Unit II
Management Information Systems
The MIS is defined as an integrated system of man and machine for providing the information to support the operations, the management and the decision making function in the organization.
The concept of the Management Information System (MIS) has evolved over a perick-: of time comprising many different facets of the organizational function. MIS is a necessity of all the organizations. The initial concept of MIS was to process data from the organization and present it in the form of reports at regular intervals. The system was largely capable of handling the data from collection to processing. It was more impersonal, requiring each individual to pick and choose the processed data and use or his requirements. This concept was further modified when a distinction was made between data and information. The information is a product of an analysis of data. This concept is similar to a raw material and the finished product. What are needed are information and not a mass of data. However, the data can be analyzed in a number of ways, producing different shades and specifications of the information as a product. It was, therefore, demanded that the system concept be an individual- oriented, as each individual may have a different orientation. Towards the information this concept was further modified, that the system should present information in such a form and format that it creates an impact on its user, provoking a decision or an investigation.
The MIS is a product of a multi- disciplinary approach to the business management. It is a product which needs to be kept under a constant review and modification to meet the corporate needs of the information. It is prescribed product design for the organization. The MIS differs since the people in two organizations involved in the same business. The MIS is for the people in the organization. The MIS model may be the same but it differs greatly in the contents
The MIS is a dynamic concept subject to change, time and again, with a change in the business management process. It continuously interacts with the internal and the external environment of the business and provides a corrective mechanism in the system so that the change needs of information are met effectively. The M1S, therefore, is a dynamic design the primary objective of which is to provide the information for decision making and it is developed considering the organizational fabric, giving due regard to the people in the organizational the management functions and the managerial control.

A classical system is recommended to assure the development of a management information system that is fully responsive to a client's performance objectives and resource constraints. Like most complex systems, management information system can be described in number of ways. Multiple approaches are used in this section to explain structure of an organization information system or management information system.
This approach includes the following major components:
Operational elements
System support includes all of the resources required to operate, maintain, and rove the system. A crucial aspect of the system operation phase is the fact that the design team will, at some point, be ending its involvement in the MIS. At that point, important that the client have the personnel know-how and resources to continue ration of the system, maintain it, and improve it. It is necessary to develop a system is easy to use and improve. To accomplish this goal, training materials and procedures can be developed that can be used to assure the continued operation of them in the future. There are certain kinds of operational elements which play an important role in eloping an effective MIS like:
Element | Description |
Hardware | Multiple computer systems : mainframes, minicomputers, personal computers. Computer system components are : central processor(s), memory hierarchy, input and output devices. Communications : local area networks, metropolitan area networks, and wide area networks. |
Software | Systems software and applications software |
Database | Organised collections of data used by applications software. |
Personnel | Professional cadre of computer specialists; and users in certain aspects of their work. |
Procedures | Specifications for the use and operation of computerized information systems collected in user manuals, operator manuals, and similar documents. |
Data processing is term used to describe the series of actions taken to provide useful information from data. Data processing systems, whether manual, mechanical or electronic are used to produce the management information system for running the organization. Data is the term used to describe the basic fact regarding an organization's activities which are collected and input to a system. The facts are to produce useful output or information. The process of output or information is also known as reporting system. Therefore, the data processing system processes the transactions and processes the reports. Prior to computer (before use of computers), this was done manually. In the age of computer other data processing methods continue to be used to organization where it is fell that electronic data processing (EDP) method. But it is not distracted other data processing methods, may be used in conjunction with computer data processing, for example, to produce input or deal with output. Data processing involves a number of transaction and file maintenance in order to provide a database for generating and providing information to various users at the management levels. A transaction is an activity like making a purchase or sales, manufacturing product or recruiting employees. It may be internal in nature and can also involve an external agency.
The records to be transacted can be routed through the following ways.
1. Direct transaction to the action (automatic action).
2. Report or explain the performance (through the information report).
3. Communicate the information about the issue (ad hoc support).
The other processing activities are master file maintenance, report generation inquiry and creating support applications. The output of these processing functions provides right information to other management activities. They are routine and are in a programmed form.
A MIS is more comprehensive than data processing which only processes transaction and produces reports. Before the advent of computers, data processing was performed manually or with simple machines. MIS encompasses processing in support of a wider range of organizational functions and management process. The system also includes inaction processing.
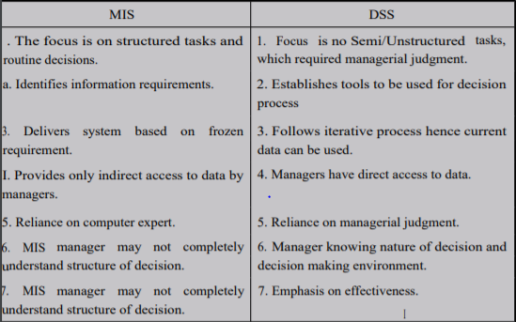
MIS and Decision Support System
Management Information System
MIS is an information system which processes data and converts it into information. A management information system uses TPS for its data inputs. The information generated by the information system may be used for control of operations,strategic and long-range planning. Short-range planning management control and other managerial problem solving. It encompasses processing in support of a wide range of organizational functions and management process. The functional areas of business may be marketing, production, human resource, finance and accounting.
Decision Support System(DSS)
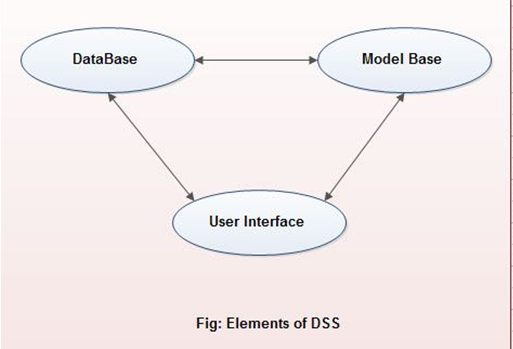
It is an information system application that assists decision-making. DSS tends to be used in planning, analyzing, alternatives, and trail and error search solution. The elements of the DSS include database, model base and software. The application areas of DSS are Production, finance and Marketing.
Information Resource Management (IRM) is a program of activities directed at king effective use of information technology within an organization. These activities go from global corporate information planning to application system development,ration, and maintenance and support of end-user computing. Information resource management has become a popular way to emphasize a major change in the management and mission of the information systems function in many organizations.
IRM may be viewed as having five major dimensions:
Strategic Management
Information technology must be managed to contribute to a firm's strategic objectives and competitive advantages, not just for operational efficiency or decision making.
Operational Management
Information technology and information systems can be managed by functional organizational structures and managerial techniques commonly used throughout other business units.
Resource Management
Data and information, hardware and software, telecommunications networks, and IS personnel are vital organizational resources that must be managed like other business assets.
Technology Management
All technologies that process, store, and communicate data and information throughout the enterprise should be managed as integrated systems of organizational resources.
Distributed Management
Managing the use of information technology and information system resources in business units or workgroups is a key responsibility of their managers, - matter what their function or level in the organization.
References-