UNIT -1
Foundation of Information System
System
In a system, network of components work towards a single objective, if there is lack of co-ordination among components, it leads to counterproductive results. A system may have following features:
Adaptability: Some systems are adaptive to the exterior environment, while some systems are non-adaptive to the external environment. For example, anti-lock braking system in car reacts depending on the road conditions, whereas the music system in the car is independent of other happening with the car.
Limitation: Every system has pre-defined limits or boundaries within which it operates. This limits or boundaries can be defined by law or current state of technology.
Information
Common definition of information is data. However, data is no true information. Data gets its meaning and significance if only it is information. Information is represented with data, symbols and letters.
Information has following properties:
Objective: One of the key properties of information is its objectiveness. Objective information is a key component of any modern scientific research.
Subjective: Set of information which is useful to science may be abstract or irrelevant for others. Therefore, information is subjective also.
Temporary: Information is temporary with every update in the database.
Representation of Information
Information is represented with help of data, numbers, letters or symbols. Information is perceived in a way it gets represented. Decimal system and binary system are two ways of representing information. The binary circuits of computers are designed to operate under two states (0,1).
Organization of Information
The way in which information is organized directly affect the way the information is managed and retrieved.
The simplest way of organizing information is through linear model. In this form, data is structured one after another, for example, in magnetic tapes, music tapes, etc.
In a binary tree model, data is arranged in an inverted tree format where it assumes two values.
The hierarchy model is derived from a binary tree model. In this model, branch can assume multi-value data, for example in the UNIX operating system this model is used for its file system.
The hypertext model is another way of organizing information; World Wide Web is an example of this model.
Random access model is another way of organizing information. This model is used for optimum utilization of available computer storage space. Here data is stored in specified location under direction of the operating system.
Networking Information
Information is networked through network topology. The layout of all the connected devices, and it provides virtual shape or structure to the network is known as network topology. The physical structure may not be representative of network topology. The basic types of topology are bus, ring, star, tree and mesh.
The above topologies are constructed and managed with help of Hubs, Switches, Bridges, Routers, Brouters and Gateways.
Securing Information
Security of information as well as an information system is critical. Data back-up is on the way through which Information can be made secured. Security management for network and information system is distinct for different setup like home, small business, medium business, large business, school and government
Information system
An information system is integrated and co-ordinate network of components, which combine together to convert data into information.
Summary:
Data vs. Information
Data
Information
Data Manipulation
Input-process-output
Several subsystems make up this corporate accounting system.
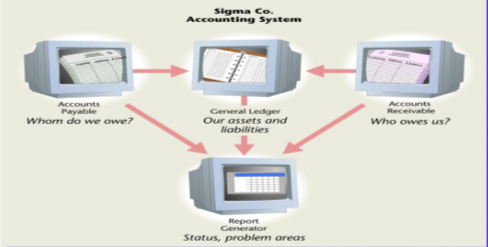
Systems thinking
Qualities of humans and computers that contribute to synergy

When combined resources produce output that exceeds the sum of the outputs of the same resources employed separately
Allows human thought to be translated into efficient processing of large amounts of data
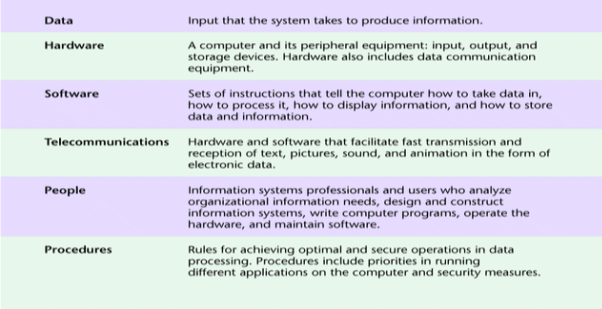
Components of information systems
An information system is essentially made up of five components hardware, software, database, network and people. These five components integrate to perform input, process, output, feedback and control.
Hardware consists of input/output device, processor, operating system and media devices. Software consists of various programs and procedures. Database consists of data organized in the required structure. Network consists of hubs, communication media and network devices. People consist of device operators, network administrators and system specialist.
Information processing consists of input; data process, data storage, output and control. During input stage data instructions are fed to the systems which during process stage are worked upon by software programs and other queries. During output stage, data is presented in structured format and reports.
Classification of Information System
In any given organization information system can be classified based on the usage of the information. Therefore, an information system in an organization can be divided into operations support system and management support system.
In an organization, data input is done by the end user which is processed to generate information products i.e. reports, which are utilized by internal and or external users. Such a system is called operation support system.
The purpose of the operation support system is to facilitate business transaction, control production, support internal as well as external communication and update organization central database. The operation support system is further divided into a transaction-processing system, processing control system and enterprise collaboration system.
2. Transaction Processing System (TPS)
In manufacturing organization, there are several types of transaction across department. Typical organizational departments are Sales, Account, Finance, Plant, Engineering, Human Resource and Marketing. Across which following transaction may occur sales order, sales return, cash receipts, credit sales; credit slips, material accounting, inventory management, depreciation accounting, etc.
These transactions can be categorized into batch transaction processing, single transaction processing and real time transaction processing.
3. Process Control System
In a manufacturing organization, certain decisions are made by a computer system without any manual intervention. In this type of system, critical information is fed to the system on a real-time basis thereby enabling process control. This kind of systems is referred as process control systems.
4. Enterprise Collaboration System
In recent times, there is more stress on team effort or collaboration across different functional teams. A system which enables collaborative effort by improving communication and sharing of data is referred to as an enterprise collaboration system.
5. Management Support System
Managers require precise information in a specific format to undertake an organizational decision. A system which facilitates an efficient decision-making process for managers is called management support system.
Management support systems are essentially categorized as management information system, decision support system, expert system and accounting information system.
Management information system provides information to manager facilitating the routine decision-making process. Decision support system provides information to manager facilitating specific issue related solution.
Further Classification
An information system can be categorized based upon activity into strategic planning system, tactical information system and operational information system.
Uses
References