UNIT I
The Concept of Business Environment
Concept of business environment
You can start a business, but you need financial resources, such as finance, that you have to rely on financial institutions to succeed. Acceptance of social norms that must depend on society. Appropriate market conditions that must depend on the market. Sale of products / services that must be customer dependent. Labor that must depend on society.
Then there are natural resources and raw materials, which must depend on nature. Also, government legal support that must depend on the government. There are many factors and aspects that affect the business environment. These factors are many different components of a single concept called the business environment.
These business-dependent factors aren't stopped, they're very dynamic and constantly changing. For example, the trend, the Fidget Spinner trend, has provided the greatest impetus for the silicone mold industry to date.
The changing needs of customers and new innovations in the market are part of the business environment. The challenge for companies in this tech era is not to enter the market, but to survive in the market. Surviving the market means adapting to change as soon as possible. Adapting to change means being aware of the business environment.
Meaning of business environment
The power to compose a business environment is its suppliers, competitors, consumer groups, media, governments, customers, economic conditions, market conditions, investors, technologies, trends, and several other institutions operating outside the business. Makes up the business environment. These forces affect your business, even when it's outside the boundaries of your business.
For example, government tax changes can reduce customer purchases. Here, businesses need to reestablish prices to survive change. The business was not involved in initiating the change, but had to adapt to the change in order to survive or take advantage of profitable opportunities. Now let's talk about the importance of the business environment.
Importance of business environment
From the above, it can be said that the business environment is the most important aspect of any business. Recognizing ongoing changes not only helps businesses adapt to these changes, but also helps them use them as opportunities.
The business environment poses threats and opportunities for any business. A good business manager not only identifies and evaluates the environment, but also responds to these external forces. Considering the following facts, you can understand the importance of the business environment.
1. You can identify business opportunities:
Not all changes are negative. If you understand and evaluate them, they can be the reason for your business's success. It is very necessary to identify change and use it as a tool to solve business and population problems.
For example, Phanindra Sama was plagued by ticket reservations in India. He used to travel long distances to travel agencies to book tickets, but even after traveling this distance, he wasn't sure if his seat was confirmed. He saw the opportunity to establish an app in the face of problems and co-founded an online ticket booking app called "redBus".
2. Helps to utilize useful resources:
Careful scanning of your business environment can help you leverage the useful resources your business needs. This helps businesses track these resources and convert them into goods and services.
3. Dealing with change:
Businesses need to be aware of the ongoing changes in their business environment, including changing customer requirements, new trends, new government policies, and technological changes. If your business is aware of these regular changes, you can provide a response to address those changes.
For example, when the Android OS market blossomed and customers began to prefer Android devices with simple interfaces and apps, Nokia couldn't keep up with the changes by not implementing Android OS on Nokia devices. They did not adapt and lost tremendous market price .
4. Planning support:
Solve the problem or take the opportunity. After analyzing the changes presented, the business can incorporate plans to counter the changes for a safe future.
5. Helps improve performance:
Companies that scan the environment thoroughly not only address the changes presented, but also thrive with them. Adapting to external forces helps businesses improve performance and survive in the market.
Characteristics of business environment:
(A) Overall external force-
The business environment includes everything outside the organization.
When all these forces are applied, a business environment is formed.
Example: When Pepsi and Coca-Cola got permission to start a business in India, it was an opportunity for them and a threat to local manufacturers such as Goldspot and Camp Cola.
(B) Certain general forces-
A specific force is a force that directly influences the operating activities of a company.
Examples: suppliers, customers, investors, competitors, finance personnel, etc.
General power is the power that indirectly influences the functioning of a company.
Examples: economic, social, political, legal and technical conditions.
(C) Mutual relationship-
The various forces of the business environment are interrelated.
One component of the business environment affects the functionality of the other.
Example: Increased people's life expectancy and health consciousness are driving the demand for diet coke, olive oil and many other health products.
(D) Dynamic nature-
The business environment is dynamic in nature and continues to change in the following ways:
(A) Technical improvement,
(B) Changes in consumer preferences,
(C) Entering new competition into the market.
Example: Many established companies in the FMCG (Fast-moving Consumer Goods) sector are focusing on producing products using natural ingredients in their "Patanjali Products" entry.
(E) Uncertainty-
Due to future uncertainties, changes in the business environment cannot be accurately predicted. It is very difficult to predict changes in the economic and social environment.
Example: The entry of many new companies has caused the price of Android smartphones to drop significantly.
(F) Complexity-
All the forces of a business environment are interrelated and dynamic and difficult to understand. The complex nature of the business environment can be understood with partial research.
Example: Raising the Goods and Services Tax to 15% increases government revenue (economic), improves people's social existence (social), reduces rich personal disposable income, and thereby inflation Helps to control.
(G) Theory of relativity-
The business environment varies by location, region, and country.
Example: In China, as electricity consumption increases, electricity to the industry is provided at a lower price, which leads to mass production, but in India, high electricity consumption results in expensive electricity and production decreases. To do. The production cost will be high.
Planning purely means what to do in the future. When the business environment presents problems and opportunities, it is up to the business to decide what plans need to be devised to address the future.
Key takeaways:
The environment consists of economic and non-economic variables that provide opportunities and threats to the enterprise. This is largely out of control, so companies adjust their operations to these environmental factors.
The macro environment consists of:
(A) Economic environment:
The economic environment is made up of economic power that influences business activities. Mining and industry production, agriculture, infrastructure, national income, per capita income, money supply, price levels, monetary and fiscal policies, population, business cycle, economic policies, infrastructure facilities, financial facilities, etc. make up the economic environment. The economic environment affects the activities of a company. In a capitalist economy, businesses have the freedom to choose their profession. Economic decisions on investment, production and sales are driven by profit motives. The factor of production is privately owned and production activities are initiated by private entrepreneurs.
In a socialist economy, these decisions are made by the public sector, which is guided by social welfare rather than profit maximization. The economy is managed by a central master plan created by the country. In a mixed economy, the public and private sectors coexist and own the factors of production, either alone or jointly. Rare economic resources are allocated to various business activities. Decisions on resource allocation regarding what to produce, how to produce, and for whom. The nature of technology, production technology, timing of production, etc. vary depending on the economy. This constitutes the economic environment of the economy.
The economic environment impacts your business in the following ways:
(i) There is no complete capitalization or socialism. To varying degrees, free market economies and centralized plans coexist. In the world of liberalization and globalization, we combine national planning with free pricing to make macroeconomic decisions for the welfare of corporate entrepreneurs and society. "The economy that a company runs is not just a free corporate economy that uses prices and markets. It is, to some extent, directed or indirect by a system of planning, management, regulation and coordination."
(ii) The state controls the economy (or businesses) through planning and regulation. It imposes responsibility for social response (responsibility to society) on companies by the principles of the welfare state enacted through laws that enforce minimum wages, commodity management, fair trade practices, etc. The legislative body promotes economic growth, efficiency and fairness. Social responsibility is the result of business interactions with the economic environment.
(iii) Some companies will be positively affected by government policy and others will be negatively affected. For example, restrictive import policies protect domestic industries, while free import policies can harm domestic industries.
(iv) Government-provided incentives and incentives affect businesses in many ways. To enjoy economies of scale, companies set up businesses in big cities, but the government encourages the establishment of units in underdeveloped areas by offering various tax incentives. Therefore, the country's economic environment eliminates regional disparities and promotes fair economic growth.
(v) Government promotes the industrial sector of the economy by providing incentives to the priority sectors that produce commodities that are essential to the economy.
(vi) The modern economy is an open system. The economic environment of one country affects the economic environment of another country. Multinational companies operate around the world and offer many benefits to host and home countries. It developed science and technology and unified the world economy.
The economic system helps answer questions such as:
Therefore, the economic environment plays a vital role in shaping the economic culture. Market power and national planning provide constraints for companies to perform their functions. “Progressive management needs to be continually informed about the magnitude and direction of changes in the domestic and international economic environment.”
(B) Non-economic environment:
It consists of a socio-cultural, demographic, natural, physical, technical, political and legal environment that affects and affects the economic environment. Many variables affect the non-economic environment.
Some of the key areas of the non-economic environment are described below.
(I) Political and legal environment:
It is the national legislative, administrative and judicial environment that shapes and manages business activities. The legislature explains the laws and policies of action that companies must follow, the administration implements the decisions made by the legislature (parliament), and the judiciary ensures that the legislature and administration function for the benefit of society. To do. A stable political environment leads to business growth. The business operates in a government-regulated environment. Various laws have been enacted to regulate the functioning of companies. They relate to product standards, product packaging, environmental and ecosystem balance protection, banning advertising of certain products (liquor), advertising of certain products with statutory warnings (tobacco), and more.
There are laws to prevent restrictive trade practices and concentration of economic power in the hands of a few. Regulations encourage companies to enter the underdeveloped region and products are reserved for the small sector. The liberalization policy allowed Indian industry to operate in the international market and foreign companies to operate in the Indian market. This will give you access to market growth and diversification, as well as advanced science and technology for Indian entrepreneurs. At the same time, it threatens small Indian companies that cannot compete with large foreign companies.
The political and legal environment provides many laws and regulations that affect business. It provides enterprises with opportunities, threats, and challenges. Governments interact with businesses at the local, state, and central levels and regulate their functions through various rulings.
Governments interact with businesses in the following ways:
1. As a regulator:
Regulate the business of your business by facilitating activities in certain areas and restricting them in other areas. These regulations prevent unhealthy competition between businesses and protect consumer interests from false advertising and unfair trading practices.
Therefore, the political and legal environment plays two important roles.
(A) Role of promotion:
Securing goods that cannot be produced by large companies, large industrial parks and industries (industrial parks, industrial parks, loan facilities, etc.) to be set up in underdeveloped areas.
(B) Role of suppression:
Business organizations must work within the legal framework of the country. You have to obey the law and you have to obey the judicial interpretation.
2. As a supplier:
It supplies resources to business concerns.
3. As a competitor:
Compete with private entrepreneurs in areas such as telecommunications, electricity and construction.
4. As a customer:
It supports business houses by buying their products.
Companies should have a healthy interaction with the government. They need to promote economic growth and indulge in activities that know the legal system.
Some of the laws that exist in the country for the smooth operation of a company are as follows.
Economic Law [Air (Pollution Prevention and Control) Law of 1981; Consumer Protection Law of 1986; Essential Commodity Law, 1955; Foreign Exchange Control Law of 1999; Foreign Trade (Development and Regulation) Law of 1992; Industry (Development and Regulation) Act, 1951; Patent Act 1970; Standards of the 1976 Metering Act; Trademark Act, 1999],
The political legal system helps answer questions such as:
a) Is the political situation of the country stable so that the government policy does not change many times?
b) Are political organizations promoting business activities? In other words, is the paperwork done without delay because of bureaucracy and bureaucracy?
c) Is the judiciary effective in coping decisions?
In a business conflict or litigation?
d) Do government policies encourage business growth in terms of incentives, markets, taxes, etc.?
e) Is the licensing process for starting a new business generous or rigorous?
f) To what extent are import / export policies promoted to promote import / export, etc.?
(ii) Sociocultural environment:
It represents the values, culture, beliefs, norms and ethics of the society in which the company operates. People are important to an organization both as a human resource and as a customer. Their purchasing habits, purchasing abilities, preferences, preferences and education affect businesses.
Companies change their production and marketing plans to meet consumer demand. The social environment is made up of social values. Concerns about social issues such as environmental protection from pollution, provision of employment opportunities, and health care for the elderly and the elderly. Indulge in consumerism, that is, fair trading practices to satisfy human needs.
The cultural environment represents the values and beliefs of society. These beliefs shape people's attitudes and help businesses determine their perception of their needs. The socio-cultural environment encourages companies to support the social and cultural values of society by encouraging art projects, sports, communication media, education, religion, charitable donations, counselling centers, vocational training centers, etc. Useful for.
Therefore, the socio-cultural environment affects:
(A) Business goals:
Social objectives are constructed with economic objectives, as society requires corporate organizations to take care of their interests.
(B) Organizational process:
Various organizational processes such as motivation, leadership and management policy are organized within the constraints of the national cultural system. Democratic leadership styles are adopted at the request of employees to promote employee diversity, encourage participatory decision-making, and promote commitment to the organization.
(C) Goods and services produced:
Business houses produce profitable products, but it is just as important that these products are desired by society. Socially acceptable products promote both business image and profit.
The socio-cultural system helps answer questions such as:
i. What are the expectations of society from business.
ii. Can your business live up to these expectations.
iii. Are social goals part of the company's overall goal framework.
iv. Does your business meet the ethics and values of society? If not, is it possible to change it.
(iii) International environment:
It represents the global environment that is characterized by a "world without borders." The Indian economy entered the world in 1991 through a liberalization policy. Since then, there have been significant economic and political changes, and the role played by the private sector has increased.
The global business environment is heavily influenced by the principles and agreements of the World Trade Organization (WTO). The WTO monitors and regulates businesses traded in the international environment.
This has had a major impact in the following areas:
1. Import liberalization.
2. Opportunity for Indian companies to enter overseas markets through exports and investments.
3. Invite Indian companies to participate in foreign capital and foreign technology in order to expand their business and improve their competitiveness.
4. Promote global sourcing by Indian companies.
5. Benefit from global sourcing by foreign companies.
6. Improve corporate efficiency and dynamism to survive in global competition. Inefficient companies have to leave the market.
Conclusion:
All business development depends heavily on the ability to adapt to the environment. For example, if the government changes economic policy, companies need to respond appropriately to that change. Similarly, companies need to be keenly aware of and respond appropriately to technological changes that can obsolete existing products. Therefore, we can see that the relationship between the business and its environment is very close and continuous. This association helps enterprises enhance their capabilities and allocate resources more efficiently. Like living things, business has ecology. To survive in this vibrant ecology, businesses need their unique capabilities and strengths.
Key takeaways:
Definition: Environmental Scan
Environmental scanning is the process of analysing internal and external factors in the environment. Environmental scanning is the process by which an organization conducts research to identify opportunities and threats in the industry.
Environmental scans are part of the SWOT analysis. The information gained through the environmental scan can be used by leaders to design new goals and strategies or modify existing goals and strategies. Organizations need to be agile in responding to environmental challenges while maximizing the opportunities available.
Importance and necessity of environmental scanning
Environmental scanning is an important aspect of predicting the future and preparing for a volatile business environment. The frequency of environmental scans depends on your organization's needs. Organizations operating in industries that are heavily impacted by innovation must constantly monitor their environment and use the results to design their processes. On the other hand, some organizations may need to perform environmental scans on an ad hoc basis.
The following are the necessity and importance of Environmental Scanning.
1] SWOT Analysis
As we saw earlier in the sense of environmental scanning, it's a complex process. A closer look at an organization's internal and external environment reveals invaluable information: the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a company. Let's take a quick look.
Strengths: As a result of analysing the internal environment of a company, it is possible to identify the strengths that give the company a competitive advantage. Entrepreneurs can use this information to maximize these strengths and benefit more.
Weaknesses: Internal environment surveys have also pointed out weaknesses in the company.
Opportunities: Analysing the external environment helps identify possible opportunities. Entrepreneurs can be prepared to take advantage of these.
Threats: Analysing the external environment can also help identify business threats and other factors from competitors. The company can come up with strategies to spread or minimize its impact.
2. Optimal use of resources:
Proper environmental assessment helps to make the best use of terrifying human, natural and capital resources. A systematic analysis of the business environment helps companies reduce waste and make the best use of available resources without realizing that they cannot effectively use internal and external environmental resources.
4. Survival and growth:
A systematic analysis of the business environment helps companies maximize their strengths, minimize their weaknesses, seize opportunities, and spread threats. This allows companies to survive and grow in a highly competitive business world.
4. To plan a long-term business strategy:
Business organizations have short-term and long-term goals. Appropriate analysis of environmental factors helps companies develop plans and policies that may help them easily achieve their organizational goals. Without an environmental scan, companies cannot develop strategies for business success.
5. Environmental scans help you make decisions.
Decision making is the process of choosing the best option from the various options available. Environmental analysis is a very important tool for understanding and making decisions in every aspect of the business. The success of a company depends on its ability to make accurate decisions. Environmental analysis research allows businesses to choose the best options for their success and growth.
Area to be scanned for environment-
a) Economic situation.
b) Competition.
c) Global opportunities.
d) Employment trends.
e) Technological progress.
f) industry.
g) Geopolitical climate.
Environmental Analysis
Definition: Environmental analysis is described as the process of inspecting all internal or external components that affect an organization's performance. Internal components show the strengths and weaknesses of business entities, and external components show opportunities and threats outside the organization.
Performing an environmental analysis requires a constant flow of relevant information in order to find the best course of action. Strategic planners use the information gathered from environmental analysis to anticipate future trends. This information can also be used to evaluate your production environment and set your organization's goals.
Check if your current strategy can achieve the goals defined by your organization. If your existing strategy does not meet these goals. Then a new strategy is devised or the old strategy is modified accordingly.
Check if your current strategy can achieve the goals defined by your organization. If the existing strategy fails to meet these goals, a new strategy will be devised or the old strategy will be modified accordingly.
Benefits of environmental analysis
The internal insights provided by environmental analysis are used to assess employee performance, customer satisfaction, maintenance costs, and take corrective action as necessary. In addition, external metrics help you be positive about your environment and tailor your strategy to your organization's goals.
Environmental analysis helps detect threats early and helps organizations develop strategies for survival. In addition, identify opportunities to take the largest share of the market over competitors, such as prospects, new products, segments, and technologies.
Environmental analysis is a continuous process that continuously scans for forces affecting the business environment and follows a holistic approach that covers 360 degrees of the horizon rather than specific segments.
Business environment Analysis process
The business environment analysis process involves many steps, including:
1. Gathering the necessary information.
2. Scan and search for information.
3. Obtaining information by spies.
4. Predict the situation.
5. Observe the environment.
6. Evaluation.
1. Gathering the necessary information
Gathering the information, you need is the first step in the business environment analysis process. It also includes observing various factors that are prevalent in a particular area. When you analyze and create an environment, you must first collect verbal information from various sources about the environmental elements of that particular business.
2. Scan and search for information
Scanning and searching are important techniques for business environment analysis. Once the required information has been collected, it should be scanned. What's more, you can continue to search for other relevant information. This technique gives results on already established hypotheses. This allows analysts to know what the general conditions are at one time in a particular business.
3. Obtaining information by spies
Spies are also a method of business environment analysis. If you need to analyze the activity of a particular business and cannot collect such information in the traditional way, rely on espionage techniques. This happens especially when there is business competition. In most cases, this technique is used to collect conflict information.
4. Situation forecast
Scan provides images about the past and present. However, strategic decision-making requires a future direction. Predictions are scientific guesses based on some serious research. Therefore, it is especially useful to know how the situation of business and society as a whole is shaped.
5. Observation of the environment
You can analyze the business environment just by observing. Observations reveal a variety of conditions that are prevalent at any given time. This will help you understand the entire existing environment and make the right decisions.
6. Evaluation
The assessment is done to determine the impact on your organization's current and potential strategies. Assessment involves identifying and assessing how and why current and anticipated environmental changes affect the strategic management of an organization. It aims to answer questions such as what are the key issues posed by the environment. What is the impact of such issues on the organization?
Or
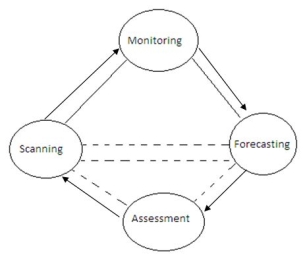
Environmental scanning:
Scanning is the process of analyzing your environment to identify factors that can affect your business. Its purpose is to identify new trends or early warning signals. These trends may have evolved or suddenly appeared over time. Environmental scans alert organizations to potentially significant forces in the external environment and enable them to take appropriate strategic initiatives before they become important to the organization. Scans are basically exploratory. There are many environmental factors that affect business operations. Not all of these factors are relevant to the enterprise.
Therefore, it is necessary to identify important and high-priority factors. Several factors influence the choice of relevant environmental factors, such as business philosophy, age, size, power, geographic aspects, and the industry of the organization.
Environmental Scan: Scanning and searching are important techniques for business environmental analysis. Once the required information is collected, it should be scanned. What's more, you can continue to search for other relevant information. This technique gives results on already established hypotheses. This allows analysts to know what the general conditions are at one time in a particular business.
Environmental monitoring: At this stage, information from the relevant environment is collected. Once the environment-related factors are identified, appropriate data about these factors is collected to identify new patterns and trends in them.
The four stages given above are intertwined as can be seen below:
Key takeaways:
Capitalism:
Here is a bird's-eye view of the New York Stock Exchange. Scholars do not always agree with a single definition of capitalism. For our purposes, we define capitalism as an economic system that is privately owned (rather than state-owned) and has the impetus to generate profits and thus wealth. This is the type of economy that is taking place in the United States today. Under capitalism, people invest capital (money or property invested in a business venture) into a business to produce a product or service that can be sold to consumers in the market. Investors in a company are generally entitled to receive a portion of the profits earned from the sale after the costs of production and distribution have been removed. These investors often reinvest their profits to improve and expand their businesses or to acquire new businesses. Consider this example to illustrate how this works. Sarah, Antonio, and Chris have each invested $ 250,000 in a start-up that offers innovative baby products. When the company makes a profit of $ 1 million in the first year, a portion of that profit is returned to Sarah, Antonio and Chris in return for the investment. Sarah reinvests in the same company to fund the development of a second product line, Antonio uses his returns to help another start-up in the tech sector, and Chris buys a yacht.
To provide goods and services, owners hire wage-paying workers. The cost of raw materials, the retail price charged to consumers, and the amount paid for wages are determined by the laws of supply and demand and competition. Prices tend to rise when demand exceeds supply. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to fall. Competition arises when multiple companies sell similar products and services to the same buyer. Competition is good for consumers because companies try to get consumers to buy from consumers rather than from competitors, which can lead to lower prices and better quality.
Wages tend to be set in a similar way. Those who lack talent, skills, education, or training and are in need of a company tend to earn more than those who do not have equivalent skills. Labor competition helps determine the amount of people to be paid. When many people are unemployed and short of work, they are often less willing to accept their services than when they are in high demand. In this scenario, the company can maintain or increase profits by not raising the wages of its workers.
Actual capitalism:
When capitalists began to dominate the economies of many countries during the Industrial Revolution, the rapid growth of companies and their tremendous profitability create huge companies that can monopolize the entire industry for some owners. Gave the necessary capital to. Many companies controlled all aspects of the industry's production cycle, from raw materials to the stores where they were produced and sold. These companies could use their wealth to buy or curb competition.
In the United States, the predatory tactics used by these massive monopolies have taken action by the government. Beginning in the late 1800s, the government lifted its monopoly and passed a series of legislation regulating how major industries such as transportation, steel production, oil and gas exploration and refining do business. The main legislation was the Sherman Act of 1890, the Clayton Act of 1914, and the Federal Trade Commission Act of 1914. These laws first restricted the formation of cartels and prohibited other collusions that were deemed to restrict trade. Second, they restricted mergers and acquisitions of organizations that could significantly reduce competition. Third, they banned the creation of monopolies and the abuse of monopoly power. The United States is considered a capitalist country. However, the US government is having a significant impact on private sector through the laws it passes and the regulations enforced by government agencies. The government has some control over the way businesses do business through taxes, wage regulations, guidelines for protecting worker safety and the environment, and financial rules of banks and investment firms. State and federal governments own, operate, or control most of a particular industry, including post offices, schools, hospitals, highways, railroads, and many water and sewage and power companies. The debate over how much government should be involved in the economy remains controversial today. Some criticize involvement such as socialism (a type of state-owned economy), while others consider intervention and oversight to protect the rights of workers and the well-being of the general public.
Socialism:
Colourful paintings depicting Mao Zedong and other symbols of Chinese Communism are shown here.
Socialism is an economic system in which government ownership of goods and their production (often referred to as "state-owned") promotes equal sharing of work and wealth among members of society. Under socialism, everything people produce, including services, is considered a social product. Anyone who contributes to the production of goods or the provision of services is entitled to a portion of the profits arising from their sale or use. Governments must be able to control property, production, and distribution to ensure that all members of society gain a fair share.
While the focus of socialism is to benefit society, capitalism aims to benefit individuals. Socialists argue that capitalist economies lead to inequality and individuals who use their power at the expense of unfair distribution of wealth and society. Socialism ideally seeks to control the economy to avoid the problems inherent in capitalism.
Opinions are divided on how well the economy should be managed in socialism. Extreme people believe that everything but the most personal is public property. Other socialists believe that only critical services such as health care, education and utilities (electricity, telecommunications, sewage) require direct control. Under this form of socialism, farms, small shops, and businesses can be privately owned but subject to government regulation.
Another area that socialists disagree with is at what level society should exercise its control. In communist countries such as the former Soviet Union and modern China, Vietnam and North Korea, the country dominates both politics and economy, and many commodities are shared. Ideally, these products will be available to everyone as needed, but in theory they often have different results. Communist governments generally have the power to tell businesses what to produce, how much to produce, and what to charge. There are various practices both inside and outside the communist country. For example, China is still considered a communist nation, but it employs many aspects of the market economy. Other socialists believe that control should be decentralized so that it can be exercised by those most affected by the controlled industry. One example is a town that jointly owns and manages businesses that residents depend on.
Due to economic challenges, some of these communist countries have moved from central planning to help market power determine many production and pricing decisions. Market socialism describes a subtype of socialism that adopts certain characteristics of capitalism. For example, allow limited personal ownership or look at market demand. This could include situations such as the profits that a company would generate by sending it directly to its employees or using it as public funds (Gregory and Stuart2003). Many Eastern European countries and some South American countries have mixed economies. The major industries are nationalized and are directly controlled by the government. However, although most businesses are privately owned, they are regulated by the government.
Key takeaways:
References: