Payments & Invoicing |
Rescue Time | Time Tracking |
Sales force/Zoho/Bitrix24 | Customer Relationship Management |
Advantages:
Technology changes the definition of the phrase "do business." Computers allow you to create more documents than typewriters or mimeograph machines. Computers simplify commerce and enable products and services to be sold worldwide. With them, you'll file and store more information than thousands of file folders and cabinets.
Computer for General Business
In an office with a computer network, you can communicate over your company intranet or the Internet. Intranet is very valuable. You can process sensitive information within your company's network without worrying about unauthorized users accessing your organization's private network. Computers are also needed for organizations that have teleworkers or remotely located employees. In these situations, the computer issued to the remote employee remains the property of the company and is returned when the employee leaves the company. To protect corporate information, businesses may implement policies that prohibit the personal use of company-issued computers.
Business computers are used to create communications, handle accounting tasks, and perform research functions. A huge number of software applications are available for organizations or business processes of virtually any size. There are many advantages of computers for conducting common commerce, one of which is to improve the accuracy of the functions previously performed by staff.
Computer for HR:
A personnel information system called HRIS is very popular. HRIS allows you to process applications and many other features quickly and efficiently. Right Team Inc. stated in the white paper series "E-HR: HR Technology Revolution-Definition and Benefits": “The state-of-the-art HR system provides the underlying data, tools and technology to manage. Perform HR activities in an integrated environment.”
The HRIS system collects data for federal, state, and local reports, such as the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, which some companies need to send to government agencies. The HRIS system also sorts employment data, processes salaries, calculates employee benefits, performs personnel audits, analyzes turnover rates, surveys opinions and collects employee responses to retirement interviews. Computers are indispensable and of great value to the human resources department. Employment behaviour produces a large amount of paper. Utilizing HRIS is an ideal solution for collecting and storing HR data.
Computers to expand your business reach
Globalization is a fashionable way to describe how companies can reach their customers, or how organizations create materials and items for end users from anywhere in the world. Computers allow you to sell your company's products and services to customers in your region and around the world. As Ghana web states, "With the introduction of computers and the Internet, the world has become a global village where individuals, businesses and countries can exchange goods and services."
Without the benefits of work computers, choosing demographics to identify and approach the market consumes a huge amount of staff time and energy. Computers provide cost-effective features for production, sale and shipping. Manufacturers use computers to make everything from ready-made garments to automobiles.
The impact of computers on small businesses
Computers have had a major impact on the operation of small and medium-sized enterprises. The growth of personal computers and computer networks continues to impact large and small businesses. The abundance and accessibility of data available online means virtually anyone can start a little business with just a computer and an online connection. Computers also affect the way small businesses do business.
Getting Started
Computers make it easier to start out a little business. With just a computer and an internet connection, you can start a business like writing a blog or buying or selling goods at home. You can also perform administrative tasks such as paying business invoices, keeping tax records, managing payroll on your computer, and marketing your business online.
Mobility
Computers increase the opportunities for places where you can run your business. If you own a laptop pc with wireless internet capabilities, you'll do business in an airport lounge, bedroom, library, or Wi-Fi cafe. This type of mobility also means that your business is not restricted to normal business hours, giving you greater flexibility.
Productivity
Computers can have a positive and negative impact on the productivity of small businesses. 24/7 access to the internet means you can increase your working hours, and tools like email and instant messaging allow for easy communication. However, the Internet offers the temptation of browsing, not work, which can be distracting for you and your employees.
Need for training
Questia Media America states that proper training in computing system applications and usage is critical to the successful use of computers in small businesses. As a result, employers or employees who have difficulty learning a new computer system or are reluctant to implement it may require additional training or coaching. This learning curve can temporarily reduce business productivity and service levels.
Employee flexibility
The Yale-New Haven Teachers Institute reports that the development of computer technology has increased the number of work functions that can be performed from home. For small business owners who are directly competing with large companies for talented workers, offering telecommuting options can provide a competitive advantage in hiring and retaining workers. I can do it.
Computer use in business
Almost every business you can think of uses a computer in some way to perform its function. From reporting to communicating with clients, computers do a lot to improve business efficiency. Computers have come a long way since the days of pens, paper, and folders stored in dusty storage compartments. Computer uses are simply endless.
Enterprises not only use computers to perform different functions, but also use different types of computers to perform those functions. These features include laptops, PCs, servers and even smart phones. Computers enable concepts such as flexible work schedules and remote workforces, allowing employees to work anytime, anywhere, whenever they want.
Computer is employed for communication
Computers are a crucial tool when it involves establishing contact with clients. They’re important when it involves maintaining that contact. this is often a really important computer application in your business, enabling you to speak together with your clients via email, IM, Skype, collaboration software, and a spread of other communication solutions that your enterprise may use.
If a corporation can stay in-tuned with its customers, it'll be easier for them to contact them and invite more information about the services and products they provide. It also makes it easier for businesses to supply customer support to their clients during a timely and efficient manner. Businesses also can keep their clients up-to-date on new developments about their business.
Communication goes beyond corporate clients. Companies also got to communicate with their employees, and computers play a crucial role. Rather than dalliance one-on-one with employees, managers can simply email employees or send messages on other acceptable communication platforms. This protects time and improves internal business communication.
Computer is employed for marketing
Computers allow businesses to perform a spread of tasks to urge started, with the assistance of the web , computers can assist you map your business. Using computers, IT developers' business teams can use media during a sort of formats, including text, images, and videos, to make professional websites with compelling graphics and content. They perform program optimization (SEO) on their websites to point out them prominently in Google's search results, attract traffic, and ultimately sell their products to website visitors.
Computers allow businesses to make and run entire marketing campaigns across all social media platforms on the web. Companies can use special software to make ads for websites and social media platforms.
Key takeaways:
Office Information Management: Definition
What does Office Information Management (IM) mean?
Information management may be a broad term that comes with policies and procedures for centralized management and sharing of data among different individuals, organizations, and / or information systems throughout the information lifecycle.
Techopedia describes information management (IM) Information management is generally the concept of an enterprise information system in which an organization creates, owns, and manages a set of information. Information can be in the form of physical data (paper, documents, books, etc.) or digital data assets. Information management deals with the level and control of an organization's governance over information assets. Information management is usually achieved by supporting business processes and guidelines through a dedicated information management system. In addition, IM focuses on how that information is shared and delivered to different recipients, including different computing devices such as personal and organizational websites, computers, servers, applications, and mobile devices. I'm guessing.
Information management is the management of processes and systems in an organization that retrieves, creates, organizes, distributes, and uses information. According to the Information Management Process View, IM is a continuous cycle of six closely related activities.
Wilson (2002) states that the term "information management" is ambiguously used in the literature in several disciplines. In computer science and its applications, it is used as a synonym for information technology management (Synott and Gruber 1981) or is the same as "data “Management". The emphasis here is on the relationship between the underlying structure of quantitative data and the design of the database.
Business or business administration research has similar implications for technology management, with an emphasis on the relationship between information technology and business performance and competitiveness (cited in Synott 1987, Wilson, 2002).
In the fields of library science and informatics, information awareness processes data, organizational intelligence, competitive intelligence, all kinds of external information resources, and related technologies (manual or machine) from these various sources. Compared to other disciplines, information management in this latter context is more widely associated with the meaning of information to information users and the problem of information retrieval (Wilson, 2002).
Difference between Information and Data, Process
Information:
The information is structured, organized, and the processed data is provided in context, making the information clear. This makes the information relevant and useful to those who need it. The data suggest that raw facts and numbers about individuals, places, or other issues are represented by numbers, letters, or symbol types.
Information is knowledge that has been modified and categorized into easy-to-understand types that can be used to make decisions. In short, when knowledge becomes purposeful at the time of transformation, it is called information. It is available from a variety of sources, including newspapers, the internet, television, people, and books.
Data:
The data is a raw, unorganized fact that needs to be processed to make it meaningful.
Data is an individual unit of information. In the analysis process, the data is represented by variables. Data is always interpreted by humans or machines to derive meaning. Therefore, the data is meaningless. The data contains raw numbers, statements, and characters.
The main differences between data and information-
Conclusion-
Simply put, data is unorganized information and information is processed data. These two terms are so closely intertwined that it is very common for people to juxtapose them. In a technical glossary, data means input and is used to produce output, or information.
Data are facts and explanations from which information can be extracted. The data alone has no specific meaning. That is, unless the data is explained and interpreted, it is just a collection of numbers, words, and symbols. Unlike information that doesn't really make sense, the user can understand it with normal care.
Difference between Information and Data:
S.NO | DATA | INFORMATION |
1 | Data are the variables which help to develop ideas/conclusions. | Information’s are the meaningful of data. |
2 | Data are text and numerical values. | Information is refined form of actual data. |
3 | Data doesn’t rely on Information. | While Information relies on Data. |
4 | Bits and Bytes are the measuring unit of data. | Information is measured in meaningful units like time, quantity, etc. |
5 | Data can be easily structured as the following: | Information can also be structured as the following: |
6 | Data does not have any specific purpose | Information carries a meaning that has been assigned by interpreting data. |
7 | It is low-level knowledge. | It is the second level of knowledge. |
8 | Data does not directly helps in decision making. | Information directly helps in decision making. |
Comparison Chart:
BASIS FOR COMPARISON | DATA | INFORMATION |
Meaning | Data means raw facts gathered about someone or something, which is bare and random. | Facts, concerning a particular event or subject, which are refined by processing is called information. |
What is it? | It is just text and numbers. | It is refined data. |
Based on | Records and Observations | Analysis |
Form | Unorganized | Organized |
Useful | May or may not be useful. | Always |
Specific | No | Yes |
Dependency | Does not depend on information. | Without data, information cannot be processed. |
Office Systems and Procedures and Flow of Work
Meaning of office system:
A business has a specific purpose that is clearly defined. These goals can only be achieved if approached in a systematic way. The business itself is a system of several subsystems.
Marvin R. Gore stated that a business is a system with goals and objectives for its outcomes, and that a business can be divided into smaller systems that vary by the organization of the business.
George R.Terry says that each business has many subsystems such as production control systems, marketing systems, and office systems. Therefore, the office system itself is a subsystem of the entire business.
The office system is a continuation of several integrated steps to achieve the desired purpose. It is defined as a network of routines designed and integrated to perform office work. In other words, the system consists of various interconnected routines.
System definition:
"The success of a business, government, or non-profit venture depends on maximizing the use of people, information, and resources said by Miltion Reitzfeld. Such utilities develop, install, and install the right systems and procedures. It can only be achieved by monitoring. "
According to Littlefield, a system may be defined as "the foundation of interrelated and interdependent parts that operate in sequence according to a given plan to achieve a goal or set of goals."
Office system principles:
Every office has its own system. The system is not the same in all offices. They depend on the type and size of your business. However, no matter which system evolves, maximum efficiency should be guaranteed. The following are some of the key principles of the office system.
1. You need to ensure a good workflow with no bottlenecks.
2. Avoid unnecessary duplication of work and records.
3. Staff movement should be minimized.
4. Unnecessary writing is avoided.
5. You need to make the most of your area of expertise.
6. The amount of paperwork must be absolutely minimal.
7. You must use the principle of management by exception.
8. You need to offer the potential to get the most out of your machine.
Meaning of Procedure:
The term procedure refers to a planned set of operations to handle recurring business transactions uniformly and consistently. Procedures are pre-planned routines for processing routine tasks in a uniform, step-by-step manner. This is a management guide on who, what, how and when to do it. Some organizations have written records of systems and procedures. It may be in the form of a book or loose-leaf.
Definition:
"Office procedures are a series of priestly acts organized under supervision to achieve the purpose of the office." as per Charles O. Liberty,
Zane K. Quible defines systems, procedures, and methods as follows:
System: Interrelated steps required to achieve well-defined goals.
Procedure: Related methods required to complete the work process.
Method: Specific clerical or mechanical operation or activity.
To explain the concept of the system, the system (purchase system) designed for purchasing office supplies is shown below.
Step 1: Select the supplier.
Method:
A. Please fill out the quotation form.
B. Submit the form to a potential vendor
C. Get a quote from the vendor.
D. Catalogue each quote
Step 2: Order consumables:
Method:
A. Fill out the purchase order
B. Send the purchase order to the vendor
Procedure: 3. Receive supplies:
Method:
A. Check your order to see quantity and acceptability
B. Deliver supplies to the appropriate department.
C. Notify accounts payable.
Importance of systems and procedures:
1. The system concept follows a unified procedure for similar transactions, which helps reduce errors and wasteful movements of machine operations.
2. The cost of daily office work is reduced.
3. Responsibilities can be easily corrected.
4. A good office system and procedures will help your office run smoothly and help reduce work delays.
5. Helps to ship work quickly.
6. Systems and procedures include internal checks. They help prevent fraud and manage their work.
7. A good system helps maintain better coordination between departments.
8. Help management train staff.
9. A good system reduces the chance of error and improves the efficiency of your organization.
10. A good system tells employees what to do.
One is to provide information about when, where, and the organizations that support different systems.
Workflow:
The workflow is related to how work moves from one operation to another. It indicates the speed at which it travels and the amount of work that passes through its smoothness of passage.
Workflows are aimed at increasing the efficiency of all office activities, reducing costs and eliminating delays. Work flow is a problem that an administrator should solve.
Flowcharts are created to help you understand if your workflow is ideal and if there is room for improvement. The following types of flowcharts can be used for analysis.
a. Office layout chart.
This chart analyzes the workflow of each part of the office and eliminates wasted movement and backtracking. The chart has lines showing the movement of office forms and documents from operational to operational.
b. Flow process chart:
Process charts are also known as work simplification charts. Charts use specific standard symbols to show the workflow for specific procedures. Charts are symbolic graphics that are easy to view and read.
Helps simplify the task. These standard symbols were developed by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York.
c. Management type flowchart:
Management type flowcharts are fully illustrated charts, with each related operation or step described in short, descriptive text. Reading and writing of chart is horizontally from left to right.
Linear workflow:
A smooth workflow can be ensured by adopting a linear workflow method. This method can be applied not only to factories but also to offices. It can be described as a way of working as you progress from one task to another. It should follow a course that is as close to a straight line as possible. Work must always move forward and go straight to avoid wasting time, effort, and delays in the flow of information.
Advantages of linear workflow:
Below is a list of the benefits of a linear workflow.
1. Speed up: Work speed is greatly improved because the work is moved in the smallest area.
2. Less messenger work: Because the work flows in a straight line, the desks can be aligned, the distance between operations is short, and documents and files are passed from desk to desk. The clerk is easy. It reduces the work of messengers.
3. Low paper loss: This method is processed in a systematic way, so paper is rarely misplaced or lost.
4. Use of Conveyors: Certain organizations use conveyors to transfer files from one location to another. Such an arrangement can help speed up your work.
5. Keep executives and clerks on desks: Because the work moves in a straight line, this method avoids unnecessary movements and allows employees to sit in chairs and work.
Smooth workflow issues:
The smooth flow of work faces many problems and needs to be addressed to improve the efficiency of office routines. It can only be resolved by the manager. The outline of the problem is as follows.
1. Unequal workflow: Work in the office cannot be equal throughout the day, week, or year. Work can be heavy on certain days of the week or heavy on certain periods of the week. For example, you may receive more emails in the morning and Monday. Anomalous workflow problems can be solved by collecting relevant statistics and their analysis.
2. Work interruption: Work interruption is internal or external. Internal interruptions can occur due to lack of materials needed for the work, lack of necessary information, or changes in the work due to changes in the plan. Interruptions in external work can be caused by calls to external employees or calls from outside.
3. Different operations require different times: This is a major workflow issue that requires different times to complete different operations in a job. For example, the first sequence of operations may take 1 minute and the next may take 3 minutes.
4. Lack of standards: If the work to be done by an individual who cannot match the standards is fixed, the stable flow of work can also be affected. Without standards, some employees may be overloaded with heavy work and others may have less work.
5. Lack of planning and schedule: If the office manager does not plan and schedule work ahead of time, it cannot be done quickly or not done within the allotted time.
6. Layout error: If the office layout is not created according to a well-developed plan, it can affect a stable workflow. Cross-crossing and backtracking procedures affect the workflow.
System and Procedure Benefits:
Below are some of the benefits you might get if the right systems and procedures were available in the office.
System and Procedure Restrictions:
Key takeaways:
Office Personnel Relations
What is the definition of employee relationship?
The definition of employee relationships refers to the organization's efforts to build and maintain positive relationships with employees. The organization wants to maintain employee loyalty and work involvement by maintaining positive and constructive employee relationships. The human resources department of an organization usually manages the efforts of relationships with employees. However, some organizations may have the role of a dedicated employee relationship manager. The typical responsibilities of an employee relationship manager are to act as a liaison or intermediary between the employee and the manager, as well as fair compensation, beneficial benefits, proper work-life balance, and rational includes advice on creating or creating policies on employee issues such as working hours. When it comes to relationships with employees, the HR department has two main functions. First, human resources can help prevent and resolve issues and disputes between employees and management. Second, we help create and implement policies that are fair and consistent for everyone in the workplace.
To maintain good relationships with employees, organizations must first consider them to be stakeholders and contributors to the company, not just paid workers. This perspective encourages managers and executives to seek employee feedback, appreciate their opinions, and consider employee experience in making decisions that affect the entire company.
Why relationships with employees are important?
A company that has a good relationship with its employees has many benefits. In general, employee involvement, motivation, understanding, and maintenance are easy.
Here are just a couple of benefits of building a positive employee-related workplace.
Employee Involvement
According to a survey of employee involvement, 90% of leaders understand how important employee involvement is. However, only 50% know how to deal with this issue.
Relationships with employees play an important role here. Companies with good employee communication have proven to have a much higher employee involvement rate.
Here are some tips for improving employee communication and increasing employee engagement.
Employee Satisfaction
Employee involvement is often related to employee satisfaction. Employees with low engagement are less satisfied. Poor employee relationships can be one of the main causes.
In addition, 65% of US employees say that employer communication affects job satisfaction. Forty-five percent of them say their employers are not communicating well with their employees.
Employee Productivity
Employee satisfaction and engagement increase employee productivity. Companies with well-structured employee relationships enjoy higher productivity, revenue, and profits. In addition, organizations with high-engagement employees have an average three-year revenue growth rate of 2.3 times that of companies with low-engagement teams.
Employee Retention
Employee Advocacy
Employee Experience
Employee Empowerment
How to implement an employee relationship plan?
The first step towards planning and implementing a successful employee relationship strategy is to have a well-written set of policies in place.
Employee relationship policies should explain employer philosophies, rules, and procedures for dealing with employee-related issues and resolving workplace issues.
In addition, it is important to understand that employee relationships programs are not a one-size-fits-all solution.
What works for a company with 100 employees in the United States may not work for a company with 5,000 employees in China. In other words, employee relationships programs depend on the size, location, industry, culture, and many other factors of the company.
However, every good employee relationship plan has some characteristics.
What do employee-related professionals do?
Especially in large companies, it is important to have employee-related professionals to improve communication with employees.
These professionals are part of the Communications or Human Resources department. Their main task is to inform employees and ensure that company policies and procedures are followed.
Employee Relations Specialist Duties and Responsibilities
Here are some of the most important obligations and responsibilities of employee relationship managers and specialists:
Office Supervision
"Director" consists of two words: "super" (excellent or extra) and "vision" (visual or perspective). The literal meaning of the term "supervisor" is to "supervise" or "inspect" the work of others. Therefore, "supervision" refers to the work of others, the act of inspecting or supervising whether they are working properly.
A business organization has "supervisors" and "subordinates." According to M.S. Vitoles oversight refers to direct and immediate guidance and control in the performance of a subordinate's duties. Therefore, the activities of the director relate to the direction, guidance, management and supervision of his subordinates. The supervisor performs these tasks. R.C. Alan calls it a "responsible job" above the "work job".
Supervision is the instruction, guidance, and management to ensure that the workforce is functioning as planned and maintaining a time schedule. In addition, they are getting as much help as possible to accomplish their assigned job.
The director is Latin. Super means "from above" and vision means "see". Supervision in the normal sense means supervising the activities of others. Management and supervision means "supervising subordinates with the aim of supervising employees authoritatively once they do something wrong."
Supervision should be done at all levels of management from top to bottom. Lower-level managers or front-line supervisors oversee the work of operations staff, while intermediate and top managers remain busy monitoring the work of their subordinate management members. However, in the usual sense, oversight involves coaching and coaching non-administrative members of the organization.
Director-Importance-
Oversight is primarily concerned with overseeing or monitoring the performance of workers under his control. He plays an important role in the management system. He is a person who connects directly with the worker and acts as an important link between the manager and the worker
The importance of supervision is often explained as follows.
1. Issuing orders and instructions:
Workers need supervisory guidance at every stage. He answers their doubts and tells them the right way to get the job done. Subordinates can improve their performance if they know what they need to do.
2. Work planning and organization:
The boss acts as a planner and guide for his subordinates. He creates a work schedule so that the work flow is uniform and stable. Supervisors set production targets for workers and determine methods and procedures for performing their work.
3. It’s important at all levels:
Supervision means supervising and monitoring subordinates. Top management spends only 20% of his time overseeing, but the overseer (or overseer or overseer or overseer or section chief) spends about 80% of his time overseeing. Top management oversees managers and supervisors oversee workers. Supervision on the front line or firing line is of utmost importance, as the actual work is done at that level.
4. Important links between workers and managers:
The supervisor is the representative of the management and is a very important person from the worker's point of view. He communicates management policies to workers (downward communication) and provides feedback to management about what is happening at the lowest level (upward communication).
5. Motivate your subordinates:
The supervisor is the leader of the lowest rung of the management ladder. He serves as a guide to friends, philosophers, and workers. He stimulates teamwork and ensures maximum cooperation from employees. He is the one who can help you get the most out of your manpower.
6. Feedback to workers:
The supervisor compares the worker's actual performance to established standards, identifies the worker's weaknesses, and proposes corrective actions to overcome them. In this way, workers can improve their performance in the future.
7. Appropriate assignment of work:
Supervisors systematically coordinate the activities and resources of the group. He assigns work to each worker and delegate’s authority to the worker. Workers are frustrated when the work they are doing is not properly placed. If jobs are not properly assigned, some workers may be idle and others may be overloaded.
Roles and functions-
1. As a key man in management:
Supervisors are key figures in the organization to make decisions, manage work, and interpret managerial policies to workers. He / she represent the manager to the workers. Therefore, management is judged to be judged by the workers. He / she are also the protagonist to get the job done. But in reality, he / she is less than the key number.
2. The person in the middle:
In this view, supervisors must work between two forces: management and workers. There are many technical and production-oriented expectations from managers, and many compensation-oriented expectations from workers.
3. Supervisor as a marginal person:
According to this sociological concept, the supervisor is excluded from the main activity and influences his department, or he / she is just at the limit.
4. Supervisor as another worker:
From this perspective, a boss is like a worker who feels unauthorized and not a manager. Only his / her designation will change.
5. Supervisor as a Relationship Specialist:
In this view, the supervisor is considered to be a relationship expert who takes care of the human side of the business.
Function:
The supervisor should do the following:
1. Help his / her workers develop their innate qualities to improve their performance.
2. Help subordinates adapt to work requirements and grow.
3. Make workers loyal to the organization.
4. Provide expertise, skills, knowledge and experience to encourage workers to learn without fear or hesitation.
5. Encourage free communication.
6. Develop employee potential to the extent that supervision is not required.
7. Cooperate with other supervisors.
8. Prove a good connection between management and workers.
9. Solve personal problems of subordinates as much as possible.
10. Maintain discipline.
11. Correct the mistakes of subordinates.
12. Explore new areas of knowledge.
13. Introducing new, useful and scientific methods of production and management.
14. Have a clear understanding of his / her action plan.
15. Know his / her work, obligations, responsibilities, authority, accountability, etc.
16. Reasonably and scientifically share responsibilities and obligations to subordinates.
17. Listen to and investigate the dissatisfaction of your subordinates.
18. Delegate authority and win their trust..
The role of the director tells us very little about the broad aspects of the director and the factors that govern effective director performance. The Supervisor Performance Survey shows the following factors that explain the best supervisor performance:
(1) Preferred working environment:
The best supervisors create and maintain high performance standards in a comfortable working environment. He is goal-oriented and strives to achieve the expected results by adopting the right type of leadership to stimulate confidence and voluntary discipline from his people. A good working environment can ensure that he voluntarily accepts his authority from his people, so that obedience and loyalty can be easily ensured from the workers.
(2) Individual maturity and sensitivity:
The best supervisors acquire personal maturity and emotional stability, empathy, sensitivity to the emotions of others, and the ability to understand the emotions and emotions of those who work under his command. He has the knack for saying the right thing at the right time, never losing control under pressure or tension, and showing a good sense of humor.
(3) Relationship Specialist:
The best supervisors are practitioners of industrial psychology. He recognizes individual differences and group spirits and harmonizes interpersonal relationships. As the leader of his section, he needs to harness human emotions, emotions and attitudes for maximum productivity without sacrificing employee satisfaction.
(4) Technical work knowledge:
The best supervisors are technically competent. He has sufficient knowledge and information to quickly understand technical problems and devise the best feasible solutions. He gets the job done easily.
(5) Self-development and subordinate development:
Effective supervisors are deeply interested in human resource development. He places equal emphasis on the growth of his personality and the growth of his subordinates. He is trying to assign an interesting and rewarding job to his subordinates. A purposeful job creates interest and vitality in the work and provides employees with job satisfaction. A rewarding job will help promote his subordinates.
(6) Knowledge and execution of company plans and policies:
The best supervisors are fully aware of management plans and policies and implement them thoroughly. He also keeps up with changes in corporate policies and procedures and provides complete information.
Work Measurement
Definition:
Work measurement is an implementation of a set of techniques designed to find the work content of a particular task or activity by ascertaining the actual time required for a qualified worker to perform the task can be defined t a given performance level.
The essence of work measurement is to see what the work of a particular activity is under consideration. It helps to:
Work Measurement Techniques
Work measurements techniques help create realistic work schedules by properly assessing human work. This helps check workers and avoid idle time by comparing the actual time spent by the worker with the time allowed.
Procedures Related To Work Measurement
Purpose of work measurement:
The main purposes of work measurement are:
(1) The target time for each job can be scientifically estimated, and this estimation can prepare a realistic schedule and necessary personnel.
(2) By comparing the basic times, it is possible to make a sound comparison of alternative methods.
(3) A useful wage incentive system can be formulated based on the target time.
(4), it may lead to an appropriate balance of work allocation.
(5) Helps analyze activity to perform jobs with the aim of eliminating or reducing unnecessary or repetitive operations to minimize human effort.
(6) Standardize efficient operation methods.
(7) Standardize the conditions for efficient performance.
(8) Determine the ratio of humans and machines to use both effectively and efficiently
(9) To provide information and foundations for production planning and scheduling activities.
Control Process
Proper performance of management controls is critical to the success of your organization. After the plan is about, management must take a series of steps to make sure that the plan is executed. The essential management process steps are often performed in almost any application, like improving product quality, reducing waste, or increasing sales. The essential control process involves the subsequent steps:
Setting Performance Criteria:
The manager must convert the plan into performance criteria. These performance criteria can take the shape of goals, like revenue from sales over a period of your time .The standards must be achievable, measurable and clear.
Actual performance measurement:
Without measuring performance, you can't make certain that the standards are met.
Compare actual performance to standards or goals:
Approve or reject the merchandise or result.
Deviation analysis:
Administrators got to identify why the standards aren't met. This step also includes determining if more control is required or if the quality must be changed.
Take corrective action:
After the rationale for the deviation is identified, the manager can develop an answer to the matter of meeting the standards and make changes to the method or behavior.
Consider a fictitious company, the XYZ Group, whose profits on luxury sunglasses have diminished thanks to employee theft. Senior managers make plans to eliminate the occurrence of employee theft. it's been determined that an item has been stolen from the company's warehouse. Executives set a zero theft ($ 0) goal within three months (step 1). The corporate is currently losing a mean of $ 1,000 a month thanks to employee theft.
To prevent unwanted activity, XYZ installed cameras within the warehouse and placed locks within the cabinet where the foremost expensive sunglasses were stored. Only the warehouse manager has the keys to those cabinets.
Three months later, the XYZ manager will contact the bookkeeper to urge sales and inventory figures for the last three months (step 2). The manager then compares the numbers to the previous period, taking under consideration deliveries, returns, and defective orders (step 3). the corporate decided to possess lost $ 200 within the first month, $ 300 within the second month, and $ 200 within the third month thanks to the theft. this is often an improvement, but it hasn't reached its goal. The administrator then makes suggestions for adjusting the system (step 4).
XYZ senior management approves the proposal to determine a intolerance policy against employee theft. Now, if there's evidence that an employee has stolen sunglasses, that employee's job is completed. The worker Handbook has been updated to incorporate changes, and XYZ executives meet with all warehouse employees to speak policy changes (step 5).
Control Timing
Controls are often categorized consistent with the time a process or activity occurs. Time-related controls include feedback, proactive, and simultaneous controls. Feedback control is about the past. Proactive control predicts future impacts. Concurrency control has relevancy to this.
Feedback
Feedback occurs after an activity or process is complete. It's reactive for instance; feedback control involves assessing a team's progress by comparing production criteria to actual production output. Production will continue once the standards or goals are met. If not, you'll make adjustments to the method or standard.
As an example of feedback control, a sales goal is about, the sales team works to realize the goal for 3 months, and at the top of the three month period, the manager confirms the result and therefore the sales goal is achieved. Determine if it had been as a part of the method , the manager also can implement changes if the goal isn't achieved. Three months after the changes are implemented; the manager reviews the new results to ascertain if the goals are achieved.
The disadvantage of feedback control is that you simply can only make changes after the method has already completed or the action has been performed. things may have ended before the administrator noticed the matter . Therefore, feedback control is best fitted to processes, behaviors, or events that repeat over time than non-repeating processes, behaviors, or events.
Proactive Control
Prophylactic control, also referred to as pre-control, preventive control, or feed forward control, involves predicting problems instead of expecting bad results and responding later. It's about prevention or intervention. An example of proactive control is when an engineer runs a test on a prototype vehicle braking system before the vehicle design is mass-produced.
Proactive Control looks forward to problems which will reasonably occur and devises ways to stop them. you cannot control the unexpected An unlikely incident like "God's act".
Simultaneous Control
Concurrent control provides monitoring during a process or activity. Simultaneous control could also be supported standards, rules, code, and policies.
An example of simultaneous control is fleet tracking. Fleet tracking with GPS allows administrators to watch company vehicles. The administrator can determine when the vehicle will reach the destination and the way fast it'll move between destinations. Administrators can plan more efficient routes and warn drivers to reroute to avoid congestion. It also discourages employees from performing personal errands during working hours.
In another example, Keen Media seeks to mitigate employee inefficiencies by monitoring internet activity. Consistent with company policy, employees keep a digital record of their activities during working hours. IT staff also can access an employee's computer to work out what proportion time is spent on the online to try to personal matters or "browse the web."
What is the purpose of the performance standard?
Before considering the purpose of the performance standard, let's take a step back and define performance management.
The performance criteria are as follows:
Therefore, if performance is inadequate, the employer or supervisor should issue a Performance Improvement Plan (PIP). The purpose of this document is to help improve employee performance.
PIP occurs during the review phase, the final phase of the performance management cycle. Simply put, this is the phase in which managers track employee performance by making assessments. We mentioned earlier that this cycle begins with the setting of performance criteria.
Performance management currently includes three levels within the organization.
What are the three levels of performance?
Performance management are often focused on the whole organization or its departments. What's more, it can emphasize the performance of individual employees. Therefore, there are three levels of performance management.
The purpose of this level is to achieve the goals of the entire organization. Therefore, this is the highest rank in your organization to use performance management standards.
To achieve these goals, company management strives to answer these questions.
Does this company have a strategy to reach that goal? If so, is the company implementing this strategy?
Is your organization producing the expected results?
Operational Performance Management
The purpose here is to achieve operational goals. This level focuses on processes within the organization, such as projects and activities. Therefore, the purpose is to see if these particular projects / activities are working.
Individual Performance Management
Finally, this level emphasizes the performance of every employee within the company. The process begins by setting work goals and criteria, reviewing employee performance, and improving each employee's learning skills.
To achieve these goals, company management needs to get answers to these questions.
When reviewing an employee's work, performance criteria are your reference point. These standards are very important because they analyze different areas of performance. Let's look at how to properly determine performance criteria and what to consider when doing so.
What should be considered when establishing performance standards?
There are four points to consider ensuring that the criteria are suitable for a particular position.
Having motivational performance standards gives workers inspiration to do their jobs better. In addition, if you can see the progress within the project, this will be a driving force.
Key takeaways:
References: